Sustainable Algae-Derived Carbon Particles from Hydrothermal Liquefaction: An Innovative Reinforcing Agent for Epoxy Matrix Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of ADC Particles
2.3. Fabrication of ADC-Reinforced Epoxy Matrix Composites (EMCs)
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of ADC Particles
3.2. Reinforcing Effect of ADC Particles
3.2.1. Tensile Properties
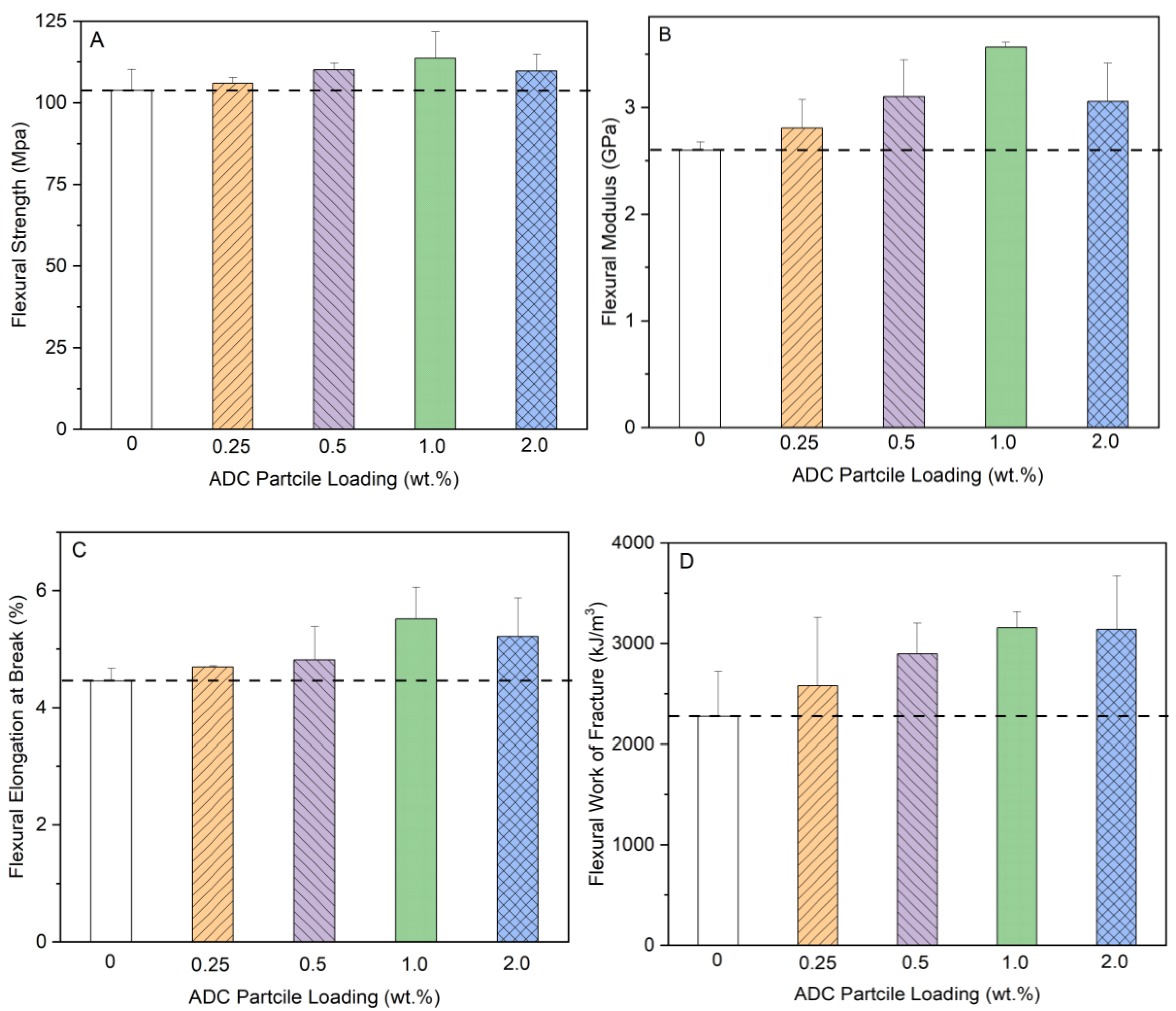
3.2.2. Flexural Properties
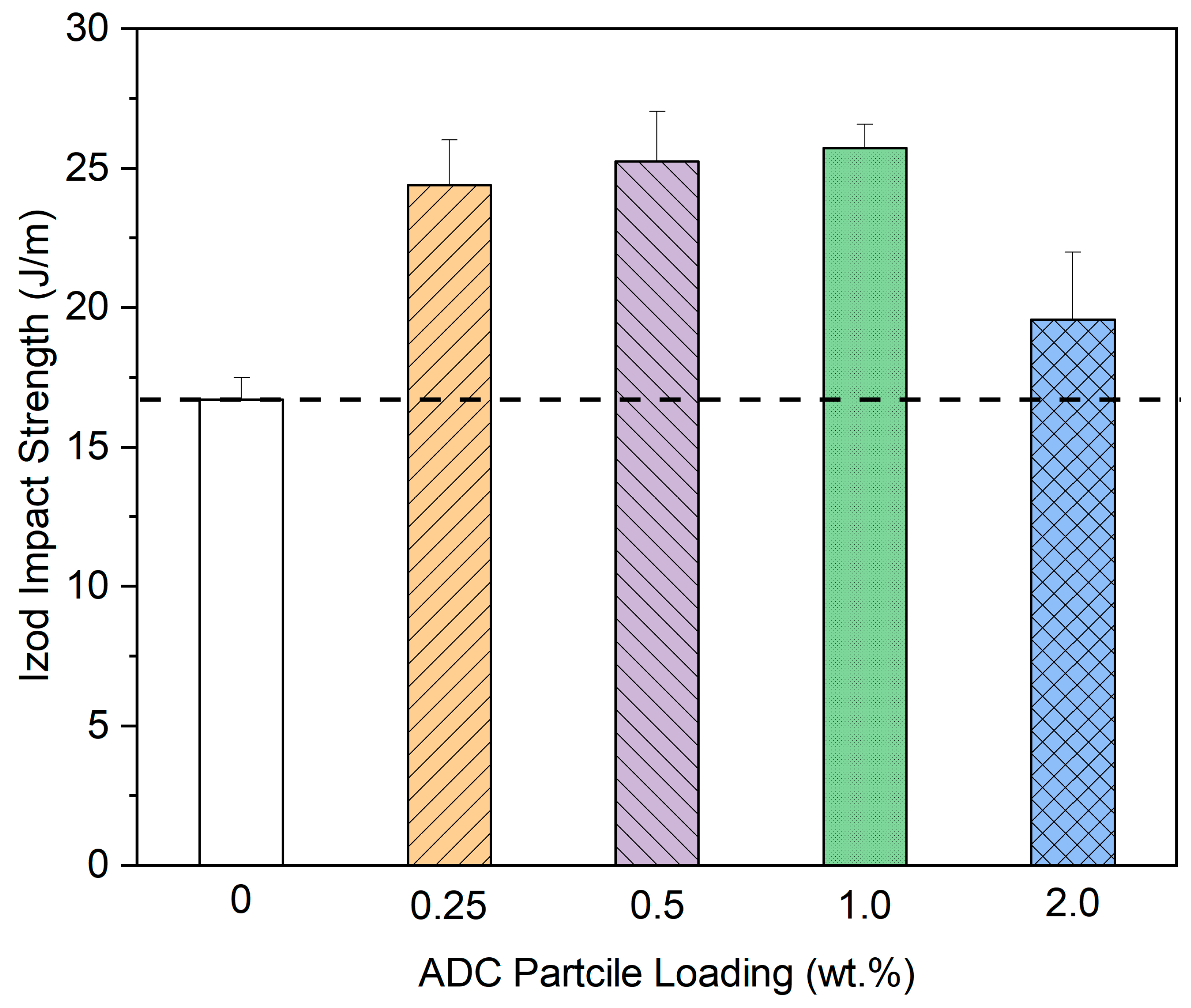
3.2.3. Impact Property
3.3. Discussion on the Reinforcing Mechanism of ADC Particles
3.4. Thermal Stability of ADC-Reinforced EMCs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- May, C.A. Epoxy Resins: Chemistry and Technology, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1988; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Tee, Z.Y.; Yeap, S.P.; Hassan, C.S.; Kiew, P.L. Nano and non-nano fillers in enhancing mechanical properties of epoxy resins: A brief review. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2022, 61, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnati, S.R.; Agbo, P.; Zhang, L. Applications of silica nanoparticles in glass/carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy nanocomposite. Compos. Commun. 2020, 17, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matykiewicz, D. Hybrid epoxy composites with both powder and fiber filler: A Review of Mechanical and Thermomechanical Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, S.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Hassan, S.B.; Kana, M.G.Z.; Raheem, I.A. Epoxy resin-based composites, mechanical and tribological properties: A review. Tribol. Ind. 2015, 37, 500–524. [Google Scholar]
- Mali, A.; Agbo, P.; Mantripragada, S.; Zhang, L. Surface-modified electrospun glass nanofibers from silane treatment and their use for high-performance epoxy-based nanocomposite materials. Materials 2023, 16, 6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashanth, S.; Subbaya, K.M.; Nithin, K.; Sachhidananda, S. Fiber reinforced composites—A review. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 6, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilyeu, B.; Brostow, W.; Menard, K.P. Epoxy thermosets and their applications I: Chemical structures and applications. J. Mater. Educ. 1999, 21, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Hoa, S.V. Toughening mechanism of epoxy resins with micro/nano particles. J. Compos. Mater. 2007, 41, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.C.; Mai, Y.