Coupled Coordination and Influencing Factors of Tourism Urbanization and Resident Well-Being in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
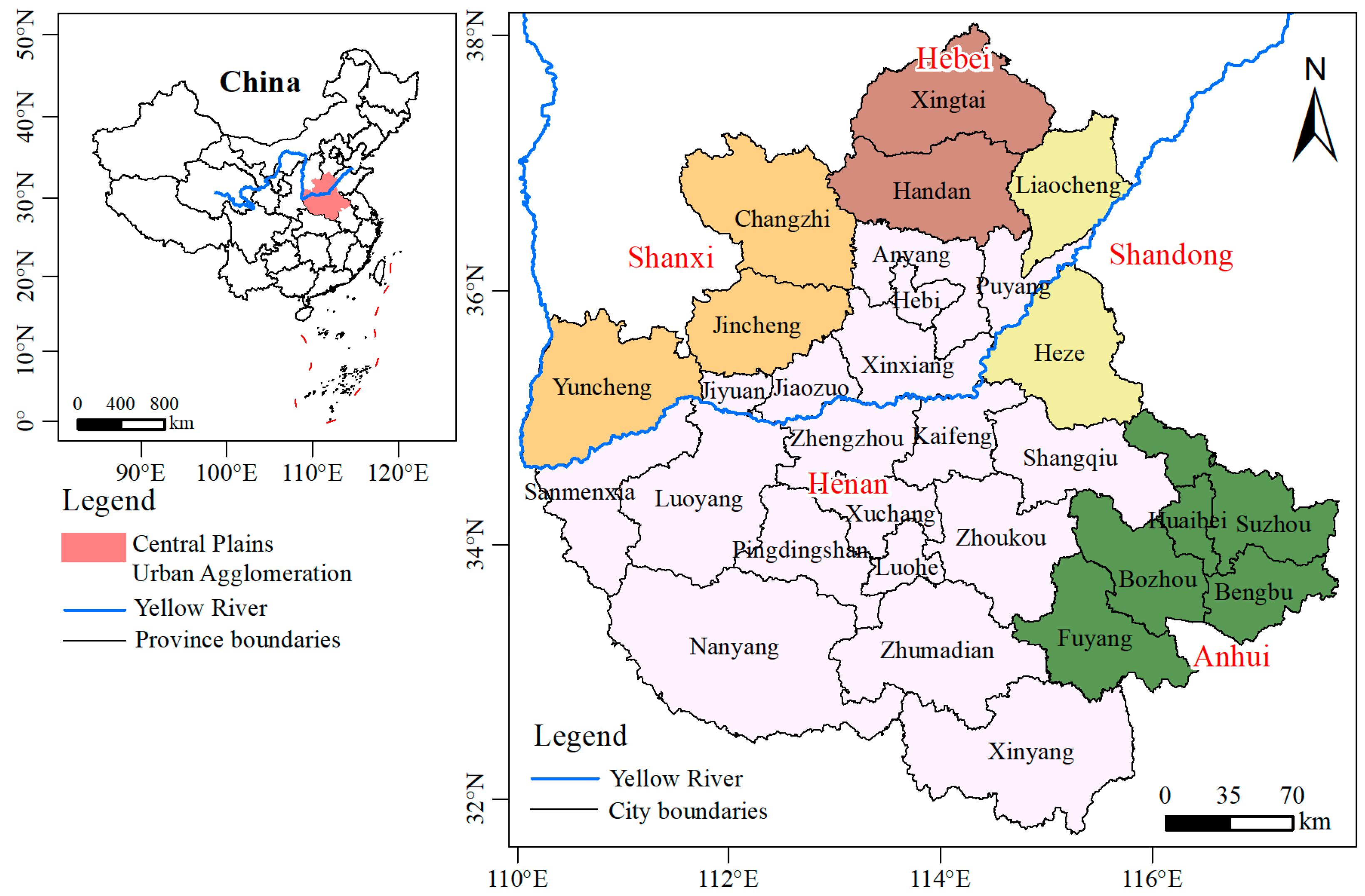
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sources of Data
3. Research Methods
3.1. Tourism Urbanization Response Coefficient
3.2. Construction of the Resident Well-Being Index System
3.3. Coupling Coordination Degree
3.4. Random Forest
4. Results Analysis
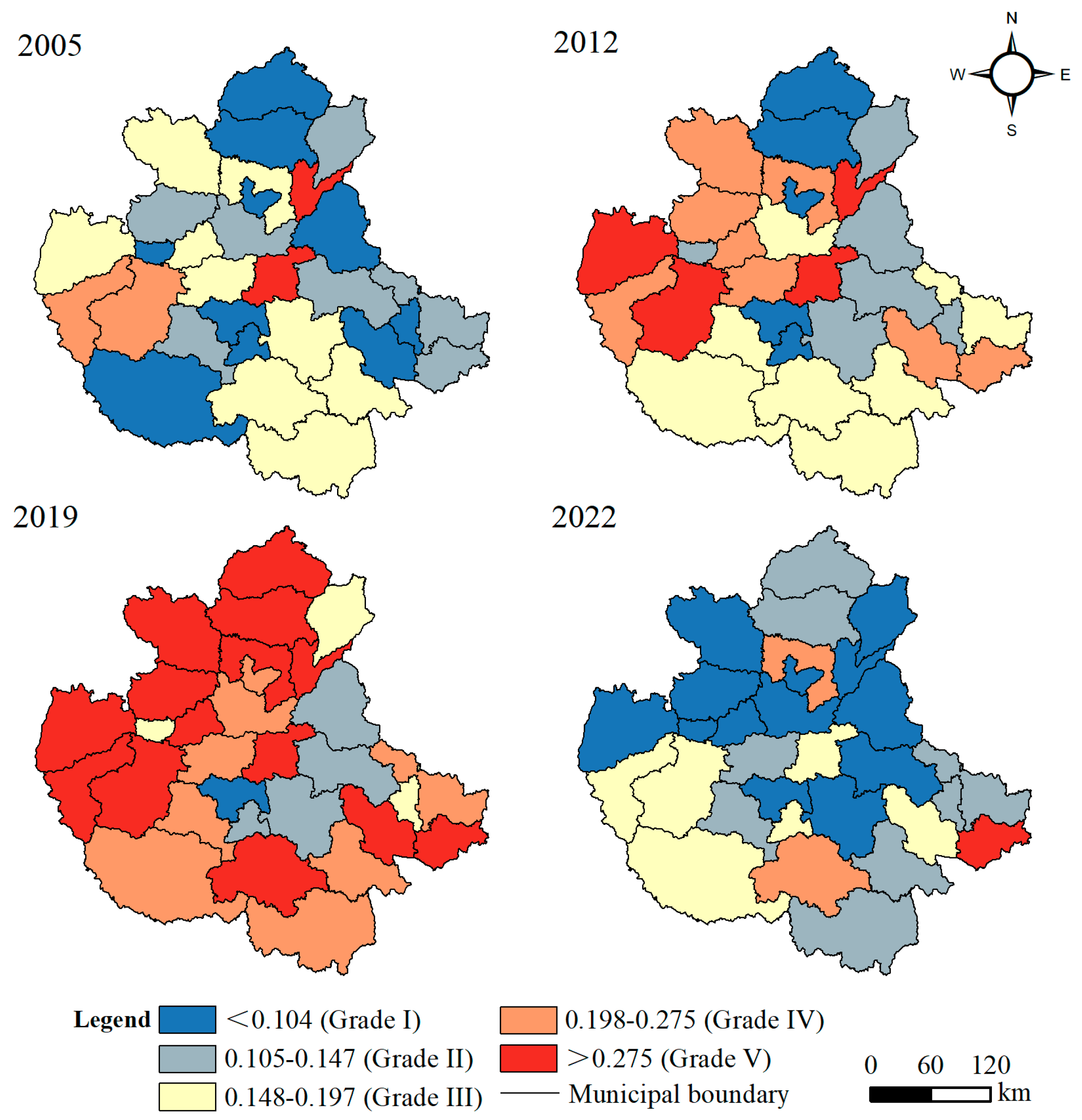
4.1. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Tourism Urbanization and Residents’ Well-Being
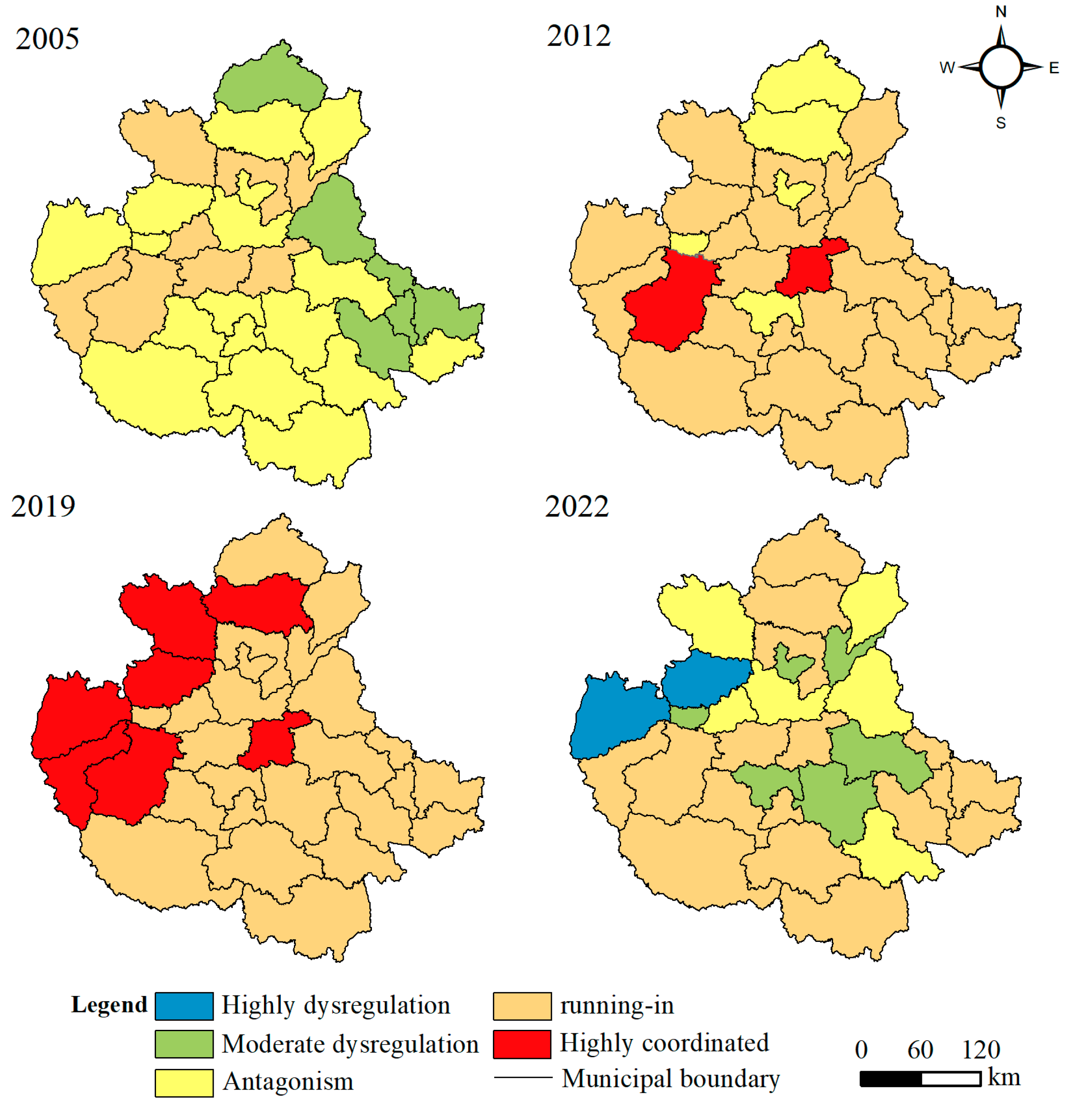
4.2. Spatiotemporal Evolution of the Coupling Coordination Degree of the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration
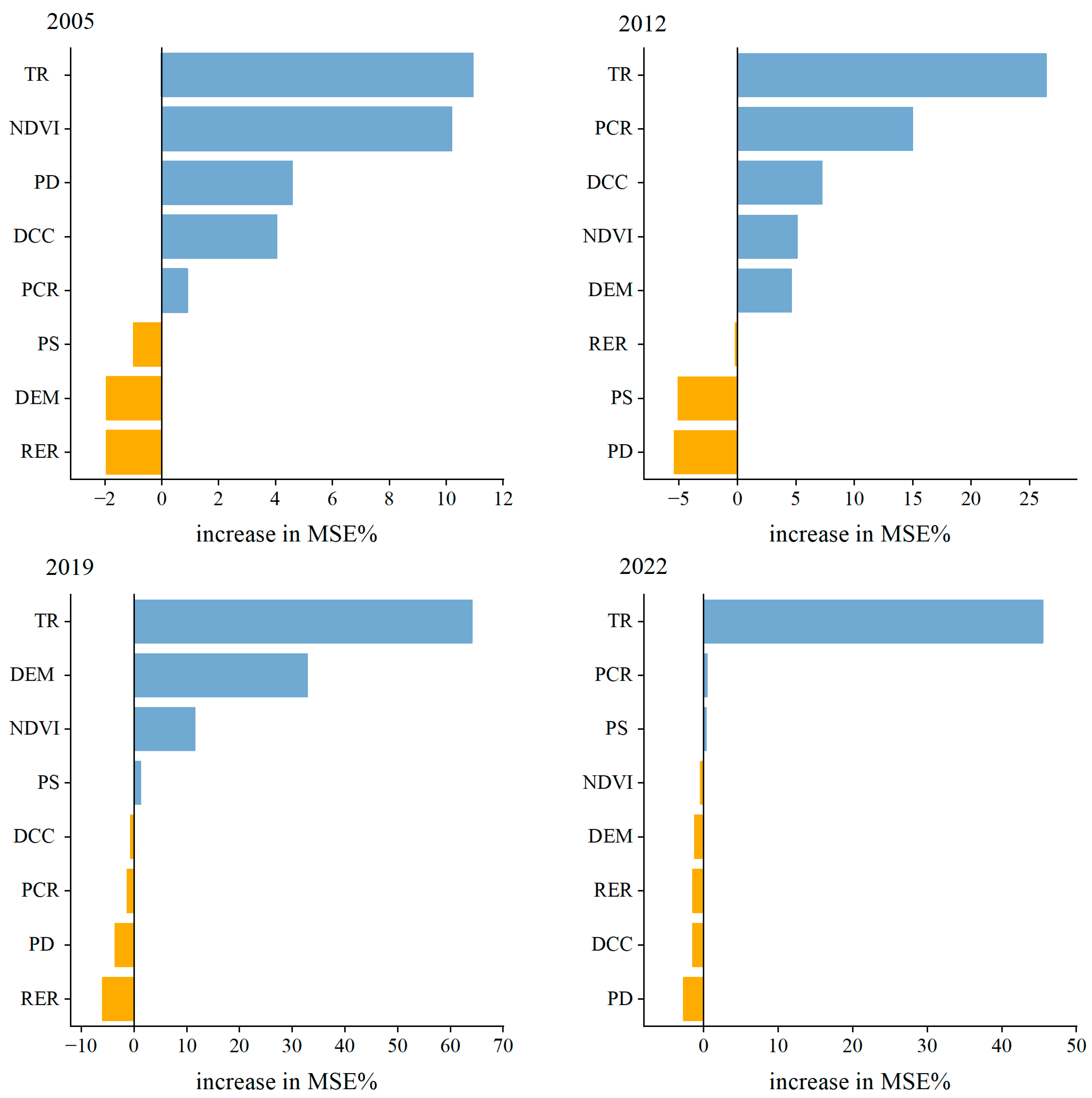
4.3. Analysis of Influencing Factors
5. Discussion
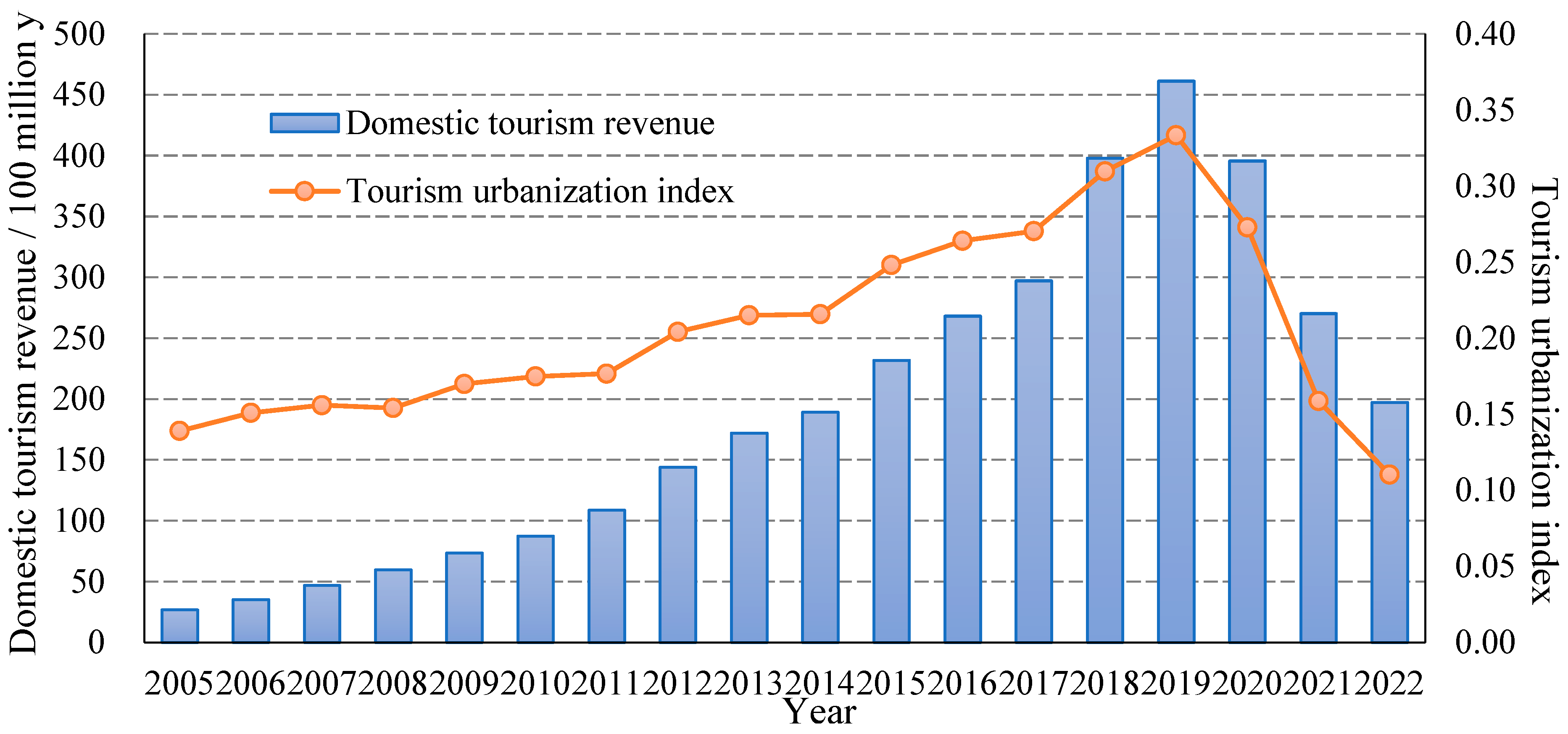
5.1. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Tourism Urbanization and Residents’ Well-Being
5.2. Coupled Coordination and Its Influences
5.3. Suggestions for Countermeasures
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niu, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, F. Urban Agglomeration Formation and Its Spatiotemporal Expansion Process in China: From the Perspective of Industrial Evolution. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, P. Tourism Urbanization. Int. J. Urban. Reg. Res. 1991, 15, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Impact of rural tourism on residents’ well-being in traditional ancient villages: A case of North Guangxi. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Tang, J.X.; Ma, X.F. Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Model of Tourism Urbanization in Concentrated Continuous Poor Areas: Taking Wuling Mountainous Area in Hunan as an Example. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 214–222+230. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.D.; Chen, M.X. Several viewpoints on the background of compiling the “National New Urbanization Planning (2014–2020)”. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Wang, K.; Gan, C.; Ma, X. The Impacts of Tourism Development on Urban–Rural Integration: An Empirical Study Undertaken in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Land 2023, 12, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.H.; Su, M.M.; Gan, C.; Yu, Z.H. Tourism development and resident wellbeing in urban agglomeration: A coupling coordination analysis of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 421, 138361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, G.; Shen, H. The Influence of Tourism’s Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity on the Urban–Rural Relationship: A Case Study of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Wondirad, A. Tourism Network in Urban Agglomerated Destinations: Implications for Sustainable Tourism Destination Development through a Critical Literature Revie. Sustainability 2021, 13, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohar, A. Tourism and Urbanization, An Interconnected Evolution. Sustain. Environ. 2021, 6, 96–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Sun, H. Network of Tourism-Industrial Complex in Cities: Typologies and Implications through a Critical Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Chen, Y.; Cao, W.; Yu, R.; Cheng, J.L. Coupling and interaction mechanism between green urbanization and tourism competitiveness: An empirical study in the Yellow River Basin of China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamizo-Nieto, F.J.; Nebot-Gómez de Salazar, N.; Rosa-Jiménez, C.; Reyes-Corredera, S. Indicators for measuring tourism intensification in urban areas through their associative network: Case studies from the Spanish Mediterranean coast. Eur. J. Tour. Res. 2022, 32, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; He, M.-e.; Liu, C. Tourism Competitiveness Evaluation Model of Urban Historical and Cultural Districts Based on Multi-Source Data and the AHP Method: A Case Study in Suzhou Ancient City. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.F.; Chen, J. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and mechanism of regional tourism urbanization and residents’ happiness level adaptability. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2024, 79, 1007–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, N.; Ma, Y.F.; Li, T.S.; Bai, K. Study on the coordinative development between tourism industry and urbanization based on coupling model: A case study of Xi’an. Tour. Trib. 2013, 28, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.Q.; Li, Y.Z. Research on coupling coordination degree between tourism industry and urbanization of Changshan Islands. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2016, 32, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Huang, Z.; Yin, S.; Hsu, W.L. Temporal and Spatial Coupling Characteristics of Tourism and Urbanization with Mechanism of High-Quality Development in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ajlani, H.; Van Ootegem, L.; Verhofstadt, E. What is Important for Well-Being? Soc. Indic. Res. 2019, 143, 955–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundimeda, H.; Atkinson, G. Measuring Global Human Progress: Are We on the Right Track? Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2024, 49, 599–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, L. Exploring the nexus between perceived ecosystem services and well-being of rural residents in a mountainous area, China. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 164, 103215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.J.; Wang, G.G.; Yang, Y.P. An assessment of sustainable wellbeing and coordination of mountain areas: A case study of Qinba Mountain Area in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, L.R.; Jennings, V.; Cloutier, S.A. Public Parks and Wellbeing in Urban Areas of the United States. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, S.H.; Elizabeth, P.; Buck, K.D. Downscaling a human well-being index for environmental management and environmental justice applications in Puerto Rico. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 123, 102231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, M.C.; Cheng, S.H.; Dupre, S.; Edmond, J.; Garside, R.; Glew, L.; Holland, M.B.; Levine, E.; Masuda, Y.J.; Miller, D.C.; et al. What are the effects of nature conservation on human well-being? A systematic map of empirical evidence from developing countries. Environ. Evid. 2016, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwongoso, A.J.; Sirima, A.; Mgonja, J.T. Impacts of Tourism Development on Residents’ Quality of Life: Efficacy of Community Capitals in Gateway Communities, Northern Tanzania. Appl. Res. Qual. Life 2023, 18, 2511–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, C. Spatio-temporal differentiation and policy optimization of ecological well-being in the Yellow River Delta high-efficiency eco-economic zone. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Guo, J.; Du, M.; Hao, C.; Hu, R. Analysis of coordinated development of “society-ecology-policy” and spatio-temporal variation of people’s livelihoods and well-being in the Yellow River basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornioli, A.; Vermeulen, S.J.; van Haaren, J.; Valente, R.; Mingardo, G. The Impacts of Tourism Stays on Residents’ Self-Reported Health: A Pan-European Analysis on the Role of Age and Urbanization Level. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, X. Effects of Domestic Tourism on Urban-Rural Income Inequality: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Voda, M.; Wang, K. Balancing efficiency and fairness: The role of tourism development in economic growth and urban–rural income gap. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 5259–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Tian, L.; Shan, Y. How Tourism Industry Development Affects Residents’ Well-Being: An Empirical Study Based on CGSS and Provincial-Level Matched Data. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.N.; Yang, M.W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, P.N. Classification, Evolution Trend, and Research Prospect of Rural Multifunction in Metropolitan Suburbs. Trop. Geogr. 2024, 44, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zmyślony, P.; Kowalczyk, A.J.; Dembińska, M. Deconstructing the Overtourism-Related Social Conflicts. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Tang, J. Nonlinear impact and spatial effect of tourism urbanization on human settlement environment: Evidence from the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Yang, M.Y.; Zhou, X.L.; Li, Z.G.; Li, H.D.; Zhai, F.F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.X. Research on the spatial correlation and formation mechanism between traditional villages and rural tourism. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z. The spatial pattern and governance of Zhongyuan Urban-Rural System in its development trajectory. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1261–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Du, J. The Impact of New Urbanization Construction on Sustainable Economic Growth of Resource-Based Cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2023, 30, 96860–96874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook (2006–2023); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China.
- China Urban Statistical Yearbook. China Urban Statistical Yearbook (2006–2023); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China.
- Henan Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Henan Statistical Yearbook (2006–2023); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China.
- Shanxi Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Shanxi Statistical Yearbook (2006–2023); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China.
- Hebei Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Hebei Statistical Yearbook (2006–2023); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China.
- Shandong Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Shandong Statistical Yearbook (2006–2023); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China.
- Anhui Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Anhui Statistical Yearbook (2006–2023); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China.
- Luo, J.M.; Qiu, H.; Lam, C.F. Urbanization impacts on regional tourism development: A case study in China. Curr. Issues. Tour. 2015, 19, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderwick, H.; Hutchings, A.; Briggs, A.; Mays, N. The impacts of collaboration between local health care and non-health care organizations and factors shaping how they work: A systematic review of reviews. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Kim, B. Culture and Art Education to Promote Cultural Welfare in Civil Society. Soc. Sci. 2019, 8, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, L. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Road Networks and Urban Expansion. Land 2017, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, M.; Madureira, J.; Mendes, A.S.; Torres, A.; Teixeira, J.P.; Oliveira, M.D. Environmental determinants of population health in urban settings. A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesari, K.K.; Soni, R.; Jamal, Q.M.S.; Tripathi, P.; Lal, J.A.; Jha, N.K.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Kumar, P.; Tripathi, V.; Ruokolainen, J. Wastewater Treatment and Reuse: A Review of its Applications and Health Implications. Water Air Soil. Poll. 2021, 232, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Jang, G. Coupling Coordination Relationship between Tourism Industry and Ecological Civilization: A Case Study of Guangdong Province in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, H.; Kuang, F. Spatial-temporal coupling analysis of ecosystem service and well-being of farmers and herdsmen: A case study of Qilian Mountain National Park. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 6527–6539. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Spatial structure and driving pathways of the coupling between ecosystem services and human well-beings: A case study of Guangzhou. J. Nat. Res. 2023, 38, 760–778. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorska, D.; Łaszkiewicz, E.; Krauze, K.; Sikorski, P. The role of informal green spaces in reducing inequalities in urban green space availability to children and seniors. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 108, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.F.; Hu, S.L. Coordinated development and evolution of natural resource-driven tourism urbanization and residents’ happiness: Take Zhangjiajie as an example. J. Nat. Resour. 2023, 38, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Qu, M.; Xu, T.P.; Choi, S. The dynamic nexus between economic growth, renewable energy use, urbanization, industrialization, tourism, green supply chain management, and CO2. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, G.M.; Tang, Y.B.; Song, N.; Li, J.P. Research on Tourism Urbanization and Influencing Factors of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2022, 38, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Luo, Y.T.; Han, Y.J.; Li, J. Evolution of Regional Disparities in Human Well-being in China and Its Influencing Factors: An Analysis Based on the Human Development Index (HDI). Prog. Geogr. 