Abstract
The spatial morphology of traditional villages stems from prolonged interactions between socio-economic conditions and the regional natural environment under specific historical contexts. Over time, these settlements have acquired distinct spatial patterns through continuous adaptation to their surrounding ecosystems. Nevertheless, accelerated urbanization now exerts dual pressures—disrupting the spatial order and degrading natural ecosystems. In this context, an integrated analysis of the relationship between village spatial patterns and ecological conditions is essential for elucidating their formative mechanisms. The Xiangjiang River Basin is Hunan’s cultural core, and the spatial distribution of traditional villages is directly related to environmental variables. This study uses bivariate spatial autocorrelation and geographically weighted regression to investigate the relationship between the spatial distribution of traditional villages and ecological environmental appropriateness. The findings indicate the following: (1) The spatial distribution density of traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin exhibits a negative correlation with the Ecological Environment Index (EEI), as evidenced by a Moran’s I value of −0.228. This suggests that traditional villages tend to be less concentrated in areas with a higher ecological suitability. (2) Among natural factors, the Relief Degree of Land Surface (RDLS), the Temperature Humidity Index (THI), and the Land Cover Index (LCI) display positive correlations with village density, with regression coefficients of 0.865, 0.003, and 11.599, respectively. In contrast, the Water Resource Index (WRI) shows a negative correlation, with a coefficient of −6.448, and (3) the impact of ecological suitability factors on village distribution is spatially heterogeneous: microtopographic variation is the primary driver in flat terrains, whereas the ecological carrying capacity exerts a greater influence in mountainous areas. These findings clarify the role of ecological suitability in shaping the spatial characteristics of traditional villages and provide a scientific basis for developing protection strategies that integrate ecological sustainability with cultural–heritage preservation.
1. Introduction
Traditional villages serve as spatial carriers shaped by the long-term interaction between humans and the natural environment. They are not only material records of regional cultural heritage but also living expressions of ecological adaptation wisdom. Their spatial distribution reflects the dynamic balance between human activity and the natural landscape throughout history. Ecological environmental suitability, as a comprehensive measure of natural geographic factors, influences the location, form, and evolution of villages through topography, hydrology, climate, and other environmental conditions. In recent years, policy documents such as the Guiding Opinions on Effectively Strengthening the Protection of Traditional Villages in China [1], the Strategic Plan for Rural Revitalization (2018–2022) [2], and the Five-Year Action Plan for Improving and Upgrading Rural Habitat (2021–2025) [3] have emphasized the need for a long-term mechanism that integrates traditional village protection with ecological sustainability. These policies underscore the growing importance of evaluating ecological suitability in policy planning and implementation.
In traditional village ecological research, existing studies primarily focus on ecological sensitivity analysis [4,5,6], ecological construction wisdom [7,8,9], and ecological landscape protection and design [10,11,12]. By utilizing their natural and human ecological resources, carefully conserved and methodically restored village historical sites have supported new sectors like cultural tourism and ecological leisure since the rural revitalization strategy was put into place [13,14]. This enhances the economic vitality of traditional villages while maintaining a balance between cultural heritage preservation and socio-economic development. However, there are fewer articles that study the correlation between traditional villages and the ecological and natural environment. In spatial research on traditional villages, domestic scholars mainly examine the spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors [15,16,17], spatiotemporal evolution patterns [18,19], and spatial layout optimization [4,20,21]. However, most studies are conducted at the provincial and municipal levels based on administrative divisions, which presents certain limitations. Given that human settlements in river basins exhibit a distinctive “nature–humanity” coupling, analyzing the relationship between the spatial distribution and the ecological environmental suitability of traditional villages from a basin perspective offers a more comprehensive understanding of their complex interactions [22].
In summary, the fruitful research results of scholars on rural settlements have provided important theoretical support for the reconstruction of the territorial spatial planning system and the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy. However, there is still some room for expansion in the existing research: first, the unevenness of the spatial scale. Existing research focuses on the analysis of spatial patterns of provincial and municipal administrative units, and pays insufficient attention to the basin units with complete eco-geographical characteristics. This limitation of scale selection makes it difficult to reveal the synergistic mechanism of the natural–human elements in the basin. The second is the limitation of methodology. Existing studies mainly use a qualitative analysis to analyze the adaptability of the spatial pattern of traditional villages to the natural ecological environment, and there is a lack of a quantitative analysis framework for the study of the correlation between traditional villages and the suitability of the ecological environment. Current research primarily focuses on preserving village architectural forms and exploring cultural values but lacks a quantitative analysis of the relationship between traditional villages and ecological environmental suitability at the basin scale. To address this gap, this study integrates the spatial control requirements of the Hunan Provincial Ecological Protection Red Line Plan [23] with data on 205 national traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin. Using the ArcGIS tool, the village density and ecological environmental suitability are analyzed within a 1 km × 1 km grid framework. Spatial autocorrelation and geographically weighted regression methods are then applied to quantitatively assess the impact of ecological environmental suitability factors on the spatial distribution of traditional villages, providing deeper geographic insights into their correlation. This study aims to offer theoretical support for a village protection model that prioritizes ecological sustainability and cultural continuity within the policy framework, ultimately achieving a multidimensional balance between cultural heritage preservation, ecological security, and rural development.
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
The Xiangjiang River is part of the Dongting Lake system within the Yangtze River Basin. Originating in Lanshan County, Yongzhou City, Hunan Province, it flows through Yongzhou, Chenzhou, Hengyang, Zhuzhou, Xiangtan, and Changsha before emptying into Dongting Lake at Xiangyin County. The river spans 948 km, draining a basin area of 94,721 square kilometers. Geographically, the Xiangjiang River Basin lies between the latitudes of 24°31′–28°45′ N and longitudes of 110°30′–114° E. It is bordered by the Mufu and Luoxiao Mountains, which separate Hunan from Jiangxi and the Poyang Lake system to the east. To the south, it shares a watershed with the Pearl River system in Guangxi, while in the west, the Hengshan Mountain Range separates it from the Zishui River. To the north, it connects with Dongting Lake. The Xiangjiang River Basin exhibits diverse and complex landforms dominated by mountains and hills. The climate is marked by cold, wet winters; hot, humid summers; and pronounced seasonality, with heavy precipitation in spring and summer followed by relatively dry conditions in autumn and winter. The basin is also the most densely populated and highly urbanized region in Hunan Province and serves as the province’s leading center of economic, social, and cultural development (Figure 1) [24,25].
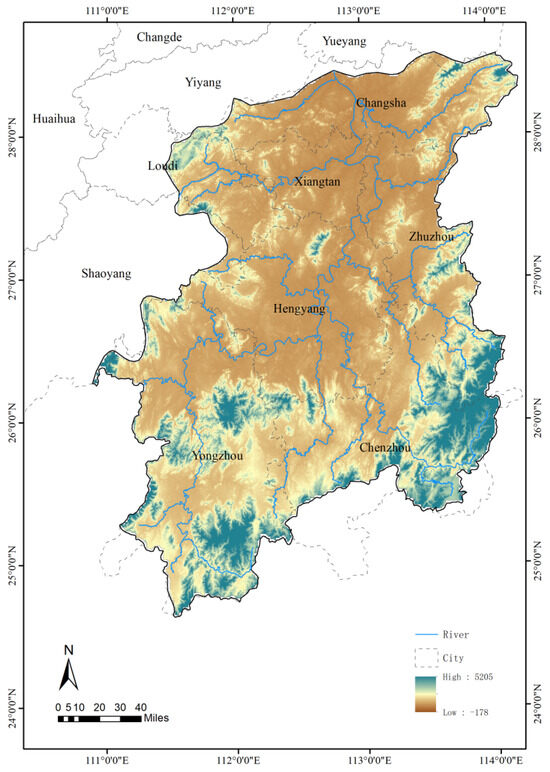
Figure 1.
