Investigating the Influence of Renewable Energy Use and Innovative Investments in the Transportation Sector on Environmental Sustainability—A Nonlinear Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Transport Infrastructure Innovations and Environmental Sustainability
2.2. Renewable Energy Consumption and Environmental Sustainability
2.3. Total Energy Supply and Environmental Sustainability
2.4. Economic Growth and Environmental Sustainability
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Sourcing
3.2. Empirical Model
Nonlinear Model
3.3. Econometric Approaches
3.3.1. BDS Test
3.3.2. Unit Root Tests
3.3.3. NARDL Bounds Test
3.3.4. NARDL Estimation Model
4. Empirical Outcomes and Discussion
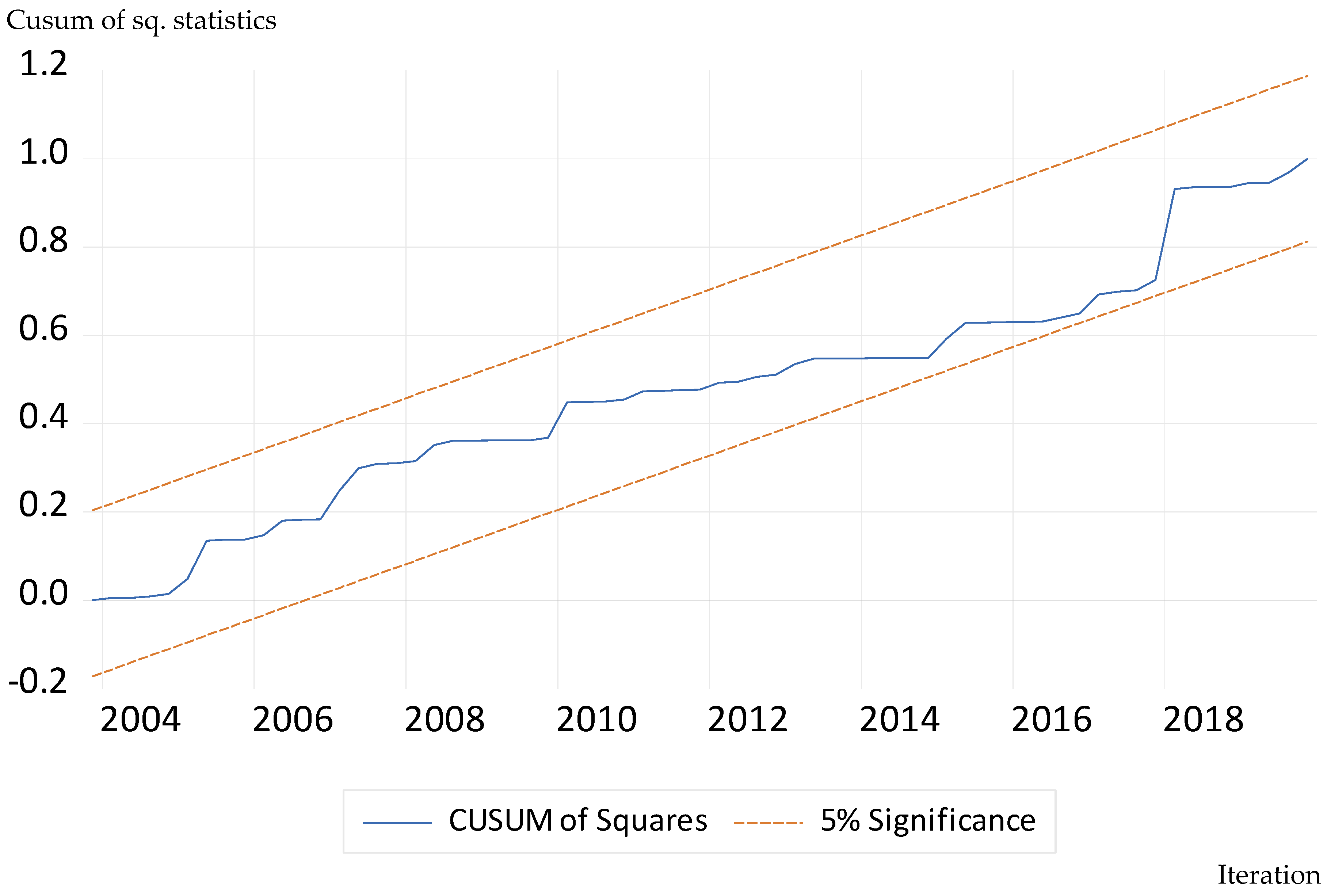
Residual Diagnostics
5. Conclusions, Policy Recommendations, and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pirgmaier, E.; Hinterberger, F. What Kind of Growth is Sustainable?: A Presentation of Arguments. In Growth in Transition; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2013; pp. 13–53. [Google Scholar]
- Munasinghe, M. Sustainability in the Twenty-First Century: Applying Sustainomics to Implement the Sustainable Development Goals; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Hu, J.; Afshan, S.; Irfan, M.; Hu, M.; Abbas, S. Bridging resource disparities for sustainable development: A comparative analysis of resource-rich and resource-scarce countries. Resour. Policy 2023, 85, 103981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement. 1991. Available online: https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w3914/w3914.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Røpke, I. The unsustainable directionality of innovation–The example of the broadband transition. Res. Policy 2012, 41, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dai, X.; Wang, Q.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Ni, B.J. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Detection, occurrence and removal. Water Res. 2019, 152, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.J.; Pan, S.Y.; Lee, I.; Kim, H.; You, Z.; Zheng, J.M.; Chiang, P.C. Green transportation for sustainability: Review of current barriers, strategies, and innovative technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 326, 129392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y. A comprehensive analysis of the spatio-temporal variation of urban air pollution in China during 2014–2018. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, M. Influence from the business environment on environmental purchasing—Drivers and hinders of purchasing green transportation services. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2011, 17, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Hashim, H.; Ho, C.S.; Van Fan, Y.; Klemeš, J.J. Sustaining the low-carbon emission development in Asia and beyond: Sustainable energy, water, transportation, and low-carbon emission technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 146, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Ma, G.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Guo, X.; Chen, S. Towards Visual Interaction: Hand Segmentation by Combining 3D Graph Deep Learning and Laser Point Cloud for Intelligent Rehabilitation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.Y.; Lin, B. Renewable energy substitution and energy technology impact in a transitional economy: A perspective from Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 360, 132163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, S.; Shen ZJ, M. Smart urban transport and logistics: A business analytics perspective. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2022, 31, 3771–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgatzi, V.V.; Stamboulis, Y.; Vetsikas, A. Examining the determinants of CO2 emissions caused by the transport sector: Empirical evidence from 12 European countries. Econ. Anal. Policy 2020, 65, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Topcu, B.A.; Sarıgül, S.S.; Vo, X.V. The effect of financial development on renewable energy demand: The case of developing countries. Renew. Energy 2021, 178, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z.; Delucchi, M.A.; Bazouin, G.; Dvorak, M.J.; Arghandeh, R.; Bauer, Z.A.; Cotte, H.; de Moor, G.M.T.H.; Goldner, E.G.; Heier, C.; et al. A 100% wind, water, sunlight (WWS) all-sector energy plan for Washington State. Renew. Energy 2016, 86, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint Akadiri, S.; Alola, A.A.; Akadiri, A.C.; Alola, U.V. Renewable energy consumption in EU-28 countries: Policy toward pollution mitigation and economic sustainability. Energy Policy 2019, 132, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, S.; Nawaz, A.; Hussain, A.; Bhatti, M.A. Linking non renewable energy, renewable energy, globalization and CO2 emission under EKC hypothesis: Evidence from ASEAN-6 countries through advance panel estimation. Pak. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2022, 10, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, J.P.C.; Moutinho, V. CO2 emissions, non-renewable and renewable electricity production, economic growth, and international trade in Italy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohler, A.; Fetters, I. The causal relationship between renewable electricity generation and GDP growth: A study of energy sources. Energy Econ. 2014, 43, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yu, L.; Mao, J. What really influences the development of renewable energy? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 62213–62236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueiro-Ferreira, R.M.; Alonso-Fernández, P. Interaction between renewable energy consumption and dematerialization: Insights based on the material footprint and the Environmental Kuznets Curve. Energy 2023, 266, 126477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yufenyuy, M.; Pirgalıoğlu, S.; Yenigün, O. The asymmetric effect of biomass energy use on environmental quality: Empirical evidence from the Congo Basin. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 27, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, G.; Valero, A. Strategic mineral resources: Availability and future estimations for the renewable energy sector. Environ. Dev. 2022, 41, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani-Oskooee, M.; Fariditavana, H. Nonlinear ARDL approach and the J-curve phenomenon. Open Econ. Rev. 2016, 27, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Yu, B.; Greenwood-Nimmo, M. Modelling asymmetric cointegration and dynamic multipliers in a nonlinear ARDL framework. Festschr. Honor. Peter Schmidt Econom. Methods Appl. 2014, 281–314. [Google Scholar]
- Çıtak, F.; Uslu, H.; Batmaz, O.; Hoş, S. Do renewable energy and natural gas consumption mitigate CO2 emissions in the USA? New insights from NARDL approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 63739–63750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Shin, Y.; Smith, R.P. Pooled Mean Group Estimation of Dynamic Heterogeneous Panels. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Ramzan, M.; Iqbal, H.A.; Awosusi, A.A.; Kinsola, G.D. The environmental sustainability effects of financial development and urbanization in Latin American countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 57983–57996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulding, K.E. The economics of the coming spaceship Earth. In Environmental Quality in a Growing Economy; RFF Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- .Mishan, E.J. Evaluation of life and limb: A theoretical approach. J. Political Econ. 1971, 79, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodland, R. The Concept of Environmental Sustainability. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1995, 26, 1–24. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/2097196 (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Meadows, D. Indicators and information systems for sustainable development. In The Earthscan Reader in Sustainable Cities; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2021; pp. 364–393. [Google Scholar]
- Nwafor, M.E.; Onya, O.V. Road transportation service in Nigeria: Problems and prospects. Adv. J. Econ. Mark. Res. 2019, 4, 104–117. [Google Scholar]
- Kapur, R.; Das, S.; Nandineni, R.D. Sustainable transportation infrastructure’s role in attaining sustainable development goals. In Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilani, M.; Diop, N.; De Wolf, D. A multimodal transport model to evaluate transport policies in the north of France. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, S.; Hammam, S. Do Transport Infrastructures Promote the Foreign Direct Investments Attractiveness? Empirical Investigation from Four North African Countries. Rom. Econ. J. 2018, 20, 110–125. [Google Scholar]
- 3Gorus, M.S.; Aydin, M. The relationship between energy consumption, economic growth, and CO2 emission in MENA countries: Causality analysis in the frequency domain. Energy 2019, 168, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magazzino, C.; Giolli, L. The relationship among railway networks, energy consumption, and real added value in Italy. Evidence from ARDL and Wavelet analysis. Res. Transp. Econ. 2021, 90, 101126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beşer, N.Ö.; Tütüncü, A.; Beşer, M.; Magazzino, C. The impact of air and rail transportation on environmental pollution in Turkey: A Fourier cointegration analysis. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2024, 35, 1836–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touratier-Muller, N.; Machat, K.; Jaussaud, J. Impact of French governmental policies to reduce freight transportation CO2 emissions on small-and medium-sized companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edenhofer, O.; Flachsland, C.; Debiel, T.; Hippler, J.; Roth, M.; Ulbert, C. Transforming the Global Energy System-Pathways Towards a Sustainable Energy Supply. In Global Trends 2013; Stiftung Entwicklung und Frieden/Development and Peace Foundation: Bonn, Germany, 2012; pp. 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kaygusuz, K. Dynamics of Energy Utilization Patterns in Turkey for Sustainable Development. J. Eng. Res. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 399–407. Available online: https://www.journaleras.com/index.php/jeras/article/view/60 (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Rosenberg, H. Transport of iron into bacterial cells. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1979; Volume 56, pp. 388–394. [Google Scholar]
