Abstract
The Mediterranean region is highly vulnerable to environmental and anthropogenic pressures, including climate change, which significantly affect its aquatic ecosystems, especially shallow lakes. This study examines the fish community and ecological quality of Lake Paralimni, a shallow mesotrophic lake in Central Greece that experienced complete desiccation between 1991 and 1996. Using field surveys, fish species composition, abundance, and biomass were assessed, and the lake’s ecological quality was evaluated through the Greek Lake Fish Index (GLFI) alongside an integrated SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) and AHP (Analytic Hierarchy Process) analysis. Six fish species from three families were recorded, predominantly native and endemic, with introduced species representing a minor fraction. While GLFI rated the lake’s quality as “Good,” other multi-metric indicators downgraded it to “Moderate”, highlighting the importance of comprehensive assessments. SWOT analysis revealed strengths such as high native biodiversity and legal protection under Natura 2000, but also weaknesses like fluctuating water levels and limited monitoring. Opportunities include sustainable fisheries and conservation efforts, while threats involve climate change, eutrophication, and illegal species introductions. AHP emphasized threats and weaknesses as top priorities. The study recommends hydrological regulation, invasive species control, and long-term monitoring for sustainable lake management and biodiversity conservation.
1. Introduction
The Mediterranean region is among the most vulnerable areas to environmental changes [1]. These changes, driven primarily by climate change and anthropogenic pressures, may significantly alter the hydrology of aquatic ecosystems in the region [2]. Shallow lakes and their associated fish communities, which are vital components of freshwater ecosystems, are particularly vulnerable to these impacts. Fish play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and supporting ecological balance. In addition, freshwater fish communities contribute to ecosystem services such as recreational fishing, food provision, and cultural value [3,4,5]. However, freshwater ecosystems face growing threats from multiple environmental pressures, including habitat degradation, climate change, invasive species introductions, and pollution [6,7,8]. Biodiversity loss presents a significant challenge to lake fish populations, which are particularly sensitive to environmental changes and habitat disturbances [9]. Declines in water quality, alterations in hydrological regimes, and competition from invasive species further exacerbate the risks to native fish communities [10]. Climate change intensifies these threats by altering temperature and oxygen levels, potentially leading to shifts in species distribution or even local extinctions [8,11,12]. Given the ecological importance of freshwater fish for ecosystem stability and the delivery of key ecosystem services [13], effective conservation strategies are urgently needed. Moreover, robust risk assessment and management frameworks are essential to safeguard the ecological integrity and sustainable use of these aquatic systems [14]. Sustainable lake management in complex socio-ecological contexts requires an integrated understanding of ecological conditions and structured tools for action prioritization [15]. Yet, few studies have systematically combined ecological assessments with strategic planning tools, such as SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) [16,17,18]. This study addresses this gap by integrating fish-based ecological quality assessment with SWOT–AHP analysis to develop a risk-informed and management-oriented approach for Mediterranean lakes. SWOT enables qualitative identification of internal and external factors affecting lake ecosystems, while AHP adds quantitative prioritization, enabling objective, transparent decision-making. Together, these tools form a hybrid framework capable of linking biological conditions with management priorities, in line with EU policies like the Water Framework Directive (WFD, 2000/60/EC), which aims for good ecological and chemical status of all water bodies [19]. Maintaining a good ecological status is essential not only for biodiversity protection but also for ensuring long-term ecosystem services such as water purification, fisheries, and recreation [3,20], contributing directly to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) [21]. Incorporating SWOT–AHP into lake management can help identify system-level strengths and weaknesses, align actions with WFD objectives, and support evidence-based policy formulation by ranking strategies based on environmental, economic, and social criteria.
This study uses Lake Paralimni as a case study to demonstrate the application of the SWOT–AHP method for assessing ecological risk and prioritizing lake management strategies. Specifically, it assesses the fish community structure, evaluates ecological quality using the Greek Lake Fish Index (GLFI), and identifies management priorities using the integrated framework. The findings emphasize the value of strategic planning in protecting freshwater biodiversity and promoting sustainable ecosystem governance, especially for small lakes in water-stressed regions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Lake Paralimni (Figure 1) is in Central Greece (Eastern Mediterranean), specifically in the Boeotian Kifissos River basin. Its geographic coordinates are approximately 38.45° N latitude and 23.22° E longitude. Together with Lake Yliki, it forms part of a hydrological network that historically encompassed the Kopaida basin [22], situated in a typical Mediterranean climate zone characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The two lakes are hydrologically connected via a 2.5 km canal located southwest of Lake Paralimni, enabling water exchange and contributing to the lake’s fluctuating water levels. Historically, Lake Paralimni was significantly larger, with a stable surface area of 14.7 km2 in the 1940s. However, extensive water withdrawals for irrigation and groundwater pumping led to the complete desiccation of the lake between 1991 and 1996. Additionally, it has periodically been used to supply drinking water to the Municipality of Chalkida [23].
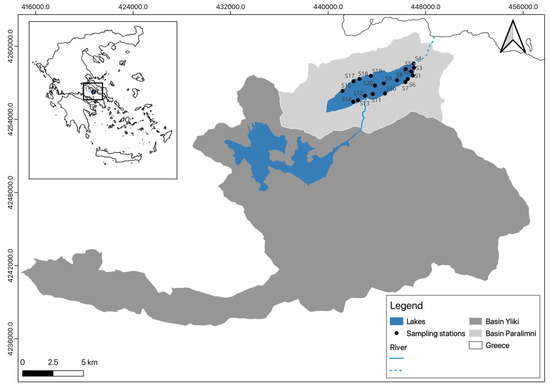
Figure 1.
Location map of Lake Paralimni and the Boeotian Kifissos River basin. The sampling stations where benthic gillnets were deployed for fish monitoring in October 2022 are also indicated (S1, S2, …S20).
In recent years, direct water extraction for drinking purposes has been halted to prevent further water loss. Despite this, the lake has shrunk to an area of about 4 km2 and has an average depth of 5 m, classifying it as a shallow lake. It discharges periodically into the North Euboean Gulf through a seasonal stream. The lake is considered mesotrophic but shows tendencies toward eutrophication, indicating moderate nutrient levels with potential risks of algal blooms [24].
