AI Literacy in Achieving Sustainable Development Goals: The Interplay of Student Engagement and Anxiety Reduction in Northern Cyprus Universities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
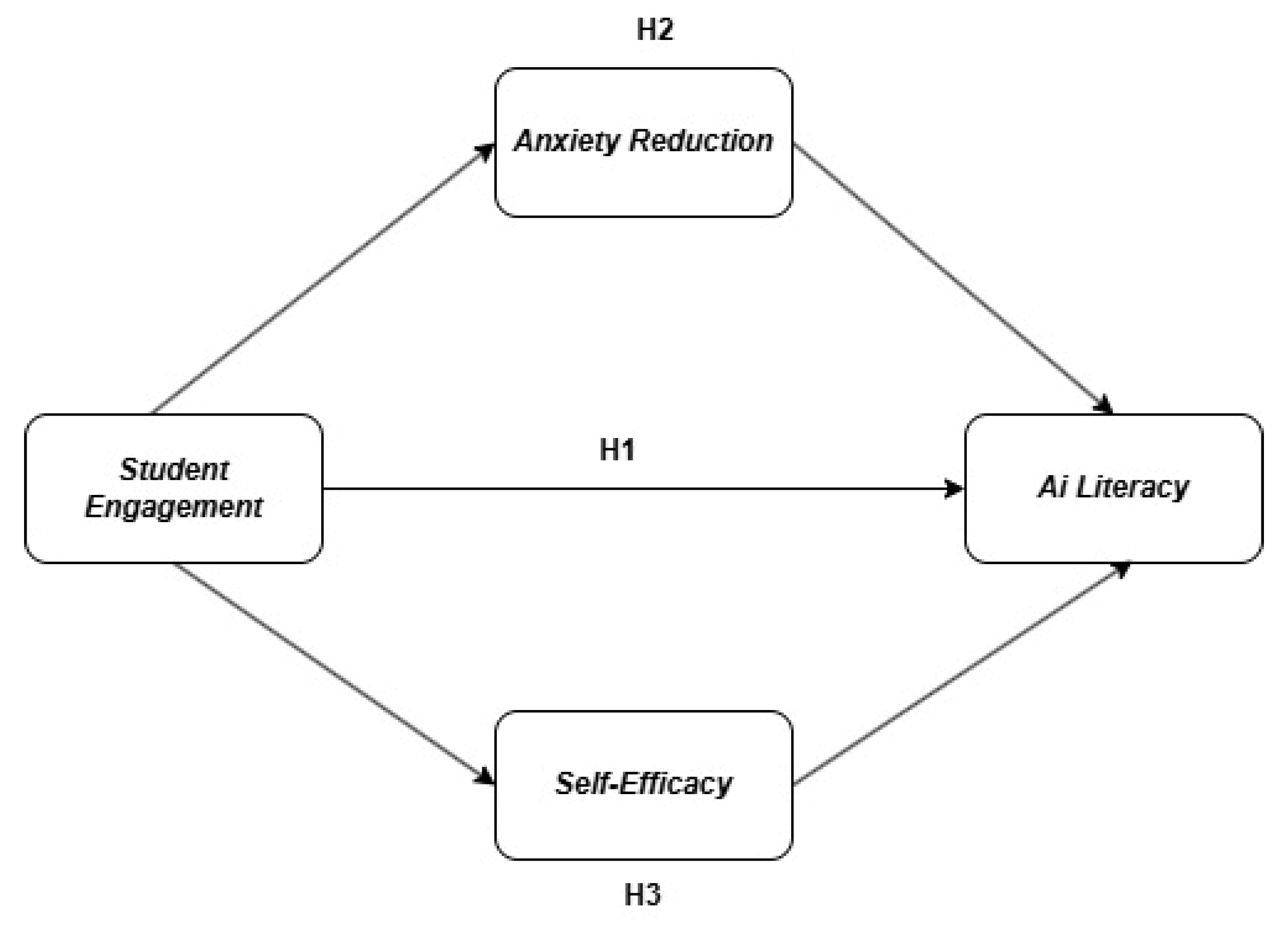
2.1. Theoretical Background and Hypothesis Development
2.2. Student Engagement and AI Literacy
2.3. Reduction in Anxiety as a Mediator
2.4. Self-Efficacy as a Mediator
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling and Data Collection Procedure
3.2. Respondents’ Profile
3.3. Measurement
4. Analysis and Results
4.1. Outer Model Assessment
4.2. Structural Model Assessment
4.2.1. Mediation Analysis
4.2.2. Model Fit
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
6.1. Theoretical Implications
6.2. Practical Implications
7. Limitations and Future Research Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiao, H.; Zhao, A. Artificial Intelligence-Based Language Learning: Illuminating the Impact on Speaking Skills and Self-Regulation in Chinese EFL Context. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1255594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Cui, W.; Yuan, X. Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: The Impact of Need Satisfaction on Artificial Intelligence Literacy Mediated by Self-Regulated Learning Strategies. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M. Student Engagement and Speaking Performance in AI-Assisted Learning Environments: A Mixed-Methods Study from Chinese Middle Schools. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 30, 7143–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güner, H.; Er, E. AI in the classroom: Exploring students’ interaction with ChatGPT in programming learning. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2025, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, T.; Gericke, N.; Boeve-de Pauw, J.; Olsson, D.; Chang, T.C. A Cross-Cultural Comparative Study of Sustainability Consciousness between Students in Taiwan and Sweden. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 6287–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, W.; Xiang, N.; Huang, Y.; Western, M.; McCourt, B.; McCarthy, I. The Impact of Effective Teaching Practices on Academic Achievement When Mediated by Student Engagement: Evidence from Australian High Schools. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowler, V. Student Engagement Literature Review; The Higher Education Academy: York, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Groccia, J.E. What Is Student Engagement? New Dir. Teach. Learn. 2018, 2018, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelson, R.D.; Flick, A. Defining Student Engagement. Change Mag. High. Learn. 2010, 43, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, M.A.; Lawson, H.A. New Conceptual Frameworks for Student Engagement Research, Policy, and Practice. Rev. Educ. Res. 2013, 83, 432–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reschly, A.L.; Christenson, S.L. The Intersection of Student Engagement and Families: A Critical Connection for Achievement and Life Outcomes. In Handbook of Student Engagement Interventions: Working with Disengaged Students; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašpar, D.; Mabić, M. Student Engagement in Fostering Quality Teaching in Higher Education. J. Educ. Soc. Res. 2015, 5, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, W.; Sabbah, K.; Abuzant, M. Affective Engagement of Higher Education Students in an Online Course. Emerg. Sci. J. 2021, 5, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kürtül, N.; Efendioğlu, A.; Yanpar Yelken, T. The Adaptation of Student Engagement Scale in Higher Education (HES). Int. J. Curric. Instr. 2016, 13, 3197–3211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wei, L.; Cai, J. Life Satisfaction and L2 Engagement in Adolescents. ELT J. 2024, 78, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damon, W.; Lerner, R.M. Child and Adolescent Development An Advanced Course; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Olufunmilayo Ogunsanya, O.; Solanke, O.E.; Olatoye, A.A. Computer Anxiety and Use of Online Resources by Distance Learning Students in Two Universities in Oyo State, Nigeria. Inf. Knowl. Manag. 