- IEA. Energy, Water and the Sustainable Development Goals; IEA: Paris, France, 2018; Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/energy-water-and-the-sustainable-development-goals (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- IEA. World Energy Outlook 2024; IEA: Paris, France, 2024; Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2024 (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- EUROSTAT. Database. 2018. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/data/database (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Soytas, U.; Magazzino, C.; Mele, M.; Schneider, N. Economic and environmental implications of the nuclear power phase-out in Belgium: Insights from time-series models and a partial differential equations algorithm. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2022, 63, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjanne, A.; Korhonen, J.M. Abandoning the concept of renewable energy. Energy Policy 2019, 127, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percebois, J.; Pommeret, S. New challenges for French energy policy. Reflets Phys. 2024, 77, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrouhi, B.E.; Schall, E.; Lamrani, B.; Chaibi, Y.; Kousksou, T. Energy transition in France. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W.; Pandiyan, G. Decomposition of energy-induced CO2 emissions in manufacturing. Energy Econ. 1997, 19, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaker, M. Spillovers in the development of new pollution abatement technology: A new look at the Porter hypothesis. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2006, 52, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberger, J.K.; Krausmann, F.; Getzner, M.; Schandl, H.; West, J. Development and dematerialization: An international study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikayilov, J.I.; Galeotti, M.; Hasanov, F.J. The impact of economic growth on CO2 emissions in Azerbaijan. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, A.; Zwickl, K. Fifty Shades of Green: Revisiting decoupling by economic sectors and air pollutants. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 133, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, F.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y. Evaluating provincial carbon emission characteristics under China’s carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orubu, C.O.; Omotor, D.G. Environmental quality and economic growth: Searching for environmental Kuznets curves for air and water pollutants in Africa. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 4178–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smulders, J.A. Economic growth, liberalization, and the environment. In Encyclopedia of Energy Economics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Stagl, S. Delinking Economic Growth from Environmental Degradation? A Literature Survey on the Environmental Kuznets Curve Hypothesis. 1999. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=223869 (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Hill, R.J.; Magnani, E. An exploration of the conceptual and empirical basis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Aust. Econ. Pap. 2002, 41, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addai, K.; Serener, B.; Kirikkaleli, D. Empirical analysis of the relationship among urbanization, economic growth, and ecological footprint: Evidence from Eastern Europe. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 27749–27760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Rahman, S.U.; Afshan, S.; Ali MS, E.; Ashfaq, H.; Idrees, S. Green investment, institutional quality, and environmental performance: Evidence from G-7 countries using panel NARDL approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 100845–100860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, R.U. Sustainability economics: Where do we stand? Ecol. Econ. 2008, 67, 281–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Kowalski, M.; Haberl, H. Tons, joules, and money: Modes of production and their sustainability problems. Soc. Nat. Resour. 1997, 10, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Murad, M.W.; Noman AH, M.; Ozturk, I. Relationships among carbon emissions, economic growth, energy consumption and population growth: Testing Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis for Brazil, China, India and Indonesia. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsamara, M.; Mrabet, Z.; Saleh, A.S.; Anwar, S. The environmental Kuznets curve relationship: A case study of the Gulf Cooperation Council region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 33183–33195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A.; Sarkodie, S.A. Investigation of environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: The role of energy and financial development. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A.; Ulucak, R.; Dogan, E. Analyzing the environmental Kuznets curve for the EU countries: The role of ecological footprint. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29387–29396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N.; Ozturk, I. Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Asian countries. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökmenoğlu, K.; Taspinar, N. The relationship between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, and FDI: The case of Turkey. J. Int. Trade Econ. Dev. 2016, 25, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M.T.; Mazhar, M. Financial Development and Ecological Footprint: A global Panel Data Analysis. Pak. J. Commer. Soc. Sci. (PJCSS) 2019, 13, 487–514. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10419/201002 (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Heckscher, E.F.; Heckscher, G. An Economic History of Sweden; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1954; Volume 95. [Google Scholar]
- Assamoi, G.R.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Gnangoin YT, B. Investigating the pollution haven hypothesis in Cote d’Ivoire: Evidence from autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) approach with structural breaks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 16886–16899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. World Bank’s World Development Indicators. 2024. Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- OECD Database. OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development). 2024. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/data/indicators.html?orderBy=mostRelevant&page=0 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Saboori, B.; Sulaiman, J.; Mohd, S. Economic growth and CO2 emissions in Malaysia: A cointegration analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 2012, 51, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazkar, M.H.; Dehbidi, N.K.; Ozturk, I.; Al-Mulali, U. The impact of age structure on carbon emission in the Middle East: The panel autoregressive distributed lag approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 33722–33734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, C. Testing for Non-linearity in Daily Sterling Exchange Rates. Appl. Financ. Econ. 1996, 6, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kočenda, E. Macroeconomic convergence in transition countries. J. Comp. Econ. 2001, 29, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, D.A.; Fuller, W.A. Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perron, P. Testing for a unit root in a time series with a changing mean. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 1990, 8, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, R.F.; Granger, C.W. Cointegration and error correction: Representation, estimation, and testing. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1987, 55, 251–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Sun, X. The role of Fintech, natural resources, and renewable energy consumption in Shaping environmental sustainability in China: A NARDL perspective. Resour. Policy 2024, 88, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Shin, Y.; Smith, R.J. Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J. Appl. Econom. 2001, 16, 289–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyanto, S.S. Monte Carlo power comparison of seven most commonly used heteroscedasticity tests. Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput. 2022, 51, 2065–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, H.; Günther, M. On the Ramsey test analysis of ‘because’. Erkenntnis 2019, 84, 1229–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.Y.; Mun, H.H.; Kim, T.H.; Jeong, J. The effect of a variance shift on the Breusch–Godfrey’s LM test. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2010, 17, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W.; Newbold, P. Spurious regressions in econometrics. J. Econom. 1974, 2, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Lanvin, B.; León, L.R.; Wunsch-Vincent, S. (Eds.) Global Innovation Index 2021: Tracking Innovation Through the COVID-19 Crisis. World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). 2021. Available online: https://books.google.com.cy/books?hl=en&lr=&id=43FMEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=IEA+(2019)+-+The+car+industry+is+one+of+the+highest+spenders+on+research+and+development (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Serrenho, A.C.; Norman, J.B.; Allwood, J.M. The impact of reducing car weight on global emissions: The future fleet in Great Britain. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2017, 375, 20160364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reigner, H.; Brenac, T. Safe, sustainable but depoliticized and uneven–A critical view of urban transport policies in France. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 121, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, W.A.; Taylor, M.S. The green Solow model. J. Econ. Growth 2010, 15, 127–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, A.; Ajaz, T.; Li, J.C.; Irfan, M.; Suksatan, W. Investigating the asymmetric linkages between infrastructure development, green innovation, and consumption-based material footprint: Novel empirical estimations from highly resource-consuming economies. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouse, G.; Khan, S.A.; Rehman, A.U. ARDL Model as a Remedy for Spurious Regression: Problems, Performance and Prospectus. 2018. Available online: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/83973/1/MPRA_paper_83973.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- Brown, R.L.; Durbin, J.; Evans, J.M. Techniques for testing the constancy of regression relationships over time. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1975, 37, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breusch, T.S.; Pagan, A.R. A Simple Test for Heteroscedasticity and Random Coefficient Variation. Econometrica 1979, 47, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


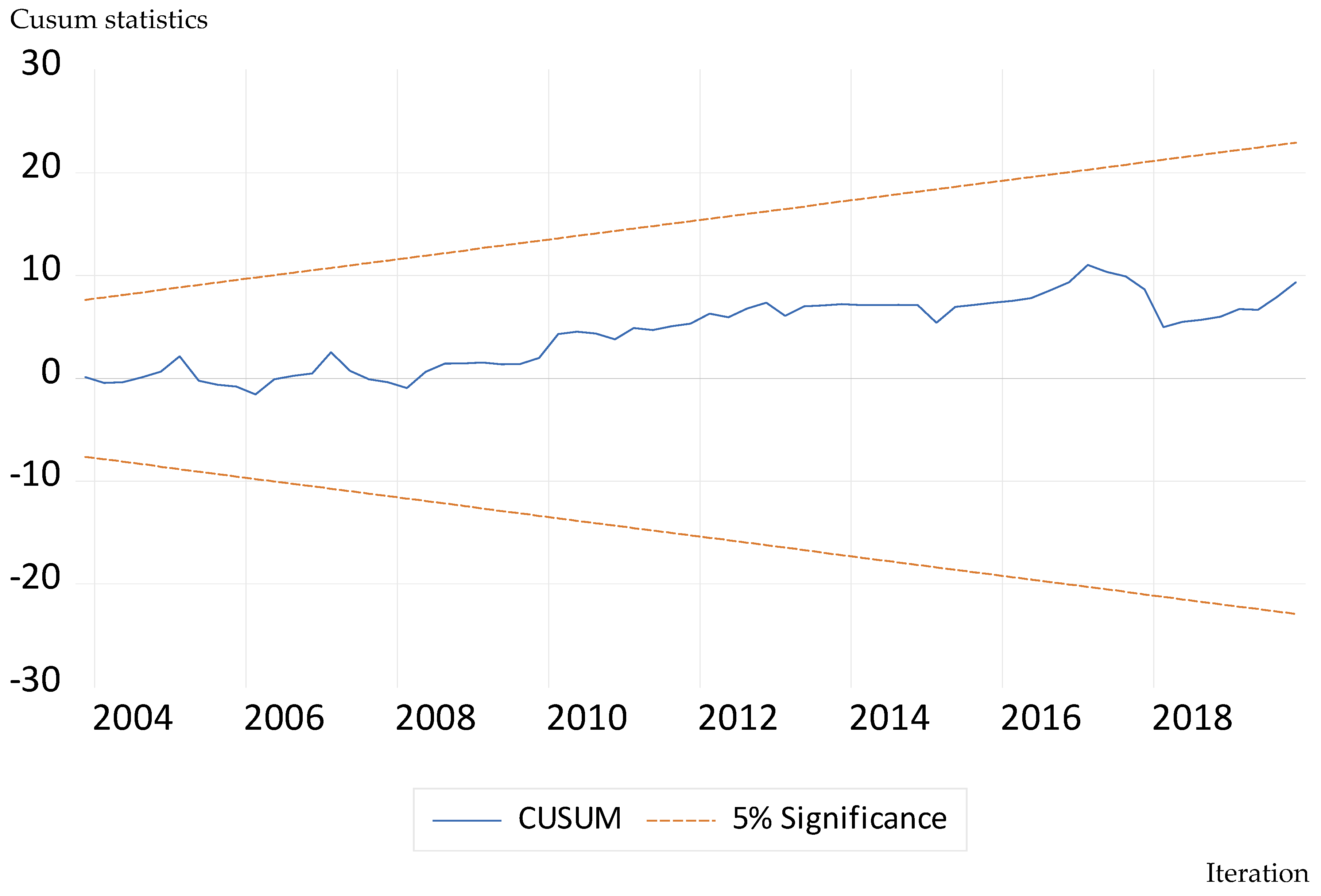
| Variable Sourced | CODE | Definition of Variable | Role | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-country carbon emissions | LCO2 | Production-based carbon emissions | Proxy for environmental sustainability and dependent variable | World bank |
| Renewable energy | REN | Naturally regeneratable energy | Independent variable | OECD database |
| Transport investment innovations | LTII | Investments in the fundamental transport development framework of an economy that provide an enabling environment for the operation of an effective transport system | Independent variable | OECD database |
