Challenges and Remediation Strategies for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Contamination in Composting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sustainable Organic Waste Management-Composting
3. The Composting Process
3.1. Stages of Composting
- Pre-treatment: The starting materials (feedstock) undergo pre-treatment (screening, sorting, crushing, and homogenising) to achieve optimal conditions to aid microbial growth, which accelerates the composting process. Certain conditions must be met: carbon-to-nitrogen (C:N) ratio between 25–30:1, a moisture level between 45% and 65%, a neutral pH between 5.5 and 8.5, and a well-structured pile for adequate ventilation with particle sizes between 3 and 15 mm; these values may differ slightly across various references [41].
- Primary fermentation: During the initial composting phase, the pile temperature rapidly increases to >60 °C from ambient temperatures, driven by the intense activity of thermophilic bacteria. Abundant O2 is required for breaking down organic compounds such as proteins, fats, and carbohydrates [42].
- Secondary fermentation: In this maturation stage, further decomposition by actinomycetes and fungi, which become more active at this stage, occurs, utilising organic materials unused by other microorganisms [43]. The remaining organic matter is converted into more stable humus or humus precursors within the compost pile.
- Post-treatment and storage: At this stage, the final product can undergo a range of procedures to ensure the product’s high-quality standard as a commercial fertiliser. Those procedures include screening, sieving, drying, nutrient supplementation, microbe inoculation, pelleting, packaging, etc., to ensure the product meets the standards required for commercial compost.
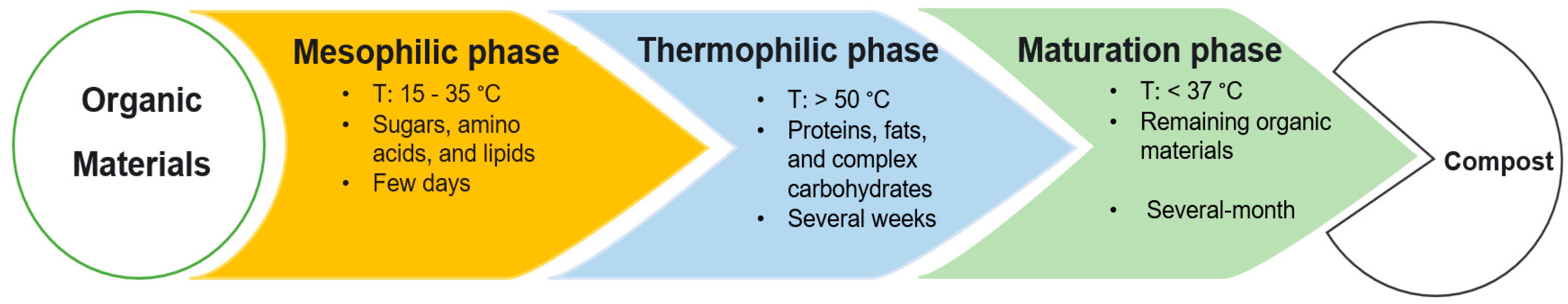
3.2. Phases of Composting
4. Compost Quality
5. Compost Contaminants
6. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)
7. The Source of PFAS in Compost
8. Potential Treatment of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Composts
| Approach | Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitability for Use in Compost | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobilisation | Phytoremediation |
|
|
| [158,159,160] |
| Soil flushing and soil washing |
|
|
| [161,162,163] | |
| Immobilisation | Sorption and stabilisation |
|
|
| [125,126,162,164] |
| Destruction | Bioremediation (biological treatment) |
|
|
| [165,166] |
| Thermal treatment |
|
|
| [162,167,168] |
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Census Bureau. International Data Base; U.S. Census Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- Nanda, S.; Berruti, F. Municipal solid waste management and landfilling technologies: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1433–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Van Woerden, F. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjuan-Delmás, D.; Taelman, S.E.; Arlati, A.; Obersteg, A.; Vér, C.; Óvári, Á.; Tonini, D.; Dewulf, J. Sustainability assessment of organic waste management in three EU Cities: Analysing stakeholder-based solutions. Waste Manag. 2021, 132, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Z. Adoption of solid organic waste composting products: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. Solid waste issue: Sources, composition, disposal, recycling, and valorization. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 1275–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makan, A.; Assobhei, O.; Mountadar, M. Initial air pressure influence on in-vessel composting for the biodegradable fraction of municipal solid waste in Morocco. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, M.G.; Miller, B.E.; Farrell-Poe, K.L. The Composting Process; Utah State University Extension: Logan, UT, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Senesi, N.; Brunetti, G. Chemical and Physico-Chemical Parameters for Quality Evaluation of Humic Substances Produced during Composting. In The Science of Composting; de Bertoldi, M., Sequi, P., Lemmes, B., Papi, T., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, R. The Practical Handbook of Compost Engineering; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, Ó.J.; Ospina, D.A.; Montoya, S. Compost supplementation with nutrients and microorganisms in composting process. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, J.; Mickan, B.S.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Kirkham, M.B.; Bolan, N.S. Physical, chemical, and microbial contaminants in food waste management for soil application: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; de Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manage. 2011, 7, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S.EPA. PFAS Master List of PFAS Substances (Version 2). Available online: https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/PFASMASTER (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Miranda, D.A.; Benskin, J.P.; Awad, R.; Lepoint, G.; Leonel, J.; Hatje, V. Bioaccumulation of Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in a tropical estuarine food web. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abercrombie, S.A.; de Perre, C.; Choi, Y.J.; Tornabene, B.J.; Sepúlveda, M.S.; Lee, L.S.; Hoverman, J.T. Larval amphibians rapidly bioaccumulate poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances. Ecotoxicol Environ. Saf 2019, 178, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Lu, H.; Xiong, T.; Zhi, Y.; Munoz, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Bioaccumulation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Ferns: Effect of PFAS Molecular Structure and Plant Root Characteristics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 4443–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomford, P. 104-Week Dietary Chronic Toxicity and Carcinogenicity Study with Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid Potassium Salt (PFOS.; T-6295) in Rats; Covance Laboratories: Madison, WI, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Temkin, A.M.; Hocevar, B.A.; Andrews, D.Q.; Naidenko, O.V.; Kamendulis, L.M. Application of the key characteristics of carcinogens to per and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Toxicity and Human Health Review: Current State of Knowledge and Strategies for Informing Future Research. Environ. Toxicol Chem. 2021, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahm, S.; Bonde, J.P.; Chiu, W.A.; Hoppin, J.; Kanno, J.; Abdallah, M.; Blystone, C.R.; Calkins, M.M.; Dong, G.-H.; Dorman, D.C.; et al. Carcinogenicity of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Kim Lazcano, R.; Yousefi, P.; Trim, H.; Lee, L.S. Perfluoroalkyl Acid Characterization in U.S. Municipal Organic Solid Waste Composts. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaram, A.K.; Panneerselvan, L.; Surapaneni, A.; Lee, E.; Kannan, K.; Megharaj, M. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in commercial composts, garden soils, and potting mixes of Australia. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizkarguenaga, E.; Zabaleta, I.; Mijangos, L.; Iparraguirre, A.; Fernández, L.; Prieto, A.; Zuloaga, O. Uptake of perfluorooctanoic acid, perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctane sulfonamide by carrot and lettuce from compost amended soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, Z.R.; Sun, M.; DeWitt, J.C.; Knappe, D.R. Recently detected drinking water contaminants: GenX and other per-and polyfluoroalkyl ether acids. J.-Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2018, 110, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusseau, M.L.; Anderson, R.H.; Guo, B. PFAS concentrations in soils: Background levels versus contaminated sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J.L.; Berger, U.; Chaemfa, C.; Huber, S.; Jahnke, A.; Temme, C.; Jones, K.C. Analysis of per-and polyfluorinated alkyl substances in air samples from Northwest Europe. J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, S.; Ravindra, K. Municipal solid waste landfills in lower- and middle-income countries: Environmental impacts, challenges and sustainable management practices. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 174, 510–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatlu, E.A.; Barzinpour, F.; Yaghoubi, S. A sustainable model for municipal solid waste system considering global warming potential impact: A case study. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 169, 108127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M. Global Waste on Pace to Triple by 2100. Retrieved from The World Bank. 2013. Available online: http://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Abdullah, N.; Al-Wesabi, O.A.; Mohammed, B.A.; Al-Mekhlafi, Z.G.; Alazmi, M.; Alsaffar, M.; Anbar, M.; Sumari, P. Integrated Approach to Achieve a Sustainable Organic Waste Management System in Saudi Arabia. Foods 2022, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laner, D.; Crest, M.; Scharff, H.; Morris, J.W.; Barlaz, M.A. A review of approaches for the long-term management of municipal solid waste landfills. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 498–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqua, A.; Hahladakis, J.; Al-Attiya, W. An overview of the environmental pollution and health effects associated with waste landfilling and open dumping. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 58514–58536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbhuiya, N.H.; Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Chandel, M.K.; Arnusch, C.J.; Tour, J.M.; Singh, S.P. The Future of Flash Graphene for the Sustainable Management of Solid Waste. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15461–15470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AEAS. Australian Organics Recycling Industry Capacity Assessment: 2020–2021; Australian Economic Advocacy Solutions: Bulimba, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Khater, E.-S.G. Some physical and chemical properties of compost. Int. J. Waste Resour. 2015, 5, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.; O’Neill, T.; Rynk, R.; Gilbert, J.; Wisbaum, S.; Halbach, T. Chapter 5—Passively aerated composting methods, including turned windrows. In The Composting Handbook; Rynk, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 159–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Xu, F.; Ge, X.; Li, Y. Chapter Four—Biological treatment of organic materials for energy and nutrients production—Anaerobic digestion and composting. In Advances in Bioenergy; Li, Y., Ge, X., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 4, pp. 121–181. [Google Scholar]
