Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Leisure Urban Spaces and the Correlation with Population Activity Intensity: A Case Study of Nanjing, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
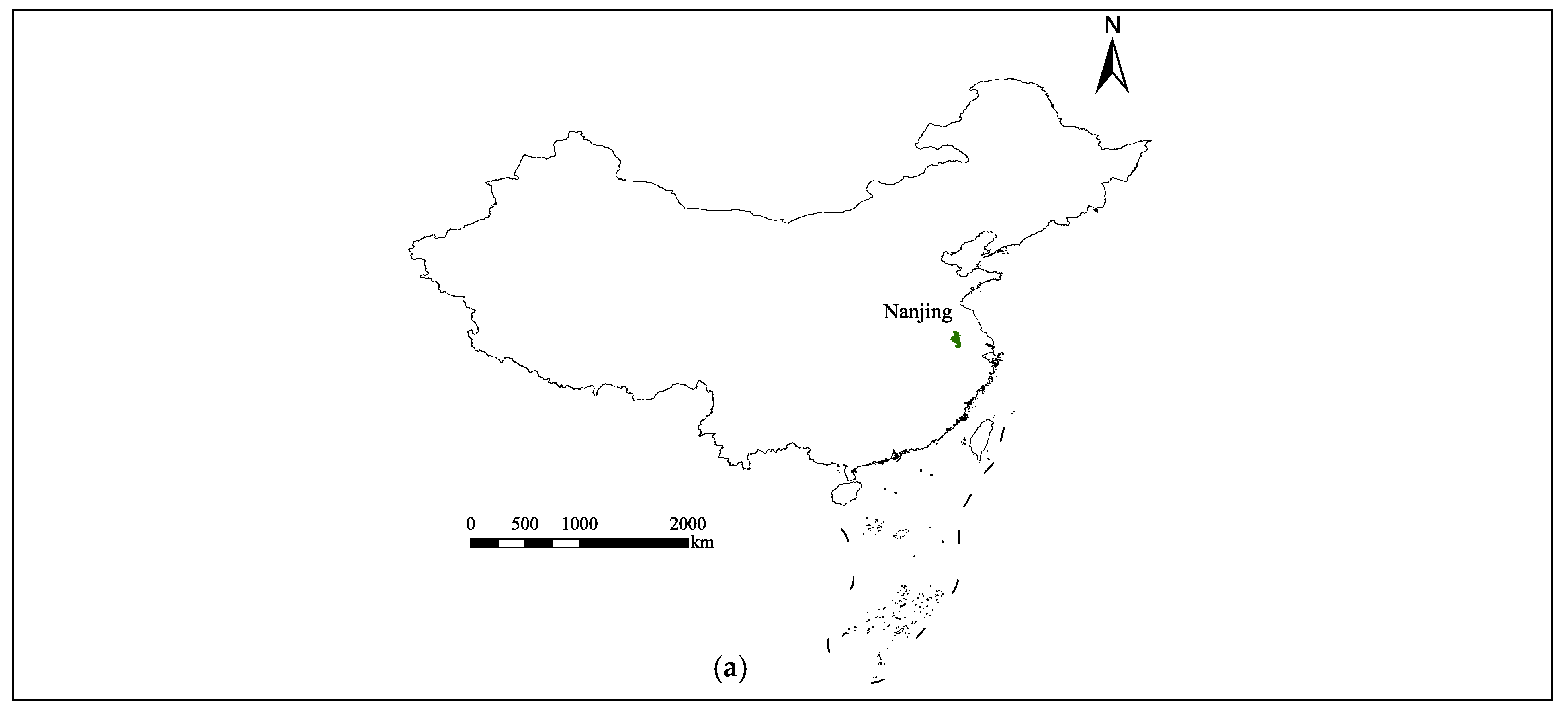
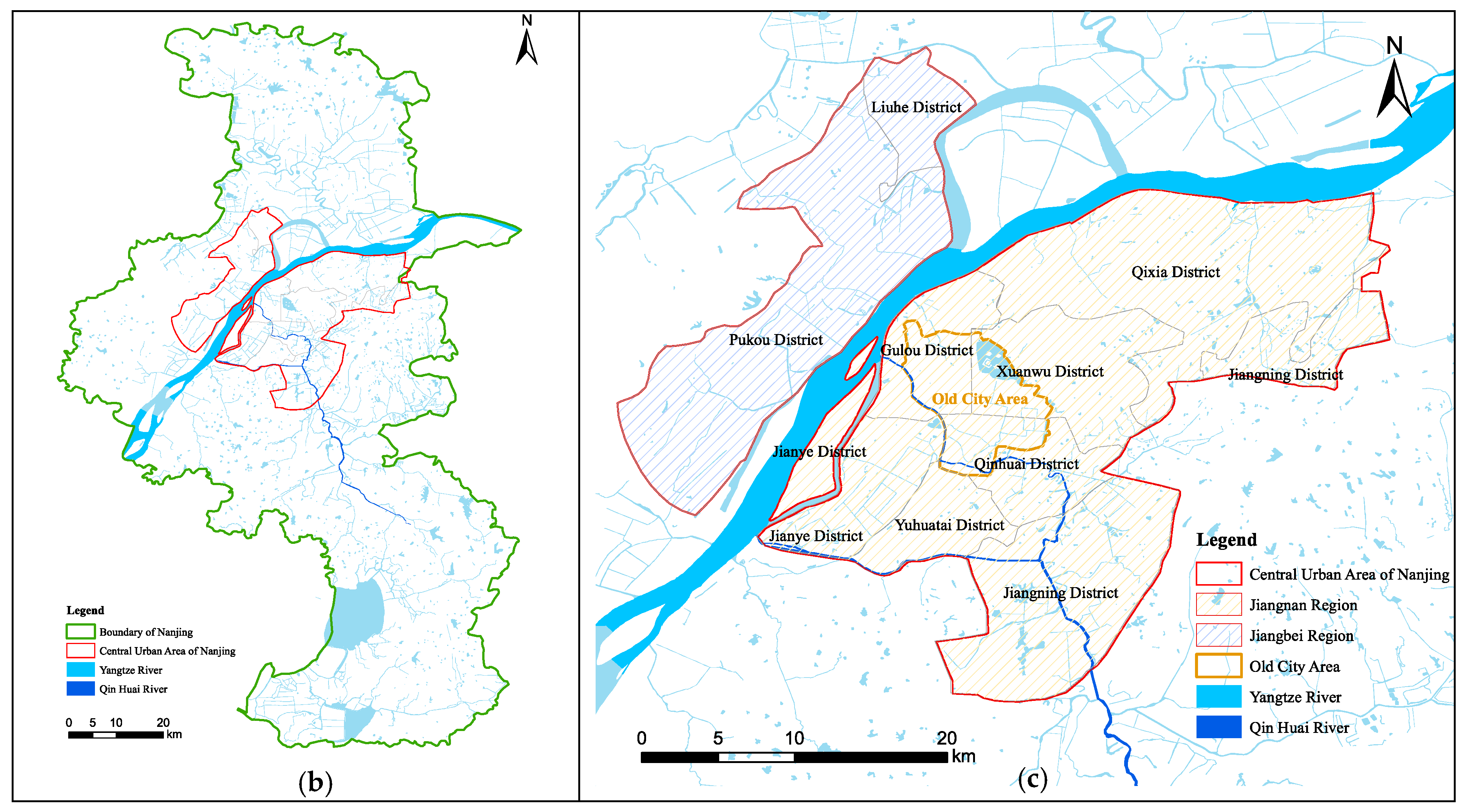
2.1. Study Area
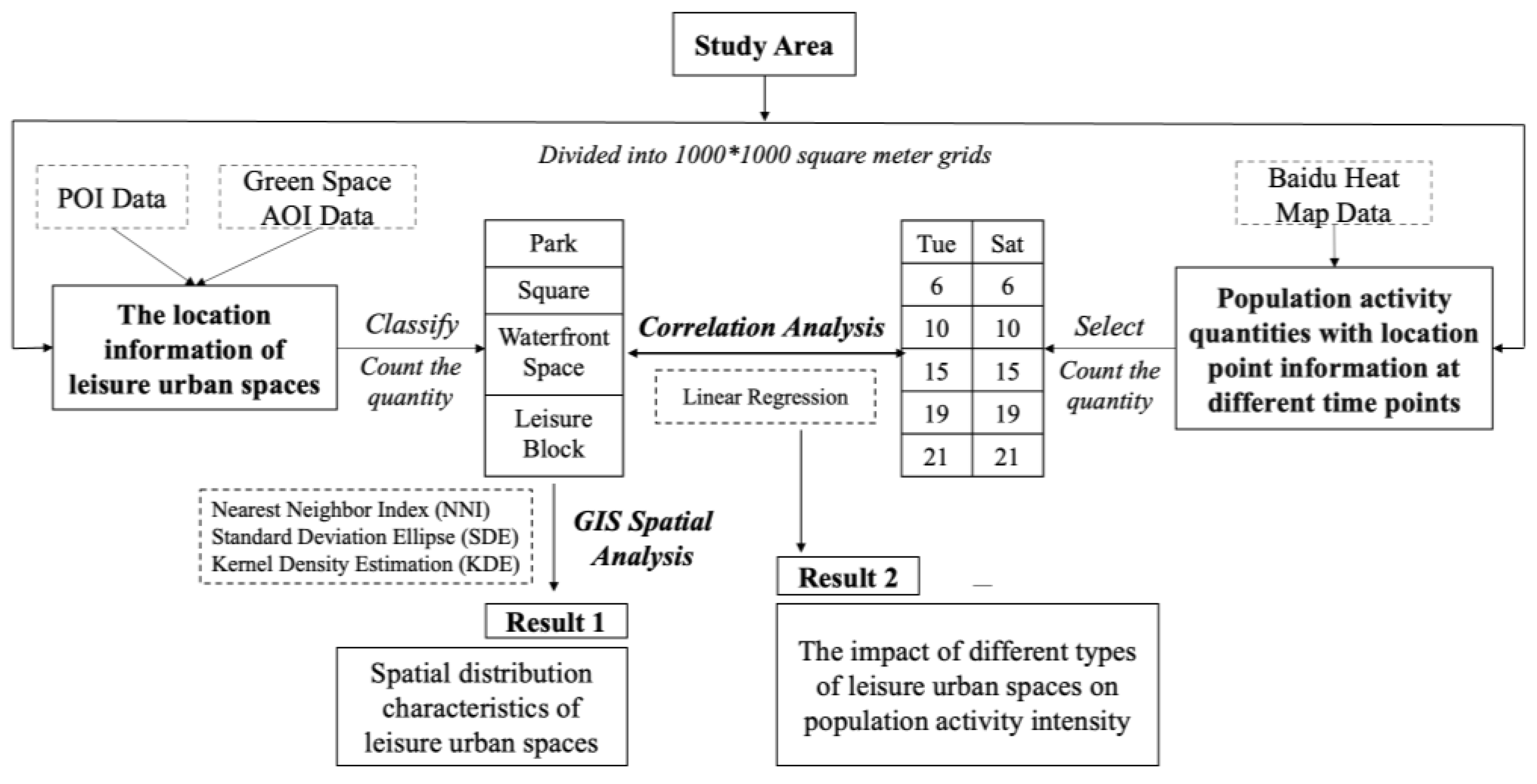
2.2. Analytical Framework
2.3. Data and Pre-Processing
2.3.1. POI Data and AOI Data
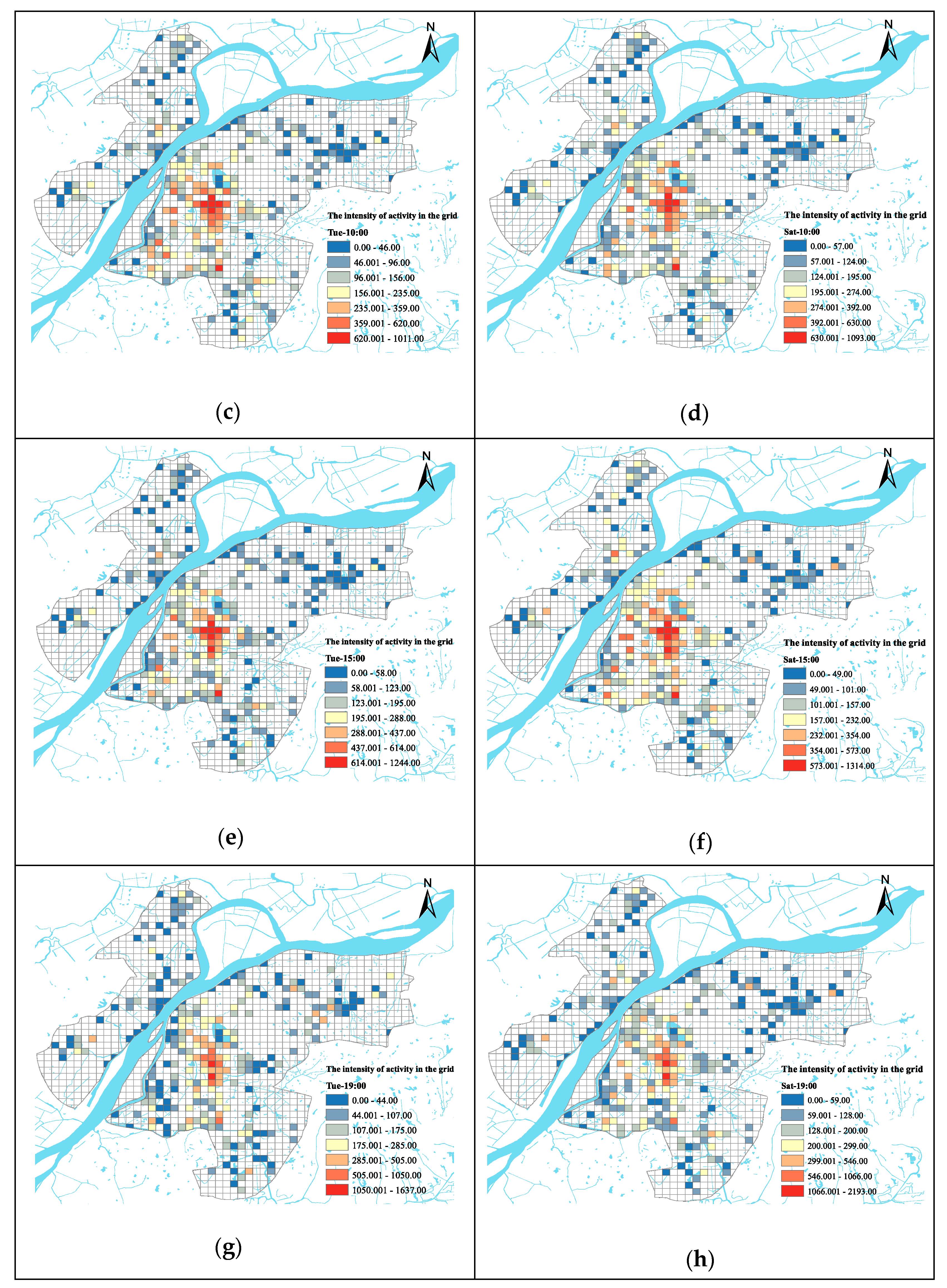
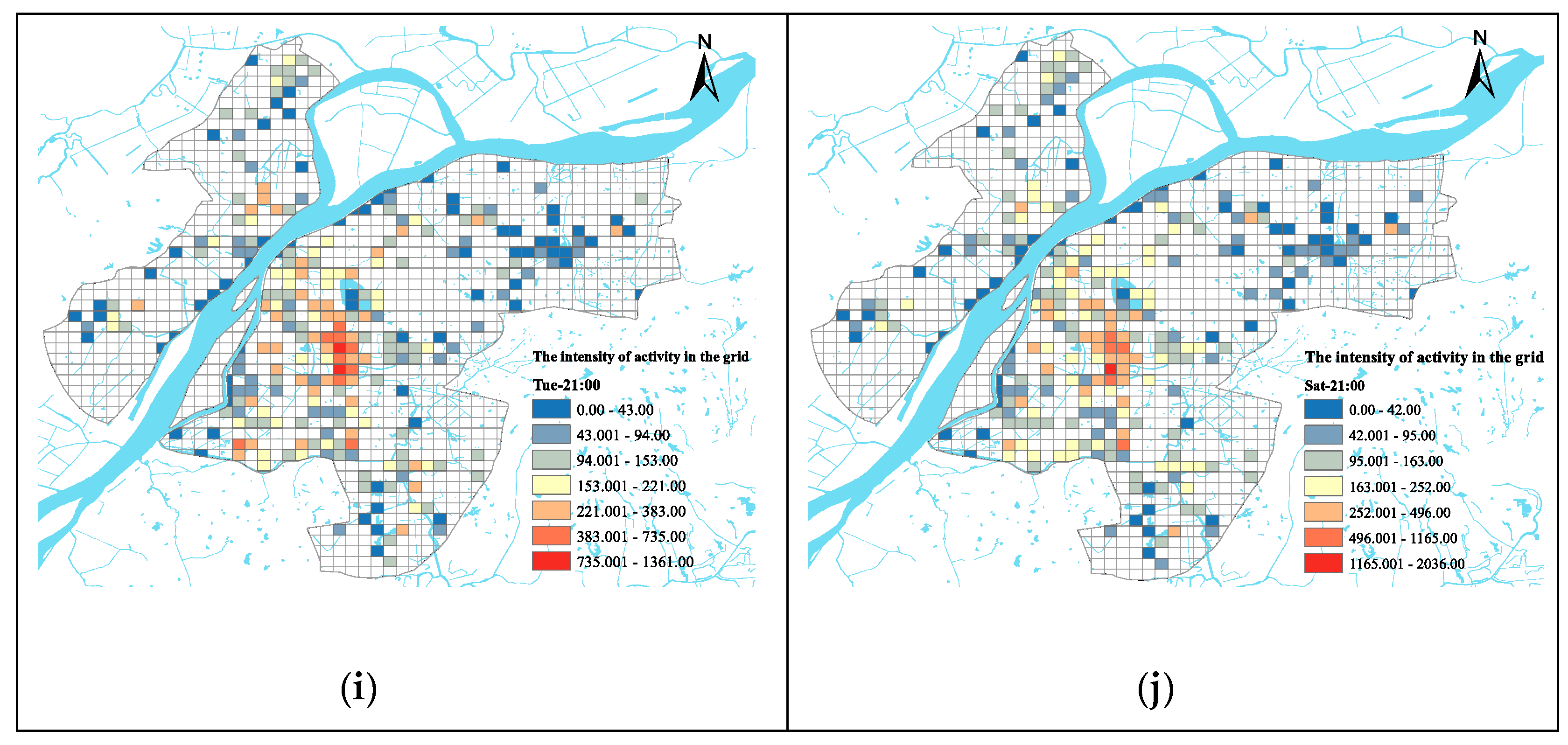
2.3.2. Baidu Heat Map Data
2.4. Research Methods
2.4.1. GIS Spatial Analysis
2.4.2. Correlation Analysis
3. Results
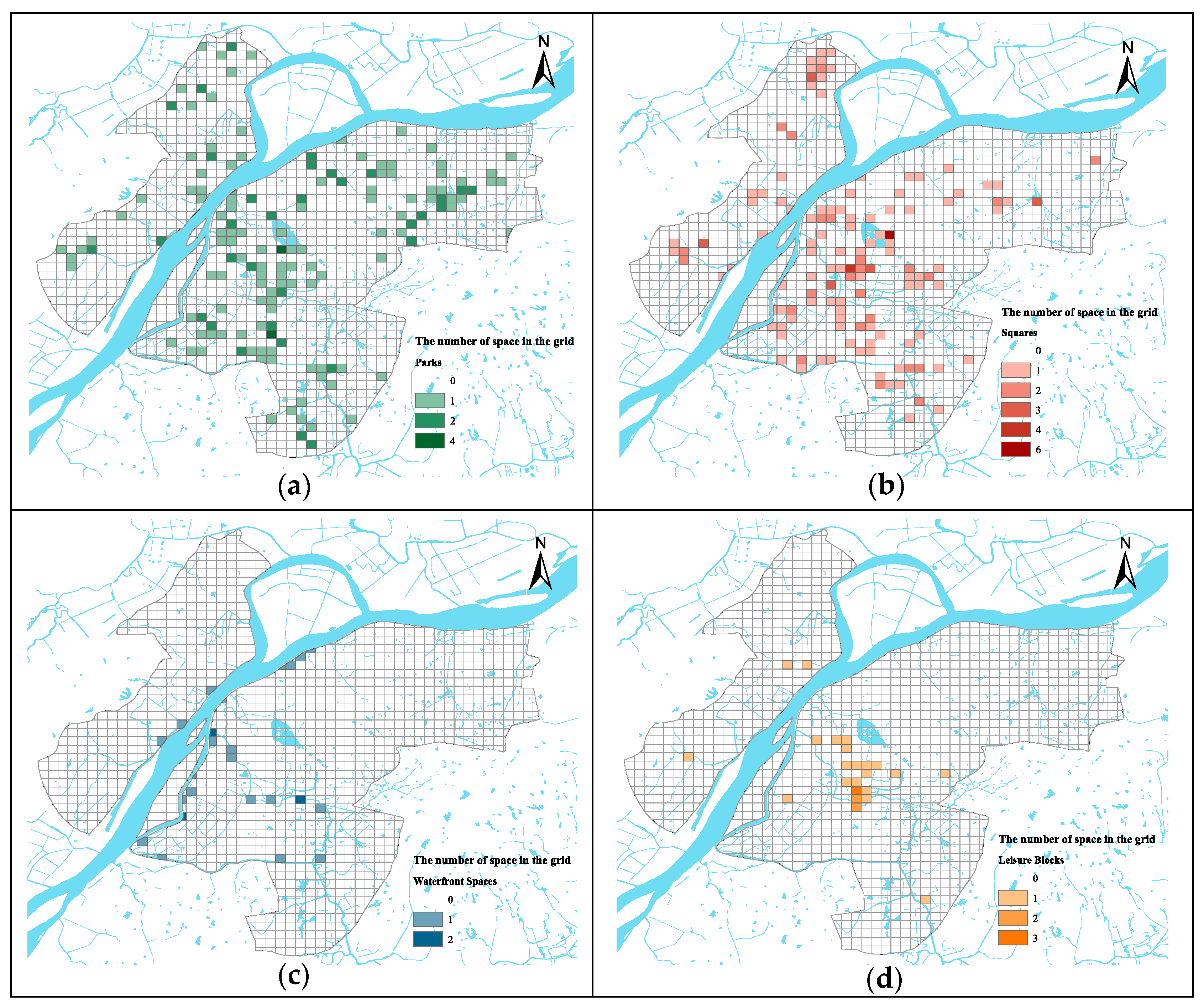
3.1. Distribution Characteristics of Leisure Urban Spaces
3.1.1. Nearest Neighbor Analysis
3.1.2. Standard Deviation Ellipse Analysis
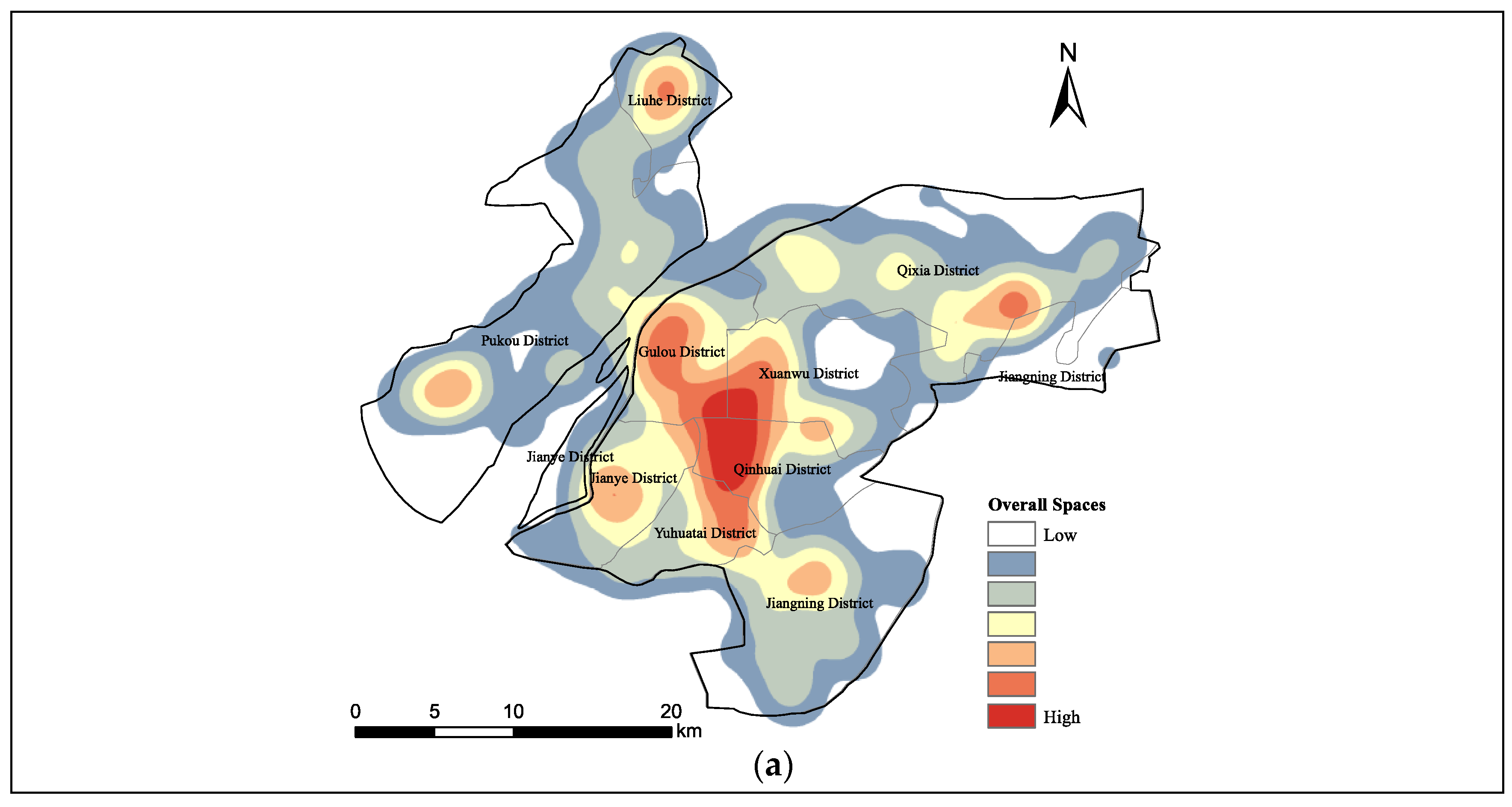
3.1.3. Kernel Density Distribution
3.2. Correlation between the Distribution of Leisure Urban Spaces and the Intensity of Population Activity
4. Discussion
4.1. Clustering Trends and Distribution Patterns of Leisure Urban Spaces
4.2. Impact of Leisure Urban Space Configuration on Residents’ Activity Patterns
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Urban Planning Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corbusier, L.; Eardley, A. The Athens Charter; Grossman Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1973; ISBN 0-670-13970-X. [Google Scholar]
- Lubowiecki-Vikuk, A.; Đerčan, B.M.; de Sousa, B.M.B. Sustainable Development and Leisure Services: Changes and Trends. In Handbook of Sustainable Development Leisure Services; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Ma, Y. How Do Ecological and Recreational Features of Waterfront Space Affect Its Vitality? Developing Coupling Coordination and Enhancing Waterfront Vitality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Research on the Vitality Evaluation of Parks and Squares in Medium-Sized Chinese Cities from the Perspective of Urban Functional Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, M.; Fluehr, J.; McKeon, T.; Branas, C. Urban Green Space and Its Impact on Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.P.; Elliott, L.R.; Gascon, M.; Roberts, B.; Fleming, L.E. Blue Space, Health and Well-Being: A Narrative Overview and Synthesis of Potential Benefits. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, V.; Bamkole, O. The Relationship between Social Cohesion and Urban Green Space: An Avenue for Health Promotion. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Shen, G.Q.; Choi, S. Underlying Relationships between Public Urban Green Spaces and Social Cohesion: A Systematic Literature Review. City Cult. Soc. 2021, 24, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Liao, C.; Nong, H.; Yang, P. Understanding Recreational Ecosystem Service Supply-Demand Mismatch and Social Groups’ Preferences: Implications for Urban–Rural Planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2024, 241, 104903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, I.Y.; Luo, J.; Chan, E.H. Spatial Justice in Public Open Space Planning: Accessibility and Inclusivity. Habitat Int. 2020, 97, 102122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Feng, Z.; Li, J.; Khan, M.S.; Jing, Y. The Distribution and Accessibility of Urban Parks in Beijing, China: Implications of Social Equity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Song, C.; Chan, C.-S.; Pei, T.; Wenting, Y.; Xin, Z. Spatial-Temporal Distribution Characteristics and Evolution Mechanism of Urban Parks in Beijing, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 64, 127265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Xu, G.; Qi, J.; Bao, H. Identifying the Spatial Patterns and Influencing Factors of Leisure and Tourism in Xi’an Based on Point of Interest (POI) Data. Land 2023, 12, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, C. Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of High-Quality Tourist Attractions in Shandong Province, China. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Chen, Z.; Ai, S.; Zhou, J.; Lu, L.; Yang, T. The Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of Urban Cultural and Entertainment Facilities in Beijing. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Duan, L.; Liritzis, I.; Li, J. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Intangible Cultural Heritage in the Yellow River Basin. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 66, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yi Ming, Y.; Shi, B. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Causes of Public Sports Venues in China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Hu, A. Reading and Interpretation of “Classification and Requirements of Urban Public Leisure Spaces”. Pop. Stand. 2014, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mehhdi, R.; Johari, M.Y.M.; Afshin, S. Terminology of Urban Open and Green Spaces. In Proceedings of the 11th ASEAN Postgraduate Seminar (APGS 2017), At Faculty of Built Environment, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, A.M.; Remali, A.M.; MacLean, L. Deciphering urban life: A multi-layered investigation of St. Enoch Square, Glasgow CIty Centre. ArchNet-IJAR 2017, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangi, Z.A.D.; Tanvir, H.; Imtiaz, A.M. Rethinking Urban Water-Front as a Potential Public Open Space: Interpretative Framework of Surma Waterfront. Archit. Res. 2020, 10, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Carmona, M. Public Places Urban Spaces: The Dimensions of Urban Design; Routledge: London, UK, 2021; ISBN 1-315-15845-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Pang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Lu, C.; Tang, X.; Cheng, W. Mapping Urban Spatial Structure Based on POI (Point of Interest) Data: A Case Study of the Central City of Lanzhou, China. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Ye, J.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y. Urban Functional Zone Classification Based on POI Data and Machine Learning. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjing GOV. Natural Conditions. 