A Comprehensive Review of the Invasive Species Phytolacca acinosa Roxb.
Abstract
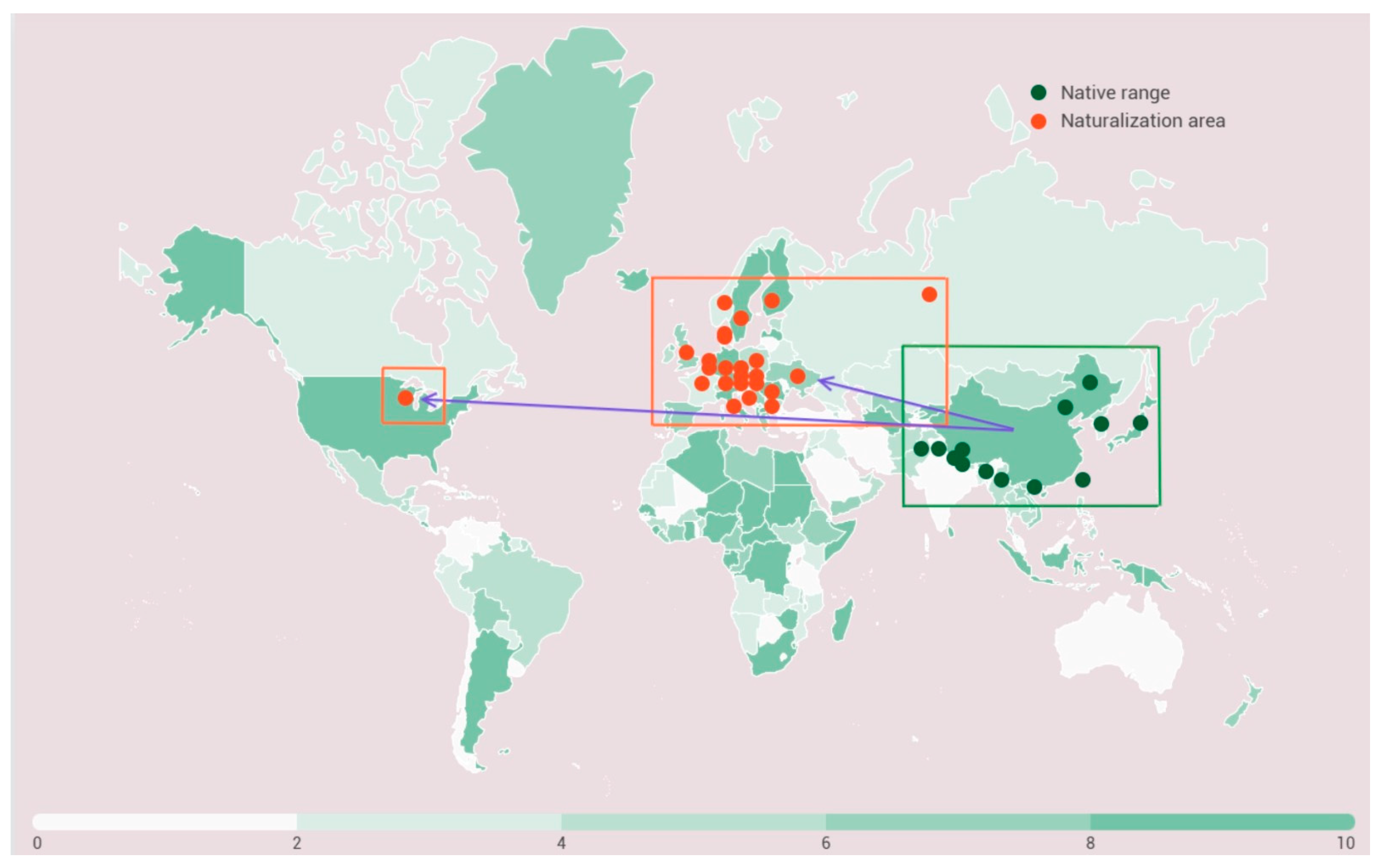
1. Introduction
2. Methodological Insights
3. Taxonomy
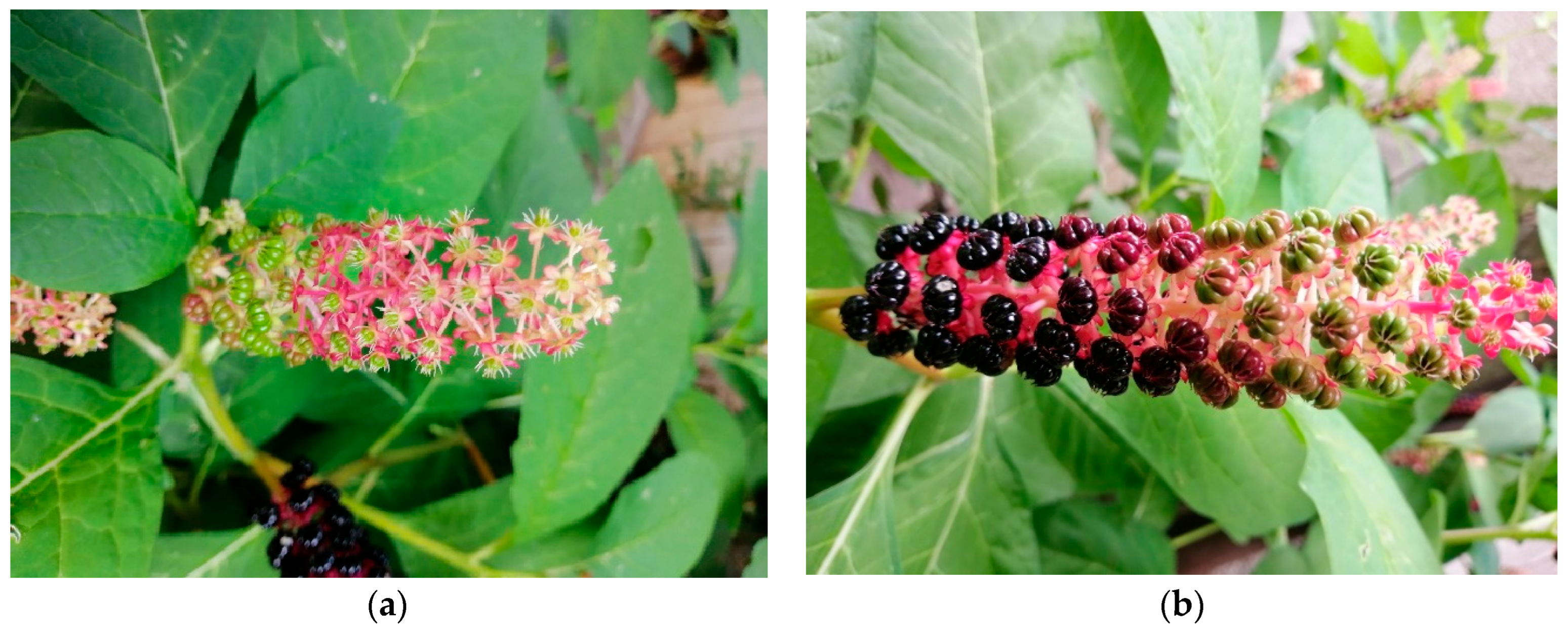
4. Biology
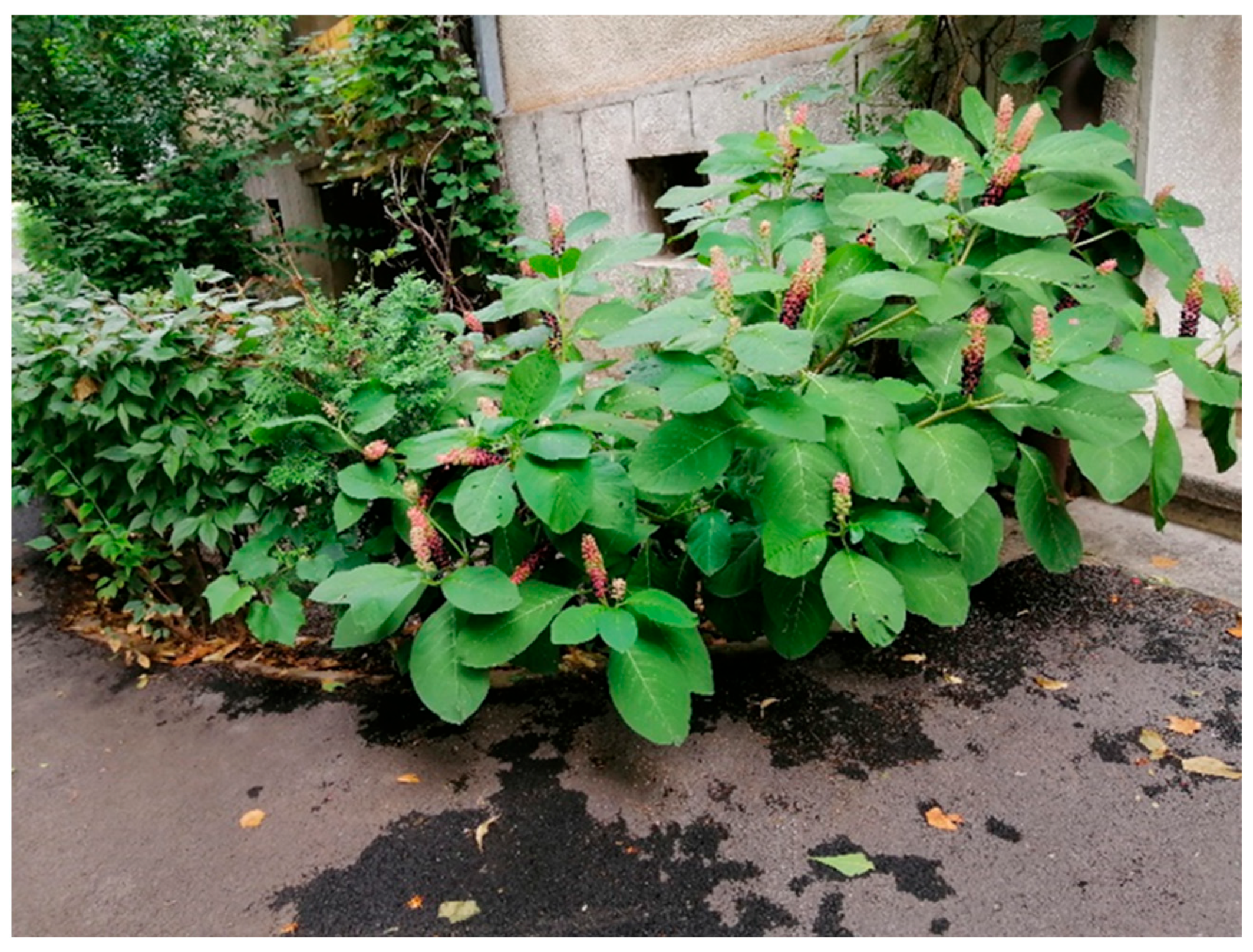
5. Ecological Features and Characteristic Habitats
6. Phytochemistry and Medicinal Properties
6.1. Ethnomedicinal Uses
6.2. Phytochemicals and Pharmacological Effects
7. Phytoremediation
8. Other Properties
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Misra, S.; Maikhuri, R.K.; Kala, C.P.; Rao, K.S.; Saxena, K.G. Wild leafy vegetables: A study of their subsistence dietetic support to the inhabitants of Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, India. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2008, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckerle, C.S.; Inechein, R.; Huber, F.K.; Yang, Y. Mao’s heritage: Medicinal plant knowledge among the Bai in Shaxi, China, at a crossroads between distinct local and common wide spread practice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, M.S.; Khoja, A.A.; Waheed, M.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Alamri, S.; Alfagham, A.T.; Al-Humaid, L.A.; Bussmann, R.W. Food ethnobotany of forest resource in the high-altitude Himalaya Mountains: Enhancing the food sovereignty of ethnic groups. For. Policy Econ. 2024, 164, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abekura, F.; Park, J.; Kwak, C.-H.; Ha, S.-H.; Cho, S.-H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Ha, K.-T.; Chang, H.-W.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chung, T.-W.; et al. Esculentoside B inhibits inflammatory response through JNK and downstream NF-κB signaling pathway in LPS-triggered murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 68, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash Radha, S.; Sharma, N.; Kumar, A.; Kumari, N.; Puri, S.; Pundir, A.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.K.; Rais, N.; Dey, A.; et al. A survey on ethnoveterinary medicines used by the tribal migratory shepherds of Northwestern Himalaya. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 296, 115467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.-G.; Cai-Rang, X.-D.; Tan, X.-Y.; Li, C.-Y.; Zeng, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Processing methods and the underlying detoxification mechanisms for toxic medicinal materials used by ethnic minorities in China: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 305, 116126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.S.; Waheed, M.; Khoja, A.A.; Amjad, M.S.; Bussman, R.W.; Ali, K. A cross-cultural study of high-altitude botanical resources among diverse ethnic groups in Kashmir Himalaya, India. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2023, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Ju, D.W.; Fang, J. Effects of Phytolacca acinosa polysaccharide on splenic lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine secretion from splenic lymphocyte and macrophage. Acta Pharm. Sin. 1993, 28, 732–737. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.B.; Zheng, Q.Y. Effects of Phytolacca acinosa polysaccharides I with different schedules on its antitumor efficiency in tumor bearing mice and production of IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, TNF, CSF activity in normal mice. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 1997, 19, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Jiang, E.; Cai, B. Development of an ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry method for comparative pharmacokinetics of six triterpenoids in rat plasma and application to different forms of Phytolacca acinosa. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasemi, S.V.; Khazaei, H.; Morovati, M.R.; Joshi, T.; Aneva, I.Y.; Farzaei, H.M.; Echeverría, J. Phytochemicals as treatment for allergic asthma: Therapeutic effects and mechanisms of action. Phytomedicine 2024, 122, 155149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.G.; Chen, Y.X.; Reeves, R.D.; Baker, A.J.; Lin, Q.; Fernando, D.R. Manganese uptake and accumulation by the hyperaccumulator plant Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. (Phytolaccaceae). Environ. Pollut. 2004, 131, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Huang, H.; Gupta, D.K. Uptake and accumulation of phosphorus by dominant plant species growing in a phosphorus mining area. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Luo, S.; Chen, J.; Wan, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, F. A comparative analysis of endophytic bacterial communities associated with hyperaccumulators growing in mine soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7538–7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Fu, H.; Chen, G.; Feng, T.; Chen, Z. Preparation of magnetic hydrochar derived from iron-rich Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. for Cd removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- POWO—Plants of the World Online. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/ (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Starodubtseva, E.A. Contribution to the floras of Lipetsk and Voronezh Regions (new vascular plant records from Usmansky pine forest). Turczaninowia 2021, 24, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidov, N.T.; Leostrin, A.V. Additions to the flora of Northwestern European Russia. Botanicheskii Zhurnal 2024, 109, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosyakin, S.L.; Mosyakin, A.S. Lockdown botany 2020: Some noteworthy records of alien plants in Kyiv City and Kyiv Region. Ukr. Bot. J. 2021, 78, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shynder, O.I.; Kolomiychuk, V.P.; Melezhyk, O.V. Spontaneous flora of O.V. Fomin Botanical Garden of Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Ukraine. Environ. Socio-Econ. Stud. 2022, 10, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martan, V.B.; Šoštarić, R. Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. (Phytolaccaceae), a new alien species in the Croatian flora. Acta Bot. Croat. 2016, 75, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strgulc Krajšek, S.; Kladnik, A.; Skočir, S.; Bačič, M. Seed germination of invasive Phytolacca americana and potentially invasive P. acinosa. Plants 2023, 12, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essl, F.; Rabitsch, W. Neobiota in Österreich; Umweltbundesamt: Vienna, Austria, 2002; pp. 1–432. [Google Scholar]
- Csiky, J.; Balogh, L.; Dancza, I.; Gyulai, F.; Jakab, G.; Király, G.; Lehoczky, É.; Mesterházy, A.; Pósa, P.; Wirth, T. Checklist of alien vascular plants of Hungary and their invasion biological characteristics. Acta Bot. Hung. 2023, 65, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrzykiewicz-Raszewska, M. Phytolacca acinosa Roxb.—A new anthropophyte in the flora of Poland. Bot. Steciana 2009, 13, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sîrbu, C.; Oprea, A. Plante Adventive în Flora Românei; Ion Ionescu de la Brad Publishing House: Iaşi, Romania, 2011; pp. 1–724. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasiu, P. Raport Privind Conținutul Bazei de Date GIS cu Distribuția Speciilor de Plante Alogene din România și Metode de Actualizare; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission—Joint Research Centre—European Alien Species Information Network (EASIN). Available online: https://easin.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- Euro+Med PlantBase. Available online: http://www.europlusmed.org/ (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Botta-Dukát, Z.; Balogh, L. The Most Invasive Plants in Hungary; Institute of Ecology and Botany, Hungarian Academy of Sciences: Vácrátót, Hungary, 2008; pp. 1–255. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.C.; Lu, A.M.; Hu, Z.H. Floral organogenesis and ring meristem in Phytolacca. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Kai, L. PHYTOLACCACEAE. Available online: http://flora.huh.harvard.edu/china/mss/volume05/Phytolaccaceae.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Decraene, L.P.R.; Vanvinckenroye, P.; Smets, E.F. A study of floral morphological diversity in Phytolacca (Phytolaccaceae) based on early floral ontogeny. Int. J. Plant Sci. 1997, 158, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhang, L. Solirubrobacter phytolaccae sp. nov., an endophytic bacterium isolated from roots of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, L.; Si, M.; Li, C.; Zhao, L.; Wei, Y.; Shen, X. Solirubrobacter taibaiensis sp. nov., isolated from a stem of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. Anton. Leeuw. Int. J. Microbiol. 