Lake Paralimni is part of the Natura 2000 network (Lakes Yliki and Paralimni—Boeotian Kifissos System, GR2410001), underlining its ecological significance. Additionally, it is subject to a Public Health Decree (Ministerial Decision A5/2280/A.F. 720, 13 December 1983) aimed at protecting the drinking water sources of the city of Athens.
The fish community of Lake Paralimni includes 11 recorded species from five families, with a high proportion of endemic species [25,26] (Table 1). Notable endemics include Luciobarbus graecus, Leucos ylikiensis, and Scardinius graecus, highlighting the lake’s value as a conservation hotspot. However, species introductions pose ecological risks. Alien species, such as Ctenopharyngodon idella, Hypophthalmichthys molitrix, and Hypophthalmichthys nobilis, were introduced to improve fisheries productivity and control macrophyte overgrowth. Additionally, Silurus aristotelis, originally native to the Acheloos River basin in Western Greece, was translocated and may impact native fish populations [25].

Table 1.
Fish species reported in Lake Paralimni [25,26].
Fishing intensity in Lake Paralimni remains low, with fewer than 10 professional fishermen operating in the area. However, recreational and competitive carp fishing has increased in recent years. While overall fishing pressure is currently limited, the absence of systematic long-term monitoring raises concerns about undetected ecological changes, shifts in fish populations, and the long-term effects of non-native species.
2.2. Data Sources
Primary data used in the SWOT analysis were obtained from fish samplings conducted at Lake Paralimni in October 2022. Sampling was conducted during a period when surface water temperature exceeded 15 °C, following the guidelines of the international standard ISO EN 14757 CEN [28]. Benthic Nordic multi-mesh gillnets (consisting of 10 different mesh panels (30 m × 1.5 m, length × height) with mesh sizes ranging from 8 to 70 mm knot to knot, i.e., 8, 14, 16, 20, 24, 30, 36, 45, 55, 70 mm) were deployed at 20 locations throughout the lake (Figure 1). The total fishing effort was determined based on (a) the surface area and maximum depth of the lake, (b) general guidelines provided by [28] regarding fishing effort estimation and its distribution across depth zones, (c) recommendations by [29] to reduce the [28] recommended effort, aiming to lower monitoring costs and protect species. The fishing effort was distributed across three depth zones. The gillnets were deployed in the evening (e.g., 18:00–20:00) and retrieved the following morning (e.g., 06:00–08:00), ensuring a soaking time of approximately 12 h. Fish were identified to the species level, and each individual was measured for Total length (TL, mm) and Body weight (W, g). Finally, the abundance and biomass of each species were estimated based on the total number of individuals and total weight.
Simultaneously, an oxygen and temperature profile was recorded by conducting on-site measurements at 1-m depth intervals at the deepest point of the lake using a portable multiparameter instrument.
Additional (secondary) data used for SWOT analysis were derived from existing literature (e.g., prior ecological assessments [30,31,32], water quality data, habitat condition [33,34] national and regional environmental databases, expert consultations with fisheries biologists and regional water authorities), and focused-group discussions with stakeholders (e.g., fishers, planners, ecologists). Land-use metrics (e.g., percentage of non-natural land cover) were extracted from official GIS land-use datasets [35].
2.3. Ecological Quality Assessment
The ecological quality of Lake Paralimni was assessed based on the fish catch data using the Greek Lake Fish Index (GLFI) [36]. This index incorporates two fish-based metrics: (a) the relative numerical abundance of introduced species (including both alien and translocated) and (b) the relative biomass of omnivorous species. Both metrics respond to overall lake degradation and eutrophication [36]. In addition to biological metrics, the index incorporates several environmental descriptors that define lake typology, such as altitude, maximum depth, and alkalinity, the latter serving as an indicator of the geological influence on water chemistry. The GLFI also integrates pressure indicators, including the percentage of non-natural land cover (NNLC) in the drainage basin, the Lake Habitat Modification Score (LHMS), reflecting the extent of overall degradation [37], and the Total phosphorus (TP) concentrations (µg/L) in water, as a proxy for nutrient enrichment and eutrophication. The GLFI produces a score ranging from 0 (highly degraded conditions) to 1 (undisturbed conditions) [36]. Additionally, the lake’s ecological quality, as evaluated by various Greek biological indices—including the phytoplankton index (HeLPhy) [30], the benthic macroinvertebrate index (GLBiI) [31], and the macrophyte index (HeLM) [32]—was obtained from the available literature. Finally, the “one-out, all-out” approach was applied to determine the lake’s ecological status. According to this approach, the overall status of a water body is assigned based on the lowest classification among the assessed biological quality elements [38].
2.4. The SWOT–AHP Method
SWOT analysis is a structured decision-support tool used to qualitatively identify and evaluate the internal and external factors influencing ecosystem management. It helps identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats affecting a lake’s ecological integrity [39,40,41,42].
In lake ecosystems, typical strengths include biodiversity, legal protection (e.g., Natura 2000), and low anthropogenic disturbance. Weaknesses may involve insufficient long-term monitoring, invasive species, or hydrological instability. Opportunities can arise from conservation funding, policy support, or local engagement. Threats include climate-induced droughts, nutrient loading, illegal species introductions, or land-use change. Combined with ecological assessment, SWOT provides a framework for identifying conservation needs and informing policy-aligned management strategies [43].
To transform qualitative SWOT results into measurable decision criteria, the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) can be employed [17,44]. AHP is a multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) technique that allows pairwise comparison of alternatives and criteria to assign relative importance values [45,46].
The SWOT–AHP process used in this study included three main levels:
- Goal level—Prioritizing effective, sustainable management strategies for Lake Paralimni.
- Criteria level—SWOT categories (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats).
- Alternative level—Proposed strategies for conservation and lake management.
Key SWOT elements were identified through a combination of field-based ecological quality assessment, literature reviews, focused-group discussions with stakeholders (fishermen, ecologists, planners), and expert consultation with fisheries biologists and regional water authorities.
Each identified factor was inserted into a pairwise comparison matrix using Saaty’s 1–9 scale (Table 2), where 1 indicates equal importance, and 9 represents extreme importance of one element over another as determined through expert judgment.

Table 2.
Scale of comparative importance in pairwise comparisons between SWOT factors, using Saaty’s 1–9 scale [47].
