Geospatial Analysis of Urban Warming: A Remote Sensing and GIS-Based Investigation of Winter Land Surface Temperature and Biophysical Composition in Rajshahi City, Bangladesh
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Used and Methods
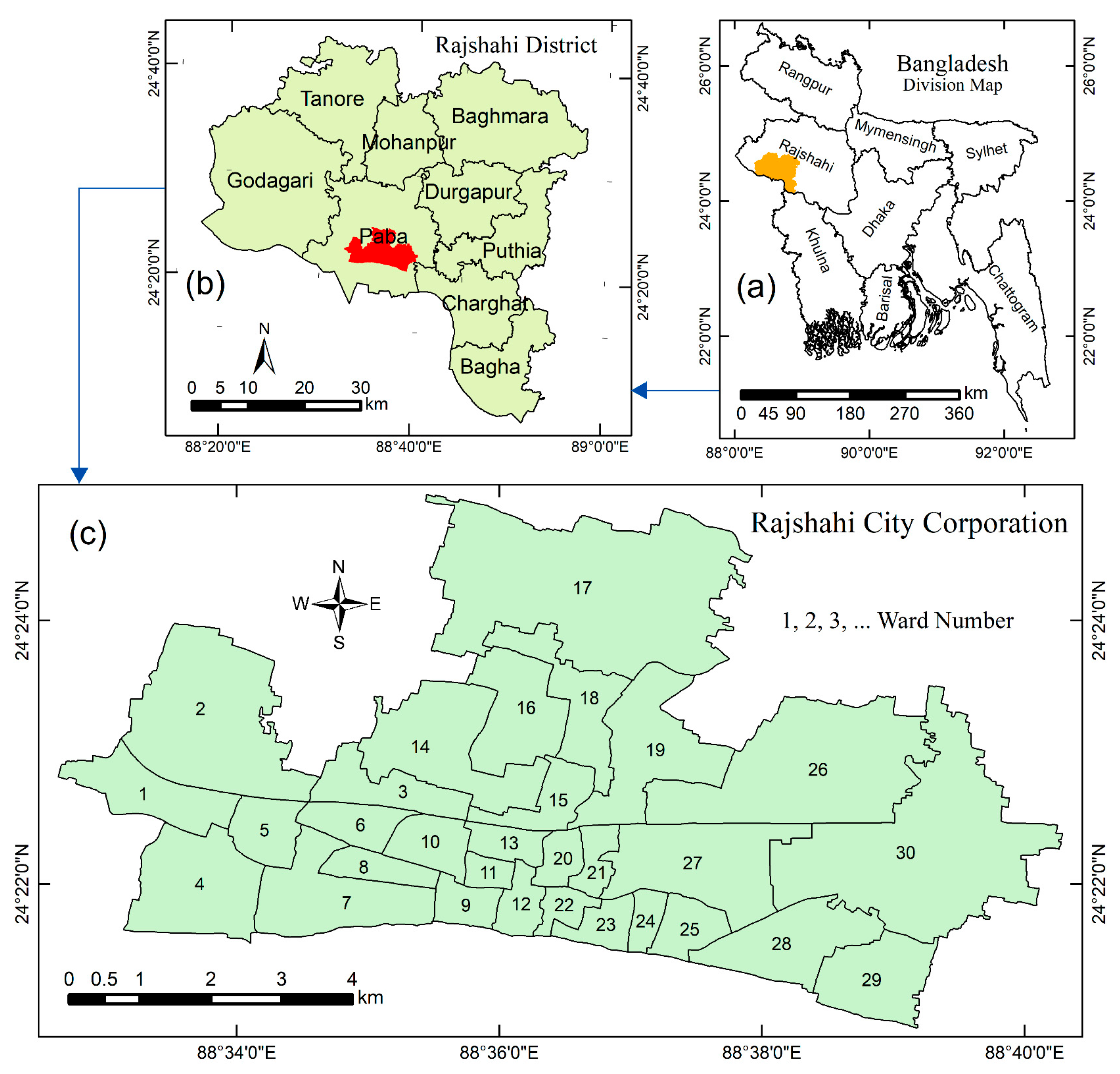
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Used
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Pre-Processing of Landsat Data
2.3.2. Retrieval of LST from Thermal Landsat TM and ETM+ Images (for 1990, 2000, and 2010)
- Step 1: Convert DN (Digital Number) Value to Radiance ()
- Step 2: Convert Radiance to At-sensor Brightness Temperature (°C) ()
- Step 3: Calculation of NDVI and Proportion of Vegetation () for Emissivity Correction
- Step 4: Estimation of Emissivity (ε)
- Step 5: LST in Degrees Celsius ()
2.3.3. Urban Thermal Field Variance Index (UTFVI)
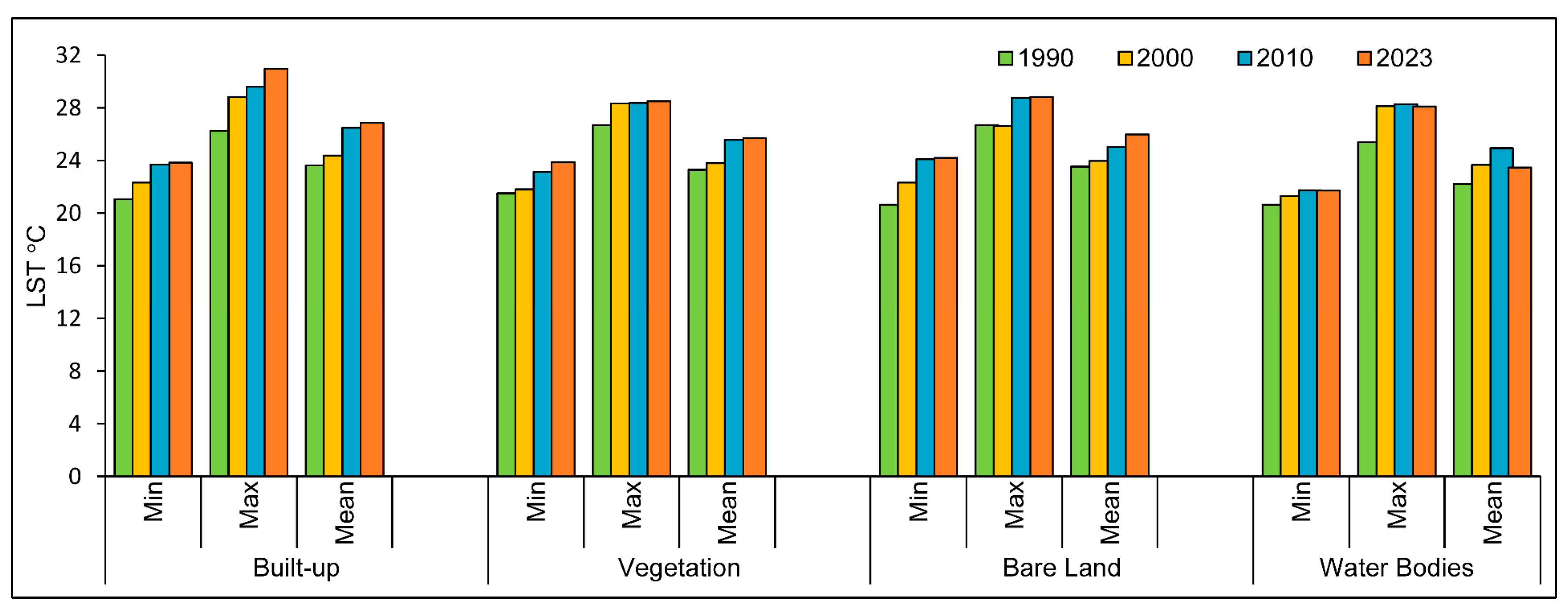
2.3.4. LULC and Biophysical Compositions
2.3.5. Spatial Trend and Hotspot Analysis of LST Change
3. Results
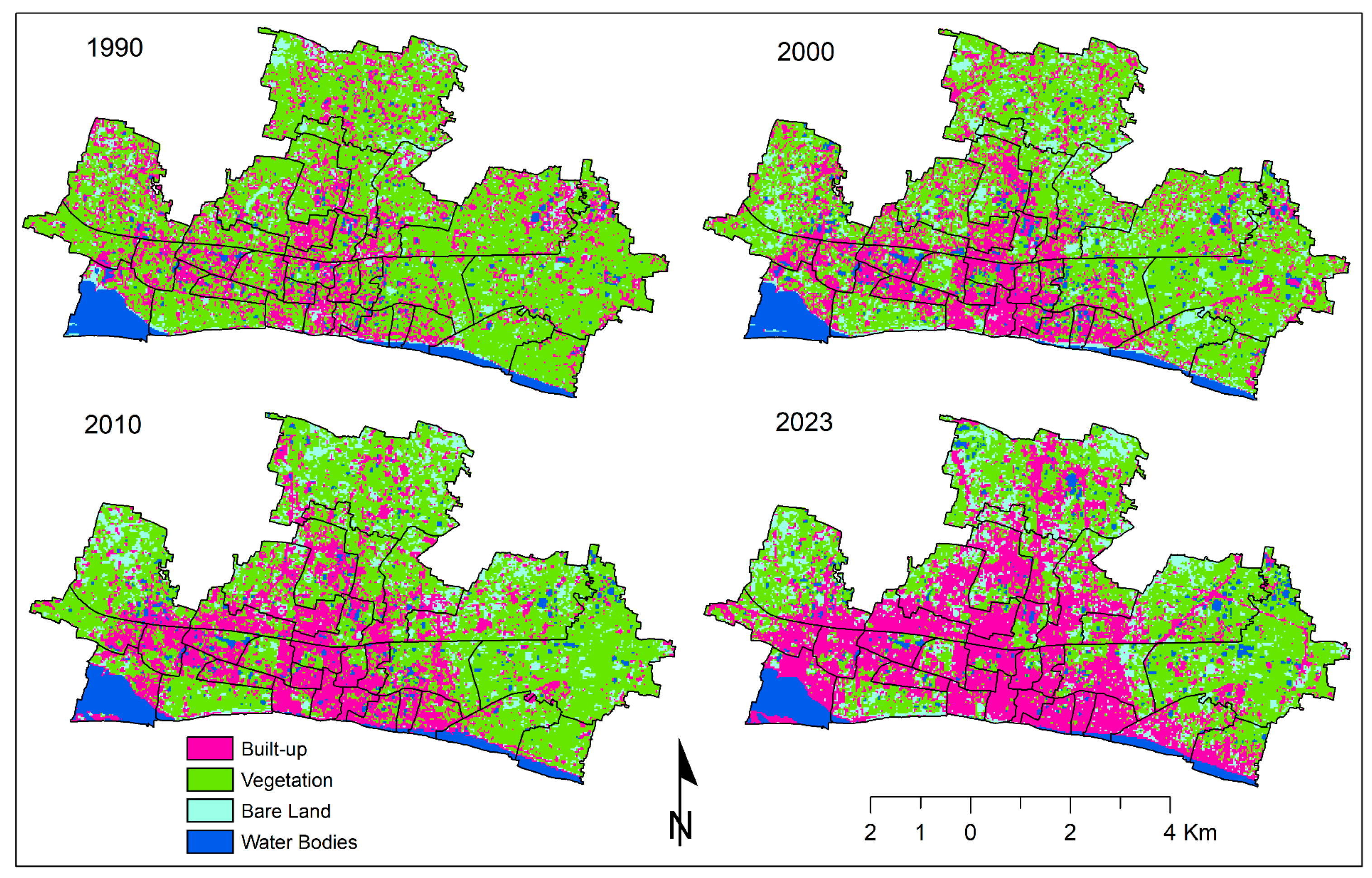
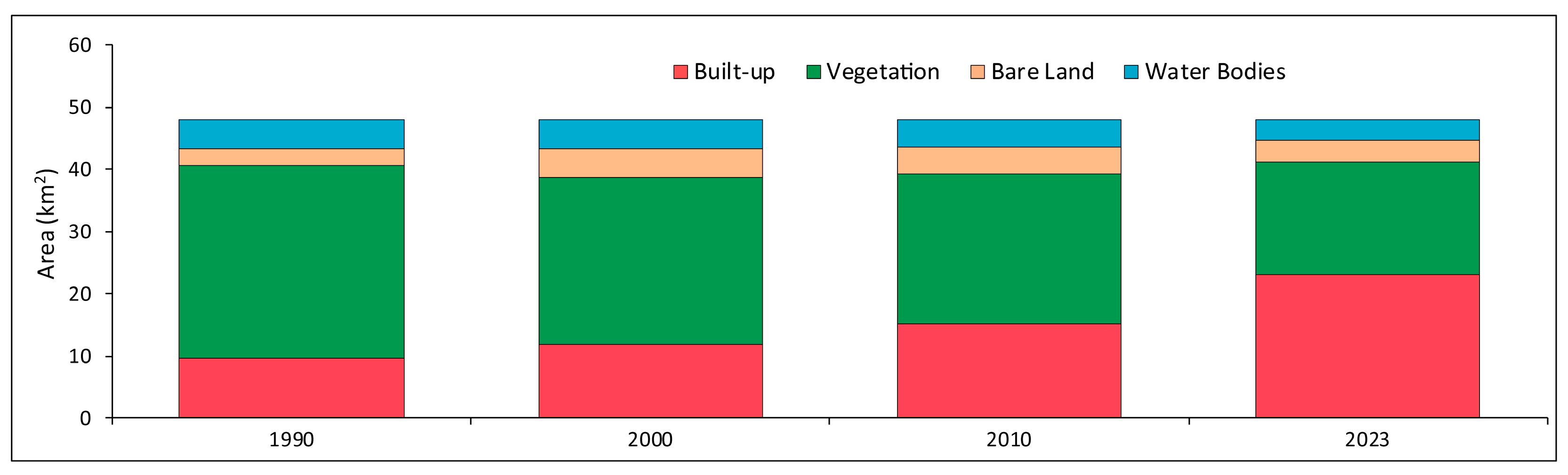
3.1. Land Use/Land Cover (LULC): Pattern and Changes
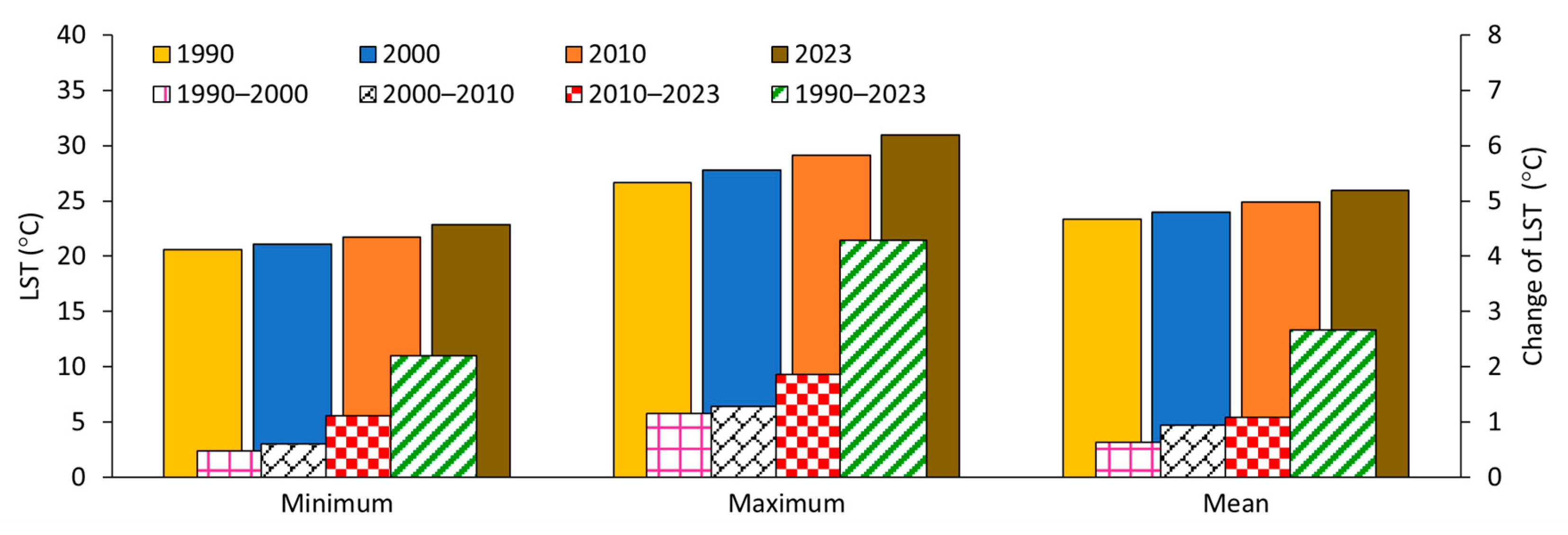
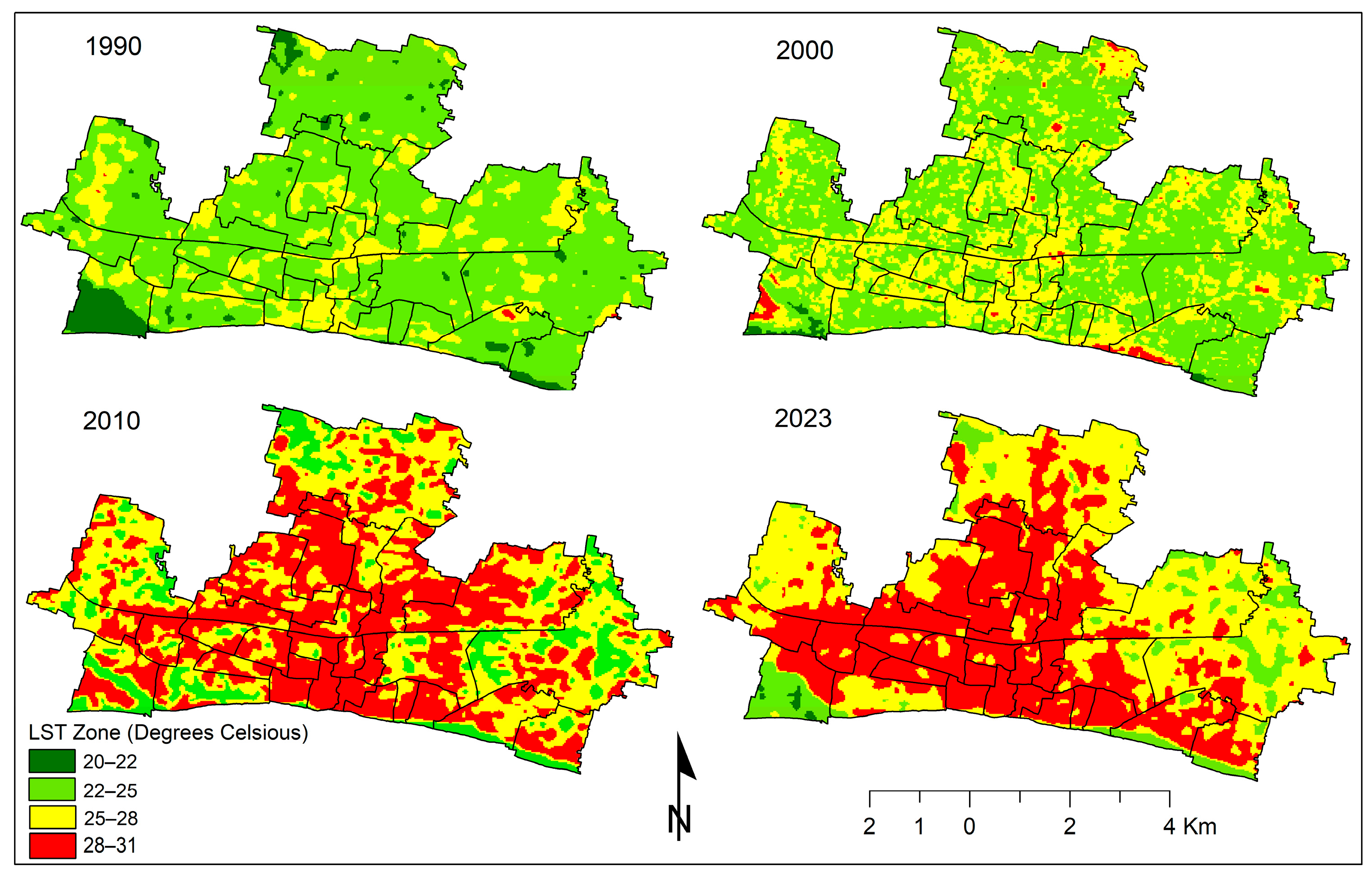
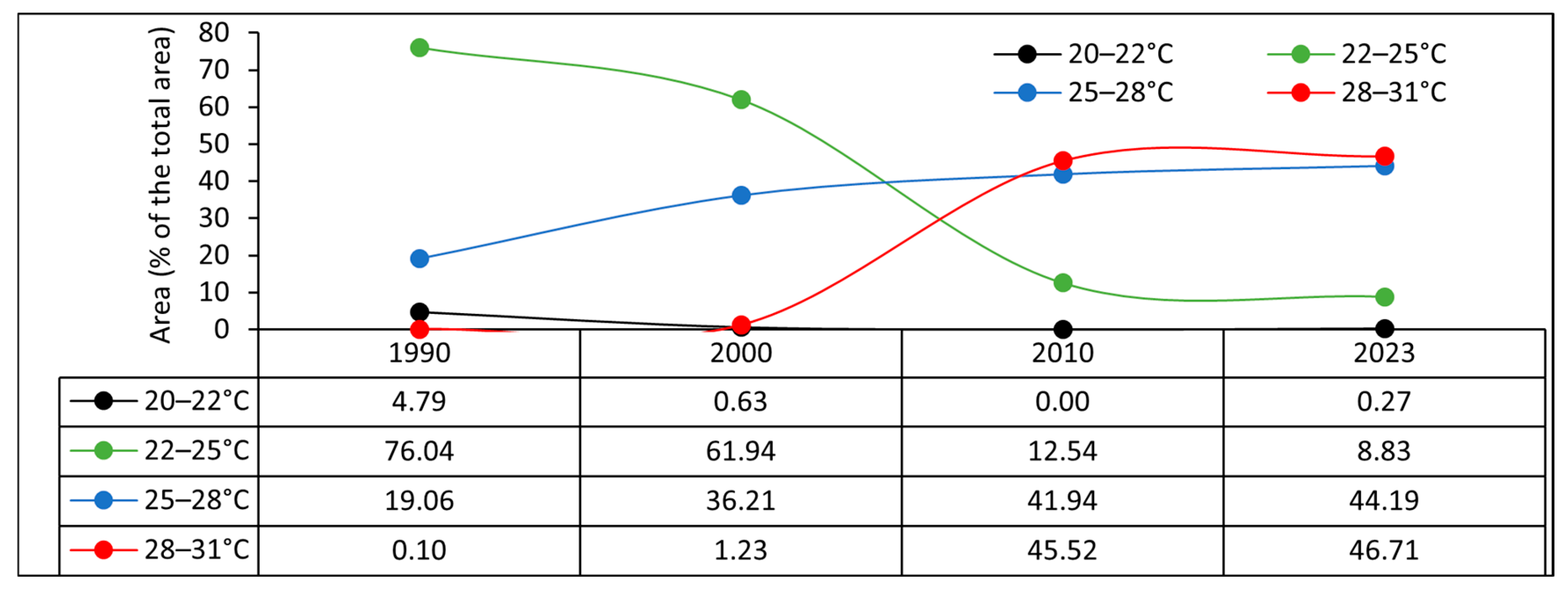
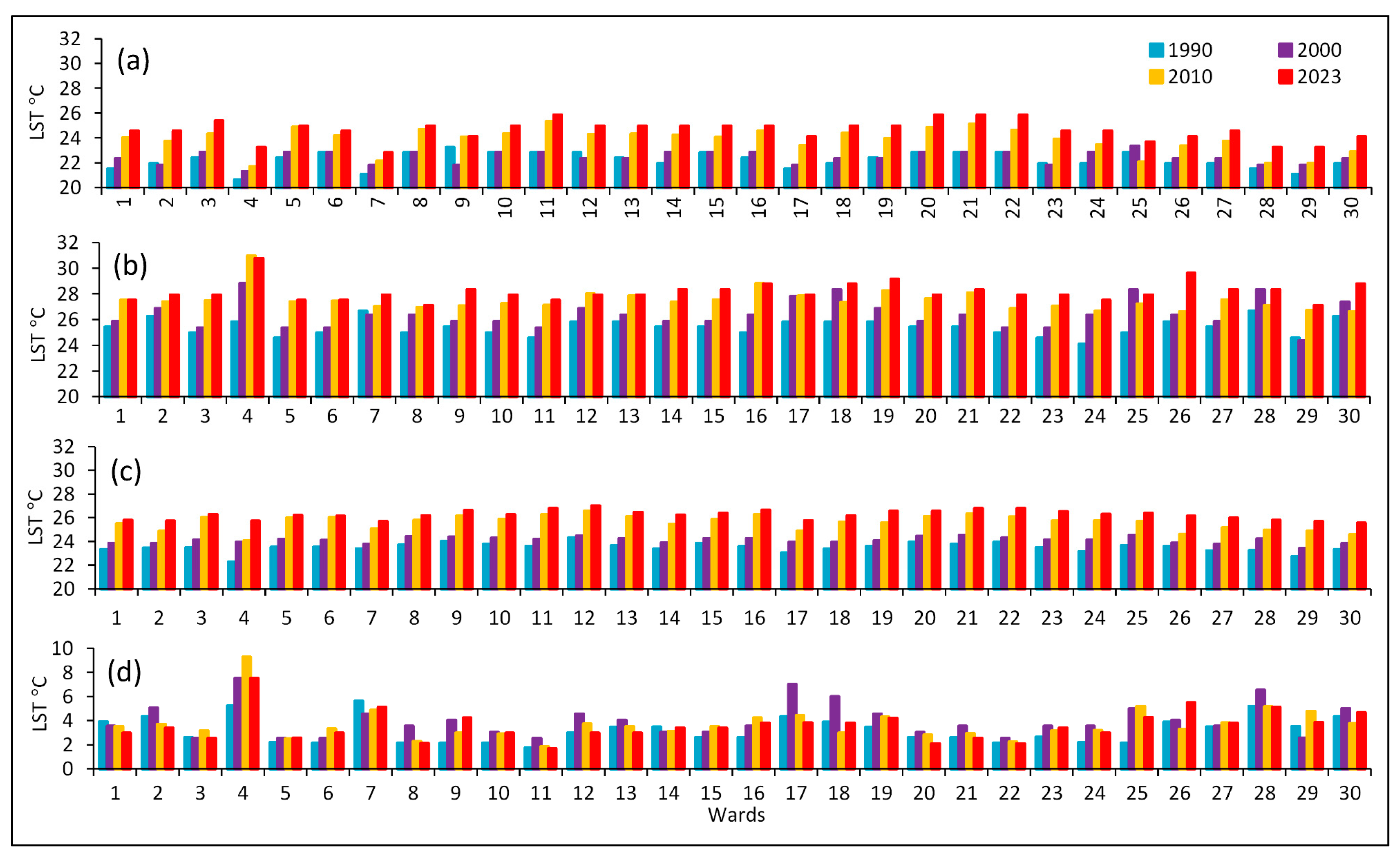
3.2. Urban Climate: LST Distribution and Dynamics
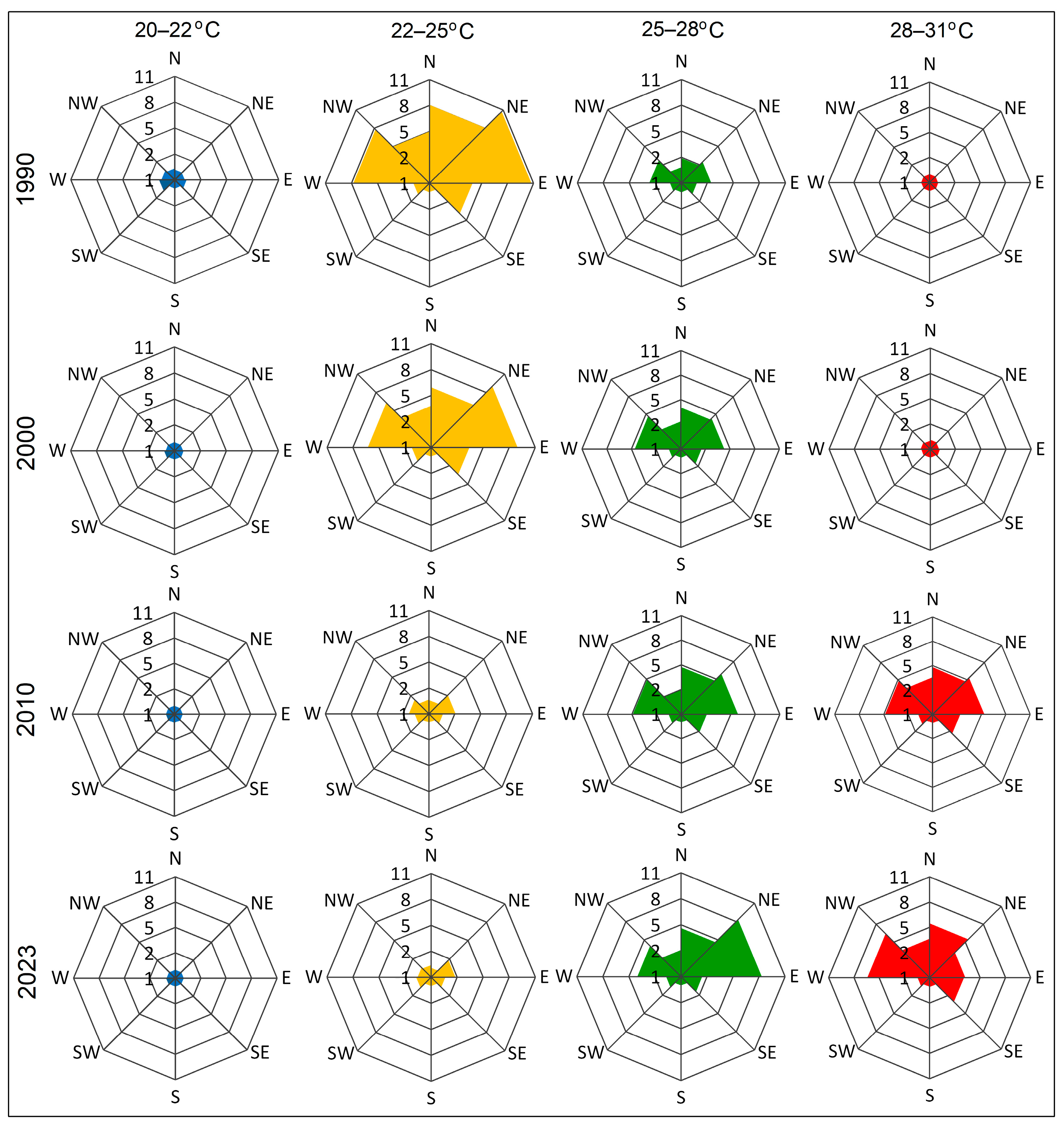
3.3. Zonal and Directional Analysis of LST
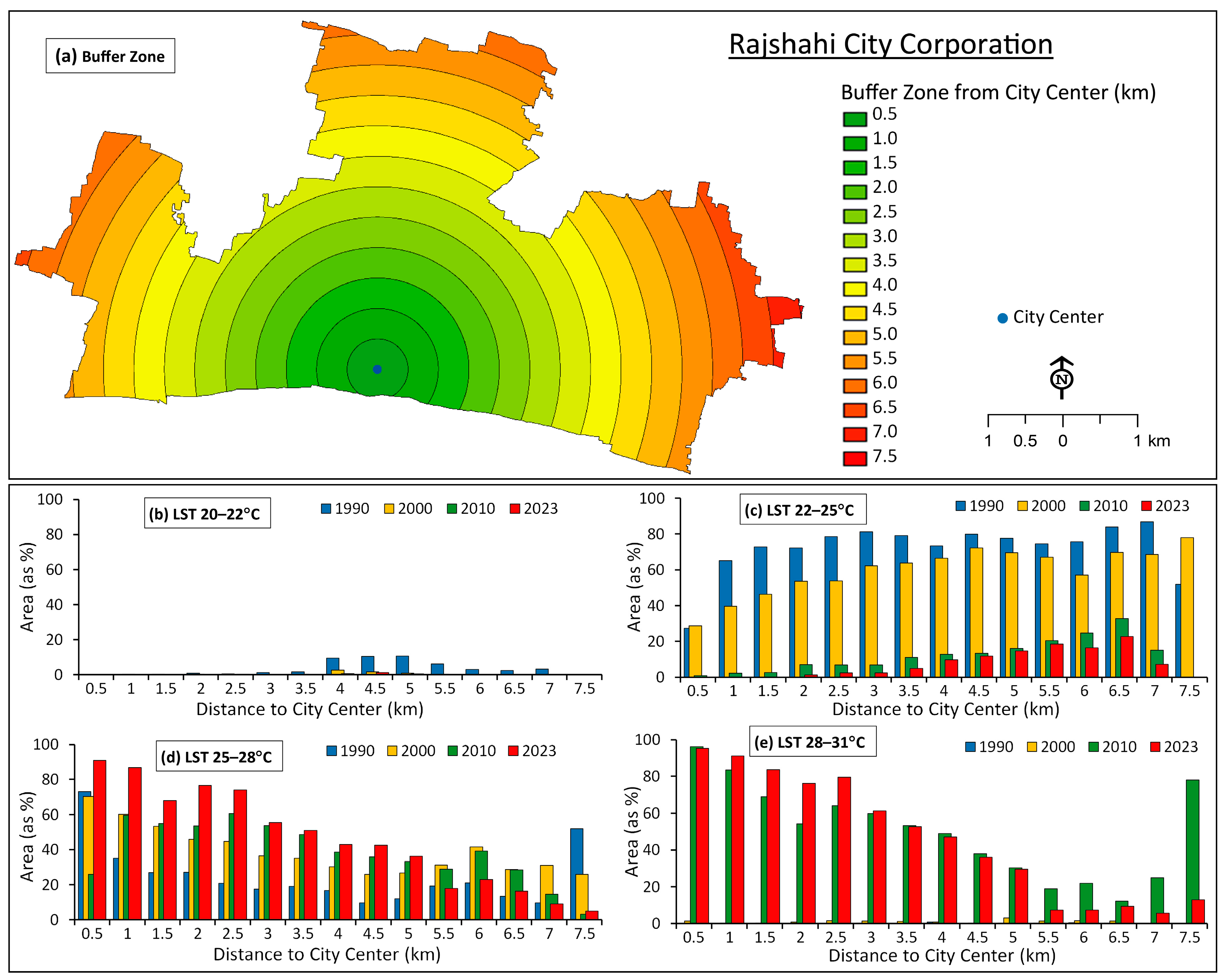
3.4. Urban–Rural Gradient of LST
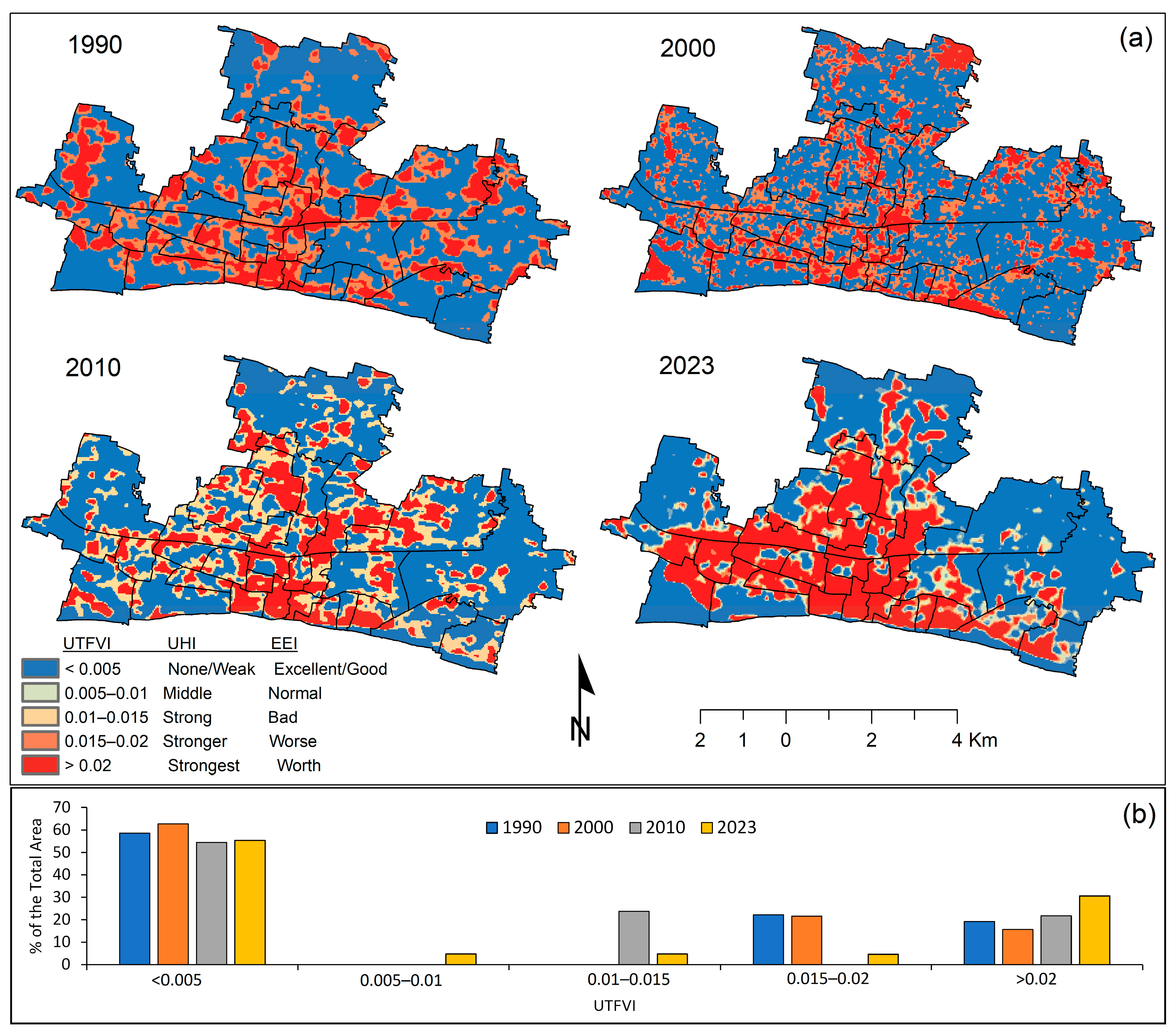
3.5. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Surface Urban Heat Island Intensity Using UTFVI
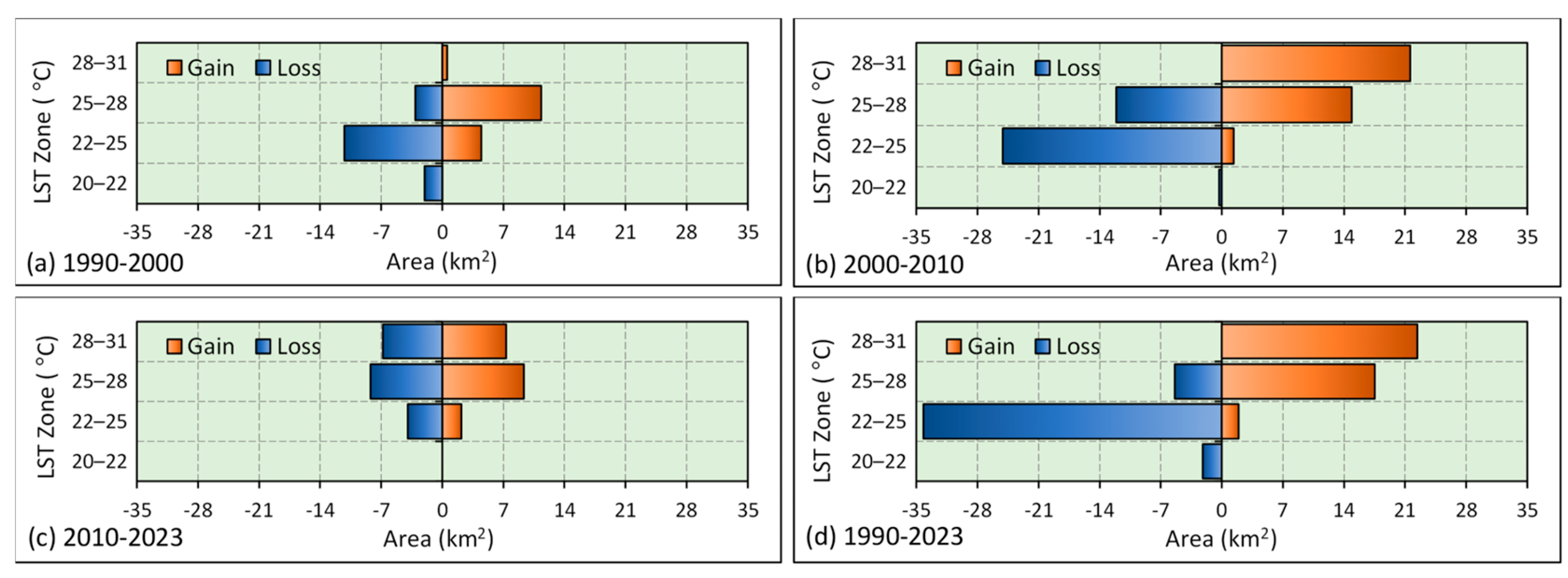
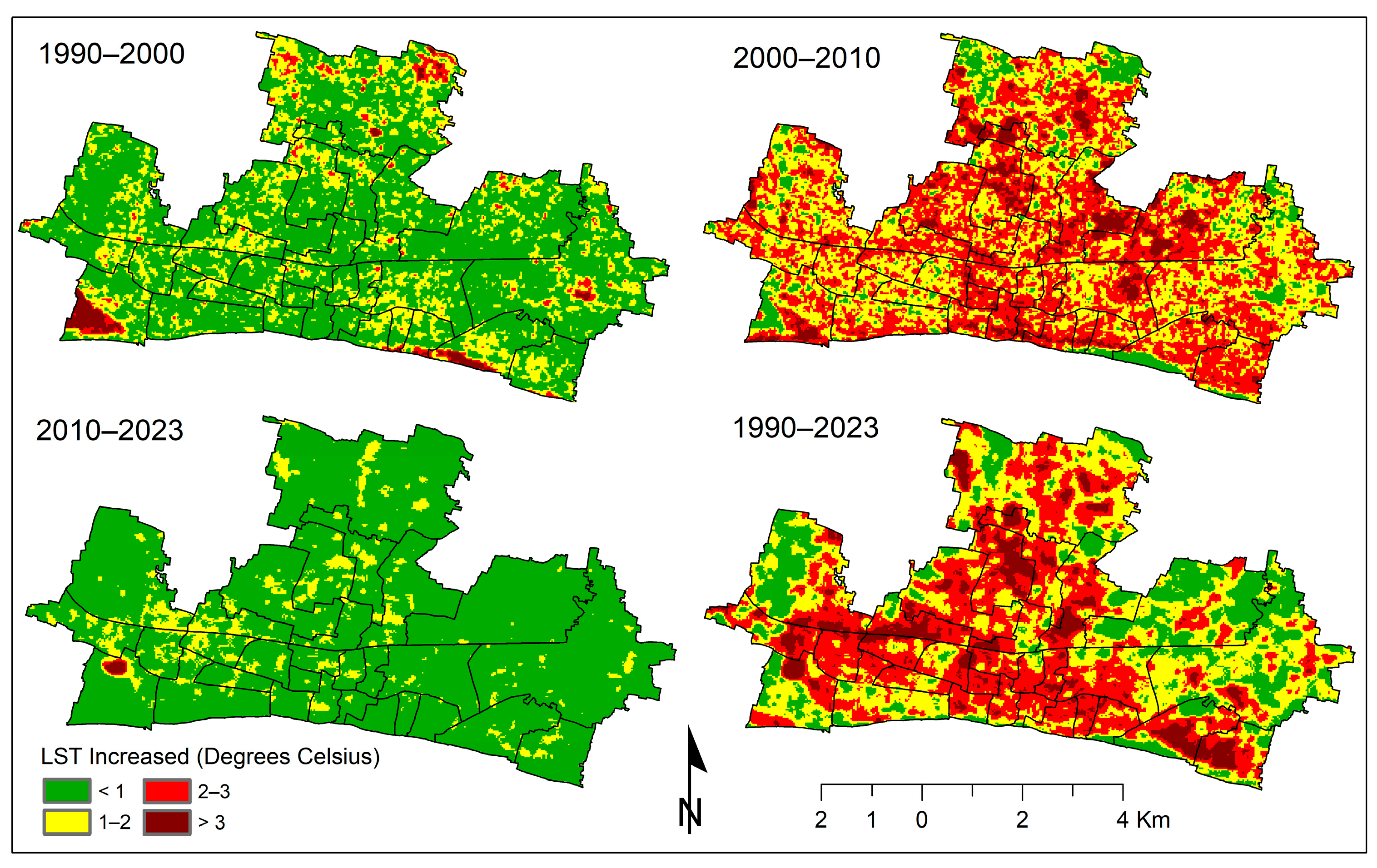
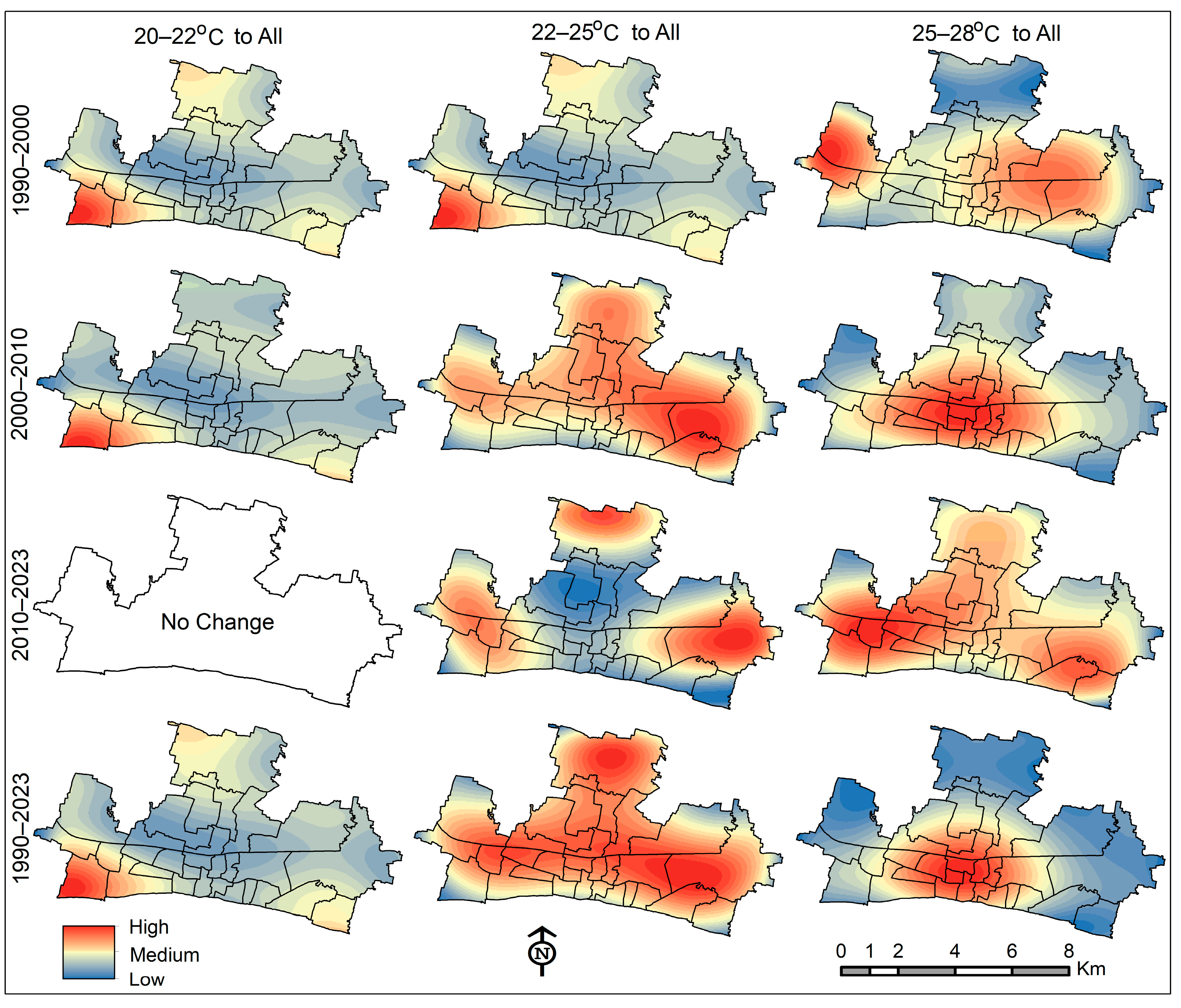
3.6. Spatial Trend of LST Change
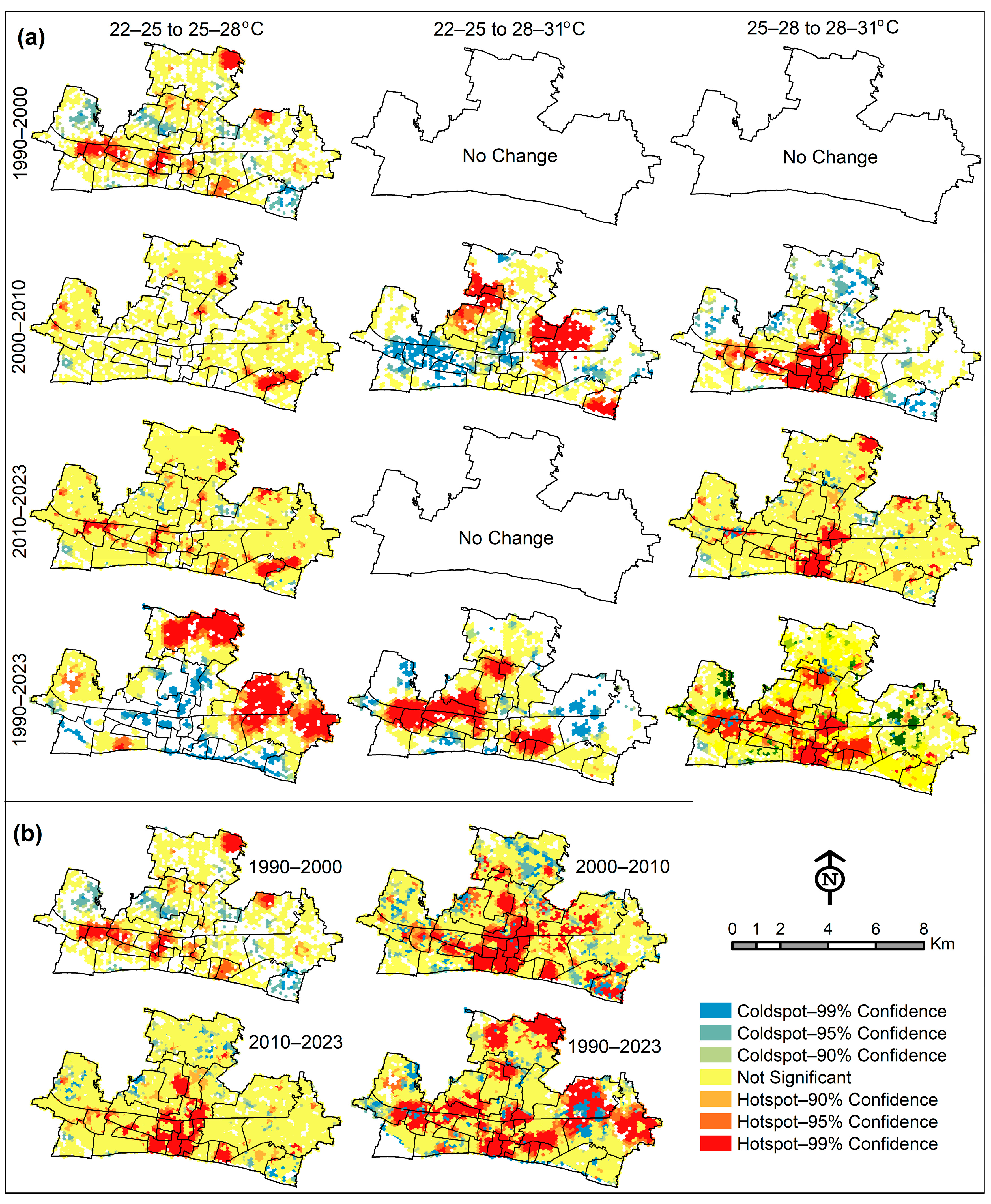
3.7. Hotspot Analysis of LST Change
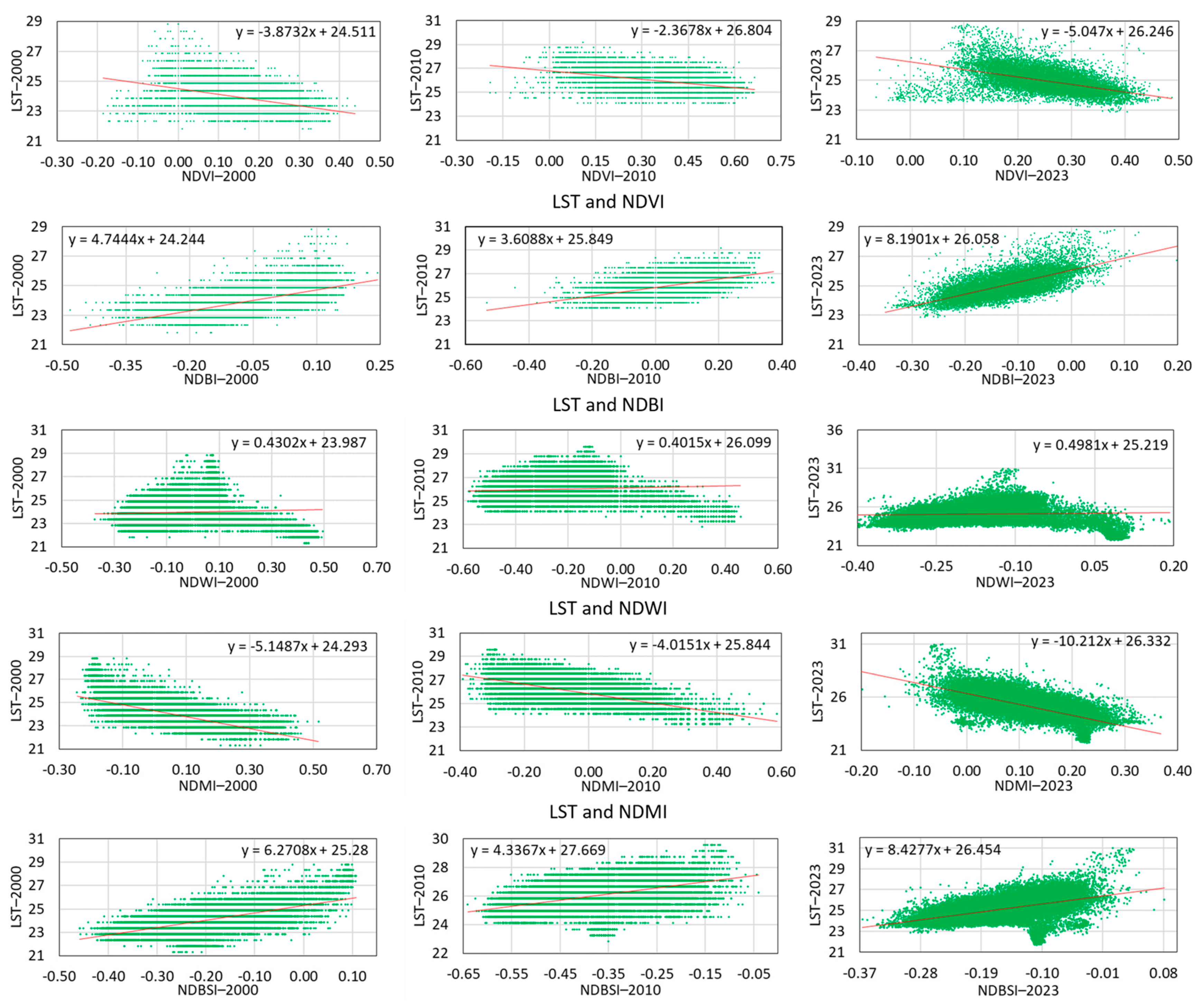
3.8. Relationship Between LST, LULC, and Biophysical Component
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abulibdeh, A. Analysis of urban heat island characteristics and mitigation strategies for eight arid and semi-arid gulf region cities. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, B.; Bandyopadhyay, J.; Banik, P. Monitoring the effect of urban development on urban heat island based on remote sensing and geo-spatial approach in Kolkata and adjacent areas, India. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarif, M.O.; Ranagalage, M.; Gupta, R.; Murayama, Y. Monitoring urbanization induced surface urban cool island formation in a South Asian megacity: A case study of Bengaluru India (1989–2019). Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhou, Y.; Chu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, A.; Guo, J. Implications of temporal change in urban heat island intensity observed at Beijing and Wuhan stations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, L.; Hao, L.; Sun, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C. Spatiotemporal trends of urban heat island effect along the urban development intensity gradient in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Modulation of Wintertime Canopy Urban Heat Island (CUHI) Intensity in Beijing by Synoptic Weather Pattern in Planetary Boundary Layer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.Z. Monitoring and assessing urban heat island variations and effects in the United States. U.S. Geol. Surv. Fact Sheet 2021, 2021–3031, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S. A Summary of Climate Averages for Ireland: 1981–2010. In Climatological Note 2012; No.14; Met Éireann: Dublin, Ireland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.R.; Lateh, H. Climate change in Bangladesh: A spatio-temporal analysis and simulation of recent temperature and rainfall data using GIS and time series analysis model. