Study on Fish Diversity and Drivers Based on Environmental DNA in Chishui River, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Environmental Variable Acquisition
2.3. DNA Analysis
2.4. Bioinformatics
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
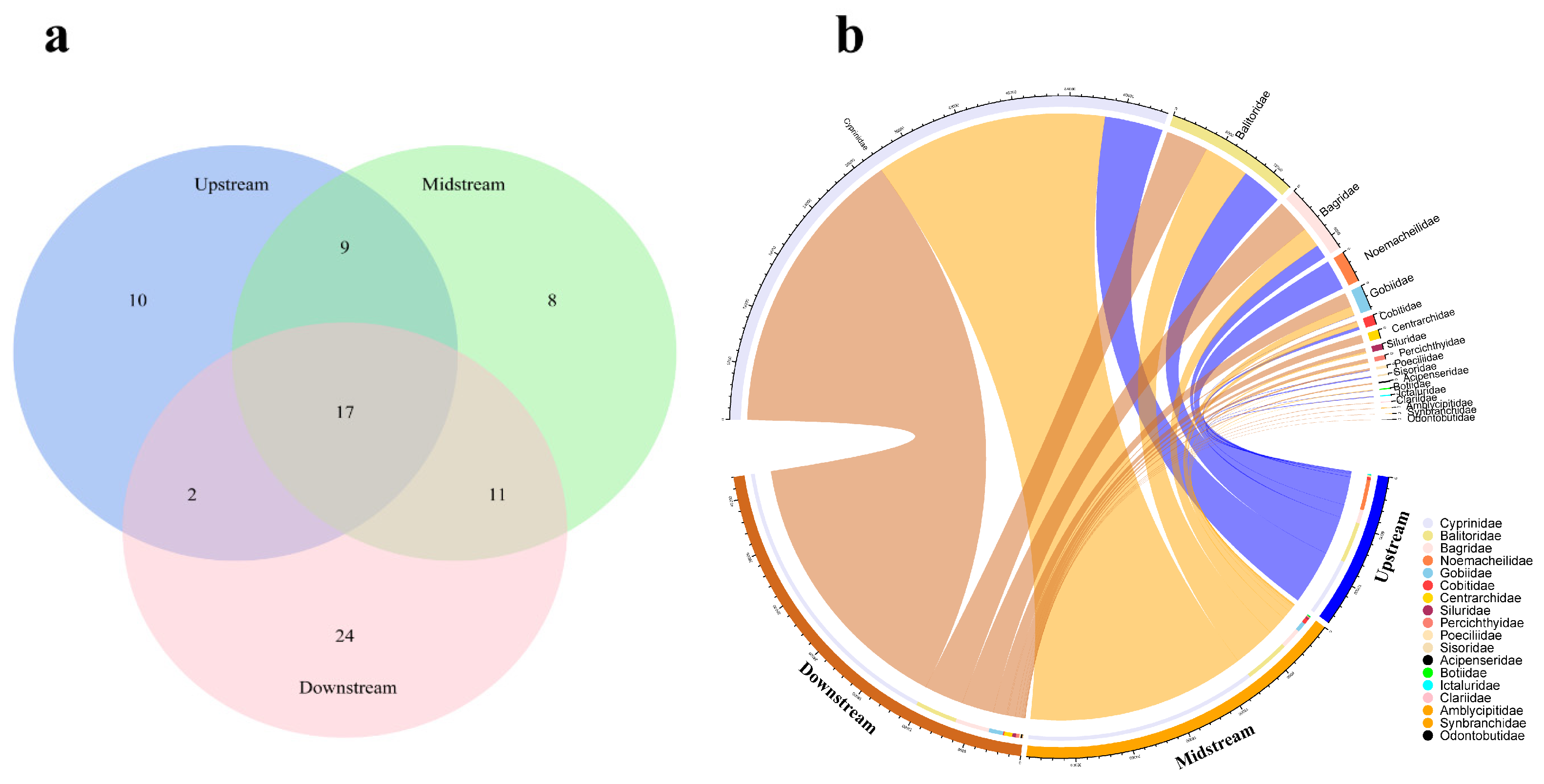
3.1. Fish Composition in the Chishui River
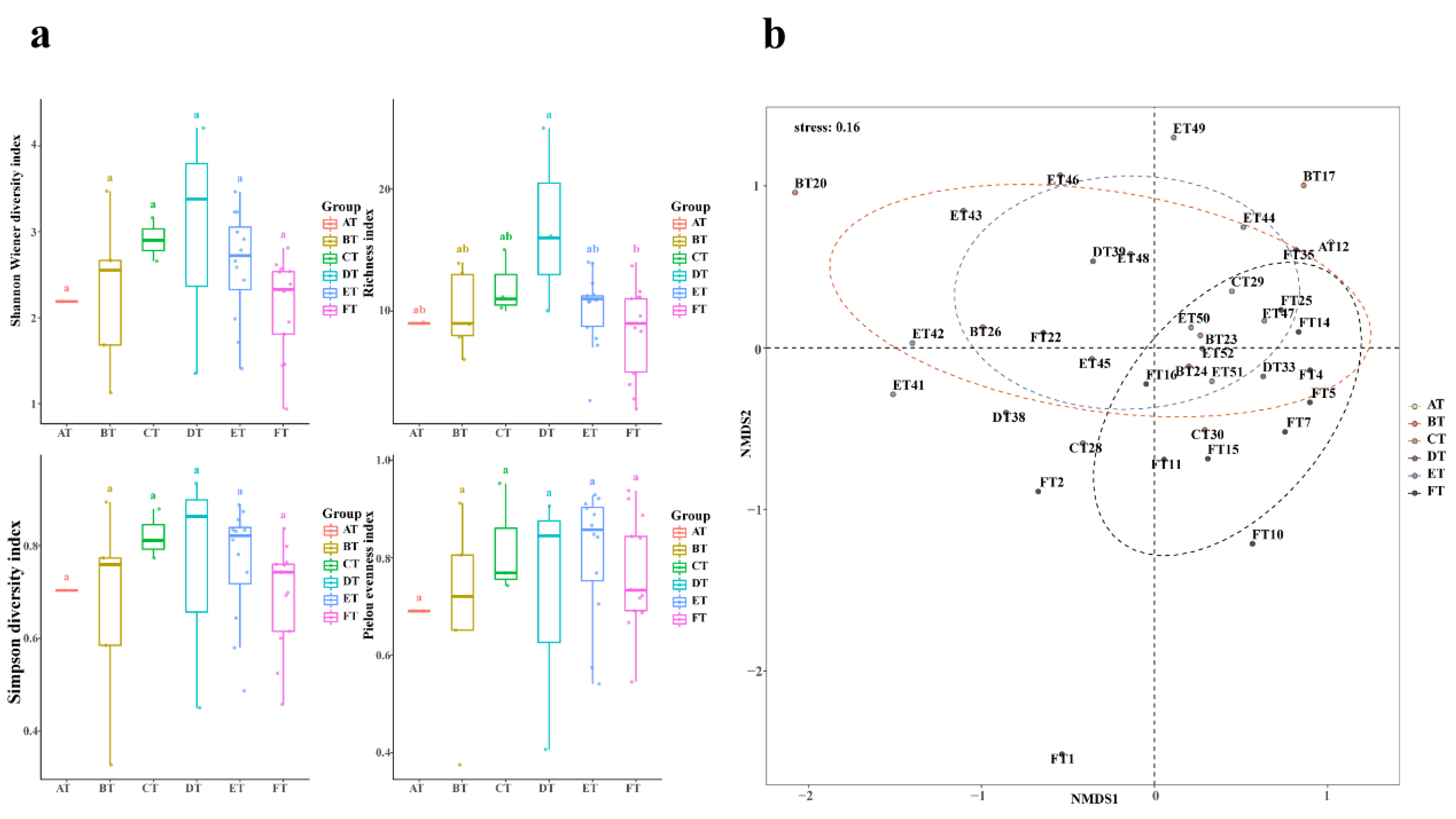
3.2. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Fish Alpha Diversity
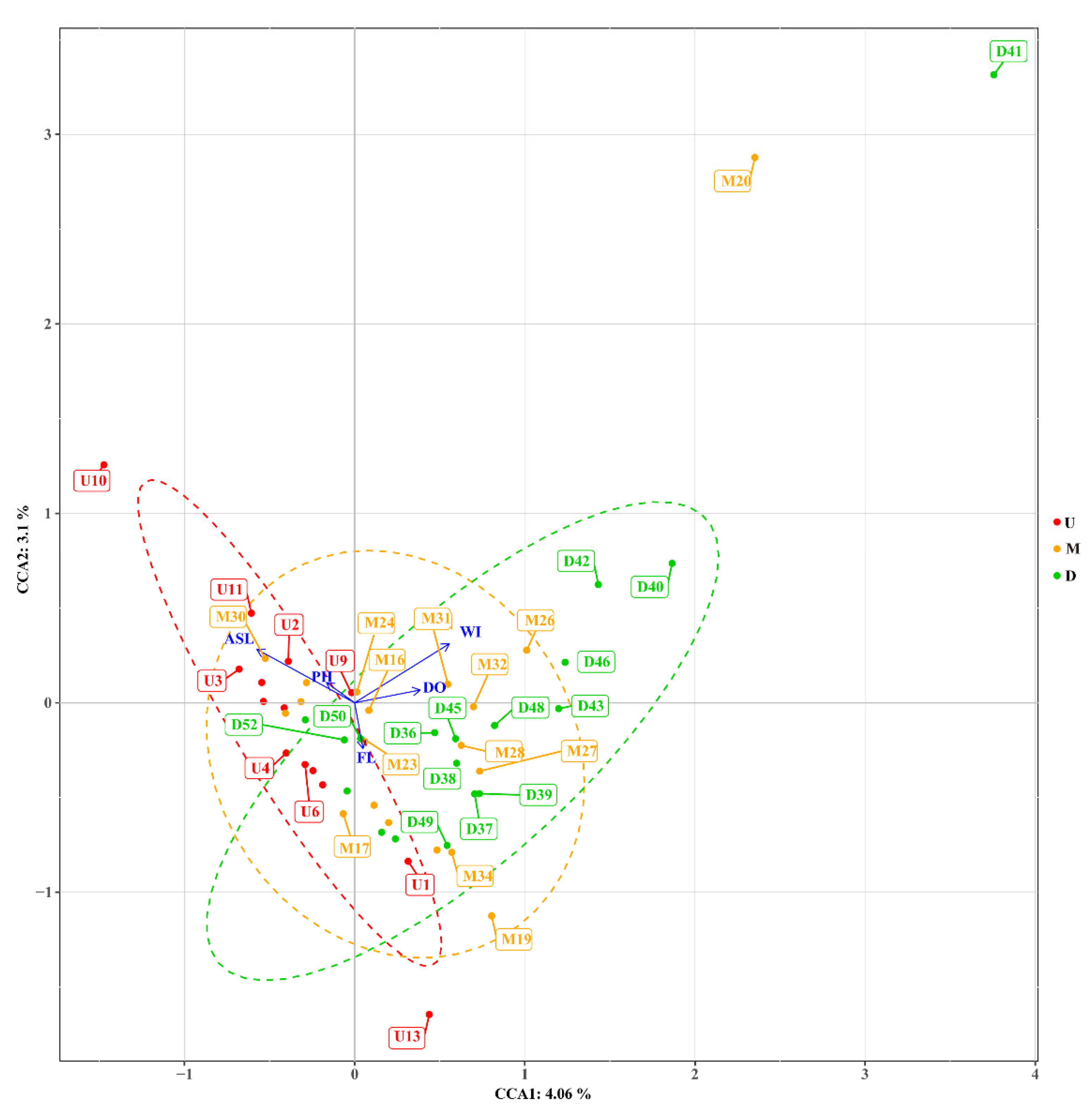
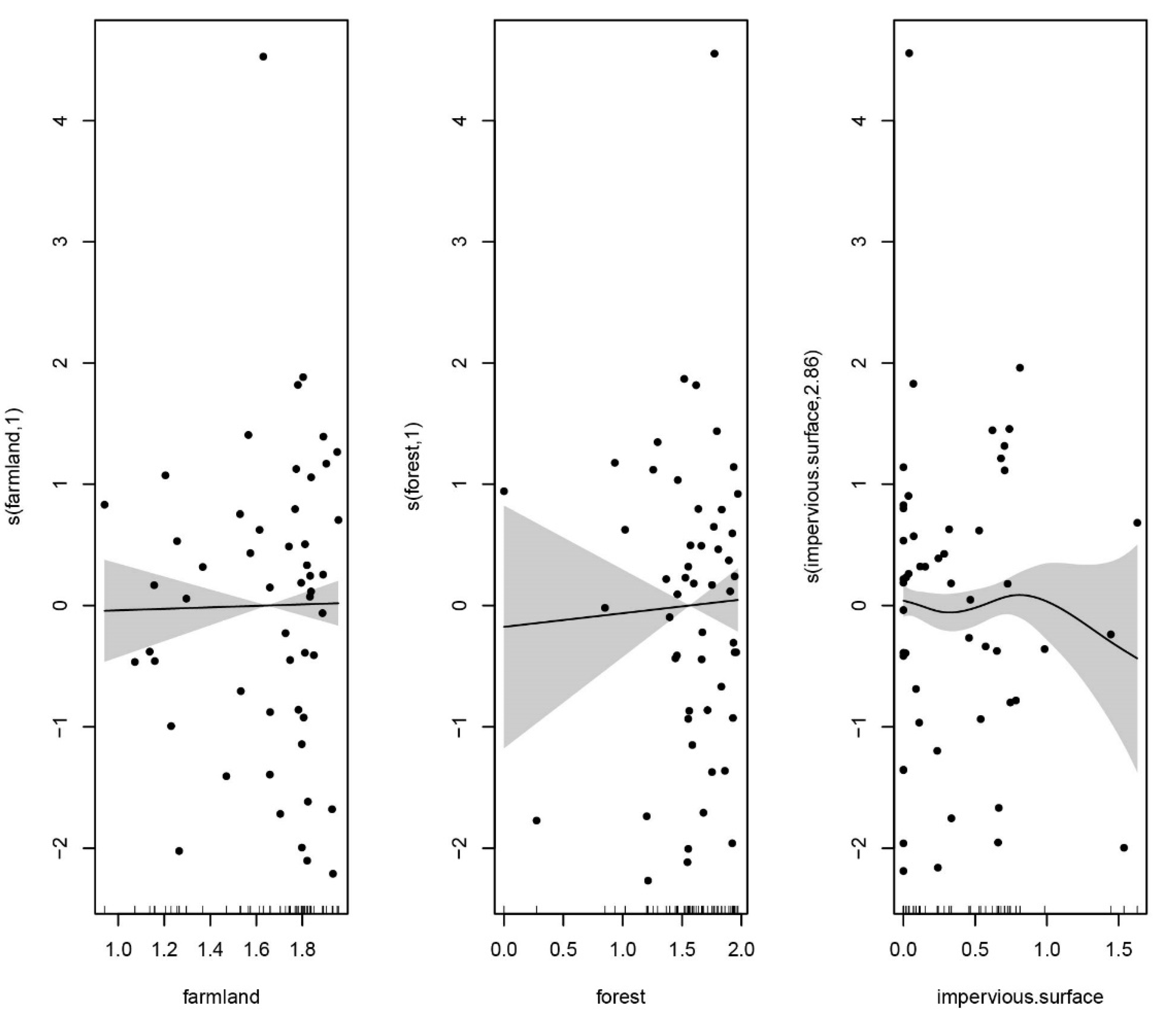
3.3. Fish Diversity Responds to Environmental Variables and Anthropogenic Activities
4. Discussion
4.1. Compared with Previous Studies
4.1.1. Comparison with Traditional Survey Records
4.1.2. Consistency with Traditional Surveys
4.1.3. New Record Species Detected by eDNA Method
4.1.4. Alien Species
4.2. Thoughts on the Spatial Distribution Pattern and Driving Factors of Fish Species in the Chishui River
4.2.1. Comparison of Different Spatial Fish Communities
4.2.2. Fish Diversity Responds to Environmental Variables and Anthropogenic Activities
4.3. Limitations and Prospects
Fish Survey Limitations Based on eDNA Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.P.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2018, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, S.J.; Twardek, W.M.; Lynch, A.J.; Cowx, I.G.; Olden, J.D.; Funge-smith, S.; Lorenzen, K.; Arlinghaus, R.; Chen, Y.; Weyl, O.L.F.; et al. A global perspective on the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on freshwater fish biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 253, 108932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tickner, D.; Opperman, J.J.; Abell, R.; Acreman, M.; Arthington, A.; Bunn, S.E.; Cooke, S.J.; Dalton, J.T.; Darwall, W.; Edwards, G.L.; et al. Bending the curve of global freshwater biodiversity loss: An emergency recovery plan. BioScience 2020, 70, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, M.S.; Tedesco, P.A.; Hugueny, B.; Jézéquel, C.; Beauchard, O.; Brosse, S.; Oberdorff, T. Anthropogenic stressors and riverine fish extinctions. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 79, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, I.; Abell, R.; Darwall, W.; Thieme, M.; Tickner, D.; Timboe, I.A. The freshwater biodiversity crisis. Science 2018, 362, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villéger, S.; Brosse, S.; Mouchet, M.; Mouillot, D.; Vanni, M.J. Functional ecology of fish: Current approaches and future challenges. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 79, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Logez, M.; Xu, J.; He, S.; Villéger, S.; Brosse, S. Human impacts on global freshwater fish biodiversity. Science 2021, 371, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigand, H.; Beermann, A.J.; Čiampor, F.; Costa, F.O.; Csabai, Z.; Duarte, S.; Geiger, M.F.; Grabowski, M.; Rimet, F.; Rulik, B.; et al. DNA barcode reference libraries for the monitoring of aquatic biota in Europe: Gap-analysis and recommendations for future work. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jarić, I.; Roberts, D.L.; He, Y.; Du, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Wei, Q. Extinction of one of the world’s largest freshwater fishes: Lessons for conserving the endangered Yangtze fauna. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yu, F.; Xia, Z.; Qiang, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. Changes in fish assemblages following the implementation of a complete fishing closure in the Chishui River. Fish. Res. 2021, 243, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. Spatial organisation of fish assemblages in the Chishui River, the last free-flowing tributary of the upper Yangtze River, China. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2020, 30, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collen, B.; Whitton, F.; Dyer, E.E.; Baillie, J.E.; Cumberlidge, N.; Darwall, W.R.; Pollock, C.; Richman, N.I.; Soulsby, A.M.; Böhm, M. Global patterns of freshwater species diversity, threat and endemism. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. J. Macroecol. 2014, 23, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, S.; Guilhaumon, F.; Villéger, S.; Amoroso, S.; França, S.; Pasquaud, S.; Cabral, H.N.; Vasconcelos, R.P. Biogeographical region and environmental conditions drive functional traits of estuarine fish assemblages worldwide. Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 752–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.C.; Sui, X.; Liang, S.; Chen, Y. Non-native freshwater fish species in China. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 651–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geist, J.; Hawkins, S.J. Habitat recovery and restoration in aquatic ecosystems: Current progress and future challenges. Aquat. Conserv.-Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2016, 26, 942–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qu, X.; Xiong, F.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hughes, R.M. Challenges to saving China’s freshwater biodiversity: Fishery exploitation and landscape pressures. Ambio 2020, 49, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.M.; Zhao, H.T.; Miao, Z.G.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhang, F.T.; Wang, J.W. Status and conservation of fish resources in the Chishui River. Biodivers. Sci. 2010, 18, 162–172. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, O.; Sanderson, E.W.; Magrach, A.; Allan, J.; Beher, J.; Jones, K.R.; Possingham, H.P.; Laurance, W.F.; Wood, P.R.; Fekete, B.M.; et al. Global terrestrial Human Footprint maps for 1993 and 2009. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hou, J.; Yang, J.; Liao, W.J.; Lu, J.C.; He, X.G. Captive density on growth performance and health status of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus Salmoides). Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2022, 46, 671–678. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Liu, F.; Xia, Z.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Tang, R.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, M.; Zou, X. Integration of ABC curve, three dimensions of alpha diversity indices, and spatial patterns of fish assemblages into the health assessment of the Chishui River basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75057–75071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Lin, P.-C.; Li, M.-Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.-L.; Liu, H.-Z. Situations and conservation strategies of fish resources in the Yangtze River basin. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2019, 43, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickler, K.M.; Fremier, A.K.; Goldberg, C.S. Quantifying effects of UV-B, temperature, and pH on eDNA degradation in aquatic microcosms. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.A.; Turner, C.R.; Jerde, C.L.; Renshaw, M.A.; Chadderton, W.L.; Lodge, D.M. Environmental Conditions Influence eDNA Persistence in Aquatic Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilliod, D.S.; Goldberg, C.S.; Arkle, R.S.; Waits, L.P. Factors influencing detection of eDNA from a stream-dwelling amphibian. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscari, E.; Wu, J.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, S.; Cattelan, S.; Wang, C.; Du, H.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Ruan, R.; et al. The last giants of the Yangtze River: A multidisciplinary picture of what remains of the endemic Chinese sturgeon. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 157011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Shen, L.; He, Y.F.; Tian, H.W.; Gao, L.; Wu, J.M.; Wei, Q.W. Status of aquatic organisms resources and their environments in the Yangtze River system (2017–2021). Aquaculture and Fisheries 2023, 47, 3–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Dai, Y.X.; Liu, H.Z.; Ai, Z.-J.; Ouyang, D.D.; Peng, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yu, D. Analysis of introduction source and ecological adaptability of exotic fishes Rhynchocypris oxycephalus and Barbatula toni in Chishui River. Chin. J. Zool. 2021, 56, 214–228. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.J.; Jiang, W.; Tang, X.L. Discussion on the possibility of mud carp (Cirrhinus molitorella) invasion to the Yangtze river. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2012, 21, 30–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Oberdorff, T.; Dias, M.S.; Jézéquel, C.; Albert, J.S.; Arantes, C.C.; Bigorne, R.; Carvajal-Vallejos, F.M.; De Wever, A.; Frederico, R.G.; Hidalgo, M.; et al. Unexpected fish diversity gradients in the Amazon basin. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugueny, B.; Movellan, A.; Belliard, J. Habitat fragmentation and extinction rates within freshwater fish communities: A faunal relaxation approach. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 20, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, L. Entropy and diversity. Oikos 2006, 113, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.K.; Caruso, T.; Buscot, F.; Fischer, M.; Hancock, C.; Maier, T.S.; Rillig, M.C. Choosing and using diversity indices: Insights for ecological applications from the German Biodiversity Exploratories. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 3514–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertora, A.; Grosman, F.; Sanzano, P.; Rosso, J.J. Fish assemblage structure in a Neotropical urbanized prairie stream exposed to multiple natural and anthropic factors. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2022, 31, 224–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, D.; Lee, S.W.; Kang, G.; Seo, J.; Lee, S. Stressor identification and health assessment of fish exposed to wastewater effluents in Miho Stream, South Korea. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 2282–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morosawa, T. Hypoxia tolerance of three native and three alien species of bitterling inhabiting Lake Kasumigaura, Japan. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 91, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Turner, C.J.; Deiner, K.; Klymus, K.E.; Thomsen, P.F.; Murphy, M.J.; Spear, S.E.; McKee, A.M.; Oyler-McCance, S.J.; Cornman, R.S.; et al. Critical considerations for the application of environmental DNA methods to detect aquatic species. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Fronhofer, E.A.; Mächler, E.; Walser, J.C.; Altermatt, F. Environmental DNA reveals that rivers are conveyer belts of biodiversity information. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Duan, C.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, Q.L.; Shen, Y.J. Fish diversity in Chongqing section of the national nature reserve for rare and endemic fish in the upper Yangtze river based on eDNA technology. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2022, 46, 2–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Species | Feeding Habits | Habit Characteristics | Upstream | Midstream | Downstream | Sequence Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acipenseriformes | ||||||
| Acipenseridae | ||||||
| 1. Acipenser sinensis | carnivorous | bottom | + | + | 142 | |
| Cypriniformes | ||||||
| Cyprinidae | ||||||
| 2. Opsariichthys bidens | carnivorous | middle and upper class | + | 495 | ||
| 3. Zacco platypus | omnivorous | middle and lower class | + | + | + | 23,874 |
| 4. Ctenopharyngodon idella | herbivorous | middle and lower class | + | + | + | 1689 |
