The Impact of Smart City Construction on the Spatial Distribution of Urban Carbon Emissions Based on the Panel Data Analysis of 277 Prefecture-Level Cities in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
1.2. Research Gaps
1.3. Research Contribution
2. Bibliometric Analysis on SC and CE
2.1. Data Sources and Methods
2.2. Research Hotspots and Trend
2.2.1. Keywords Co-Occurrence and Keywords Burst Analysis
2.2.2. Keywords Timeline View Analysis
2.2.3. Co-Author Network Analysis
2.3. Research on the Impact of SCs on CEs
3. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
3.1. SC Can Reduce CE
3.2. Smart City Pilot Policy Presents Regional Heterogeneity in CER Effect
3.3. Smart City Pilot Policy Shows Resource Differences in Reducing CE
4. Model Design
4.1. Variables Selection
4.1.1. Explained Variable
4.1.2. Core Explanatory Variables
4.1.3. Control Variable
4.2. Data Sources of Empirical Analysis and Descriptive Statistics
5. Results
5.1. Benchmark Regression Analysis
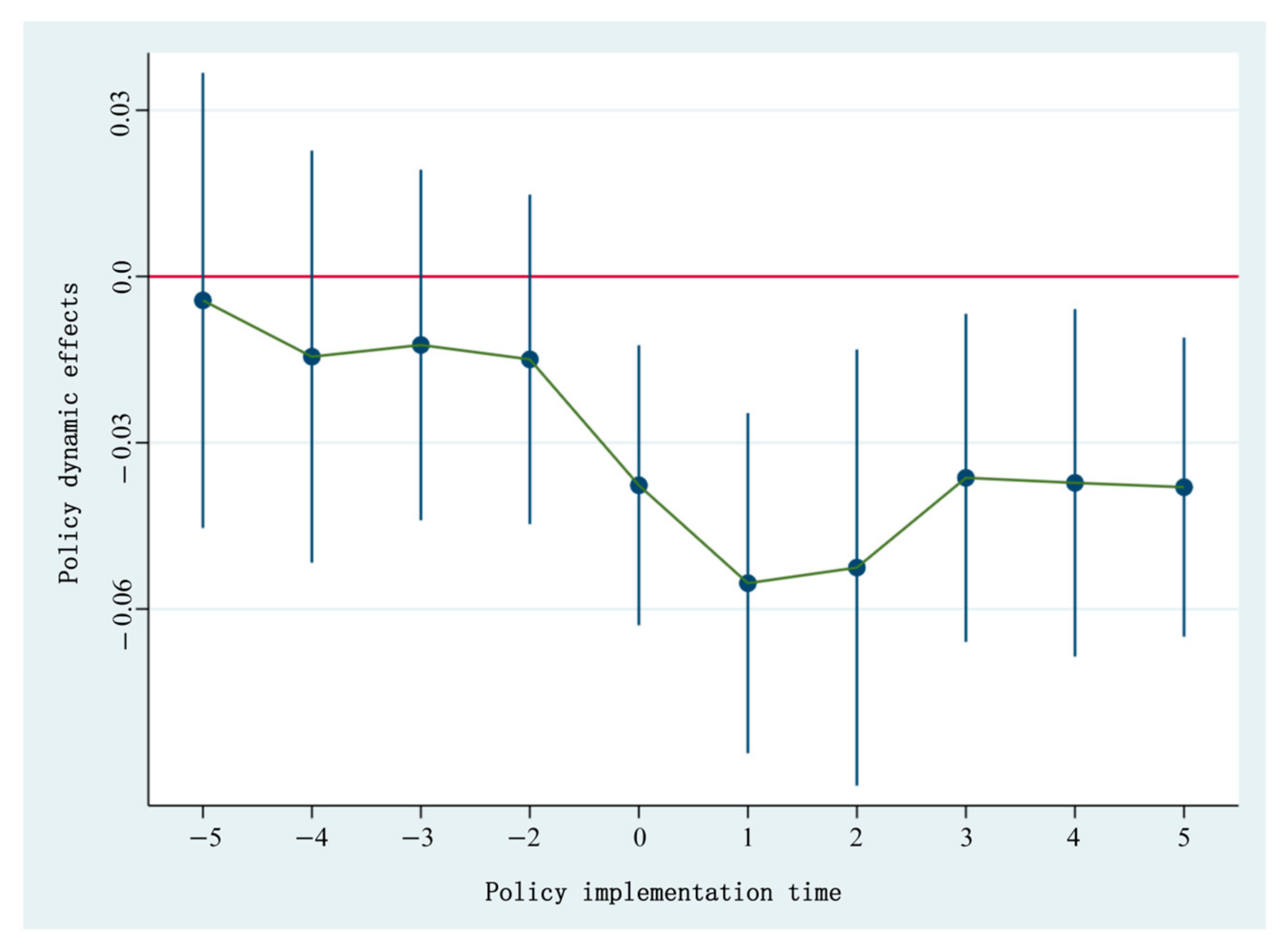
5.2. Parallel Trend Test
6. Robustness Test
6.1. Placebo Test
6.2. Other Robustness Tests
6.3. PSM-DID
6.4. DDML Causal Identification
7. Heterogeneity Analysis
7.1. Regional Heterogeneity
7.2. Resource Endowment Heterogeneity
8. Discussion, Conclusions, and Implications
9. Policy Implications
9.1. Social Governance
9.2. Urban Infrastructure
9.3. Industry Development
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, X.; Gu, X.C.; Yu, H.R.; Long, A.H.; Tiando, D.S.; Ou, S.Y.; Li, J.F.; Rong, Y.J.; Tang, G.L.; Zheng, Y.J.; et al. The Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Drivers of Habitat Quality in the Hung River Valley. Land 2021, 10, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandh, S.A.; Shafi, S.; Peerzada, M.; Rehman, T.; Bashir, S.; Wani, S.A.; Dar, R. Multidimensional analysis of global climate change: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 24872–24888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbling, M.; Meierrieks, D. Global warming and urbanization. J. Popul. Econ. 2023, 36, 1187–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, T.; Anderegg, W.R.L. A vast increase in heat exposure in the 21st century is driven by global warming and urban population growth. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 73, 103098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute for Sustainable Development Goals, Tsinghua University. Available online: https://thusdg.tsinghua.edu.cn/info/1141/3964.htm (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Ma, L.; Li, D.N. Would macro policy promote green and low-carbon transformation of energy companies? Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2024, 96, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.H.; Suo, C.; Wu, L.P.; Berrill, P. Consumption structure optimization for reducing energy footprint. Econ. Syst. Res. 2023, 35, 458–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollebregt, M.; Mugge, R.; Thuerridl, C.; van Dolen, W. Reducing without losing: Reduced consumption and its implications for well-being. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 45, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, V.; Esau, I.; Pettersson, L. Using web GIS to promote stakeholder understanding of scientific results in sustainable urban development: A case study in Bergen, Norway. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 2517–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M. A Responsible Major Power in the International Community: China’s Identity Claims and Practical Construction in Contemporary Times. J. Univ. Int. Relat. 2008, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Shi, L.; Ruan, G.C. Construction and Recognition of National Identity: An Analysis and Reflection on China’s Image as a Responsible Major Power. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2021, 29, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M. A Bigger Bang for a Bigger Buck: What China’s Changing Attitude Toward UN Peacekeeping Says About Its Evolving Approach to International Institutions. Foreign Policy Anal. 2017, 13, 338–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- People’s Daily. Implement the “Double Carbon” Action to Build a Beautiful China. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/yaowen/liebiao/202404/content_6948005.htm (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Angelidou, M. Smart cities: A conjuncture of four forces. Cities 2015, 47, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Government Accountability Office (U.S. GAO). AIMD-95-23 Information Superhighway: An Overview of Technology Challenges. Available online: https://www.gao.gov/products/aimd-95-23 (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- IBM. Available online: https://public.dhe.ibm.com/software/info/television/advertising/thesmartercity/GBE03227USEN.PDF (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Blasi, S.; Ganzaroli, A.; De Noni, I. Smartening sustainable development in cities: Strengthening the theoretical linkage between smart cities and SDGs. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 10379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomstyn, A.; Jonker, A. What is a Smart City? 2023. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/smart-city (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. The Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development Issued a Notice to Carry out the National Smart City Pilot. Available online: https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/zc/wjk/art/2012/art_17339_212182.html (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Yan, D.; Liu, H.; Yao, P. Assessing Energy Efficiency for Economic and Sustainable Development in the Region of European Union Countries. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 779163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, J. Digital Economy, Green Dual Innovation and Carbon Emissions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Duan, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, H. Analysis of the Impact of the Digital Economy on Carbon Emission Reduction and Its Spatial Spillover Effect—The Case of Eastern Coastal Cities in China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Meng, C.; Tan, J.; Zhang, G. Do