2014, 106, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magray, J.A.; Wani, B.A.; Islam, T.; Javid, H.; Ganie, A.H.; Qadir, R.U.; Nawchoo, I.A. From sprouting to senescence: Phenological chronicles of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. in the Himalayan Highlands. Res. Sq. 2024, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sîrbu, I.; Ştefan, N.; Oprea, A. Plante Vasculare din România. Determinator Ilustrat de Teren; Victor B Victor Publishing House: Bucharest, Romania, 2013; pp. 1–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Durka, W. Blüten- und Reproduktionsbiologie. In BIOLFLOR—Eine Datenbank mit Biologisch-Ökologischen Merkmalen zur Flora von Deutschland. Schriftenreihe für Vegetationskunde; Klotz, S., Kühn, I., Durka, W., Eds.; Umweltforschungszentrum Leipzig-Halle GmbH: Halle, Germany, 2002; Volume 38, pp. 133–175. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, L.-J.; Wang, X.-F. The unusual gynoecium structure and extragynoecial pollen-tube pathway in Phytolacca (Phytolaccaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 2018, 304, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sádlo, J.; Chytrý, M.; Pergl, J.; Pyšek, P. Plant dispersal strategies: A new classification based on themultiple dispersal modes of individual species. Preslia 2018, 90, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.C.; Bahukhandi, A.; Dhyani, V.; Parihar, N.; Pandey, V.; Bhatt, I.D. Comparative assessment of morphological, physiological attributes of two high value medicinal herbs of Himalaya under different growth conditions. Vegetos 2024. [CrossRef]
- Krishan, R.; Sharma, R.K.; Sharma, S.S. Assessment of seed biology of the Himalayan medicinal herb Phytolacca acinosa Roxb., the Indian pokeweed, from the perspective of longevity, conservation and propagation. Nucleus 2022, 65, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, M.; Ju, R.; Li, B.; Wang, Y. Rapid seedling emergence of invasive Phytolacca americana is related to higher soluble sugars produced by starch metabolism and photosynthesis compared to native P. acinosa. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1255698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magray, J.A.; Wani, B.A.; Javid, H.; Islam, T.; Ganie, A.H.; Qadir, R.U.; Nawchoo, I.A. Vegetative propagation of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. by rhizome cuttings: A step towards conservation and cultivation approach. Front. Conserv. Sci. 2024, 5, 1386204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chytrý, M.; Tichý, L.; Dřevojan, P.; Sádlo, J.; Zelený, D. Ellenberg-type indicator values for the Czech flora. Preslia 2018, 90, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, L.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. Effect of plant VOCs and light intensity on growth and reproduction performance of an invasive and a native Phytolacca species in China. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magray, J.A.; Wani, B.A.; Islam, T.; Ganie, A.H.; Nawchoo, I.A. Phyto-ecological analysis of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. assemblages in Kashmir Himalaya, India. Front. For. Glob. Change 2022, 5, 976902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, J.; Manish, K.; Nautiyal, D.C.; Lakhanpaul, S.; Pandit, M.K. Changes in vegetation composition and structure following landslide-induced disturbance in the Himalaya. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2024, 17, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.Z.; Pant, S.; Bhat, J.A.; Shukla, G. Distribution and survival of medicinal and aromatic plants is threatened by the anticipated climate change. Trees For. People 2024, 16, 100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- eFloras.org. Available online: http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200007011 (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Anastasiu, P.; Gavrilidis, A.A.; Miu, V.I.; Niculae, M.I.; Sîrbu, I.M. Raport Final Privind Distribuția Speciilor de Plante Alogene din Hot-spot-uri și Căile Prioritare de Pătrundere; Ministerul Mediului, Apelor și Pădurilor & Universitatea din București: Bucharest, Romania, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiu, P.; Preda, C.; Rozylowicz, L.; Sîrbu, I.M.; Manta, N. Lista Speciilor Alogene de Interes Pentru România; Ministerul Mediului, Apelor şi Pădurilor&Universitatea din Bucureşti: Bucharest, Romania, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiu, P.; Gavrilidis, A.A.; Miu, V.I.; Niculae, M.I.; Sîrbu, I.M. Raport Final Privind Distribuția Speciilor de Plante Alogene Rezultată din Activitatea de Inventariere cu efort redus (an 3 cartare); Ministerul Mediului, Apelor şi Pădurilor&Universitatea din Bucureşti: Bucharest, Romania, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenberg, R.; Kenis, M.; Blick, T.; Hänggi, A.; Gassmann, A.; Weber, E. An Inventory of Alien Species and their Threat to Biodiversity and Economy in Switzerland; CABI Bioscience Switzerland Centre: Delémont, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 1–416. [Google Scholar]
