The Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis Mechanisms of the Zaozigou Geothermal Field
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Background
3. Sampling and Methods
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Types of Water Chemistry
4.2. Groundwater Characteristic Coefficient
4.3. Isotopic Chemical Characteristics
4.3.1. Geothermal Water Source
4.3.2. Elevation of Geothermal Water Supply Area
4.3.3. Age Calculation of Geothermal Water
4.4. Estimation of Geothermal Reservoir Temperature
4.4.1. Cation Geothermometer
4.4.2. Silica Geothermometer
4.4.3. Geothermal Reservoir Temperature Estimation
4.4.4. Silicon–Enthalpy Model
4.5. Geothermal Water Circulation Depth
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.; Kong, X.J.; Yuan, L.J.; Gao, J.; Shen, P.F.; Feng, H.; Hao, W.J.; He, Y.C. General situation and suggestions of development and utilization of geothermal resources in China. China Min. Mag. 2020, 29, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Luo, Z.; Du, J.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis of geothermal water in Xiaoyangkou, Nantong, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Han, S.; Wang, G. Study on Chemical Genesis of Deep Geothermal Fluid in Gaoyang Geothermal Field. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 9, 787222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procesi, M.; Marini, L.; Cinti, D.; Sciarra, A.; Basile, P.; Mazzoni, T.; Zarlenga, F. Preliminary fluid geochemical survey in Tete Province and prospective development of geothermics in Mozambique. Geotherm. Energy 2022, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollaro, C.; Fuoco, I.; Gennaro, E.; Giuliani, L.; Iezzi, G.; Marini, L.; Vespasiano, G. Advanced