Effect of Soil Erosion on Soil and Plant Properties with a Consequence on Related Ecosystem Services
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
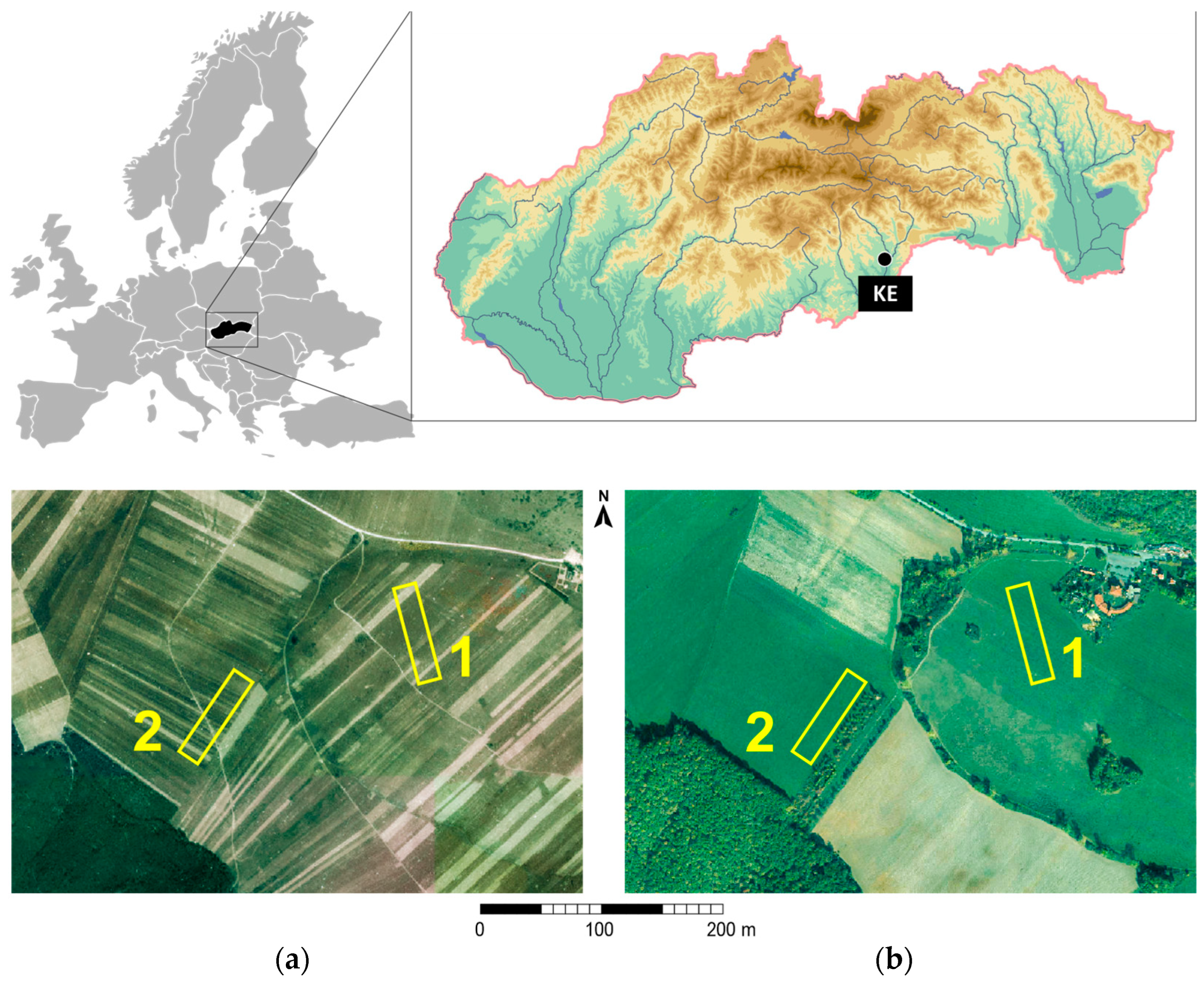
2.1. Sites Description
2.2. Soil and Plant Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Soil Loss Rate Calculation
2.4. Estimation of Soil Ecosystem Services Using Models
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
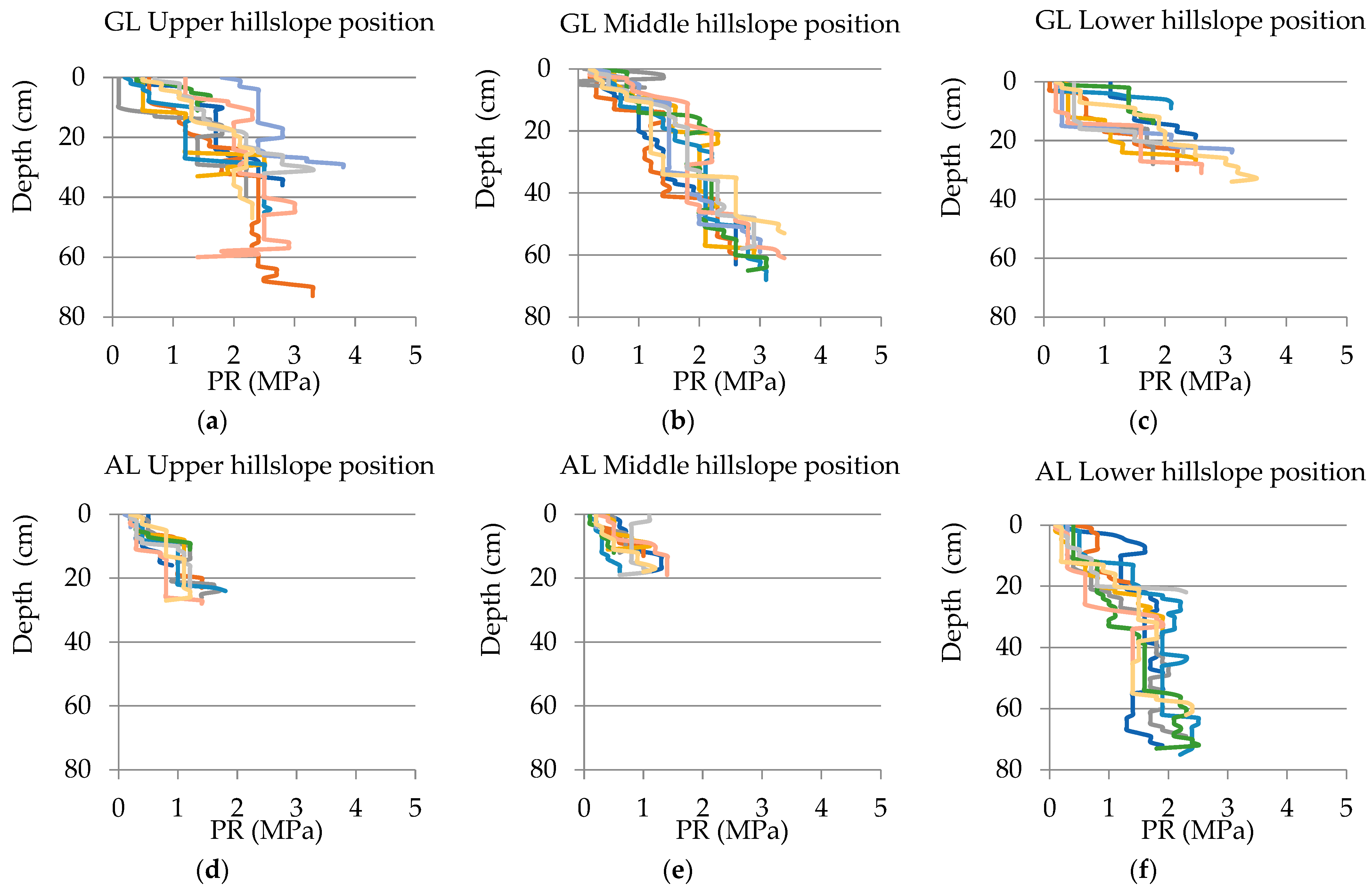
3.1. Basic Soil Physical and Chemical Properties under Different Land Use, Hillslope Position, and Soil Depth
3.2. Grassland and Silage Maize Properties and Content of Nutrients with Different Hillslope Positions
3.3. Relationships between Soil and Plant Properties
3.4. Annual Soil Loss by Water Erosion
3.5. Potential of Soil Ecosystem Services Affected by Water Erosion
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil and Plant Properties Affected by Water Erosion
4.2. Ecosystem Services Affected by Water Erosion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer., L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schütt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuo, D.; Xu, M.; Gao, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S. Changed surface roughness by wind erosion accelerates water erosion. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swezey, S.C.; Fitzwater, B.A.; Whittecar, G.R.; Mahan, A.A.; Garrity, C.P.; González, W.B.A.; Dobbs, K.M. The Carolina Sandhills: Quaternary eolian sand sheets and dunes along the updip margin of the Atlantic Coastal Plain province, southeastern United States. Quat. Res. 2016, 86, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Yu, Y. Natural and anthropogenic rates of soil erosion. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.D.; Bouma, J.; Wallinga, P.T.; Smith, P.; Cerda, A.; Montanarella, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Pachepsky, Y.; van der Putten, W.H.; Bardgett, R.; et al. The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Soil 2016, 2, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, A.J.T.; Fullen, M.A.; Jorge, M.d.C.O.; Bezerra, J.F.R.; Shokr, M.S. Slope processes, mass movement and soil erosion: A review. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, R.G.; West, A.J. Mountains, erosion and the carbon cycle. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalise, D.; Kumar, L.; Kristiansen, P. Land degradation by soil erosion in Nepal: A Review. Soil. Syst. 2019, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Spinoni, J.; Meusburger, K.; Michaelides, S.; Beguería, S.; Klik, A.; Petan, S.; Janeček, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Mapping monthly rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 79, 1298–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poręba, G.J.; Śnieszko, Z.; Moska, P. Influence of pedon history and washing nature on luminescence dating of Holocene colluvium on the example of research on the Polish loess areas. Quat. Int. 2013, 296, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porder, S.; Johnson, A.H.; Xing, H.X.; Brocard, G.; Goldsmith, S.; Pett-Ridge, J. Linking geomorphology, weathering and cation availability in the Luquillo Mountains of Puerto Rico. Geoderma 2015, 249, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halecki, W.; Kruk, E.; Ryczek, M. Evaluation of water erosion at a mountain catchment in Poland using the G2 model. Catena 2018, 164, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, E.A.; Larsen, I.J.; Yu, Q. The extent of soil loss across the US Corn Belt. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 118, e1922375118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilček, J.; Koco, Š. Integrated index of agricultural soil quality in Slovakia. J. Maps 2018, 14, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobza, J.; Barančíková, G.; Makovníková, J.; Pálka, B.; Styk, J.; Širáň, M. Current state and development of land degradation processes based on soil monitoring in Slovakia. Agriculture 2017, 63, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessert, A. Geomorphology of the Slovak Karst (Eastern Part). J. Maps 2016, 12, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, J.; Elečko, M.; Pristaš, J.; Reichwalder, P.; Snopko, L.; Vass, D.; Steiner, A. A Legend to the Geological Map of the Slovak Karst in 1:50,000; Geological Institute of Dionýz Štúr: Bratislava, Slovakia, 1997; 255p. (In Slovak) [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.isric.org/sites/default/files/WRB_fourth_edition_2022-12-18.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Kobza, J.; Barančíková, G.; Dodok, R.; Hrivňáková, K.; Makovníková, J.; Styk, J.; Širáň, M. Monitoring and Evaluation of Soil Properties in Slovakia and the Potential of Their Development; Soil Science and Conservation Research Institute: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2013; 184p. (In Slovak) [Google Scholar]
- Klika, J.; Novák, A.; Gregor, A. Practical Lessons in Phytocenology, Ecology, Climatology and Soil Science; NCSAV: Praha, Czech Republic, 1954. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Blake, G.R.; Hartage, K.H. Particle density. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1, Physical and Mineralogical Methods—Agronomy Monograph No.9; American Society of Agronomy—Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitin, V.; Fishman, V. On the improvement of methods for determination of soil carbon. Chem. Agric. 1969, 3, 76–77. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: A modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H. Biochemistry: An Analysis of Global Change; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1991; 432p, ISBN 978-0-12-625157-9. [Google Scholar]
- McKague, K.; Eng, P.; OMAFRA Factsheet. Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE). Ontario’s Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Agribusiness and Ministry of Rural Affairs 2023. Available online: https://files.ontario.ca/omafra-universal-soil-loss-equation-23-005-en-2023-03-02.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Onderka, M.; Pecho, J. Update of the erosive rain factor in Slovakia using data from the period 1961–2009. Contrib. Geophys. Geod. 2019, 49, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Larson, W.E. Estimating soil water retention characteristics from particle size distribution, organic matter percent, and bulk density. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1633–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botula, Y.D.; Cornelis, W.M.; Baert, G.; Van Ranst, E. Evaluation of pedotransfer functions for predicting water retention of soils in Lower Congo (D.R.Congo). Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 111, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Fernández, J.; González-Zamora, A.; Sánchez, N.; Gumuzzio, A. A soil water based index as a suitable agricultural drought indicator. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevage, M.J.; Ritchie, J.T.; Bland, W.L.; Dugas, W.A. Lower limit of soil water availability. Agron. J. 1996, 88, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Hao, T.; Tan, W. Responses of soil organic carbon turnover to nitrogen deposition are associated with nitrogen input rates: Derived from soil 14C evidences. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.; Gurmesa, G.A.; Yu, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Fang, H.; Mo, J. Effects of nitrogen deposition on carbon cycle in terrestrial ecosystems of China: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decree of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of the Slovak Republic No. 59 of 2013 on the Protection and Usage of Agricultural Land (In Slovak). Available online: https://www.slov-lex.sk/pravne-predpisy/SK/ZZ/2013/59/ (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Bayat, H.; Sheklabadi, M.; Moradhaseli, M.; Ebrahimi, E. Effects of slope aspect, grazing, and sampling position on the soil penetration resistance curve. Geoderma 2017, 303, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasbi, M.; Hemmat, A.; Vafaian, M.; Masaddeghi, M. Evaluation of Soil Compaction Strength (Pre-compaction Stress) Using Plate Sinkage and Uniaxial Confined Compression Tests. JWSS-J. Water Soil Sci. 2008, 12, 245–254. Available online: http://jstnar.iut.ac.ir/article-1-883-en.html (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Milodowski, D.T.; Mudd, S.M.; Mitchard, E.T.A. Erosion rates as a potential bottom-up control of forest structural characteristics in the Sierra Nevada Mountains. Ecology 2015, 96, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, H.; Ghadiri, H.; Rose, C.W.; Yu, B.; Hussein, J. An investigation of flow-driven soil erosion processes at low stream powers. J. Hydrol. 2007, 342, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.L.M.P.; Dinis, P.A.; Souza, C.S.; Lima, M.I.P.; Cunha, P.P.; Azevedo, J.M.; Singh, V.P.; Abreu, J.M. Patterns of grain-size temporal variation of sediment transported by overland flow associated with moving storms: Interpreting soil flume experiments. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 2605–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yao, W.; Liu, G.; Xiao, P.; Sun, W. Experimental study of sediment transport processes and size selectivity of eroded sediment on steep Pisha sandstone slopes. Geomorphology 2020, 363, 107211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangeon, T.; Legout, C.; Esteves, M.; Gratiot, N.; Navratil, O. Variability of the particle size of suspended sediment during highly concentrated flood events in a small mountainous catchment. J. Soils Sediments 2012, 2, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Shi, P. Aggregate-associated