Abstract
Behavior related to the overseas market has become an essential method for enterprises to acquire international resources. We aimed to do so using a difference-in-differences (DID) approach with the collected data of companies from China’s high-polluting industries in the A-share market between 2011 and 2019. The present papers aims to find the influence of the behavior towards the enterprises’ green transformation. The research results showed the following: (1) The behavior related to the overseas market not only increased enterprises’ environmental protection investment but also promoted enterprises’ green technology innovation, which promoted enterprises’ green transformation. (2) The mechanism analysis shows that corporate investment in protection of the environment increased mainly through the improved consciousness for the responsibility of environment, while corporates’ green technology innovation not only requires the increased awareness for environmental responsibility but also requires enterprises to learn advanced environmental protection methods and knowledge. (3) The role of the behavior related to the overseas market in promoting the green transformation of enterprises was more obvious in state-owned enterprises, and the enterprises with relatively better business performance were more enthusiastic about green technology innovation because of the motivation of advantage creation; thus, the promoting effect of the behavior related to the overseas market on the enterprises’ green transformation was more obvious. This paper provides empirical evidence and policy implications to help promote the green transformation of enterprises.
1. Introduction
Based on the previous research, the rapid development of energy-intensive and high-polluting industries has also brought great pressure upon China’s resources and environment. The development of ecological civilization is inseparable from the efforts of all social subjects, and in comparison to scientific research institutions and universities, enterprises are an important subject of green development. To accelerate China’s green and low-carbon development and build a strong country with an ecological civilization, it is imperative to promote the green transformation of businesses. Particularly over these past years, green innovation has shown the ability to decrease pollution emissions during production [1], which is critical to resolving the issue of environmental pollution and economic growth in China [2]. In order to solve environmental problems, it is crucial to put the green transformation into act as soon as possible. Only in this way can it be better applied because it is necessary to combine these elements at the level of production concept and system construction not only to increase the expenditure on end-of-line treatment but also to lessen the amount of emissions both from technology and infrastructure [3,4]. At the same time, with the flourishing economy, the rise of China’s production costs and the gradual relocation of the manufacturing industry, China is experiencing great changes unseen in a century, and it is urgent to adapt to the changing roles and make good use of both international and domestic resources for development.
The corporate behavior related to the overseas market refers to the establishment of subsidiaries and associated companies abroad, which is the primary method for corporations to continuously obtain overseas resources and explore international markets. Promoting enterprises to “go global” is conducive to strengthening corporate brand building and enhancing the competitive power both at home and abroad, and it is also conducive to enterprises coping with the impact of trade protectionism and resolving excess capacity. Especially in these years, behavior related to the overseas market has become an important way for enterprises to acquire international resources [5], which has become the main way for enterprises to continuously obtain overseas resources and explore the international market. Thus, “going out” has become a strategic choice for many enterprises for further studying green transformation and obtaining greater investments on a relatively higher level abroad. Enterprises need to improve the level of international operation and accelerate their integration into the global supply chain, industrial chain, and value chain as soon as possible and strive to form the ability to allocate factor resources and lay out market networks on a global scale.
There has been some research focusing on corporate behavior under environmental regulation. Some previous studies were carried out from the perspective of the influence of environmental protection policies, while others examined regulations whose behavior is positively correlated [6] or negatively correlated [7] under different environmental regulation situations and environmental control intensities, and media attention [8], community pressure, and consumer pressure [9] also play an active role; some studies mainly analyzed the impact of mandatory action and policies in improving or inhibiting enterprises’ green transformation through quasi-natural experiments, including cleaner production policies [10], environmental technical standards [11], environmental taxes [12], mandatory disclosure of CSR policies [13], green credit policies, and so on [14,15,16]. In recent days, many scholars are focusing on corporate governance, arguing that the disclosures from the government, the society, as well as the environment itself show the influence on the green innovation [17,18], which is conveniently beneficial for transformation.
