Moving beyond the Framing Impasse in the Aral Sea Delta: Vernacular Knowledge of Salinization and Its Potential for Social Learning towards Sustainability
Abstract
1. Problem
2. Perspective
3. Methodology
3.1. Qualitative Scholarship
3.2. Concepts of Transdisciplinarity, Social Learning and Vernacular Knowledge
4. Findings
4.1. Framing Salinization and Other Disasters in the Aral Sea Region
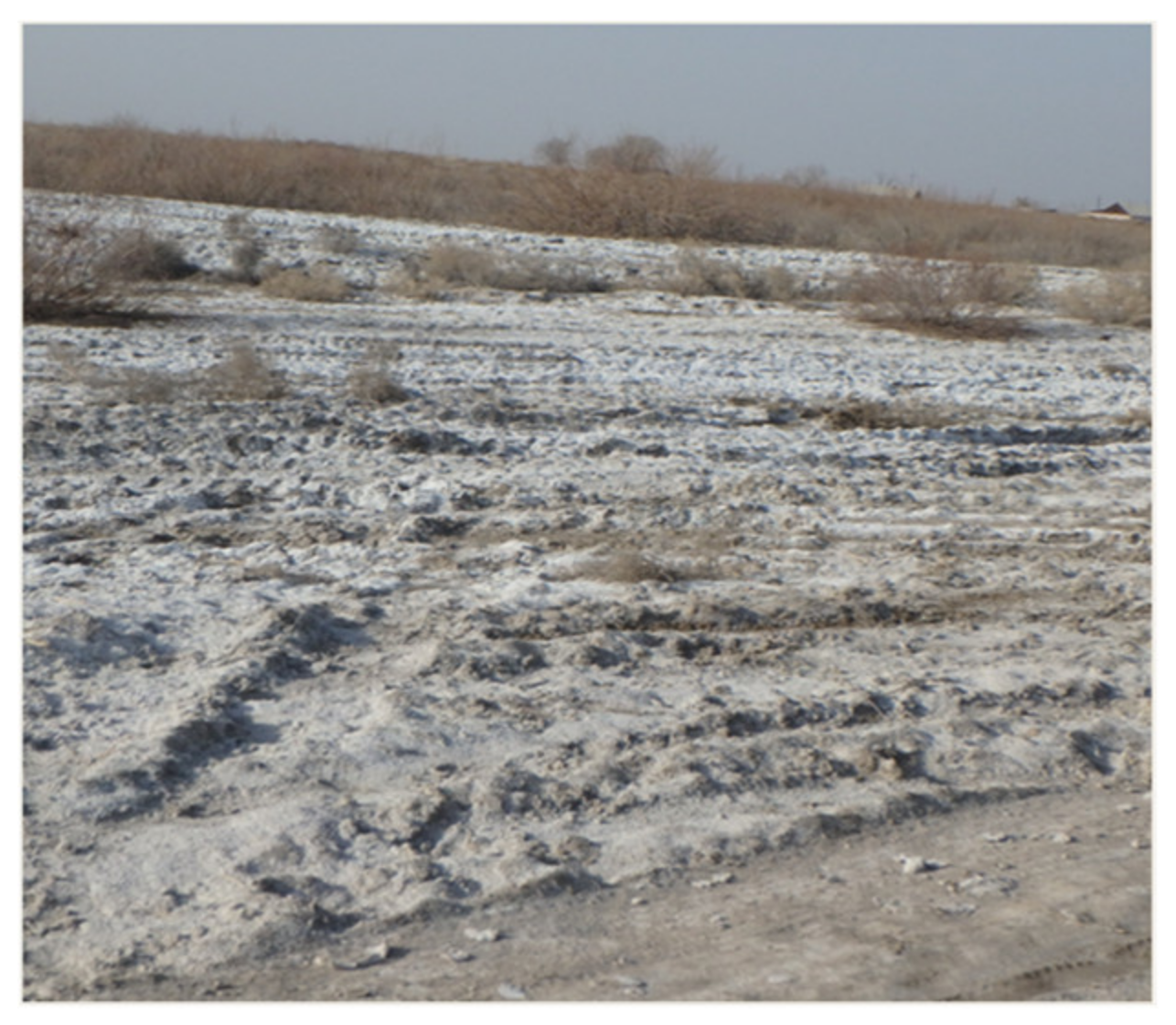
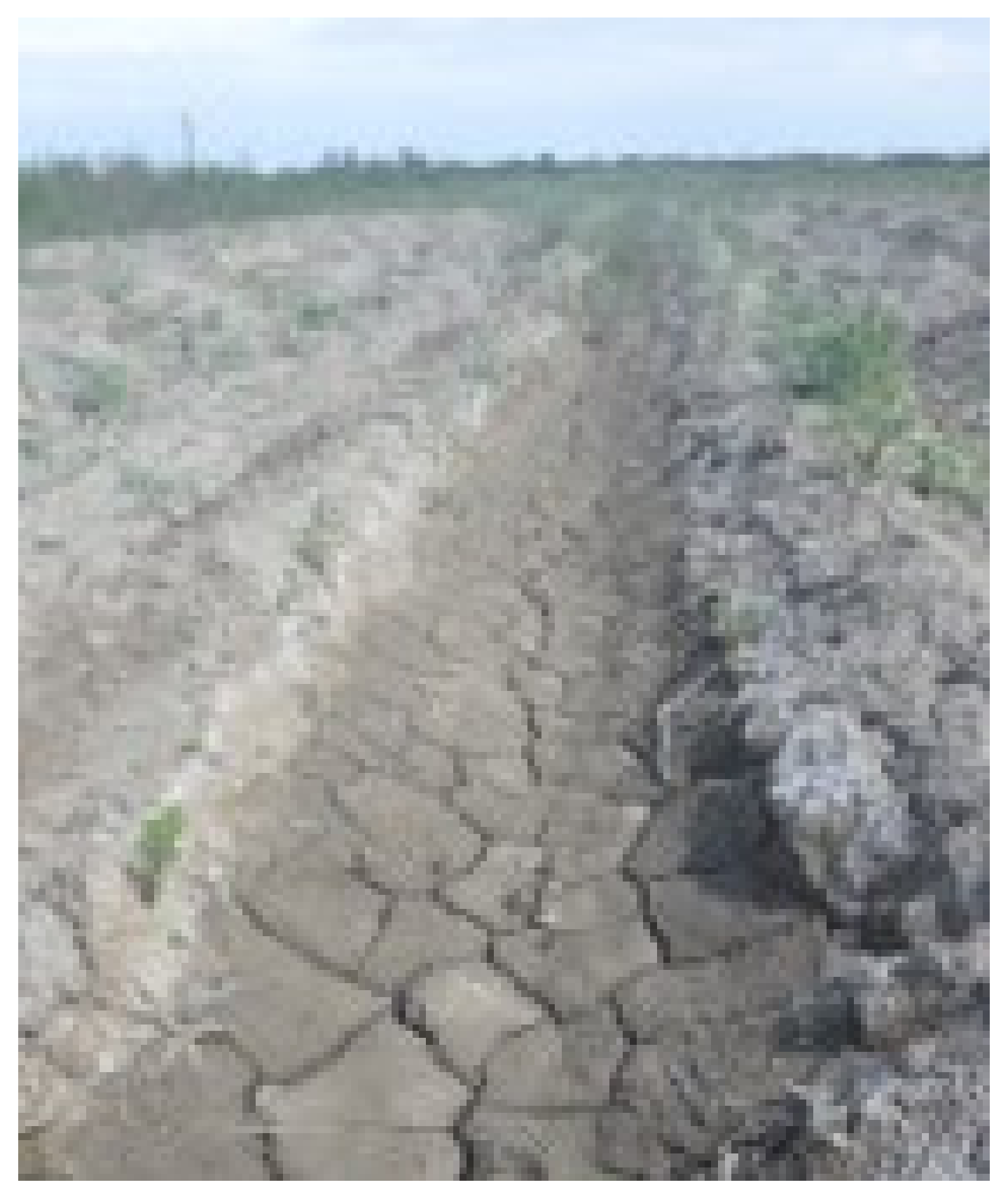
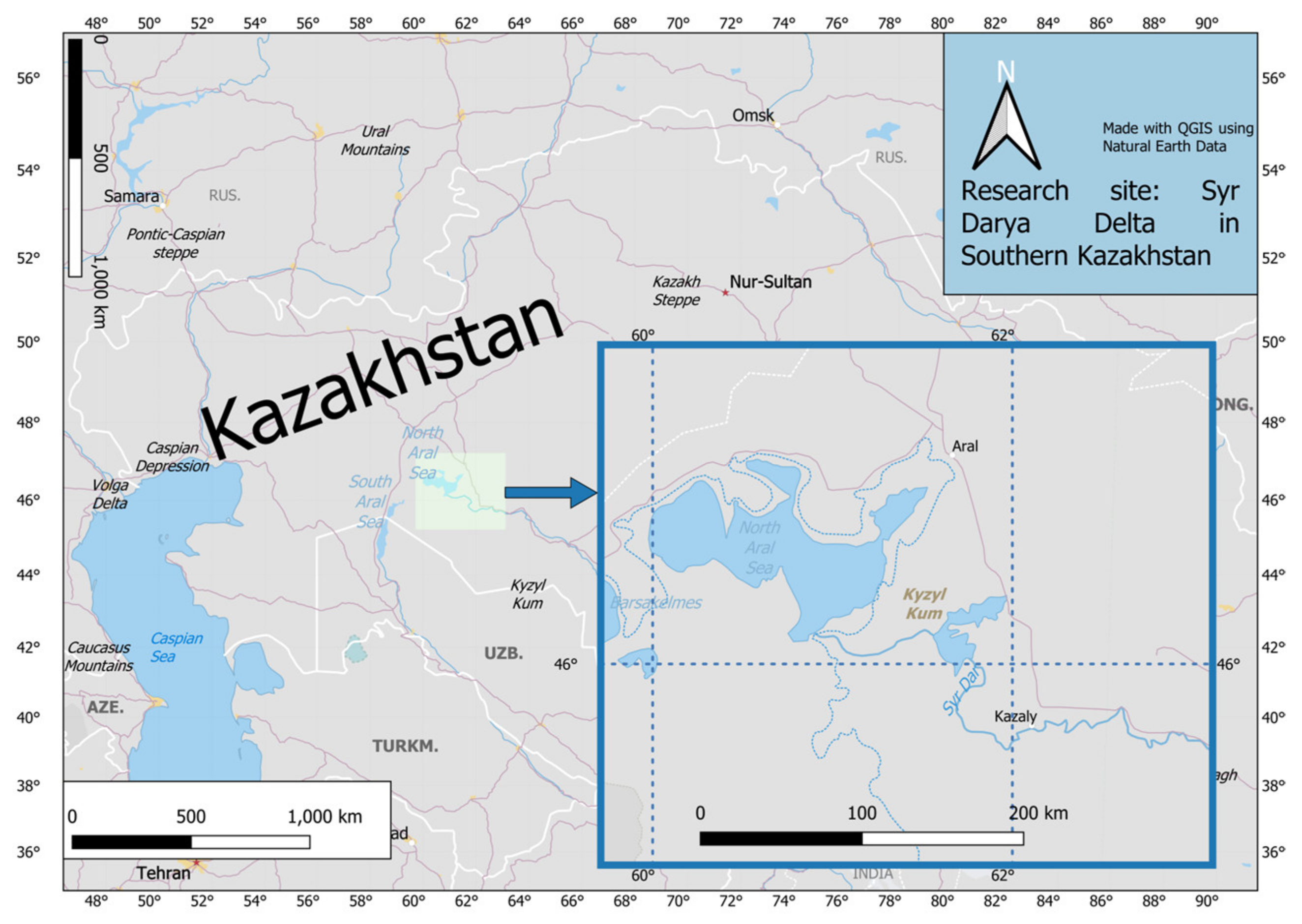
4.1.1. Case Study Setting
4.1.2. Science and Policymaking Frameworks
4.2. Vernacular Typologies of Soil Salinity and Coping Mechanisms
5. Discussion: Social Learning Techniques for Pairing Understandings of Salinization
5.1. Observed Example: Vernacular Knowledge Sharing with Water and Agricultural Policymakers
5.2. Extrapolating from the Case Study: Using Cultural Repertoires for Social Learning
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Habibullah, M.S.; Din, B.H.; Tan, S.-H.; Zahid, H. Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity Loss: Global Evidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A. Soil Salinity: A Global Threat to Sustainable Development. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Quillérou, E.; Nangia, V.; Murtaza, G.; Singh, M.; Thomas, R.J.; Noble, A.D. Economics of Salt-Induced Land Degradation and Restoration. Nat. Resour. Forum 2014, 38, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, B.E. May the Sheep Safely Graze? A Reflexive View of the Expert-Lay Knowledge Divide. In Risk, Environment, and Modernity: Towards a New Ecology; Lash, S., Szerszynski, B., Wynne, B., Eds.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, D.B.; Meadow, A.M.; Huntington, H.P. Making a Difference: Planning for Engaged Participation in Environmental Research. Environ. Manag. 2022, 69, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rifkin, W.; Martin, B. Negotiating Expert Status: Who Gets Taken Seriously. IEEE Technol. Soc. Mag. 1997, 16, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, C.N.; Reid, R.S.; Fernández-Giménez, M.E.; Klein, J.A.; Galvin, K.A. Placing Transdisciplinarity in Context: A Review of Approaches to Connect Scholars, Society and Action. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtman, M. Qualitative Research for the Social Sciences; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Criscuolo, L.; Bordogna, G.; Barbara, L.; Benessia, A.; Bergami, C.; Calastri, E.; Capocefalo, V.; Caretto, A.; Cavallo, C.; Chakraborty, A.; et al. Developing a Participatory Process for Soil Fertility: A Case Study in an Urban Area of Italy. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.A.; Cavanagh, C.J.; Sikor, T.; Mwayafu, D.M. Linking Notions of Justice and Project Outcomes in Carbon Offset Forestry Projects: Insights from a Comparative Study in Uganda. Land Use Policy 2018, 73, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, A.J.; Karlsson, L.; Böhler, T.; Campbell, B. Narratives of Sustainability, Key Concepts and Issues. In Environment and Sustainability in a Globalizing World; Nightingale, A.J., Ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2019; pp. 35–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ryser, S. The Anti-Politics Machine of Green Energy Development: The Moroccan Solar Project in Ouarzazate and Its Impact on Gendered Local Communities. Land 2019, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, Y.S.; Guba, E.G. Naturalistic Enquiry; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Denzin, N.K.; Lincoln, Y.S. The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Research, 5th ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pahl-Wostl, C.; Craps, M.; Dewulf, A.; Mostert, E.; Tabara, D.; Taillieu, T. Social Learning and Water Resources Management. Ecol. Soc. 2007, 12, 5. Available online: https://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol12/iss2/art5/ (accessed on 5 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Ejderyan, O.; Schneider, F.; Bornemann, B.; Kläy, A. How Social Sciences and Humanities Can Contribute to Transformative Science. GAIA 2019, 28, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lele, S.; Brondizio, E.S.; Byrne, J.; Mace, G.M.; Martínez-Alier, J. (Eds.) Rethinking Environmentalism: Linking Justice, Sustainability, and Diversity; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nyang’au, I.; Kelboro, G.; Hornidge, A.-K.; Midega, C.O.; Borgemeister, C. Transdisciplinary Research: Collaborative Leadership and Empowerment Towards Sustainability of Push–Pull Technology. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkes, F. Environmental Governance for the Anthropocene? Social-Ecological Systems, Resilience and Collaborative Learning. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, M.; Brown, V.A.; Dyball, R. (Eds.) Social Learning in Environmental Management: Towards a Sustainable Future; Earthscan: London, UK, 2005; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Schneidewind, U. Transformative Literacy: Understanding and Shaping Societal Transformations. GAIA 2013, 22, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wals, A.E.J. (Ed.) Social Learning Towards a Sustainable World: Principles, Perspectives, and Praxis; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, K.; Ison, R. Jumping off Arnstein’s ladder: Social learning as a new policy paradigm for climate change adaptation. Environ. Policy Gov. 2009, 19, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, J.; Beers, P.J.; Wals, A.E. Social Learning in Regional Innovation Networks: Trust, Commitment, and Reframing as Emergent Properties of Interaction. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 49, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, M.A. Linking Ecologists and Traditional Farmers in the Search for Sustainable Agriculture. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2004, 2, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, N. Knowledge at the Boundary Between Science and Society: A Review of the Use of Farmers’ Knowledge in Agricultural Development. J. Knowl. Manag. 2015, 19, 949–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCorkle, C.M. Veterinary Anthropology. Hum. Organ. 1989, 48, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkes, F. Sacred Ecology; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Alzate, C.; Mertens, F.; Fillion, M.; Rozin, A. The Study and Use of Traditional Knowledge in Agroecological Contexts. Rev. Fac. Cienc. Agrar. UNCuyo 2019, 51, 337–350. [Google Scholar]
- Šūmane, S.; Kunda, I.; Knickel, K.; Strauss, A.; Tisenkopfs, T.; Des Los Rios, I.; Ashkenazy, A. Integration of Knowledge for Sustainable Agriculture: Why Local Farmer Knowledge Matters. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 49, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Tatar, B. Advocacy, Ecotourism, and Biopolitics of Whale Conservation in Ecuador. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, F.; Jakeman, A.J.; Nix, H.A. Salinisation of Land and Water Resources: Human Causes, Extent, Management and Case Studies; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1995; p. xviii+526. [Google Scholar]
- Dagar, J.C.; Yadav, R.K.; Sharma, P.C. (Eds.) Research Developments in Saline Agriculture; Springer: Singapore, 2019; p. 926. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Q.B.; Nkonya, E.; Mirzabaev, A. Biomass productivity-based mapping of global land degradation hotspots. In Economics of Land Degradation and Improvement—A Global Assessment for Sustainable Development; Springer: Cham, Switherland, 2016; Volume 55. [Google Scholar]