The priority weight vector for each matrix was calculated by normalizing each column (i.e., dividing each element by its column sum) and then averaging the rows. This process yields the relative weight of each element within its matrix. To ensure that the comparisons were logically consistent, a consistency test was performed. Initially, the Weighted Sum Vector (WSV) was calculated by multiplying the comparison matrix A by the priority weights vector w (i.e., WSV = A × w). Subsequently, each row of the WSV was divided by its corresponding priority weight to yield the consistency vector and then the principal eigenvalue was estimated. The above was used to estimate the Consistency Index () with n the number of rows and finally the Consistency Ratio (). RI is a Random Index (depends on the matrix sizes, e.g., for n = 4, RI = 0.90, and for n = 5, RI = 1.12 [47]). This ratio is computed to measure the consistency of pairwise comparisons. A CR below an acceptable threshold (typically 0.1) confirms that the comparisons are logically consistent and reliable for decision-making [18,44,47,48].
The SWOT–AHP approach was applied to Lake Paralimni to guide management priorities for fish community sustainability. Based on the combined ecological and stakeholder inputs:
- SWOT categories were ranked by importance (e.g., threats > weaknesses > strengths > opportunities),
- Factors within each SWOT group were weighted (e.g., Water Level Fluctuations, Climate-induced Droughts),
- Management strategies were evaluated and prioritized across three AHP criteria: environmental impact, feasibility, and urgency.
The weighted results were integrated into a final decision matrix to guide management action planning. A visual representation of this framework is presented in Figure 2.
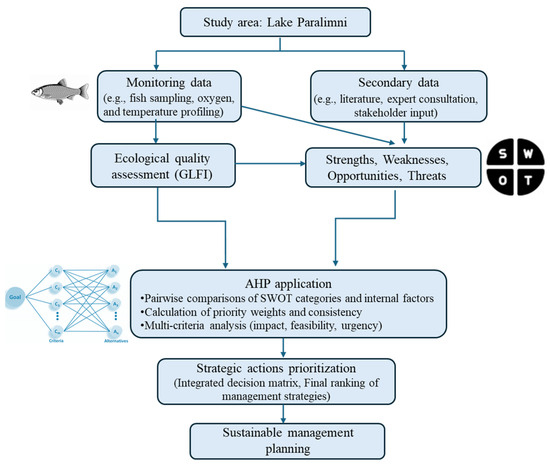
Figure 2.
Hierarchical flowchart of the methodology followed, combining biological assessment and SWOT–AHP analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Field Survey
The vertical profile of temperature (T, °C) and dissolved oxygen (DO, mg/L) recorded in the water column during the field survey is depicted in Figure 2. Dissolved oxygen (DO) concentrations exhibited a gradual decline below a depth of 6 m. Near the surface, DO levels exceeded 10 mg/L, decreasing steadily to approximately 6 mg/L at a depth of 11 m (Figure 2). In contrast, temperature remained relatively stable throughout the water column, ranging from 18.4 °C to 19.2 °C, with only a slight decline observed in the bottom layers (Figure 3).
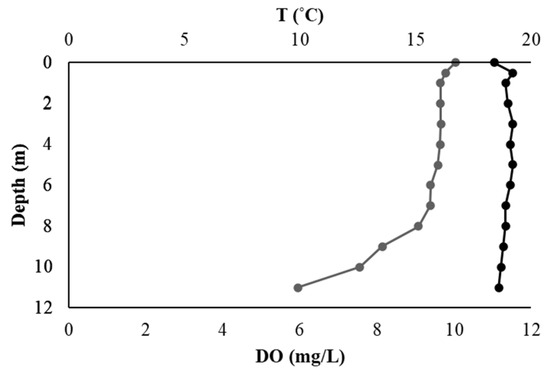
Figure 3.
Vertical profiles of temperature (T, °C) and dissolved oxygen (DO, mg/L) in the water column of Lake Paralimni, recorded in October 2022. Temperature is shown in black and DO in grey.
As for the fish, a total of 3635 fish, with a combined weight of approximately 81 kg, were caught during the survey, representing six species from three families (Table 3). The most abundant species in terms of the number of individuals was Luciobarbus graecus, followed closely by Leucos ylikiensis (Table 3). In terms of biomass, Leucos ylikiensis was the dominant species, followed by Luciobarbus graecus. The presence of the alien Carassius gibelio was also confirmed in the lake. Overall, the fish community of Lake Paralimni was dominated by native and endemic species, while the introduced species (Carassius gibelio and Silurus aristotelis) accounted for only a small proportion of the total catch.

Table 3.
List of fish species recorded in Lake Paralimni during the fish monitoring survey (October 2022). The total number of individuals (N) and total biomass (W, kg) per species are provided. The species classification into feeding groups according to their diet is also provided.
The highest fish abundance and biomass were recorded in the shallow zone (0–2.9 m depth), whereas the deepest zone (>6 m depth) exhibited the lowest abundance and biomass (Figure 4). However, zero catches were not observed at any depth (Figure 5).
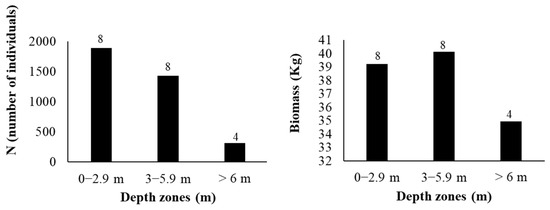
Figure 4.
Fish abundance Ν (number of individuals) and biomass (kg) per depth zone (m) in Lake Paralimni, October 2022. The numbers above each column represent the number of gillnets deployed in each depth zone.
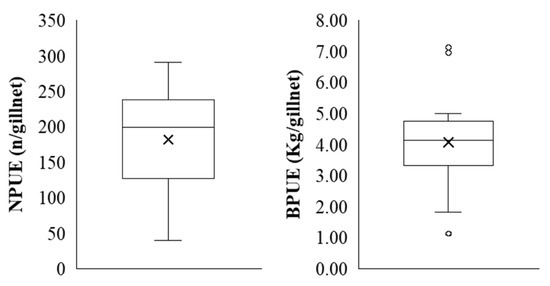
Figure 5.