argillic alteration at Cave di Caolino, Lipari, Aeolian Islands (Italy): Implications for the mitigation of volcanic risks and the exploitation of geothermal resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 889, 164333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.X.; Shi, X. The control of basin mountain structure pattern on the distribution of geothermal field and the types of geothermal resources in Gansu Province. In Proceedings of the International Geothermal Society Western Pacific Papers, Chengdu, China, 1 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Sun, Z.X.; Li, B.X. Distribution characteristics, development status and prospect of geothermal resources in Gansu Province. Acta Geol. Gansu 2005, 14, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, X.M.; Wang, D.Y.; Li, F.J. Analysis of geological conditions on geothermal and the conceptual model of geothermal reservoir in Lanzhou-Minhe Basin. Northwestern Seismol. J. 2003, 3, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, F.; Ma, G. Analysis on the occurrence characteristics of geothermal resources in Lanzhou. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2005, 32, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Li, W.X. Genetic model and geological model of geothermal water in Yongdeng County, Lanzhou City. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2015, 34, 194–220. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.W.; Yao, J.L.; He, J.H. Environmental isotope characteristics and groundwater recharge in groundwater level rise area in Zhangye City. Arid Land Geogr. 2009, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; Qin, X.; Wang, Y. Glacier meltwater runoff process analysis based on δD and δ18O isotope and chemistry in the Laohugou glacier basin of the Qilian Mountains. Arid Land Geogr. 2015, 38, 927–935. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.R.; Li, H.Y.; Cao, S.C.; Liu, K.F.; Wang, K. Deep ground temperature variation and mutation of the Hexi Corridor region in recent 31 years. Arid Land Geogr. 2013, 36, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z. Discussion on feature of isotope component from atmospheric water, groundwater and underground water in Northwest area, China. Acta Geol. Gausu 1993, 2, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Jin, G.; Liao, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, P. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the origin of Late Triassic granitoids from the Qinling orogen, central China: Implications for a continental arc to continent-continent collision. Lithos 2010, 117, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.F.; Yu, H.C.; Deng, J.; McIntire, D.; Gou, Z.Y.; Geng, J.Z.; Chang, Z.S.; Zhu, R.; Li, K.N.; Goldfarb, R. The giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit in West Qinling, China: Magmatic- or metamorphic-hydrothermal origin? Miner. Depos. 2020, 55, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.P.; Zhang, G.W.; Neubauer, F.; Liu, X.M.; Genser, J.; Hauzenberger, C. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, China: Review and synthesis. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.F.; Deng, J. Petrogenesis of granitoids in the Dewulu skarn copper deposit:implications for the evolution of the Paleotethys ocean and mineralization in western Qinling, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 90, 1078–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.X.; Li, J.W.; Jin, X.Y.; Vasconcelos, P.; Zhu, R. 40Ar/39Ar and U-Pb constraints on the age of the Zaozigou gold deposit, Xiahe-Hezuo district, West Qinling orogen, China: Relation to Early Triassic reduced intrusions emplaced during slab rollback. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 101, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, H.; Jia, R.; Yan, K.; Li, P.; Wang, T.; Wei, L. Construction of the geological model of “Trinity” prospecting prediction in Zaozigou gold deposit, Gansu Province. Miner. Explor. 2019, 10, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T11615-2010; Geologic Exploration Standard of Geothermal Resources. Chinese Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Güler, C.; Thyne, G.D.; McCray, J.E.; Turner, K.A. Evaluation of graphical and multivariate statistical methods for classification of water chemistry data. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, K.; Lu, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, K.; Wu, X. A review of geothermal energy resources, development, and applications in China: Current status and prospects. Energy 2015, 93, 466–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, J.; Absar, A.; Bhat, G.; Cadel, G.; Hafiz, M.; Hakhoo, N.; Kashkari, R.; Moore, J.; Ricchiuto, T.E.; Thurow, J.; et al. Hot springs and the geothermal energy potential of Jammu & Kashmir State, N.W. Himalaya, India. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 126, 156–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.P.; Liu, E.K.; Wang, D.S.; Jia, Y.K.; Sun, J.C. Composition of stable isotopes of precipitation and controlling factors in China. Bull. Inst. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. CAGS 1991, 7, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Maloszewski, P.; Zuber, A. Comment on “Convergent radial dispersion in a double-porosity aquifer with fracture skin: Analytical solution and application to a field experiment in fractured chalk” by Allen F. Moench. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloszewski, P.; Zuber, A. On the calibration and validation of mathematical models for the interpretation of tracer experiments in groundwater. Adv. Water Resour. 1994, 15, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.C.; Wang, E.L.; Liu, C.L. Characteristics and origin oftritium in the potassium-rich brine in Lop Nur, Xinjiang. Nucl. Tech. 2004, 27, 710–715. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Mao, X.; Tong, S.; Feng, L. Using hydrochemical geothermometers calculate exchange temperature of deep geothermal system in west coastal area of Guangdong Province. Earth Sci.-J. China Univ. Geosci. 2016, 41, 2075–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Guo, Y. Fundamentals of Geothermics; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Z.; Rong, F.; Chen, K.; Nan, D.; Liu, S.J.; Liu, S. Characteristics and Source Mechanism of Geothermal Field in Cuona, Tibet. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2021, 40, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggenbach, W.F. Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2749–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Lu, C.; Gan, H.; Zhao, L. Evolution of Deep Parent Fluids of Geothermal fields in the Nimu–Nagchu Geothermal belt, Tibet, China. Geothermics 2018, 71, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnorsson, S. Application of the silica geothermometer in low temperature hydrothermal areas in Iceland. Am. J. Sci. 1975, 275, 763–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Q.; Peng, Q.; Duan, Q.S.; Xia, Y.L. Hydrochemistry characteristics and origin of geothermal water in northeastern Guizhou. Earth Sci. 2019, 44, 2874–2886. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. A Research on Geochemical Characteristics of Geothermal Fluids in Southeast Yunnan Province, China; Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, R.O.; Truesdell, A.H. Geochemical indicators of subsurface temperature. Part II. Estimation of temperature and fraction of hot water mixed with cold water. J. Res. US Geol. Surv. 1974, 2, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, X.J.; Lin, W.J.; Liu, Z.M.; Xing, L.; Wang, G. Hydrochemical characteristics of geothermal water in Guide Basin. Earth Sci. 2016, 41, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, N.; Yu, S.; Ding, H.; Zhang, M. Occurrence features of geothermal resources and geothermal potential assessment in Gansu Province. Geol. China 2020, 47, 1804–1812, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
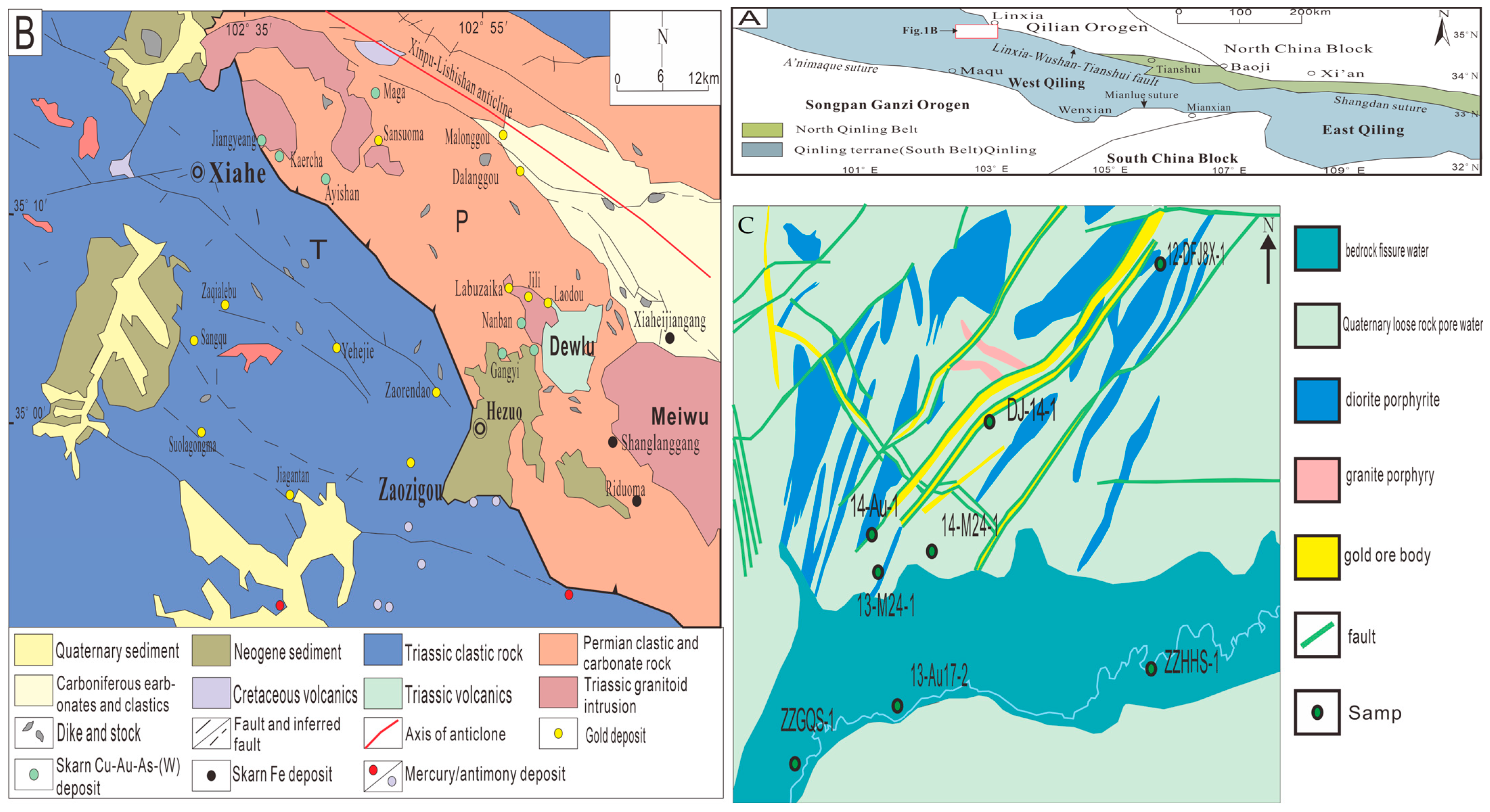
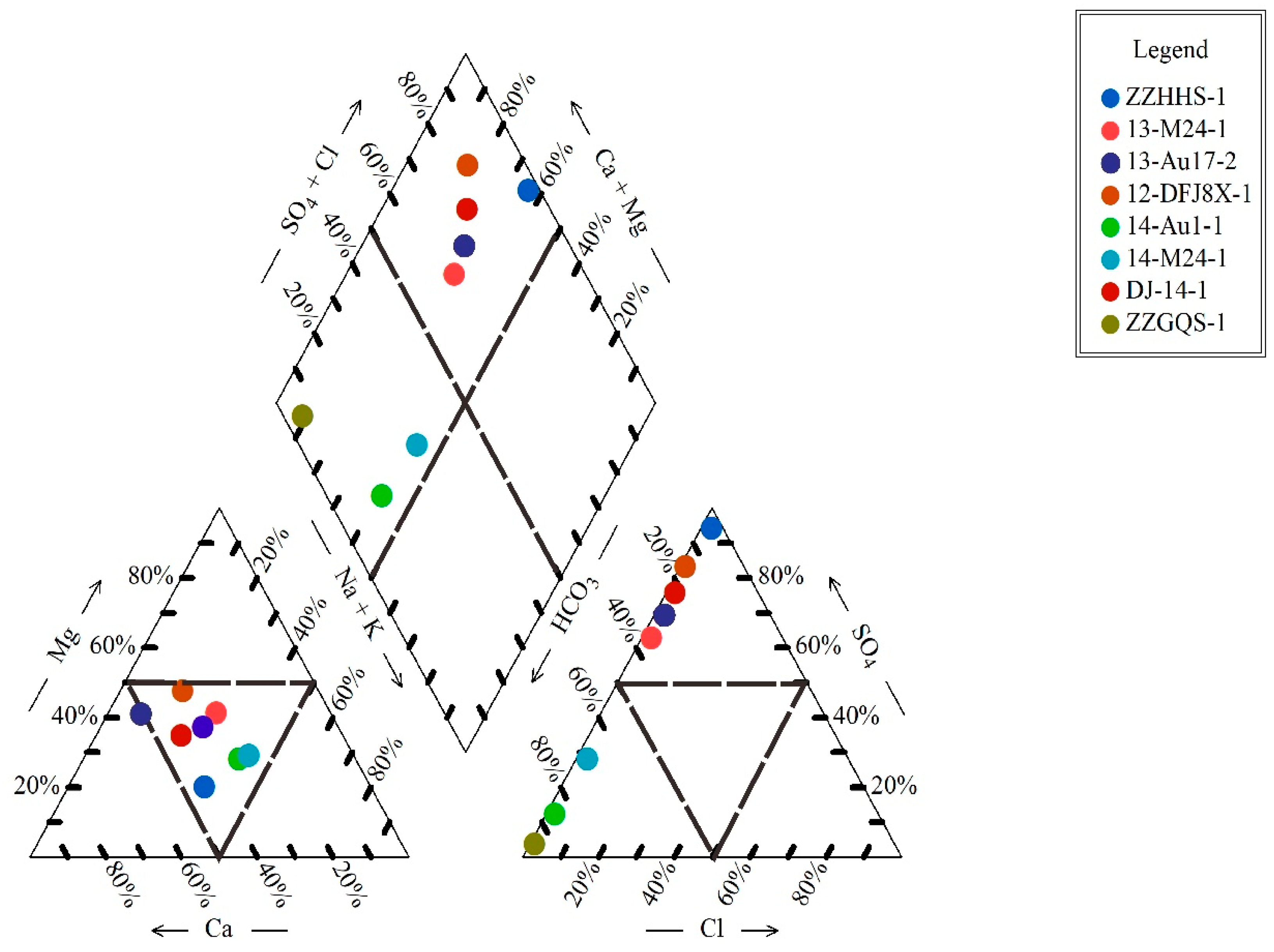
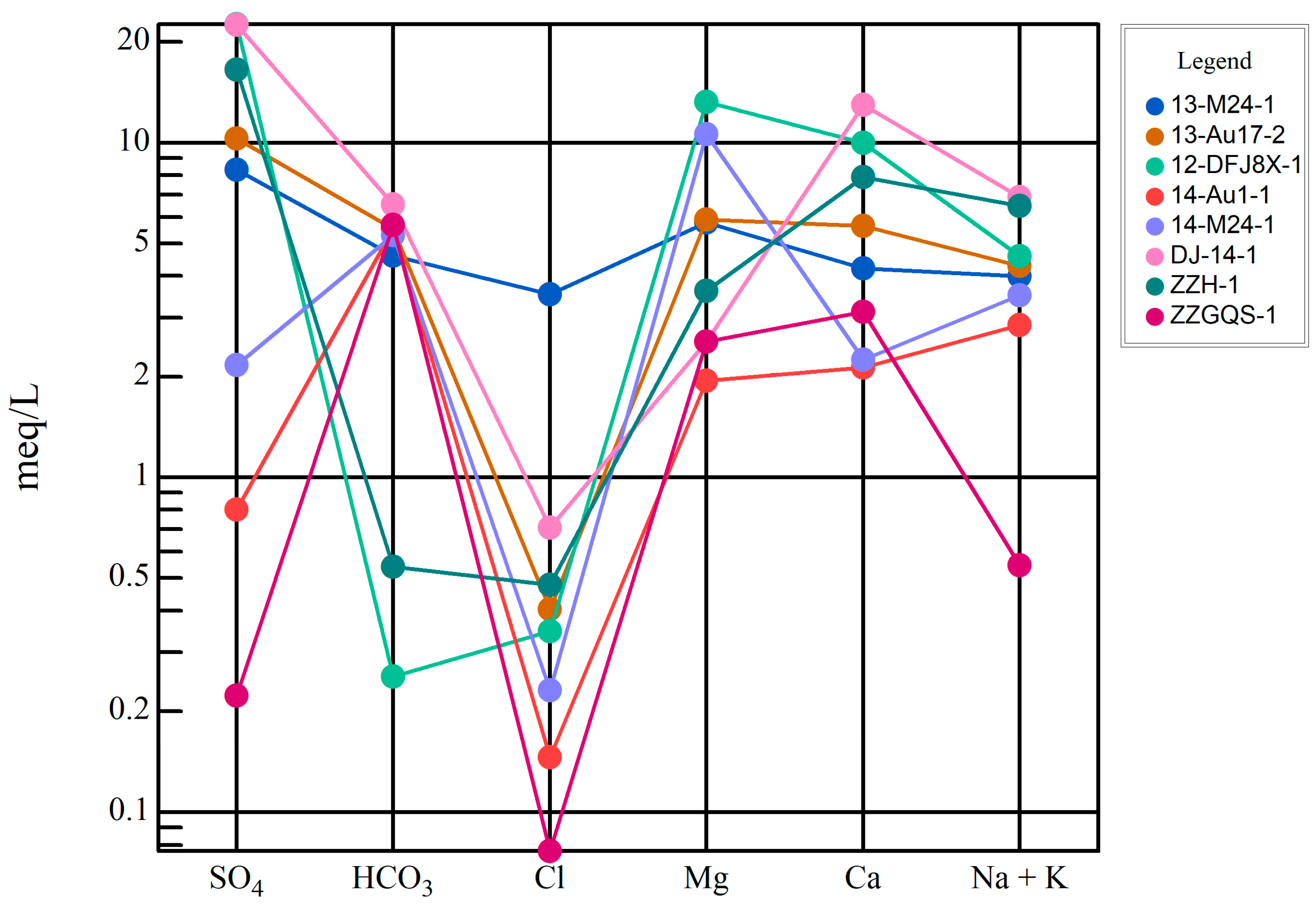

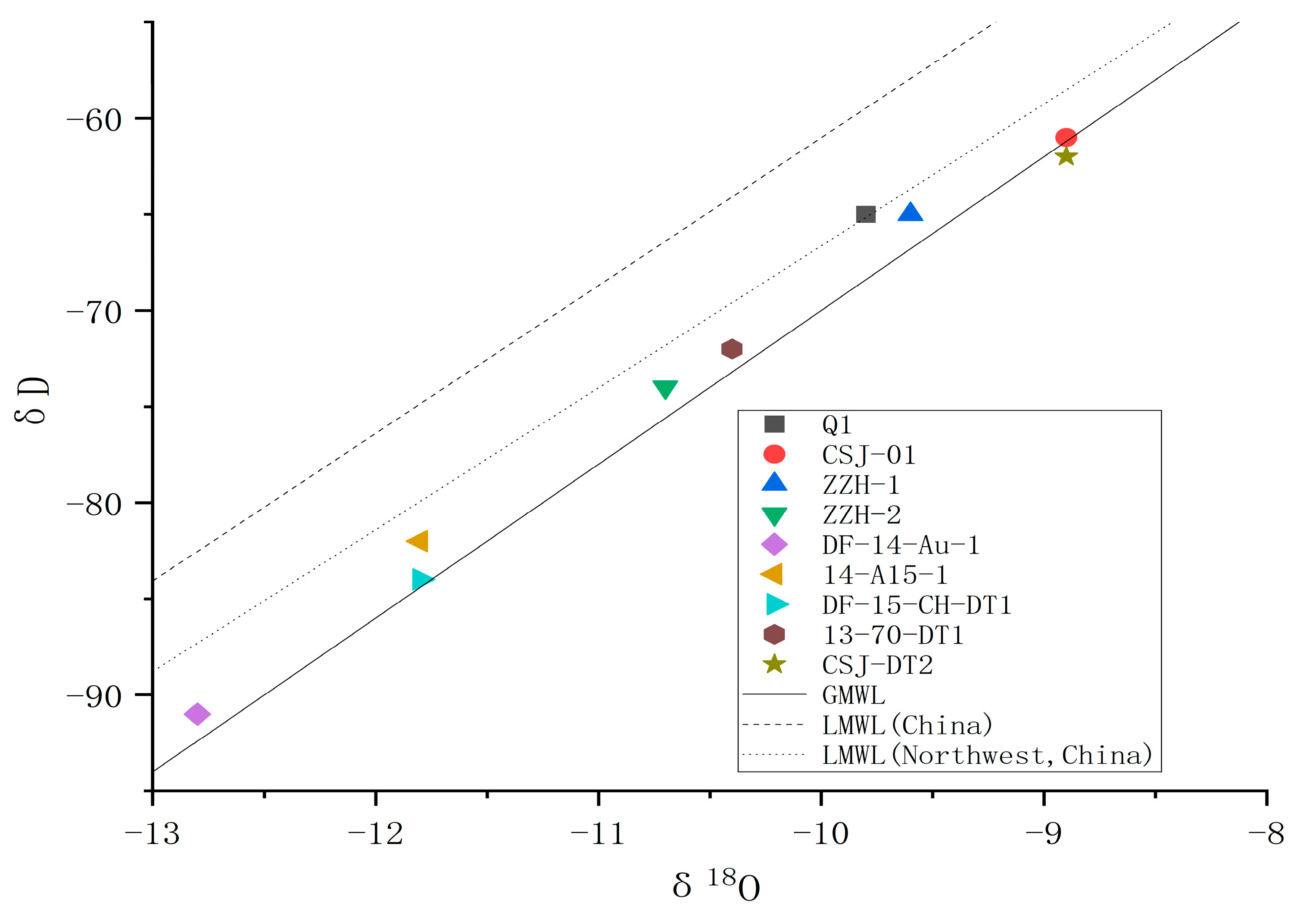
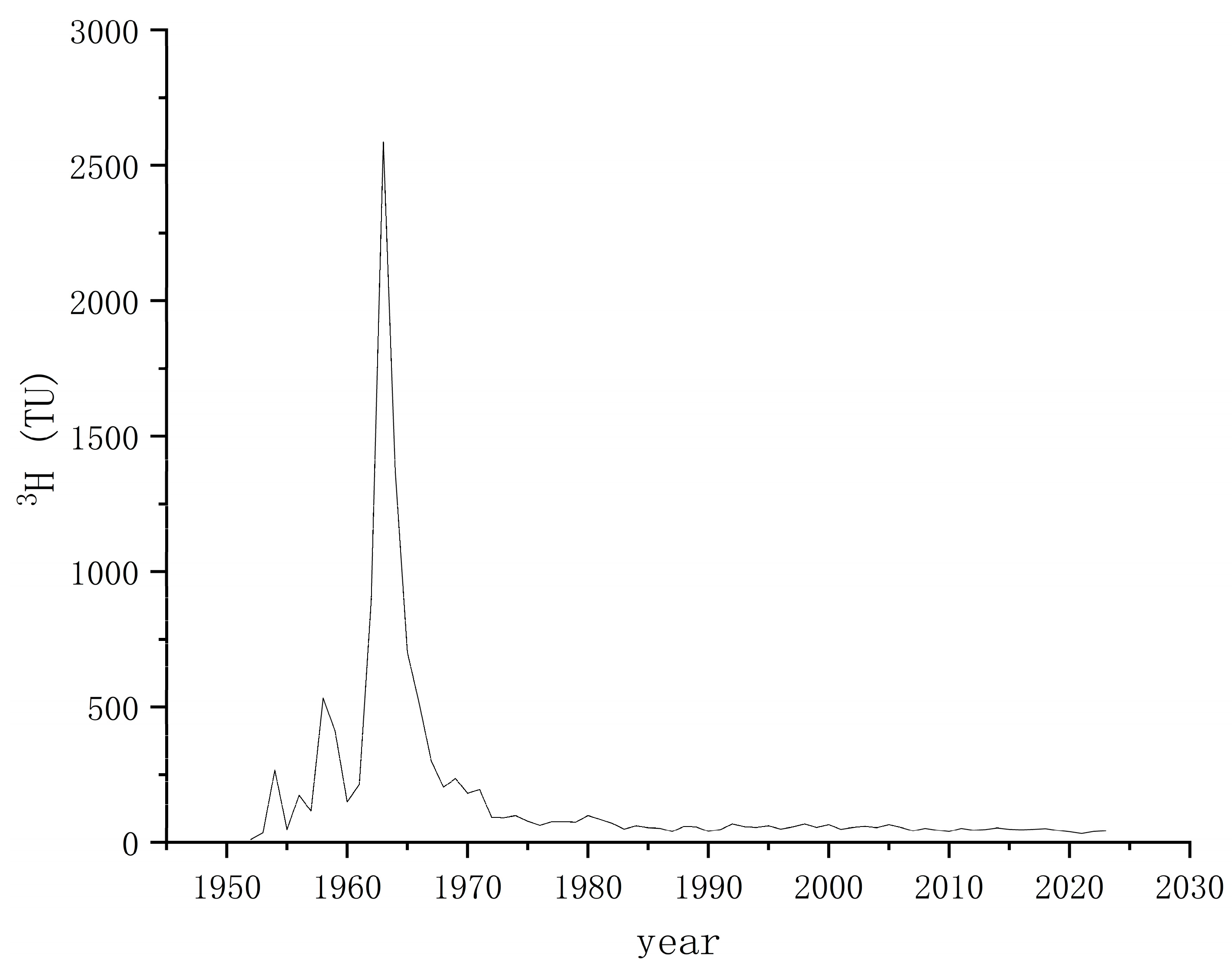
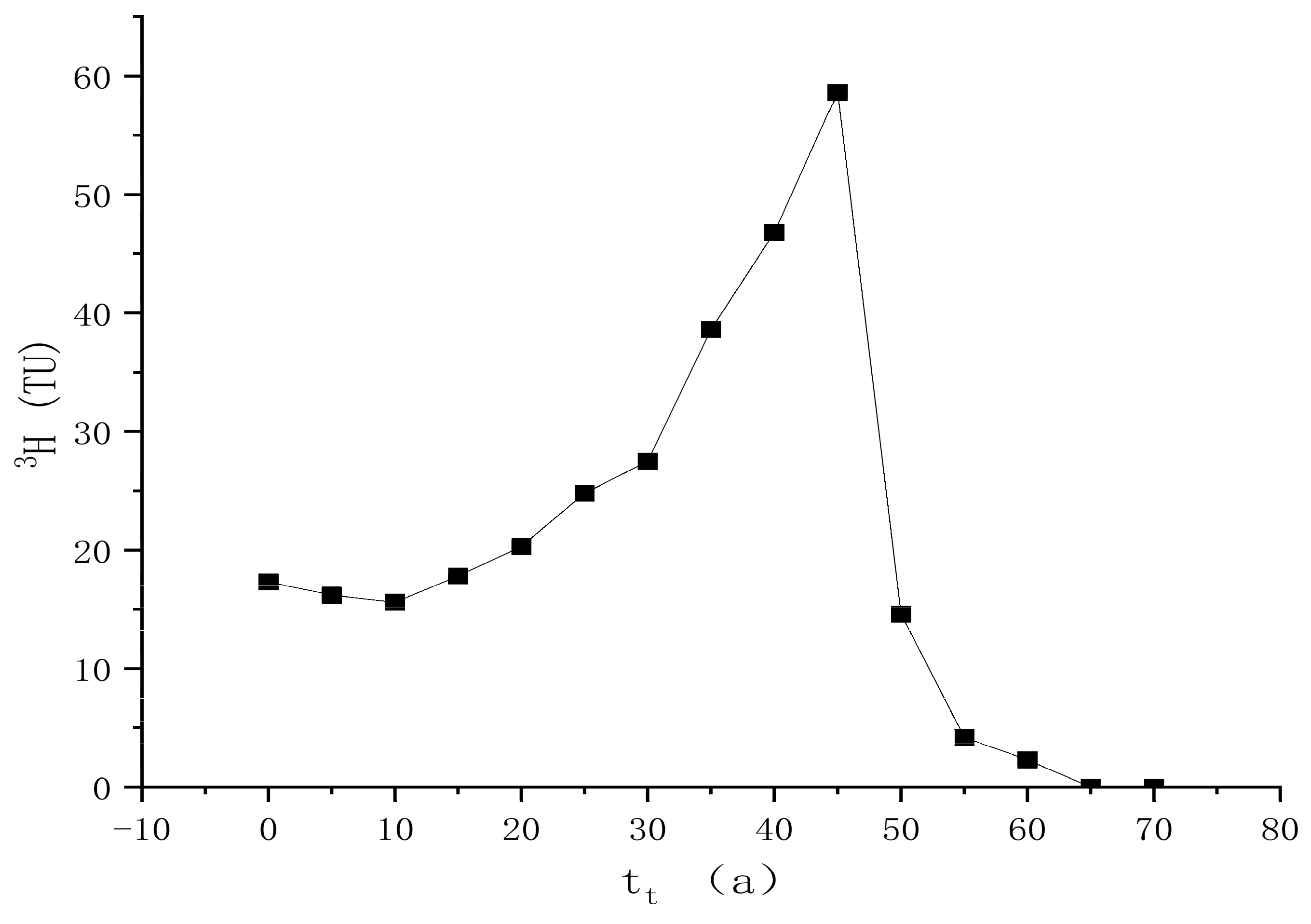


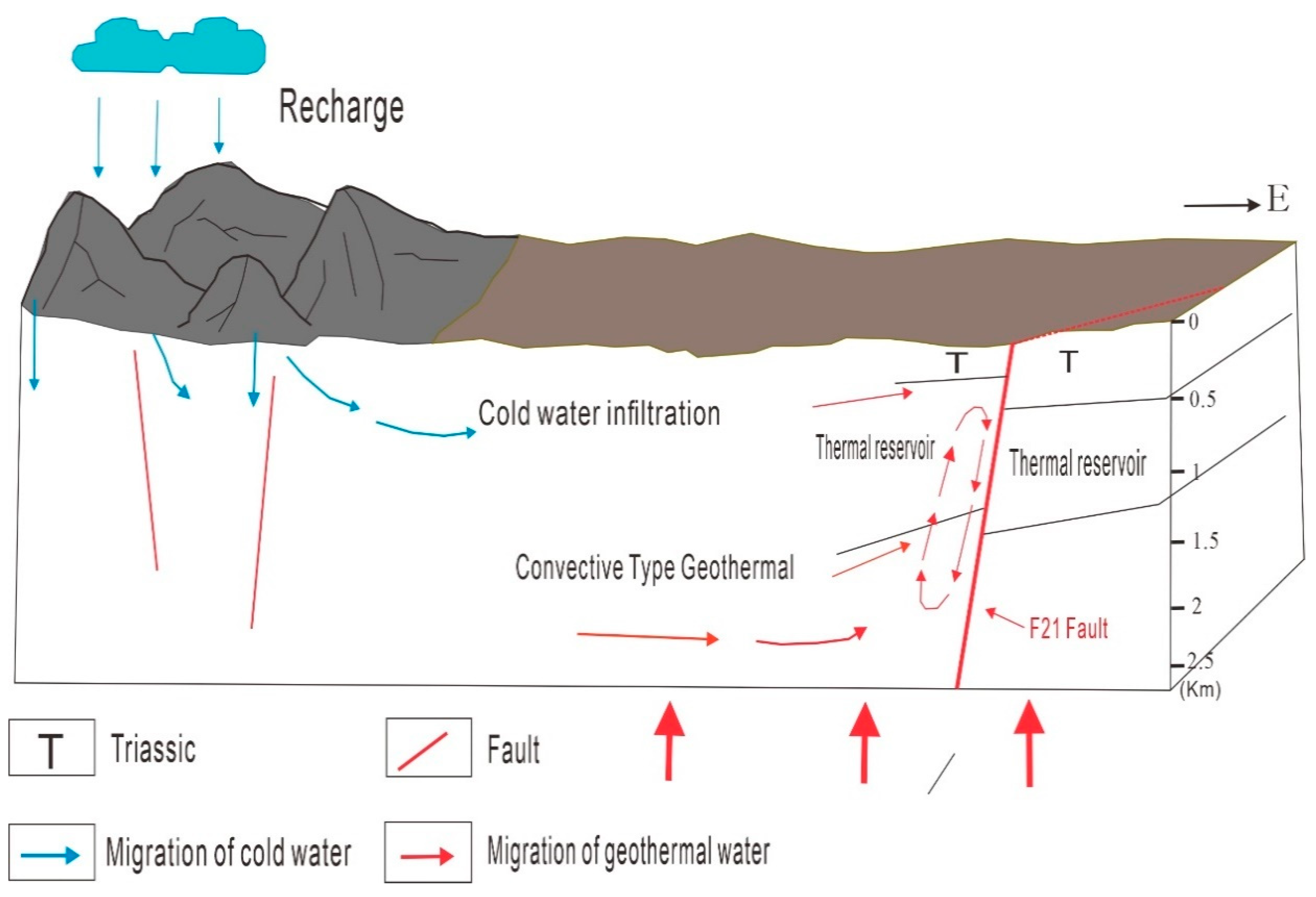
