1. Introduction
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is considered a powerful strategic marketing tactic that offers a competitive advantage over rivals [
1,
2]. Consumers’ perceptions of an organization’s CSR programs have a direct impact on their loyalty [
3]. CSR impacts consumer behavior, leading customers to prefer socially responsible companies when evaluating similar products [
2,
4]. The CSR initiatives are exponentially growing globally to boost companies reputations and draw in more consumers [
5]. Companies have acknowledged the importance of CSR in enhancing decision-making for the mutual benefit of all stakeholders [
6]. CSR refers to meeting the expectations of your stakeholders [
1]. Most customers (77%) are driven to support businesses that share their commitment in positively impacting the world [
7].
In addition to affecting how consumers see a company’s performance, loyalty, and faith in the brand, CSR directly affects the financial outcomes for businesses [
8,
9]. Other aspects impacted by CSR include consumer perceptions of trustworthiness and corporate performance [
10,
11]. In most cases, a company’s bottom line will improve if its leaders prioritize social responsibility. CSR initiatives may help businesses improve their public perception [
12] and significantly influence both the public’s awareness and prosperity of a company [
13,
14].
The notion of customer loyalty (CL) has recently emerged as hot subject in academic and professional communities [
15]. Customer satisfaction (CS), Trust (Tr) [
16], and service quality (SQ) [
17] are several key elements that researchers have identified as being influential in consumer loyalty. Loyalty has been the subject of several studies in the Indian setting, although the telecom industry has received very little attention. With a customer base of 1148.43 million, it is crucial to explore the aspects of CSR and CL in the Indian telecommunication sector, which is the world’s second-largest market [
18]. The telecom business is highly dynamic since customers have many alternatives and may easily move to a different service provider [
19]. Companies in India’s telecom industry, such as Jio, Airtel, VodafoneIdea, and BSNL, are often involved in community development initiatives. These initiatives cover a wide range of activities, including promoting education, water purification, and rural development, to name a few. Because of the dearth of studies in the literature on consumer loyalty in this highly unpredictable service sector, the present study addresses that need. Additionally, this study considers the paucity of research on consumer behavior in the telecom industry about the mediating and serial mediation effects of customer loyalty and corporate social responsibility. Customer satisfaction (CS) and trust (Tr) are considered mediators in this study. Furthermore, this study investigates the function of consumer satisfaction and customer trust as sequential mediators of CSR, SQ, and CL. To fill the gap in the existing research, the following research questions are addressed in the present study:
Do CSR and SQ affect customer loyalty?
Do CS and Tr mediate the relationship between CSR, SQ, and CL?
Do demographic factors impact the relationship between CSR and CL?
1.1. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
In the existing literature, CSR is characterized in numerous ways, from a requirement [
20] to the expectations of stakeholders that it factors into the triple bottom line of environmental, social, and economic performance. The European Union (EU) defines CSR as “a concept whereby companies integrate social and environmental concerns in their business operation and in their interaction with their stakeholders voluntarily” [
21]. A significant idea in the realm of CSR is the relationship between businesses and society. Scholars have spent the last three decades investigating the causes and effects of CSR and its various dimensions, i.e., customer loyalty, customer trust, and customer commitment [
22,
23,
24]. CSR has developed into a widely discussed topic in several disciplines, including business [
25,
26], management [
27], and sociology [
25,
26]. The current understanding of CSR [
28] “captures a perspective in which a business sees added value in serving a wider array of societal needs and expectations and perceiving net benefits to flow from socially responsible action”. Consulting services focusing on CSR reputation and communication strategies are in high demand among Fortune 500 companies due to the prominence of this issue for these businesses [
29].
1.2. Customer Loyalty (CL)
The research into customer loyalty has largely progressed along two main lines: behavioral, which examines how frequently and for how long customers buy a given brand, and attitudinal, which refers to the range of client loyalty, ranging from the most devoted to the least devoted [
30]. The behavioral approach has been criticized for failing to differentiate between genuine and situational forms of loyalty. In contrast, the attitudinal approach has been criticized for being less effective in revealing the true nature of loyalty. Scholars recommend combining the two methods [
31,
32,
33] to compensate for their respective limitations and yield a more nuanced understanding of customer loyalty.
