A Unified Generalized Extreme Value Distribution Framework for Estimating Lake Reference Nutrient Conditions with Confidence Intervals: A Case Study of Hongze Lake, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
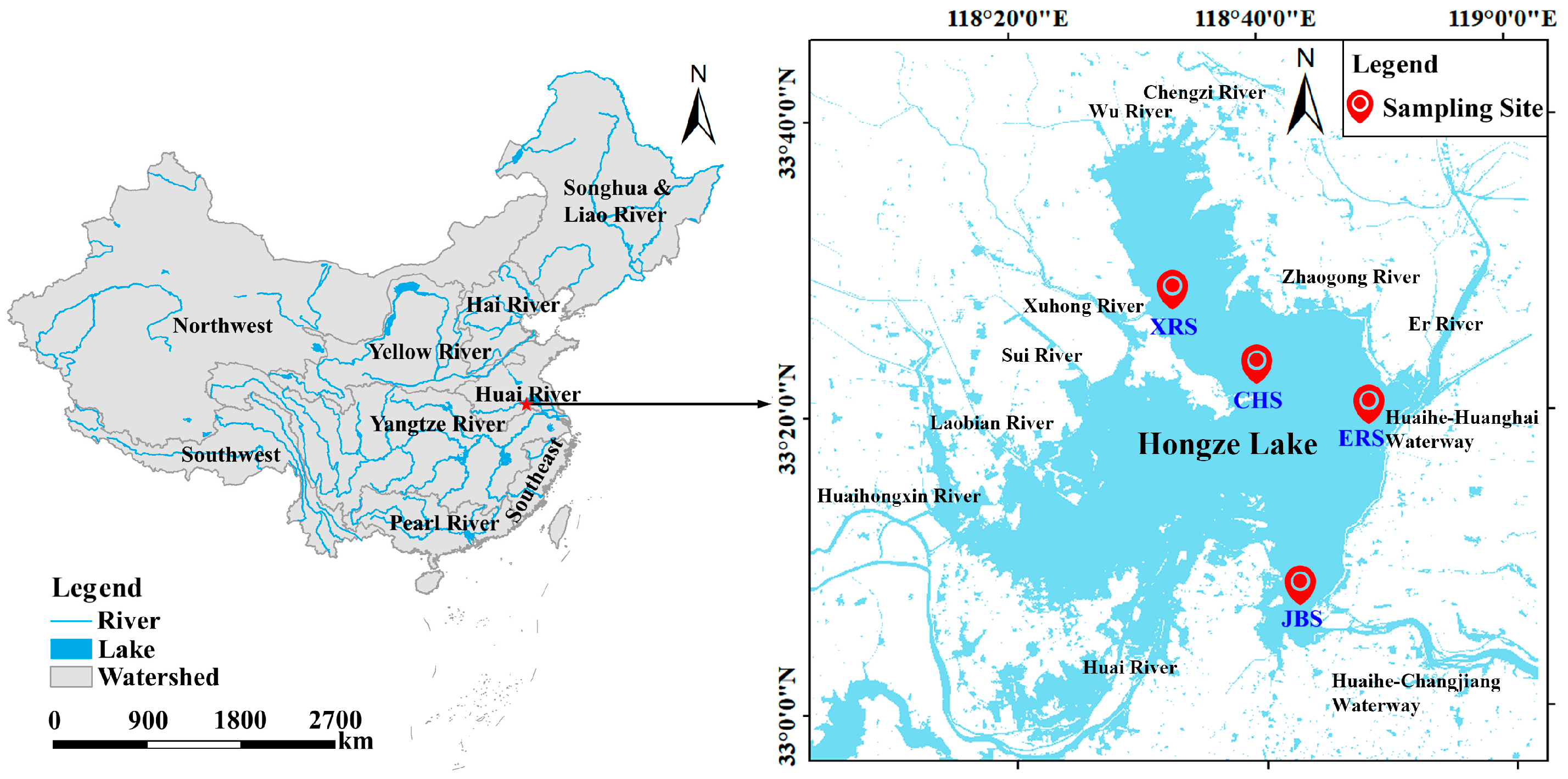
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
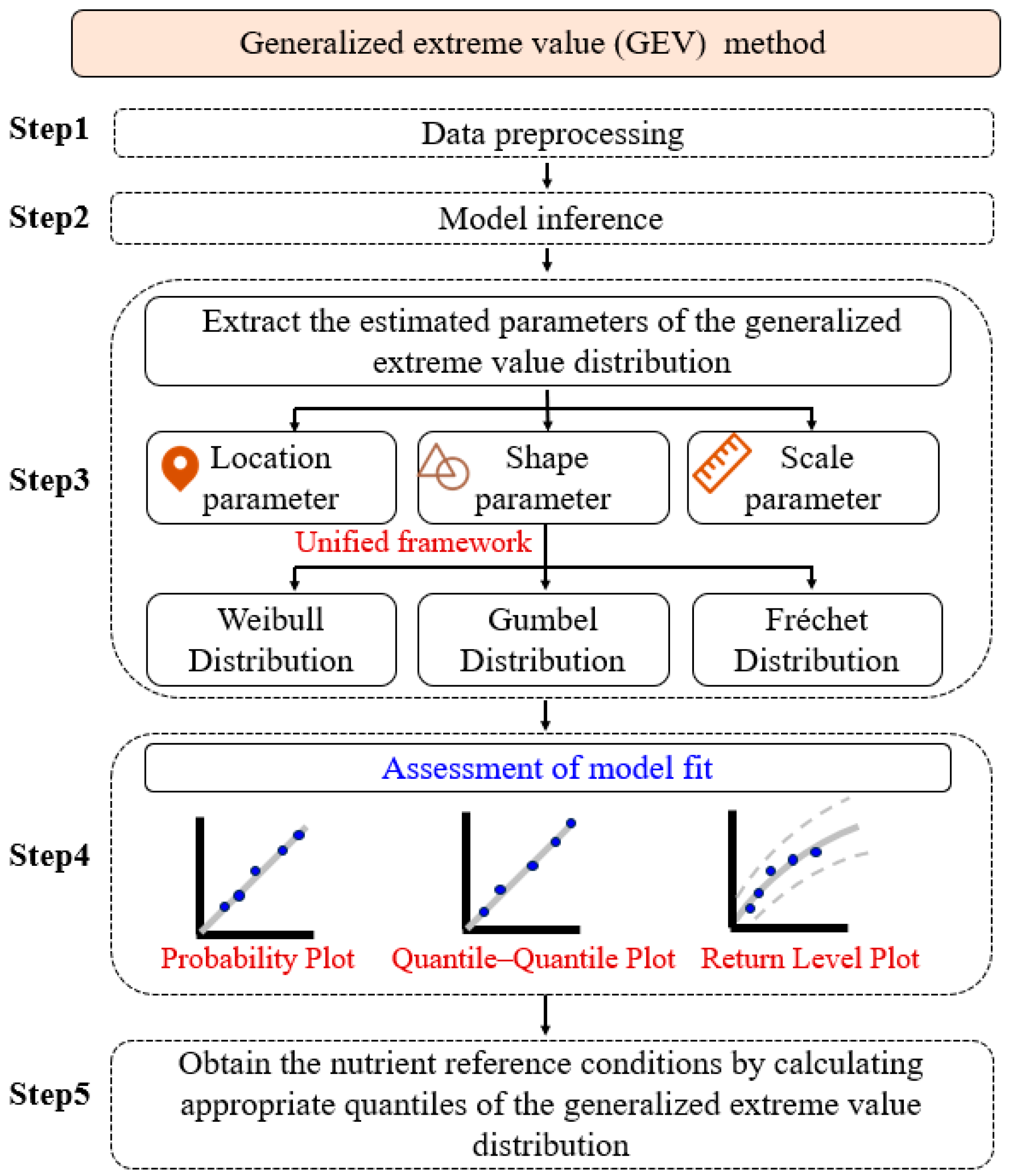
2.3. Generalized Extreme Value (GEV) Method
3. Results and Discussion
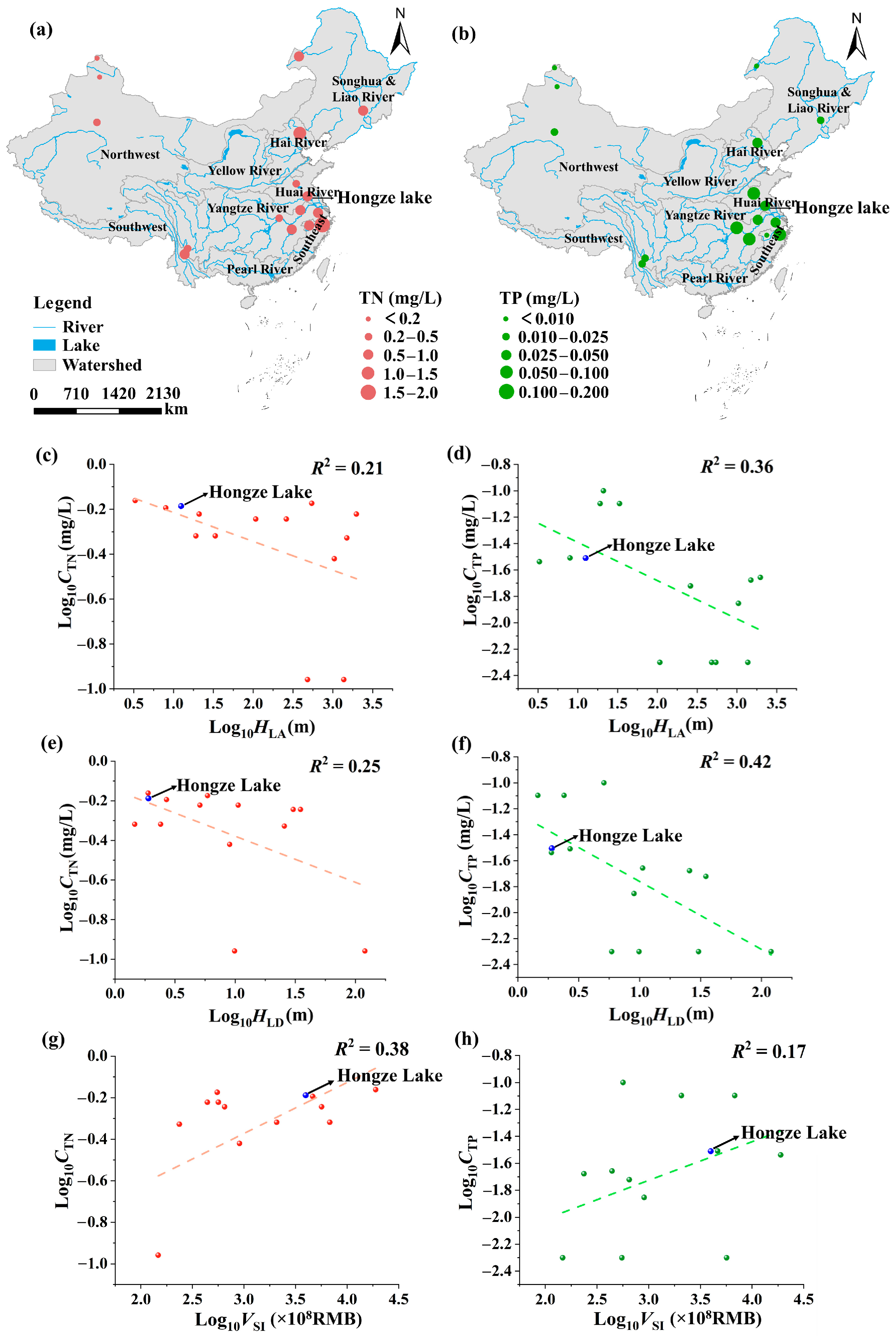
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution Pattern of Nutrients
3.1.1. Spatial Distribution Pattern of Nutrients
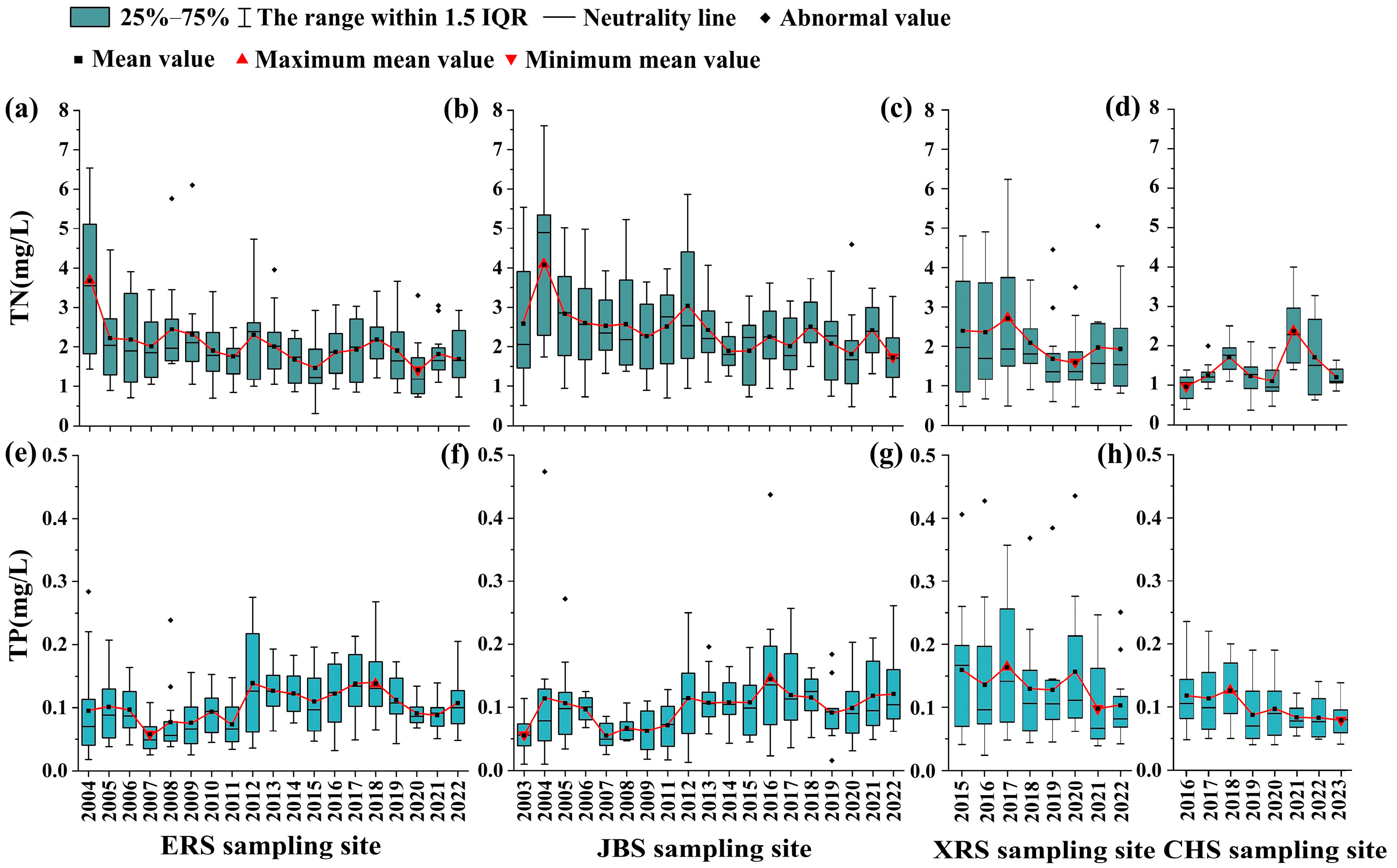
3.1.2. Temporal Distribution Pattern of Nutrients
3.2. Reference Conditions for TN and TP
3.2.1. Reference Conditions
3.2.2. Comparison of Reference Conditions with Previous Studies
| Ecosystem (Country or Region) | Method | TN (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 220 lakes and reservoirs in Kansas, USA | Reference water body and trisection method | 0.20–0.70 | 0.019–0.062 | [50] |
| Red River basin, USA | Linear regression model and classification and regression tree method | 0.75–2.11 | 0.100–0.220 | [51] |
| Streams, Genesee River watershed, USA | Soil and water assessment tool model | - | 0.076 | [52] |
| 49 reservoirs of São Paulo State, Brazil | Lake population distribution method and trisection method | 0.25 | 0.010 | [15] |
| 17 reservoirs of São Paulo State, Brazil | Trisection method | 0.35 | 0.010 | [47] |
| 319 sampling sites in rivers and streams in São Paulo State, Brazil | Trisection method | 0.34 | 0.040 | [10] |
| Nine lakes, Europe | Paleolimnological reconstruction method | - | 0.013–0.067 | [16] |
| Pusiano Lake, Italy | Process-based watershed model | - | 0.008 | [14] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ríos-Henríquez, C.; Fuentes, N. Temporal Environmental Status of a Shallow Lake Using Alpha and Beta Diversity on Phytoplankton Communities. Water 2024, 16, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azman, M.H.A.; Hamdan, R.; Ali, Z.M.; Siddiqui, Z.; Azlan, M.A.N. Inventory of Pollution Sources for The Lakes of Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2024, 16, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husk, B.; Julian, P.; Simon, D.; Tromas, N.; Phan, D.; Painter, K.; Baulch, H.; Sauve, S. Improving water quality in a hypereutrophic lake and tributary through agricultural nutrient mitigation: A Multi-year monitoring analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.M.; Xu, H.Y.; Guo, M.; Zhu, T.Y.; Cai, W.; Miao, L.Z.; Ji, S.; Tang, G.L.