soil organic carbon dynamics as affected by erosion and deposition along contrasting hillslopes in the Chinese Corn Belt. Catena 2021, 199, 105106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Mena, M.; Carrillo-L’épez, E.; Boix-Fayos, C.; Almagro, M.; García Franco, N.; Díaz-Pereira, E.; Montoya, I.; de Vente, J. Long-term effectiveness of sustainable land management practices to control runoff, soil erosion, and nutrient loss and the role of rainfall intensity in Mediterranean rainfed agroecosystems. Catena 2020, 187, 104352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morford, S.L.; Houlton, B.Z.; Dahlgren, R.A. Geochemical and tectonic uplift controls on rock nitrogen inputs across terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2016, 30, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, R.G.; Galy, A.; West, A.J.; Hovius, N.; Roberts, G.G. Geomorphic control on the δ15N of mountain forests. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, S.R.; Taylor, P.G.; Porder, S.; Cleveland, C.C.; Asner, G.P.; Townsend, A.R. Topographic controls on soil nitrogen availability in a lowland tropical forest. Ecology 2015, 96, 1561–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoxiao, W.; Wang, Y. Using 137Cs to quantify the redistribution of soil organic carbon and total N affected by intensive soil erosion in the headwaters of the Yangtze River, China. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2008, 66, 2007–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y.; Chang, X.; Nie, X.; Liu, L.; Haibing, X.; Yinmei, L.; Zeng, G. Response of soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks to soil erosion and land use types in the Loess hilly–gully region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 166, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertol, I.; Engel, F.L.; Mafra, A.L.; Bertol, O.J.; Ritter, S.R. Phosphorus, potassium and organic carbon concentrations in runoff water and sediments under different soil tillage systems during soybean growth. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, M.; Augustin, J. Erosion effects on soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics on cultivated slopes: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2021, 397, 115045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, M.H.; Sardans, J.; Lü, X.T.; Wang, C.; Peñuelas, J.; Wang, Z.; Han, X.G.; Jiang, Y. Carbon and nitrogen allocation shifts in plants and soils along aridity and fertility gradients in grasslands of China. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 6927–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Lu, M.; Schädel, C.; Han, W. Terrestrial C:N stoichiometry in response to elevated CO2 and N addition: A synthesis of two meta-analyses. Plant Soil 2011, 343, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Porder, S.; Houlton, B.Z.; Chadwick, O.A. Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: Mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen-phosphorus interactions. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gűsewell, S. N: P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OldeVentrik, H.; Wassen, M.J.; Verkroost, A.W.M.; De Ruiter, P.C. Species richness-productivity patterns differ between N-, P-, and K-limited wetlands. Ecology 2003, 84, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominati, E.; Mackay, A.; Green, S.; Patterson, M. A soil change-based methodology for the quantification and valuation of ecosystem services from agro-ecosystems: A case study of pastoral agriculture in New Zealand. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 100, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff-Knopp, B.; Kuhn, T.K.; Burkhard, B. The impact of soil erosion on soil-related ecosystem services: Development and testing a scenario-based assessment approach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, F.; Francksen, R.M.; Zavattaro, L.; Abdalla, M.; Hejduk, S.; Enri, S.R.; Pittarello, M.; Price, P.N.; Schils, R.L.; Smith, P.; et al. The role of grassland for erosion and flood mitigation in Europe: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 348, 108443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Poesen, J.; Lugato, E.; Scarpa, S.; Montanarella, L.; Borrelli, P. A Soil Erosion Indicator for Supporting Agricultural, Environmental and Climate Policies in the European Union. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruysschaert, G.J.; Poesen, G.; Verstraeten, G.; Govers, G. Soil loss due to harvesting of various crop types in contrasting agro-ecological environments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 120, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koco, Š.; Vilček, J.; Torma, S. Alternative Mapping Methods of Water Erosion. Agroporadenstvo 2023. Available online: https://www.agroporadenstvo.sk/nove-poznatky-poda?article=3047 (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Skuodienė, R.; Kinderienė, I.; Tomchuk, D.; Šlepetys, J. Root development of temporary and permanent grasslands and their anti-erosion significance on a hilly terrain. Zemdirb.-Agric. 2020, 107, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Liu, B.; Gu, Z.; Rong, L.; Feng, D. Quantifying soil erosion effects on soil productivity in the dry-hot valley, southwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.M.; Govers, G.; Jones, R.A.; Rounsevell, M.D. The effect of soil erosion on Europe’s crop yields. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Meng, Q.; Lin, A.; Li, J. Trade-off analyses and optimization of water-related ecosystem services (WRESs) based on land use change in a typical agricultural watershed, southern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trnka, M.; Balek, J.; Semenov, M.A.; Semerádová, D.; Bělínová, M.; Hlavinka, P.; Olesen, J.E.; Eitzinger, J.; Schaumberger, A.; Zahradnicek, P.; et al. Future agroclimatic conditions and implications for European grasslands. Biol. Plant. 2020, 64, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wösten, J.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Rawls, W. Pedotransfer functions: Bridging the gap between available basic soil data and missing soil hydraulic characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2001, 251, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrer, C.; Phillips, R.P.; Hungate, B.A.; Rosende, J.; Pett-Ridge, J.; Craig, M.E.