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 128, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Weng, Q. Use of impervious surface in urban land use classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrat, C.; Lemonsu, A.; Masson, V.; Guedalia, D. Impact of urban heat island on regional atmospheric pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1743–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, P.; Bou-Zeid, E. Heatwaves and urban heat islands: A comparative analysis of multiple cities. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xiao, J.; Bonafoni, S.; Berger, C.; Deilami, K.; Zhou, Y.; Frolking, S.; Yao, R.; Qiao, Z.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite remote sensing of surface urban heat islands: Progress, challenges, and perspectives. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, F.; Li, Z.L. Towards a local split window method over land surfaces. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1990, 11, 369–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshwari, A.; Mani, N. Estimation of land surface temperature of Dindigul district using Landsat 8 data. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2014, 3, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, J.M.; Becker, F. Terminology in thermal infrared remote sensing of natural surfaces. Remote Sens. Rev. 1995, 12, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voogt, J.A.; Oke, T.R. Thermal remote sensing of urban climates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, S.; Adams, E.A.; Neville, G.; Wada, Y.; de Sherbinin, A.; Mullin Bernhardt, E.; Adamo, S.B. Urban growth and water access in sub-Saharan Africa: Progress, challenges, and emerging research directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, C. Surface urban heat island in China’s 32 major cities: Spatial patterns and drivers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarini, M.; Molini, A.; Marpu, P.R.; Ouarda, T.B.; Ghedira, H. Urban climate modifcations in hot desert cities: The role of land cover, local climate, and seasonality. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 9980–9989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Lyu, D.; Du, Y.; Qiao, R.; Wu, J. How to effectively mitigate urban heat island effect? A perspective of water body patch size threshold. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 202, 103873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.N.; Chakraborti, S.; Saha, G.; Banerjee, A.; Singh, D. Analysing the dynamic relationship of land surface temperature and landuse pattern: A city level analysis of two climatic regions in India. City Environ. Interact. 2021, 8, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, A.S.M.; Khan, N.; Islam, A.R.M.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Shahid, S. Changes in urbanization and urban heat island effect in Dhaka city. Theoret. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 147, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.; Duguay, C.; Saunders, W.; Hachem, S. Pan-arctic land surface temperature from MODIS and AATSR: Product development and intercomparison. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3833–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, A.; Balzter, H.; Smith, C. Spatial variation of the daytime Surface Urban Cool Island during the dry season in Erbil, Iraqi Kurdistan, from Landsat 8. Urban Clim. 2015, 14, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukwattage, N.; Dayawansa, N.D.K. Urban heat islands and the energy demand: An analysis for Colombo city of Sri Lanka using thermal remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. GIS 2012, 1, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Sresto, M.A.; Siddika, S.; Fattah, M.A.; Morshed, S.R.; Morshed, M.M. A GIS and remote sensing approach for measuring summer-winter variation of land use and land cover indices and surface temperature in Dhaka district, Bangladesh. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Lu, D.; Schubring, J. Estimation of land surface temperature—vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishola, K.A.; Okogbue, E.C.; Adeyeri, O.E. Dynamics of surface urban biophysical compositions and its impact on land surface thermal field. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Dodd, J.K.; Benjamin, S.G.; Cooper, J.M. Satellite estimation of surface energy balance, moisture availability and thermal inertia. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1981, 20, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M.; Oke, T.R.; Emery, W.J. Satellite-derived urban heat islands from 3 coastal cities and the utilization of such data in urban climatology. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1989, 10, 1699–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniello, C.; Morgan, K.; Busbey, A.; Newland, L. Mapping micro-urban heat islands using Landsat TM and a GIS. Comput. Geosci. 1995, 21, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.P.; Quattrochi, D.A. Land-use and land-cover change, urban heat island phenomenon, and health implications: A remote sensing approach. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Paolini, L. Land surface temperature retrievalfrom LANDSAT TM 5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, X.; Guo, C.; Li, L.; Song, G.; Zhen, X.; Yuan, D.; Kalkstein, A.J.; Li, F. The urban heat island and its impact on heat waves and human health in Shanghai. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2010, 54, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veena, K.; Parammasivam, K.M.; Venkatesh, T.N. Urban Heat Island studies: Current status in India and a comparison with the international studies. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 129, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotharkar, R.; Bagade, A.; Singh, P.R. A systematic approach for urban heat island mitigation strategies in critical local climate zones of an Indian city. Urban Clim. 2020, 34, 100701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrar, R.; Sarkar, S.K.; Nishtha, K.T.; Talukdar, S.; Rahman, A.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Mosavi, A. Assessing the spatial mapping of heat vulnerability under Urban Heat Island (UHI) Effect in the Dhaka metropolitan area. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Dar, S.N. Dynamics of land use land cover and its impact on land surface temperature: A study of Faridabad District, India. GeoJournal 2024, 89, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P. Remote sensing of urban heat islands from an environmental satellite. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1972, 53, 647. [Google Scholar]