Location map of the Xiangjiang River Basin.
As the cultural center of Hunan and a transitional area inside the South Ridge ecological barrier, the Xiangjiang River Basin is located on the southern bank of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Traditional villages in the basin are embedded in a complex “landscape-settlement-agriculture” ecosystem [26,27,28,29]. Their spatial distribution and evolution reflect the intricate interactions between human settlements and natural geographic factors (Figure 2 and Figure 3).
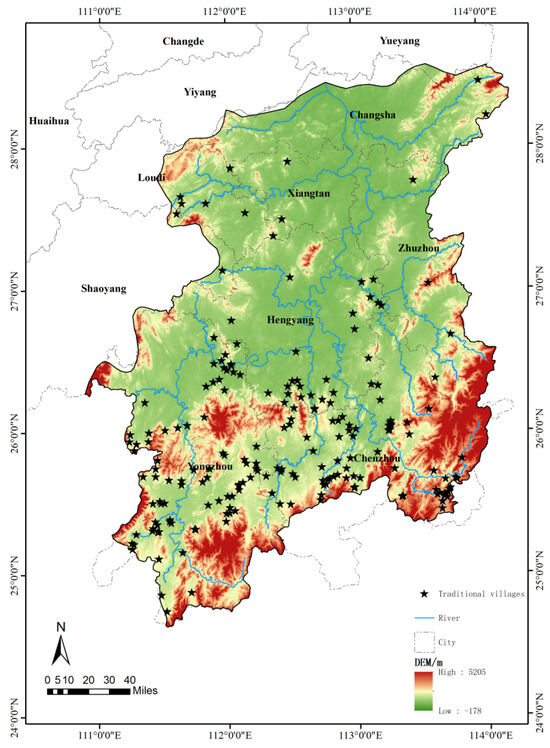
Figure 2.
Distribution of traditional villages in the Xiangjiang Basin.
Figure 3.
Traditional villages in the Xiangjiang Basin.
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
The list of traditional villages was derived from six batches of Chinese traditional villages published by the Ministry of Housing and Urban–Rural Development and other relevant ministries, totaling 205 villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin. Google Earth was used to determine the geographic coordinates of these villages, and the GIS10.8 software was employed to construct their vector data. The DEM data for the Xiangjiang River Basin, obtained from the Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn/, accessed on 13 April 2025) with a resolution of 30 m, were used to calculate the Relief Degree of Land Surface and other relevant metrics. The climate data, including precipitation, average temperature, and relative humidity from 22 meteorological stations within and around the Xiangjiang Basin (1981–2021), were sourced from the China Meteorological Data Network (https://data.cma.cn/, accessed on 13 April 2025). The NDVI data at a 1-km resolution were acquired from the MOD13A3 dataset released by NASA, covering monthly values from 2000 to 2024, available through the NASA Data Center (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/, accessed on 13 April 2025). Additionally, the 2020 Chinese land use remote sensing data were obtained from the Center for Resource, Environment and Science and Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 13 April 2025). These data, generated through the manual visual interpretation of Landsat 8 remote-sensing images, classify land use into six primary types (e.g., cropland, forest, and watershed) and 25 secondary types (Table 1), aligning with the requirements of this study. The soil data were obtained from the Geographic Data Sharing Infrastructure, global resources data cloud (www.gis5g.com, accessed on 13 April 2025).

Table 1.
The 6 primary types and 25 secondary types of land use.
3. Methods
Using ArcGIS, this study first quantified four ecological suitability indicators for the Xiangjiang River Basin: the Relief Degree of Land Surface, the Temperature Humidity Index, the Water Resource Index, and the Land Cover Index. The kernel density estimation was then applied to derive the spatial density of traditional villages. Finally, a bivariate global Moran’s I statistic and a geographically weighted regression model were employed to analyze the relationship between village density and ecological suitability, and to identify the spatial differentiation attributable to each factor (Figure 4).
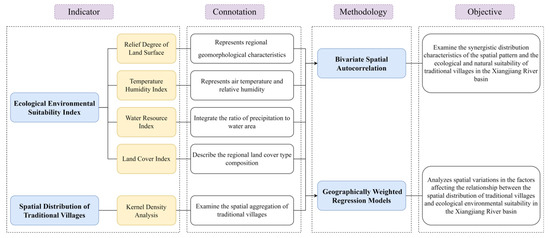
Figure 4.
Methodological flowchart.
3.1. Ecological Environmental Suitability Evaluation
Based on the typical natural characteristics of the study area—such as its hilly topography, humid subtropical climate, dense water network, and rich vegetation cover—and supported by the literature research, this study selects four key elements to evaluate the ecological and natural suitability: the Relief Degree of Land Surface (RDLS), the Temperature Humidity Index (THI), the Water Resource Index (WRI), and the Land Cover Index (LCI) [30].
3.1.1. Relief Degree of Land Surface
The Relief Degree of Land Surface (RDLS) is a key quantitative index for assessing topography. It effectively represents the regional geomorphological characteristics, highlights the gradient variations in the topographic elements, and reveals the spatial differentiation patterns within the study area [31]. As a crucial factor in evaluating ecological environmental suitability, the RDLS also indicates both the development potential and disaster risk of traditional villages. Its calculation formula is as follows:
represents the Relief Degree of Land Surface, while denotes the average elevation (m) of the region. and correspond to the highest and lowest elevations (m), respectively. is the total area of the region (km2), and in this study, a 5 km × 5 km grid is used as the regional unit, making it equal to 25 km2. represents the area of flat land (km2) within the region. Based on the study by Zhou Zixiang [32] and other studies [33,34], and considering the characteristics of the study area, terrain with a slope of less than 5° is classified as flat land.
3.1.2. Temperature Humidity Index
The Temperature Humidity Index (THI) is a parameter that combines air temperature and relative humidity to quantify the human body’s perception of the thermal environment, offering an intuitive measure of the combined effects of heat and humidity [35]. Thus, the THI not only reveals the climatic factors influencing traditional village site selection but also provides a scientific basis for the sustainable development of villages in contemporary contexts. The THI is calculated as follows:
In this paper, relevant parameters are obtained using the Kriging interpolation. represents the Temperature Humidity Index of the Xiangjiang River Basin; denotes the monthly mean temperature of the region (°C), and represents the monthly mean relative air humidity of the region (%). represents the monthly mean temperature of the interpolated projection surface, and denotes the difference between the region’s elevation and the elevation of the interpolated surface (m). represents the monthly average relative humidity (%) of the interpolated surface, and is a constant. The higher the value of the THI, the more favorable the temperature and humidity conditions are for human habitation.
3.1.3. Water Resource Index
In this study, a water resources evaluation system was developed by integrating the ratio of precipitation to the water area. The precipitation indicator captures the climate-driven natural water-supply potential and represents the primary recharge of the regional water resources through the atmospheric water cycle. The size and distribution of the watershed areas are strongly controlled by topography: low-lying plains—susceptible to waterlogging—typically possess larger watershed areas, whereas mountainous regions exhibit smaller catchments because rapid runoff limits water retention. Consequently, the watershed parameter quantifies the spatial carrying capacity of surface-water systems and reflects the hydrological-regulation capability shaped by the topographic and geomorphological conditions [36]. The formula is:
where, WRI is the Water Resource Index, is the normalized annual precipitation, is the normalized watershed area, is the soil erodibility factor, and , , and are the weights of precipitation, the watershed area, and the soil factor, respectively.