2023. Available online: https://www.nanjing.gov.cn/zjnj/zrzk/201910/t20191014_1676314.html (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Teng, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, L. Monitoring and Analysis of Population Distribution in China from 2000 to 2020 Based on Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquet, O.; Hirsch, J.A.; Kerr, J.; Jankowska, M.M.; Mitchell, J.; Hart, J.E.; Laden, F.; Hipp, J.A.; James, P. GPS-Based Activity Space Exposure to Greenness and Walkability Is Associated with Increased Accelerometer-Based Physical Activity. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Ge, J. What Drives the Spatial Heterogeneity of Urban Leisure Activity Participation? A Multisource Big Data-Based Metrics in Nanjing, China. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, J.; Shen, P. Revealing the Correlation between Population Density and the Spatial Distribution of Urban Public Service Facilities with Mobile Phone Data. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Gong, A.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, S. Mapping Population Distribution with High Spatiotemporal Resolution in Beijing Using Baidu Heat Map Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Song, P.; Tian, G.; Mayer, A.L. Comparing Human Activity Density and Green Space Supply Using the Baidu Heat Map in Zhengzhou, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Luo, L.; Shen, X.; Xu, Y. Influence of Built Environment and User Experience on the Waterfront Vitality of Historical Urban Areas: A Case Study of the Qinhuai River in Nanjing, China. Front. Archit. Res. 2023, 12, 820–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lu, H.; Zheng, T.; Rong, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Yan, Y.; Tang, L. Vitality of Urban Parks and Its Influencing Factors from the Perspective of Recreational Service Supply, Demand, and Spatial Links. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Li, G. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics and Mechanism Analysis of Urban Population Density: A Case of Xi’an, Shaanxi, China. Cities 2019, 86, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, S.T.; Liu, Y. Spatial Pattern of Leisure Activities among Residents in Beijing, China: Exploring the Impacts of Urban Environment. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjing GOV. The Seventh National Census Data 2021. Available online: https://www.nanjing.gov.cn/zgnjsjb/jrtt/202202/t20220222_3299732.html (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Liu, S.; Long, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H. Quantifying and Characterizing Urban Leisure Activities by Merging Multiple Sensing Big Data: A Case Study of Nanjing, China. Land 2021, 10, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjing GOV. Survey Report on Satisfaction with Urban Parks and Greening in Nanjing. 2021. Available online: https://www.nanjing.gov.cn/hdjl/zjdc/wsdc/202110/t20211021_3165310.html (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Nanjing GOV. Territorial Spatial Master Planning of Nanjing (2021–2035). 2022. Available online: https://www.nanjing.gov.cn/zgnjsjb/jrtt/202210/t20221029_3740005.html (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Luo, S.; Liu, Y.; Du, M.; Gao, S.; Wang, P.; Liu, X. The Influence of Spatial Grid Division on the Layout Analysis of Urban Functional Areas. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pentland, A.; Moro, E. Identifying Latent Activity Behaviors and Lifestyles Using Mobility Data to Describe Urban Dynamics. EPJ Data Sci. 2023, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, P.J.; Evans, F.C. Distance to Nearest Neighbor as a Measure of Spatial Relationships in Populations. Ecology 1954, 35, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qian, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wei, X.; Guang, X. The Influence of Strip-City Street Network Structure on Spatial Vitality: Case Studies in Lanzhou, China. Land 2021, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefever, D.W. Measuring Geographic Concentration by Means of the Standard Deviational Ellipse. Am. J. Sociol. 1926, 32, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Cui, L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Miao, D. Study on the Spatial Variation of China’s Territorial Ecological Space Based on the Standard Deviation Ellipse. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 982734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Lin, A.; Zhou, Z. Evolution of the Pattern of Spatial Expansion of Urban Land Use in the Poyang Lake Ecological Economic Zone. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, A.W.; Azzalini, A. Applied Smoothing Techniques for Data Analysis: The Kernel Approach with S-Plus Illustrations; OUP Oxford: Oxford UK, 1997; Volume 18, ISBN 0-19-154569-4. [Google Scholar]
- Neter, J.; Kutner, M.H.; Nachtsheim, C.J.; Wasserman, W. Applied Linear Statistical Models; McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Cao, X.; Wu, F.; Chen, C. Spatial Pattern and Drivers of China’s Public Cultural Facilities between 2012 and 2020 Based on POI and Statistical Data. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, J.; Ma, Y. Exploring the Relationship between Potential and Actual of Urban Waterfront Spaces in Wuhan Based on Social Networks. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tian, F.; Lin, L.; Fan, J. Study on the Morphological Analysis and Evolution of the Street Network in the Historic Urban Area of Changsha City from 1872–2023. Land 2024, 13, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Liu, C.; Mu, T.; Xu, X.; Tian, G.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, G. Spatiotemporal Fluctuations in Urban Park Spatial Vitality Determined by On-Site Observation and Behavior Mapping: A Case Study of Three Parks in Zhengzhou City, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 64, 127246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Huang, G.; Wu, J.; Guo, X. How Do Travel Distance and Park Size Influence Urban Park Visits? Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 52, 126689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Mi, X.; Wang, Z. Vitality Evaluation of the Waterfront Space in the Ancient City of Suzhou. Front. Archit. Res. 2021, 10, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhu, X.; He, Q. An Assessment of Urban Park Access Using House-Level Data in Urban China: Through the Lens of Social Equity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yue, W.; La