1.3. Service Quality (SQ)
Providing excellent service is essential for keeping existing customers acquiring new ones and even luring rivals’ consumers [
34,
35]. The term “service quality” directs attention to how satisfied a client is with the service regarding its consistency, timeliness, and responsiveness [
36]. Customers may trust that their demands are being considered and that their service provider can meet those needs if they consistently deliver and maintain high quality. This eventually enables clients to create higher faith in the company’s reliability and the standards of the services provided. In the telecommunications and mobile service industries, for instance, research has shown that higher service quality leads to more trust on the part of customers [
36].
1.4. Customer Satisfaction (CS)
The satisfaction level of customers is determined by weighing their “actual” experiences against their “perceived” ones [
37]. Customer satisfaction indicates contentedness [
38]. Customer satisfaction was described as “the positive response of customer fulfillment” [
39]. Customer satisfaction is an assessment made after consumption [
40]. Furthermore, it was observed that customer happiness is a significant element in the marketing literature and can be used to indicate a company’s achievement [
41].
1.5. Consumer Trust (Tr)
Customers’ trust is essential if you want to win their loyalty [
42]. Several studies [
43,
44,
45] have corroborated that trust is pivotal for understanding consumer loyalty. Empirical research has shown that trust acts as a crucial intermediary between business actions and customer loyalty [
43,
44], lending credence to the centrality of relationship marketing theory in marketing science. Furthermore, trust is crucial to establishing connections in the hospitality sector. Several studies, [
46,
47] among others, have demonstrated that trust is a significant factor in fostering loyalty.
1.6. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
1.6.1. Customer Loyalty and Corporate Social Responsibility
CSR represents the pre-eminent strategy for augmenting brand loyalty [
48]. Customers might find it hard to choose when competing telecommunications companies provide identical offerings. Thus, a correlation has been identified between CSR initiatives and customer satisfaction with the products or services of a business [
49,
50,
51,
52,
53]. CSR was positively related to consumer loyalty [
41,
54]. Some scholars feel that CSR activities do not improve loyalty [
55], even though they are among the most significant techniques for emphasizing firm policies that conform with society’s values [
56]. CSR has a causal link to repeat business from existing customers [
57]. Therefore, our working hypothesis for this line of inquiry is as follows:
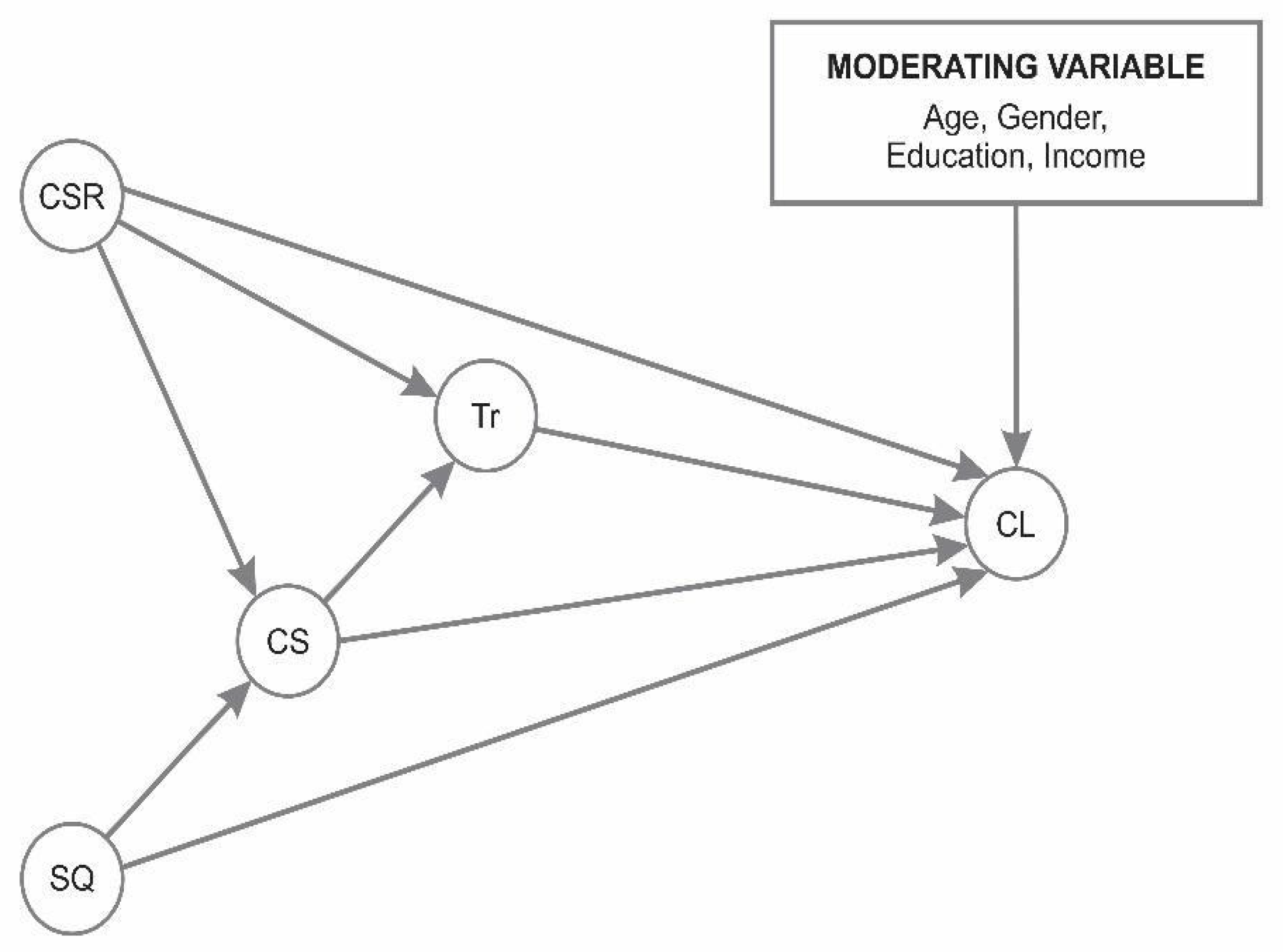
H1: There is a significant positive impact of CSR on CL.
1.6.2. Service Quality and Customer Loyalty
A positive association exists between service quality (SQ) and client loyalty in five service industries [
