Research on Impact of Design Innovation Factors on Pure Technical Efficiency of Manufacturing Innovation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Status
3. Methods and Data Processing
3.1. Methods
3.1.1. Z-Score Standardization
3.1.2. Pearson Correlation Coefficient
3.1.3. Super Efficiency BCC Model
3.1.4. Tobit Regression
3.2. Research Object and Data Sources
4. Variable Construction and Proposed Hypotheses
4.1. Selection of Design Innovation Components
4.2. Construction of Pure Technical Efficiency Indicator for Manufacturing Innovation
4.3. Hypotheses
5. Results and Proposal
5.1. Data Calculation
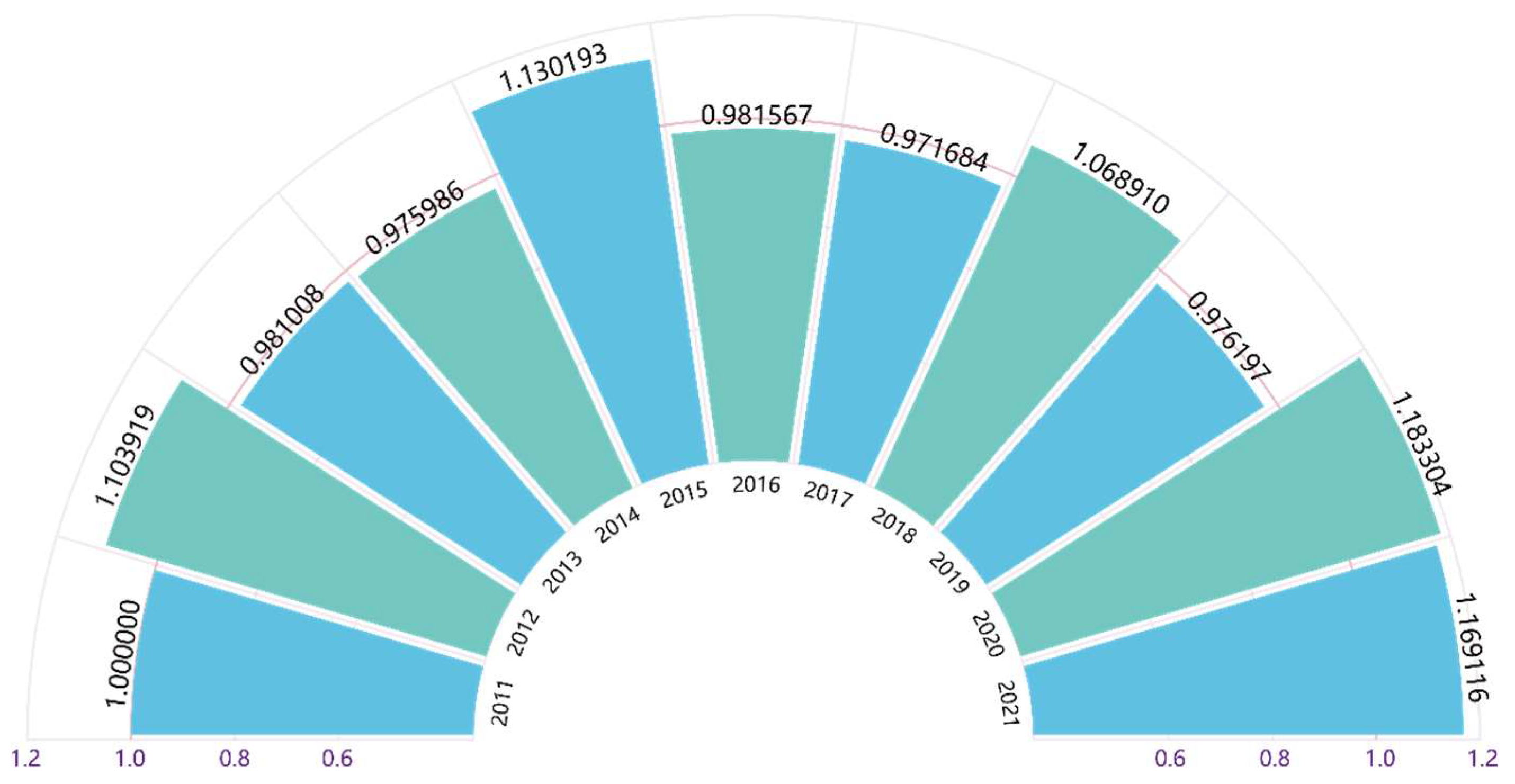
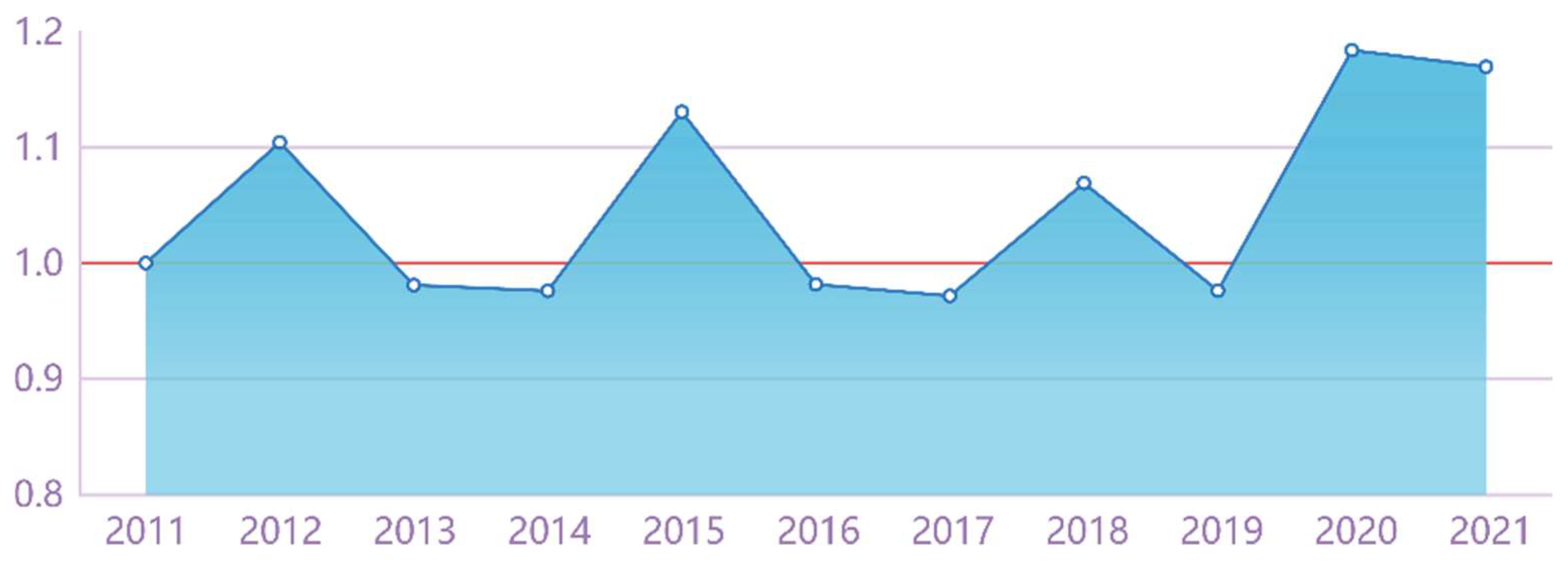
5.1.1. Calculation of Pure Technical Efficiency of Manufacturing Innovation in Zhejiang Province
5.1.2. Analysis of Design Innovation Factors Influencing Pure Technological Efficiency of Manufacturing
5.2. Conclusions
5.2.1. Results Discussion
5.2.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Q.-H.; Qi, Z.-Y.; Yu, Y.-T. Industrialization and Economic Growth in China: A Panel Test of Kaldor’s Growth Laws. In Proceedings of the 2018 25TH Annual International Conference on Management Science & Engineering, Frankfurt, Germany, 17–20 August 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 382–389. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Industrial Economics of CASS. China Industrial Development Report 2021, 1st ed.; Economy & Management Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Banker, R.D.; Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W. Some Models for Estimating Technical and Scale Inefficiencies in Data Envelopment Analysis. Manag. Sci. 1984, 30, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Su, H.; Zhou, B. Research on Innovation Efficiency of China’s Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Industry. Chin. J. New Drugs 2021, 30, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Tang, Q. Research on the Efficiency Measurement of High-quality Development of Sharing Manufacturing in China Based on Three-stage DEA-Malmquist Method. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2022, 41, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Pan, J. Research on the Efficiency Evaluation and Countermeasures of High-quality Development of Manufacturing Industry in Shaanxi Province based on SBM-DEA. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2022, 42, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Cai, X.; Pan, H.; Liu, Y. Collaborative Agglomeration of Finance and Manufacturing in the Yangtze River Economic Belt and Its Impact on Manufacturing Innovation Efficiency. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2023, 32, 895–904. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Mu, R.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Q. Influence of Specialized Agglomeration and Diversified Agglomeration on the Innovation Efficiency of Manufacturing Industry. Forum Sci. Technol. China 2019, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, C. Industrial Design to Enhance the Key to Development of the Manufacturing Industry. Art Des. 2009, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Fu, Z.; Fang, S. Industrial Creativity Industry: A New Engine for the Transformation and Upgrading of Manufacturing Industry. Zhejiang Econ. 2009, 5, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Several Opinions of the State Council on Further Promoting the Integrated Development with Relevant Industries of Cultural Creativity and Design Services Government Information Disclosure Column [2023–03–02]. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2014-03/14/content_8713.htm (accessed on 14 March 2014).