Nevertheless, the green transformation and corporate behavior related to overseas markets have not received much attention in previous research. The studies that are currently in place only focus on the influence of corporate behavior on green innovation for enterprises [19], continued development [20], or environmental protection for corporate entities [21]. Most scholars at the macro level are interested in studying how environmental regulations affect the creation of green technologies. For example, Porter and Linde claimed that environmental regulation will lead to an “innovation compensation” effect, and empirical studies have validated their claim [22,23]. In fact, as an important symbol of enterprises’ “going global”, the academic community primarily concentrates on its implications on traditional technological innovation, ignoring the differences in the motivation of enterprises’ green transformation, and there are certain differences between the environmental protection investment based on end-of-line governance and the green transformation mode based on green technology innovation. Moreover, based on previous research on corporates’ green transformation, little attention has been paid to the spontaneous strategic behavior related to the overseas market, which makes it difficult to form effective theoretical and empirical support for the construction of enterprises’ green transformation behavior models based on different motivations. Therefore, it is necessary to combine the strategic choices and other behaviors of enterprises in the current international situation with the green transition and consider some external influencing elements like the policies and internal factors such as corporate strategic choices, etc. Thus, the research goal of this paper is to explore whether enterprises can achieve green transformation in the process of “going out” and analyze the influence mechanism.
Therefore, the following two aspects are meaningful for this research. (1) Focusing on the green transformation of enterprises, we examine the impact of enterprises’ behavior related to the overseas market for further understanding and exploring the mechanism. (2) We attempt to conduct a theoretical and empirical investigation on how enterprises can take advantage of exogenous innovation advantages brought by the behavior related to the overseas market as well as the feasibility path through different green transformation motives. As a result, it is increasingly accessible for enterprises to grasp a new round of development opportunities, integrate into the new pattern of dual-cycle development, and achieve high-quality development.
2. Literature Review and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Corporate Behavior Related to the Overseas Market and Green Transformation
2.1.1. Research on the Corporate Behavior Related to the Overseas Market
The research focusing on the influence of corporate actions related to the overseas market mainly includes enterprises’ innovation, firm performance, technological level, and corporate environmental protection [24,25]. It has been stated that the corporate behavior related to the overseas market plays a crucial role in improving production technology and optimizing resource allocation and will also lead to profit shifting. The strengthening of overseas-related behaviors is beneficial in helping enterprises carry out more specialized division of labor for their overseas subsidiaries and enhance mutual cooperation and internal transfer of knowledge resources among overseas subsidiaries [26]. Furthermore, there have been studies examining the impact of foreign investment. They discovered that foreign investment incentivizes companies to be more responsible for the environment [27].
In addition, some studies have shown that the extent to which overseas subsidiaries diversify geographically will boost the amount and character of the OFDI enterprises. This is because innovation is the result of knowledge fusion in different fields, and corporate behavior related to the overseas market helps to increase the possibility of complementary investment allocation globally, ultimately promoting enterprise innovation [28,29]. The geographic layout of overseas subsidiaries possesses an influence on the innovation of corporations when it comes to importing high-tech intermediate goods and the mobilization of human capital. The overseas mergers and acquisitions of enterprises can help their shareholders generate greater value, and the effect is more obvious for companies with a larger scale and more overseas business experience [30].
2.1.2. Research on the Corporate Green Transformation
Under the stricter environmental regulation currently, enterprises tend to accelerate the pace of green transformation, including green innovation and investment in environmental protection. Firstly, enterprises choose to use more advanced technologies to execute an environmentally friendly transformation of the business structure or production process of enterprises so as to reduce pollutant emissions or improve energy and resource utilization efficiency from the source. The regulation of the environment is one of the most importance influencing variables in the research of corporate environmental protection investment. When regional environmental regulations are weak, complying with environmental regulations comes at a cheaper cost, and most enterprises pursue opportunism, paying lower costs while using resource and environmental externalities, so they do not need to invest too much in environmental protection. As regional environmental regulations are strengthened, enterprises will have a stronger incentive to act in response to the way of production. Porter’s hypothesis suggests that complying with environmental regulations makes environmental investment more cost-effective and conducive to technological innovation.