Box-and-whisker plots of fish catches per sampling station, based on the number of individuals (NPUE, n/gillnet) and biomass (BPUE, kg/gillnet) in Lake Paralimni, October 2022. The horizontal line within the box represents the median value, while the “x” marker denotes the mean. The box represents the interquartile range (IQR), encompassing 50% of the data between the first (Q1) and third quartile (Q3). The vertical whiskers extend to the minimum and maximum values within the data range, excluding outliers, which are represented as circles.
3.2. Ecological Quality
Omnivorous species accounted for 47.04% of the total biomass in the benthic gillnet catch, while introduced species represented 2.59% of the total number of individuals. The Ecological Quality Ratio (EQR) for omnivorous species biomass (EQR-OMNIb) was 0.752, and for introduced species abundance (EQR-Introduceda) it was 0.613. These values yielded a final GLFI score of 0.68, corresponding to a “Good” ecological quality classification for Lake Paralimni.
The lake’s ecological quality assessment, incorporating different biological quality elements and multi-metric indices, yielded the following results: GLFI indicated a “Good” status, HeLPhy and HeLM both indicated a “High” status [30,32], while GLBiI assessed a “Moderate” status [31]. Thus, based on the “one-out, all-out” principle, the overall ecological status of the lake was classified as “Moderate”.
3.3. SWOT–AHP Analysis
The aggregation of primary and secondary data available for Lake Paralimni resulted in the list of SWOT factors presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) analysis for the fish fauna of Lake Paralimni.
The AHP analysis showed that threats (53.93%) were the most critical factor for Lake Paralimni’s management, followed by weaknesses (29.50%), while strengths (11.01%) and opportunities (5.56%) were assigned lower priority (Table 5). The CI was 0.0782, and the CR was 0.0869 (i.e., <0.1), confirming acceptable consistency and reliability of the comparisons.

Table 5.
Pairwise Comparison using Saaty’s 1–9 scale and Priority Weights of SWOT Factors in the AHP Analysis for Lake Paralimni.
Within strengths, the low abundance of invasive species was the most significant factor (38.4%), followed by biodiversity (30.0%) and Natura 2000 protection (19.1%) (Table 6). Among weaknesses, water level fluctuations were identified as the most critical issue (55.8%), reflecting the lake’s hydrological instability, followed by connectivity risks (26.3%), which increase the potential for species introductions (Table 6). Conservation and restoration initiatives (55.8%) ranked as the most valuable opportunity, whereas climate change and droughts (49.3%) emerged as the most severe threat, emphasizing the risk of declining water levels (Table 6).

Table 6.
Pairwise comparisons of factors within each SWOT category (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) using Saaty’s 1–9 scale for Lake Paralimni.
The AHP analysis used to prioritize management measures for Lake Paralimni was structured to ensure consistency between environmental impact and urgency (Table 7), reflecting the assumption that the ecological significance of each measure is inherently tied to its immediacy of implementation. Under this framework, Hydrological regulation and water level management emerged as the top priority, combining the highest feasibility (50.28%) with substantial environmental impact and urgency (42.45% each) (Table 7). Climate adaptation and drought mitigation ranked as a high-priority action, with scores exceeding 26% across all criteria. Illegal species monitoring and prevention was classified as a moderate priority (17.7% for both impact and urgency; 13.4% feasibility). Agricultural runoff control was ranked lower due to feasibility constraints (6.8%) despite moderate ecological importance (8.4%). Lastly, Conservation and habitat restoration was identified as a long-term action, with the lowest scores across all dimensions (4.2% impact and urgency; 3.5% feasibility).

Table 7.
Pairwise comparisons of five key management strategies for Lake Paralimni evaluated based on three criteria: Environmental impact, Feasibility, and Urgency. The comparisons were conducted using Saaty’s 1–9 scale.
These strategic priorities are visualized in Figure 6, which presents the average relative weights of the five key management strategies across the three AHP evaluation criteria.
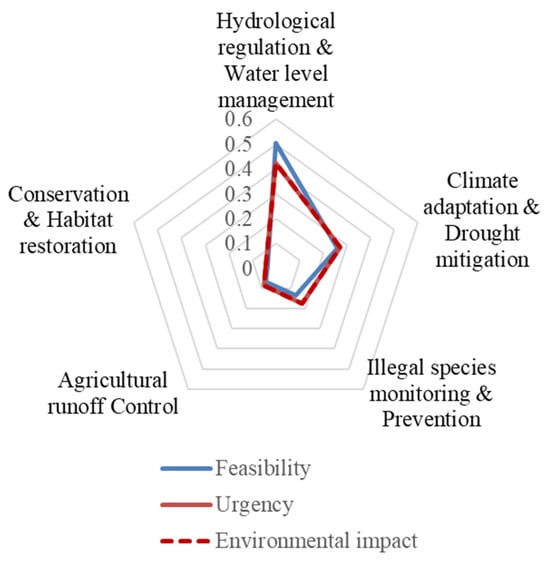
Figure 6.
Strategic polygon illustrating the prioritization of management strategies—hydrological regulation, climate adaptation, illegal species prevention, agricultural runoff control, and habitat restoration—based on AHP-derived weights for Environmental impact, Feasibility, and Urgency in Lake Paralimni.
4. Discussion
4.1. Fish Fauna Composition and Ecological Insights
The results of the fish monitoring survey in Lake Paralimni reveal valuable insights into the structure and distribution of its fish community, offering guidance for future ecosystem management strategies. The fish assemblage in Lake Paralimni is characterized by a predominance of native and endemic species, although introduced species such as Carassius gibelio and Silurus aristotelis were also recorded.
It is worth mentioning here that this is the first documentation of Carassius gibelio in Lake Paralimni. According to local fishermen, this species was absent prior to the early 2000s. Its introduction was likely facilitated either through hydrological connectivity with Lake Yliki or via informal stocking by local anglers/fishermen. The introduction of non-native fish species, whether deliberate or accidental, is a common phenomenon worldwide with potentially significant ecological implications. While the full extent of these impacts often remains uncertain [49,50], non-native species introductions generally contribute to the homogenization of aquatic ecosystems, posing risks to native biodiversity and altering ecosystem functioning [51,52,53]. The absence of Pelasgus marathonicus and Telestes beoticus in this survey is also noteworthy. These species, typically associated with riverine environments, may have historically been present but have declined due to past hydrological alterations and habitat fragmentation.