- Han, S.; Wang, W. Comparative Study on Alternative Approaches to the Measurement of Technical Efficiency. China Soft Sci. 2004, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, M.J. The Measurement of Productive Efficiency. J. R. Stat. Society. Ser. A (Gen.) 1957, 120, 253–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibenstein, H. Allocative efficiency vs. ‘x-efficiency’. Am. Econ. Rev. 1966, 56, 392–415. [Google Scholar]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q. Review of Technical Efficiency and Frontier Theory. Collect. Essays Financ. Econ. 2005, 2, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, B.; Fang, Y. Total Factor Productivity Growth and Technological Progress in Communication Equipment Manufacturing Industry. Econ. Manag. J. 2009, 35, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, C.; Guan, Z.; Chen, G.; Liu, Z. Research on the Innovation Efficiency of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises under the Innovation-driven Development Strategy. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2018, 14, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Song, D.; Liu, G. The Threshold Effect of Environmental Regulations on Manufacturing Green Technology Innovation Capabilities. Commer. Res. 2018, 4, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Meng, G. Two-stage DEA Evaluation of Technological Innovation Efficiency in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Industry under the Perspective of Government Incentive Policies. Chin. J. Pharm. 2022, 53, 912–918. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Liu, S. The Impact of Mergers and Acquisitions on Corporate Technological Innovation Capabilities—Based on Perspective of China’s Manufacturing Sub-sectors. Financ. Account. Mon. 2018, 1, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Song, Z. Innovation Efficiency of Manufacturing Industry from the Perspective of Innovation Value Chain—Taking Hebei Province as an example. China Bus. Mark. 2017, 31, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.; Zhong, G. Does International Trade in China’s Equipment Manufacturing Industry Promote Its Technological Development—DEA-BASED Panel Data Analysis. Economist 2014, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y. Analysis of Technological Innovation Efficiency of China’s Manufacturing Industry. Stat. Decis. 2017, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Gao, N. Discuss of Chinese industrial structure adjustment based on design innovation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Tsinghua International Design Management Symposium, Shenzhen, China, 1–2 December 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, H. Upgrading of Industrial Design Industry and Manufacturing Industry: Mechanism, Current Situation and Countermeasures. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences, Shanghai, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.; Guo, M. Analysis of the Mechanism and Effect of China’s Creative Industries in Promoting Manufacturing Upgrading. Jianghuai Trib. 2015, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, L. Research on Public Policy Formulation of China’s Design Industry Based on the Perspective of Manufacturing Demand. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, M.Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, W. The role of new industrial design training model in the transformation and upgrading of manufacturing industry. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 573, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H. Research on P2P Traffic Classification Method Based on Pearson Coefficient Distance Weight KNN Algorithm. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University of Technology, Zhuzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, P.; Petersen, N.C. A Procedure for Ranking Efficient Units in Data Envelopment Analysis. Manag. Sci. 1993, 39, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. Bank Branch Efficiency Measurement and Analysis of Influencing Factors-An Empirical Study Based on Super-efficiency DEA and Tobit Model. Econ. Sci. 2010, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, W.H. On the Asymptotic Bias of the Ordinary Least Squares Estimator of the Tobit Model. Econometrica 1981, 49, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Tan, Z. Research on Improving Efficiency of Independent Innovation in China’s Manufacturing Industry. Econ. Manag. 