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal dynamics and modeling of thiacloprid in paddy multimedia systems with the effect of wetting-drying cycles. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.P.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, R.J.; Liu, J.B.; Yu, C.Q.; Chen, F.H. Nitrogen and phosphorus trends in lake sediments of China may diverge. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.D.; Song, K.S.; Lyu, L.L.; Fang, C.; Shang, Y.X.; Liu, G.; Du, J. A national-scale data set for dissolved carbon and its spatial pattern in lakes and reservoirs across China. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.M.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.M.; He, Z.J.; Peng, X.L.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.G. Comparative limnological study on annual dynamic pattern of nutrients in water column of three suburb lakes adjacent to Lake Poyang. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environment Protection Agency. Nutrient Criteria Technical Guidance Manual: Lakes and Reservoirs; United States Environment Protection Agency, Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 3–58.
- Qin, B.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.D.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zheng, J.A. Reconstruction and Trends of Total Phosphorus in Shallow Lakes in Eastern China in The Past Century. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, D.G.F.; Dodds, W.K.; Calijuri, M.D. Defining Nutrient and Biochemical Oxygen Demand Baselines for Tropical Rivers and Streams in So Paulo State (Brazil): A Comparison Between Reference and Impacted Sites. Environ. Manag. 2011, 48, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Jin, J.L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.B.; He, J.; Wang, Z.S. Inference of reference conditions for nutrient concentrations of Chaohu Lake based on model extrapolation. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.L.; Ma, C.Z.; Xi, B.