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Keenan, T.F.; Sulman, B.N.; Stocker, B.D.; et al. A trade-off between plant and soil carbon storage under elevated CO2. Nature 2021, 591, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukubye, K.; Mutema, M.; Buthelezi, N.; Muchaonyerwa, P.; Cerri, C.; Chalplot, V. On the impact of grassland management on soil carbon stocks: A worldwide meta-analysis. Geoderma Reg. 2022, 28, e00479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Jones, A.; Montanarella, L. The LUCAS topsoil database and derived information on the regional variability of cropland topsoil properties in the European Union. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 7409–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeplau, C.; Zopf, D.; Greiner, B.; Geerts, R.; Korvaar, H.; Thumm, U.; Don, A.; Heidkamp, A.; Flessa, H. Why does mineral fertilization increase soil carbon stocks in temperate grasslands? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, T.; Bragazza, L.; Levasseur, C.; Libohova, Z.; Sinaj, S. Long-term soil organic carbon dynamics in temperate cropland-grassland systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 305, 107184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kögel-Knabner, I.; Amelung, W. Soil organic matter in major pedogenic soil groups. Geoderma 2021, 384, 114785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, O.; Ballabio, C.; Himics, M.; Scarpa, S.; Matthews, F.; Bogonos, M.; Poesen, J.; Borrelli, P. Projections of soil loss by water erosion in Europe by 2050. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 124, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J. Grassland ecosystem services: A systematic review of research advances and future directions. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 793–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
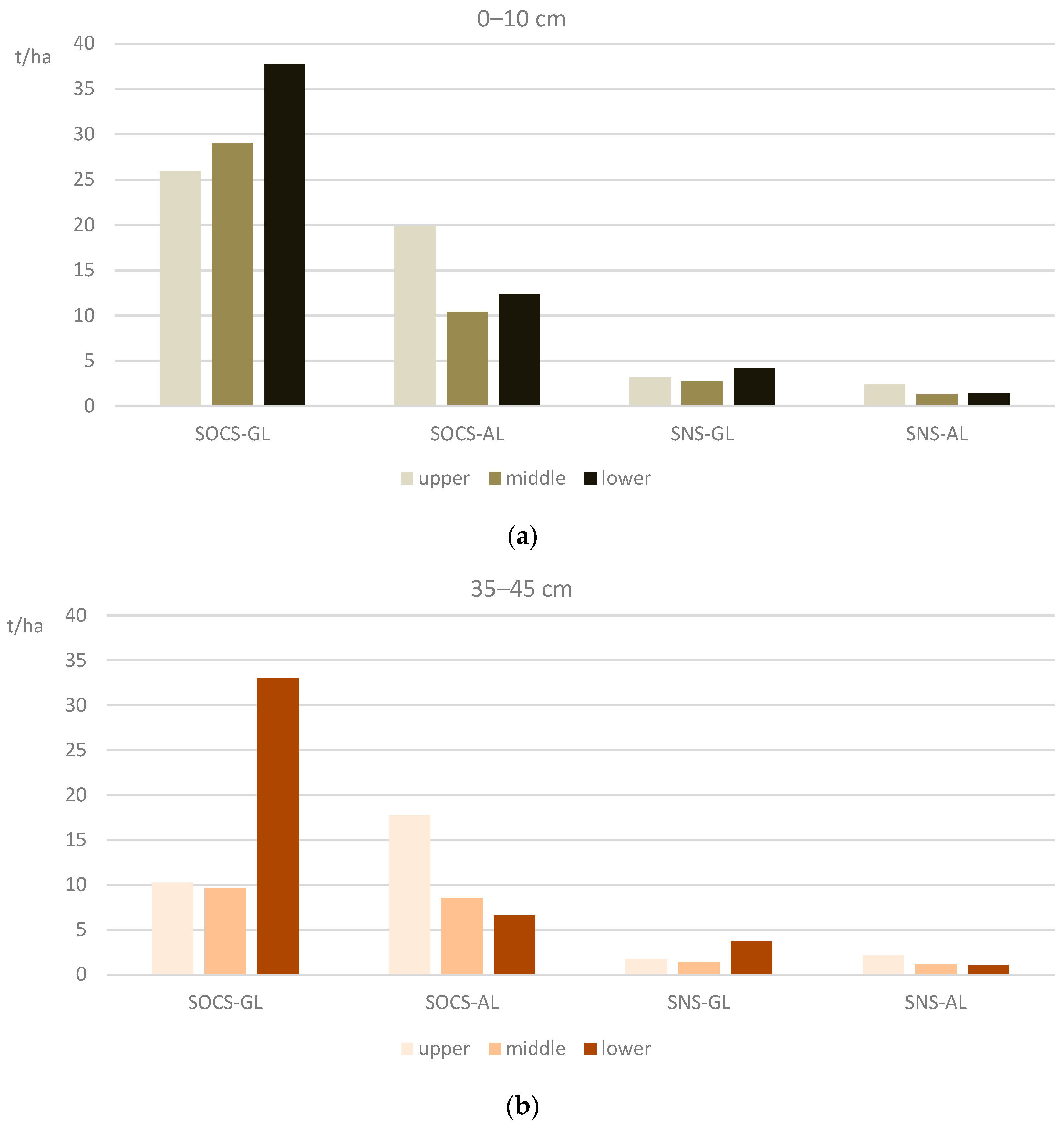

| Land Use | Hillslope Position | Soil Depth (cm) | BD (g.cm−3) | PD (g.cm−3) | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) | Gravel (%) | SM (%) | ST (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grassland | Upper | 0–10 | 1.45 ± 0.05 | 2.69 ± 0.02 | 31.43 ± 2.36 | 24.15 ± 1.42 | 44.42 ± 3.50 | 2.3 ± 0.4 | 33.8 ± 6.06 | 14.5 ± 0.44 |
| 35–45 | 1.55 ± 0.04 | 2.70 ± 0.01 | 39.58 ± 2.55 | 33.12 ± 2.21 | 27.30 ± 2.64 | 5.8 ± 1.0 | 19.3 ± 3.70 | 9.4 ± 0.48 | ||
| Middle | 0–10 | 1.42 ± 0.02 | 2.70 ± 0.01 | 35.01 ± 1.26 | 23.11 ± 1.12 | 41.88 ± 0.92 | 5.9 ± 0.7 | 40.8 ± 2.28 | 13.8 ± 0.51 | |
| 35–45 | 1.48 ± 0.04 | 2.71 ± 0.01 | 40.56 ± 1.55 | 35.12 ± 1.07 | 24.32 ± 2.34 | 10.3 ± 0.5 | 23.8 ± 1.48 | 8.8 ± 0.45 | ||
| Lower | 0–10 | 1.41 ± 0.02 | 2.70 ± 0.01 | 38.25 ± 1.75 | 28.14 ± 1.23 | 33.61 ± 1.71 | 5.7 ± 1.1 | 38.0 ± 1.87 | 15.0 ± 0.77 | |
| 35–45 | 1.52 ± 0.03 | 2.71 ± 0.01 | 43.78 ± 3.82 | 39.98 ± 1.38 | 16.24 ± 3.25 | 10.2 ± 0.5 | 21.0 ± 3.16 | 9.7 ± 0.13 | ||
| Arable land | Upper | 0–10 | 1.55 ± 0.11 | 2.64 ± 0.01 | 21.69 ± 3.88 | 54.98 ± 3.06 | 23.38 ± 4.69 | 5.1 ± 0.2 | 15.8 ± 1.15 | 10.9 ± 0.45 |
| 35–45 | 1.51 ± 0.04 | 2.66 ± 0.01 | 46.23 ± 2.42 | 38.88 ± 1.73 | 14.89 ± 1.47 | 10.4 ± 0.5 | 9.0 ± 0.90 | 6.0 ± 0.25 | ||
| Middle | 0–10 | 1.59 ± 0.05 | 2.65 ± 0.01 | 25.89 ± 2.43 | 47.95 ± 1.94 | 26.21 ± 2.67 | 20.3 ± 2.5 | 19.3 ± 1.17 | 10.4 ± 0.80 | |