smart cities promote a green economy? Evidence from a quasi-experiment of 253 cities in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 99, 107009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Liu, Y.F.; Sheng, M.S.; Wen, L. Effects of digital economy on carbon emission reduction: New evidence from China. Energy Policy 2022, 171, 113271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Z.; Song, W. Analysis of the Impact of Carbon Trading Policies on Carbon Emission and Carbon Emission Efficiency. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Qi, J.; Xian, Q.; Chen, J.D. The Carbon Emission Reduction Effect of China’s Carbon Market—From the Perspective of the Coordination between Market Mechanism and Administrative Intervention. China Ind. Econ. 2021, 8, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Xu, Y.M. Impact of green finance on China’s pollution reduction and carbon efficiency: Based on the spatial panel model. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 94, 103382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. Digital economy development, corporate social responsibility and low-carbon innovation. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2023, 30, 1664–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, D.; Pudney, S.; Pevcin, P.; Dvorak, J. Evidence-Based Public Policy Decision-Making in Smart Cities: Does Extant Theory Support Achievement of City Sustainability Objectives? Sustainability 2022, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z. Applications of Digital Technologies in Promoting Sustainable Construction Practices: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Xu, L.; Gu, Y. Smart Technology on Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction in Transportation System: A Case Study of Beijing. Urban Transp. China 2016, 14, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.X.; Hong, T.; Kang, C.Q. Review of Smart Meter Data Analytics: Applications, Methodologies, and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 3125–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.B.; Song, M.; Zhu, L. Economic evaluation of the trilateral FTA among China, Japan, and South Korea with big data analytics. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 128, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, M.H.; Zhou, M. A comparative study on decoupling relationship and influence factors between China’s regional economic development and industrial energy–related carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 142, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D.; Wu, Y.Y.; Wen, J.; Cheng, S.L.; Wang, J.L. Regional differences in China’s fossil energy consumption: An analysis for the period 1997–2013. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 142, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Liu, Y.B.; Elahi, E.; Meng, X.; Deng, W.F. A new type of urbanization policy and transition of low-carbon society: A “local- neighborhood” perspective. Land Use Policy 2023, 131, 106709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T. An optimization model for green supply chain management by using a big data analytic approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 142, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.X.; Wen, Y.; Xiong, B.B.; Yang, M.; Chen, X.H. Allocation of carbon dioxide emission permits with the minimum cost for Chinese provinces in big data environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P. Pricing policies and coordination of low-carbon supply chain considering targeted advertisement and carbon emission reduction costs in the big data environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, H.; Fan, J. Revolutionizing Retail: Examining the Influence of Blockchain-Enabled IoT Capabilities on Sustainable Firm Performance. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.R.; Li, X.R.; Wang, S.Y. Discovering research trends and opportunities of green finance and energy policy: A data-driven scientometric analysis. Energy Policy 2021, 154, 112295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.D.; Wang, B.; Dong, K.Y.; Dong, X.C. How does the digital economy improve high-quality energy development? The case of China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 184, 121960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.H.; Yan, L.; Chen, H.C. The Impact of the Digital Economy on Provincial Carbon Productivity: Empirical Evidence from China. Sage Open 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.J.; Wu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, H.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, X.Y. How does digitalization drive carbon emissions? The inverted U-shaped effect in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 102, 107203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Zhong, R.Y. Digital Economy, Green Technology Innovation, and Urban Low-Carbon Transformation. China Bus. Mark. 2023, 37, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.X.; Zhou, J.P.; Liu, C.J. The impact of digital economy on urban carbon emissions: Based on the analysis of spatial effects. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 111–129. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.L.; Jia, F. How Can the Digital Economy Promote Carbon Emission Reduction-An Investigation Based on Urban Carbon Emission Intensity and Carbon Emission Efficiency. World Surv. Res. 2023, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.J.; Huang, Y.F.; Wang, P.; Sun, D.L. The Impact of Smart City Construction on the Achievement of “Dual Carbon” Goals-An empirical analysis based on provincial panel data using mediating effects. Price Theory Pract. 2023, 10, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Chen, Q.; Yang, T.; Yi, C.; Chen, J. Visualization and Analysis of Hotspots and Trends in Seafood Cold Chain Logistics Based on CiteSpace, VOSviewer, and RStudio Bibliometrix. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, F. Analysis and Visualization of Authors and Social Networks of Educational Policy--Empirical Study on Authors of Articles of Educational Policy from 2005 to 2015 using CiteSpace. Int. Comp. Educ. 2017, 39, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Chen, S.H.; Miao, J.F. Does smart city pilot improve urban green economic efficiency: Accelerator or inhibitor. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 104, 107328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.Q.; Ding, H.; Wei, P.; Liu, J.J. Can Smart City Construction Reduce Environmental Pollution. China Ind. Econ. 2018, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, C.W.; Yan, C.H. Logic and Suggestions for New Infrastructure to Promote the Achievement of the “Double Carbon” Goal. Price Theory Pract. 2022, 4, 5–8+52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.B.; Chen, S.Q.; Cao, L.J. Is the City Low Carbon Because of “Smart”? Exploration from the Pilot Policy of Smart City. Econ. Rev. 2022, 6, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Ning, X.; Li, L. Gauging the Impacts of Urbanization on CO2 Emissions from the Construction Industry: Evidence from China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Mao, K.Z. Analysis of the Correlation between Urbanization and Environmental Impact in Our Country. Jiangxi Soc. Sci. 2014, 34, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Bae, J. Urbanization and Industrialization Impact of CO2 Emissions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.Z.; Fan, H.M. Influence of urbanization on the quality of environment: An analysis based on 27 national panel data. Urban Probl. 2016, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tang, M.G. How Does Land Urbanization Affect Ecological Environment Quality? Analysis Based on Dynamic Optimization and Spatially Adaptive Semi-parametric Model. Econ. Res. J. 2019, 54, 72–85. [Google Scholar]
- Montjoy, R.S.; O’Toole, L.J. Toward a Theory of Policy Implementation: An Organizational Perspective. Public Adm. Rev. 1979, 39, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Koblianska, I.I.; Yan, X. Research on Collaborative Innovation Path of Data Resources for Sustainable Development of Smart City. Int. J. Ecol. Dev. 2022, 37, 26–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Wu, L.H. Study on the impact of Smart City pilot on urban green innovation: Analysis based on TOE framework. Urban Probl. 2022, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.G.; Shi, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.T.; Chen, W. Empowering smart city situational awareness via big mobile data. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2024, 25, 286–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.M.; Huang, G.X. Is the Digital Economy Making Cities more Resilient?—Empirical Evidence from 285 Chinese Cities. Reg. Econ. Rev. 2023, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Fang, L.K.; He, J. Can smart city construction promote digital-reality integration? Causal inference based on double machine learning. Ind. Econ. Res. 2024, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Gong, Z.M. The Impact of Digital Economy Level on Green High-quality Development in Chinese Cities. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y. Research on the Impact of Smart City Construction on Carbon Emission Efficiency Under the Green Development Goals. Inq. Into Econ. Issues 2024, 155–171. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, T.; Levine, R.; Levkov, A. Big bad banks? The winners and losers from bank deregulation in the United States. J. Financ. 2010, 65, 1637–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, D. Carbon Emission Reduction Effects of the Smart City Pilot Policy in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.T.; Yu, Y.W.; Ge, L.M.; Guo, Y.G. Smart Carbon Reduction: The Effect and Mechanism of Digital Economy Development on Urban Carbon Emissions. J. Guangdong Univ. Financ. Econ. 2023, 38, 4–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Z.Q. Research on the Impact of Smart City Construction on Collaborative Governance of Pollution Reduction and Carbon Reduction. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2024, 43, 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- EDGAR—Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research. Available online: https://edgar.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- CEADs-China Emission Accounts and Datasets. Available online: https://www.ceads.net.cn/data/ (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Zhang, M.D.; Yang, Y.X. The Impact and Mechanism of Low-Carbon City Construction on Ecological Resilience: A Quasi-Natural Experiment Based on the Low-Carbon City Pilot Policy. East China Econ. Manag. 2025, 39, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.J.; Shen, Z.P.; Wang, R.C. Spatial Structure Evolution of Regional Economic Growth and Its Inequality in China since 1978. Geogr. Sci. 2006, 26, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.B.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.Y. The Current Situation, Causes and Countermeasures of the Economic Divide between the South and North in China. J. Hebei Univ. Econ. Bus. 2019, 40, 1–9+39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.T.; Zhang, N. Does smart city policy improve energy efficiency? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auty, R. Sustaining Development in Mineral Economies: The Resource Curse Thesis, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.J.; Yu, S.Y.; An, X.M.; Wang, J.D. Connection and Utilization of Government Data and Social Data: Connotation, Model and Verification of “Three Spirals” Operation Mechanism. China Soft Sci. 2021, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.P. Deep Integration of Digital Economy and Entity Economy to Promote “Progress” Vitality of China’s Economic Development. Frontiers 2024, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Wang, X.Y. The Impact Assessment of Smart City Pilot Policy on Urban Low-Carbon Economic Development: Evidence from Chinese Prefecture-level Cities. Shanghai Urban Manag. 2023, 32, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Guedes, A.L.A.; Alvarenga, J.C.; Goulart, M.D.S.; Rodriguez, M.V.R.Y.; Soares, C.A.P. Smart Cities: The Main Drivers for Increasing the Intelligence of Cities. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.; Welker, P. Interstitiality in the smart city: More than top-down and bottom-up smartness. Urban Stud. 2023, 60, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