Secondly, enterprises make the decision to increase investments in environmental protection. As is shown among the previous studies, environmental regulation has the ability to reduce the negative effects of the market. Hence, environmental regulation has the potential to affect the input behaviors, output behaviors, and technological innovation of enterprises by imposing environmental restrictions on businesses and encouraging the industrial structure to rationalize [31,32,33]. Despite the need for a large investment, a long development cycle, and high uncertainty, green technology innovation in enterprises can provide them with a competitive innovation model.
The stimulative elements of corporate green transformation can be mainly divided into external pressure motivation and internal tool motivation. Motivated by external pressure, corporate green behavior aims to obtain legitimacy and external resources. The influence of external factors on the way corporations enact environmentally friendly behavior is limited when external stakeholders fail to effectively monitor and sanction corporate pollution or non-compliance or when firms are less dependent on external resources [34]. In addition, green behaviors driven by external pressures often lead to opportunistic behaviors of firms, including but not limited to regulatory arbitrage [35] and selective information disclosure [36]. In addition, regulatory-motivated businesses tend to adopt reactive environmental strategies that try to meet the requirements of stakeholders instead of moving beyond the expectations. As a result, the environmental performance of firms that adopt reactive environmental strategies is significantly lower than that of proactive environmental strategies [37,38].
Over the past few years, the green credit policy has been proven to have a significant improvement effect on the environmental performance of companies, according to research, and the promotion of corporate ESG has been relatively obvious due to the development of green finance [39]. Furthermore, a number of scholars have conducted research on the factors that affect the development of green technology innovation. They noticed that there are numerous factors that can help to develop green technology innovations: containing a financial structure that is reasonable [40], the construction of telecom infrastructure [41], and executive features [42]. Under the motivation of internal tools, enterprises regard green behavior as a resource and opportunity and actively pursue green behavior. Perceived reputation improvement [43] and financial performance feedback [44] are important motivations influencing enterprises to actively practice green behaviors. Some studies have concluded that corporate green behavior creates new and competitive resources for firms [45], improves corporate reputation, and reduces the cost of capital [46]. There are some examined studies in which corporate identity causes an enterprise to focus more on its own reputation and encourage its green behavior by leveraging the prestige regime: The direct investigation of studies has revealed that the impact of corporate reputation on corporate green behavior is positive [47].
2.1.3. Corporate Behavior Related to the Overseas Market and Green Transformation
Based on the system of corporate behavior in the green transformation that has been studied in previous research, reverse spillover and learning effects through overseas investment have been shown in some studies to affect corporate environmental protection [48,49,50]. As producers of environmental pollution, the lack of enterprises’ social environmental consciousness has seriously affected the environment and endangered people’s health. In regard to the lack of the joint responsibility, the strength of both responsibilities and standards information disclosure requirements can both urge corporations to be more conscious of green transformation, in which enterprises are guided by green development through intensive utilization of environmental friendliness and resources, with a focus on green innovation, insisting on greening the whole production process and ultimately achieving both ecological and economic improvement [51,52]. When companies venture into the foreign market, they can acquire advanced technological knowledge and management experience through information exchange and imitation learning. By giving more emphasis to environmental protection, these enterprises can accelerate the process of green transformation even more. Their understanding of environmental protection can be enhanced through this method [53]. Dual institutional pressure from the host country and China will be faced by enterprises when moving into the overseas market, along with the spillover and learning effects. Through this method, enterprises will enhance their awareness of environmental protection. To clarify, businesses that opt for the “going out” route have to meet more rigorous standards of conduct, including environmental protection rules [54,55].