3.1.4. Land Cover Index
The Land Cover Index is an integrated measure of the land cover system that systematically characterizes the composition of regional land cover types and their spatial configuration. This index includes data on both native vegetation cover and human-made construction areas. Its dynamic evolution is influenced by natural factors, such as climate and geomorphology, as well as by human activities, including urban development, agricultural expansion, and other modifications. Previous studies have demonstrated the significance of land cover in ecological assessments. Ding [37] used land use types as the basis for evaluating the landscape ecological risk, while Xiang [38] incorporated the NDVI as an indicator in a flood disaster risk assessment in the Xiangjiang Basin, noting that the NDVI reflects the capacity of geological soils to redistribute precipitation. Therefore, land cover is not only closely related to environmental livability, but also serves as an important indicator of regional ecological risk [39,40,41].
represents the Land Cover Index, and is the regional normalized vegetation index. denotes the weight of each land use type. Based on the actual land use conditions in the study area, 18 land use types within the Xiangjiang River Basin were selected for analysis. The corresponding weights were determined by considering the specific characteristics of the region, referencing both previous research findings and the Technical Specification for the People’s Republic of China Environmental Protection Industry Standard: Technical Specification for the Evaluation of Ecological Environmental Conditions [42,43] (Table 2).

Table 2.
The weight of each land use type.
3.1.5. Ecological Environmental Suitability Index
represents the Ecological Environmental Suitability Index, while , , , and correspond to the Standardized Relief Degree of Land Surface, the Land Cover Index, the Water Cover Index, and the Temperature Humidity Index, respectively. , , , and are the weights assigned to these indices. Feng divided China into eight natural regions—Northeast, North, Central, South, Southwest, Inner Mongolia, Northwest, and Qinghai-Tibet—based on the country’s natural geographic zoning scheme. He assigned weights to each natural factor according to its correlation with the regional population density. The Xiangjiang River Basin, located in Central China, follows this classification. Therefore, drawing on Feng’s methodology and the specific conditions of the Xiangjiang Basin, the corresponding weights for the four indices were determined accordingly [30] (Table 3).

Table 3.
Correlation coefficient and weight of the ecological factor index and population density in central China.
3.2. Kernel Density Analysis
The kernel density analysis is a method used to characterize the spatial clustering of geographic elements through probability density functions. This approach involves constructing a moving window with a set bandwidth parameter, smoothing discrete observation samples, and calculating the distribution intensity of element points within a defined unit area. The resulting density values correlate positively with the degree of spatial concentration: high-density zones represent core agglomerations, while low-density zones indicate sparsely distributed areas [44]. In this study, the kernel density analysis is employed to examine the spatial aggregation of traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin, providing insights into their distribution across the region.
where is the kernel density function, is the kernel function, represents the number of observation points, is the radius of the search grid, and is the distance from the center point of the grid to a known point.
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Ecological Suitability and Traditional Village Distribution
3.3.1. Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation Results
Bivariate spatial autocorrelation builds upon the univariate spatial autocorrelation method (Moran’s I) to quantify spatial interaction patterns among the geographic elements by constructing a spatial weight matrix. The global bivariate Moran’s I index provides an overall characterization of spatial dependence among multiple elements by calculating the spatial lag covariance. In contrast, the local bivariate Moran’s I index reveals the heterogeneous nature of the element associations within micro-spatial units through the LISA cluster analysis [45]. In this study, the bivariate spatial autocorrelation method, implemented using the Geoda1.20 software, was employed to examine the synergistic distribution characteristics of the spatial pattern and the ecological and natural suitability of traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin.
represents the total number of cell grids, denotes the spatial weight matrix, corresponds to the density of traditional villages in the first variable, refers to the ecological and natural suitability index in the second variable, is the mean value of the first variable, is the mean value of the second variable, and represents the variance of both variables.
3.3.2. Geographically Weighted Regression Models
The geographically weighted regression (GWR) model is a local linear regression technique that models spatially varying relationships. It explains local spatial relationships and spatial heterogeneity by generating a local regression model in space [46]. The formula is as follows:
represents the global dependent variable, denotes the observed value of the kth variable for the ith study unit, indicates the geographic location coordinate of the study unit, is the regression constant, is the regression coefficient of the kth variable, and represents the random error. This study employs a geographically weighted regression (GWR) model using GIS to analyze the spatial variation in the factors influencing the relationship between the spatial distribution of traditional villages and the ecological suitability in the Xiangjiang River Basin. The four indices used to assess ecological suitability serve as the explanatory variables. Given the uneven distribution of traditional villages across the study area, an adaptive kernel function is applied, and the model’s optimal bandwidth is determined using the corrected Akaike Information Criterion (AICc). The bandwidth corresponds to the distance or number of neighboring elements that minimizes the AICc value.
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Ecological Environmental Suitability Analysis
This study utilized ArcGIS and multi-source spatial data to quantify the ecological-environmental suitability of the Xiangjiang River Basin. The LCI, WRI, RDLS, and THI were first normalized. The weightings for these four indices were adopted from previous studies, and a basin-wide Ecological Environmental Suitability Index (EEI) surface was generated via spatial overlay. The standardized EEI values range from 0.23 to 0.88, forming a positive gradient in which higher scores denote more favorable ecological and livability conditions. As illustrated in Figure 5, the EEI exhibits a distinct zonal pattern: the core high-suitability zone lies on the compound alluvial plain of the river’s middle and lower reaches. In the Zhuzhou core area, for example, the mean EEI is about 0.75, attributable to flat topography, a dense hydrological network, and a favorable climate. Conversely, low-suitability zones cluster in the hilly source region of southern Yongzhou, where fragmented terrain and pronounced seasonal variability in water resources restrict ecological suitability.
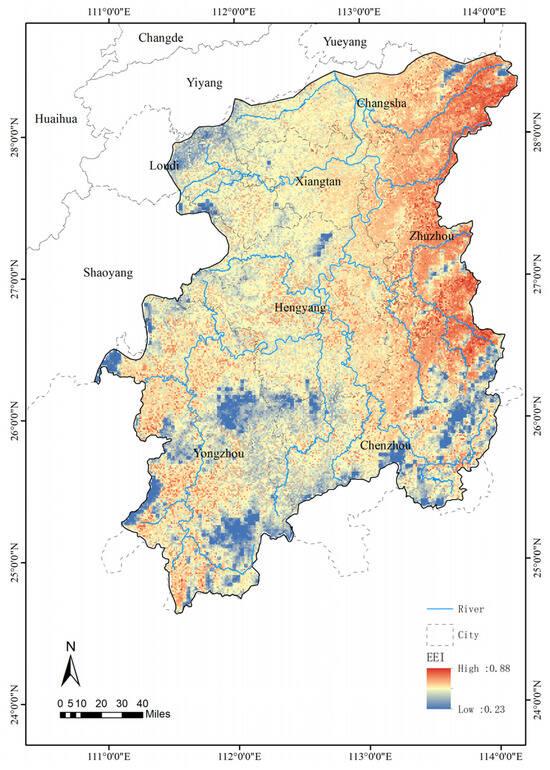
Figure 5.
Ecological Environmental Suitability Index of the Xiangjiang River Basin.