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wu, F.C.; Liu, H.L. Development of methods for establishing nutrient criteria in lakes and reservoirs: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herlihy, A.T.; Kamman, N.C.; Sifneos, J.C.; Charles, D.; Enache, M.D.; Stevenson, R.J. Using multiple approaches to develop nutrient criteria for lakes in the conterminous USA. Freshw. Sci. 2013, 32, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, F.; Viviano, G.; Carraro, E.; Manfredi, E.C.; Lami, A.; Musazzi, S.; Marchetto, A.; Guyennon, N.; Tartari, G.; Copetti, D. Total phosphorus reference condition for subalpine lakes: A comparison among traditional methods and a new process-based watershed approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 145, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Silva, S.; Frascareli, D.; Silva, D.; Figueira, R.C.L.; Bittencourt, M.D.; Moschini-Carlos, V.; Pompêo, M. An abiotic typology and reference conditions for nutrients and chlorophyll-a in subtropical reservoirs (Sao Paulo State, Brazil). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 16029–16041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennion, H.; Simpson, G.L.; Anderson, N.J.; Clarke, G.; Dong, X.H.; Hobaek, A.; Guilizzoni, P.; Marchetto, A.; Sayer, C.D.; Thies, H.; et al. Defining ecological and chemical reference conditions and restoration targets for nine European lakes. J. Paleolimnol. 2011, 45, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Cheng, H.M.; Cheng, J.L. Estimation of the Nutrient and Chlorophyll a Reference Conditions in Taihu Lake Based on A New Method with Extreme-Markov Theory. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapra, S.C.; Flynn, K.F.; Rutherford, J.C. Parsimonious Model for Assessing Nutrient Impacts on Periphyton-Dominated Streams. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.L.; Ma, C.Z.; Xi, B.D.; Su, J.; Zan, F.Y.; Jiang, T.T. Defining Reference Nutrient Concentrations in Southeast Eco-Region Lakes, China. Clean-Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Montoya, M.D.; Arce, M.I.; Vidal-Abarca, M.R.; Suárez, M.L.; Prat, N.; Gómez, R. Establishing physico-chemical reference conditions in Mediterranean streams according to the European Water Framework Directive. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2257–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Li, Q.L.; Hua, Z.L.; Hong, B. The improved MEI model for forecasting TP reference concentration in Lake Taihu basin. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 347–351. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Z.L.; Han, A.Q. Improved stressor-response model of total phosphorus in Taihu Lake based on nonparametric regression. Water Resour. Prot. 2019, 35, 20–24,46. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, S. An Introduction to Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values; Springer: London, UK, 2001; pp. 92–104. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, R.W.; Parlange, M.B.; Naveau, P. Statistics of extremes in hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 1287–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Aldahan, A.; He, P.; Lu, X.; Ji, Y.; Yi, P.; Li, K.; Chen, X.G. Impact of water diversion practices on spatiotemporal changes in hydrologic and hydrochemical landscapes of surface and groundwater. Catena 2025, 249, 108661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, S.T.; Xu, W.C.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y.P. Maximum water level of Hongze Lake and its relationship with natural changes and human activities from 1736 to 2005. Quat. Int. 2013, 304, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.H.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.M.; Wang, Q.; Huang, C.C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.B.; Du, C.G.; Mu, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Remote sensing monitoring of the suspended particle size in Hongze Lake based on GF-1 data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 3179–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Cheng, H.M.; Shao, Z.C.; Jiang, X.C.; Li, Z.W.; Yang, F.K.; Cheng, J.L. Optimizing agricultural water-land resource allocation in water-economic-environment cycles considering uncertainties of spatiotemporal water footprints. J. Clean Prod. 2025, 501, 145348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.M.; Wang, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Nong, X.Z.; Jiang, X.C.; Wu, H.N.; Chen, Z.X.; Wang, M.L.; Cheng, J.L. Divergent responses of optimal land and water allocation to different hydrological regimes in the agricultural water-food-carbon nexus system. J. Hydrol. 