- Manyapu, V.; Lepcha, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Kumar, R. Chapter One—Role of psychrotrophic bacteria and cold-active enzymes in composting methods adopted in cold regions. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Gadd, G.M., Sariaslani, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; Volume 121, pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.; Liu, T. Chapter 4—Composting system and mature end-products production. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Pandey, A., Awasthi, M., Zhang, Z., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshins, C.; Michel, F.; Louis, P.; Richard, T.L.; Rynk, R. Chapter 3—The composting process. In The Composting Handbook; Rynk, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 51–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasaki, K.; Hirai, H.; Mimoto, H.; Quyen, T.N.M.; Koyama, M.; Takeda, K. Succession of microbial community during vigorous organic matter degradation in the primary fermentation stage of food waste composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zubair, M.; Kong, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, H.; Tong, L.; Zhu, R.; Lv, Y.; Li, Z. Shifts in bacterial diversity characteristics during the primary and secondary fermentation stages of bio-compost inoculated with effective microorganisms agent. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 382, 129163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andraskar, J.; Yadav, S.; Kapley, A. Challenges and Control Strategies of Odor Emission from Composting Operation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 2331–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajalakshmi, S.; Abbasi, S. Solid waste management by composting: State of the art. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 38, 311–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliotti, G.; Valentini, F.; Erriquens, F.; Said-Pullicino, D. Evaluating the efficiency of the composting process: A comparison of different parameters. In Geophysical Research Abstracts; European Geosciences Union: Perugia, Italy, 2005; p. 09606. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, E. The Science of Composting; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Termorshuizen, A.; Moolenaar, S.; Veeken, A.; Blok, W. The value of compost. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2004, 3, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.; Ali, M.H.; Samal, K. Assessment of compost maturity-stability indices and recent development of composting bin. Energy Nexus 2022, 6, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehouwer, R.; Cooperband, L.; Rynk, R.; Biala, J.; Bonhotal, J.; Antler, S.; Lewandowski, T.; Nichols, H. Chapter 15—Compost characteristics and quality. In The Composting Handbook; Rynk, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 737–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biala, J.; Wilkinson, K. International Comparison of the Australian Standard for Composts, Soil Conditioners and Mulches (as4454-2012); Australian Organics Recycling Association: Hove, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Standard, A. Composts, Soil Conditioners and Mulches; Standards Australia International Ltd.: Sydney, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ozores-Hampton, M.; Biala, J.; Evanylo, G.; Faucette, B.; Cooperband, L.; Roe, N.; Creque, J.A.; Sullivan, D. Chapter 16—Compost use. In The Composting Handbook; Rynk, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 777–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R. Risks and benefits of soil amendment with composts in relation to plant pathogens. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2011, 40, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, K.W.; Nichols, E. 24—Composting of food-chain waste for agricultural and horticultural use. In Handbook of Waste Management and Co-Product Recovery in Food Processing; Waldron, K., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2009; pp. 583–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Cotton, M. Changes in Soil Properties and Carbon Content Following Compost Application: Results of On-farm Sampling. Compos. Sci. Util. 2011, 19, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haderlein, A.; Legros, R.; Ramsay, B. Enhancing pyrene mineralization in contaminated soil by the addition of humic acids or composted contaminated soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 56, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zeng, G.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.; Wan, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, B. The potential impact on the biodegradation of organic pollutants from composting technology for soil remediation. Waste Manag. 2018, 72, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwo, A.M.; Gbadebo, A.M.; Oyedepo, J.A.; Ojekunle, Z.O.; Alo, O.M.; Oyeniran, A.A.; Onalaja, O.J.; Ogunjimi, D.; Taiwo, O.T. Bioremediation of industrially contaminated soil using compost and plant technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 304, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimambro, M.; Lillywhite, R.; Rahn, C. The Physical, Chemical and Microbial Characteristics of Biodegradable Municipal Waste Derived Composts. Compos. Sci. Util. 2013, 15, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.; Mail, M.; Heyse, R.; Amelung, W. Plastic in compost: Prevalence and potential input into agricultural and horticultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupper, T.; Bürge, D.; Bachmann, H.J.; Güsewell, S.; Mayer, J. Heavy metals in source-separated compost and digestates. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medyńska-Juraszek, A.; Bednik, M.; Chohura, P. Assessing the Influence of Compost and Biochar Amendments on the Mobility and Uptake of Heavy Metals by Green Leafy Vegetables. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupper, T.; Bucheli, T.D.; Brändli, R.C.; Ortelli, D.; Edder, P. Dissipation of pesticides during composting and anaerobic digestion of source-separated organic waste at full-scale plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7988–7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebielska, I.; Sidełko, R. Polychlorinated biphenyl concentration changes in sewage sludge and organic municipal waste mixtures during composting and anaerobic digestion. Chemosphere 2015, 126, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beníšek, M.; Kukučka, P.; Mariani, G.; Suurkuusk, G.; Gawlik, B.M.; Locoro, G.; Giesy, J.P.; Bláha, L. Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds in composts and digestates from European countries as determined by the in vitro bioassay and chemical analysis. Chemosphere 2015, 122, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Sarkar, B.; Vithanage, M.; Singh, G.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Ramadass, K.; Vinu, A.; Sun, Y.; Ramanayaka, S.; et al. Distribution, behaviour, bioavailability and remediation of poly- and per-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in solid biowastes and biowaste-treated soil. Environ. Int. 2021, 155, 106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, G.; Kankarla, V.; McLennon, E.; Pal, S.; Sihi, D.; Dari, B.; Diaz, D.; Nocco, M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Integrated Crop-Livestock Systems: Environmental Exposure and Human Health Risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Buser, A.M.; Cousins, I.T.; Demattio, S.; Drost, W.; Johansson, O.; Ohno, K.; Patlewicz, G.; Richard, A.M.; Walker, G.W.; et al. A New OECD Definition for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15575–15578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development. Reconciling terminology of the universe of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Recommendations and practical guidance. Ser Risk Manag 2021, 61, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrino, D.A.; Almeida, C.M.R.; Mucha, A.P.; Carvalho, M.F. Revisiting pesticide pollution: The case of fluorinated pesticides. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kiss, L.; Mei, H.; Remete, A.M.; Ponikvar-Svet, M.; Sedgwick, D.M.; Roman, R.; Fustero, S.; Moriwaki, H.; Soloshonok, V.A. Chemical aspects of human and environmental overload with fluorine. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 4678–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliano, E.; Sgroi, M.; Falciglia, P.P.; Vagliasindi, F.G.; Roccaro, P. Removal of poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from water by adsorption: Role of PFAS chain length, effect of organic matter and challenges in adsorbent regeneration. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulanger, B.; Vargo, J.D.; Schnoor, J.L.; Hornbuckle, K.C. Evaluation of perfluorooctane surfactants in a wastewater treatment system and in a commercial surface protection product. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Saito, N.; Sasaki, K.; Inoue, K.; Koizumi, A. Perfluorooctane sulfonate contamination of drinking water in the Tama River, Japan: Estimated effects on resident serum levels. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 71, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallen, C.; Drage, D.; Eaglesham, G.; Grant, S.; Bowman, M.; Mueller, J. Australia-wide assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in landfill leachates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 331, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Simcik, M.F.; Halbach, T.R.; Gulliver, J.S. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in soils and groundwater of a US metropolitan area: Migration and implications for human exposure. Water Res. 2015, 72, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, L.; Dudarev, A.A.; Huber, S.; Odland, J.Ø.; Nieboer, E.; Sandanger, T.M. Partition of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in whole blood and plasma, assessed in maternal and umbilical cord samples from inhabitants of arctic Russia and Uzbekistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.W.; Mair, D.C.; Lange, C.C.; Harrington, L.M.; Church, T.R.; Goldberg, C.L.; Herron, R.M.; Hanna, H.; Nobiletti, J.B.; Rios, J.A. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in American Red Cross adult blood donors, 2000–2015. Environ. Res. 2017, 157, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, N.; Kannan, K.; Taniyasu, S.; Horii, Y.; Petrick, G.; Gamo, T. A global survey of perfluorinated acids in oceans. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frömel, T.; Knepper, T.P. Biodegradation of fluorinated alkyl substances. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology Volume 208: Perfluorinated Alkylated Substances; De Voogt, P., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, M.; Bujas, T.A.D.; Small, J.; Wells, R.S.; Fair, P.A.; Bossart, G.D.; Solomon, K.R.; Muir, D.C.G. Biomagnification of Perfluoroalkyl Compounds in the Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) Food Web. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4138–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, E.I.; Yeung, L.W.; Taniyasu, S.; Lam, P.K.; Kannan, K.; Yamashita, N. Trophic magnification of poly-and perfluorinated compounds in a subtropical food web. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5506–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Working towards a Global Emission Inventory of PFAS: Focus on PFCAS—Status Quo and the Way Forward. 2015. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/risk-management/Working%20Towards%20a%20Global%20Emission%20Inventory%20of%20PFAS.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Young, C.J.; Mabury, S.A. Atmospheric perfluorinated acid precursors: Chemistry, occurrence, and impacts. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 208, 1–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, H.M.; Ruyle, B.J.; Thackray, C.P.; Chovancova, A.; Dassuncao, C.; Becanova, J.; Vojta, S.; Lohmann, R.; Sunderland, E.M. PFAS and Precursor Bioaccumulation in Freshwater Recreational Fish: Implications for Fish Advisories. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 15573–15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, H.; Sadia, M.; Krauss, T.; Baabish, A.; Yeung, L.W. Perfluoroalkane acids in human milk under the global monitoring plan of the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (2008–2019). Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drage, D.S.; Sharkey, M.; Berresheim, H.; Coggins, M.; Harrad, S. Rapid Determination of Selected PFAS in Textiles Entering the Waste Stream. Toxics 2023, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Fletcher, T.; Savitz, D.A. Epidemiologic evidence on the health effects of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, C.C.; Bech, B.H.; Brix, N.; Nohr, E.A.; Bonde, J.P.E.; Henriksen, T.B. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances and human fetal growth: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2015, 45, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.G.; Jones, K.C.; Sweetman, A.J. A First Global Production, Emission, And Environmental Inventory For Perfluorooctane Sulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3M. Phase-out plan for POSF-based products. Filtr. Sep. 2000, 37, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, N.M.; Evans, A.T.; Fritz, M.K.; Peak, S.A.; von Holst, H.E. Trends in the Regulation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Fluorinated alternatives to long-chain perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs), perfluoroalkane sulfonic acids (PFSAs) and their potential precursors. Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brendel, S.; Fetter, É.; Staude, C.; Vierke, L.; Biegel-Engler, A. Short-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Acids: Environmental Concerns and a Regulatory Strategy under REACH. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, Z.; Ahrens, L.; Huang, P.; Cai, M.; Yang, H.; He, J.; Sturm, R.; Ebinghaus, R.; et al. Occurrence of Perfluoroalkyl Compounds in Surface Waters from the North Pacific to the Arctic Ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Arevalo, E.; Strynar, M.; Lindstrom, A.; Richardson, M.; Kearns, B.; Pickett, A.; Smith, C.; Knappe, D.R.U. Legacy and Emerging Perfluoroalkyl Substances Are Important Drinking Water Contaminants in the Cape Fear River Watershed of North Carolina. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoiber, T.; Evans, S.; Naidenko, O.V. Disposal of products and materials containing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A cyclical problem. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossen, C.P.; Schattman, R.E.; MacRae, J.D. Evidence of compost contamination with per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from “compostable” food serviceware. Biointerphases 2023, 18, 030501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallen, C.; Eaglesham, G.; Drage, D.; Nguyen, T.H.; Mueller, J. A mass estimate of perfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) release from Australian wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hu, J.; Tanaka, S.; Fujii, S. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in sewage treatment plants. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2399–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominic Schliebs. Critical Evaluation of Composting Operations and Feedstock Suitability Phase 2—Contamination; Department of Environment and Science, Queensland Government: Brisbane, Australia, 2019.
- Gaines, L.G.T. Historical and current usage of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A literature review. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2023, 66, 353–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, G.; Michaud, A.M.; Liu, M.; Vo Duy, S.; Montenach, D.; Resseguier, C.; Watteau, F.; Sappin-Didier, V.; Feder, F.; Morvan, T.; et al. Target and Nontarget Screening of PFAS in Biosolids, Composts, and Other Organic Waste Products for Land Application in France. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6056–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim Lazcano, R.; Choi, Y.J.; Mashtare, M.L.; Lee, L.S. Characterizing and Comparing Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Commercially Available Biosolid and Organic Non-Biosolid-Based Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8640–8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Peng, H.; Huang, C.; Hu, J. Ubiquitous Occurrence of Fluorotelomer Alcohols in Eco-Friendly Paper-Made Food-Contact Materials and Their Implication for Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, W.; Miao, J.; Jiang, H.; Yang, Q. Degradation and effect of 6:2 fluorotelomer alcohol in aerobic composting of sludge. Biodegradation 2021, 32, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinglasan, M.; Ye, Y.; Edwards, E.; Mabury, S. Fluorotelomer alcohol yields poly and perfluorinated acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knepper, T.P.; Lange, F.T. Polyfluorinated Chemicals and Transformation Products; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Lasee, S.; McDermett, K.; Kumar, N.; Guelfo, J.; Payton, P.; Yang, Z.; Anderson, T.A. Targeted analysis and Total Oxidizable Precursor assay of several insecticides for PFAS. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2022, 3, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S.EPA. Persistent Chemical Contaminants; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2021.
