Analysis of Emergency Cooperative Strategies in Marine Oil Spill Response: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Emergency Response to Marine Oil Spills
2.2. Emergency Cooperation in Accident Response
2.3. Stochastic Evolutionary Game Theory in Emergency Management
3. Model Construction
3.1. Problem Description
3.2. Main Parameters and Model Assumptions
3.3. Payoff Matrix and Replicator Dynamic Equations
4. Stochastic Evolutionary Game Model
4.1. Stochastic Disturbances in the Strategies of the Three Parties
4.2. Analysis of the Existence and Stability of Equilibrium Points
5. Numerical Simulation
5.1. Simulation Analysis of System Evolution Under Different Initial Strategy Conditions
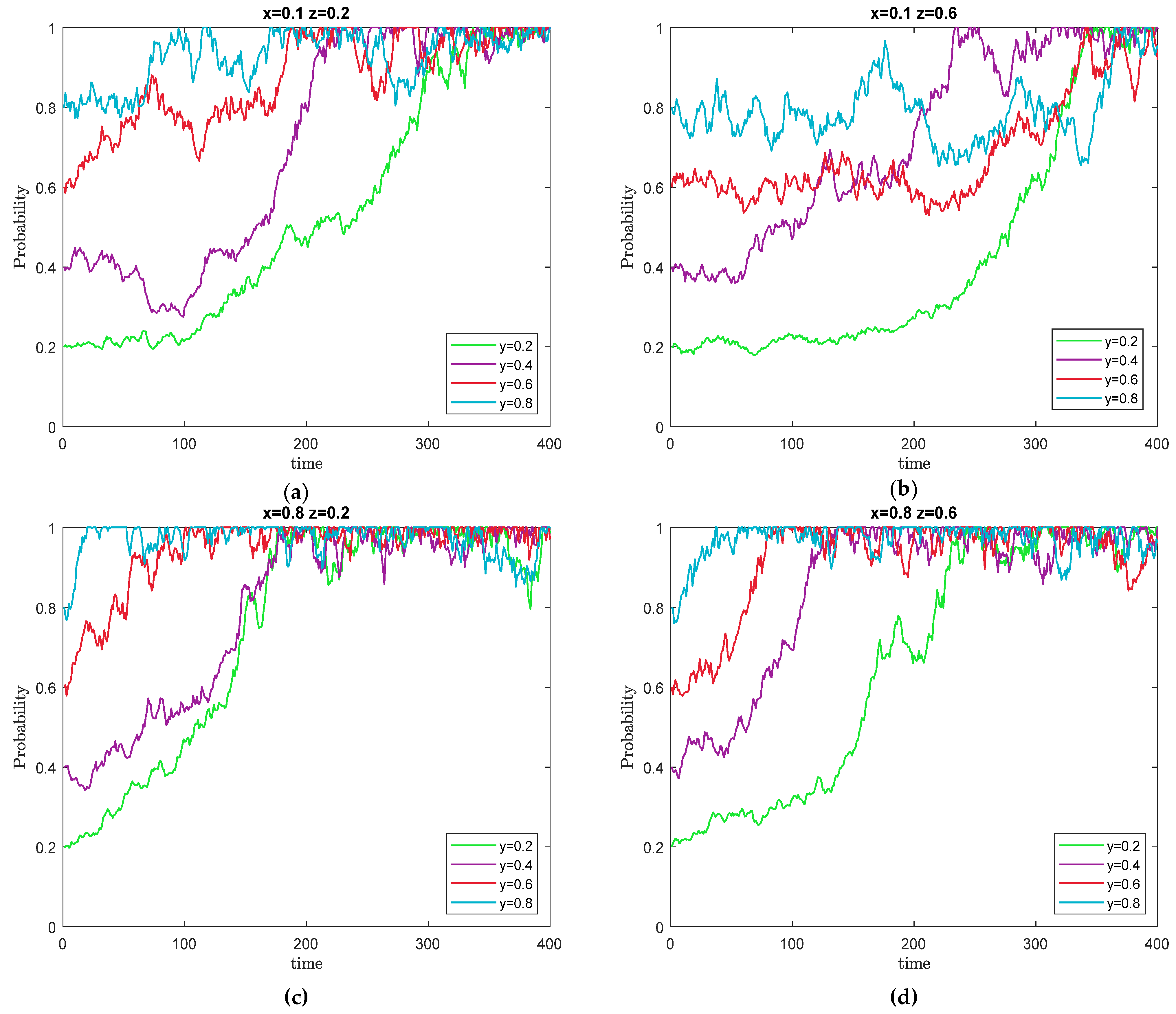
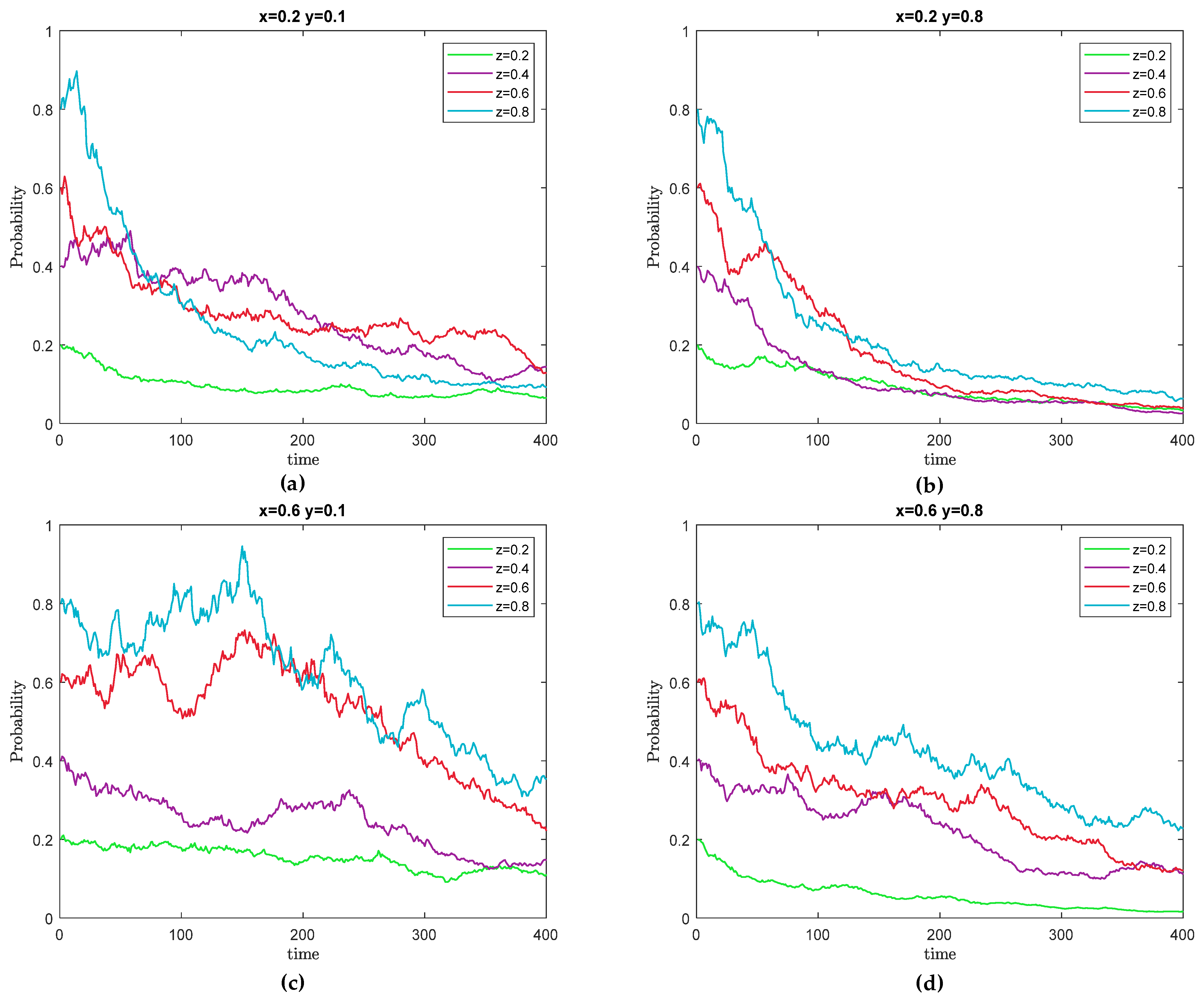
5.2. Changes in the Strategy Probabilities of Port Enterprises and Specialized Oil Spill Cleanup Units
5.3. Changes in the Strategies of the Local Government and Specialized Oil Spill Cleanup Units
5.4. Changes in the Strategy Probabilities of the Local Government and Port Enterprises
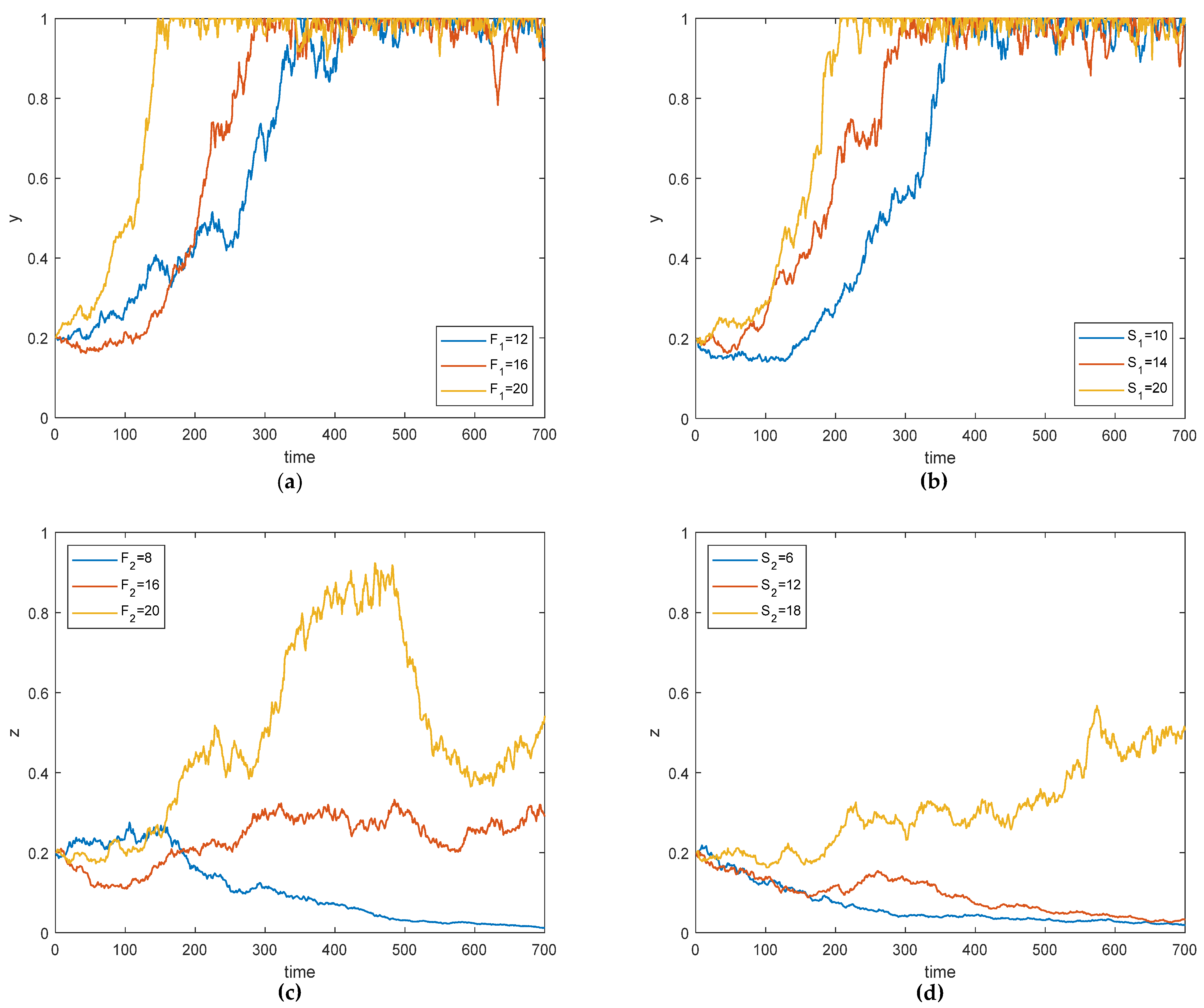
