Sources of the Trace Metals Contaminating Soils in Recreational Forest and Glade Areas in Krakow, a Large City in Southern Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
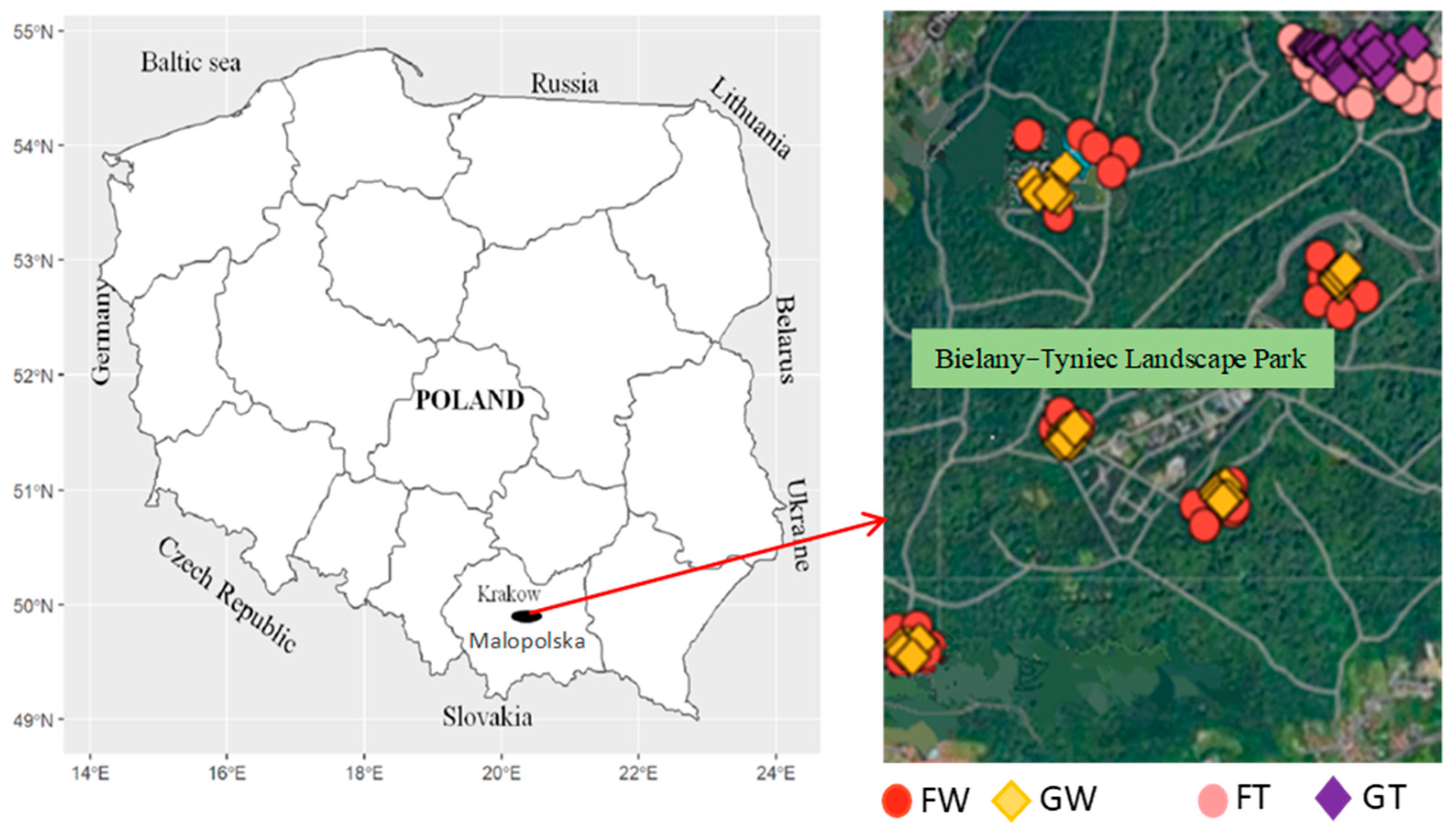
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Statistical and Geostatistical Analyses
2.3.1. Calculation of Soil Quality Enzyme Index (SQe)
2.3.2. Calculation of Soil Pollution Indices
Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo)
Nemerov Pollution Index
Potential Ecological Risk Index
Pollution Load Index (PLI)
3. Results
3.1. Basic Physical and Chemical Properties
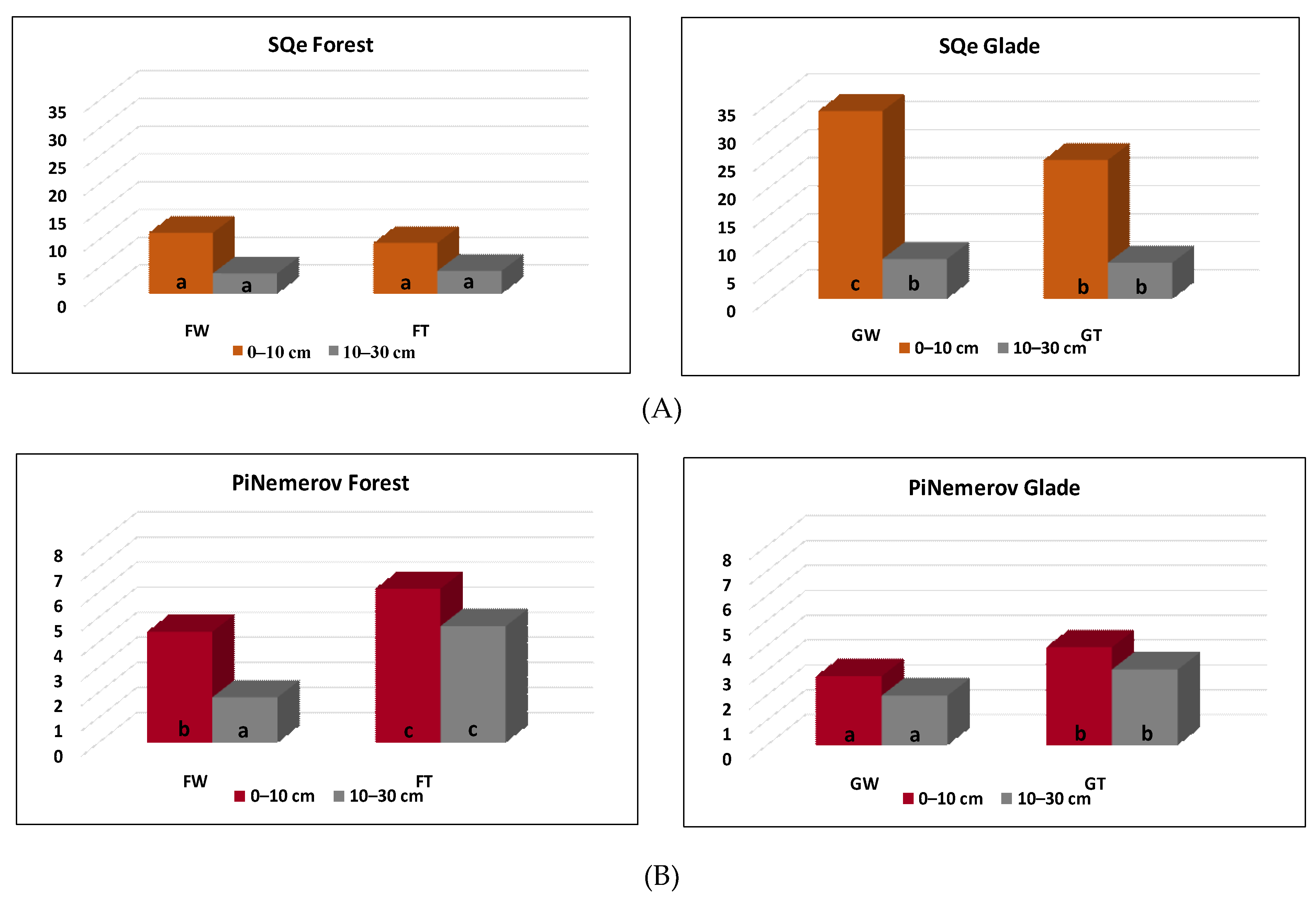
3.2. Enzyme Activity and Soil Quality Enzyme Index
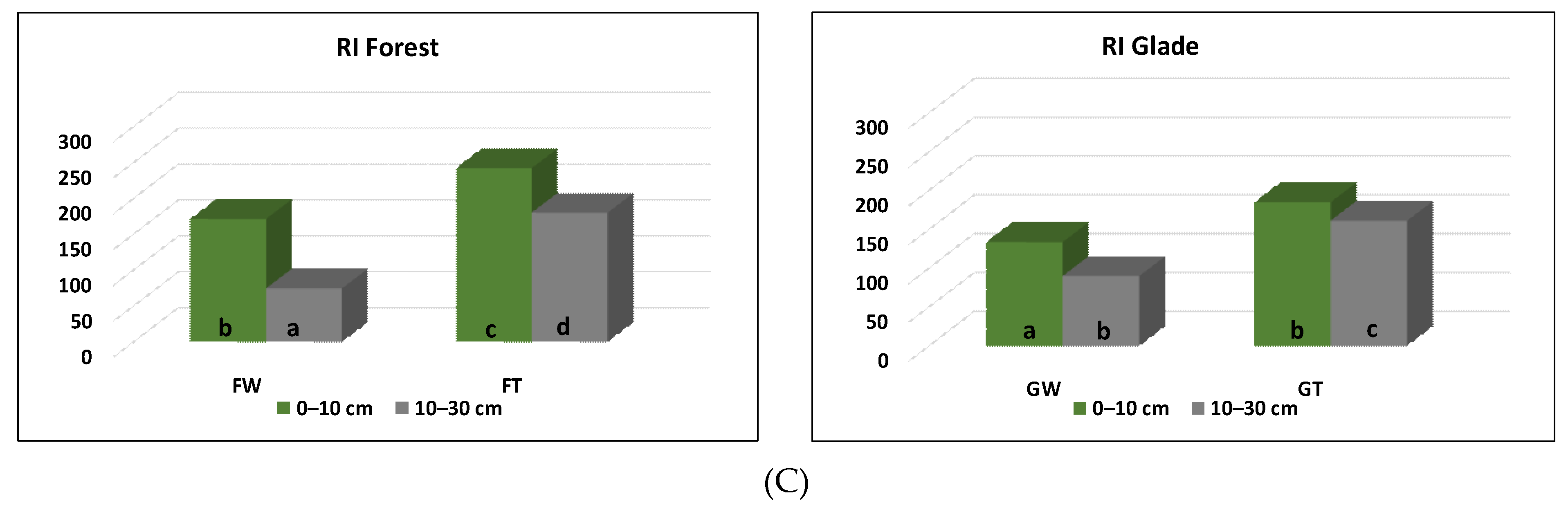
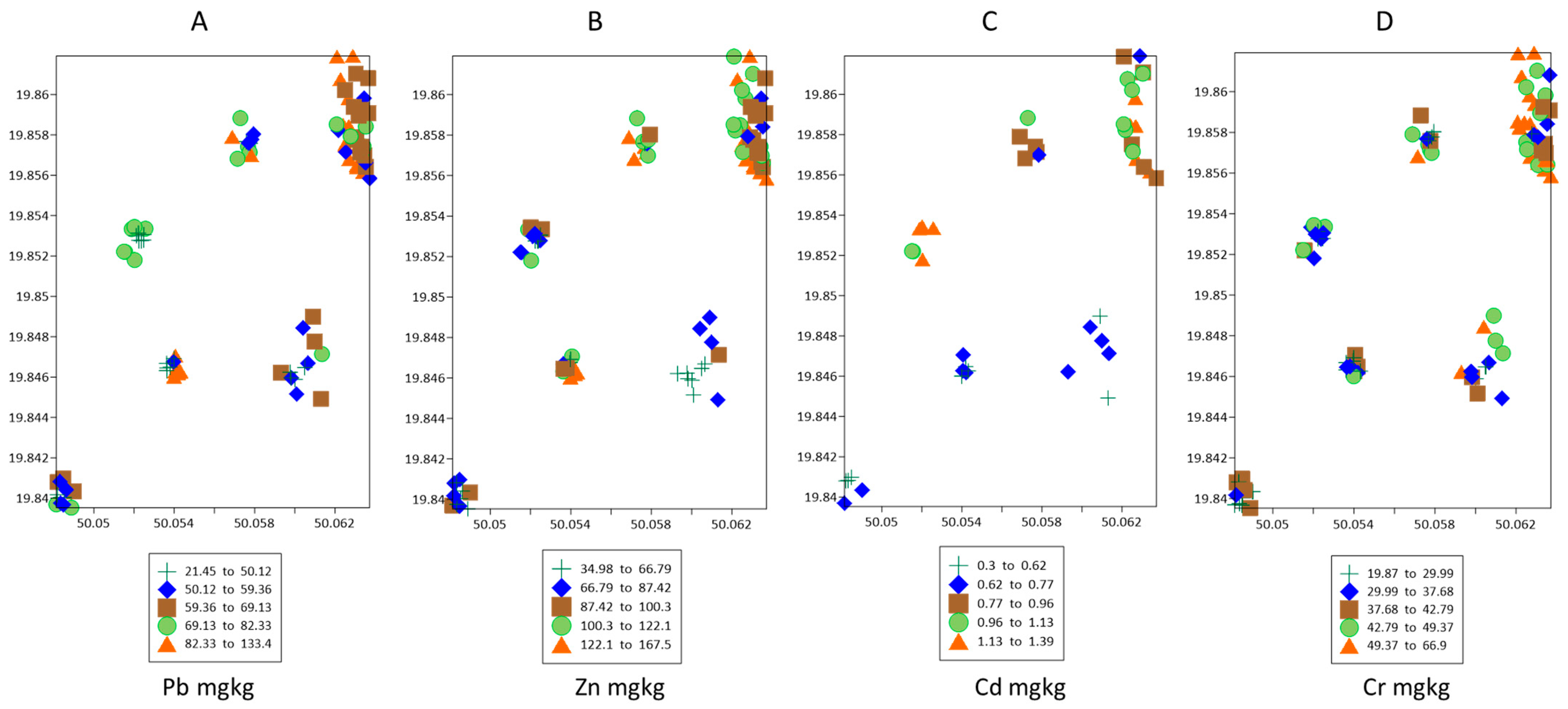
3.3. Concentrations of Zn, Cr, Pb, and Cd and TM Contamination Indices
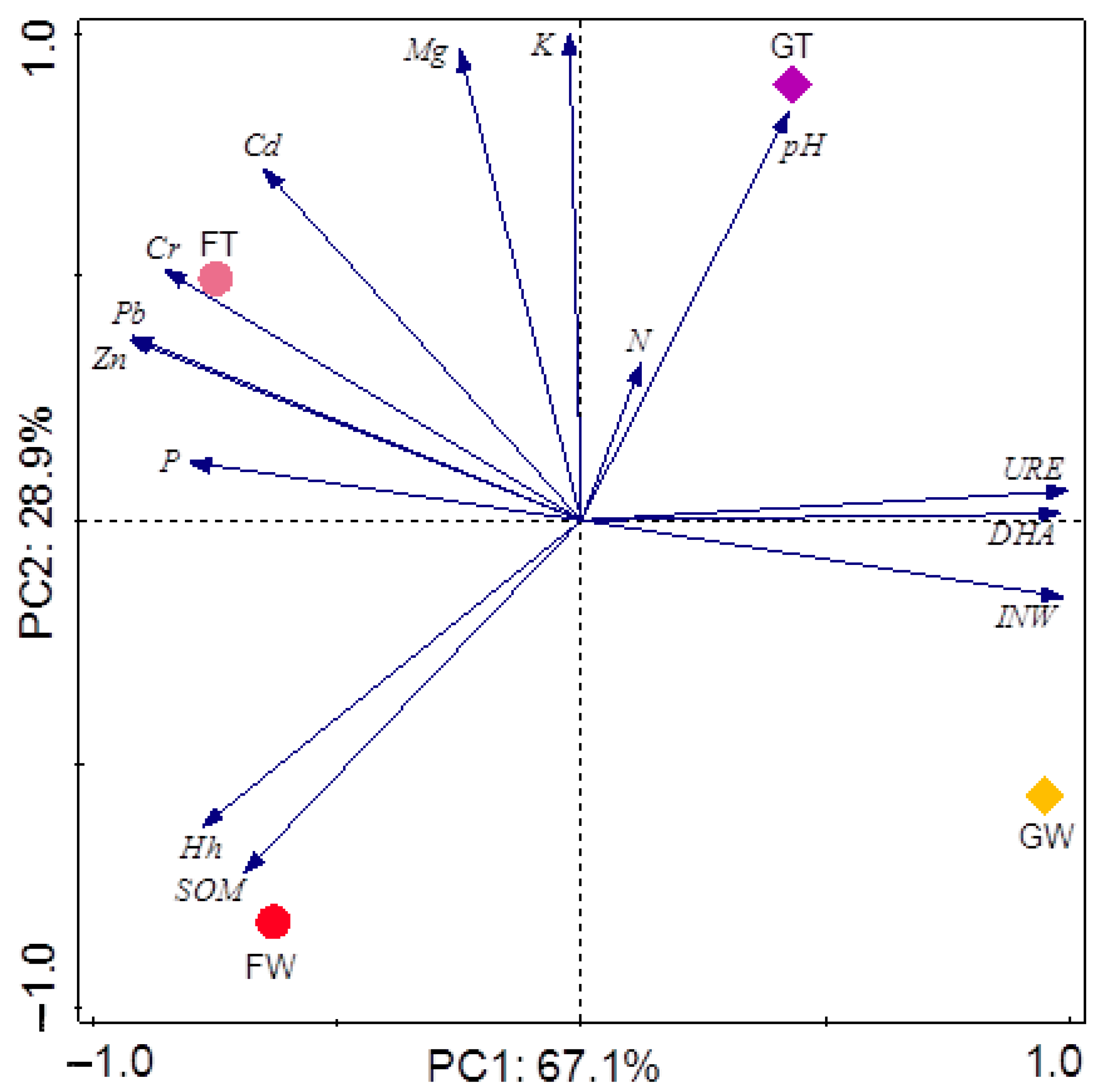
3.4. Main Factors Shaping the Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of TM Contents and Their Sources
4.2. TM Accumulation and the Properties of Forest and Glade Soils
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sager, M. Urban soils and road dust—Civilization effects and metal pollution—A Review. Environments 2020, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samek, L.; Stegowski, Z.; Furman, L.; Fiedor, J. Chemical content and estimated sources of fine fraction of particulate matter collected in Krakow. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissmannová, H.D.; Pavlovský, J. Indices of soil contamination by heavy metals—Methodology of calculation for pollution assessment (minireview). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewumi, A.J.; Ogundele, O.D. Hidden hazards in urban soils: A meta-analysis review of global heavy metal contamination (2010–2022), sources and its Ecological and health consequences. Sustain. Environ. 