| Gross domestic product per capita | LGDP | Per unit total gross value of residents by mid-year population, plus any product taxes (constant 2015 USD) | Proxy for economic growth (independent variable) | OECD database |
| Total energy supply | LTES | Overall energy supply required in an economy, excluding international aviation and maritime bunkers | Independent variable | OECD database |
| Variable | LCO2 | LGDP | LTES | LTII | REN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 3.067 | 12.345 | 2.407 | 23.620 | 8.099 |
| Median | 3.083 | 12.358 | 2.406 | 23.672 | 7.439 |
| Max. | 3.133 | 12.421 | 2.436 | 23.925 | 12.950 |
| Min. | 2.996 | 12.246 | 2.357 | 23.364 | 5.327 |
| Std. Dev. | 0.046 | 0.047 | 0.016 | 0.172 | 2.035 |
| Skewness | −0.094 | −0.600 | −0.145 | −0.088 | 0.710 |
| Kurtosis | 1.368 | 2.370 | 2.610 | 1.610 | 2.292 |
| Jarque–Bera | 11.240 | 7.655 | 0.986 | 8.178 | 10.498 |
| Probability | 0.004 | 0.021 | 0.610 | 0.016 | 0.005 |
| Variables | LCO2 | LGDP | LTES | LTII | REN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimension | BDS Stat. | BDS Stat. | BDS Stat. | BDS Stat. | BDS Stat. |
| 2 | 0.190 * | 0.207 * | 0.165 * | 0.196 * | 0.174 * |
| 3 | 0.320 * | 0.353 * | 0.265 * | 0.328 * | 0.285 * |
| 4 | 0.404 * | 0.454 * | 0.326 * | 0.416 * | 0.354 * |
| 5 | 0.456 * | 0.524 * | 0.365 * | 0.474 * | 0.394 * |
| 6 | 0.486 * | 0.573 * | 0.398 * | 0.512 * | 0.416 * |
| At Level | At First Difference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | ADF | Break Point | Variable | ADF | Break Point |
| LCO2 | −3.215 | 2010 | LCO2 | −5.177 ** | 2008 |
| LGDP | −3.130 | 2010 | LGDP | −6.086 *** | 2018 |
| LTES | −1.681 | 2019 | LTES | −5.157 ** | 1997 |
| LTII | −4.759 ** | 2013 | LTII | −5.945 *** | 2014 |
| REN | −2.116 | 2004 | REN | −5.537 ** | 1998 |
| a. | |||||||||
| N-ARDL Bounds Results | |||||||||
| F-Statistics | 3.302 ** | ||||||||
| K | 8 | ||||||||
| b. | |||||||||
| 0.031 | Coeff. | Std. Error | t-Stats | Prob | Variable | Coeff. | Std. Error | t-Stats | Prob |
| Positive shock periods | Negative shock periods | ||||||||
| LGDP_ | −3.272 | 1.579 | −2.072 | 0.041 ** | LGDP_ | 8.059 | 3.663 | 2.199 | 0.031 ** |
| LTES_ | 5.885 | 2.150 | 2.736 | 0.007 * | LTES_ | −4.793 | 1.981 | −2.419 | 0.018 * |
| LTII_ | 0.650 | 0.174 | 3.716 | 0.000 * | LTII_ | 0.491 | 0.226 | 2.173 | 0.033 ** |
| REN_ | −0.035 | 0.010 | −3.572 | 0.000 * | REN_ | 0.0301 | 0.016 | 1.929 | 0.057 ** |
| Test | F-Statistic | Prob. |
|---|---|---|
| B-P-G Heteroskedasticity | 1.601 | 0.068 *** |
| Ramsey Reset approach | 1.422 | 0.237 |
| Serial Correlation | 2.508 | 0.089 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adgheem, M.A.A.; Tenekeci, G. Investigating the Influence of Renewable Energy Use and Innovative Investments in the Transportation Sector on Environmental Sustainability—A Nonlinear Assessment. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104311
Adgheem MAA, Tenekeci G. Investigating the Influence of Renewable Energy Use and Innovative Investments in the Transportation Sector on Environmental Sustainability—A Nonlinear Assessment. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104311
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdgheem, Mohammed Adgheem Alsunousi, and Göktuğ Tenekeci. 2025. "Investigating the Influence of Renewable Energy Use and Innovative Investments in the Transportation Sector on Environmental Sustainability—A Nonlinear Assessment" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104311
APA StyleAdgheem, M. A. A., & Tenekeci, G. (2025). Investigating the Influence of Renewable Energy Use and Innovative Investments in the Transportation Sector on Environmental Sustainability—A Nonlinear Assessment. Sustainability, 17(10), 4311. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104311







