Physicochemical and Nutritional Characterization of Green Banana Flour from Discarded Cavendish Bananas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
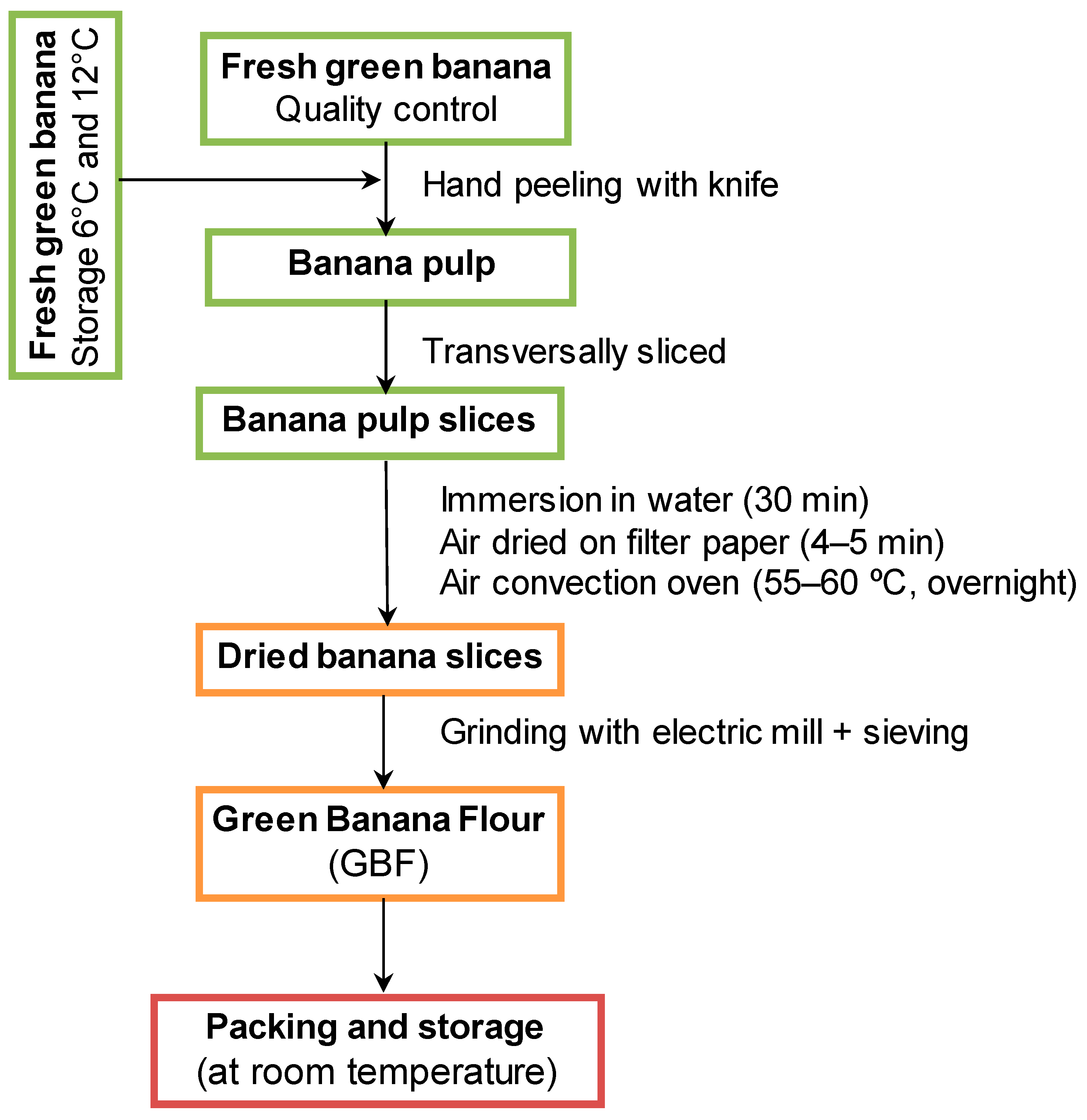
2.1. Preparation of Banana Flour
2.2. Optimization of GBF Production
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. GBF Preservation at Room Temperature
2.5. Influence of Green Banana Storage Conditions on the Physicochemical Characteristics of the GBF Produced
2.6. Food Preparation and Acceptance Study
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of GBF Production
3.2. Physicochemical and Nutritional Characteristics of the GBF
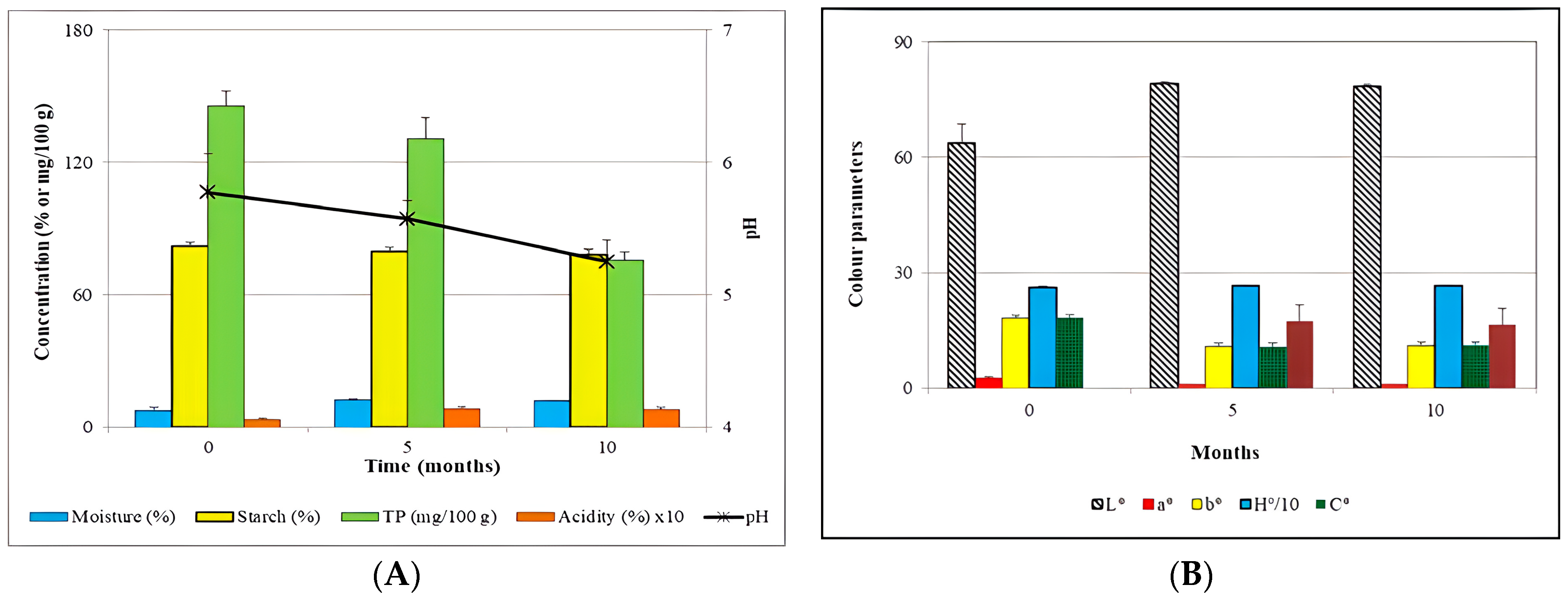
3.3. Physicochemical Changes in GBF during Storage at Room Temperature
3.4. Physicochemical Changes of the GBF According to the Storage Conditions of the Green Bananas Waste Used in Their Preparation
3.5. GBF Evaluation in Food Preparation
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- InfoAgro. Plátano de Canarias bate su récord histórico en volumen de producción y comercialización. Available online: https://www.infoagro.com/noticias/2024/platano_de_canarias_bate_su_record_historico_en_volumen_de_produccion_.asp (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- DOUE. Reglamento de Ejecución (UE) n.° 1333/2011 DE LA COMISIÓN de 19 de diciembre de 2011 por el que se fijan las normas de comercialización para los plátanos, las reglas para el control de la aplicación de dichas normas de comercialización y los requisitos aplicables a las notificaciones en el sector del plátano. Diario Oficial de la Unión Europea L 336, 20 December 2011; 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Asprocan (Asociación de Organizaciones de Productores de Plátanos de Canarias). Available online: https://platanodecanarias.es/asprocan-pdc/cifras (accessed on 14 January 2024).