| Sample ID | Depth | Temp | Ph | TDS | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | CO32− | Charge Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (°C) | (mg/L) | (%) | ||||||||||
| 13-M24-1 | 538 | 22 | 8.21 | 788 | 88.7 | 5.42 | 84.3 | 70.1 | 125 | 399 | 280 | 0 | 2.94 |
| 13-Au17-2 | 582 | 24 | 8.15 | 924 | 95 | 5.65 | 113 | 71.5 | 14.3 | 494 | 337 | 0 | 2.93 |
| 12-DFJ8X-1 | 602 | 26 | 8.095 | 1805 | 99.4 | 10.3 | 200 | 161 | 12.3 | 1086 | 15.5 | 0 | 1.09 |
| 14-Au1-1 | 635 | 32 | 8.13 | 348 | 63.8 | 3.04 | 42.7 | 23.6 | 5.17 | 38.5 | 337 | 0 | 4.48 |
| 14-M24-1 | 653 | 40 | 8.21 | 414 | 73.5 | 11.8 | 45 | 129 | 8.2 | 104 | 323 | 0 | 2.66 |
| DJ-14-1 | 687 | 20 | 8.01 | 1886 | 151 | 11.8 | 260 | 30.9 | 25.1 | 1081 | 399 | 0 | 1.16 |
| ZZH-1 | - | 11 | 7.94 | 276 | 144 | 8.38 | 158 | 43.8 | 16.9 | 794 | 33 | 0 | 1.41 |
| ZZGQS-1 | - | 9 | 8.3 | 311 | 11.6 | 1.59 | 62.6 | 30.9 | 2.72 | 10.7 | 346 | 0 | 1.97 |
| Serial Number | Type | rNa+/rCl− | rCl−/rHCO3− + rCO32− |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZZHHS-1 | surface water | 13.138 | 0.881 |
| 13-M24-1 | geothermal well | 10.942 | 0.076 |
| 13-Au17-2 | geothermal well | 10.244 | 0.096 |
| 12-DFJ8X-1 | geothermal well | 12.461 | 0.082 |
| 14-Au1-1 | geothermal well | 19.029 | 0.026 |
| 14-M24-1 | geothermal well | 13.821 | 0.043 |
| DJ-14-1 | geothermal well | 9.276 | 0.108 |
| ZZGQS-1 | hot spring | 6.576 | 0.013 |
| Sample ID | δ18O | δD | 3H | Recharge Elevation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‰ | ‰ | Tu | m | |
| Q1 | −65 | −9.8 | 14.0 ± 1.0 | 3117 |
| CSJ-01 | −61 | −8.9 | 16.6 ± 1.1 | 3153 |
| ZZH-1 | −65 | −9.6 | 13.1 ± 1.0 | 3152 |
| ZZH-2 | −74 | −10.7 | 8.4 ± 0.9 | 3327 |