- DiTomaso, J.M.; Kyser, G.B.; Oneto, S.R.; Wilson, R.G.; Orloff, S.B.; Anderson, L.W.; Wright, S.D.; Roncoroni, J.A.; Miller, T.L.; Prather, T.S.; et al. Weed Control in Natural Areas in the Western United States; Weed Research and Information Center, University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–544. Available online: https://wric.ucdavis.edu/information/natural%20areas/wr_P/Phytolacca.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Li, N.; Ma, Z.; Li, M.; Xing, Y.; Hou, Y. Natural potential therapeutic agents of neurodegenerative diseases from the traditional herbal medicine Chinese dragon’s blood. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.P.; Zhang, W.F.; Yi, P.; Lan, J.J.; Xia, B.; Jiang, S.; Lou, H.Y.; Pan, W.D. Novel flavones from the root of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. Chem. Biodiversity 2017, 14, e1700361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, D.N.; Munjal, R.C.; Singh, A.K. Phytochemical investigations of the fruits of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. Planta Medica 1977, 32, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, M.; Mir, T.A.; Jan, H.A.; Bussmann, R.W.; Aneaus, S. Ethnomedicinal study of plants utilized in pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum healthcare in Kashmir Himalaya. J. Herb. Med. 2023, 42, 100767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, T.A.; Jan, M.; Khare, R.K. Ethnomedicinal application of plants in Doodhganga forest range of district Budgam, Jammu and Kashmir, India. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 46, 101366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.K. Traditional phytotherapy among the sherpas of Helambu, Central Nepal. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1989, 27, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganie, H.A.; Tali, A.B.; Khuroo, A.A.; Reshi, A.Z.; Nawchoo, I.A. Impact assessment of anthropogenic threats to high-valued medicinal plants of Kashmir Himalaya, India. J. Nat. Conserv. 2019, 50, 125715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.; Bhatt, A.; Lal, B. Ethnobotanical knowledge among the semi-pastoral Gujjar tribe in the high altitude (Adhwari’s) of Churah subdivision, district Chamba, Western Himalaya. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2019, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.Y.; Xie, J.-X.; But, P.P.-H. Fertility regulating agents from traditional chinese medicines. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1986, 15, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelzer, G.; Gurib-Fakim, A. Plant Resources of Tropical Africa 11(1): Medicinal Plants 1. PROTA Foundation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 1–790. [Google Scholar]
- Ogutu, A.I.; Lilechi, D.B.; Mutai, C.; Bii, C. Phytochemical analysis and antimicrobial activity of Phytolacca dodecandra, Cucumis aculeatus and Erythrina excelsa. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2012, 6, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, C. Medicinal properties and anti-inflammatory components of Phytolacca (Shanglu). Digit. Chin. Med. 2021, 4, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, C.; Vergoten, G. Esculentosides: Insights into the potential health benefits, mechanisms of action and molecular targets. Phytomedicine 2020, 79, 153343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Liu, C.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Liu, N.; Zhang, D.; Han, S.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Yuan, R.; et al. Integrating non-targeted metabolomics and toxicology networks to study the mechanism of Esculentoside A-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinaş, I.C.; Oprea, E.; Geană, E.I.; Luntraru, C.M.; Gîrd, C.E.