2024, 10, 2293239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reizer, M.; Juda-Rezler, K. Explaining the high PM10 concentrations observed in Polish urban areas. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2016, 9, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styszko, K.; Szramowiat, K.; Kistler, M.; Kasper-Giebl, A.; Samek, L.; Furmanc, L.; Pacyna, J.; Gołas, J. Mercury in atmospheric aerosols: A preliminary case study for the city of Krakow, Poland. Comptes Rendus Chimie 2015, 18, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styszko, K.; Samek, L.; Szramowiat, K.; Korzeniewska, A.; Kubisty, K.; Rakoczy-Lelek, R.; Kistler, M.; Giebl, A.K. Oxidative potential of PM10 and PM2.5 collected at high air pollution site related to chemical composition: Krakow case study. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 1123–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, G.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Rozbicka, K.; Rogula-Kopiec, P.; Mathews, B.; Brandyk, A. Concentration, Chemical Composition and Origin of PM1: Results from the First Long-term Measurement Campaign in Warsaw (Poland). Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 636–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Ambient Air Pollution Database May 2016; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Traczyk, P.; Gruszecka-Kosowska, A. The condition of air pollution in Kraków, Poland, in 2005–2020, with health risk assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rataj, M.; Holewa-Rataj, J. Analysis of air quality changes in Malopolska in the years 2012–2020. Nafta-Gaz 2020, 11, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gąsiorek, M.; Kowalska, J.; Mazurek, R.; Pajak, M. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal pollution in topsoil of historical urban park on an example of the Planty Park in Krakow (Poland). Chemosphere 2017, 179, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajduga, G.; Generowicz, A.; Kryłów, M. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust collected in Cracow. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 100, 00026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, I.A.; Gabiana, C.C.; Dumo, J.R.E.; Salmo, S.G.; Guzman, M.A.L.G.; Valera, N.S.; Espiritu, E.Q. Heavy metal concentrations in soils and vegetation in urban areas of Quezon City, Philippines. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roje, V.; Orešković, M.; Rončević, J.; Bakšić, D.; Pernar, N.; Perković, I. Assessment of the trace element distribution in soils in the parks of the city of Zagreb (Croatia). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golia, E.E.; Papadimou, S.G.; Cavalaris, C.; Tsiropoulos, N.G. Level of Contamination Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in the Urban Soils of Volos City (Central Greece). Sustainability 2021, 13, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Turek, A.; Szczesio, M.; Wolf, W.M. Comprehensive Evaluation of Metal Pollution in Urban Soils of a Post-Industrial City—A Case of Łódź, Poland. Molecules 2020, 25, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sołek-Podwika, K.; Podwika, M.; Niemyska-Łukaszuk, J. Trace element concentration in soil of selected forests of Krakow city. Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2013, 20, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, H.; Francini, G.; Allen, J.A.; Jumpponen, A.; Hui, N.; Kotze, D.J. Urban parks provide ecosystem services by retaining metals and nutrients in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaño-López, F.; Biswas, A. Are heavy metals in urban garden soils linked to vulnerable populations? A case study from Guelph, Canada. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudabadi, E.; Sarmadian, F.; Nazary Moghaddam, R. Spatial distribution of soil heavy metals in different land uses of an industrial area of Tehran (Iran). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3283–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Polskie Miasta-w 2023 Roku Nie-Schodzily z Czolowek. Zachwycal Sie Nimi Caly Swiat. Available online: https://www.national-geographic.pl/traveler/artykul/te-polskie-miasta-w-2023-roku-nie-schodzily-z-czolowek-zachwycal-sie-nimi-caly-swiat-231213093607 (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Central Statistical Office (CSO 2023). Urząd Statystyczny w Krakowie/m. Kraków. Available online: https://krakow.stat.gov.pl (accessed on 10 May 2024). (In Polish)
- Bokwa, A. Evolution of studies on local climate of Kraków. Acta Geographica Lodziensia 2019, 108, 7–20. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.H. Soil Sampling, Preparation and Analysis; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA; Singapore, 2005; p. 408. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowska, A.; Gawliński, S.; Szczubiałka, Z. Methods of Soil and Plant Analyses and Evaluation; Instytut Ochrony Środowiska: Warszawa, Poland, 1991; p. 234. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Gorlach, E.; Mazur, T. Agricultural chemistry. In Basics of Nutrition and Principles of Fertilization; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2001; p. 347. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Hendershof, W.H.; Lalande, H.; Reyes, D.; MacDonald, J.D. Trace element assessment. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis; Carter, M.R., Gregorich, E.G., Eds.; Taylor and Francis Group, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Alef, K.; Nannipieri, R. Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA; San Francisco, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 318–320. [Google Scholar]