58]. The research substantiates this concept by demonstrating that when consumers have a favorable perception of the service they receive, they are more inclined to engage in choices that contribute to the company’s long-term prosperity [
59]. Although a positive relationship was found between service quality and customer loyalty in a hospitality industry study [
60], no significant relationship was found in a study of Indonesian bank customers [
61]. We postulate the following to examine this mystery further:
H2: There is significant positive impact of SQ on CL.
1.6.3. CSR and CS, Tr
Companies undertake ethical and socially responsible measures to demonstrate their dedication to society [
62] and enhance their reputation among the general public [
63]. For instance, it was discovered that CSR is widely recognized as one of the most impactful and efficient strategies to inspire confidence in a company [
64]. In other words, trust is “the expectation of ethically justifiable behaviour” [
65]. Furthermore, CSR seems to be the primary precursor to ethical capital [
24,
66]. Companies that engage in CSR regularly report increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, market value, and positive brand image [
16]. Increasing client trust and improving the company’s reputation are two benefits of operating a business ethically [
67]. Customers’ trust is influenced by how they see the company’s CSR efforts.
H3: There is a significant positive impact of CSR on Tr.
Most researchers fall short when asked to define their notion of satisfaction [
68]. While customer satisfaction can be conceptualized as an affective condition that arises from an evaluation of a product or service and the subsequent response of an individual [
69], it is only possible to achieve in its entirety by giving top priority to customers’ wants and needs [
70]. According to [
71], a customer’s happiness level is affected by the emotional and logical processing of their interactions with the business.
CSR aims to help businesses realize financial and other benefits through doing the right thing by their stakeholders. However, consumers need special attention, as CSR efforts considerably influence consumer-based outcomes [
72]. According to recent research [
73], customers are more likely to be pleased with goods produced by socially responsible businesses. Service quality and brand attitude are two areas where customer satisfaction is positively affected by CSR [
8,
74].
H4: There is a significant positive impact of CSR on CS.
1.6.4. SQ and CS
Substantial studies have demonstrated a direct correlation between high-quality service and satisfied clients. Any business that values its clients enough to invest in maintaining a long-term connection with them will work hard to ensure their complete satisfaction. Multiple studies have demonstrated that SQ precedes and drives CS [
75,
76]. There are only a few studies in the service industry which are indicative of the existence of a strong and positive association between SQ and CS [
53,
61,
77,
78].