Therefore, the behavior related to the overseas market can raise the awareness of the environmental responsibility of enterprises. The pursuit of innovations for green technology is a key part of enterprises’ environmental responsibilities [56], and with the improvement of environmental awareness, enterprises will take charge of innovating with green technology and improving the output of relevant green patented technologies. At this time, enterprises will see a rise in the number of green technology innovations. In addition, when an enterprise has behavior related to the overseas market, it can achieve reverse technology spillover effects by integrating the resources and innovation base of the original overseas enterprises or obtaining the required product innovation resources and learning new technologies through overseas markets so as to increase the innovation level in green technology throughout the enterprise. Therefore, when companies have a higher awareness of environmental responsibility due to their involvement in the overseas market, their focus on protecting the environment and using green technology will intensify. Overall, the impact path of corporate behavior related to the overseas market on green transition is shown in Figure 1. The theoretical hypothesis that follows is proposed as a result of this.
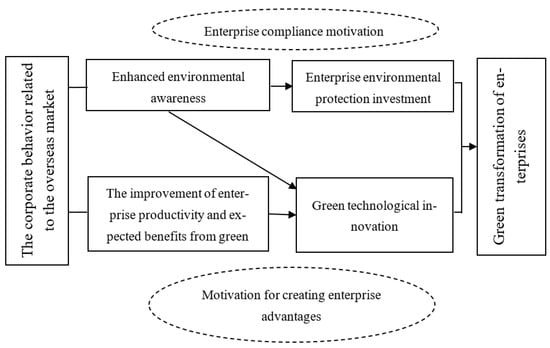
Figure 1.
The impact path of corporate behavior related to the overseas market on green transition.
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
The corporate behavior that pertains to the foreign market can promote enterprise green transformation by improving the awareness of corporate environmental responsibility.
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
The corporate behavior that focuses on the overseas market can encourage innovation in green technology by increasing marginal capital efficiency through reverse spillover and learning effects.
2.2. Analysis of Heterogeneity
2.2.1. The Heterogeneity of the Enterprise Ownership
China’s market is not entirely based on business rules, and on account of the particularity of state-owned enterprises, more financial support will be given by financial institutions to these enterprises [57], and green technology innovation activities require higher funds. Meanwhile, owing to their important status, state-owned enterprises are not only given more expectations in fulfilling the requirements and responsibilities from the people and the society but also need to serve China’s ecological civilization construction. Moreover, when companies venture into the foreign market, there are dangers that their conduct will not be in line with the standards in the locale. If this is the case, it is more likely that their production activities will result in environmental damage being exposed. The government, the public, and the media will be interested in the enterprise’s involvement in overseas markets, according to this perspective [58,59,60]. Therefore, state-owned enterprises are more motivated and have financial advantages to utilize the technological reverse spillover effect and grasp the opportunities of technological innovation brought by the behavior related to the overseas market due to the fact that state-owned enterprises have more legitimate reviews and have more social responsibilities. On the basis of the analysis discussed above, the following hypothesis is put forward.
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
In contrast to enterprises not owned by the government, the behavior related to the overseas market of state-owned enterprises has an effect that is more noticeable on the promotion of green transition.
2.2.2. The Heterogeneity of the Motivation of Enterprise Green Transformation
In the current international situation, to enhance their competitive edge, more enterprises in China choose the “going out” development path. Thus, more and more Chinese enterprises need to adapt to stricter environmental standards in developed countries after implementing the “going out” strategy in order to improve their competitiveness [61], and enterprises with higher levels of environmental awareness and environmental responsibility will be favored by the international market [62]. Therefore, higher environmental standards and meeting environmental information disclosure requirements will drive enterprises to accelerate their green transformation, that is, to achieve strategies to prevent and control pollution or improve the ecological environment during the production process, as well as the technical improvements of the product. The behavior related to the overseas market can promote foreign exchanges and cooperation, help in learning the advanced concepts of management and green production from foreign countries, and improve the sustainability of production and operation models.