- del Mar Verde-Méndez, C.; Forster, M.P.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.A.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E.M.; Díaz-Romero, C. Content of free phenolic compounds in banana from Tenerife (Canary Islands) and Ecuador. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2003, 217, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, M.P.; Rodríguez Rodríguez, E.; Díaz Romero, C. Differential characteristics in the chemical composition of bananas from Tenerife (Canary Islands) and Ecuador. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7586–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juárez-García, E.; Agama-Acevedo, E.; Sáyago-Ayerdi, S.G.; Rodríguez-Ambriz, S.L.; Bello-Pérez, L.A. Composition, digestibility and application in breadmaking of banana flour. Plant Foods Human Nutr. 2006, 61, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pico, J.; Xu, K.; Guo, M.; Mohamedshah, Z.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Martínez, M.M. Manufacturing the ultimate green banana flour: Impact of drying and extrusion on phenolic profile and starch bioaccessibility. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurore, G.; Parfait, B.; Fahrasmane, L. Bananas, raw materials for making processed food products. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2009, 20, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragati, S.; Genitha, I.; Ravish, K. Comparative study of ripe and unripe banana flour during storage. J. Food Proc. Technol. 2014, 5, 1000384. [Google Scholar]
- Falcomer, A.L.; Riquette, R.F.R.; de Lima, B.R.; Ginani, V.C.; Zandonadi, R.P. Health benefits of green banana consumption: A systematic review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi de Alcântara, R.; Aparecida de Carvalho, R.; Maria Vanin, F. Evaluation of wheat flour substitution type (corn, green banana and rice flour) and concentration on local dough properties during bread baking. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoozani, A.A.; Birch, J.; Bekhit, A.E.A. Production, application and health effects of banana pulp and peel flour in the food industry. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño-Rodríguez, O.; Agama-Acevedo, E.; Pacheco-Vargas, G.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J.; Bello-Pérez, L.A. Physicochemical, microstructural and digestibility analysis of gluten-free spaghetti of whole unripe plantain flour. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radünz, M.; Camargo, T.M.; Nunes, C.F.P.; Pereira, E.D.S.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Hackbart, H.C.D.S.; Radünz, A.F.O.; Radünz, A.L.; Gularte, M.A.; Barbosa, F.D.F. Gluten-free green banana flour muffins: Chemical, physical, antioxidant, digestibility and sensory analysis. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.A.; Barbosa, J.L., Jr.; Barbosa, M.I.M.J. Green banana flour as a functional ingredient in food products. Ciência Rural 2015, 45, 2252–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Thomas, L.; Khashawi, R. Influence of hot air and freeze-drying on functional, rheological, structural and dielectric properties of green banana flour and dispersions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P&G Food Industries. Green Banana Flour. Available online: https://www.pgfoodsind.com/products/green-banana-flour (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Borges, C.V.; Amorim, E.P.; Leonel, M.; Gomez, H.A.G.; Santos, T.P.R.; Ledo, C.A.S.; Belin, M.A.F.; Almeida, S.L.; Minatel, I.O.; Lima, G.P.P. Post-harvest physicochemical profile and bioactive compounds of 19 bananas and plantains genotypes. Bragantia 2019, 78, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, K.R.; Uribe, S.J. [Relation of starch and soluble sugars during the maturation process of ‘Prata’ banana]. J. Agric. Technol. Sci. 2018, 12, 51–56. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano, A.; Rosell, C.M.; Cornejo, F. Physicochemical and nutritional characteristics of banana flour during ripening. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Loesecke, W.H. Bananas Chemistry, Physiology and Technology; Interscience Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 18th ed.; Horwitz, W., Jr., Latimer, G.W., Eds.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bondet, V.; Brand-Williams, B.; Berset, W. Kinetics and mechanisms of antioxidant activity using the DPPH• free radical method. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 30, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Montelongo, R.; Lobo, M.G.; González, M. Antioxidant activity in banana peel extracts: Testing extraction conditions and related bioactive compounds. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção Barroso, W.; Carvalho Abreu, I.; Sousa Ribeiro, L.; Quintino da Rocha, C.; Possolo de Souza, H.; Martins de Lima, T. Chemical composition and cytotoxic screening of Musa cavendish green peels extract: Antiproliferative activity by activation of different cellular death types. Toxicology In Vitro 2019, 59, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyasi, T.A.; Jideani, A.I.O.; Mchau, G.R.A. Effects of organic acid pretreatment on microstructure, functional and thermal properties of unripe banana flour. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, A.C.; Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Méndez-Montealvo, G.; Almeida, C.A.; Lajolo, F. Rheological and functional properties of flours from banana pulp and peel. Starch-Stärke 2010, 62, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, E.W.; Tadini, C.C.; Tribess, T.B.; Zuleta, A.; Binaghi, J.; Pak, N.; Vera, G.; Dan, M.C.T.; Bertolini, A.C.; Cordenunsi, B.R.; et al. Chemical composition and nutritional value of unripe banana flour (Musa acuminata var. Nanicão). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2011, 66, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Prado Ferreira, M.; Teixeira Tarley, C.R. Assessment of in vitro bioacessibility of macrominerals and trace elements in green banana flour. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2020, 92, 103586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarawong, C.; Schoenlechner, R.; Sekiguchi, K.; Berghofer, E.; Ng, P.K. Effect of extrusion cooking on the physicochemical properties, resistant starch, phenolic content and antioxidant capacities of green banana flour. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savlak, N.; Türker, B.; Yeşilkanat, N. Effects of particle size distribution on some physical, chemical and functional properties of unripe banana flour. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segundo, C.; Román, L.; Gómez, M.; Martínez, M.M. Mechanically fractionated flour isolated from green bananas (M. cavendishii var. nanica) as a tool to increase the dietary fiber and phytochemical bioactivity of layer and sponge cakes. Food Chem. 2017, 219, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.J.; Hung, C.C. Chemical composition and in vitro starch digestibility of green banana (cv. Giant Cavendish) flour and its derived autoclaved/debranched powder. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemeh, S.R.; Saifullah, R.; Abbas, F.M.A.; Azhar, M.E. Total phenolics, flavonoids and antioxidant activity of banana pulp and peel flours: Influence of variety and stage of ripeness. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Nutrition Board; Institute of Medicine of the National Academies. Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements; Otten, J.J., Hellwig, J.P., Meyers, L.D., Eds.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Cook, A.; Subar, A.F.; Cleveland, L.; Friday, J. Assessing fruit and vegetable intakes: Toward the year 2000. Am. J. Public Health 1995, 85, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brat, P.; Bugaud, C.; Guillermet, C.; Salmon, F. Review of banana green life throughout the food chain: From autocatalytic induction to the optimization of shipping and storage conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 262, 109054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Green Banana Flour | |
|---|---|---|
| With Citric Acid | Without Citric Acid | |
| Moisture (%) | 7.24 ± 1.69 | 7.24 ± 1.71 |
| Starch (%) | 81.87 ± 2.11 | 82.09 ± 1.55 |
| Protein (%) | 5.36 ± 0.20 | 5.48 ± 0.22 |
| Fiber (%) | 7.64 ± 0.33 | 7.72 ± 0.32 |
| Ash (%) | 3.68 ± 0.21 | 3.48 ± 0.23 |
| P (g kg−1) | 0.91 ± 0.07 | 0.90 ± 0.06 |
| K (g kg−1) | 14.30 ± 0.68 | 14.19 ± 0.80 |
| Ca (g kg−1) | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 0.16 ± 0.04 |
| Mg (g kg−1) | 1.39 ± 0.08 | 1.33 ± 0.16 |
| Fe (mg kg−1) | 11.14 ± 3.01 | 11.09 ± 3.12 |
| Cu (mg kg−1) | 2.54 ± 1.08 | 2.51 ± 0.98 |
| Zn (mg kg−1) | 7.42 ± 1.05 | 7.39 ± 1.31 |
| Mg (mg kg−1) | 2.63 ± 0.36 | 2.69 ± 0.29 |
| pH | 5.72 ± 0.09 | 5.77 ± 0.30 |
| Acidity (%) | 0.55 ± 0.19 | 0.34 ± 0.06 |
| L* | 63.95 ± 5.57 | 63.63 ± 5.09 |
| a* | 2.84 ± 1.00 | 2.41 ± 0.53 |
| b* | 20.11 ± 1.18 | 18.11 ± 0.73 |
| C* | 20.32 ± 1.29 | 18.28 ± 0.73 |
| H° | 262 ± 2.34 | 262 ± 1.66 |
| TP (mg GAE 100 g−1) | 141.8 ± 6.63 | 145.6 ± 6.76 |
| DPPH (mM TE 100 g) | 3.39 ± 0.72 | 3.33 ± 0.68 |
| Nutrient | Intake Per Serving (mg or g per day) | Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) * | % DRI ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starch (g) | 49.2 | 130 | 37.84 |
| Protein (g) | 3.25 | 56 (46) | 5.81 (7.07) |
| Fiber (g) | 4.61 | 42 (33.6) | 11.0 (13.7) |
| TP (mg GAE) | 86.2 | 100 | 86.2 |
| K (g) | 0.85 | 4.7 (3.5) | 18.2 (24.4) |
| Ca (mg) | 9.68 | 1000 | 0.97 |
| P (mg) | 54.3 | 700 | 7.76 |
| Mg (mg) | 81.7 | 420 (320) | 19.5 (25.5) |
| Fe (mg) | 0.67 | 8 (18) | 8.33 (3.70) |
| Zn (mg) | 0.44 | 11 (8) | 4.04 (5.56) |
| Cu (mg) | 0.15 | 0.9 | 16.9 |
| Mn (mg) | 0.16 | 2.3 (1.8) | 6.94 (8.87) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martín Lorenzo, M.; Piedra-Buena Díaz, A.; Díaz Romero, C.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E.M.; Lobo, M.G. Physicochemical and Nutritional Characterization of Green Banana Flour from Discarded Cavendish Bananas. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6647. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156647
Martín Lorenzo M, Piedra-Buena Díaz A, Díaz Romero C, Rodríguez-Rodríguez EM, Lobo MG. Physicochemical and Nutritional Characterization of Green Banana Flour from Discarded Cavendish Bananas. Sustainability. 2024; 16(15):6647. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156647
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartín Lorenzo, Mercedes, Ana Piedra-Buena Díaz, Carlos Díaz Romero, Elena M. Rodríguez-Rodríguez, and M. Gloria Lobo. 2024. "Physicochemical and Nutritional Characterization of Green Banana Flour from Discarded Cavendish Bananas" Sustainability 16, no. 15: 6647. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156647
APA StyleMartín Lorenzo, M., Piedra-Buena Díaz, A., Díaz Romero, C., Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E. M., & Lobo, M. G. (2024). Physicochemical and Nutritional Characterization of Green Banana Flour from Discarded Cavendish Bananas. Sustainability, 16(15), 6647. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156647