2018, 37, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Gössling, S.; Scott, D.; Hall, C.M. Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 29, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.F.; Chen, J. Research on the influence mechanism of tourism urbanization on residents’ happiness level. J. Nat. Sci. Hunan Norm. Univ. 2023, 46, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, S.-S. Tourism recovery strategy against COVID-19 pandemic. Tour. Econ. 2020, 26, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Sun, H.; Gao, J.; Chen, F.; Zhou, C. Spatiotemporal Differentiation of Coupling and Coordination Relationship of Tourism–Urbanization–Ecological Environment System in China’s Major Tourist Cities. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dimensions | Indicators | Units | Weight | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entropy Weight Method | AHP | Weighted Average | |||
| Economic Well-being | GDP per capita | 10,000 yuan | 0.080 | 0.107 | 0.093 |
| GDP density | 10,000 yuan/km2 | 0.146 | 0.091 | 0.119 | |
| Ratio of per capita disposable income between urban and rural residents | nondimensionalization | 0.082 | 0.090 | 0.086 | |
| Health Well-being | Number of medical beds per 10,000 people | units | 0.062 | 0.078 | 0.070 |
| Number of health technical personnel per 10,000 people | units | 0.060 | 0.074 | 0.067 | |
| Proportion of public health expenditure to public budget expenditure | % | 0.053 | 0.071 | 0.062 | |
| Social Well-being | Number of primary and secondary schools per 10,000 people | units | 0.068 | 0.069 | 0.068 |
| Public library collection size | 10,000 units | 0.076 | 0.065 | 0.070 | |
| Number of public libraries per 10,000 people | units | 0.091 | 0.064 | 0.078 | |
| Safety Well-being | Grain yield per unit area | t/km2 | 0.059 | 0.057 | 0.058 |
| Water supply coverage rate | % | 0.062 | 0.062 | 0.062 | |
| Highway network density | km/km2 | 0.058 | 0.052 | 0.055 | |
| Environmental Well-being | Per capita park green space | m2 | 0.031 | 0.042 | 0.036 |
| Domestic sewage treatment rate | % | 0.050 | 0.038 | 0.044 | |
| Domestic waste treatment rate | % | 0.022 | 0.041 | 0.031 | |