Similarly, the absence of Anguilla anguilla in the catch may be attributed to a combination of factors. These include the known limitations of gillnet sampling and the broader population decline observed across Europe—caused by overfishing, habitat degradation, and migration barriers [54,55]. Moreover, the recruitment of the species in Lake Paralimni may be further impeded by the disrupted connectivity with the sea, as overflow events toward the Euboean Gulf have become increasingly rare in recent years, thereby hindering the upstream migration and recolonization of Anguilla anguilla.
The relatively low abundance of non-native species in Lake Paralimni represents a positive ecological indicator. Introduced species are known to impact native fish populations through competition, predation, hybridization, habitat degradation, and disease transmission [56,57]. Even at low densities, introduced species can initiate long-term ecosystem shifts, as their ecological effects often unfold gradually over time [50], particularly in ecosystems with high endemic biodiversity like Lake Paralimni. The persistence of native and endemic species in the lake suggests that, thus far, non-native introductions have not caused major ecological imbalances, further indicating a relatively stable trophic web. However, without continuous monitoring, it remains uncertain whether their presence will eventually disrupt trophic interactions or induce shifts in community structure. Additionally, the ecological role of Silurus aristotelis, translocated from Western Greece, warrants further investigation, as predatory species can significantly influence prey abundance and trophic dynamics [58,59].
Fish abundance and biomass were highest in the shallow zones (0–2.9 m), reflecting the ecological preferences of many species for warmer, more productive areas with abundant food resources and a heterogeneous microhabitat structure [60]. These conditions are likely optimal for growth and reproduction [61]. In contrast, the lowest values were recorded in deeper zones (>6 m), likely due to reduced resource availability and lower temperatures [62]. However, the absence of zero catches in these deeper areas suggests that fish were distributed throughout the water column, likely supported by dissolved oxygen concentrations remaining above 5 mg/L. The lake’s temperature and oxygen profiles indicated well-mixed thermal conditions, with moderate oxygen depletion at depth—possibly driven by limited light penetration and reduced biological activity. Notably, hypoxic conditions commonly observed in eutrophic Mediterranean lakes [63,64] were not detected in this study.
4.2. Ecological Quality
The Greek Lake Fish Index (GLFI) developed using functional groups rather than individual species identities [29], provides a robust ecological assessment framework for Greek lakes with high endemic fish diversity. The classification of Lake Paralimni as having “Good” ecological quality under the GLFI indicates a moderate level of ecological integrity despite its history of hydrological disturbances. This suggests that the lake has maintained functional ecological processes and has not suffered severe degradation from eutrophication, pollution, or excessive anthropogenic pressures. However, this classification was somewhat unexpected, considering the lake’s history of hydrological instability, including its complete desiccation from 1991 to 1996. The recovery of the fish community likely reflects the positive influence of hydrological connectivity with Lake Yliki, which facilitated recolonization, along with limited fishing pressure that allowed populations to rebound (personal communication with professional fishermen).
Despite the GLFI classification, the overall ecological status of Lake Paralimni was downgraded to “Moderate” due to the integration of multiple biological indices using the “one-out, all-out” approach. Specifically, the Greek Lake Benthic Invertebrate Index (GLBiI) assessed the lake as “Moderate” [31]. These discrepancies between indices reflect differences in biological responses to environmental stressors, as fish, phytoplankton, macrophytes, and benthic macroinvertebrates respond uniquely to variations in water quality, hydrology, and habitat conditions. Discrepancies may also arise from differences in sampling periods and indicator sensitivities. These findings underscore the importance of a multidimensional assessment approach, as emphasized by [19]. By integrating multiple biological indices, a more comprehensive evaluation of ecological conditions can be achieved, ensuring that potential stressors affecting different biological communities are effectively captured.
4.3. The SWOT–AHP Analysis in Fish and Water Resources Management
SWOT and AHP analyses have been widely utilized in water resource and aquatic ecosystem management, highlighting their role in sustainable conservation strategies [16,18,65]. These frameworks provide a structured approach for assessing ecological, economic, and social factors that influence decision-making [16,18,65,66]. Their application spans diverse aquatic environments, including freshwater lentic and lotic systems, as well as coastal and marine ecosystems [16,18,65,66,67,68]. Although the outcomes of these analyses may be influenced by author subjectivity [69], they continue to offer valuable insights for ecosystem management.
In this study, the combined use of SWOT and AHP analyses was employed to identify key conservation and management priorities for a Mediterranean lake, with a focus on sustaining its fish fauna. The approach revealed notable strengths, such as the dominance of native fish species, alongside key weaknesses like water level fluctuations. Identified opportunities included the promotion of sustainable fisheries practices, while primary threats encompassed the impacts of climate change and species introductions—factors known to influence lake ecosystems [8,70]. Similar methodologies have been applied in fisheries conservation globally. For instance, [71] used a SWOT framework to evaluate sturgeon stock restoration in the Iranian waters of the Caspian Sea, identifying major threats such as ineffective management, unsustainable fishing, habitat degradation, and socio-economic pressures. Likewise, [67] implemented a combined SWOT–AHP approach to design a sustainable fisheries strategy in a marine protected area in Indonesia, highlighting the value of structured decision-making in balancing conservation goals with economic needs. These examples further underscore the utility of SWOT and AHP analyses in supporting sustainable resource management across aquatic systems.
4.4. Management Priorities and Conservation Strategies
Our study highlighted the key ecological dynamics and conservation challenges in Lake Paralimni, underscoring the necessity for targeted management interventions. Based on the SWOT–AHP analysis, the most pressing concerns for the lake’s fish community revolve around hydrological instability, climate-induced drought risks, and the potential ecological impacts of introduced species. To address these challenges, a multi-faceted, science-based management strategy is required, aligning with the principles of ecosystem-based management and the objectives of the WFD.
Hydrological regulation and water level management should be prioritized to prevent excessive water withdrawals, particularly during dry seasons. Implementing adaptive water management strategies, such as controlled water transfers from Lake Yliki, could mitigate extreme fluctuations. A hydrological monitoring network would provide real-time data on water levels, rainfall, and inflows, allowing timely interventions [70]. Establishing drought contingency plans, informed by climate modeling and hydrological assessments, would improve preparedness for extreme weather events.