| 5. Rhynchocypris lagowskii | herbivorous | middle and upper class | + | 209 | ||
| 6. Rhynchocypris oxycephalus ﹡ | carnivorous | upper class | + | + | 6295 | |
| 7. Chanodichthys dabryi dabryi | carnivorous | middle and upper class | + | 26 | ||
| 8. Culter alburnus | carnivorous | middle and upper class | + | 18 | ||
| 9. Hemiculter tchangi ★ | omnivorous | middle and lower class | + | 361 | ||
| 10. Hemiculterella sauvagei ★ | omnivorous | middle and upper class | + | + | + | 452 |
| 11. Megalobrama pellegrini ★ | omnivorous | middle and lower class | + | 1248 | ||
| 12. Megalobrama skolkovii | omnivorous | middle and lower class | + | 201 | ||
| 13. Pseudobrama simoni | herbivorous | middle and lower class | + | 21 | ||
| 14. Xenocypris davidi | omnivorous | middle and lower class | + | + | + | 1016 |
| 15. Xenocypris microlepis | herbivorous | middle and lower class | + | + | 613 | |
| 16. Aristichthys nobilis | planktonic | middle and upper class | + | + | 164 | |
| 17. Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | planktonic | upper class | + | 317 | ||
| 18. Rhodeus ocellatus | herbivorous | middle and upper class | + | + | + | 266 |
| 19. Rhodeus sinensis | herbivorous | middle and upper class | + | 248 | ||
| 20. Abbottina rivularis | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | 631 | |
| 21. Coreius heterodon | omnivorous | bottom | + | 13 | ||
| 22. Hemibarbus labeo | benthic | middle and lower class | + | + | 52 | |
| 23. Hemibarbus maculates | benthic | middle and lower class | + | 847 | ||
| 24. Platysmacheilus exiguus | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | + | 1445 |
| 25. Platysmacheilus nudiventris ★ | carnivorous | middle and lower class | + | 62 | ||
| 26. Pseudorasbora parva | omnivorous | upper class | + | + | + | 8140 |
| 27. Rhinogobio typus | omnivorous | bottom | + | 133 | ||
| 28. Rhinogobio cylindricus | omnivorous | bottom | + | 36 | ||
| 29. Saurogobio dabryi dabryi | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | 136 | |
| 30. Squalidus argentatus | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | 614 | |
| 31. Carassius auratus | omnivorous | middle class | + | + | + | 1941 |
| 32. Cyprinus carpio | omnivorous | bottom | + | 77 | ||
| 33. Procypris rabaudi ★ | omnivorous | bottom | + | 90 | ||