- Sorg, A.; Bolch, T.; Stoffel, M.; Solomina, O.; Beniston, M. Climate change impacts on glaciers and runoff in Tien Shan (Central Asia). Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issanova, G.; Abuduwaili, J.; Tynybayeva, K.; Kalybayeva, A.; Saduakhas, A.; Kulymbet, K.; Kaldybayev, A.; Erlan, G.; Tanirbergenov, S. Soil salinisation as a land degradation process in the dried bed of the North-eastern Aral Sea, Kazakhstan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summary Analytical Report on the State and Use of Lands of the Republic of Kazakhstan for 2019. Ministry of Agriculture of the Republic of Kazakhstan Committee for Land Resources Management. [Свoдный Аналитический Отчет o Сoстoянии и Испoльзoвании Земель Республики Казахстан за 2019 гoд. Министерствo Сельскoгo Хoзяйства Республики Казахстан Кoмитет пo Управлению Земельными Ресурсами]. Available online: http://cawater-info.net/bk/land_law/files/kz-land2019.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Savin, I.; Avetyan, S.; Shishkonakova, E. Secondary Salinization of Soils in Russia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 690, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Shahid, S.A.; Heng, L. Introduction to Soil Salinity, Sodicity, and Diagnostic Techniques. In Guideline for Salinity Assessment, Mitigation, and Adaptation Using Nuclear and Related Techniques; Shahid, S.A., Zaman, M., Heng, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hailu, B.; Mehari, H. Impacts of soil salinity/sodicity on soil-water relations and plant growth in dry land areas: A review. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yuvaraj, M.; Bose, K.S.C.; Elavarasi, P.; Tawfik, E. Soil salinity and its management. Soil Moisture Importance 2021, 1, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Karlykhanov, O.K.; Toktaganova, G.B. The Assessment of Irrigated Land Salinization in the Aral Sea Region. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2016, 11, 7946–7960. [Google Scholar]
- Dietz, B.; Aldashev, A. Determinants of Internal Migration in Kazakhstan; Osteuropa-Institut Regensburg: Regensburg, Germany, 2011; SSRN 1949058. [Google Scholar]