| DF-14-Au-1 | −91 | −12.8 | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 3309 |
| 14-A15-1 | −82 | −11.8 | 5.3 ± 0.8 | 3334 |
| Estimation Method | 13-M24-1 | 13-Au17-2 | 12-DFJ8X-1 | 14-Au1-1 | 14-M24-1 | DF-14-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz geothermometer (°C) | 42.3 | 47.46 | 54.81 | 59.93 | 70.27 | 39 |
| Chalcedony geothermometer (°C) | 9.69 | 14.89 | 22.43 | 27.73 | 38.48 | 6.26 |
| lg(Q/K)-T geothermometer (°C) | 42 | 48 | 52 | 55 | 70 | 38 |
| Silicon–enthalpy geothermometer (°C) | 152 | 143 | 161 | 170 | 246 | 106 |
| Cold water mixing ratio (%) | 91.3 | 89.1 | 90.4 | 91.4 | 94.5 | 83.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, A. The Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis Mechanisms of the Zaozigou Geothermal Field. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166790
Wang Y, Li B, Chen A. The Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis Mechanisms of the Zaozigou Geothermal Field. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):6790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166790
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuang, Baozhu Li, and Aibing Chen. 2024. "The Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis Mechanisms of the Zaozigou Geothermal Field" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 6790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166790
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, B., & Chen, A. (2024). The Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis Mechanisms of the Zaozigou Geothermal Field. Sustainability, 16(16), 6790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16166790