The Temperature Humidity Index is generally high in the Xiangjiang River Basin (Figure 6b), which is situated in a typical mid-subtropical monsoon humid climate zone. The middle- and high-altitude regions, including the Jiuyi Mountain Range, Luoxiao Mountain Range, and Yangming Mountain System, display relatively low values of this index. This pattern is explained by two primary factors. First, the air temperature declines with increasing altitude. Second, the attendant decrease in atmospheric water-vapor pressure limits the humidity at higher elevations. Consequently, these areas exhibit both low temperatures and low humidity. This synergy between temperature and humidity parameters causes the mountain systems to form the core units of the Temperature Humidity Index’s decreasing gradient in the basin. The spatial distribution of the Water Resource Index in the Xiangjiang River Basin demonstrates a gradual decrease from east to west (Figure 6d). The eastern region experiences greater precipitation due to the humid airflow transported by the southeasterly summer monsoon. Additionally, the eastern slopes of mountain ranges lie on the windward side, where moist air ascends, cools, and condenses, leading to topographic rainfall. As a result, the eastern mountainous areas are characterized by significantly higher precipitation levels. Furthermore, the basin’s hydrological system displays marked asymmetry: on the east bank, major tributaries such as Xiao Shui, Chun Ling Shui, and Lei Shui account for approximately two-thirds of the total catchment area. In contrast, tributaries on the west bank, originating in the Hengshao Hills, are constrained by the terrain, resulting in shorter channel lengths and lower runoff volumes—except for Lian Shui, which maintains a comparatively large catchment area [47]. In terms of topography, while the Xiangjiang River Basin as a whole has relatively gentle terrain, its overall Land Cover Index remains low, primarily due to the high intensity of agricultural development and soil degradation (Figure 6a,c).
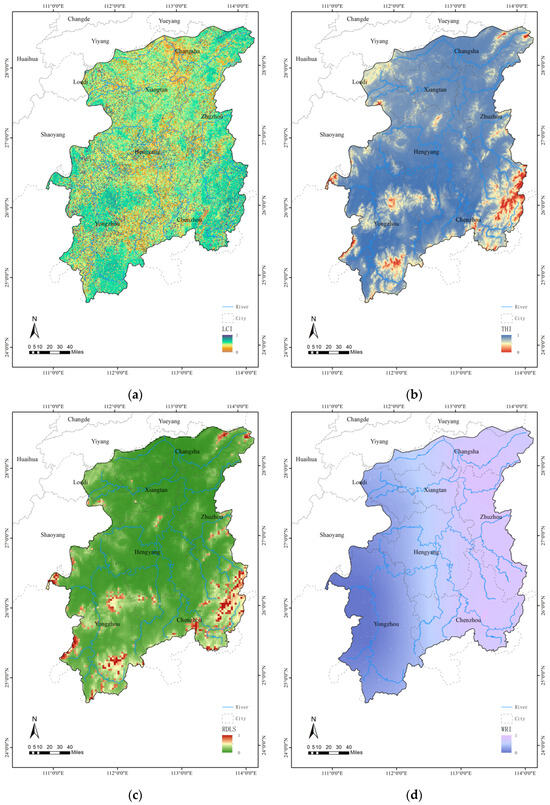
Figure 6.
Standardized factors in the Xiangjiang River Basin. (a) Standardized Land Cover Index for the Xiangjiang River Basin; (b) Standardized Temperature Humidity Index for the Xiangjiang River Basin; (c) Standardized Relief Degree of Land Surface in the Xiangjiang River Basin; (d) Standardized Water Resource Index for the Xiangjiang River Basin.
4.2. Characterization of the Spatial Distribution of Traditional Villages
In this study, the spatial kernel density analysis was used to objectively assess the spatial distribution characteristics of traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River watershed. The findings reveal significant regional variation in the spatial distribution of traditional villages: ① Density gradient: The village density is higher in the southern part of the basin and lower in the northern part. Specifically, traditional villages are concentrated in the southern regions of Yongzhou and Chenzhou, whereas the northern Chang-Zhu-Tan urban agglomeration exhibits a relatively low density of such settlements. ② Spatial pattern: The distribution exhibits a multi-centered agglomeration structure. Prominent clusters are located in the core areas of the Jiangyong and Dao Counties, the Ningyuan and Xintian Counties, Beihu District, Qiyang City, the Changning and Zixing Cities, and Rucheng County. ③ Longitudinal variation: The lower reaches of the basin—encompassing Changsha, Zhuzhou, Xiangtan, and Hengyang—are characterized by a more dispersed, point-like distribution of villages, while the upper and middle reaches contain more densely clustered settlements. This ”southern density, northern sparsity, and multi-core coexistence” pattern reflects the long-term influence of historical human–environment interactions on village development. The natural barrier of the Nanling Mountains in the middle and upper reaches has created relatively isolated geographical units, which have facilitated both defense system construction and the management of agro-forestry complexes through vertical zoning. In contrast, the downstream alluvial plain, with its farming advantages, has suffered from frequent floods during the Ming and Qing Dynasties [48]. The region’s accelerated urbanization since modern times has further contributed to the decline in the survival rate of traditional villages (Figure 7).
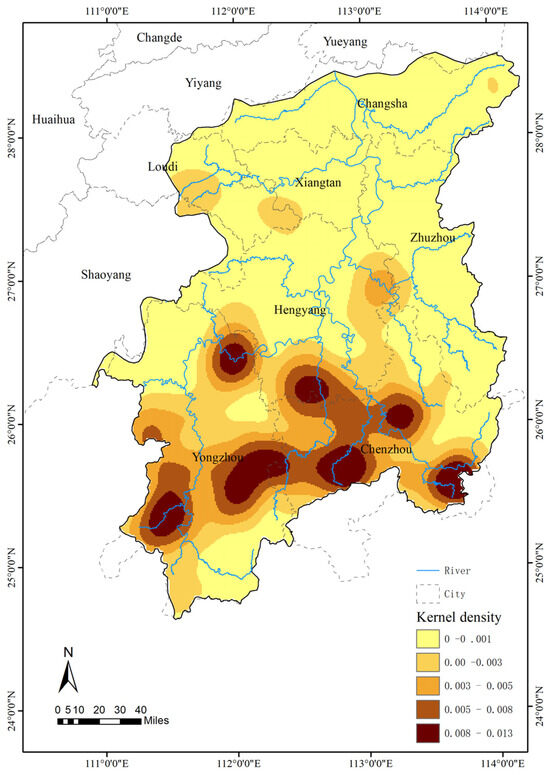
Figure 7.
Kernel density of traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin.
4.3. Analysis of the Correlation
4.3.1. Relationship Between Traditional Village Density and Ecological Environmental Suitability
In order to investigate the relationship between the ecological and natural suitability index and the degree of spatial agglomeration of traditional villages, this study applied a bivariate spatial autocorrelation model (Bivariate Moran’s I) using the spatial econometric analysis module of the Geoda software. After constructing the spatial weight matrix and performing a Monte Carlo simulation test, the statistical results (Figure 8) indicated a global Moran’s I index of −0.228 (p = 0.001) and a Z-score of −13.546 (>|2.58| critical value). These findings show that, in the Xiangjiang River Basin, there is a strong negative geographical association between the density of traditional villages and ecological environmental appropriateness. Specifically, this implies that traditional villages are sparsely distributed in regions with better ecological environmental suitability and more densely packed in places with poor suitability. Based on these findings, the local spatial autocorrelation (LISA) model was employed to further analyze the coupling characteristics of ecological environmental suitability and the spatial density of traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin.