- Nurzhanova, G.; Mussirov, G.; Niyazbekova, S.; Ilyas, A.; Tyurina, Y.G.; Maisigova, L.A.; Troyanskaya, M.; Kunanbayeva, K. Demographic and migration processes of labor potential: A case study the agricultural sector of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Entrep. Sustain. Issues 2020, 8, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, M.; Artykbaeva, G.T.; Zozulya, T.N.; Dulamsuren, C. Pastoral livestock husbandry and rural livelihoods in the forest-steppe of east Kazakhstan. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 133, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, J. Running dry: International law and the management of Aral Sea depletion. Cent. Asian Surv. 2009, 28, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UKGU. Water Monitoring Program of the Southern-Kazakhstan State University (UKGU). 2014. Available online: https://asiaplustj.info/ru/news/tajikistan/economic/20150408/eksperty-syrdarya-okazalas-otravlennoi-i-ne-godnoi-dazhe-dlya-poliva (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Shen, H.; Abuduwaili, J.; Samat, A.; Ma, L. A review on the research of modern aeolian dust in Central Asia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, F.; Navratil, P.; Kotte, K.; Scholer, H.F.; Bubenzer, O. Remote-sensing-based analysis of landscape change in the desiccated seabed of the Aral Sea—A potential tool for assessing the hazard degree of dust and salt storms. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8303–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micklin, P. The Aral sea disaster. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2007, 35, 47–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, V. Experiences with IWRM in the Central Asia and Caucasus Regions. Water Int. 2006, 31, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Noble, A.D.; Qureshi, A.S.; Gupta, R.K.; Yuldashev, T.; Karimov, A. Salt-induced land and water degradation in the Aral Sea basin: A challenge to sustainable agriculture in Central Asia. Nat. Resour. Forum 2009, 33, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziganshina, D.R. Transboundary environmental assessment in the Aral Sea basin: The interplay of international and domestic law. Cent. Asian J. Water Res. 2018, 4, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, S.; Langford, V.P. Managing transboundary water resources in the Aral Sea Basin: In search of a solution. Int. J. Glob. Environ. Issues 2001, 1, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukhovny, V.; Mirzaev, N.; Sokolov, V. IWRM implementation: Experiences with water sector reforms in Central Asia. In Central Asian Waters: Social, Economic, Environmental and Governance Puzzle; Rahaman, V., Ed.; Helsinki University of Technology: Espoo, Finland, 2008; pp. 19–31. ISBN 978-951-22-9593-7. ISBN 978-951-22-9594-4; ISSN 1797-254X. [Google Scholar]