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of Phytolacca americana L. fruits and leaves extracts. Farmacia 2021, 69, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, A.; Gattuso, M.; Pérez, P.; Zacchino, S. Evidence for the mechanism of action of the antifungal phytolaccoside B isolated from Phytolacca tetramera Hauman. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, Z.; Mazhar, H.; Muhammad, A. Carotenoid and phenolic profiles and antioxidant and anticholinesterase activities of leaves and berries of Phytolacca acinosa. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.M.; Liu, J.X.; Wang, Z.M.; Wang, W.H. Phytolacacinoside A, a new triterpenoid saponin from Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 11, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Jiang, L.; Wei, J.; Qiao, A.; Wei, M.; Soromou, L.-W.; Xie, X.; Zhou, X.; Ci, X.; Wang, D. Protective effect of esculentoside A on lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 185, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; He, Y.; Liao, Y. Esculentoside A ameliorates DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis by suppressing the ROS-NLRP3 axis via activating the Nrf2 pathway. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2023, 50, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Sheng, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, J.; Wei, S.; Tang, L. Study on pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. and its mechanism. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 2022, 38, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Liang, S.; Fang, H.; Cao, J. Esculentoside A alleviates intestinal dysmotility in ulcerative colitis by regulating H2S/CSE and NO/nNOS systems. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, 7757833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Xue, S.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, H.; Sang, W.; Wang, C.; Xue, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ma, J. Esculentoside A protects against osteoarthritis by ameliorating inflammation and repressing osteoclastogenesis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 82, 106376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, S.; Razdan, T.K.; Andotra, C.S. Acinospesigenin-A, -B, and -C: Three new triterpenoids from Phytolacca acinosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1121–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, T.; Mendel, J.T.; Lavezo, J.L. Structural analysis of a type 1 ribosome inactivating protein reveals multiple L-asparagine-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine monosaccharide modifications: Implications for cytotoxicity. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 5737–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.P.; Qian, D.H. Antitumor activity and tumor necrosis factor production of Phytolacca acinosa polysaccharides I in mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 1993, 14, 542–545. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.B.; Chen, W.Z.; Bao, E.J.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Song, H.L.; Fang, J.; Xu, Y.X.; Chen, H.S. Effects of Phytolacca acinosa polysaccharides I combined with interleukin-2 on the cytotoxicity of murine splenocytes against tumor cells. Acta Pharm. Sin. 1995, 30, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.B.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Chen, H.S. Effect of Phytolacca acinosa polysaccharides I on production of colony-stimulating factors of mouse splenocytes in vitro. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 1993, 14, S30–S33. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.B.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Qian, D.H.; Fang, J.; Ju, D.W. Effects of Phytolacca acinosa polysaccharides I on immune function in mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 1993, 14, 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, P.; He, T.; Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Lin, P.; Hou, J.; Sun, H.; Ma, H. Mechanistic insights into xanthomicrol as the active anti-HCC ingredient of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb.: A network pharmacology analysis and transcriptomics integrated experimental verification. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 333, 118467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Qian, D.H.; Zheng, Q.Y. Effects of Phytolacca acinosa polysaccharides I on cytotoxicity of macrophages and its production of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 1990, 11, 375–377. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.C.; Chen, D.; Wu, X.Z.; Xie, G.R.; Ba, Y.; Yan, Z. Effects of aqueous extracts of Aconitum carmichaeli, Rhizoma bolbostemmatis, Phytolacca acinosa, Panax notoginseng and Gekko swinhonis Gūenther on Bel-7402 cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2743–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.L.; Ma, F.; Wu, X.Z. Anticancer effects of 5-fluorouracil combined with warming and relieving cold phlegm formula on human breast cancer. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2012, 18, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleri, F.D.; Chen, G.; Li, X.; Guo, M. Comparative analysis of saponins from different Phytolaccaceae species and their antiproliferative activities. Molecules 2017, 22, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debela, A.S.; Dawit, M.; Tekere, M.; Itanna, F. Phytoremediation of soils contaminated by lead and cadmium in Ethiopia, using Endod (Phytolacca dodecandra L.). Int. J. Phytorem. 2022, 24, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Yang, F.; Hu, L.; Ji, H.; Shao, J.F. Efficient cadmium uptake and accumulation in pokeweed (Phytolacca americana L.) associated with its potential for phytoremediation of cadmium-polluted soils. Plant Soil 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosjean, N.; Le Jean, M.; Berthelot, C.; Chalot, M.; Gross, E.M.; Blaudez, D. Accumulation and fractionation of rare earth elements are conserved traits in the Phytolacca genus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xu, S.; Lei, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, K.; Shi, X.; Guo, Y.; Bilyera, N.; Yuan, M.; Yao, H. Hyperaccumulator extracts promoting the phytoremediation of rare earth elements (REEs) by Phytolacca americana: Role of active microbial community in rhizosphere hotspots. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkenhaug, G.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Luo, L.; Lei, M.; Li, X.; Mulder, J. Distribution, speciation and availability of antimony (Sb) in soils and terrestrial plants from an active Sb mining area. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.-Y.; Zhao, L.L.; Zheng, C.-J.; Zhu, J.-W. Characteristics of the hyperaccumulator plant Phytolacca acinosa (Phytolaccaceae) in response to excess manganese. J. Plant Nutr. 2013, 36, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tang, K.; Xu, X.; Cai, C. Interaction of Fe-Mn plaque and Arthrobacter echigonensis MN1405 and uptake and translocation of Cd by Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Liu, J.; Long, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sunahara, G.I.; Jiang, P.; You, S.; Lin, H.; Xiao, H. Phytoextraction of cadmium-contaminated soils: Comparison of plant species and low molecular weight organic acids. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2019, 22, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Dong, M.; Mao, P.; Zhuang, P.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Netherway, P.; Li, Z. Evaluation of phytoremediation potential of five Cd (hyper)accumulators in two Cd contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, Z.H. Heavy metal uptake by bryophytes and vascular plants in a manganese carbonate slag field, China. Plant Biol. 2022, 24, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, S.; Pandey, D.K.; Singh, D. Assessment of potentially toxic elements in some wild edible plants of district Doda, Jammu and Kashmir, India. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 267, 107604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, F.; Bao, Q.; Wei, X.; Tie, B.; Zhang, S.; Han, N.; Huang, Y. Effects of chelating agents and organic acids on remediation of cadmium and arsenic complex contaminated farmland by Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 1936–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ai, P.; Yang, Y.-X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Effect of chelating agent on remediation of Cd and Cu contaminated soil by Phytolacca. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2019, 41, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.H.; Shi, J.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Xue, S.G.; Wu, B.; Huang, Y.Y. An investigation of cellular distribution of manganese in hyperaccumlator plant Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. using SRXRF analysis. J. Environ. Sci.