| Number | Interval | Level |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [0, 0.20] | High dysregulation |
| 2 | (0.20, 0.40] | Moderate dysregulation |
| 3 | (0.40, 0.50] | Antagonism |
| 4 | (0.50, 0.70] | Running-in |
| 5 | (0.70, 1] | Highly coordinated |
| Dimension | Indicator | Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Natural | Elevation | Digital elevation model (DEM) |
| Vegetation index | Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | |
| Society | Population density | Area of the region/Total resident population of the region |
| Distance to the nearest provincial capital city | Straight-line distance from the centre of the study area to the nearest provincial capital city centre | |
| Per capita road area in the city | Total urban road area/Total resident population | |
| Industry | Visitor count | Total number of tourists received annually, including domestic and inbound tourists |
| Regime | Fiscal revenue and expenditure ratio | General public budget expenditure/General public budget revenue |
| Policy support | Proportion of words related to “tourism” and “well-being” in the national economic and social development plan text |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Li, F.; Guo, L.; Jia, Y.; Feng, F. Coupled Coordination and Influencing Factors of Tourism Urbanization and Resident Well-Being in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104351
Liu D, Li F, Guo L, Jia Y, Feng F. Coupled Coordination and Influencing Factors of Tourism Urbanization and Resident Well-Being in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104351
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Di, Fengming Li, Lin Guo, Yongfang Jia, and Feng Feng. 2025. "Coupled Coordination and Influencing Factors of Tourism Urbanization and Resident Well-Being in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration, China" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104351
APA StyleLiu, D., Li, F., Guo, L., Jia, Y., & Feng, F. (2025). Coupled Coordination and Influencing Factors of Tourism Urbanization and Resident Well-Being in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability, 17(10), 4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104351