-W. Failure mechanisms in toughened epoxy resins—A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1988, 31, 179–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, A.C.; Kausch, H.H.; Stieger, H.R. The fracture of particulate-filled epoxide resins. J. Mater. Sci. 1983, 18, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunjarrao, S.C.; Singh, R.P. Characterization of the fracture behavior of epoxy reinforced with nanometer and micrometer sized aluminum particles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2296–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Jain, A. Thermo-mechanical behavior of TiO2 dispersed epoxy composites. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2017, 184, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanya, O.T.; Oji, B.; Owoeye, S.S.; Egbochie, E.J. Influence of particle size and particle loading on mechanical properties of silicon carbide–reinforced epoxy composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 4787–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiura, A.I.; Mamunya, Y.P.; Kulish, M.P. Metal-filled epoxy composites: Mechanical properties and electrical/thermal conductivity. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2019, 59, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, F.P.; Morreale, M. Green composites: A brief review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aup-Ngoen, K.; Noipitak, M. Effect of carbon-rich biochar on mechanical properties of PLA-biochar composites. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 15, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, C.; Tamrakar, S.; Kiziltas, A.; Xie, X. Incorporation of biochar to improve mechanical, thermal and electrical properties of polymer composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, O.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Hui, D.; Lau, K.T. Mechanical and flammability characterizations of biochar/polypropylene biocomposites. Compos. Part B 2016, 106, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamuddin, S.; Hossain, N.; Qureshi, S.S.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; Tanjung, F.A.; Elshikh, M.S.; Siddiqui, M.T.H.; Baloch, H.A.; Mubarak, N.M.; Griffin, G.; et al. Experimental investigation of physicochemical, thermal, mechanical and rheological properties of polylactide/rice straw hydrochar composite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Lu, W.; Zhang, D.; Ren, X.; Yu, W.; Wu, J.; Zhou, L.; Han, X.; Yi, W.; et al. Properties evaluation of biochar/high-density polyethylene composites: Emphasizing the porous structure of biochar by activation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollakota, A.R.K.; Kishore, N.; Gu, S. A review on hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1378–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbo, P.; Mali, A.; Deng, D.; Zhang, L. Bio-oil-based epoxy resins from thermochemical processing of sustainable resources: A short review. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H. Hydrothermal liquefaction for algal biorefinery: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 38, 933–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yeh, T.; Song, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, S. A review of bio-oil production from hydrothermal liquefaction of algae. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 48, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbo, P.; Mali, A.; Kelkar, A.D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Injecting sustainability into epoxy-based composite materials by using bio-binder from hydrothermal liquefaction processing of microalgae. Molecules 2024, 29, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantripragada, S.; Dong, M.; Zhang, L. Sustainable filter/adsorbent materials from cellulose-based nanofibrous membranes with soy protein coating for high-efficiency GenX fluorocarbon remediation from water. Cellulose 2023, 30, 7063–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.L. Fracture Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Wang, T. An improved crack-bridging model for rigid particle-polymer composites. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2019, 211, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mali, A.; Agbo, P.; Mantripragada, S.; Jadhav, V.S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Sustainable Algae-Derived Carbon Particles from Hydrothermal Liquefaction: An Innovative Reinforcing Agent for Epoxy Matrix Composite. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6870. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166870
Mali A, Agbo P, Mantripragada S, Jadhav VS, Wang L, Zhang L. Sustainable Algae-Derived Carbon Particles from Hydrothermal Liquefaction: An Innovative Reinforcing Agent for Epoxy Matrix Composite. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):6870. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166870
Chicago/Turabian StyleMali, Abhijeet, Philip Agbo, Shobha Mantripragada, Vishwas S. Jadhav, Lijun Wang, and Lifeng Zhang. 2024. "Sustainable Algae-Derived Carbon Particles from Hydrothermal Liquefaction: An Innovative Reinforcing Agent for Epoxy Matrix Composite" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 6870. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166870
APA StyleMali, A., Agbo, P., Mantripragada, S., Jadhav, V. S., Wang, L., & Zhang, L. (2024). Sustainable Algae-Derived Carbon Particles from Hydrothermal Liquefaction: An Innovative Reinforcing Agent for Epoxy Matrix Composite. Sustainability, 16(16), 6870. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166870