| 35–45 | 1.58 ± 0.03 | 2.70 ± 0.03 | 48.97 ± 4.23 | 39.01 ± 3.61 | 12.02 ± 4.38 | 30.4 ± 3.1 | 11.8 ± 2.15 | 8.5 ± 0.55 | ||
| Lower | 0–10 | 1.35 ± 0.06 | 2.63 ± 0.02 | 17.71 ± 2.78 | 53.15 ± 2.62 | 29.14 ± 3.44 | 30.5 ± 3.1 | 19.8 ± 1.78 | 9.9 ± 0.70 | |
| 35–45 | 1.53 ± 0.10 | 2.70 ± 0.09 | 16.78 ± 1.04 | 46.99 ± 1.01 | 36.23 ± 1.53 | 50.7 ± 3.9 | 14.8 ± 1.25 | 8.6 ± 0.40 |
| Land Use | Hillslope Position | Soil Depth (cm) | pH | SOC (g.kg−1) | SOM (g.kg−1) | SN (g.kg−1) | SOC/SN | SP (mg.kg −1) | SK (mg.kg −1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grassland | Upper | 0–10 | 5.04 ± 0.10 | 18.23 ± 2.81 | 31.42 ± 4.84 | 2.22 ± 0.29 | 8.21 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 116.20 ± 5.31 |
| 35–45 | 5.16 ± 0.07 | 6.98 ± 2.08 | 12.02 ± 3.59 | 1.19 ± 0.10 | 5.89 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 84.40 ± 0.02 | ||
| Middle | 0–10 | 5.14 ± 0.13 | 21.52 ± 2.98 | 37.09 ± 5.13 | 2.02 ± 0.20 | 10.66 | 1.28 ± 0.76 | 198.73 ± 47.02 | |
| 35–45 | 4.78 ± 0.28 | 7.25 ± 0.65 | 12.50 ± 1.12 | 1.05 ± 0.19 | 6.89 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 99.84 ± 2.78 | ||
| Lower | 0–10 | 5.89 ± 0.10 | 28.19 ± 2.10 | 48.62 ± 3.61 | 3.13 ± 0.29 | 9.01 | 22.83 ± 2.67 | 349.30 ± 3.50 | |
| 35–45 | 5.93 ± 0.15 | 24.15 ± 6.71 | 41.64 ± 11.58 | 2.75 ± 0.50 | 8.78 | 18.07 ± 8.50 | 321.33 ± 50.55 | ||
| Arable land | Upper | 0–10 | 5.22 ± 0.03 | 13.50 ± 3.31 | 23.27 ± 5.71 | 1.62 ± 0.09 | 8.33 | 24.91 ± 3.54 | 145.71 ± 20.67 |
| 35–45 | 5.23 ± 0.07 | 13.05 ± 1.70 | 22.50 ± 2.93 | 1.58 ± 0.13 | 8.27 | 22.71 ± 2.50 | 130.75 ± 16.09 | ||
| Middle | 0–10 | 4.85 ± 0.15 | 8.15 ± 0.77 | 14.04 ± 1.32 | 1.09 ± 0.10 | 7.47 | 5.12 ± 2.10 | 168.75 ± 29.79 | |
| 35–45 | 4.89 ± 0.12 | 7.73 ± 1.89 | 13.32 ± 3.27 | 1.04 ± 0.22 | 7.41 | 4.59 ± 3.41 | 179.65 ± 50.13 | ||
| Lower | 0–10 | 5.46 ± 0.14 | 13.09 ± 3.00 | 22.56 ± 5.18 | 1.58 ± 0.09 | 8.31 | 4.84 ± 6.47 | 221.93 ± 86.20 | |
| 35–45 | 5.54 ± 0.08 | 8.63 ± 2.26 | 14.87 ± 3.90 | 1.42 ± 0.23 | 6.10 | 4.33 ± 6.70 | 182.87 ± 63.75 |
| Hillslope Position | Shoot Biomass (g.m−2) | Root Biomass (g.m−2) | R/S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grasslands | Upper | 188 ± 88 b | 837 ± 47 ns | 5.23 ± 1.40 ns |
| Middle | 95 ± 35 c | 663 ± 121 ns | 6.57 ± 1.57 ns | |
| Lower | 223 ± 59 a | 611 ± 52 ns | 2.61 ± 0.65 ns | |
| p value | 0.009 | 0.179 | 0.107 | |
| Arable land | Upper | 1186 ± 495 ns | 340 ± 79 a | 0.32 ± 0.14 ns |
| Middle | 1445 ± 448 ns | 307 ± 24 ab | 0.23 ± 0.08 ns | |
| Lower | 1104 ± 593 ns | 184 ± 45 b | 0.21 ± 0.11 ns | |
| p value | 0.826 | 0.003 | 0.171 |
| Hillslope Position | PN (g.kg−1) | PP (g.kg−1) | PK (g.kg−1) | PC/PN | PC/PP | PN/PP | PN/PK | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grasslands | Upper | 20.77 ± 1.16 b | 2.97 ± 0.18 b | 27.93 ± 3.10 ns | 22.93 ± 1.29 a | 160.41 ± 10.57 a | 7.00 ± 0.40 ns | 0.75 ± 0.11 ns |
| Middle | 21.56 ± 1.96 b | 3.23 ± 0.21 a | 22.43 ± 3.16 ns | 22.20 ± 2.20 a | 147.79 ± 10.92 a | 6.68 ± 0.36 ns | 0.97 ± 0.10 ns | |
| Lower | 26.81 ± 2.60 a | 4.02 ± 0.28 a | 31.19 ± 3.28 ns | 17.86 ± 1.65 b | 118.56 ± 8.32 b | 6.99 ± 0.36 ns | 0.86 ± 0.06 ns | |
| p value | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.836 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.118 | 0.120 | |