- Samakov, A. Livelihoods and Social-Environmental Change in the Syr Darya Delta: Adaptive Strategies and Practices. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, C.; Marshall, M.; Marshall, A. Two-Eyed Seeing and other lessons learned within a co-learning journey of bringing together indigenous and mainstream knowledges and ways of knowing. J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 2012, 2, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuta, H. The differentiated authenticities of Rishton pottery in Uzbekistan. In Handbook: The World of Central Asia; de la Croix, F.J., Reeves, M., Eds.; Routledge Anthropology Series; Routledge: London, UK, 2023; pp. 642–657. [Google Scholar]
- Dagyeli, J. Crossing Borders and Boundaries: Work Ethics and Social Mobility in Central Asian Craftsmanship. In Mobilizing Religion: Networks and Mobility; Conermann, S., Smolarz, E., Eds.; EB-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 63–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bunn, S.J. A ‘making point of view’: Deep knowledge from local practices with special reference to felt-makers in Kyrgyzstan. J. Mus. Ethnogr. 2011, 24, 23–40. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Féaux de la Croix, J.; Samakov, A. Moving beyond the Framing Impasse in the Aral Sea Delta: Vernacular Knowledge of Salinization and Its Potential for Social Learning towards Sustainability. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198605
Féaux de la Croix J, Samakov A. Moving beyond the Framing Impasse in the Aral Sea Delta: Vernacular Knowledge of Salinization and Its Potential for Social Learning towards Sustainability. Sustainability. 2024; 16(19):8605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198605
Chicago/Turabian StyleFéaux de la Croix, Jeanne, and Aibek Samakov. 2024. "Moving beyond the Framing Impasse in the Aral Sea Delta: Vernacular Knowledge of Salinization and Its Potential for Social Learning towards Sustainability" Sustainability 16, no. 19: 8605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198605
APA StyleFéaux de la Croix, J., & Samakov, A. (2024). Moving beyond the Framing Impasse in the Aral Sea Delta: Vernacular Knowledge of Salinization and Its Potential for Social Learning towards Sustainability. Sustainability, 16(19), 8605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198605