H5: There is a significant positive impact of SQ on CS.
1.6.5. CS and Tr on CL
Trust is an important concept in the marketing and consumer behavior literature for establishing a lasting partnership [
79,
80]. Trust is the cornerstone of any healthy relationship, as stated by [
81]. Customers’ impressions of the value of the services they receive are influenced by their confidence level in the telecom industry [
45], which impacts their loyalty to the service provider. Keeping customers happy over time takes careful relationship management from telecom providers [
82,
83]. Customer trust is a primary explanation for brand loyalty [
43]. According to the study of [
42], a company’s success depends on its potential to earn the trust and loyalty of its clients. In the service sector, trust is essential to developing connections. Studies have shown that trust is crucial to establishing and maintaining consumer loyalty [
11,
46]. Previous studies [
81,
84] have found that trust between a business and its client is a key factor in the retention of clients.
H6: There is significant positive impact of Tr on CL.
There is consensus in the marketing literature that happy consumers are more loyal consumers. Customers’ emotional evaluations of pleasure are integral to developing their loyalties [
85]. Several researchers have substantiated the positive correlation between customer satisfaction and customer loyalty [
86,
87,
88,
89,
90,
91]. Other scholars have discussed the link between customer satisfaction and loyalty, highlighting the distinct nature of the two terms [
92,
93]. According to their feedback, satisfied customers are the most loyal.
Satisfied customers are likelier to repurchase and refer others [
87]. A loyal client base has been shown to have a direct correlation with a high degree of customer satisfaction, as many studies have proved. This motivates the following hypothesis:
H7: There is a significant positive impact of CS on CL.
1.6.6. CS and Tr
Trust is a pivotal determinant in consumer satisfaction, as indicated by numerous studies [
41]. Placing trust in an organization entails having confidence in its dependability and openness. Customers generally hold a negative perception of telecommunications service providers due to their belief that these organizations partake in unethical practices, including charging for superfluous services, disclosing customer information, and implementing complex policies. Therefore, earning consumers’ confidence in the telecommunications sector is challenging. As a result, customer satisfaction is a paramount determinant of customer trust [
94], a critical element in establishing a prosperous, enduring alliance. According to the research of [
95], there is an inextricable link between happy consumers and trust in online retail. Consequently, [
45,
84] discovered that an association exists between customer satisfaction and consumer trust. Hence, we propose the following hypothesis for further examination:
H8: There is significant positive impact of CS on Tr.
1.6.7. Mediation-Corporate Social Responsibility, Customer Satisfaction, Trust, and Consumer Loyalty
Customers are a top priority for businesses that already have them, according to marketing professionals [
96]. Researchers have investigated this relationship and found that it has negative implications for CSR [
97]. After discussing how CSR is supposed to affect consumer happiness and customer loyalty, this literature review proposes that CS might mediate between CSR and CL. Customers’ satisfaction, as stated by [
41], may operate as a go-between for brand loyalty and CSR. According to academics and industry professionals [
73,
98], CL plays a pivotal role in moderating consumers’ actions. Indirectly, CSR impacts consumer retention and loyalty. So, it seems safe to assume the following:
H9: Customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between CSR and CL.
Previous research has demonstrated that consumer trust will affect customer loyalty [
99]. Another study revealed that CSR influences people’s trust [
63]. Information on the company’s transparency and honesty is typically included in CSR plans [
16]. Consumers are inclined to develop enduring relationships with businesses when they are well-informed on CSR practices demonstrating support for the sector’s sustainable environment. Trust is a possible mediator between CSR and CL [
41]. This leads us to hypothesize the following:
H10: Trust mediates the relationship between CSR and CL.
1.6.8. Mediation-Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction, and Consumer Loyalty
In earlier studies, [
100,
101] put out the disconfirmation hypothesis, which states that CS performs a mediating role between SQ and CL. The evidence in the literature lends credence to the concept that the connection between the quality of service and loyalty could potentially be influenced by consumer satisfaction. For instance, it has been hypothesized that customer satisfaction plays a pivotal role in mediating the relationship between service quality and customer loyalty in the Bangladeshi telecommunications sector [
102]. The association between SQ and CL was found to be mediated by CS in a study of Indonesian bank customers [
61]. The mediating role of customer satisfaction in the relationship between service quality and customer loyalty has been established in prior research [
77,
78]. This leads to the following hypothesis:
H11: Customer satisfaction mediates the relationship between SQ and CL.