5.5. Simulation Analysis of the Impact of the Local Government Incentives and Penalties on the Strategies
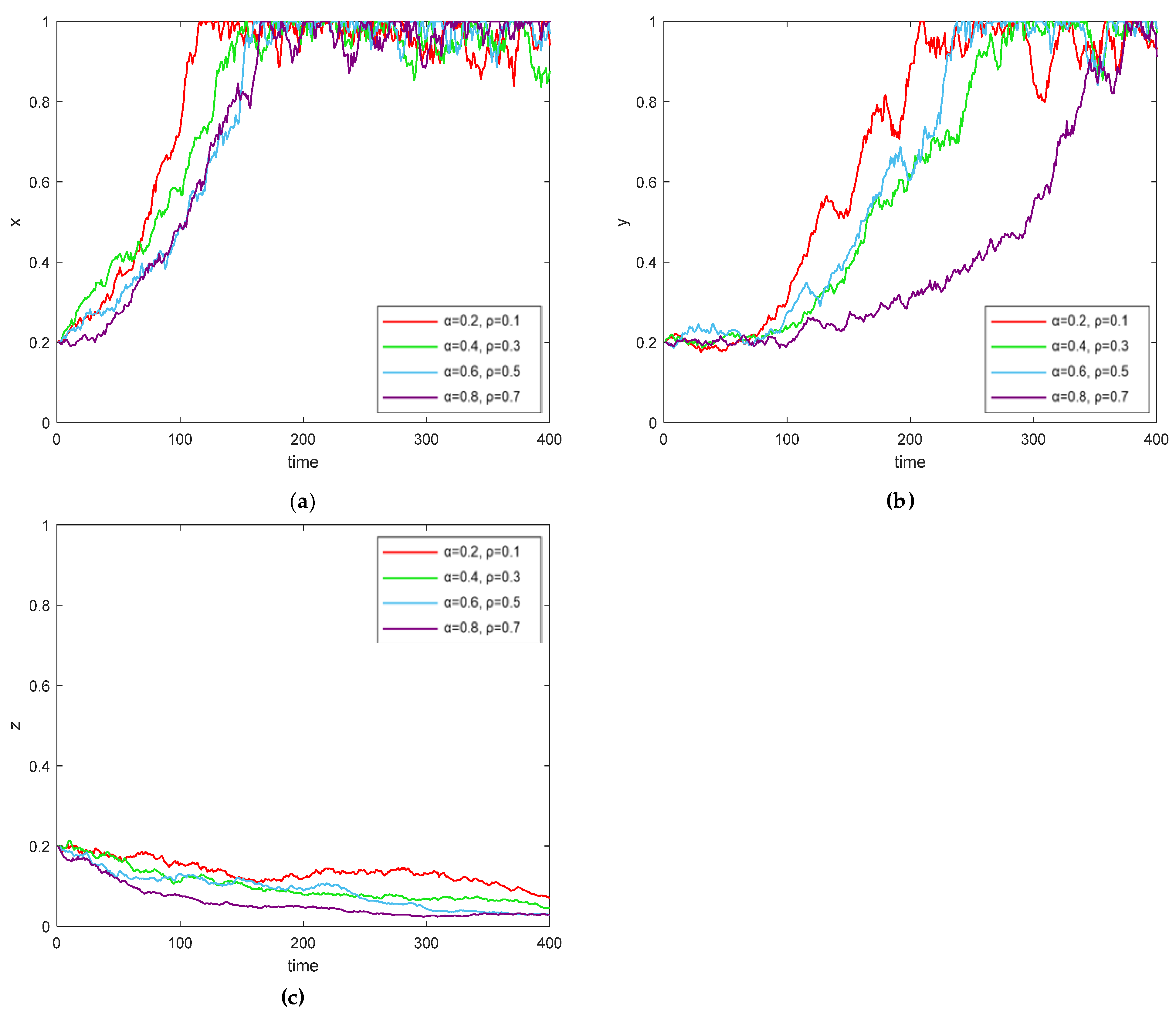
5.6. Simulation Analysis of the Impact of Emergency Response Efficiency Coefficient and Emergency Cooperation Effect Coefficient
5.7. Simulation Analysis of the Effect of Random Disturbance Intensity on Evolutionary Results
6. Conclusions
6.1. Management Significance
- (1)
- Effective government regulation is essential for promoting active participation by port enterprises in maritime oil spill response cooperation and for increasing the willingness of specialized oil spill cleanup units to engage in coordinated efforts. The local government should develop and refine relevant policies and regulations, raise public awareness, strengthen the environmental accountability of port enterprises, and ensure that regulatory measures are implemented effectively. These actions can boost the motivation of port enterprises to cooperate and encourage the adoption of more proactive emergency response strategies. Moreover, differentiated incentives and penalties can be tailored according to the level of cooperation demonstrated by port enterprises