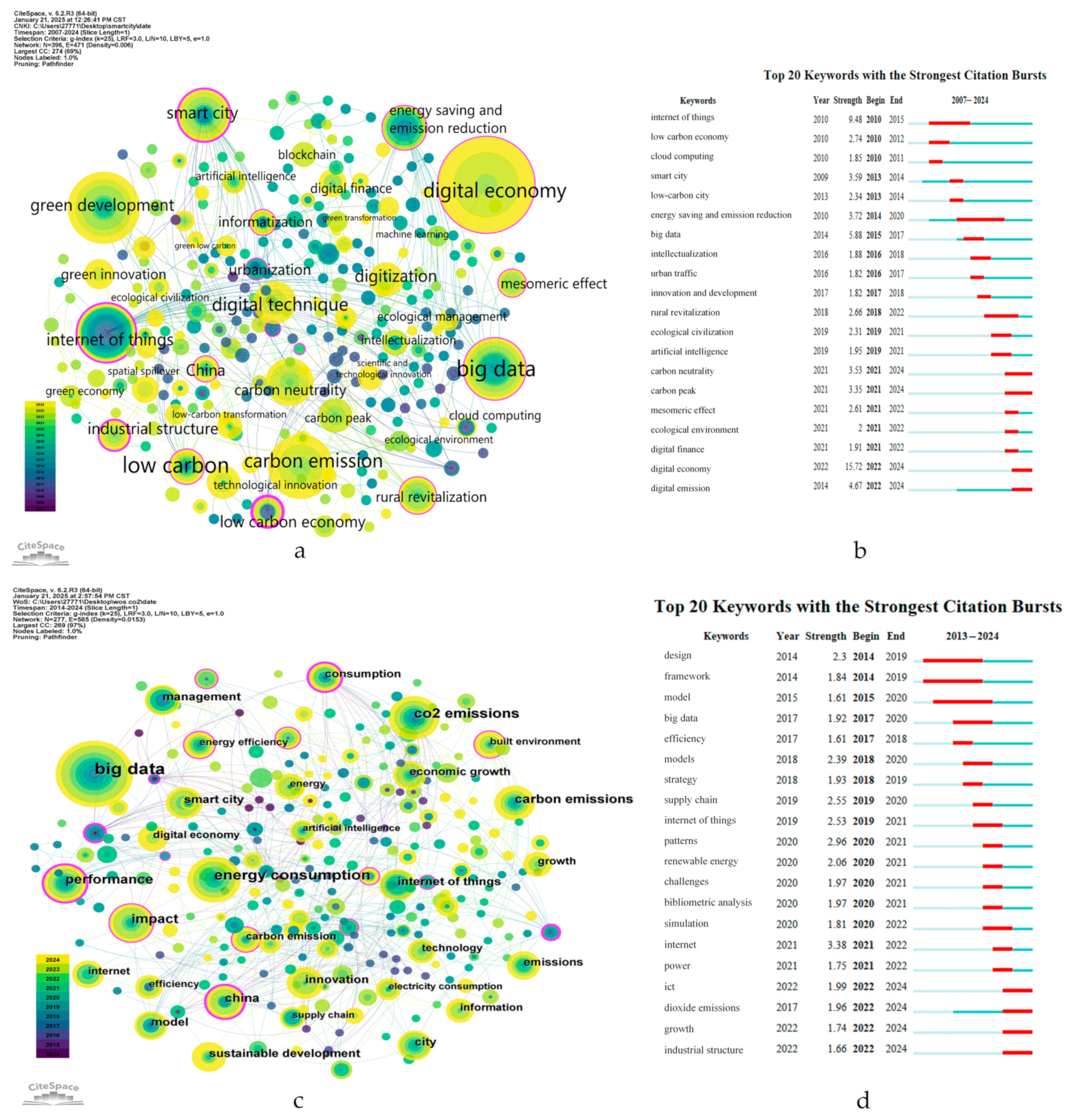

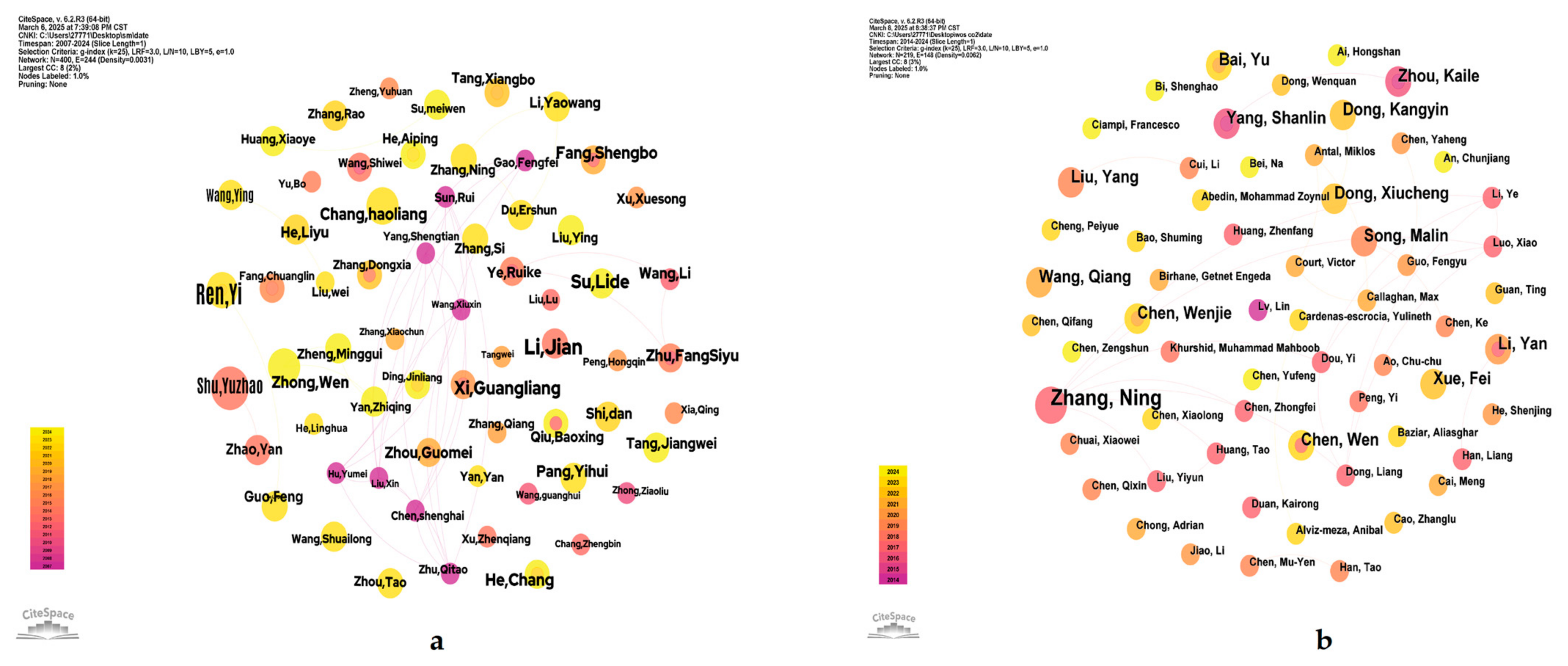


| No. | Count | Centrality | Year | Keyword |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 88 | 0.11 | 2022 | digital economy |
| 2 | 52 | 0.08 | 2013 | green development |
| 3 | 41 | 0.07 | 2014 | carbon emission |
| 4 | 40 | 0.11 | 2014 | big data |
| 5 | 37 | 0.39 | 2010 | internet of things |
| 6 | 31 | 0.32 | 2009 | smart city |
| 7 | 23 | 0.01 | 2021 | carbon neutrality |
| 8 | 21 | 0.11 | 2010 | energy conservation and emission reduction |
| 9 | 19 | 0.09 | 2021 | digital technology |
| 10 | 14 | 0.11 | 2018 | rural revitalization |
| No. | Count | Centrality | Year | Keyword |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 85 | 0.03 | 2017 | big data |
| 2 | 42 | 0.06 | 2017 | energy consumption |
| 3 | 38 | 0.08 | 2015 | co2 emissions |
| 4 | 29 | 0.33 | 2017 | performance |
| 5 | 29 | 0.16 | 2014 | impact |
| 6 | 26 | 0.08 | 2017 | carbon emissions |
| 7 | 21 | 0.24 | 2016 | china |
| 8 | 20 | 0 | 2019 | internet of things |
| 9 | 19 | 0.04 | 2021 | smart city |
| 10 | 19 | 0.03 | 2021 | innovation |
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI | 4120 | 0.017044 | 0.936223 | −2.31048 | 2.093797 |
| smartcity | 4120 | 0.196845 | 0.397662 | 0 | 1 |
| X1 | 4120 | 10.4929 | 0.704759 | 8.76155 | 11.97025 |
| X2 | 4120 | 5.739698 | 0.885837 | 2.903069 | 7.20406 |
| X3 | 4120 | 0.404058 | 0.092948 | 0.194533 | 0.661696 |
| X4 | 4120 | 2.302118 | 1.06766 | 0.895133 | 6.441953 |
| (1) CI | (2) CI | (3) CI | (4) CI | (5) CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | |||||
| smartcity | −0.0325 *** | −0.0343 *** | −0.0343 *** | −0.0350 *** | −0.0351 *** |
| (0.0103) | (0.0103) | (0.0103) | (0.0103) | (0.0103) | |
| X1 | 0.0565 *** | 0.0564 *** | 0.0445 *** | 0.0284 | |
| (0.0156) | (0.0157) | (0.0166) | (0.0191) | ||
| X2 | 0.00125 | 0.00451 | 0.00391 | ||
| (0.0207) | (0.0207) | (0.0207) | |||
| X3 | −0.191 ** | −0.175 ** | |||
| (0.0766) | (0.0769) | ||||
| X4 | −0.0135 ** | ||||
| (0.00624) | |||||
| Constant | 0.0234 *** | −0.569 *** | −0.575 *** | −0.392 ** | −0.194 |
| (0.00305) | (0.163) | (0.185) | (0.199) | (0.219) | |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 4120 | 4120 | 4120 | 4120 | 4120 |
| R-squared | 0.974 | 0.974 | 0.974 | 0.974 | 0.974 |
| (1) CI | (2) CI | (3) CI | (4) CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | ||||
| smartcity | −0.0351 *** | −0.0348 *** | ||
| (0.0103) | (0.0103) | |||
| X1 | 0.0284 | 0.0238 | 0.0380 ** | 0.0294 |
| (0.0191) | (0.0185) | (0.0185) | (0.0206) | |
| X2 | 0.00391 | 0.000491 | −0.00495 | 0.00242 |
| (0.0207) | (0.0193) | (0.0191) | (0.0260) | |
| X3 | −0.175 ** | −0.201 *** | −0.214 *** | −0.160 * |
| (0.0769) | (0.0747) | (0.0723) | (0.0864) | |
| X4 | −0.0135 ** | −0.0129 ** | −0.00852 | −0.0138 ** |
| (0.00624) | (0.00617) | (0.00608) | (0.00663) | |
| L1_smartcity | −0.0405 *** | |||
| (0.0105) | ||||
| L2_smartcity | −0.0321 *** | |||
| (0.0102) | ||||
| Constant | −0.194 | −0.158 | −0.331 | −0.188 |
| (0.219) | (0.206) | (0.205) | (0.246) | |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 4120 | 3742 | 3443 | 3862 |