Rosa, D. Which Communities Have Better Accessibility to Green Space? An Investigation into Environmental Inequality Using Big Data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 204, 103919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Xiong, J.; Qin, H.; Hu, J.; Deng, J.; Han, G.; Yan, J. Influence of Thermal Comfort of Green Spaces on Physical Activity: Empirical Study in an Urban Park in Chongqing, China. Build. Environ. 2022, 219, 109168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, J.; Schubert, S.; Sauter, T.; Tunn, S.; Schneider, C.; Salim, M. Modelling the Impact of an Urban Development Project on Microclimate and Outdoor Thermal Comfort in a Mid-Latitude City. Energy Build. 2023, 296, 113324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Average Observational Distance (m) | Expected Average Distance (m) | NNI (R) | Z-Value | p-Value | Spatial Distribution Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 612.29 | 1175.94 | 0.52 | −18.5 | 0 | Clustered |
| Parks | 779.13 | 1199.82 | 0.65 | −9.15 | 0 | Clustered |
| Squares | 775.17 | 1346.89 | 0.58 | −10.46 | 0 | Clustered |
| Waterfront Spaces | 1338.97 | 1735.60 | 0.77 | −2.3 | 0.02 | Weakly clustered |
| Leisure Blocks | 1766.75 | 1788.38 | 0.99 | −0.12 | 0.9 | Random |
| Area (Km2) | Center X | Center Y | XStdDist | YStdDist | Rotation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 545.9836 | 118.7848 | 32.0595 | 0.1093 | 0.1087 | 132.4345 |
| Parks | 614.4414 | 118.7989 | 32.0667 | 0.1233 | 0.1084 | 65.9951 |
| Squares | 485.4175 | 118.7855 | 32. 0588 | 0.097 | 0.109 | 159.8054 |
| Waterfront Spaces | 242.0485 | 118.7483 | 32.0497 | 0.0638 | 0.0826 | 23.8854 |
| Leisure Blocks | 275.7554 | 118.7836 | 32.0251 | 0.0439 | 0.1369 | 144.099 |
| Workday | 6:00 | 10:00 | 15:00 | 19:00 | 21:00 |
| Overall | 42.183 *** | 78.741 *** | 64.289 *** | ||
| Parks | −54.468 ** | −26.308 * | |||
| Squares | |||||
| Waterfront Spaces | −22.026 *** | −61.777 ** | −70.212 ** | −70.398 ** | −78.694 ** |
| Leisure Blocks | 25.176 *** | 71.621 *** | 111.947 *** | 217.578 *** | 169.428 *** |