- Cassida, L.E.; Klein, D.A.; Santoro, T. Soil dehydrogenase activity. Soil. Sci. 1964, 98, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Brenner, J.M. Assay of urease activity in soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberger, J.R.; Johanson, J.B. Method of measuring invertase activity in soils. Plant Soil 1983, 74, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistica (Data Analysis Software System), version 13.3; StatSoft Inc.: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2019.
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, version 5.0; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Gascó, G.; Gutiérrez, B.; Méndez, A. Soil biochemical activities and the geometric mean of enzyme activities after application of sewage sludge and sewage sludge biochar to soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, R.; Ochoa, V.; Hinojosa, M.B.; Carreira, A. Suitability of enzyme activities for the monitoring of soil quality improvement in organic agricultural systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geo J. 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination—A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnowska, K. Ogólna zawartość metali ciężkich w skałach macierzystych jako tło geochemiczne gleb. Rocz. Glebozn. 1996, XLVII, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L.; Liming, L.; Jiewen, Y. Assessment of Heavy Metals Contamination of Paddy Soil in Xiangyin County, China. In Symposium 4.1.2 Management and Protection of Receiving Environments, 19th World Congress of Soil Science, Soil Solutions for a Changing World 19, Brisbane, Australia, 1–6 August 2010; pp. 17–20, (CABI Digital Library, Brisbane).