| 34. Acrossocheilus monticola ★ | omnivorous | upper class | + | + | + | 221 |
| 35. Acrossocheilus yunnanensis | omnivorous | bottom | + | 5246 | ||
| 36. Percocypris pingi ★ | carnivorous | middle and upper class | + | 56 | ||
| 37. Spinibarbus sinensis | omnivorous | middle and upper class | + | + | 2370 | |
| 38. Bangana rendahli ★ | herbivorous | bottom | + | 50 | ||
| 39. Cirrhinus molitorella﹡ | herbivorous | middle and upper class | + | 21 | ||
| 40. Garra imberba | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | 686 | |
| 41. Pseudogyrinocheilus procheilus | herbivorous | bottom | + | + | 1211 | |
| 42. Sinocrosssocheilus labiatus ★ | herbivorous | bottom | + | + | 926 | |
| 43. Schizothorax kozlovi ★ | omnivorous | bottom | + | 39 | ||
| 44. Schizothorax prenanti ★ | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | + | 1799 |
| Nemacheilidae | ||||||
| 45. Barbatula nuda﹡ | omnivorous | bottom | + | 1557 | ||
| 46. Homatula potanini ★ | carnivorous | bottom | + | 1761 | ||
| 47. Homatula variegatus | carnivorous | bottom | + | 17 | ||
| Cobitidae | ||||||
| 48. Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | + | 878 |
| 49. Paramisgurnus dabryanus | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | 153 | |
| Botiidae | ||||||
| 50. Botia superciliaris | carnivorous | bottom | + | + | 118 | |
| Balitoridae | ||||||
| 51. Lepturichthys fimbriata | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | 255 | |
| 52. Metahomaloptera omeiensis omeiensis | omnivorous | bottom | + | 42 | ||
| 53. Sinogastromyzon sichangensis ★ | herbivorous | bottom | + | + | + | 13,868 |
| 54. Sinogastromyzon szechuanensis ★ | herbivorous | bottom | + | 61 | ||
| Siluriformes | ||||||
| Amblycipitidae | ||||||
| 55. Liobagrus marginatus ★ | carnivorous | bottom | + | 32 | ||
| Sisoridae | ||||||
| 56. Euchiloglanis davidi ★ | omnivorous | bottom | + | 48 | ||
| 57. Glyptothorax sinensis | carnivorous | bottom | + | + | 115 | |
| Siluridae | ||||||
| 58. Silurus meridionalis | carnivorous | bottom | + | + | 236 | |
| 59. Silurus asotus | carnivorous | bottom | + | + | 364 | |
| Clariidae | ||||||
| 60. Clarias gariepinus﹡ | omnivorous | bottom | + | 45 | ||
| Bagridae | ||||||
| 61. Hemibagrus macropterus | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | 606 | |
| 62. Leiocassis crassilabris | carnivorous | bottom | + | + | 101 | |