and the severity of oil spill risks. For instance, enterprises that fail to meet their emergency response obligations or display a passive attitude may be subject to environmental taxes or other economic sanctions to heighten their risk awareness and promote active engagement. Local government also plays a vital role in optimizing the oil spill contingency compensation mechanism and ensuring the execution of cooperative agreements. By implementing rational resource allocation strategies and well-designed incentive systems, local authorities can significantly enhance overall emergency response effectiveness and foster the sustainable development of regional oil spill response cooperation.
- (2)
- The fine mechanism serves as a key tool for strengthening the local government oversight in maritime oil spill response cooperation. To ensure effective implementation of contingency plans, local authorities must rigorously supervise the cooperative actions of port enterprises and specialized oil spill cleanup units, imposing strict penalties on those that violate cooperation protocols or fail to respond adequately to spill incidents. Increasing fines for enterprises that neglect their emergency cooperation duties or hinder the development of the regional contingency system can significantly enhance regulatory effectiveness and encourage firms to take greater environmental responsibility. To reinforce the penalty system, the local government can adopt a range of regulatory measures. These may include ordering non-compliant enterprises to suspend operations for rectification, integrating their records into credit supervision systems, and increasing the cost of non-compliance through public disclosures or industry bulletins. Such measures can effectively curb non-cooperative behavior among port enterprises and specialized oil spill cleanup units, thereby supporting the stable operation of the emergency response cooperation framework, strengthening overall response capacity, and minimizing the environmental damage caused by oil spill incidents.
- (3)
- In the maritime oil spill response system, each game subject is committed to maximizing the benefits and adjusting its strategy continuously. The introduction of stochastic perturbation leads to obvious oscillation characteristics for each participant in the strategy evolution process. Under normal perturbation, port enterprises are most significantly affected, showing high instability, followed by the local government, while specialized oil spill cleanup units remain stable; In contrast, under strong perturbation, port enterprises show obvious speculative tendencies, while specialized oil spill cleanup units also show more prominent speculative behavior and are more affected by external perturbation. In contrast, the local government has demonstrated a stronger capacity to counter disturbances. Therefore, the local government formulates special funding support policies for oil spill prevention and control and provides financial incentives to encourage port enterprises to participate in emergency response cooperation continuously. In addition, in the face of sudden external perturbations, such as extreme weather and sudden environmental events, an oil spill contingency reserve system needs to be set up, including financial reserves, emergency material reserves, and a training system for professionals, to improve the response capability of the entire system.