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Song, X.; Jones, K.; Sweetman, A.J.; Johnson, A.C.; Zhang, M.; Lu, X.; Su, C. Multiple crop bioaccumulation and human exposure of perfluoroalkyl substances around a mega fluorochemical industrial park, China: Implication for planting optimization and food safety. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sungur, Ş.; Çevik, B.; Köroğlu, M. Determination of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) contents of compost amended soils and plants grown in these soils. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J.; Bean, E.Z.; Hinz, F.O.; Wilson, P.C.; Reisinger, A.J. Leaching of select per-/poly-fluoroalkyl substances, pharmaceuticals, and hormones through soils amended with composted biosolids. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 343, 118185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhler, K.; Susset, B.; Grathwohl, P. Production of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) from precursors in contaminated agricultural soils: Batch and leaching experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, H.; Moodie, D.; Vero, C. PFAS in biosolids: A review of international regulations. Water EJ 2021, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E. Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Removal from Landfill Leachate: Efficiency Evaluation in Column Experiments. Master’s Thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Ulrich, B.A.; Chen, B.; Higgins, C.P. Sorption of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Relevant to Aqueous Film-Forming Foam (AFFF)-Impacted Groundwater by Biochars and Activated Carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6342–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaggia, A.; Conte, L.; Falletti, L.; Fant, M.; Chiorboli, A. Use of strong anion exchange resins for the removal of perfluoroalkylated substances from contaminated drinking water in batch and continuous pilot plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.Y.; Fu, Q.S.; Criddle, C.S.; Leckie, J.O. Effect of flux (transmembrane pressure) and membrane properties on fouling and rejection of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes treating perfluorooctane sulfonate containing wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2008–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.J.; Thoma, E.; Sahle-Damesessie, E.; Crone, B.; Whitehill, A.; Shields, E.; Gullett, B. Supercritical Water Oxidation as an Innovative Technology for PFAS Destruction. J. Environ. Eng. 2022, 148, 05021006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBeath, S.T.; Mora, A.S.; Zeidabadi, F.A.; Mayer, B.K.; McNamara, P.; Mohseni, M.; Hoffmann, M.R.; Graham, N.J. Progress and prospect of anodic oxidation for the remediation of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and wastewater using diamond electrodes. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 30, 100865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.J.; Stevenson, P.; Murphy, P.J.C. PFAS removal from groundwaters using Surface-Active Foam Fractionation. Remediat. J. 2021, 31, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCleaf, P.; Englund, S.; Östlund, A.; Lindegren, K.; Wiberg, K.; Ahrens, L. Removal efficiency of multiple poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in drinking water using granular activated carbon (GAC) and anion exchange (AE) column tests. Water Res. 2017, 120, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolan, N.; Sarkar, B.; Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Wijesekara, H.; Kannan, K.; Tsang, D.C.; Schauerte, M.; Bosch, J.; Noll, H. Remediation of poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) contaminated soils–to mobilize or to immobilize or to degrade? J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleep, J.A.; Juhasz, A.L. A Review of Immobilisation-Based Remediation of Per- and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Soils. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2021, 7, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, J.T.; Anderson, R.H.; Lang, J.R.; Liles, D.; Matteson, K.; Olechiw, T. Field-scale demonstration of PFAS leachability following in situ soil stabilization. ACS Omega 2021, 7, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, D.A.; Kabiri, S.; Ho, J.; Bowles, K.C.; Davis, G.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Kookana, R.S. Stabilisation of PFAS in soils: Long-term effectiveness of carbon-based soil amendments. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niarchos, G.; Ahrens, L.; Kleja, D.B.; Leonard, G.; Forde, J.; Bergman, J.; Ribeli, E.; Schütz, M.; Fagerlund, F. In-situ application of colloidal activated carbon for PFAS-contaminated soil and groundwater: A Swedish case study. Remediat. J. 2023, 33, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Tran, H.-T.; Pu, M.; Zhang, T. Transformation characteristics of organic matter and phosphorus in composting processes of agricultural organic waste: Research trends. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2023, 6, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Jia, C.; Zhao, D.; You, C.; Chen, H.; Jiang, G. Effect of cationic and anionic surfactants on the sorption and desorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) on natural sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milinovic, J.; Lacorte, S.; Rigol, A.; Vidal, M. Sorption of perfluoroalkyl substances in sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8339–8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senevirathna, S.; Mahinroosta, R.; Li, M.; KrishnaPillai, K. In situ soil flushing to remediate confined soil contaminated with PFOS-an innovative solution for emerging environmental issue. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.M.H.; Bräunig, J.; Kookana, R.S.; Kaserzon, S.L.; Knight, E.R.; Vo, H.N.P.; Kabiri, S.; Navarro, D.A.; Grimison, C.; Riddell, N.; et al. Assessment of Mobilization Potential of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances for Soil Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 10030–10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.-Y.; Chen, W.-Y.; Gu, B.-H.; Liu, X.-C.; Chen, F.; Chen, Z.-H.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-X.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.-J. Morphology, ecology, and contaminant removal efficiency of eight wetland plants with differing root systems. Hydrobiologia 2009, 623, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobelius, L.; Lewis, J.; Ahrens, L. Plant Uptake of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances at a Contaminated Fire Training Facility to Evaluate the Phytoremediation Potential of Various Plant Species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12602–12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, D.K.; Morris, L.A.; Sutter, L.; Costanza, J.; Pennell, K.D. Accumulation of six PFAS compounds by woody and herbaceous plants: Potential for phytoextraction. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2020, 22, 1538–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaine, A.C.; Rich, C.D.; Sedlacko, E.M.; Hundal, L.S.; Kumar, K.; Lau, C.; Mills, M.A.; Harris, K.M.; Higgins, C.P. Perfluoroalkyl acid distribution in various plant compartments of edible crops grown in biosolids-amended soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7858–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Shan, X.-Q.; Zhang, S. Field study on the uptake and translocation of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in biosolids-amended soils. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, S.E.; Arp, H.P.H.; Slinde, G.A.; Wade, E.J.; Bjørseth, K.; Breedveld, G.D.; Straith, B.F.; Moe, K.G.; Jartun, M.; Høisæter, Å. Sorbent amendment as a remediation strategy to reduce PFAS mobility and leaching in a contaminated sandy soil from a Norwegian firefighting training facility. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sörengård, M.; Kleja, D.B.; Ahrens, L. Stabilization and solidification remediation of soil contaminated with poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 367, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Arias E, V.A.; Kambala, V.; Mallavarapu, M.; Naidu, R. Remediation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Contaminated Soils by Modified Clay Adsorbent—A Risk-Based Approach. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräunig, J.; Baduel, C.; Barnes, C.M.; Mueller, J.F. Sorbent assisted immobilisation of perfluoroalkyl acids in soils—effect on leaching and bioavailability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorengard, M.; Kleja, D.B.; Ahrens, L. Stabilization of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) with colloidal activated carbon (PlumeStop®) as a function of soil clay and organic matter content. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lath, S.; Navarro, D.A.; Losic, D.; Kumar, A.; McLaughlin, M.J. Sorptive remediation of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) using mixed mineral and graphene/carbon-based materials. Environ. Chem. 2018, 15, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askeland, M.; Clarke, B.O.; Cheema, S.A.; Mendez, A.; Gasco, G.; Paz-Ferreiro, J. Biochar sorption of PFOS, PFOA, PFHxS and PFHxA in two soils with contrasting texture. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liang, Y. Changing bioavailability of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) to plant in biosolids amended soil through stabilization or mobilization. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.G.; Lim, H.-J.; Na, S.-H.; Choi, B.-I.; Shin, D.-S.; Chung, S.-Y. Biodegradation of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) as an emerging contaminant. Chemosphere 2014, 109, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetverikov, S.; Sharipov, D.; Korshunova, T.Y.; Loginov, O. Degradation of perfluorooctanyl sulfonate by strain Pseudomonas plecoglossicida 2.4-D. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2017, 53, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinezhad, A.; Challa Sasi, P.; Zhang, P.; Yao, B.; Kubátová, A.; Golovko, S.A.; Golovko, M.Y.; Xiao, F. An investigation of thermal air degradation and pyrolysis of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances and aqueous film-forming foams in soil. Acs EsT Eng. 2022, 2, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lu, X.; Li, X.-Y.; Shih, K. Effectiveness and mechanisms of defluorination of perfluorinated alkyl substances by calcium compounds during waste thermal treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5672–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Patel, S.; Halder, P.; Patel, T.; Hedayati Marzbali, M.; Pramanik, B.K.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; de Figueiredo, C.C.; Bergmann, D.; Surapaneni, A.; et al. Removal of PFAS from biosolids using a semi-pilot scale pyrolysis reactor and the application of biosolids derived biochar for the removal of PFAS from contaminated water. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassalle, J.; Gao, R.; Rodi, R.; Kowald, C.; Feng, M.; Sharma, V.K.; Hoelen, T.; Bireta, P.; Houtz, E.F.; Staack, D. Degradation of PFOS and PFOA in soil and groundwater samples by high dose Electron Beam Technology. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 189, 109705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, G.; Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Yao, Y.; Fallgren, P.H.; Jin, S. Electrochemical destruction and mobilization of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in saturated soil. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, L.P.; Kueper, B.H.; Jaansalu, K.M.; Patch, D.J.; Battye, N.; El-Sharnouby, O.; Mumford, K.G.; Weber, K.P. Mechanochemical remediation of perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) amended sand and aqueous film-forming foam (AFFF) impacted soil by planetary ball milling. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battye, N.J.; Patch, D.J.; Roberts, D.M.; O’Connor, N.M.; Turner, L.P.; Kueper, B.H.; Hulley, M.E.; Weber, K.P. Use of a horizontal ball mill to remediate per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Bezerra de Souza, B.; Casarini, M.M.; Kewalramani, J.A. A Review of PFAS Destruction Technologies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayakaduwage, S.; Ekanayake, A.; Kurwadkar, S.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Vithanage, M. Phytoremediation prospects of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanwal, P.; Kumar, A.; Dudeja, S.; Chhokar, V.; Beniwal, V. Recent advances in phytoremediation technology. Adv. Environ. Biotechnol. 2017, 227–241. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, X.; Shi, Q.; Gan, J. Uptake, accumulation and metabolism of PFAS in plants and health perspectives: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 2745–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svab, M.; Kubal, M.; Müllerova, M.; Raschman, R. Soil flushing by surfactant solution: Pilot-scale demonstration of complete technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahinroosta, R.; Senevirathna, L. A review of the emerging treatment technologies for PFAS contaminated soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høisæter, Å.; Arp, H.P.H.; Slinde, G.; Knutsen, H.; Hale, S.E.; Breedveld, G.D.; Hansen, M.C. Excavated vs novel in situ soil washing as a remediation strategy for sandy soils impacted with per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances from aqueous film forming foams. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biek, S.K.; Khudur, L.S.; Rigby, L.; Singh, N.; Askeland, M.; Ball, A.S. Assessing the impact of immobilisation on the bioavailability of PFAS to plants in contaminated Australian soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 20330–20342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, B.; Kang, P.; Wei, T.; Zhao, Y. Challenges of aqueous per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and their foreseeable removal strategies. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahsavari, E.; Rouch, D.; Khudur, L.S.; Thomas, D.; Aburto-Medina, A.; Ball, A.S. Challenges and current status of the biological treatment of PFAS-contaminated soils. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 602040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Taylor, P.H.; Buck, R.C.; Kaiser, M.A.; Giraud, R.J. Thermal degradation of fluorotelomer treated articles and related materials. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-G.; Birch, Q.T.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Dionysiou, D.D. Advanced destruction technologies for PFAS in soils: Progress and challenges. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 33, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Composting System | Description |
|---|---|
| Static pile composting |
|
| Windrow composting |
|
| In-vessel composting |
|
| Vermicomposting |
|
| Purpose of Use | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Soil Amendment: |
|
| Plant Growth: |
|
| Erosion control: |
|
| Waste management: |
|
| Carbon sequestration: |
|
| Environmental impact: |
|
| Contaminant Type | Explanation of Risk | References |
|---|---|---|
| Inorganic Contaminants | ||
| Heavy metals (e.g., Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Pb, Ni and Zn) |
0.13→4.1→20→60→16→54→155 Below the legal threshold values, which are: Cd→Co→Cr→Cu→Ni→Pb→Zn 1→ - → - →100→30→120→400
| [62,63] |
| Organic contaminants | ||
| Pesticides (e.g., DDT, cyprodinil, dichlobenil, aldrin, and chlordane) |
Pesticides (Sum) 43→28→10→14
| [64] |
| Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) |
| [65] |
| Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) |
| [66] |
| Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) |
| [23,67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khair Biek, S.; Khudur, L.S.; Ball, A.S. Challenges and Remediation Strategies for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Contamination in Composting. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4745. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16114745
Khair Biek S, Khudur LS, Ball AS. Challenges and Remediation Strategies for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Contamination in Composting. Sustainability. 2024; 16(11):4745. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16114745
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhair Biek, Sali, Leadin S. Khudur, and Andrew S. Ball. 2024. "Challenges and Remediation Strategies for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Contamination in Composting" Sustainability 16, no. 11: 4745. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16114745
APA StyleKhair Biek, S., Khudur, L. S., & Ball, A. S. (2024). Challenges and Remediation Strategies for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Contamination in Composting. Sustainability, 16(11), 4745. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16114745