2020, 10, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberger, C.D.; Gonzalez-Reigosa, F.; Martinez-Urrutia, A.; Natalicio, L.F.S.; Natalicio, D.S. Development of the Spanish edition of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Interam. J. Psychol. 1971, 5, 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre, P.; Gardner, R.C. Methods and Results in the Study of Anxiety and Language Learning: A Review of the Literature. Lang. Learn. 1991, 41, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social Foundations of Thought and Action; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bandura, A. The Social and Policy Impact of Social Cognitive Theory. In Social Psychology and Evaluation; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Khatri, B.B.; Karki, P.D. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Higher Education: Growing Academic Integrity and Ethical Concerns. Nepal. J. Dev. Rural. Stud. 2023, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Lin, Z. Artificial Intelligence in Education: A Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 75264–75278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titko, J.; Steinbergs, K.; Achieng, M.; Uzule, K. Artificial Intelligence for Education and Research: Pilot Study on Perception of Academic Staff. Virtual Econ. 2023, 6, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Y. Exploring the Effects of Artificial Intelligence Application on EFL Students’ Academic Engagement and Emotional Experiences: A Mixed-Methods Study. Eur. J. Educ. 2024, 60, e12812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojo-Lucena, F.-J.; Aznar-Díaz, I.; Cáceres-Reche, M.-P.; Romero-Rodríguez, J.-M. Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: A Bibliometric Study on Its Impact in the Scientific Literature. Educ. Sci. 2019, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X. Exploring Engagement, Self-Efficacy, and Anxiety in Large Language Model EFL Learning: A Latent Profile Analysis of Chinese University Students. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeoguine, E.; Eteng-Uket, S. Artificial Intelligence Tools and Higher Education Student’s Engagement. Edukasiana J. Inov. Pendidik. 2024, 3, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siminto, S.; Akib, A.; Hasmirati, H.; Widianto, D.S. Educational Management Innovation by Utilizing Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education. Al-Fikr. J. Manaj. Pendidikan 2023, 11, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadi, L.; Moukarzel, D.; Daccache, S. Students’ Engagement for Better Learning at a Lebanese Francophone University: A Case Study. Middle East. J. Res. Educ. Soc. Sci. 2021, 2, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearsley, G.; Shneiderman, B. Engagement Theory: A Framework for Technology-Based Teaching and Learning. Educ. Technol. 1998, 38, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Loots, S.; Strydom, F.; Posthumus, H. Learning from Students: Factors That Support Student Engagement in Blended Learning Environments within and beyond Classrooms. J. Stud. Aff. Afr. 2023, 11, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltby, A.; Mackie, S. Virtual Learning Environments—Help or Hindrance for the ‘Disengaged’ Student? ALT-J 2009, 17, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dos Santos, L.M. Stress, Burnout, and Low Self-Efficacy of Nursing Professionals: A Qualitative Inquiry. Healthcare 2020, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L. The Correlation between Business English Freshmen’s Learning Motivation and Self-Efficacy. Adv. Educ. Technol. Psychol. 2023, 7, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokool-Ramdoo, S. Beyond the Theoretical Impasse: Extending the Applications of Transactional Distance Theory. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distance Learn. 2008, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Huang, C.; Han, Z.; He, T.; Li, M. Investigating the Influence of Interaction on Learning Persistence in Online Settings: Moderation or Mediation of Academic Emotions? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health Artic. 2025, 17, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntharalingam, H. Enhancing Digital Learning Outcomes Through the Application of Artificial Intelligence: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. (IJISRT) 2024, 9, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Chai, C.S.; Lin, P.Y.; Jong, M.S.Y.; Guo, Y.; Qin, J. Promoting Students’well-Being by Developing Their Readiness for the Artificial Intelligence Age. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Gupta, M.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, D. STAR-3D: A Holistic Approach for Human Activity Recognition in the Classroom Environment. Information 2024, 15, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergast, D.; Allen, J.; McGregor, G.; Ronksley-Pavia, M. Engaging Marginalized, “at-Risk” Middle-Level Students: A Focus on the Importance of a Sense of Belonging at School. Educ. Sci. 2018, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrajeh, T.S.; Shindel, B.W. Student Engagement and Math Teachers Support. J. Math. Educ. 2020, 11, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Hong, A.J.; Song, H.D. The Relationships of Family, Perceived Digital Competence and Attitude, and Learning Agility in Sustainable Student Engagement in Higher Education. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, K.; Whatman, S. Pedagogical Approaches of a Targeted Social and Emotional Skilling Program to Re-Engage Young Adolescents in Schooling. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.T.K.; Leung, J.K.L.; Chu, K.W.S.; Qiao, M.S. AI Literacy: Definition, Teaching, Evaluation and Ethical Issues. ASIS&T Annu. Meet. 2021, 58, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southworth, J.; Migliaccio, K.; Glover, J.; Glover, J.N.; Reed, D.; McCarty, C.; Brendemuhl, J.; Thomas, A. Developing a Model for AI Across the Curriculum: Transforming the Higher Education Landscape via Innovation in AI Literacy. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2023, 4, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Rau, P.-L.P. Development of an AI Literacy Scale Using Multiple-Choice Questions. In Affective and Pleasurable Design; AHFE International: New York, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S. The Influence of AI-Powered Learning Platforms on Student Engagement and Performance: Emerging Technologies in Education. Int. J. Res. Publ. Rev. J. 2024, 5, 1816–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R. Research on the Current Situation of Artificial Intelligence Literacy of Teacher Trainees and Strategies to Improve It. Adv. Educ. Technol. Psychol. 2024, 8, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühl, N.; Meske, C.; Lobana, J. Investigating the Role of Explainability and AI Literacy in User Compliance. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.12660. [Google Scholar]
- Farrelly, T.; Baker, N. Generative Artificial Intelligence: Implications and Considerations for Higher Education Practice. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.-C.; Yang, Y. Developing and Validating an Artificial Intelligent Empowerment Instrument: Evaluating the Impact of an Artificial Intelligent Literacy Programme for Secondary School and University Students. Res. Pract. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. 2024, 20, 024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, I.; Semenov, A.L.; Gorsky, M. Smart Learning in the 21st Century: Advancing Constructionism Across Three Digital Epochs. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cécillon, F.X.; Mermillod, M.; Leys, C.; Lachaux, J.P.; Le Vigouroux, S.; Shankland, R. Trait Anxiety, Emotion Regulation, and Metacognitive Beliefs: An Observational Study Incorporating Separate Network and Correlation Analyses to Examine Associations with Executive Functions and Academic Achievement. Children 2024, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawanti, S.; Zubaydulloevna, K.M. AI Chatbot-Based Learning: Alleviating Students’ Anxiety in English Writing Classroom. Bull. Soc. Inform. Theory Appl. 2023, 7, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, L.E.; Phillips, C.; Afonso, V.M. Academic-Support Environment Impacts Learner Affect in Higher Education. Stud. Success 2023, 14, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, K.; Simpson, K.; Adams, D. Using Q-Sort Method to Explore Autistic Students’ Views of the Impacts of Their Anxiety at School. Autism 2024, 28, 2462–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durgungoz, F.C.; Durgungoz, A. “Interactive Lessons Are Great, but Too Much Is Too Much”: Hearing out Neurodivergent Students, Universal Design for Learning and the Case for Integrating More Anonymous Technology in Higher Education. High. Educ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaiari, O.; Baghaei, N.; Lahza, H.; Lodge, J.; Boden, M.; Khosravi, H. Emotionally Enriched Feedback via Generative AI. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.15077. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, Q. The Influence of Academic Self-Efficacy on University Students’ Academic Performance: The Mediating Effect of Academic Engagement. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y. Learning Engagement as a Moderator between Self-Efficacy, Math Anxiety, Problem-Solving Strategy, and Vector Problem-Solving Performance. Psych 2022, 4, 816–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, M.P.; Wut, T.M.; Lau, T.C.; Tong, W. The Interplay of Self-Efficacy, Artificial Intelligence Literacy and Lifelong Learning for Career Resilience among Older Employees: A Comparison Study between China and Malaysia. Curr. Psychol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.; Ringle, C.; Sarstedt, M.; Danks, N. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Using R: A Workbook; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Farmanesh, P.; Dehkordi, N.S.; Vehbi, A.; Chavali, K. Artificial Intelligence and Green Innovation in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises and Competitive-Advantage Drive Toward Achieving Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdar, C.C.; Cihan, M.; Yücel, D.; Serdar, M.A. Sample Size, Power and Effect Size Revisited: Simplified and Practical Approaches in Pre-Clinical, Clinical and Laboratory Studies. Biochem. Med. 2021, 31, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehbi, A.; Farmanesh, P.; Solati Dehkordi, N. Nexus Amid Green Marketing, Green Business Strategy, and Competitive Business Among the Fashion Industry: Does Environmental Turbulence Matter? Sustainability 2025, 17, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho Oh, P.; Trenerry, B.; Nair, S.; Chng, S.; Sun Lim, S.; Araral, E. Job Seekers’ Learning Attitudes in the Face of Digital Disruptions and the COVID-19 Pandemic: Investigating an Upskilling Programme in Singapore. In Proceedings of the 7th Conference of the Regulating for Decent Work Network, Virtual, 6–9 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Marcionetti, J.; Zammitti, A. Italian Higher Education Student Engagement Scale (I-HESES): Initial Validation and Psychometric Evidences. Couns. Psychol. Q. 2024, 37, 470–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Wu, Y. The Influence of Generative Artificial Intelligence on Creative Cognition of Design Students: A Chain Mediation Model of Self-Efficacy and Anxiety. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1455015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A New Criterion for Assessing Discriminant Validity in Variance-Based Structural Equation Modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.G.; Taylor, A.B.; Wu, W. Model Fit and Model Selection in Structural Equation Modeling; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Dang, M.Y. Understanding Essential Factors in Influencing Technology-Supported Learning: A Model toward Blended Learning Success. J. Inf. Technol. Educ. Res. 2020, 19, 489–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Dimensions | OL | Cronbach’s α | CR (rho_a) | CR (rho_c) | AVE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI literacy | Awareness | AIL1 | I am capable of differentiating between smart and non-smart devices. | 0.759 | 0.931 | 0.932 | 0.942 | 0.646 |
| AIL2 | I’m not sure how AI technology can assist me. | 0.856 | ||||||
| AIL3 | I can recognize the artificial intelligence (AI) technology used in the programs and goods I utilize. | 0.779 | ||||||
| Usage | AIL4 | I am proficient in using AI products or programs to assist me in my day-to-day tasks. | 0.792 | |||||
| AIL5 | Generally speaking, I have little trouble learning how to use new AI products or applications. | 0.827 | ||||||
| AIL6 | I can increase my productivity at work by using AI tools or applications. | 0.818 | ||||||
| Evaluation | AIL7 | I can assess an AI product’s or application’s strengths and weaknesses after using it for some time. | 0.801 | |||||
| AIL8 | I can select the best option from a range of options that a smart agent provides. | 0.764 | ||||||