Eutrophication prevention is another critical issue, as agricultural runoff remains a potential threat [72], emphasizing the need for adaptive nutrient management strategies. Enforcing stricter agricultural runoff regulations, including controlled fertilizer application, could minimize the risk of eutrophication. Introducing buffer zones and restoring riparian vegetation would help filter nutrients and sediments before they reach the lake [73], and also, along with the restoration of wetland habitats, will enhance water retention and reduce the impacts of seasonal droughts. A long-term water quality monitoring program should be maintained to track nutrient concentrations and detect early signs of degradation.
Species introductions continue to pose a significant concern, underscoring the need for stricter regulations to prevent unauthorized fish stocking. This is particularly important as rising temperatures may increasingly favor invasive species over native ones, potentially disrupting trophic interactions and further stressing native fish populations [72,74]. To address this, public outreach programs targeting local fishermen and recreational anglers should highlight the ecological risks associated with illegal introductions. In parallel, a systematic monitoring program should be implemented to track both the abundance and ecological impact of non-native species.
Sustainable fisheries management offers an opportunity for conservation and economic benefits. Establishing a regulated recreational fishing framework and incorporating catch-and-release policies for vulnerable native species could support conservation efforts while fostering ecotourism. The introduction of a permit system for recreational anglers, currently absent in Greece [75], could generate revenue that could be reinvested in conservation and monitoring programs.
Scientific data should play a central role in policy-making and management strategies. Ecological indices like the GLFI provide valuable insights into the lake’s ecological status, and decision-makers should incorporate these assessments into water management policies. Strengthening collaborations between researchers, policymakers, and local stakeholders would enhance adaptive management efforts, ensuring that conservation strategies evolve in response to emerging threats and ecological changes.
Public engagement is essential for long-term conservation success. Raising awareness about the lake’s ecological significance, biodiversity value, and conservation challenges through education programs and outreach initiatives can foster a sense of stewardship among local communities. Organizing stakeholder workshops, citizen science programs, and educational campaigns focused on the risks of invasive species, sustainable fishing practices, and climate resilience can improve compliance with conservation regulations.
Overall, Lake Paralimni serves as an important case study highlighting the value of integrating ecological assessments with structured decision-making tools like SWOT and AHP. This approach not only identifies key conservation priorities but also provides a framework for sustainable lake management that can be applied to similar freshwater ecosystems. We acknowledge that future work could incorporate more rigorous methodologies, including long-term ecological monitoring, advanced modeling, and participatory stakeholder engagement.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrates that the ecological sustainability of shallow Mediterranean lakes such as Lake Paralimni depends on the implementation of a scientifically informed, ecosystem-based management approach. Through the integration of a biological quality index, the SWOT–AHP analysis identified critical stressors, including hydrological instability and nutrient enrichment, underscoring the need for targeted remediation efforts. Key management priorities include enhancing hydrological regulation, mitigating eutrophication through nutrient load reductions, controlling non-native species, and reinforcing catchment-level land-use planning. Given the vulnerability of Mediterranean lakes to seasonal fluctuations, eutrophication, and anthropogenic pressures, these priorities should be pursued within the framework of adaptive management strategies that are responsive to climatic variability and anthropogenic drivers. Furthermore, aligning these actions with the objectives of the EU Water Framework Directive and leveraging structured decision-support tools—such as the integrated SWOT–AHP framework presented in this study—can facilitate more transparent and evidence-based policy formulation. The methodological approach employed here provides a transferable model for assessing and managing similar lentic ecosystems facing multifactorial pressures across the Mediterranean basin, particularly under similar socio-economic and ecological conditions, including EU water policy frameworks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: O.P.; Developing methods: O.P.; Conducting the research: O.P. and D.C.B.; Data analysis: O.P. and D.C.B.; Data interpretation and Preparation of figures and tables: O.P.; Writing: O.P. and D.C.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financed by the Goulandris Natural History Museum Greek Biotope/Wetland Centre in the framework of the research project “Fish sampling in Greek lakes”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The research received approval from the relevant committee in Greece for the conducted fish samplings.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper. For additional information, please contact the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the four anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions, which helped improve the clarity and quality of this manuscript. During the preparation of this manuscript, the authors used ChatGPT (OpenAI, GPT-4) for the purposes of language editing and refinement. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Beklioglu, M.; Romo, S.; Kagalou, I.; Quintana, X.; Bécares, E. State of the art in the functioning of shallow Mediterranean lakes: Workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionello, P.; Abrantes, F.; Gacic, M.; Planton, S.; Trigo, R.; Ulbrich, U. The climate of the Mediterranean region: Research progress and climate change impacts. Reg. Environ. Change 2014, 14, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.J.; Cooke, S.J.; Arthington, A.H.; Baigun, C.; Bossenbroek, L.; Dickens, C.; Harrison, I.; Kimirei, I.; Langhans, S.D.; Murchie, K.J.; et al. People need freshwater biodiversity. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2023, 10, e1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzetti, B.; Lanzanova, D.; Liquete, C.; Reynaud, A.; Cardoso, A.C. Assessing water ecosystem services for water resource management. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 61, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J.; Alahuhta, J.; Bini, L.M.; Cai, Y.; Heiskanen, A.S.; Hellsten, S.; Kortelainen, P.; Kotamäki, N.; Tolonen, K.T.; Vihervaara, P.; et al. Lakes in the era of global change: Moving beyond single-lake thinking in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem services. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantonati, M.; Poikane, S.; Pringle, C.M.; Stevens, L.E.; Turak, E.; Heino, J.; Richardson, J.S.; Bolpagni, R.; Borrini, A.; Cid, N.; et al. Characteristics, main impacts, and stewardship of natural and artificial freshwater environments: Consequences for biodiversity conservation. Water 2020, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.M.V.; Thouillot, M.; Frossard, V.; Desgué-Itier, O.; Barouillet, C.; Baulaz, Y.; Clément, J.-C.; Domaizon, I.; Dorioz, J.-M.; Goulon, C.; et al. Expanding the European Water Framework Directive indicators to address long-term climate change impacts on lakes using mechanistic lake models. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winfield, I.J.; Baigún, C.; Balykin, P.A.; Becker, B.; Chen, Y.; Filipe, A.F.; Gerasimov, Y.V.; Godinho, A.L.; Hughes, R.M.; Koehn, J.D.; et al. International perspectives on the effects of climate change on inland fisheries. Fisheries 2016, 41, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comte, L.; Buisson, L.; Daufresne, M.; Grenouillet, G. Climate-induced changes in the distribution of freshwater fish: Observed and predicted trends. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comte, L.; Olden, J.D. Climatic vulnerability of the world’s freshwater and marine fishes. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlund, C.M.; Hammer, M. Ecosystem services generated by fish populations. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makanda, K.; Nzama, S.; Kanyerere, T. Assessing the role of water resources protection practice for sustainable water resources management: A review. Water 2022, 14, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoglu, E.; Williams, B. Determinants of urban expansion and agricultural land conversion in 25 EU countries. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 717–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, F.; Baycan, T. Application of combined Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and SWOT for integrated watershed management. Int. J. Anal. Hierarchy Process 2014, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Thungngern, J.; Wijitkosum, S.; Sriburi, T.; Sukhsri, C. A review of the analytical hierarchy process (AHP): An approach to water resource management in Thailand. Appl. Environ. Res. 2015, 37, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacal, J.C.; Taboada, E.B.; Mehboob, M.S. Strategic implementation of integrated water resource management in selected areas of Palawan: SWOT-AHP method. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and Council. Directive 2000/60/EC Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy; Official Journal of the European Communities L327:1–73; European Parliament and Council: Strasbourg, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tolonen, K.T.; Hämäläinen, H.; Lensu, A.; Meriläinen, J.J.; Palomäki, A.; Karjalainen, J. The relevance of ecological status to ecosystem functions and services in a large boreal lake. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.T.; Goethals, P.L. Opportunities and challenges for the sustainability of lakes and reservoirs in relation to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Water 2019, 11, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, A.J. The Lake Copais, Boeotia, Greece: Its drainage and development. (Includes appendix). J. Inst. Civ. Eng. 1937, 5, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, S.J.; Street-Perrott, F.A.; Holmes, J.A.; Leng, M.J.; Tzedakis, C. Chemical and isotopic composition of modern water bodies in the Lake Kopais Basin, central Greece: Analogues for the interpretation of the lacustrine sedimentary sequence. Sediment. Geol. 2002, 148, 79–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamou, G.; Katsiapi, M.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Michaloudi, E. The neglected zooplankton communities as indicators of ecological water quality of Mediterranean lakes. Limnetica 2021, 40, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economidis, P.S.; Dimitriou, E.; Pagoni, R.; Michaloudi, E.; Natsis, L. Introduced and translocated fish species in the inland waters of Greece. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2000, 7, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardakas, L.; Koutsikos, N.; Perdikaris, C.; Petriki, O.; Bobori, D.; Zogaris, S.; Giakoumi, S.; Fitoka, E.; Tompoulidou, M.; Tsiaoussi, V.; et al. The fish fauna in lentic ecosystems of Greece. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2022, 23, 223–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase. World Wide Web Electronic Publication. Available online: www.fishbase.org (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- EN 14757:2005; Water Quality—Sampling of Fish with Multimesh Gillnets. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2005; 27p.
- Petriki, O.; Stergiou, K.I.; Bobori, D.C. Can fish sampling protocol (CEN, 2005) be amended for Mediterranean lakes? Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2017, 24, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiaoussi, V.; Mavromati, E.; Kemitzoglou, D. Report on the Development of the National Method for the Assessment of the Ecological Status of Natural Lakes in Greece, Using the Biological Quality Element “Phytoplankton”, 1st Revision; Greek Biotope/Wetland Centre and Special Secretariat for Waters, Ministry of Environment: Thermi, Greece, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ntislidou, C.; Lazaridou, M.; Tsiaoussi, V.; Bobori, D.C. A new multimetric macroinvertebrate index for the ecological assessment of Mediterranean lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1020–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervas, D.; Tsiaoussi, V.; Tsiripidis, I. HeLM: A macrophyte-based method for monitoring and assessment of Greek lakes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagalou, I.; Leonardos, I. Typology, classification and management issues of Greek lakes: Implication of the Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 150, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavromati, E.; Kagalou, I.; Kemitzoglou, D.; Apostolakis, A.; Seferlis, M.; Tsiaoussi, V. Relationships among land use patterns, hydromorphological features and physicochemical parameters of surface waters: WFD lake monitoring in Greece. Environ. Process. 2018, 5 (Suppl. 1), 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. Corine Land Cover; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Petriki, O.; Lazaridou, M.; Bobori, D.C. A fish-based index for the assessment of the ecological quality of temperate lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 78, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, J.S.; Carwardine, J.; Duck, R.W.; Bragg, O.M.; Black, A.R.; Cutler, M.E.J.; Soutar, I.; Boon, P.J. Development of a technique for lake habitat survey (LHS) with applications for the European Union Water Framework Directive. Aquat. Conserv. 2006, 16, 637–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, S.J.; Solheim, A.L.; Soszka, H.; Gołub, M.; Hutorowicz, A.; Kolada, A.; Picińska-Fałtynowicz, J.; Białokoz, W. Integrated assessment of ecological status and misclassification of lakes: The role of uncertainty and index combination rules. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.K.; Kang, K.H.; Lee, Y.H. Decomposition heuristic to minimize total cost in a multi-level supply chain network. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2008, 54, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, D. SWOT analysis. In Handbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace: Volumes 1–3; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 115–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazinoory, S.; Abdi, M.; Azadegan-Mehr, M. SWOT methodology: A state-of-the-art review for the past, a framework for the future. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2011, 12, 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banihabib, M.E.; Azarnivand, A.; Peralta, R.C. A new framework for strategic planning to stabilize a shrinking lake. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2015, 31, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scolozzi, R.; Schirpke, U.; Morri, E.; D’Amato, D.; Santolini, R. Ecosystem services-based SWOT analysis of protected areas for conservation strategies. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurttila, M.; Pesonen, M.; Kangas, J.; Kajanus, M. Utilizing the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in SWOT analysis—A hybrid method and its application to a forest-certification case. For. Policy Econ. 2000, 1, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, N.; Achari, A.; Choudhary, S. Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) as a powerful tool for sustainable development: Effective applications of AHP, FAHP, TOPSIS, ELECTRE, and VIKOR in sustainability. Int. Res. J. Mod. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2023, 5, 2654–2670. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, E.H.; Gass, S.I. The analytic hierarchy process—An exposition. Oper. Res. 2001, 49, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision Making with the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W. Integrated analytic hierarchy process and its applications—A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 186, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambray, J.A. Impact on indigenous species biodiversity caused by the globalisation of alien recreational freshwater fisheries. Hydrobiologia 2003, 500, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprieur, F.; Brosse, S.; García-Berthou, E.; Oberdorff, T.; Olden, J.D.; Townsend, C.R. Scientific uncertainty and the assessment of risks posed by non-native freshwater fishes. Fish Fish. 2009, 10, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villéger, S.; Blanchet, S.; Beauchard, O.; Oberdorff, T.; Brosse, S. Homogenization patterns of the world’s freshwater fish faunas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18003–18008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsch, D.K. Causes and consequences of biotic homogenization in freshwater ecosystems. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2016, 101, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriki, O.; Bobori, D.C. Compositional and functional changes within Greek (southeastern Balkans) lentic fish assemblages. Biol. Invasions 2025, 27, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feunteun, E. Management and restoration of European eel population (Anguilla anguilla): An impossible bargain. Ecol. Eng. 2002, 18, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevacqua, D.; Melià, P.; Gatto, M.; De Leo, G.A. A global viability assessment of the European eel. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 3323–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copp, G.H.; Bianco, P.G.; Bogutskaya, N.G.; Eros, T.; Falka, I.; Ferreira, M.T.; Fox, M.G.; Freyhof, J.; Gozlan, R.E.; Grabowska, J.; et al. To be, or not to be, a non-native freshwater fish? J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2005, 21, 242–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozlan, R.E.; Peeler, E.J.; Longshaw, M.; St-Hilaire, S.; Feist, S.W. Effect of microbial pathogens on the diversity of aquatic populations, notably in Europe. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratwicke, B.; Marshall, B.E. The relationship between the exotic predators Micropterus salmoides and Serranochromis robustus and native stream fishes in Zimbabwe. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 58, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucherousset, J.; Olden, J.D. Ecological impacts of non-native freshwater fishes. Fisheries 2011, 36, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, J.J.; Crowder, L.B.; Medvick, P.A. Temperature as an ecological resource. Am. Zool. 1979, 19, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winfield, I.J. Fish in the littoral zone: Ecology, threats and management. Limnologica 2004, 34, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Jensen, J.P.; Jensen, C.; Faafeng, B.; Hessen, D.O.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Brettum, P.; Christoffersen, K. The impact of nutrient state and lake depth on top-down control in the pelagic zone of lakes: A study of 466 lakes from the temperate zone to the Arctic. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzanti, M.; Seminara, M.; Baldoni, S.; Dowgiallo, M.G. Assessing hypolimnetic stress in a monomictic, eutrophic lake using profundal sediment and macrobenthic characteristics. J. Freshw. Ecol. 1998, 13, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutopoulos, D.K.; Petriki, O.; Ramfos, A.; Stoumboudi, M.T.; Stergiou, K.I.; Bobori, D.C. Portraying fisheries and ecological status of a Mediterranean lake. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2020, 50, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalár, T.; Pavolová, H.; Tokarčík, A. Analysis and model of river basin sustainable management by SWOT and AHP methods. Water 2021, 13, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifipour, R.; Mahmodi, B. Presentation of coastal environmental management plan by using SWOT/AHP methods. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2012, 16, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hasani, Q.; Julian, D.; Damai, A.A.; Yudha, I.G.; Diantari, R.; Yuliana, D.; Reza, M.; Caesario, R.; Putriani, R.B. Priority strategy in the development of sustainable capture fisheries in the Marine Protected Area of Kiluan Bay, Lampung, Indonesia. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2024, 17, 764–774. [Google Scholar]
- Walangitan, H.D.; Rotinsulu, W.C.; Paat, F.J. Analysis of management strategies for Lake Tondano ecosystem in North Sulawesi, Indonesia using SWOT and AHP methods. Rev. Gest. Soc. Ambient. 2024, 18, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, F.D.; Petrillo, A.; Autorina, C.; Carlomusto, A. Sustainable decision-making model based on analytical hierarchy process and SWOT analysis: “S-AHP” model. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Analytic Hierarchy Process 2013, Kuala Lampur, Malaysia, 19–23 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dokulil, M.T.; Teubner, K.; Jagsch, A.; Nickus, U.; Adrian, R.; Straile, D.; Jankowski, T.; Herzig, A.; Padisák, J. The impact of climate change on lakes in Central Europe. In The Impact of Climate Change on European Lakes; George, D.G., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 387–409. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi Siahkalroodi, S.; Kouchakian, H.; Mojabi, M.; Mohebi Derakhash, P.; Olad Azimi, N.; Yousefi Siahkalroodi, M. Assessment of the restoration trend of sturgeon stocks in Iranian waters of the Caspian Sea using SWOT model. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2025, 24, 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Davidson, T.; Trolle, D.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Beklioglu, M.; Brucet, S.; Volta, P.; González-Bergonzoni, I.; et al. Climate change impacts on lakes: An integrated ecological perspective based on a multi-faceted approach, with special focus on shallow lakes. J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 84–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Kronvang, B.; Olesen, J.E.; Audet, J.; Søndergaard, M.; Hoffmann, C.C.; Andersen, H.E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Liboriussen, L.; Larsen, S.E.; et al. Climate change effects on nitrogen loading from cultivated catchments in Europe: Implications for nitrogen retention, ecological state of lakes and adaptation. Hydrobiologia 2011, 663, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Moss, B.; Bennion, H.; Carvalho, L.; De Meester, L.; Feuchtmayr, H.; Friberg, N.; Gessner, M.O.; Hefting, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; et al. Chapter 5: Interaction of climate change and eutrophication. In Climate Change Impacts on Freshwater Ecosystems; Kernan, M., Battarbee, R., Moss, B., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: London, UK, 2010; pp. 119–146. [Google Scholar]
- Petriki, O.; Bobori, D.C. Unraveling Greek inland competitive fishing: Historical insights, angler profiles, and motivations through limited data integration in recreational fishing research. Fishes 2024, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).