2025, 653, 132730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dai, R.; Xu, Y.F.; Han, J.G.; Li, P.P. Statistical Assessment of Water Quality Issues in Hongze Lake, China, Related to the Operation of a Water Diversion Project. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.J.; Cai, S.Y.; Wang, H.; Cui, C.Y.; Cao, X.Y. Hydrodynamics and water quality of the Hongze Lake in response to human activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 46215–46232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Liu, C.Q.; Shi, X.L.; Li, Y.; Fan, Z.W.; Jia, B.Y.; Liao, Y.P. Ten-year Trend Analysis of Eutrophication Status and the Related Causes in Lake Hongze. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 3523–3531. [Google Scholar]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Cheng, P.; Li, X.Y. Establishing reference nutrient conditions using improved statistical methods in a river network with typical monsoon climatic pattern. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.Q.; Fan, P.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, H.T.; Wang, W.P.; Liu, H.; Messyasz, B.; Goldyn, R.; Li, B.L. Assessing the Ecosystem Health of Large Drinking-Water Reservoirs Based on the Phytoplankton Index of Biotic Integrity (P-IBI): A Case Study of Danjiangkou Reservoir. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.H.; Xu, Q.J.; Zhou, B.H.; Zhang, L.J. Building nutrient and its response indications reference state for criteria enaction: On the case of Lake Taihu, a typical shallow lake in eastern China. J. Lake Sci. 2009, 21, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.J. Practical Extremum Statistics Methods; Science and Technology; Tianjin Science and Technology Press: Tianjin, China, 2006; pp. 152–169. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.H.; Zou, L.H.; Zhang, Q.J.; Zhang, M.; Gong, Z.J.; Xie, S.Y.; Cai, Y.J. Water quality change and driving forces of Lake Hongze from 2012 to 2018. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 715–726. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Chu, E.G.; Xu, M.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y. Temporal and spatial variation analysis on nutritive salt of Hongze Lake. Environ. Eng. Res. 2015, 20, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.W.; Zhu, Y.R.; Sun, F.H.; Chen, Y.Q.; Liao, H.Q.; Ma, H.H.; Hu, X.Y. A study on the collaborative control of water quality of nitrogen and phosphorus between typical lakes and their inflow rivers in China. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 1400–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, C.W.; Zou, J.X.; Li, B.D. Impact of the second phase of the eastern route of South-to-North water diversion project on distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in Hongze Lake. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 2398–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.L.; Xi, B.D.; Su, J.; He, Z.S.; Zan, F.Y.; Yu, H. Defining physico-chemical variables, chlorophyll-a and Secchi depth reference conditions in northeast eco-region lakes, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Huo, S.L.; Xi, B.D.; Ma, C.Z.; He, Z.S. Establishing Nutrient Criteria in Nine Typical Lakes in China: A Conceptual Model. Clean-Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; Ma, C.Z.; Huo, S.L.; Zhang, D.Y.; Xu, Z.P.; Qian, G.R.; Xi, B.D. Establishing Reference Conditions for Lake Water Quality: A Novel Extrapolation Approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 2161–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, K.A.; Baron, J.S.; Brahney, J.; Oleksy, I.A.; Saros, J.E.; Hundey, E.J.; Sadro, S.A.; Kopácek, J.; Sommaruga, R.; Kainz, M.J.; et al. Mountain lakes: Eyes on global environmental change. Global Planet. Change 2019, 178, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, D.G.F.; Ogura, A.P.; Calijuri, M.D.C. Nutrient reference concentrations and trophic state boundaries in subtropical reservoirs. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, S.L.; Ma, C.Z.; Xi, B.D.; Su, J.; He, Z.S.; Li, X. Establishing water quality reference conditions for nutrients, chlorophyll a and Secchi depth for 7 typical lakes in arid and semiarid ecoregion, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4739–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.B.; Lu, J. Establishment of reference conditions for nutrients in an intensive agricultural watershed, Eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 2496–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Carney, E.; Angelo, R.T. Determining ecoregional reference conditions for nutrients, Secchi depth and chlorophyll a in Kansas lakes and reservoirs. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2006, 22, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggard, B.E.; Scott, J.T.; Longing, S.D. Sestonic Chlorophyll-a Shows Hierarchical Structure and Thresholds with Nutrients across the Red River Basin, USA. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarewicz, J.C.; Lewis, T.W.; Rea, E.; Winslow, M.J.; Pettenski, D. Using SWAT to determine reference nutrient conditions for small and large streams. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | μ | Standard Error of μ | σ | Standard Error of σ | ξ | Standard Error of ξ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | −0.976 | 0.051 | 0.345 | 0.038 | −0.473 | 0.087 |
| TP | −0.047 | 0.002 | 0.015 | 0.002 | −0.270 | 0.103 |
| Variable | 25th Percentile | Upper Limit of 95% Confidence Interval | Lower Limit of 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| TN (mg/L) | 0.651 | 0.736 | 0.565 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.031 | 0.035 | 0.026 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, A.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, W.; Ma, W.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, X.; Wang, L. A Unified Generalized Extreme Value Distribution Framework for Estimating Lake Reference Nutrient Conditions with Confidence Intervals: A Case Study of Hongze Lake, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104465
Wang A, Cheng H, Jiang W, Ma W, Yang F, Zhang L, Jiang X, Wang L. A Unified Generalized Extreme Value Distribution Framework for Estimating Lake Reference Nutrient Conditions with Confidence Intervals: A Case Study of Hongze Lake, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104465
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Anan, Haomiao Cheng, Wei Jiang, Wei Ma, Fukang Yang, Lihua Zhang, Xiaohong Jiang, and Liang Wang. 2025. "A Unified Generalized Extreme Value Distribution Framework for Estimating Lake Reference Nutrient Conditions with Confidence Intervals: A Case Study of Hongze Lake, China" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104465
APA StyleWang, A., Cheng, H., Jiang, W., Ma, W., Yang, F., Zhang, L., Jiang, X., & Wang, L. (2025). A Unified Generalized Extreme Value Distribution Framework for Estimating Lake Reference Nutrient Conditions with Confidence Intervals: A Case Study of Hongze Lake, China. Sustainability, 17(10), 4465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104465