- Matson, M.; Mcclain, E.P.; McGinnis, D.F., Jr.; Pritchard, J.A. Satellite detection of urban heat islands. Mon. Weather Rev. 1978, 106, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.C. Assessment of the urban heat island effect through the use of satellite data. Mon. Weather Rev. 1979, 107, 1554–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, A.; Rani, H.P.; Jayakumar, K.V. Monitoring of dynamic wetland changes using NDVI and NDWI based Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummari, R.; Allu, P.K.R.; Mesapam, S.; Allu, A.R.; Vinakallu, B.; Ankam, B.P. Effect of LULC Changes on Land Surface Temperature. In Developments and Applications of Geomatics; Mesapam, S., Ohri, A., Sridhar, V., Tripathi, N.K., Eds.; DEVA 2022. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2024; Volume 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Qiao, X.; Abbas, M. Addressing the impact of land use land cover changes on land surface temperature using machine learning algorithms. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuruzzaman, M. Urban heat island: Causes, effects and mitigation measures—A review. Int. J. Environ. Monit. Anal. 2015, 3, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abir, F.A.; Ahmmed, S.; Sarker, S.H.; Fahim, A.U. Thermal and ecological assessment based on land surface temperature and quantifying multivariate controlling factors in Bogura, Bangladesh. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, M.Y.; Rahman, M.Z.; Uddin, M.M.; Rahman, F.M.A. Spatio-temporal dynamic land cover changes and their impacts on the urban thermal environment in the Chittagong metropolitan area, Bangladesh. GeoJournal 2021, 86, 2119–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Zhu, X.; Rahman, M.S.; Choi, K. Simulating Land Cover Changes and Their Impacts on Land Surface Temperature in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5969–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, M.S.; Bala, S.K.; Islam, A.K.M.S.; Islam, G.M.T.; Roy, D. An Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Trends of Land Surface Temperature in the Dhaka Metropolitan Area by Applying Land sat Images. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2021, 13, 538–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, T.; Gazi, M.Y.; Mia, M.B. Assessment of Land Cover Dynamics, Land Surface Temperature, and Heat Island Growth in Northwestern Bangladesh Using Satellite Imagery. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 661–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.; Islam, M.K.; Jahan, I.; Chowdhury, M.A. Assessing the impacts of vegetation loss and land surface temperature on Surface Urban Heat Island (SUHI) in Gazipur District, Bangladesh. Comput. Urban Sci. 2024, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilek, M.U.; Cilek, A. Analyses of land surface temperature (LST) variability among local climate zones (LCZs) comparing Landsat-8 and ENVI-met model data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS). Statistical Yearbook Bangladesh-2019; Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS), Statistics & Informatics Division (SID), Ministry of Planning, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS). District Statistics, Rajshahi; Ministry of Planning, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kafy, A.A.; Rahman, M.S.; Faisal, A.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Islam, M. Modelling future land use land cover changes and their impacts on land surface temperatures in Rajshahi, Bangladesh. Rem. Sens. Appl. Soci. Environ. 2020, 18, 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Rahman, A. Urban Green and Blue Spaces Dynamics—A Geospatial Analysis Using Remote Sensing, Machine Learning and Landscape Metrics in Rajshahi Metropolitan City, Bangladesh. In Advancements in Urban Environmental Studies. GIScience and Geo-Environmental Modelling; Rahman, A., Sen Roy, S., Talukdar, S., Shahfahad, Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, P.S., Jr. An Improved Dark-Object Subtraction Technique for Atmospheric Scattering Correction of Multispectral Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 24, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Woodcock, C.E.; Seto, K.C.; Lenney, M.P.; Macomber, S.A. Classification and Change Detection Using Landsat TM Data: When and How to Correct Atmospheric Effects? Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. U.S. Geological Survey, Landsat 7 Science Data Users Handbook; U.S. Department of the Interior: Reston, VA, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A.; Skoković, D.; Mattar, C.; Cristóbal, J. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Methods from Landsat-8 Thermal Infrared Sensor Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1840–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardy, B.; Labérenne, M.; Lagacherie, P.; Dedieu, G. A Software Tool for Atmospheric Correction and Land Surface Temperature Retrieval from Landsat Thermal Data Accounting for the Spatial Variability of the Atmosphere. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, M.; Poddar, I.; Saha, A.; Islam, N.; Roy, R. Analysis of land surface temperature and its correlation with urban, water, vegetation, and surface indices in the Siliguri Urban Agglomeration area of the Himalayan foothill region. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2025, 16, 2470393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsat 8 (L8) Data Users Handbook; Version 5.0; U.S. Geological Survey: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/media/files/landsat-8-data-users-handbook (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Barsi, J.A.; Schott, J.R.; Hook, S.J.; Raqueno, N.G.; Markham, B.L.; Radocinski, R.G. Landsat-8 thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) Vicarious Radiometric Calibration. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11607–11626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdan, U.; Jovanovska, G. Algorithm for Automated Mapping of Land Surface Temperature Using LANDSAT 8 Satellite Data. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 1480307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q.; Chen, B.Q. Remote sensing of the urban heat island and its changes in Xiamen City of SE China. J. Environ. Sci. 2004, 16, 276–281. [Google Scholar]
- USGS. (U.S. Geological Survey). 2013. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/landsat-missions (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Srivastava, P.; Majumdar, T.; Bhattacharya, A.K. Surface temperature estimation in Singhbhum Shear Zone of India using Landsat-7 ETM thermal infrared data. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulde, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Kennedy, R. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diek, S.; Fornallaz, F.; Schaepman, M.E.; De Jong, R. Barest pixel composite for agricultural areas using Landsat time series. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Land surface temperature retrieval from CBERS-02 IRMSS thermal infrared data and its applications in quantitative analysis of urban heat island effect. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 10, 789–797. [Google Scholar]