2015, 29, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- What Is ‘Industrial Enterprises above Designated Size’? How to Determine? What Is the Difference between “above the Limit” and “above Designated Size”? Available online: http://tjj.qinghai.gov.cn/tjWork/tjknowledge/202104/t20210401_72295.html (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, K. An Empirical Study on the R&D Efficiency of China’s High-tech Industries. China Ind. Econ. 2006, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Comparative Study on the Core Capabilities of Art and Design Industries in Typical Countries. Des. Res. 2022, 12, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C. Research on Interactive Integration of Industrial Design Industry and Manufacturing. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y. Research on Coupling Relationship between Industrial Design Industry and Regional Economic Development. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Yao, H. Technological Progress, Technical Efficiency and Scale Adjustment of Shanghai’s Manufacturing Industry—An empirical study based on DEA. Shanghai J. Econ. 2011, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S. Examination of Productivity Changes in Sub-sectors of the U.S. Manufacturing Industry before and after the International Financial Crisis—Based on the DEA-Malmquist Index Method. Mod. Manag. Sci. 2014, 2, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, Y. Measure and Change of Technical Efficiency of China’s Manufacturing Industry. J. Beijing Univ. Posts Telecommun. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2014, 16, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lei, L. Productivity Growth, Technological Progress and Technical Efficiency of China’s Manufacturing Industry—An empirical analysis based on DEA. Mod. Econ. Sci. 2010, 32, 83–89+127. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.; Wang, H. Research on Technological Change of Chinese Manufacturing Industries. Stat. Res. 2008, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, X. Capital Formation, Total Factor Productivity Changes and Divergence in China’s Industrial Industries: A Study Based on Panel Data by Industry. J. World Econ. 2005, 9, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, C. R&D Performance Evaluation of High-Tech Industries Based on DEA-Malmquist Index Method. Stat. Decis. 2011, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tan, Q. An Empirical Analysis of the Innovation Efficiency of Manufacturing Industry—Based on DEA-Malmquist Index. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 24, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Zhong, P. Study on R&D Dynamic Efficiency of Chinese Manufacturing Industries Based on DEA Malmquist Index. R D Manag. 2011, 23, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Xiao, H. Research on Evaluation of Technological Innovation Capabilities and Efficiency of China’s Manufacturing Industry—Based on Factor Analysis and Data Envelopment Methods. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2015, 34, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Dong, L.; Hu, Z. Research on Coordination of Technological Innovation Efficiency and Industrial Competitiveness—A Study Based on Manufacturing Industry in Zhejiang Province. Sci. Technol. Econ. 2012, 25, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, R. Research on Enterprise Technological Innovation Efficiency and Its Influencing Factors. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2003, 6, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.; Ma, R.; Tian, Y. Science and Technology Funding Investment Structure and Enterprise Technological Innovation—An Empirical Study Based on China’s Large and Medium-sized Industrial Enterprises. Sci. Manag. Res. 2009, 27, 104–107. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Jiang, K.; Li, J. Convergence Analysis of China’s Regional Innovation Efficiency. Financ. Trade Econ. 2008, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Q. Data Envelopment Analysis for Performance Evaluation; Wu-Nan Culture Enterprise: Taiwan, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.; Yates, F. Statistical Methods for Research Workers; Genesis Publishing Pvt Ltd.: Delhi, India, 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 6, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the Dimension of a Model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K. Model Analysis of Industrial Design Promoting Industrial Upgrading of Changzhou Equipment Manufacturing Industry. J. Mach. Des. 2013, 30, 123–125. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K. On the Role Positioning of Industrial Design in Context of Manufacturing Industry Upgrading. Packag. Eng. 2014, 35, 130–133. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J. Vigorously Develop China’s Design Industry and Comprehensively Improve China’s Design Level. Sci. Technol. Ind. China 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Development environment (GA) | Support funds (G1) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | Financial subsidies and special funds for industries from governments at all levels in Zhejiang Province |