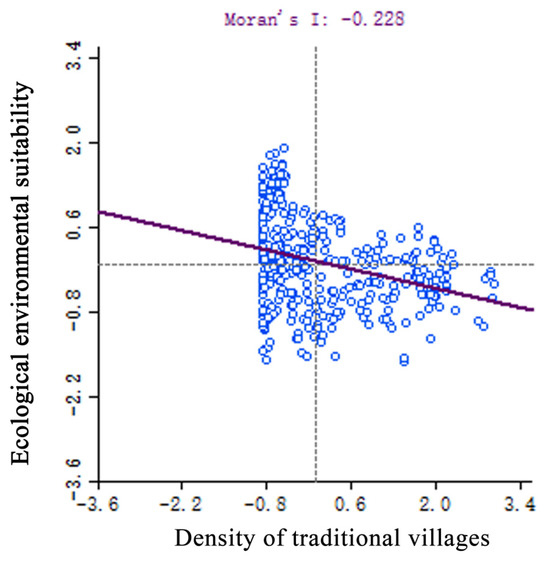
Figure 8.
Spatial autocorrelation results of the traditional village density and ecological suitability in the Xiangjiang River Basin.
The local spatial autocorrelation clustering analysis map (Figure 9) reveals that the Xiangjiang River Basin primarily consists of low–high (LH) and low–low (LL) aggregation areas. The LH aggregation area, which constitutes 21.18% of the basin’s total area, is concentrated in the Liuyang City and Zhuzhou City counties along the lower reaches of the river. This region exhibits a high ecological environmental suitability index but contains relatively few traditional villages. The LL aggregation area, accounting for 10.25% of the basin’s area, is primarily located in Ningxiang City, Lianyuan City, Zong’an County, Jianghua Yao Autonomous County, Lanshan County, and Guidong County at the basin’s edge. The high–low (HL) aggregation areas are predominantly found in Jiangyong County, Dao County, Ningyuan County, Xintian County, Zixing County, Rucheng County, and Guiyang County near the upper reaches of the Xiangjiang River. The high–high (HH) aggregation area is limited to Yongxing County and Hengdong County.
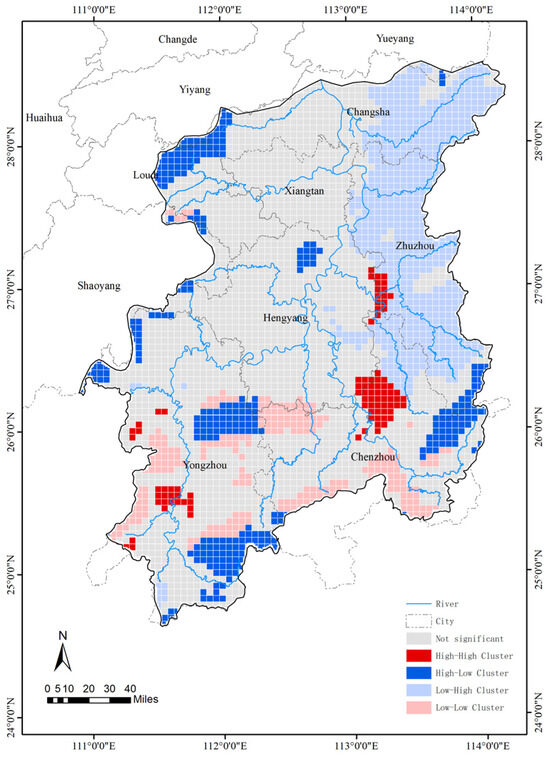
Figure 9.
Spatial density of traditional villages in Xiangjiang River Basin with an EEI cluster analysis map.
4.3.2. Influence of Ecological Environmental Suitability Factors on the Distribution Density of Traditional Villages
The study employed the THI, the RDLS, the LCI, and the WRI as explanatory factors, and the kernel density of traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin as the dependent variable. The Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) model was used to evaluate the multicollinearity among the explanatory variables before building the geographically weighted regression (GWR) model (Table 4). Those with a variance inflation factor (VIF) higher than 7.5 were not included. Consequently, the WRI, the LCI, the RDLS, and the THI were chosen for further examination.

Table 4.
OLS regression statistical results.
The OLS method is inadequate for addressing spatial non-stationarity, as it overlooks geospatial autocorrelation and local variability. In this paper, the geographically weighted regression (GWR) framework is employed to refine the analytical model. The performance evaluation reveals that the adjusted coefficient of determination (R2) for the GWR model is 0.21, a 50% improvement over the OLS global model’s R2 of 0.14. Additionally, the Akaike Information Criterion corrected (AICc) value is lower (Table 5), indicating a better model fit. It is important to note that, although the R2 value for the GWR model is within an acceptable range [49], limitations in the model’s fit remain. These may stem from the exclusion of human and economic factors. Future research could incorporate such variables through spatial lag models and other advanced methods to better elucidate the interaction mechanisms between ecological suitability and socio-cultural elements. The GWR regression coefficients are further visualized in this paper (Figure 10).

Table 5.
Comparison of the OLS and GWR models.
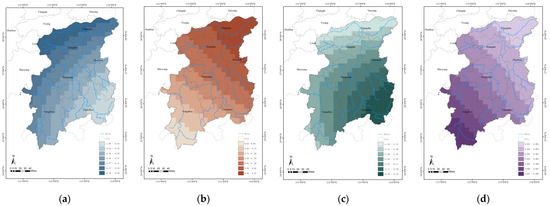
Figure 10.
Geographically weighted regression coefficients of EEI factors in the Xiangjiang River Basin: (a) Geographically weighted regression coefficients of the Water Resource Index; (b) Geographically weighted regression coefficients of the Relief Degree of Land Surface; (c) Geographically weighted regression coefficients of the Land Cover Index; (d) Geographically weighted regression coefficients of the Temperature Humidity Index.
- (1)
- Impact of the WRI
Within the Xiangjiang River Basin, the distribution density of traditional villages is strongly and negatively correlated with the Water Resource Index (WRI), although this association weakens from east to west in accordance with the basin-wide WRI gradient. High WRI regression coefficients occur in Zixing City, Yiling County, and Guidong County, whereas low coefficients are observed in Lianyuan City, Ningxiang City, and northwestern Changsha. Elevated WRI values cluster along the western Luoxiao Mountain Range, an area prone to flash floods and geohazards owing to its steep relief. During the Ming and Qing dynasties [50], frequent hydrological disasters prompted settlements to adopt a “vertical-defense” strategy that balanced flood mitigation with agricultural requirements by manipulating elevation differentials, thereby producing a decentralized settlement pattern. By contrast, the Changsha metropolitan area now relies on the modern flood-control infrastructure developed during urbanization, which substantially reduces the impact of flooding on nearby traditional villages.
- (2)
- Impact of the RDLS
Traditional communities are chosen based in large part on topographic considerations. The distribution density of traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin is positively correlated with the Relief Degree of Land Surface, according to the geographically weighted regression analysis, with the association diminishing from north to south. The topography of the basin is distinguished by lower altitudes in the north and higher elevations in the south. The spatial distribution of traditional villages is greatly influenced by the southern mountainous areas’ relief: the high-altitude terrain acts as a natural protective barrier, and the sloping land facilitates natural drainage, reducing the risk of ecological threats, such as flooding and landslides. In contrast, the northern region, despite its overall gentle topography, lacks significant natural barriers. In ancient times, when man-made water management systems were underdeveloped, topography was a crucial factor in village site selection. Additionally, there are more depressions and dykes in the north, resulting in a slightly undulating topography, which influences the distribution of traditional villages to some degree.