| Arable land | Upper | 14.66 ± 2.96 ns | 4.38 ± 0.52 ns | 7.64 ± 1.64 ns | 33.68 ± 8.48 ns | 109.61 ± 13.03 b | 3.34 ± 0.57 ns | 1.98 ± 0.62 ns |
| Middle | 13.66 ± 2.55 ns | 3.44 ± 0.38 ns | 9.83 ± 2.54 ns | 35.74 ± 6.81 ns | 139.07 ± 14.40 a | 4.00 ± 0.97 ns | 1.45 ± 0.34 ns | |
| Lower | 11.81 ± 1.49 ns | 3.45 ± 0.61 ns | 7.71 ± 0.91 ns | 40.71 ± 5.28 ns | 141.35 ± 27.79 a | 3.48 ± 0.51 ns | 1.56 ± 0.32 ns | |
| p value | 0.118 | 0.167 | 0.966 | 0.167 | 0.0472 | 0.804 | 0.213 |
| pH | SOC | SN | SP | SK | PN | PP | PK | ShB | RoB | BD | PD | Clay | Silt | Sand | Gravel | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| SOC | 0.587 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| SN | 0.682 ** | 0.950 ** | 1 | |||||||||||||
| SP | 0.477 ** | 0.490 ** | 0.490 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||
| SK | 0.700 ** | 0.714 ** | 0.720 ** | 0.528 ** | 1 | |||||||||||
| PN | 0.457 * | 0.780 ** | 0.797 ** | N.C. | N.C. | 1 | ||||||||||
| PP | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | 0.559 ** | N.C. | N.C. | 1 | |||||||||
| PK | N.C. | 0.730 ** | 0.769 ** | N.C. | N.C. | 0.869 ** | N.C. | 1 | ||||||||
| ShB | N.C. | −0.689 ** | −0.646 ** | N.C. | N.C. | −0.653 ** | N.C. | −0.788 ** | 1 | |||||||
| RoB | N.C. | 0.521 ** | 0.466 * | N.C. | N.C. | 0.726 ** | N.C. | 0.804 ** | −0.680 ** | 1 | ||||||
| BD | N.C. | −0.374 ** | −0.376 ** | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | 1 | |||||
| PD | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | 0.442 * | −0.414 * | N.C. | N.C. | 1 | ||||
| Clay | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | 0.808 ** | N.C. | 0.828 ** | −0.677 ** | 0.637 ** | N.C. | N.C. | 1 | |||
| Silt | N.C. | −0.397 ** | −0.386 ** | N.C. | N.C. | −0.765 ** | 0.411* | −0.874 ** | 0.789 ** | −0.775 ** | N.C. | −0.338 * | −0.535 ** | 1 | ||
| Sand | N.C. | N.C. | N.C. | −0.361* | N.C. | 0.523 ** | −0.530 ** | 0.684 ** | −0.683 ** | 0.696 ** | −0.435 ** | N.C. | −0.524 ** | −0.439 ** | 1 | |
| Gravel | N.C. | −0.410 ** | −0.378 ** | N.C. | N.C. | −0.658 ** | N.C. | −0.637 ** | 0.568 ** | −0.656 ** | N.C. | N.C. | −0.406 ** | 0.509 ** | N.C. | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanianska, R.; Kizeková, M.; Jančová, Ľ.; Čunderlík, J.; Dugátová, Z. Effect of Soil Erosion on Soil and Plant Properties with a Consequence on Related Ecosystem Services. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167037
Kanianska R, Kizeková M, Jančová Ľ, Čunderlík J, Dugátová Z. Effect of Soil Erosion on Soil and Plant Properties with a Consequence on Related Ecosystem Services. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167037
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanianska, Radoslava, Miriam Kizeková, Ľubica Jančová, Jozef Čunderlík, and Zuzana Dugátová. 2024. "Effect of Soil Erosion on Soil and Plant Properties with a Consequence on Related Ecosystem Services" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167037
APA StyleKanianska, R., Kizeková, M., Jančová, Ľ., Čunderlík, J., & Dugátová, Z. (2024). Effect of Soil Erosion on Soil and Plant Properties with a Consequence on Related Ecosystem Services. Sustainability, 16(16), 7037. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167037