- Naim, M.N.H.; Kafy, A.-A. Assessment of urban thermal field variance index and defining the relationship between land cover and surface temperature in Chattogram city: A remote sensing and statistical approach. Environ. Challeng. 2021, 4, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lu, D.; Moran, E.; Hetrick, S. Mapping impervious surface area in the Brazilian Amazon using Landsat Imagery. GIScience Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Pradhan, L.; Kumari, M.; Bhattacharya, P. Assessing urban heat islands and thermal comfort in Noida City using geospatial technology. Urban Climate 2021, 35, 100751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfamariam, S.; Govindu, V.; Uncha, A. Spatio-temporal analysis of urban heat island (UHI) and its effect on urban ecology: The case of Mekelle city, Northern Ethiopia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranjcic, N.; Medak, D.; Zupan, R.; Rezo, M. Machine learning methods for classification of the green infrastructure in city areas. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Lewis, H.G.; Gunn, S.R. Linear spectral mixture models and support vector machines for remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 38, 2346–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, M.B.; Pirasteh, S.; Pradhan, B.; Mahmud, A.R.; Sulaiman, W.N.A.; Moradi, A. An artificial neural network model for flood simulation using GIS: Johor River Basin, Malaysia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y. Mapping Landslide Susceptibility Using Machine Learning Algorithms and GIS: A Case Study in Shexian County, Anhui Province, China. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ma, D.; Xiong, J.; Cheng, W.; Ji, H.; Wang, N.; Guo, L.; Duan, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, G. Flash flood vulnerability assessment of roads in China based on support vector machine. Geocarto Int. 2021, 37, 6141–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, G.R.F. Urban land use land cover changes and their effect on land surface temperature: Case study using Dohuk City in the Kurdistan region of Iraq. Climate 2017, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranagalage, M.; Dmslb, D.; Murayama, Y.; Zhang, X.; Estoque, R.C.; Enc, P.; Morimoto, T. Quantifying surface urban heat island formation in the world heritage tropical mountain city of Sri Lanka. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, H. An improved approach for monitoring urban built-up areas by combining NP P-VIIRS night-time light, NDVI, NDWI, and NDBI. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, F.; Alonso, L.; Fitts, Y.; Hadjiosif, A.; Comby, J. Evaluation of the Effect of Urban Redevelopment on Surface Urban Heat Islands. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Saha, S.K. Spatial dynamics of cropland and cropping pattern change analysis using Landsat TM and IRS P6 LISS III satellite images with GIS. Geospat. Inf. Sci. 2009, 12, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geogr. Anal. 1992, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Islam, A.H.M.H.; Islam, M.N. Geospatial modelling on the spread and dynamics of 154-day outbreak of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic in Bangladesh towards vulnerability zoning and management approaches. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 2059–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Balzter, H.; Qiu, B.; Cheng, J. Directional and Zonal Analysis of Urban Thermal Environmental Change in Fuzhou as an Indicator of Urban Landscape Transformation. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousta, I.; Sarif, M.O.; Gupta, R.D.; Olafsson, H.; Ranagalage, M.; Murayama, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mushore, T.D. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Land Use/Land Cover and Its Effects on Surface Urban Heat Island Using Landsat Data: A Case Study of Metropolitan City Tehran (1988–2018). Sustainability 2018, 10, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.R. TerrSet 2020 User’s Manual; Clark Labs, Clark University: Worcester, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, A.K.; Ping, O.W. The influence of land-use/land-cover changes on land surface temperature: A case study of Kuala Lumpur metropolitan city. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 1049–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahfahad; Bindajam, A.A.; Naikoo, M.W.; Horo, J.P.; Mallick, J.; Rihan, M.; Malcoti, M.D.; Talukdar, S.; Rahman, R.; Rahman, A. Response of soil moisture and vegetation conditions in seasonal variation of land surface temperature and surface urban heat island intensity in sub-tropical semi-arid cities. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2023, 153, 367–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah, M.A.; Morshed, S.R.; Morshed, S.Y. Multi-layer perceptron-Markov chain-based artificial neural network for modelling future land-specific carbon emission pattern and its influences on surface temperature. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannaros, T.M.; Melas, D.; Daglis, I.A.; Keramitsoglou, I. Development of an operational modeling system for urban heat islands: An application to Athens, Greece. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Zou, K.; Li, G.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.; Xu, W. Evaluation of Urban Thermal Comfort and Its Relationship with Land Use/Land Cover Change: A Case Study of Three Urban Agglomerations, China. Land 2022, 11, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, C.; Li, Q. Effects of landscape pattern on land surface temperature in Nanchang, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaraki, K.F.; Hazaymeh, K.; Al-Tarawneh, O.M.; Jawarneh, R.N. Deep learning-based modeling of land use/land cover changes impact on land surface temperature in Greater Amman Municipality, Jordan (1980–2030). GeoJournal 2024, 89, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, K.; Ghafoor, G.Z.; Sharif, F.; Shahid, M.G.; Shahzad, L.; Ghafoor, N.; Hayyat, M.U.; Farhan, M. Spatio-temporal analysis of land use land cover change and its impact on land surface temperature of Sialkot City, Pakistan. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Kanchan, R. Analytical study on the relationship among land surface temperature, land use/land cover and spectral indices using geospatial techniques. Discov. Environ. 2024, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, R.; Li, F.; Yang, W.; Zhou, C.; Jin, J.; Shi, Y. Simulation of thermal effects due to different amounts of urban vegetation within the built-up area of Beijing, China. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2009, 16, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajerani, A.; Bakaric, J.; Jeffrey-Bailey, T. The urban heat island effect, its causes, and mitigation, with reference to the thermal properties of asphalt concrete. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNFCCC. The Copenhagen Accord of 18 Dec 2009, 2/CP.15. In Proceedings of the 15th Session of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, Copenhagen, Denmark, 7–18 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
| Sensor | Sensor | Data Level | Date | Band Used | Radiometric Resolution | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 5 | TM | Level 1 | 14 November 1990 and 5 November 2010 | Blue (b1) Green (b2) Red (b3) NIR (b4) SWIR-1 (b5) Thermal (b6) SWIR-2 (b7) | 0.45–0.52 µm 0.52–0.60 µm 0.63–0.69 µm 0.76–0.90 µm 1.55–1.75 µm 10.40–12.50 µm 2.08–2.35 µm | 30 30 30 30 30 120 (30) * 30 |
| Landsat 7 | ETM+ | Level 1 | 17 November 2000 | Blue (b1) Green (b2) Red (b3) NIR (b4) SWIR-1 (b5) Thermal (b6) SWIR-2 (b7) | 0.45–0.52 µm 0.52–0.60 µm 0.63–0.69 µm 0.76–0.90 µm 1.55–1.75 µm 10.40–12.50 µm 2.08–2.35 µm | 30 30 30 30 30 120 (30) * 30 |