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.F.; Silva, N.F.; Oliveira, C.M.; Matos, M.J. Heavy Metals Contamination of Urban Soils—A Decade Study in the City of Lisbon, Portugal. Soil Syst. 2021, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błońska, E.; Lasota, J.; Szuszkiewicz, M.; Łukasik, A.; Klamerus-Iwan, A. Assessment of forest soil contamination in Krakow surroundings in relation to the type of stand. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, F.U.; Faridullah, F.; Irshad, M.; Bacha, A.U.R.; Ullah, Z.; Fawad, M.; Hafeez, F.; Iqbal, A.; Nazir, R.; Alrefaei, A.F.; et al. Distribution and speciation of trace elements in soils of four land-use systems. Land 2023, 12, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, K.P.; Freer-Smith, P.; Taylor, G. The capture of particulate pollution by trees at five contrasting UK urban sites. Arboric. J. 2000, 24, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douay, F.; Pruvot, C.; Waterlot, C.; Fritsch, C.; Fourrier, H.; Loriette, A.; Bidar, G.; Grand, C.; De Vaufleury, A.; Scheifler, R. Contamination of woody habitat soils around a former lead smelter in the North of France. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5564–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruba, P.; Socha, J.; Błońska, E.; Lasota, J. Effect of variable soil texture, metal saturation of soil organic matter (SOM) and tree species composition on spatial distribution of SOM in forest soils in Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521–522, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podwika, M.; Solek-Podwika, K.; Kaleta, D.; Ciarkowska, K. The effect of land-use change on urban grassland soil quality (southern Poland). J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błońska, E.; Lasota, J.; Gruba, P. Effect of temperate forest tree species on soil dehydrogenase and urease activities in relation to other properties of soil derived from loess and glaciofluvial sand. Ecol. Res. 2016, 31, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galušková, I.; Borůvka, L.; Drábek, O. Urban soil contamination by potentially risk elements. Soil. Water Res. 2011, 6, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Khillare, P.S.; Kim, K.H. The Effect of Aircraft Traffic Emissions on the Soil Surface Contamination Analysis around the International Airport in Delhi, India. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 6, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, A.; Russell, A.; Radford, A.; Burgess, M.; Bauer, J.A.; Christiansen, S.L.; Knight, S.; Whitacre, S.; Basta, N.; Ceballos, D. Short Report: Addressing Community Air Traffic Concerns: A Pilot Study on Metals and Other Elements in Soil. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2024, 235, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massas, I.; Gasparatos, D.; Ioannou, D.; Kalivas, D. Signs for secondary buildup of heavy metals in soils at the periphery of Athens International Airport, Greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, F.B.V.; do Nascimento, C.W.A.; Araújo, P.R.M.; da Silva, F.L.; Lima, L.H.V. Soil contamination by metals with high ecological risk in urban and rural areas. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pająk, M.; Szostak, M.; Sławiński, M. Geostatistical studies of forest environment contamination in Uroczysko Grodzisko in Bielansko-Tyniecki landscape park. Arch. Fotogram. Kartogr. I Teledetekcji 2012, 24, 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, R.; Hernandez, L.; Shaw, R.; Tunstead, R.; Ferguson, R.; Peaslee, S. Trace element concentration and speciation in selected urban soils in New York City. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, A.; Kalicz, P.; Farsang, A.; Balázs, P.; Berki, I.; Bidló, A. Influence of human impacts on trace metal contamination in soils of two Hungarian cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolan, N.S.; Adriano, D.C.; Natesan, N.; Koo, B.J. Effects of organic amendments on the reduction and phytoavailability of chromate in mineral soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworska, H.; Lemanowicz, J. Heavy metal contents and enzymatic activity in soils exposed to the impact of road traffic. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, C.; Boluda, R.; Ramos, J. Determination and evaluation of cadmium, lead and nickel in greenhouse soils of Almería (Spain). Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, C.; Giraudoux, P.; Coeurdassier, M.; Douay, F.; Raoul, F.; Pruvot, C.; Waterlot, C.; de Vaufleury, A.; Scheifler, R. Spatial distribution of metals in smelter-impacted soils of woody habitats: Influence of landscape and soil properties, and risk for wildlife. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallius, M.; Janssen, N.A.; Heinrich, J.; Hoek, G.; Ruuskanen, J.; Cyrys, J.; Van Grieken, R.; de Hartog, J.J.; Kreyling, W.G.; Pekkanen, J. Sources and elemental composition of ambient PM2.5 in three European cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 337, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasota, J.; Błońska, E.; Łyszczarz, S.; Tibbet, M. Forest Humus Type Governs Heavy Metal Accumulation in Specific Organic Matter Fractions. Water Air Spoil Pollut. 2020, 231, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błońska, E. Effect of Stand Species Composition on the Enzyme Activity and Organic Matter Stabilization in Forest Soil; Scientific Papers of University of Agriculture in Krakow No. 527; University of Agriculture in Krakow: Kraków, Poland, 2015; Volume 404. [Google Scholar]
- Ciarkowska, K. Organic matter transformation and porosity development in non-reclaimed mining soils of different ages and vegetation covers: A field study of soils of the zinc and lead ore area in SE Poland. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2066–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Liu, Y.; Tian, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M. Proper land use for heavy metal-polluted soil based on enzyme activity analysis around a Pb-Zn mine in Feng County, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 28152–28164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Layer | 0–10 cm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | FW | GW | FT | GT |
| 2.0–0.05 | 25.7 ± 15.5 b | 21.8 ± 10.1 b | 13.3 ± 1.5 a | 20.0 ± 1.9 ab |
| 0.05–0.002 | 67.8 ± 14.31 a | 69.0 ± 7.43 a | 73.0 ± 8.4 a | 67.7 ± 1.6 a |
| <0.002 | 6.5 ± 2.0 a | 9.2 ± 1.03 b | 13.7 ± 3.2 c | 12.3 ± 1.4 c |
| pH KCl | 3.6 ± 0.4 a | 4.3 ± 0.5 b | 4.5 ± 0.6 b | 4.7 ± 0.4 b |
| pH H2O | 4.6 ± 0.4 a | 5.2 ± 0.5 b | 5.2 ± 0.6 b | 5.2 ± 0.4 b |
| Hh | 108.2 ± 32.0 c | 59.3 ± 16.8 a | 80.0 ± 11.2 b | 45.7 ± 14.9 a |
| SOM | 65.82 ± 20.31 c | 37.76 ± 7.43 ab | 45.14 ± 7.41 b | 27.63 ± 3.63 a |
| N | 2.30 ± 0.88 a | 2.73 ± 1.03 a | 2.91 ± 0.69 a | 2.49 ± 0.63 a |
| K | 70.31 ± 19.59 a | 77.05 ± 38.43 a | 138.29 ± 21.67 b | 174.13 ± 17.81 c |
| P | 55.47 ± 31.53 b | 21.11 ± 10.40 a | 40.58 ± 6.92 b | 41.10 ± 9.02 b |
| Mg | 61.95 ± 16.15 a | 60.74 ± 23.80 a | 119.61 ± 22.92 b | 117.33 ± 10.12 b |
| DHA | 74.07 ± 36.75 a | 134.75 ± 14.62 b | 62.66 ± 25.48 a | 122.83 ± 15.96 b |
| URE | 40.14 ± 24.58 a | 143.33 ± 23.57 c | 36.87 ± 6.32 a | 105.57 ± 53.62 b |
| INW | 0.60 ± 0.37 a | 2.08 ± 0.70 c | 0.36 ± 0.06 a | 1.29 ± 0.26 b |
| Cd | 0.74 ± 0.26 ab | 0.62 ± 0.15 a | 1.05 ± 0.18 c | 0.85 ± 0.09 b |
| Pb | 76.37 ± 12.82 b | 44.79 ± 9.06 a | 102.76 ± 29.41 c | 66.36 ± 6.54 b |
| Cr | 41.20 ± 8.05 b | 30.37 ± 5.55 a | 52.64 ± 5.27 c | 40.86 ± 6.64 b |
| Zn | 103.76 ± 32.99 b | 70.01 ± 19.99 a | 125.47 ± 15.48 c | 93.59 ± 7.81 b |
| Igeo Cd | 1.36 ± 0.54 ab | 1.16 ± 0.39 a | 1.94 ± 0.25 c | 1.65 ± 0.15 bc |
| Igeo Pb | 2.36 ± 0.24 b | 1.57 ± 0.35 a | 2.74 ± 0.46 c | 2.17 ± 0.14 b |
| Igeo Cr | 0.00 ± 0.30 b | −0.44 ± 0.27 a | 0.37 ± 0.18 c | −0.01 ± 0.24 b |
| Igeo Zn | 1.13 ± 0.47 b | 0.57 ± 0.41 a | 1.47 ± 0.18 c | 1.05 ± 0.12 b |
| PLI | 3.52 ± 0.58 b | 2.48 ± 0.28 a | 4.74 ± 0.53 c | 3.49 ± 0.19 b |
| Layer | 10–30 cm | |||
| Parameter | FW | GW | FT | GT |
| 2.0–0.05 | 25.6 ± 16.0 c | 22.9 ± 10.7 bc | 13.3 ± 1.2 ab | 15.7 ± 1.2 a |