- (3)
- Influence of the LCI
In the Xiangjiang River Basin, the distribution density of traditional villages shows a strong positive association with the Land Cover Index, indicating that traditional villages are more likely to be found in regions with more vegetation cover. High vegetation areas provide critical ecological services, such as water and soil conservation, which act as vital ecological security barriers, mitigating the risk of flash floods and supporting the sustainable development of traditional villages. The geographically weighted regression results indicate that the influence of the LCI on village density declines from southeast to northwest across the basin, implying that vegetation cover exerts a stronger control on the spatial distribution of traditional villages in the southeastern sector than in the northwestern sector. In the lower plains of the Xiangjiang River, the extensive flood-control and water-conservancy infrastructure has diminished the ecological function of native vegetation in flood attenuation and drainage. Moreover, the continuous expansion of construction land in highly urbanized zones—particularly within the Chang-Zhu-Tan urban agglomeration—has further weakened the effect of vegetation cover on village distribution.
- (4)
- Influence of the THI
The results of the geographically weighted regression indicate that the Temperature Humidity Index exhibits a weak positive correlation with the distribution density of traditional villages, suggesting a modest facilitating effect within certain spatial ranges. This influence displays spatial variation, with its intensity increasing from south to north. This pattern indicates that traditional villages in the northern mountainous regions of the Xiangjiang River Basin are more sensitive to climatic factors. These northern areas are predominantly mountainous and experience significant vertical climatic gradients. Under the conditions of temperature and humidity fluctuations caused by altitude, even slight improvements in the climate conditions can directly enhance agricultural productivity and living comfort. This spatial heterogeneity reflects not only the climatic constraints on mountainous settlements but also the adaptive wisdom embedded in the traditional siting of villages.
5. Discussion
5.1. The Relationship Between the Spatial Distribution of Traditional Villages and Ecological Environmental Suitability
The study results reveal a spatial mismatch between areas of high traditional village density and areas of high ecological environmental suitability. Specifically, traditional villages tend to be concentrated in regions with a relatively low ecological suitability. This pattern reflects the adaptive choices made by human activities in response to the ecological environment. There may be several main reasons for this phenomenon:
- (1)
- Dynamic changes in history and culture
Traditional villages were mostly formed in agricultural societies, and site selection focused more on agricultural resources, defense needs, and disaster prevention. Traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin are predominantly clustered in the upstream areas, such as the Jiangyong and Dao counties. Despite their lower ecological suitability, the natural barrier provided by the Nanling Mountain Range offers strategic advantages, including military defense, such as ease of defense and protection from external threats. This suggests that historical and cultural factors, particularly concerns for security, played a greater role in village site selection than the pursuit of ecological comfort. While areas with a higher ecological suitability are fertile, they also have a history of frequent flooding, which has led to a “flood-avoidance” settlement pattern. This tension between livability and safety has resulted in a lower traditional village density in areas with a higher ecological suitability.
- (2)
- Economic development and population migration
Regions with a low ecological suitability often lag in economic development and offer limited employment opportunities. These areas typically rely on traditional industries, such as agriculture, forestry, and fisheries, resulting in a narrow industrial base and a low economic efficiency. In contrast, regions with a high ecological suitability experience more rapid urbanization. Urban and industrial centers in these areas provide more diverse employment options and higher income levels. As a result, people migrate from rural areas to cities in search of better living conditions and economic prospects. This migration leads to a population decline in traditional villages. The loss of population disrupts traditional lifestyles and production methods, eroding cultural identity and accelerating the decline of these villages.
- (3)
- Ecological protection and policy restrictions
As the awareness of ecological conservation grows, many regions with a high ecological suitability have been designated as nature reserves, national parks, or ecological protection zones. These areas are subject to strict regulatory restrictions that prohibit or limit large-scale human development, including the construction and expansion of traditional villages. To preserve the environment and biodiversity, the government has implemented policies encouraging population relocation or centralized resettlement. As a result, the number of traditional villages originally located in ecologically suitable but environmentally fragile areas has gradually declined.
- (4)
- Tourism development and commercialization impact
During the process of cultural and tourism industrialization, ecologically attractive areas often become focal points for tourism development. As tourism expands, the original residents gradually relocate, leading to significant changes in the spatial structure and functions of traditional villages. The introduction of modern infrastructure in some villages has disrupted the original architectural styles and spatial patterns, gradually eroding their unique historical, cultural, and regional characteristics. This transformation from cultural and ecological communities into consumer-oriented landscapes threatens the authenticity and integrity of traditional villages, ultimately accelerating their decline and disappearance.
In the process of spatial reorganization driven by the combined forces of globalization and regional development, areas with a high ecological livability have become preferred spatial carriers for the expansion of industrial and urban civilizations due to their strategic geographic advantages. Areas of high ecological suitability are frequently prioritized for urbanization and industrial development—exemplified by the Chang-Zhu-Tan metropolitan area. Consequently, traditional villages confront two simultaneous pressures: extensive land conversion erodes their material and spatial foundations, while the migration of labor and talent to urban economic centers fragments village social structures. This pattern underscores the strong linkage between favorable ecological conditions and rapid socio-economic growth during industrialization and urbanization. Conversely, areas with a lower ecological suitability have retained a more intact traditional settlement pattern due to slower socio-economic development. This situation underscores the dual challenges of “cultural preservation” and “ecological protection”, while illustrating the tension between resource allocation efficiency and the preservation of cultural heritage during contemporary spatial reorganization.
5.2. Divergent Effects of Ecological Environmental Suitability Factors on the Distribution of Traditional Villages
The distribution of traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin is influenced by ecological environmental suitability factors, exhibiting significant spatial heterogeneity. From the lower reaches to the southeastern part of the basin, the dominant factors shift from topography to land cover, reflecting a pattern where “microtopography dominates in flat areas” and “ecological carrying capacity prevails in mountainous regions.” In the plains of the lower Xiangjiang River Basin, the traditional village distribution is primarily shaped by the Relief Degree of Land Surface, indicating that defense and flood control concerns take precedence over livability in these areas. In the southeastern part of the basin, the Water Resource Index has a negative impact, while the Land Cover Index exerts a positive influence. This suggests that ecological security is the primary factor driving the distribution of traditional villages in this region.
The formation and evolution of the spatial pattern of traditional villages reflect both passive adaptation and active adjustment to the geographic environment. The spatial heterogeneity of the ecological environmental suitability factors influencing village distribution illustrates the complexity of the development process. Ecological factors partially constrain village distribution and development: in the rugged mountainous areas of the Xiangjiang River’s upper reaches, villages are typically located in relatively flat river valleys or mountain basins to mitigate the risk of natural disasters. In the northwestern part of the basin, where the Water Resource Index is lower, villages tend to be situated near water sources to facilitate production and life more easily. However, human adaptation is not entirely passive; humans actively adjust to the natural environment by constructing adaptive technological systems based on local knowledge. For instance, in the mountainous regions, villages employ vertical defense strategies to overcome terrain challenges, while in the plains, topographic engineering is used to improve flood control. Thus, the spatial pattern of traditional villages results from the interplay between natural selection and cultural adaptation. The dynamic equilibrium between these forces reflects both the rigid constraints of the geographic environment and the flexible strategies employed by human wisdom to adapt, ultimately shaping the spatial differentiation of traditional villages.
6. Conclusions
Based on the GIS spatial analysis and statistical modeling, this study identifies a moderate spatial correlation between the distribution of traditional villages and ecological environmental suitability. Natural elements, such as hydrological conditions, the RDLS, the LCI, the WRI, and the THI, form the fundamental environmental background for village site selection. However, the global bivariate autocorrelation analysis yields a Moran’s I value of −0.228, indicating the limited explanatory power of ecological suitability alone in accounting for village distribution. This limitation may stem from the omission of socio-economic factors, such as the historical transport network density, clan-based settlement traditions, and local cultural policies—elements that may mediate or moderate human–environment interactions—thereby diminishing the direct influence of ecological variables. Despite this, the study affirms that ecological suitability is a factor in the formation of traditional villages, particularly in areas with complex terrain or resource-dependent communities. The distribution density of traditional villages is positively correlated with the Relief Degree of Land Surface, the Temperature Humidity Index, and the Land Cover Index, but negatively correlated with the Water Resource Index. This indicates that the influence of ecological factors varies significantly across space and demonstrates the intricate relationship between the ecological environment and village growth, as well as the interplay between ecological parameters and village spatial distribution. This paper makes a number of pertinent recommendations in light of these findings.