-China 2006, 18, 746–751. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Lin, H.; Li, B.; Dong, Y.; Yin, T.; Chen, X. Endophyte inoculation redistributed bioavailable Cd and nutrient in soil aggregates and enhanced Cd accumulation in Phytolacca acinose. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, B.; Dong, Y.; Lin, H. Endophyte colonization enhanced cadmium phytoremediation by improving endosphere and rhizosphere microecology characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, B. Increase of P and Cd bioavailability in the rhizosphere by endophytes promoted phytoremediation efficiency of Phytolacca acinosa. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, B.; Dong, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, C. Endophyte inoculation enhanced microbial metabolic function in the rhizosphere benefiting cadmium phytoremediation by Phytolacca acinosa. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Xu, T.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Rao, C.; Xiao, X.; Wan, Y.; Zeng, G.; Long, F.; Liu, C.; et al. Endophyte-assisted promotion of biomass production and metal-uptake of energy crop sweet sorghum by plant-growth-promoting endophyte Bacillus sp. SLS18. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.; Ok, Y.S.; Shen, C.; Xue, S. Biochar provides a safe and value-added solution for hyperaccumulating plant disposal: A case study of Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. (Phytolaccaceae). Chemosphere 2017, 178, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, M.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; et al. Highly efficient activation of periodate by a manganese-modified biochar to rapidly degrade methylene blue. Environ. Res. 2024, 241, 117657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, W.; Jin, Q.; Lin, H. Insights into vanadium removal performance and mechanism in aqueous solution by one-step pyrolysis prepared Phytolacca acinosa biochar composite. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 411, 125752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, P.; Sui, S.Y.; Dong, C.H.; Zhang, L. Research on the dyeing behavior of wool fabric with natural Phytolacca berry dyes. Wool Text. J. 2014, 42, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Song, J.; Xu, F.; Yun, D.; Li, C.; Liu, J. Characterization and application of guar gum/polyvinyl alcohol-based food packaging films containing betacyanins from pokeweed (Phytolacca acinosa Roxb.) berries and silver nanoparticles. Molecules 2023, 28, 6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, D.; Parashar, B.D.; Rao, K.M. Evaluation of some plant molluscicides against a freshwater snail Lymnaea luteola, the vector of animal schistosomiasis. Pharm. Biol. 2002, 40, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Extraction of Phytolacca acinosa and its mulloscacidal effects. J. Tongji Med. Univ. 1998, 18, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.-Z.; Chen, J.; Du, X.; Han, B. Screening of molluscicidal strain against Oncomelania hupensis from the rhizosphere of medicinal plant Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2010, 6, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.-Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Yao, H.; Han, F.A.; Pan, J. A high-performance molluscicidal ingredient against Oncomelania hupensis produced by a rhizospheric strain from Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2011, 7, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.-Z.; Chen, J. Biological safety of the molluscicidal ingredient from Aspergillus fumigatus SL-30 isolated from rhizosphere of Phytolacca acinosa. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2012, 30, 460–463. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.; Zhao, C.; Li, Z.; Fan, Q.; Chen, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ning, H.; Lin, R.; Li, J. Combined metabolomics and network toxicology to explore the molecular mechanism of Phytolacca acinose Roxb-induced hepatotoxicity in zebrafish larvae in vivo. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 3303014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkhurst, R.M.; Mthupha, B.M.; Liang, Y.-S.; Bruce, J.I.; Lambert, J.D.H.; Collier, T.L.; ApSimo, J.W.; Wolde-Yohannes, L.; Heath, G.E.; Jones, W.O.; et al. The molluscicidal activity of Phytolacca dodecandra I. Location of the activating esterase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 158, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.-W.; Chen, J.; Han, B.-X.; Li, C.-G.; Yang, X.-J.; Zhang, C.-X.; Yao, H. Molluscicidal effect of Phytolacca americana Linn leaf against Oncomelania hupensis and its acute toxicity. Chin. J. Schisto. Control 2011, 23, 449–452. [Google Scholar]