| Number of policy regulations (G2) (Qty.) | Design innovation policies issued by governments at all levels | |
| Economic environment (G3) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | GDP per capita | |
| Innovation atmosphere (G4) (Qty.) | Number of patents per 10,000 people | |
| Human resources (GB) | Number of full-time professionals (G5) (Qty.) | Number of full-time professionals |
| Percentage of personnel holding certificates (G6) (%) | Percentage of designers who passed Industrial Designer Professional Qualification Examination | |
| Percentage of personnel with intermediate and senior professional titles (G7) (%) | Percentage of designers with intermediate or senior professional titles | |
| Growth rate of designers (G8) (%) | Growth rate of personnel engaged in design innovation activities | |
| Scale (GC) | Design service income (G9) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | Design service income |
| Number of design enterprises (G10) (Qty.) | Number of design enterprises | |
| Number of practitioners (G11) (Qty.) | Number of practitioners | |
| Number of service enterprises (G12) (Qty.) | Number of service enterprises | |
| Output (GD) | Number of design output transactions (G13) (Qty.) | Number of design service contracts signed |
| Conversion of industrial achievements into output value (G14) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | Output value of industrialization of design results | |
| Number of patent applications (G15) (items) | Number of patents applied for this year | |
| Number of patents granted (G16) (items) | Number of patents granted this year | |
| Number of design awards at provincial level or above (G17) (items) | Number of design awards at provincial level or above | |
| Design competitions held (G18) (items) | Number of design competitions held | |
| Design activities held (G19) (Qty.) | Number of design activities held | |
| Number of foreign exchanges and cooperation (G20) (Qty.) | Number of foreign exchanges and cooperation |
| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Development environment (GA) | Number of policy regulations (G1) (Qty.) | Financial subsidies and special funds for industries from governments at all levels in Zhejiang Province |
| Economic environment (G2) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | GDP per capita | |
| Innovation atmosphere (G3) (Qty.) | Number of patents per 10,000 people | |
| Design competitions held (G4) (items) | Number of design competitions at all levels held | |
| Human resources (GB) | Number of full-time professionals (G5) (Qty.) | Number of full-time professionals |
| Percentage of personnel with intermediate and senior professional titles (G6) (%) | Percentage of designers with intermediate or senior professional titles | |
| Growth rate of designers (G7) (%) | Growth rate of personnel engaged in design innovation activities | |
| Scale (GC) | Design service income (G8) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | Design service income |
| Number of design enterprises (G9) (Qty.) | Number of design enterprises | |
| Number of service enterprises (G10) (Qty.) | Number of service enterprises | |
| Output (GD) | Number of design output transactions (G11) (Qty.) | Number of design service contracts signed |
| Conversion of industrial achievements into output value (G12) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | Output value of industrialization of design output | |
| Number of patents granted (G13) (items) | Number of patents granted in the previous year | |
| Number of design awards at provincial level or above (G14) (items) | Number of design awards at provincial level or above |
| Number of Policy Regulations (G1) (Qty.) | Economic Environment (G2) (RMB) | Innovation Atmosphere (G3) (Qty.) | Design Competitions Held (G4) (Items) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of policy regulations (G1) (Qty.) | 1 | −0.033 | −0.132 | −0.121 |
| Economic environment (G2) (RMB) | −0.033 | 1 | 0.874 * | 0.972 ** |
| Innovation atmosphere (G3) (Qty.) | −0.132 | 0.874 * | 1 | 0.930 ** |
| Design competitions held (G4) (items) | −0.121 | 0.972 ** | 0.930 ** | 1 |