| AIL9 | I can select the best AI product or application from a range for a given assignment. | 0.691 | ||||||
| Ethics | AIL10 | I always use AI goods or applications in accordance with ethical standards. | 0.680 | |||||
| AIL11 | When utilizing AI products or applications, I am mindful of privacy and information security concerns. | 0.748 | ||||||
| AIL12 | I am constantly aware of the misuse of artificial intelligence. | 0.688 | ||||||
| Self-efficacy | SE1 | Learning new abilities will not be an issue for me. | 0.810 | 0.878 | 0.883 | 0.911 | 0.673 | |
| SE2 | I’ll be able to manage the demands of work and training. | 0.793 | ||||||
| SE3 | I do not doubt that I can finish the work training. | 0.854 | ||||||
| SE4 | I’m determined to learn as much as I can during my work training. | 0.860 | ||||||
| SE5 | I do not doubt that job training will enable me to secure employment. | 0.782 | ||||||
| Student engagement | Cognitive engagement | SEN1 | My studies give me a great deal of satisfaction. | 0.723 | 0.909 | 0.911 | 0.928 | 0.647 |
| SEN2 | I consider my course to be intellectually engaging. | 0.693 | ||||||
| SEN3 | Usually, I am inspired to study. | 0.627 | ||||||
| Social engagement with the teacher | SEN4 | I interact with teachers to help them comprehend the challenges I have when studying. | 0.718 | |||||
| SEN5 | I actively seek appropriate constructive feedback from teachers regarding my progress. | 0.711 | ||||||
| SEN6 | I talk about my work with my teachers. | 0.712 | ||||||
| Social engagement with peers | SEN7 | I frequently meet with other students to talk about classes. | 0.754 | |||||
| SEN8 | I frequently work with other students. | 0.799 | ||||||
| SEN9 | I feel like I belong to a group of learners who are dedicated to learning. | 0.726 | ||||||
| Affective engagement | SEN10 | I truly enjoy attending this school. | 0.789 | |||||
| SEN11 | This course has exceeded my expectations. | 0.785 | ||||||
| SEN12 | I enjoy my time at this school a lot. | 0.769 | ||||||
| Anxiety reduction | AN1 | When faced with a challenge, I think of an original answer. | 0.837 | 0.905 | 0.905 | 0.933 | 0.778 | |
| AN2 | I consider something from a different angle. | 0.858 | ||||||
| AN3 | My thought process is creative and open-ended. | 0.891 | ||||||
| AN4 | I improvise. | 0.880 | ||||||
| AN5 | I think “outside the box”. | 0.686 |
| AI Literacy | Anxiety | Self-Efficacy | Student Engagement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI literacy | ||||
| Anxiety | 0.753 | |||
| Self-efficacy | 0.826 | 0.639 | ||
| Student engagement | 0.770 | 0.885 | 0.696 |
| H | Path | β | T-Statistics | p-Values | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Student engagement → AI literacy | 0.205 | 2.320 | 0.020 | Significant |
| H2 | Student engagement → self-efficacy → AI literacy | 0.305 | 8.238 | 0.000 | Significant |
| H3 | Student engagement → anxiety → AI literacy | 0.199 | 3.264 | 0.001 | Significant |
| DV | R2 | Q2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI literacy | 0.682 | 0.497 | 0.720 | 0.559 |
| Anxiety | 0.652 | 0.648 | 0.600 | 0.468 |
| Self-efficacy | 0.395 | 0.389 | 0.788 | 0.627 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farmanesh, P.; Vehbi, A.; Solati Dehkordi, N. AI Literacy in Achieving Sustainable Development Goals: The Interplay of Student Engagement and Anxiety Reduction in Northern Cyprus Universities. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114763
Farmanesh P, Vehbi A, Solati Dehkordi N. AI Literacy in Achieving Sustainable Development Goals: The Interplay of Student Engagement and Anxiety Reduction in Northern Cyprus Universities. Sustainability. 2025; 17(11):4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114763
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarmanesh, Panteha, Asim Vehbi, and Niloofar Solati Dehkordi. 2025. "AI Literacy in Achieving Sustainable Development Goals: The Interplay of Student Engagement and Anxiety Reduction in Northern Cyprus Universities" Sustainability 17, no. 11: 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114763
APA StyleFarmanesh, P., Vehbi, A., & Solati Dehkordi, N. (2025). AI Literacy in Achieving Sustainable Development Goals: The Interplay of Student Engagement and Anxiety Reduction in Northern Cyprus Universities. Sustainability, 17(11), 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17114763