| Landsat 8 | OLI | Level 1 | 3 November 2023 | blue (b2) Green (b3) Red (b4) NIR (b5) SWIR-1 (b6) SWIR-2 (b7) TIRS-1 (b10) | 0.45–0.51 µm 0.53–0.59 µm 0.64–0.67 µm 0.85–0.88 µm 1.57–1.65 µm 2.11–2.29 µm 10.6–11.19 µm | 30 30 30 30 30 30 100 (30) * |
| UTFVI | Urban Heat Island (UHI) Phenomenon/Heat Distribution | Ecological Evaluation Index (EEI)/Thermal Comfort |
|---|---|---|
| ≤0.005 | None/Weak | Excellent/Good |
| 0.005–0.01 | Middle | Normal |
| 0.01–0.015 | Strong | Bad |
| 0.015–0.02 | Stronger | Worse |
| ≥0.02 | Strongest | Worst |
| LST (°C) | Year | Change (°C) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2023 | 1990–2000 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2023 | 1990–2023 | |
| Minimum | 20.62 | 21.10 | 21.70 | 22.82 | 0.48 | 0.60 | 1.12 | 2.20 |
| Maximum | 26.67 | 27.82 | 29.10 | 30.96 | 1.15 | 1.28 | 1.86 | 4.29 |
| Mean | 23.32 | 23.95 | 24.90 | 25.98 | 0.63 | 0.95 | 1.08 | 2.66 |
| Increase in LST (°C) | 1990–2000 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2023 | 1990–2023 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | % | Area (km2) | % | Area (km2) | % | Area (km2) | % | |
| <1 | 33.67 | 70.15 | 3.95 | 8.23 | 43.35 | 90.31 | 9.62 | 20.04 |
| 1–2 | 12.40 | 25.83 | 19.44 | 40.50 | 4.53 | 9.44 | 17.03 | 35.48 |
| 2–3 | 1.25 | 2.60 | 21.08 | 43.92 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 16.80 | 35.00 |
| >3 | 0.68 | 1.42 | 3.53 | 7.35 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 4.55 | 9.48 |
| Total | 48.00 | 100.00 | 48.00 | 100.00 | 48.00 | 100.00 | 48.00 | 100.00 |
| UTFVI | Area (km2) | % of the Total Area | Urban Heat Island Phenomenon (UHI) | Ecological Evaluation Index (EEI) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2023 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2023 | |||
| ≤0.005 | 28.11 | 30.09 | 26.15 | 26.57 | 58.56 | 62.67 | 54.48 | 55.35 | None/Weak | Excellent/Good |
| 0.005–0.01 | - | - | - | 2.27 | - | - | - | 4.73 | Middle | Normal |
| 0.01–0.015 | - | - | 11.40 | 2.24 | - | - | 23.75 | 4.67 | Strong | Bad |
| 0.015–0.02 | 10.69 | 10.39 | - | 2.22 | 22.27 | 21.65 | - | 4.63 | Stronger | Worse |
| ≥0.02 | 9.20 | 7.53 | 10.44 | 14.70 | 19.17 | 15.69 | 21.77 | 30.63 | Strongest | Worst |
| Total | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, M.R.; Mark, B.G. Geospatial Analysis of Urban Warming: A Remote Sensing and GIS-Based Investigation of Winter Land Surface Temperature and Biophysical Composition in Rajshahi City, Bangladesh. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115107
Rahman MR, Mark BG. Geospatial Analysis of Urban Warming: A Remote Sensing and GIS-Based Investigation of Winter Land Surface Temperature and Biophysical Composition in Rajshahi City, Bangladesh. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):5107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115107
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Md Rejaur, and Bryan G. Mark. 2025. "Geospatial Analysis of Urban Warming: A Remote Sensing and GIS-Based Investigation of Winter Land Surface Temperature and Biophysical Composition in Rajshahi City, Bangladesh" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 5107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115107
APA StyleRahman, M. R., & Mark, B. G. (2025). Geospatial Analysis of Urban Warming: A Remote Sensing and GIS-Based Investigation of Winter Land Surface Temperature and Biophysical Composition in Rajshahi City, Bangladesh. Sustainability, 17(11), 5107. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17115107