- (4)
- This study demonstrates a strong positive correlation between emergency response efficiency and the effectiveness of cooperation mechanisms. Empirical analysis reveals that strengthening cooperative efforts notably enhances information sharing, improves resource coordination, and reduces response time. These findings highlight that establishing an efficient collaborative framework is essential for effective oil spill management. To improve the overall response to maritime oil spills, it is crucial to develop a regional joint emergency response system that fosters shared decision-making and communication among government bodies, port enterprises, and specialized oil spill cleanup units. Leveraging big data technologies can further enhance oil spill detection and early warning capabilities, support the development of an integrated resource coordination platform, and facilitate the creation of a regional emergency material reserve center to strengthen emergency deployment capacity.
6.2. Limitations and Research Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Macioszek, E.; Jurdana, I. Transport of Goods on the Example of a Selected Section of Transport in Poland. Sci. J. Silesian Univ. Technol. Ser. Transp. 2023, 121, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Zhu, L. Assessing the Impacts of Sanchi Incident on Chinese Law Concerning Ship-Source Oil Pollution. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 225, 106227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.F. Case Study on Emergency Response to Sudden Offshore Oil Spill Accidents. Three Gorges Eco-Environ. Monit. 2022, 7, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, F.I. Assessment of Multi-Stakeholders’ Collaborative Efforts during and after Oil Pipelines Disaster in Nigeria. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 93–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabela-Rikhotso, P.T.Z.; Van Niekerk, D.; Nemakonde, L.D. Enhancing Coordination for Effective Management of Oil Spill Pollution in South Africa. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2022, 13, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.H.; McKinnon, L.R.; Ritchie, L.; Gill, D.; Hasenaeur, T.; Giese, J. Oil Spill Preparedness and Response: Building the Capacity to Protect Public Welfare and Support Community Resilience. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 2021, 2021, 689381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y. Research on Emergency Linkage System for Ship Pollution Accidents in Coastal Areas of Zhejiang. Master’s Thesis, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Crivellari, A.; Bonvicini, S.; Tugnoli, A.; Cozzani, V. Key Performance Indicators for Environmental Contamination Caused by Offshore Oil Spills. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 153, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Cai, Q.; Lin, W.; Chen, B.; Zhang, B. Offshore Oil Spill Response Practices and Emerging Challenges. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Chen, B.; Lee, K.; Storesund, R.; Li, P.; Kang, Q.; Zhang, B. An Emergency Response System by Dynamic Simulation and Enhanced Particle Swarm Optimization and Application for a Marine Oil Spill Accident. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, M.; Sydnes, A.K. Interorganizational Coordination in Oil Spill Emergency Response: A Case Study of the Murmansk Region of Northwest Russia. Polar Geogr. 2010, 33, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydnes, M.; Sydnes, A.K. Oil Spill Emergency Response in Norway: Coordinating Interorganizational Complexity. Polar Geogr. 2011, 34, 299–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegeberg, S.; Fritt-Rasmussen, J.; Gustavson, K.; Lilover, M.-J.; Boertmann, D.; Christensen, T.; Johansen, K.L.; Spelling-Clausen, D.; Rigét, F.; Mosbech, A. EOS—Environment & Oil Spill Response. An Analytic Tool for Environmental Assessments to Support Oil Spill Response Planning: Framework, Principles, and Proof-of-Concept by an Arctic Example. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 115948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Qian, L. The Government’s Mobilization Strategy Following a Disaster in the Chinese Context: An Evolutionary Game Theory Analysis. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1411–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, J.; Yang, Z. Dynamic Optimization of Emergency Resource Scheduling in a Large-Scale Maritime Oil Spill Accident. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 152, 107028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Cao, Y. Three-Party Behavior Strategy Selection and Simulation of Monetary Compensation for Marine Environmental Damage Based on Evolutionary Game Theory. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 250, 107025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Goerlandt, F. Bayesian Inference Modeling to Rank Response Technologies in Arctic Marine Oil Spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. A Probabilistic Framework for Risk Management and Emergency Decision-Making of Marine Oil Spill Accidents. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 162, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, W.; Lyu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, P. An Adversarial Learning Approach to Forecasted Wind Field Correction with an Application to Oil Spill Drift Prediction. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Jia, Q.L.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.Q.; Bi, F.; Xu, J.L.; Gao, S. Oil Spill Drift Prediction Enhanced by Correcting Numerically Forecasted Sea Surface Dynamic Fields with Adversarial Temporal Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4701018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanael, J.; Khairilmizal, S.; Samuel, C.; Sansuddin, N.; Hussin, M.F.; Hapani, M.; Musa, N.A.; Ainul Husna, K. Challenges in Managing Emergency Offshore: A Comparison of Offshore and Onshore Perspectives. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2024, 88, 105275. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Y.; Zhang, Q. Optimization on Cooperative Government and Enterprise Supplies Repertories for Maritime Emergency: A Study Case in China. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1687814019828576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, N.; Borch, O.J.; Sydnes, A.K. Information Sharing and Emergency Response Coordination. Saf. Sci. 2020, 130, 104895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, W.L., Jr.; Streib, G. Collaboration and Leadership for Effective Emergency Management. Public Adm. Rev. 2006, 66, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, C.; Boin, A.; Keller, A. Managing Transboundary Crises: Identifying the Building Blocks of an Effective Response System. J. Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2010, 18, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W. The Research on Cooperation Mechanism of Multiple Participants in Emergency Response. Master’s Thesis, East China University of Political Science and Law, Shanghai, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.X.; Hu, D.H.; Liu, P.C. How Is Business-Government Cooperation Possible During Major Public Health Emergencies ?—The Dynamics of Inter-Organizational Relationships Under the Conditions of Asymmetric Resource Dependence. Chin. Public Adm. 2022, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, E.-K. Transboundary Crisis Networks: The Challenge of Coordination in the Face of Global Threats. Risk Manag. 2015, 17, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignami, D.F.; Ambrosi, C.; Bertulessi, M.; Menduni, G.; Pozzoni, M.; Zambrini, F. Governance Strategies and Tools towards the Improvement of Emergency Management of Natural Disasters in Transboundary Areas. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2024, 111, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qin, Y.; Xu, Z.S. Dynamic Tracking of Research Status and Hot Frontiers in the Field of Management Science. Chin. J. Manage. Sci. 2023, 31, 276–286. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, H.; An, Y.; Bai, H.; Shi, J. Intergovernmental Collaborative Governance of Emergency Response Logistics: An Evolutionary Game Study. Nat. Hazards 2025, 121, 705–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaberg, D.; Devine, L.; Zhuang, J. A Review of Game Theory Applications in Natural Disaster Management Research. Nat. Hazards 2017, 89, 1461–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, Y.; An, S.; Dong, C. How to Improve the Cooperation Mechanism of Emergency Rescue and Optimize the Cooperation Strategy in China: A Tripartite Evolutionary Game Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Hao, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, L. Evolutionary Game and Simulation Analysis on Management Synergy in China’s Coal Emergency Coordination. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1062770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yu, W.; Shen, D. Evaluating Environmental Outcome and Process-Adaptivity of Regional Collaboration: An Empirical Study from China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellomo, N.; Bingham, R.; Chaplain, M.A.J.; Dosi, G.; Forni, G.; Knopoff, D.A.; Lowengrub, J.; Twarock, R.; Virgillito, M.E. A Multiscale Model of Virus Pandemic: Heterogeneous Interactive Entities in a Globally Connected World. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 2020, 30, 1591–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, L.A. The long-run behavior of the stochastic replicator dynamics. Ann. Appl. Probab. 2005, 15, 1019–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudenberg, D.; Imhof, L.A. Imitation Processes with Small Mutations. J. Econ. Theory 2006, 131, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Wu, H.; Qu, G.; Yin, J.; Cao, J. Analysis of Multi-Agent Greenwashing Governance in China: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game Perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 492, 144729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, W.; Wang, H. Analysis of Collaborative Urban Public Crisis Governance in Complex System: A Multi-Agent Stochastic Evolutionary Game Approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, C. Understanding the Complex Adaptive Characteristics of Cross-Regional Emergency Collaboration in China: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game Approach. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Broeck, C. On the Relation between White Shot Noise, Gaussian White Noise, and the Dichotomic Markov Process. J. Stat. Phys. 1983, 31, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Di, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, J.; Yang, C. Evolutionary Game Analysis on Behavior Strategies of Multiple Stakeholders in Maritime Shore Power System. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 202, 105508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. Stochastic Evolutionary Game Analysis between Special Committees and CEO: Incentive and Supervision. Dyn. Games Appl. 2021, 11, 538–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloeden, P.E.; Platen, E. Stochastic Taylor Expansions. In Numerical Solution of Stochastic Differential Equations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 161–226. ISBN 978-3-642-08107-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo, N.; Clarke, D.; Gibelli, L.; Townsend, P.; Vreugdenhil, B.J. Human Behaviours in Evacuation Crowd Dynamics: From Modelling to “Big Data” toward Crisis Management. Phys. Life Rev. 2016, 18, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameter | Meaning | Range |
|---|---|---|
| The basic profits of port enterprises and specialized oil spill cleanup units . | ||
| Basic emergency costs for the local government , port enterprises , and specialized oil spill cleanup units . | ||
| The rewards granted to port enterprises and specialized oil spill cleanup units for positive cooperation under a strong supervision strategy by the local government. | ||
| The punishments imposed on port enterprises and specialized oil spill cleanup units for negative cooperation under a strict supervision strategy by the local government. | ||
| The additional oil spill emergency costs incurred by port enterprises and specialized oil spill cleanup units when engaging in positive cooperation. | ||
| The “free-riding” benefits for port enterprises during negative cooperation are higher in channel oil spill accidents due to abundant resources and diffuse responsibility, whereas they are lower in port-front spills due to clearer responsibility and higher risks. | ||
| The additional profits gained by specialized oil spill cleanup units from prolonging the cleanup time when choosing the “negative cooperation” strategy. | ||
| The losses incurred by the local government due to an oil spill accident primarily include marine environmental pollution and direct economic losses to coastal industries such as fisheries and tourism. | ||
| The benefits gained by the local government under a strong supervision strategy primarily include enhanced social reputation and image, as well as recognition and rewards from higher authorities. | ||
| The effect coefficient of emergency cooperation, a variable used to evaluate the effectiveness of the implementation of the overall emergency response operation when the investment of emergency resources is limited. | ||
| The emergency cooperation effectiveness coefficient, a variable used to evaluate the scale and degree of coordination among the local government, port enterprises, and specialized pollution cleanup companies during emergency response operations. |
| The Local Government | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Port enterprises | Positive cooperation | Specialized oil spill cleanup units | Positive cooperation | |
| Negative cooperation | ||||
| Negative cooperation | Positive cooperation | |||
| Negative cooperation | ||||
| The Local Government | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Port enterprises | Positive cooperation | Specialized oil spill cleanup units | Positive cooperation | |
| Negative cooperation | ||||
| Negative cooperation | Positive cooperation | |||
| Negative cooperation | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, F.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, P.; Liu, G.; Zhao, D. Analysis of Emergency Cooperative Strategies in Marine Oil Spill Response: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game Approach. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4920. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114920
He F, Xu Y, Zheng P, Liu G, Zhao D. Analysis of Emergency Cooperative Strategies in Marine Oil Spill Response: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game Approach. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):4920. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114920
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Feifan, Yuanyuan Xu, Pengjun Zheng, Guiyun Liu, and Dan Zhao. 2025. "Analysis of Emergency Cooperative Strategies in Marine Oil Spill Response: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game Approach" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 4920. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114920
APA StyleHe, F., Xu, Y., Zheng, P., Liu, G., & Zhao, D. (2025). Analysis of Emergency Cooperative Strategies in Marine Oil Spill Response: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game Approach. Sustainability, 17(11), 4920. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114920