1.6.9. Serial Mediation–Role of Serial Mediation of CS and Tr
Establishing a foundation of trust can foster an enduring correlation between the marketing literature and consumer behavior [
79]. Trust is among the most essential characteristics of an enduring relationship [
81]. Consumers’ commitment to a company can be influenced by customer feedback, crucial in the service industry [
45]. A reliable metric for managing customer interactions in the telecom industry is customer loyalty [
82]. Consumer trust explains customer satisfaction [
43]. According to previous research, customer trust in the market is crucial to fostering brand loyalty [
81].
Unhappy clients have concluded that certain telecom providers have disguised their costs and have murky practices. This makes it difficult for the telecom industry to win over the public’s trust. Customer satisfaction with CSR initiatives was studied by [
97]. When a business engages in CSR, customers are happier with the brand. Positive CSR initiatives have increased consumer satisfaction, brand loyalty, positive word-of-mouth, and repeat business. Sustainability practices are typically crucial for customers in determining whether they are happy with a business’s services [
52]. Loyalty among customers is positively correlated with an organization’s emphasis on meeting their requirements and values [
50].
H12: The relationship between corporate social responsibility and customer loyalty is serially mediated by customer satisfaction and customer trust.
Since a company’s development is mostly dependent on the quality of its service and the contentment of its consumers, these two factors are crucial to any enterprise’s success [
103]. Previous research has established that high-quality service is a precursor to happy customers [
76,
104]. When it comes to maintaining loyal customers, few things are more important than their level of happiness [
94]. Customer trust is pivotal to the accomplishment of any relationship marketing campaign [
105]. Customers without faith in the company’s products or services are unlikely to remain loyal [
106]. There are several research studies that indicate the favorable association between trust and CL [
107,
108]. Therefore, it is crucial to grasp if CS and Tr serially mediate SQ and CL.
H13: The relationship between service quality and customer loyalty is serially mediated by customer satisfaction and customer trust.
4. Discussion
The data were obtained for the current investigation from India’s telecom sector. The purpose of collecting data from this sector was to evaluate if the CSR activities and service quality offered by the telecom companies in India have any impact on the customers’ loyalty. The telecom sector in India has observed massive growth in recent years in terms of investments, subscribers, and data consumption [
123]. The option of changing service providers without changing the mobile number has brought a revolution in the industry, and the pressure is between service providers on offering better services than their competitors. A customer may shift from one service provider to another in just a few steps if a customer is unhappy, which has put the telecom industry in a tough space. Studies have indicated that the cost of obtaining a new client is significantly higher, ranging from five to twenty-five times, compared to the cost of retaining an existing customer [
124], and at the same time, increasing customer retention rates by 5% increases profits by 25% to 95% [
125].
The results from the sample revealed that CSR does not have direct impact on CL which is supported by a study conducted on Pakistani banking customers [
82], Indian FMCG customers [
9], and Saudi Arabian banking customers [
126]. A possible justification for no relationship between CSR and CL was given by [
52] who suggested that customers might not consider the CSR activities performed by the companies. The telecom companies spend huge amounts of money in the form of CSR but their inability to communicate and persuade their customers might be another reason. The finding is contrary to studies conducted by [
50,
127] who found a direct and significant relationship between CSR and CL in the Pakistani and Libyan telecom industry.
In contrast to other studies, this one refines the holistic model by using mediators simultaneously. It was found that there exists an indirect impact of CSR on CL mediated through CS and Tr which is supported by the existing literature [
41,
50]. The mediation of CS and Tr may be explained by social identity theory [
128] which may be explained in the manner by which people come to see themselves as part of a community and how this sense of belonging shapes their outlook and actions. Therefore, the inclination of customers is more towards companies which are indulged in the CSR activities.