| Number of Full-Time Professionals (G5) (Qty.) | Percentage of Personnel with Intermediate and Senior Professional Titles (G6) (%) | Growth Rate of Designers (G7) (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of full-time professionals (G5) (Qty.) | 1 | 0.900 ** | −0.078 |
| Percentage of personnel with intermediate and senior professional titles (G6) (%) | 0.900 ** | 1 | −0.368 |
| Growth rate of designers (G7) (%) | −0.078 | −0.368 | 1 |
| Design Service Income (G8) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | Number of Design Enterprises (G9) (Qty.) | Number of Service Enterprises (G10) (Qty.) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design service income (G8) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | 1 | 0.949 ** | 0.807 * |
| Number of design enterprises (G9) (Qty.) | 0.949 ** | 1 | 0.816 * |
| Number of service enterprises (G10) (Qty.) | 0.807 * | 0.816 * | 1 |
| Number of Design Output Transactions (G11) (Qty.) | Conversion of Industrial Achievements into Output Value (G12) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | Number of Patents Granted (G13) (Items) | Number of Design Awards at Provincial Level or above (G14) (Items) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of design output transactions (G11) (Qty.) | 1 | −0.757 * | 0.242 | 0.67 |
| Conversion of industrial achievements into output value (G12) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | −0.757 * | 1 | −0.582 | −0.633 |
| Number of patents granted (G13) (items) | 0.242 | −0.582 | 1 | −0.021 |
| Number of design awards at provincial level or above (G14) (items) | 0.67 | −0.633 | −0.021 | 1 |
| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Development environment (GA) | Number of policy regulations (G1) (Qty.) | Financial subsidies and special funds for industries from governments at all levels in Zhejiang Province |
| Design competitions held (G4) (items) | Number of design competitions at all levels held | |
| Human resources (GB) | Number of full-time professionals (G5) (Qty.) | Number of full-time designers |
| Growth rate of designers (G7) (%) | Growth rate of personnel engaged in design innovation activities | |
| Scale (GC) | Number of design enterprises (G9) (Qty.) | Number of design enterprises |
| Output (GD) | Number of design output transactions (G11) (Qty.) | Number of design service contracts signed |
| Conversion of industrial achievements into output value (G12) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | Output value of industrialization of design results | |
| Number of patents granted (G13) (items) | Number of patents granted in the previous year | |
| Number of design awards at provincial level or above (G14) (items) | Number of design awards at provincial level or above |
| Number of Policy Regulations (G1) (Qty.) | Design Competitions Held (G4) (Items) | Number of Full-Time Professionals (G5) (Qty.) | Growth Rate of Designers (G7) (%) | Number of Design Enterprises (G9) (Qty.) | Design Output Transactions (G11) (Qty.) | Conversion of Industrial Achievements into Output Value (G12) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | Number of Patents Granted (G13) (Items) | Number of Design Awards at Provincial Level or above (G14) (Items) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of policy regulations (G1) (Qty.) | 1 | −0.121 | 0.134 | −0.205 | 0.021 | −0.218 | 0.092 | −0.46 | 0.076 |
| Design competitions held (G4) (items) | −0.121 | 1 | 0.886 ** | −0.243 | 0.969 ** | −0.814 * | 0.933 ** | −0.438 | −0.607 |
| Number of full-time professionals (G5) (Qty.) | 0.134 | 0.886 ** | 1 | −0.078 | 0.941 ** | −0.815 * | 0.960 ** | −0.432 | −0.623 |
| Growth rate of designers (G7) (%) | −0.205 | −0.243 | −0.078 | 1 | −0.265 | 0.205 | −0.291 | 0.559 | 0.423 |
| Number of design enterprises (G9) (Qty.) | 0.021 | 0.969 ** | 0.941 ** | −0.265 | 1 | −0.767 * | 0.988 ** | −0.581 | −0.573 |
| Number of design output transactions (G11) (Qty.) | −0.218 | −0.814 * | −0.815 * | 0.205 | −0.767 * | 1 | −0.757 * | 0.242 | 0.67 |
| Conversion of industrial achievements into output value (G12) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | 0.092 | 0.933 ** | 0.960 ** | −0.291 | 0.988 ** | −0.757 * | 1 | −0.582 | −0.633 |
| Number of patents granted (G13) (items) | −0.46 | −0.438 | −0.432 | 0.559 | −0.581 | 0.242 | −0.582 | 1 | −0.021 |
| Number of design awards at provincial level or above (G14) (items) | 0.076 | −0.607 | −0.623 | 0.423 | −0.573 | 0.67 | −0.633 | −0.021 | 1 |