- Obare, B.A.; Yole, D.; Nonoh, J.; Lwande, W. Molluscicidal activity of selected plant extracts against adult and juvenile Biomphalaria pfeifferi. J. Biol. Agric. Healthc. 2016, 6, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Luo, H.; Zhong, Z.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y. The safety of Chinese medicine: A systematic review of endogenous substances and exogenous residues. Phytomedicine 2023, 108, 154534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Q.; Ren, Z.; Xiao, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q. Metabolic exploration of the developmental abnormalities and neurotoxicity of esculenttoside B, the main toxic factor in Phytolaccae radix. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 176, 113777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Wang, J.; Qian, S.; Tu, X.; Lin, G.; Wen, C.; Wang, Y. Radix phytolaccae on tissue metabolomics in rats by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 11977–11983. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, H.W.; Feng, Z.; Li, W.W.; Cheung, W.K.; Ng, T.B. Abortifacient activity in leaves, roots and seeds of Phytolacca acinosa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1987, 21, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, W.; Xu, X.; Ran, M.; Jin, Y.; Sun, X. MAP30 and luffin-α: Novel ribosome-inactivating proteins induce plant systemic resistance against plant viruses. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 191, 105342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouze, H.; El-Dougdoug, K.; Othman, B.; Gomaa, M. Molecular markers in potato cultivars treated with ribosome-inactivating proteins. Pest Technol. 2012, 6, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, K.; Jiao, Z.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Guo, Y. Overwintering hosts of Apolygus lucorum (Hemiptera: Miridae) in Northern China. Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Li, G.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Wu, K. Comparative overwintering host range of three Adelphocoris species (Hemiptera: Miridae) in Northern China. Crop Prot. 2011, 30, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dou, B.; Chen, Z.; Cao, X.; Yaun, X. Detection of potential transitional hosts and insect vectors of cherry viruses. J. Plant Prot. 2020, 47, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Bioactive Compounds | Part Plant | Pharmacological Activities | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| esculentoside A | root | anti-inflammatory, antitumoral, antioxidative, diuretic | [4,10,11,67,73,74,75,76,77,78] |
| esculentoside B | root | anti-inflammatory | [4,10,67] |
| esculentoside H | root | anti-inflammatory, antitumoral, antioxidative | [10,67] |
| esculentoside T | root | anti-inflammatory | [10] |
| phytolaccagenic acid | root | antifungal | [10] |
| carotenoids | leaf, berry | antioxidative, antichollinesterase | [72] |
| acinospesigenin-A, -B, and -C | berry | anti-inflammatory | [79] |
| pokeweed antiviral protein (PAP) | not mentioned | antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antitumoral | [80] |
| polysaccharides (PAP-I) | root | antitumoral, immunostimulation | [9,81,82,83,84] |
| flavones | root | antitumoral | [57,85] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neblea, M.A.; Marian, M.C.; Aydin, T. A Comprehensive Review of the Invasive Species Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114826
Neblea MA, Marian MC, Aydin T. A Comprehensive Review of the Invasive Species Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114826
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeblea, Monica Angela, Mădălina Cristina Marian, and Tuba Aydin. 2025. "A Comprehensive Review of the Invasive Species Phytolacca acinosa Roxb." Sustainability 17, no. 11: 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114826
APA StyleNeblea, M. A., Marian, M. C., & Aydin, T. (2025). A Comprehensive Review of the Invasive Species Phytolacca acinosa Roxb. Sustainability, 17(11), 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114826