| R2 | 0.203 | 0.142 | 0.25 | 0.455 | 0.511 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.169 | 0.106 | 0.218 | 0.432 | 0.491 |
| F | 6.05 | 3.921 | 7.896 | 19.819 | 24.828 |
| Sig. | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Weekend | 6:00 | 10:00 | 15:00 | 19:00 | 21:00 |
| Overall | 27.577 ** | 51.439 *** | 78.741 *** | 106.303 *** | |
| Parks | −54.468 ** | −57.155 * | |||
| Squares | |||||
| Waterfront Spaces | −15.583 * | −60.389 ** | −69.652 ** | −70.398 ** | −99.07 ** |
| Leisure Blocks | 21.935 *** | 86.784 *** | 125.127 *** | 217.578 *** | 264.931 *** |
| R2 | 0.147 | 0.186 | 0.275 | 0.455 | 0.523 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.111 | 0.151 | 0.245 | 0.432 | 0.503 |
| F | 4.088 | 3.921 | 5.419 | 9.016 | 26.086 |
| Sig. | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Kozlowski, M.; Ismail, S.B.; Salih, S.A. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Leisure Urban Spaces and the Correlation with Population Activity Intensity: A Case Study of Nanjing, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167160
Li X, Kozlowski M, Ismail SB, Salih SA. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Leisure Urban Spaces and the Correlation with Population Activity Intensity: A Case Study of Nanjing, China. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):7160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167160
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinyang, Marek Kozlowski, Sumarni Binti Ismail, and Sarah Abdulkareem Salih. 2024. "Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Leisure Urban Spaces and the Correlation with Population Activity Intensity: A Case Study of Nanjing, China" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 7160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167160
APA StyleLi, X., Kozlowski, M., Ismail, S. B., & Salih, S. A. (2024). Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Leisure Urban Spaces and the Correlation with Population Activity Intensity: A Case Study of Nanjing, China. Sustainability, 16(16), 7160. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167160