| Number of Policy Regulations (G1) (Qty.) | Growth Rate of Designers (G7) (%) | Number of Design Enterprises (G9) (Qty.) | Number of Patents Granted (G13) (Items) | Number of Design Awards at Provincial Level or above (G14) (Items) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of policy regulations (G1) (Qty.) | 1 | −0.205 | 0.021 | −0.46 | 0.076 |
| Growth rate of designers (G7) (%) | −0.205 | 1 | −0.265 | 0.559 | 0.423 |
| Number of design enterprises (G9) (Qty.) | 0.021 | −0.265 | 1 | −0.581 | −0.573 |
| Number of patents granted (G13) (items) | −0.46 | 0.559 | −0.581 | 1 | −0.021 |
| Number of design awards at provincial level or above (G14) (items) | 0.076 | 0.423 | −0.573 | −0.021 | 1 |
| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Development environment (GA) | Number of policy regulations (G1) (Qty.) | Financial subsidies and special funds for industries from governments at all levels in Zhejiang Province |
| Human resources (GB) | Growth rate of designers (G2) (%) | Growth rate of personnel engaged in design innovation activities |
| Scale (GC) | Number of design enterprises (G3) (Qty.) | Number of design enterprises |
| Output (GD) | Number of patents granted (G4) (items) | Number of patents granted in the previous year |
| Number of design awards at provincial level or above (G5) (items) | Number of design awards at provincial level or above |
| Primary Indicator | Secondary Indicator |
|---|---|
| Innovation input (YA) | Industrial R&D expenditure (Y1) (Unit: RMB 10,000) |
| Industrial R&D personnel investment (Y2) (person/year) | |
| New product development expenses (Y3) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | |
| Innovation output (YB) | New product sales revenue (Y4) (Unit: RMB 10,000) |
| Number of patents granted (Y5) (items) |
| Year | Industrial R&D Expenditure (Y1) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | Industrial R&D Personnel Investment (Y2) (Person/Year) | New Product Development Expenses (Y3) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | New Product Sales Revenue (Y4) (Unit: RMB 10,000) | Number of Patents Granted (Y5) (Items) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 4,891,527 | 203,904 | 6,130,552 | 107,987,720.4 | 9335 |
| 2012 | 5,632,975 | 228,618 | 6,838,103 | 142,207,376 | 12,844 |
| 2013 | 6,539,434 | 263,507 | 7,851,412 | 157,502,317.3 | 15,036 |
| 2014 | 7,328,932 | 290,339 | 8,549,299 | 174,992,037.6 | 16,824 |
| 2015 | 7,928,587 | 316,672 | 8,349,961 | 204,919,010.5 | 17,242 |
| 2016 | 8,962,107 | 321,845 | 9,616,946 | 214,084,546.4 | 19,280 |
| 2017 | 10,427,258 | 333,646 | 11,209,272 | 231,508,850.4 | 21,817 |
| 2018 | 11,396,500 | 394,147 | 12,614,705 | 252,593,555.3 | 27,998 |
| 2019 | 12,332,147 | 451,752 | 14,823,827 | 270,582,619.2 | 30,914 |
| 2020 | 13,345,322 | 480,493 | 16,876,932 | 377,564,365.4 | 35,319 |
| 2021 | 16,290,387 | 482,140 | 23,796,708 | 411,717,093.5 | 41,292 |
| Independent Variable | Regression Coefficient | SD | z Value | p Value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of policy regulations (G1) (Qty.) | 0.038 | 0.024 | 1.569 | 0.117 | −0.010~0.086 |
| Growth rate of designers (G2) (%) | −0.126 | 0.045 | −2.782 | 0.005 | −0.215~−0.037 |
| Number of design enterprises (G3) (Qty.) | 0.216 | 0.062 | 3.487 | 0.001 | 0.095~0.337 |
| Number of patents granted (G4) (items) | 0.157 | 0.071 | 2.23 | 0.026 | 0.019~0.296 |
| Design awards at provincial level or above (G5) (items) | 0.195 | 0.055 | 3.527 | 0.001 | 0.087~0.304 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, B.; Kong, S.; Ying, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Y.; Xu, J. Research on Impact of Design Innovation Factors on Pure Technical Efficiency of Manufacturing Innovation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7230. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167230
Xu B, Kong S, Ying Z, Chen J, Zhang S, Yan Y, Xu J. Research on Impact of Design Innovation Factors on Pure Technical Efficiency of Manufacturing Innovation. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):7230. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167230
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Bing, Siyuan Kong, Zhiyue Ying, Jiayang Chen, Shihao Zhang, Yuting Yan, and Jun Xu. 2024. "Research on Impact of Design Innovation Factors on Pure Technical Efficiency of Manufacturing Innovation" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 7230. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167230
APA StyleXu, B., Kong, S., Ying, Z., Chen, J., Zhang, S., Yan, Y., & Xu, J. (2024). Research on Impact of Design Innovation Factors on Pure Technical Efficiency of Manufacturing Innovation. Sustainability, 16(16), 7230. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167230