- (1)
- Accelerate the restoration of traditional villages’ natural ecosystems and develop livable, productive, and beautiful rural environments. The natural ecosystem forms the foundational support for the survival of traditional villages; thus, restoring the ecological environment of these areas is essential. In regions with high WRI values, such as Zixing City and Yanling County, flood-control systems and vegetative buffer zones should be established to improve ecological safety. In areas with a high RDLS, such as Guidong County, landslides can be mitigated through stone masonry slope reinforcement and vegetation anchoring. Meanwhile, villages located in the northern plains can implement micro-topographical modifications to enhance water retention during droughts and floods. Simultaneously, efforts should focus on restoring ecological and cultural landscapes to their original forms as much as possible. Ecological protection can be integrated with the adaptive reuse of cultural heritage by developing heritage-based workshops, eco-lodges, and other specialized industries. This approach fosters a sustainable development cycle that connects landscape restoration, cultural experiences, and community participation.
- (2)
- Inherit the wisdom of adaptive technology and realize the contemporary translation of adaptive technology. The wisdom of site selection and the layout of traditional villages reflects the deep understanding and adaptation of local residents to the natural environment. In villages along the upper reaches of the Xiangjiang River, ancient inhabitants designed their homes based on the landscape’s topography, adjusting the indoor temperature and humidity by strategically orienting buildings and incorporating courtyards. Many traditional villages feature well-designed drainage systems to mitigate flood risks, such as ditches and culverts for rainwater runoff. While it is important to preserve the construction wisdom of the past, modern technologies should also be integrated. For instance, the use of advanced thermal insulation materials for building exteriors, the implementation of rainwater and sewage diversion systems, and the adoption of modern ecological farming techniques can help traditional villages adapt to contemporary development while maintaining their cultural heritage.
- (3)
- Implementing a Zoning and Graded Protection Strategy. In Liuyang City, Zhuzhou City, and other low–high agglomeration areas, where traditional villages are sparsely distributed, priority should be given to preserving their original appearance. Based on a high ecological suitability, these scattered villages should undergo “small-scale, incremental” restoration. Additionally, ecotourism can be promoted to convert ecological value into economic benefit. In low–low agglomeration areas, such as Ningxiang City and Lianyuan City, the revitalization of traditional villages can proceed in parallel with ecological restoration. Measures such as clustered conservation and shared infrastructure should be applied to dispersed settlements. For high–low agglomeration zones with fragile ecological conditions and densely clustered villages, such as Jiangyong County and Daocheng County, strict construction boundaries should be delineated. Dual strategies of terrain-based protection and optimized water conservancy infrastructure should be implemented to mitigate soil erosion risks. In core high-concentration areas like Yongxing County and Hengdong County, a composite model of “cultural heritage revitalization and ecological resilience enhancement” is recommended. Public spaces, such as ancestral halls and study halls in traditional villages, can host traditional skills workshops, while local intangible heritage can be developed into experiential tourism products. Simultaneously, the surrounding agricultural land can be adapted to reduce surface runoff and protect village water systems.
Using geospatial analysis methods, this study preliminarily explores the correlation between natural suitability factors and the spatial distribution of traditional villages in the Xiangjiang River Basin. However, the current analytical framework presents three key scientific limitations:
- (1)
- Theoretical dimension: The existing model primarily emphasizes natural factors, such as topography, climate, and hydrology, while neglecting socio-cultural elements like population, history, and economic activity. As a result, it fails to capture the nonlinear coupling between natural and human systems.
- (2)
- Data reliability: The resolution of spatial data is constrained by the absence of historical datasets. Positioning inaccuracies of traditional village locations may compromise the precision of kernel density estimation, thereby affecting the quantitative analysis of natural factors. Additionally, rapid climate change and land-use transformations in recent decades have disrupted the human–land relationship in traditional villages. However, due to limited access to long-term historical data, the study is unable to quantitatively assess the evolving influence of natural variables on village development.
- (3)
- Temporal dimension: The study concentrates on the current spatial patterns of existing villages but lacks the dynamic tracking of village decline, disappearance, and potential regeneration over time.
Future research should incorporate socio-cultural factors into the analytical framework through multi-source data integration. By applying historical geography-based settlement restoration methods, it is possible to reconstruct the long-term morphological evolution of traditional villages—from site selection to expansion and transformation—at the basin scale. This approach can uncover the interaction mechanisms between natural and human factors across different temporal scales. Moreover, it offers a multi-dimensional analytical paradigm that integrates natural suitability assessment, historical process simulation, and modern driving-force analysis, thereby advancing the study of human–land relationships in the basin and supporting the conservation and sustainable development of traditional villages.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.C. and C.H.; methodology, W.C.; software, W.C.; validation, W.C., J.X. and C.H.; formal analysis, W.C.; investigation, C.H. and W.C.; resources, W.C. and C.H.; data curation, W.C. and L.C.; writing—original draft preparation, W.C. and C.H.; writing—review and editing, C.H., J.X. and W.C.; visualization, W.C.; supervision, C.H. and J.X.; project administration, C.H. and J.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Social Science Foundation Project of Hunan Province (23YBA103), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (2023JJ30043), the Subjects of Hunan Provincial Social Science Achievement Review Committee (XSP24YBC158), the Humanities and Social Science Research Project of Hunan Province (22YBA206), and the Changsha University of Science and Technology graduate student “Practical Innovation and Entrepreneurship Ability Improvement Program” project (CLSJCX24091).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data sources are described in Section 2.2 of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Guiding Opinions on Effectively Strengthening the Protection of Traditional Villages in China. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2016-05/22/content_5075656.htm (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China. Strategic Plan for Rural Revitalization (2018–2022). Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2018-09/26/content_5325534.htm (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- General Office of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Five-Year Action Program for Rural Habitat Improvement and Upgrading (2021–2025). Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2021-12/05/content_5655984.htm (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Li, X.Y.; Xu, W.N.; Liu, L.L.; Ji, J.J. Spatial Analysis of Ecological Sensitivity and Layout Optimization for Traditional Villages around Scenic Area from Landscape-Village Conduction Perspective: A Case Study of Jiuxian Village in Guilin. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2025, 41, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.N.; Li, X.Y.; Peng, P.Y.; Liu, L.R. Mechanism and influencing factors of ecological texture vulnerability in traditional villages around scenic area: A case study of Li River Scenic Area. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2025, 45, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.J.; Gao, Y. Ecosensitivity Evaluation of Traditional Village Cultural Landscape in Guanzhong Based on the Fusion of Multi-Source Data. Mod. Urban Res. 2022, 37, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.R.; Zi, C.X.; Yan, L.; Liu, J.J. Ecological Wisdom and Its Enlightenment in the Spatial Practice of Mountainous Traditional Village: Taking Siping Village, Ningde City as an Example. Mod. Urban Res. 2023, 38, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Huang, S.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Digital Analysis of the Water Layout Ecological Wisdom in Traditional Chinese Rural Settlements: A Case Study of Liukeng Village in Jiangxi Province. J. Resour. Ecol. 2022, 13, 371–381. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.W.; Zeng, W.; Feng, D.Y.; Fu, Y.S. Ecological wisdom for the site selection and layout of traditional villages in southwest China. J. Hum. Settl. West Chin. 2024, 39, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Cui, J.Y. Space and Landscape Evolution Mechanism and Resource Governance Characteristics of Traditional Villages from the Perspective of Social-Ecological System. Landsc. Archit. 