| 0.05–0.002 | 65.8 ± 13.8 a | 65.8 ± 6.8 a | 72.3 ± 2.5 a | 73.7 ± 2.0 a |
| 0.05–0.002 | 65.8 ± 13.8 a | 65.8 ± 6.8 a | 72.3 ± 2.5 a | 73.7 ± 2.0 a |
| pH KCl | 3.7 ± 0.3 a | 4.4 ± 0.6 b | 4.3 ± 0.6 b | 5.0 ± 0.2 c |
| pH H2O | 4.5 ± 0.2 a | 5.3 ± 0.3 b | 4.9 ± 0.2 b | 5.9 ± 0.2 c |
| Hh | 60.6 ± 16.0 c | 43.9 ± 10.7 b | 79.3 ± 11.2 d | 30.4 ± 7.5 a |
| SOM | 16.87 ± 8.37 a | 18.81 ± 6.81 a | 18.46 ± 4.49 a | 19.37 ± 2.89 a |
| N | 0.97 ± 0.59 a | 1.78 ± 0.95 b | 2.01 ± 0.45 b | 2.03 ± 0.48 b |
| K | 35.91 ± 7.70 a | 61.93 ± 34.46 b | 87.09 ± 21.97 c | 157.85 ± 43.89 d |
| P | 14.01 ± 3.49 a | 15.46 ± 9.68 a | 23.69 ± 3.58 b | 25.48 ± 8.21 b |
| Mg | 31.90 ± 6.02 a | 38.96 ± 10.37 a | 100.33 ± 19.85 b | 105.82 ± 9.532 b |
| DHA | 41.36 ± 7.34 b | 52.24 ± 10.25 c | 31.30 ± 8.17 a | 48.89 ± 18.18 bc |
| URE | 14.00 ± 10.49 a | 37.76 ± 17.77 b | 20.15 ± 5.10 a | 35.96 ± 13.68 b |
| INW | 0.12 ± 0.07 a | 0.23 ± 0.13 b | 0.12 ± 0.02 a | 0.19 ± 0.07 ab |
| Cd | 0.27 ± 0.08 a | 0.41 ± 0.12 b | 0.78 ± 0.07 c | 0.77 ± 0.08 c |
| Pb | 24.12 ± 10.06 a | 33.30 ± 6.05 b | 81.43 ± 10.00 d | 51.51 ± 4.20 c |
| Cr | 26.34 ± 5.69 a | 25.62 ± 4.73 a | 36.42 ± 5.04 b | 32.75 ± 5.66 b |
| Zn | 79.66 ± 25.66 b | 45.35 ± 11.15 a | 82.36 ± 14.02 c | 64.34 ± 8.13 b |
| Igeo Cd | −0.05 ± 0.31 a | 0.53 ± 0.45 b | 1.53 ± 0.14 c | 1.51 ± 0.14 c |
| Igeo Pb | 0.58 ± 0.46 a | 1.16 ± 0.26 b | 2.46 ± 0.29 d | 1.78 ± 0.12 c |
| Igeo Cr | −0.65 ± 0.31 a | −0.68 ± 0.26 a | −0.17 ± 0.16 b | −0.33 ± 0.22 b |
| Igeo Zn | 0.75 ± 0.48 bc | −0.03 ± 0.25 a | 0.85 ± 0.24 c | 0.50 ± 0.18 b |
| PLI | 1.70 ± 0.30 a | 1.79 ± 0.22 a | 3.38 ± 0.20 c | 2.79 ± 0.22 b |
| pH | Hh | SOM | N | K | P | Mg | DHA | URE | INW | Cd | Pb | Cr | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Hh | −0.58 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| SOM | −0.15 | 0.65 | 1 | |||||||||||
| N | 0.42 | ns | 0.41 | 1 | ||||||||||
| K | 0.68 | −0.27 | ns | 0.42 | 1 | |||||||||
| P | −0.15 | 0.62 | 0.70 | ns | 0.32 | 1 | ||||||||
| Mg | 0.58 | ns | 0.15 | 0.39 | 0.82 | 0.36 | 1 | |||||||
| DHA | 0.22 | ns | 0.41 | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 0.20 | 1 | ||||||
| URE | 0.18 | −0.16 | 0.18 | 0.39 | 0.16 | ns | ns | 0.70 | 1 | |||||
| INW | 0.16 | ns | 0.31 | 0.48 | ns | ns | ns | 0.80 | 0.81 | 1 | ||||
| Cd | 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.35 | 0.50 | 0.58 | 0.32 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 1 | |||
| Pb | ns | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.40 | 0.44 | 0.55 | 0.65 | ns | ns | ns | 0.72 | 1 | ||
| Cr | ns | 0.34 | 0.40 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.54 | ns | ns | ns | 0.63 | 0.68 | 1 | |
| Zn | −0.16 | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.57 | 0.44 | 0.16 | ns | ns | 0.46 | 0.75 | 0.56 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solek-Podwika, K.; Ciarkowska, K. Sources of the Trace Metals Contaminating Soils in Recreational Forest and Glade Areas in Krakow, a Large City in Southern Poland. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6874. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166874
Solek-Podwika K, Ciarkowska K. Sources of the Trace Metals Contaminating Soils in Recreational Forest and Glade Areas in Krakow, a Large City in Southern Poland. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):6874. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166874
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolek-Podwika, Katarzyna, and Krystyna Ciarkowska. 2024. "Sources of the Trace Metals Contaminating Soils in Recreational Forest and Glade Areas in Krakow, a Large City in Southern Poland" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 6874. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166874
APA StyleSolek-Podwika, K., & Ciarkowska, K. (2024). Sources of the Trace Metals Contaminating Soils in Recreational Forest and Glade Areas in Krakow, a Large City in Southern Poland. Sustainability, 16(16), 6874. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166874