| R-squared | 0.974 | 0.977 | 0.980 | 0.975 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | psm | psm |
| smartcity | −0.0253 ** | −0.0257 ** |
| (−2.5146) | (−2.5455) | |
| X1 | 0.0189 | 0.0206 |
| (1.0574) | (1.1415) | |
| X2 | 0.0016 | 0.0015 |
| (0.0797) | (0.0754) | |
| X3 | −0.1696 ** | −0.1648 ** |
| (−2.2969) | (−2.2108) | |
| X4 | −0.0153 *** | −0.0148 ** |
| (−2.5872) | (−2.5057) | |
| X5 | −0.0000 * | −0.0000 * |
| (−1.6689) | (−1.6717) | |
| Constant | −0.0624 | −0.0835 |
| (−0.3028) | (−0.4022) | |
| City | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 3982 | 3978 |
| R-squared | 0.978 | 0.978 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | |
| VARIABLES | CI | CI | CI | CI | CI | CI |
| smartcity | −0.239 *** | −0.179 *** | −0.124 *** | −0.100 *** | −0.070 ** | −0.076 ** |
| (0.035) | (0.035) | (0.034) | (0.034) | (0.032) | (0.032) | |
| Constant | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.005 | −0.002 | −0.000 |
| (0.017) | (0.013) | (0.011) | (0.010) | (0.008) | (0.008) | |
| Observations | 4120 | 4120 | 4120 | 4120 | 4120 | 4120 |
| Year | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| (1) CI | (2) CI | (3) CI | (4) CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VARIABLES | ||||
| smartcity | −0.0137 | −0.0604 *** | −0.0175 | −0.0480 *** |
| (0.0147) | (0.0143) | (0.0152) | (0.0137) | |
| X1 | 0.0287 | −0.00734 | −0.0497 ** | 0.0680 ** |
| (0.0272) | (0.0297) | (0.0249) | (0.0285) | |
| X2 | −0.0899 | 0.00996 | 0.106 ** | −0.0395 |
| (0.109) | (0.0175) | (0.0433) | (0.0316) | |
| X3 | −0.171 * | −0.157 | −0.250 ** | −0.147 |
| (0.103) | (0.112) | (0.120) | (0.101) | |
| X4 | 0.0261 ** | −0.0326 *** | −0.0211 ** | −0.0148 * |
| (0.0115) | (0.00813) | (0.00867) | (0.00882) | |
| Constant | 0.144 | 0.347 | 0.0504 | −0.324 |
| (0.706) | (0.327) | (0.304) | (0.354) | |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 2261 | 1859 | 1634 | 2486 |
| R-squared | 0.971 | 0.978 | 0.981 | 0.970 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Lau, A.D.; Gong, Y. The Impact of Smart City Construction on the Spatial Distribution of Urban Carbon Emissions Based on the Panel Data Analysis of 277 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114934
Li D, Zhang X, Lau AD, Gong Y. The Impact of Smart City Construction on the Spatial Distribution of Urban Carbon Emissions Based on the Panel Data Analysis of 277 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114934
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dacan, Xiaoyu Zhang, Albert D. Lau, and Yuanyuan Gong. 2025. "The Impact of Smart City Construction on the Spatial Distribution of Urban Carbon Emissions Based on the Panel Data Analysis of 277 Prefecture-Level Cities in China" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114934
APA StyleLi, D., Zhang, X., Lau, A. D., & Gong, Y. (2025). The Impact of Smart City Construction on the Spatial Distribution of Urban Carbon Emissions Based on the Panel Data Analysis of 277 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Sustainability, 17(11), 4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114934