| 63. Leiocassis longirostris | carnivorous | bottom | + | 13 | ||
| 64. Pelteobagrus eupogon | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | 292 | |
| 65. Pelteobagrus fulvidraco | omnivorous | bottom | + | + | 294 | |
| 66. Pelteobagrus vachellii | carnivorous | bottom | + | 26 | ||
| 67. Pseudobagrus brevicaudatus | carnivorous | bottom | + | 125 | ||
| 68. Pseudobagrus truncatus | omnivorous | bottom | + | 40 | ||
| 69. Pelteobagrus ussuriensis | carnivorous | bottom | + | + | + | 6062 |
| Ictaluridae | ||||||
| 70. Ictalurus punctatus﹡ | carnivorous | bottom | + | + | 99 | |
| Synbranchiformes | ||||||
| Synbranchidae | ||||||
| 71. Monopterus albus | carnivorous | bottom | + | 16 | ||
| Perciformes | ||||||
| Percichthyidae | ||||||
| 72. Siniperca chuatsi | carnivorous | bottom | + | + | 468 | |
| Odontobutidae | ||||||
| 73. Odontobutis potamophila | carnivorous | upper class | + | 12 | ||
| Gobiidae | ||||||
| 74. Rhinogobius cliffordpopei | carnivorous | bottom | + | + | 312 | |
| 75. Rhinogobius similis | carnivorous | bottom | + | + | + | 2348 |
| Centrarchidae | ||||||
| 76. Micropterus salmoides﹡ | carnivorous | middle and lower class | + | 899 | ||
| Cyprinodontiformes | ||||||
| Poeciliidae | ||||||
| 77. Gambusia affinis﹡ | omnivorous | upper class | + | + | + | 271 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, N.; Wang, J.; Xiao, N.; Gao, X.; Shen, M.; Sun, X.; Li, J. Study on Fish Diversity and Drivers Based on Environmental DNA in Chishui River, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114922
Guo N, Wang J, Xiao N, Gao X, Shen M, Sun X, Li J. Study on Fish Diversity and Drivers Based on Environmental DNA in Chishui River, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114922
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Ningning, Junqin Wang, Nengwen Xiao, Xiaoqi Gao, Mei Shen, Xiaoxuan Sun, and Junsheng Li. 2025. "Study on Fish Diversity and Drivers Based on Environmental DNA in Chishui River, China" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114922
APA StyleGuo, N., Wang, J., Xiao, N., Gao, X., Shen, M., Sun, X., & Li, J. (2025). Study on Fish Diversity and Drivers Based on Environmental DNA in Chishui River, China. Sustainability, 17(11), 4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114922