2024, 31, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, F. Ecological Landscape Design of Traditional Villages in the Context of Rural Revitalization Strategy. Build. Sci. 2023, 39, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.K. Analysis of Ecological Landscape Design Strategies for Traditional Villages in the Context of Rural Revitalization. Earthq. Resist. Eng. Retrofit. 2025, 47, 203–204. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.B.; Mao, X.H.; Yin, C.J. Research on the Conservation Performance of Tourism Based Traditional Villages from the Perspective of Rural Governance Community. J. Nat. Sci. Hunan Norm. Univ. 2025, 48, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.Y.; Xie, H.Z.; Zhu, T. The Influence of High-quality Rural Sanitation on Improving the Competitiveness of Traditional Village Ecotourism—Taking Toilet Improvement in Yunnan Province, China as an Example. J. Resour. Ecol. 2024, 15, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.J.; Meng, Y.; Yang, D.H.; Yuan, Y.Z. Study on Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Traditional Villages in Hainan Island. Areal Res. Dev. 2025, 44, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, J.W.; Deng, L.L.; Luo, J.; Tian, Y. Characteristics of multi-scale spatiotemporal pattern and influencing factors of Chinese traditional villages. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 32, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Q.; Peng, S.T.; Zhao, C.W.; Du, A. Analysis of spatial distribution characteristics and influence factors of traditional villages in Southwest China. J. Guizhou Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2025, 66, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, B.Y.; Yue, S.J. Micro-scale Analysis of the Evolution of Land Use and Spatial Structure of Tourism-oriented Traditional Villages: Taking Yuanjia Village in Liquan County of Shaanxi Province as Example. Areal Res. Dev. 2024, 43, 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.R.; Liu, S.J. Spatio-temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Traditional Villages in Jiangxi from a Multidimensional Perspective. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2024, 24, 12296–12307. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.K.; Meng, S.Y.; Xiong, Y.M.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.L. Optimizing public space structure of traditional villages coupling SNA and spatial syntax. Trans. CSAE 2024, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wang, D. Research on the Optimization Design of Traditional Village Architecture Style Based on the Concept of Co-creation: Taking Jitang Dong Village in Guizhou Province as an Example. Des. Res. 2023, 13, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Li, Z.Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, L.Y. Cultural Heritage Conservation from the Perspective of River Basin. Herit. Archit. 2024, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The People’s Government of Hunan Province. Red Line for Ecological Protection in Hunan Province. Available online: http://www.hunan.gov.cn/xxgk/wjk/szfwj/201807/t20180725_5060881.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Li, K.; Mao, D.H.; Li, J.; Jiang, Z.L. On the Evolution of Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Production-Living-Ecological Space in Xiangjiang River Basin. J. Nat. Sci. Hunan Norm. Univ. 2020, 43, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hu, H.Q. Assessment of ecological compensation standards in Hunan Xiangjiang River Basin based on ecosystem service value. Express Water Resour. Hydropower Inf. 2025, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- LI, B.H.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.L.; Dou, Y.D. Landscape gene variation and differentiation law of traditional villages in Xiangjiang River Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.X.; Hu, T.; Li, C.M.; Yang, F.L.; Zhou, K.C. Study on the Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Rural Settlements in the Xiangjiang River Basin. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 31, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.C.; Liu, P.L.; Li, B.H.; Qi, J.Q.; Hu, Z.; Deng, Y.Y. Map of traditional settlement landscape morphology gene: A case study of the Xiangjiang River Basin. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2023, 43, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P. Integration and Development of Xiangjiang River Basin Ecosystem and Xiangjiang River Battle Historical Resources—A Review of the Study on the Green Development of Xiangjiang River Basin. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2021, 42, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.M.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.Z.; Zhang, D. Establishment and Application of Human Settlements Environment Index Model (HEI) Based on GIS. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2008, 63, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.M.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.Z.; Zhang, D. Relief degree of land surface and its influence on population distribution in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 28, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.X.; Li, J.; Ren, Z.Y. The Relief Degree of Land Surface and Population Distribution in Guanzhong-Tianshui Economic Region Using GIS. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 32, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.N.; Su, W.C.; Li, Q.; Pan, Z.Z. Application of GIS and RS technologies to the evaluation of natural suitability of human habitation in Qiannan karst area. Carsol. Sin. 2016, 35, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhao, W.Q.; Su, W.C. Nature Suitability Evaluation of Human Settlement Environment Based on GIS Technique in Central Guizhou Province. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2018, 27, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.W.; Zhen, J.H. Comprehensive Suitability Evaluation and Spatial Optimization of Human Settlements Environment in Inner Mongolia. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 24, 1204–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Shi, P.J.; Feng, H.C.; Wang, X.F. Environmental suitability evaluation for human settlements in an arid inland river basin: A case study of the Shiyang River Basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 27, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.H.; Wang, D.Q. Ecological Risk Assessment of Rural Landscape of Southern Jiangsu Water Net from the Perspective of “Ecology-Production-Living” Space—A Case Study of Stone Pool Area. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2024, 39, 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; Yang, L.; Feng, C.; Sun, R.S.; Liu, C.; Lyu, L. Flood Risk Assessment in Midstream Xiangjiang River Basin and Its Driving Force Analysis. Pearl River 2025, 46, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Ouyang, Z. Relationship between land surface temperature and spatial pattern of greenspace: What are the effects of spatial resolution? Landsc. Urban Plann. 2013, 114, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J.; Hirabayashi, S.; Bodine, A.; Hoehn, R. Modeled PM2.5 removal by trees in ten U.S. cities and associated health effects. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.C.; Zhang, G.J.; Wei, X.Y.; Ma, W.T.; Cheng, J.H. Coupling Relationship Between Soil Erosion Risk and Natural Suitability of Human Settlements in Guyuan City, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 43, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.Y.; Li, X.M.; Yang, J.; Li, S.B.; Tian, S.Z. Comprehensive Suitability Evaluation of Urban Human SettlementsBased on GWR: A Case Study of Liaoning Province. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 42, 2097–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. The People’s Republic of China Environmental Protection Industry Standard: Technical Specification for the Evaluation of Ecological Environmental Conditions. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/stzl/201503/t20150324_298011.shtml (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Zhang, X.Y.; Hou, G.L.; Xu, C.J.; Jin, S.M.; Chen, H.M. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of the Liangzhu Culture settlement and its relationship with environmental changes. J. Earth Environ. 2024, 15, 277–289+325. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Zhen, S.Y.; Zuo, X.M.; Hu, X.S.; Shen, R.F. Vegetation restoration dynamics and its response to road network in southern Fujian. Chin. Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.R.; Xu, X.R.; Wang, L.; Duan, J.; Shi, S.Q.; Ren, D.D. Spatial-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of agricultural carbon emissions in the Yellow River Basin. Arid Land Geogr. 2025, 48, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.S. Talking About the Xiangjiang River. Available online: https://m.voc.com.cn/xhn/news/202408/20585857.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Wu, Y.J.; Huang, C.H. Analysis on the Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Traditional Villages under the Huxiang Culture. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2022, 22, 2863–2871. [Google Scholar]
- Ozili, P. The Acceptable R-Square in Empirical Modelling for Social Science Research. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ji, H. The City Elevation Enlightenment of Chenzhou in Qing Dynasty. Huazhong Archit. 2015, 33, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).