The study further explored the relationship between SQ and CL and positive significant relationship was observed which is supported by previous studies [
129,
130]. Since customer loyalty is directly proportional to customer happiness, it stands to reason that providing better service will lead to happier and more loyal customers. Customer Satisfaction was employed as the mediator between SQ and CL and a positive significant relationship was observed. Building internal loyalty, or the loyalty of employees, is usually the first step in improving service quality. It is believed that fostering internal loyalty among employees can enhance their customer service [
131], leading to consumer satisfaction and loyalty towards the industry or service provider. Hence, the confirmation from prior research conducted on their association remains valid, highlighting that as the quality of service improved, the levels of customer satisfaction also grew [
132,
133,
134].
A positive significant relationship was observed between CSR and CS and CSR and Tr in this study which aligned with previous studies [
29,
84]. This positive relationship may be interpreted by understanding that when customers observe that a company is socially responsible in its operation and is also indulging in CSR activities, their trust and satisfaction in the company increases.
Our research revealed that when a customer is offered good service quality, the satisfaction level of the customer increases which then increases the customers’ trust in the service provider and influences the customer’s loyalty intentions and this is reflected in the positive significant relationship between Tr and CL which is supported by the previous studies conducted in the banking sector [
135], the tourism sector [
136], and in the mobile telecommunication sector [
137]. The satisfaction of customers with organizational products has a direct impact on their trust and loyalty [
138]. The findings of our study also suggest that there is a positive significant relationship between CS and CL which corroborates the findings of [
139,
140] as customers are more likely to remain loyal to a company when they are satisfied with the services they receive, which is where customer loyalty is attained.
Our study corroborates the findings of [
141,
142] that there exists a positive significant relationship between CS and Tr which suggests that when a customer is satisfied with the services provided to them, they feel they have made the correct choice. Hence, they develop a positive trust in the service provider, and they suggest the same service providers to others as they are satisfied and have trust.
The analysis of the moderating effects indicates that income is the only sociodemographic variable that significantly moderates the relationship between CSR and CL which is supported by the earlier findings [
143]. But no moderation effect of any of the sociodemographic variables was observed between SQ and CL. The results of the moderating effects suggest that enhancements in CSR result in amplified changes in customer loyalty, specifically among high-income customers.
5. Conclusions
Our study contradicted the findings of the earlier studies and due to the conflicting conclusions, this study provides more value in terms of the model’s explanatory power, suggesting that there are more channels that connect CSR to customer loyalty while the relation between SQ and loyalty was found to be significant. The mediation analysis depicted that the inclination of customers trends more towards those companies which engage in CSR activities, which is explained by social identity theory.
The main contribution of the authors is in the analysis of the impact of the sociodemographic factors on the overall model. The results of MGA confirmed that income was one of the factors which moderates the overall model, and enhancements in CSR result in amplified changes in customer loyalty specifically for affluent customers. This can be attributed to the fact that when customers achieve financial stability, they begin to place their trust in companies that actively engage in social development initiatives. Hence, mobile carriers in India might employ this discovery to develop CSR programs that would appeal to a larger number of loyal consumers.
6. Implication
This research contributes to the current body of knowledge on corporate social responsibility and its impact on marketing strategies and customer loyalty in several significant ways. First, it contributes to the existing scant literature on how CSR in the telecom industry increases customer loyalty. In particular, the present study lends credence to the idea that CSR does not have an immediate effect on consumer loyalty. This study adds to the current body of research by demonstrating that CS and trust act as mediators in the relationship between CSR and CL, as well as between SQ and CL. In addition, this study is the first known research in the field of the telecom industry in India to take into account the moderating effect of demographic variables.
In the context of managerial implications, this study can assist the decision makers of the telecom companies in the careful implementation of their CSR activities as it has been observed that CSR has indirect effects on the loyalty of customers. Our research indicates that customers value and compensate businesses who participate in CSR initiatives, and that modern consumers are more knowledgeable about how businesses operate than in the past. Managers at large companies would do well to view CSR as a relationship-building strategy.
7. Limitation
The primary limitation of this study is the model was tested for four demographic variables, i.e., age, gender, education, and income. The future studies can be extended to recharge plan (price), occupation, region, and travel motivation. This study could provide more productive results if importance performance analysis (IPMA) can be conducted with respect to customer analysis. Also, in future, the fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) technique can be used to identify the sufficient and necessary combination of independent variables to achieve the best customer loyalty.