Thus, on the one hand, foreign markets will put forward higher requirements for enterprises’ environmental information disclosure, which will cause enterprises to have greater compliance costs and drive them to invest in environmental governance in order to meet environmental standards [63]; so, from the perspective of legitimacy, enterprises’ environmental protection investment will be increased. When corporations realize that green innovation is a new development opportunity, they will accelerate the learning and transformation of green production methods so as to enhance their competitiveness and profitability in the industry. When enterprises consciously carry out overseas market behaviors related to technological innovation, they will integrate innovation resources in a targeted manner, and the marginal capital efficiency of enterprises will be improved, which can bring innovation advantages to the improvement of green technology innovation. Conversely, foreign markets are also an important source of exogenous technological innovation for Chinese enterprises, which can help enterprises break the bottleneck of innovation, reduce costs, and achieve technological reverse spillover effects, which is crucial for enterprises to enhance the innovation quality [64]. To gain governmental support in that area, enterprises need to reduce the challenge of entering into the brand new market by behaving better, from the perspective of legitimacy. So, enterprises associated with foreign markets will pay greater attention to getting rid of pollution and minimizing harm to the atmosphere in the host nation by increasing the amount of money invested in environmental protection and green innovation [65,66]. This behavior related to the overseas market will eventually impact corporate awareness of environmental protection as well as the transformation of overseas subsidiaries [67,68] so that corporate green transformation can be promoted. Thus, hypothesis 4 is proposed.
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
Enterprises with higher business performance have the motivation to create competitive advantage, and the promotion of green technology innovation becomes more evident when it comes to behavior related to the overseas market. On the contrary, the role of the behavior related to the overseas market in increasing environmental protection investment is more obvious due to the compliance motivation of enterprises.
3. Research Design
3.1. Sample Selection and Data Sources
In accordance with the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China’s environmental information disclosure guidance for listed companies and the China Securities Regulatory Commission’s 2012 industry classification standards, the present study regarded 11 high-polluting enterprises for examples, most of which are mining and textiles, and the period validity of these samples lasted from 2011 until in the following 8 years. The data for this time period are mainly from SIPO, the data for overseas affiliations come from the basic document column of the affiliated company of the China Stock Market and Accounting Research (CSMAR), and the relevant information of the enterprise’s overseas affiliations was obtained through manual screening. CSMAR and CNRDS were used to obtain the other control variables. Table 1 illustrates the significance and calculation procedure for the primary variables.

Table 1.
The definition and explanation of variables.
3.2. Variable Setting
- (1)
- Dependent variable
The variable that is dependent on this study is the green transformation of enterprises. When confronting the pressure from environmental standards, enterprises will strengthen end-of-line governance and accelerate capital renewal, or they may opt for technological advancement that is more direct and proactive, that is, technological innovation. Therefore, this paper divides enterprises’ green transformation behavior into two categories. First of all, more investment will be made by enterprises in protecting the environment, which is manifested in the form of increasing investments in non-productive, end-of-line treatment and accelerating investments in the introduction of production equipment, and to replace traditional and outdated production equipment, more advanced and environmentally friendly equipment will be utilized. Enterprises’ green innovation, being the second priority, is to realize the green upgrading of production methods through technological innovation from the root. Therefore, for these firms, the green transformation behavior in this study is measured by two variables: corporate commitment to environmental protection and green innovation.
Firstly, “pollution control input/sales revenue” is employed to determine enterprise environmental protection investment (EPI). In contrast to the cost of protecting the environment and pollution control, pollution control investment can be seen as investment behavior for the green development of the enterprise itself, and it is also a manifestation that enterprises are taking an active part in protection movements as well as social responsibility. In addition, the absolute amount of pollution control has more connections with the scales of the object themselves, so the model test results are better after eliminating the scale effect of the enterprise.
Secondly, because patent licensing requires a certain process, this paper measures enterprise green technology innovation by the quantity of green patent applications filed by enterprises in the present year. In this current year, enterprises submitted more green patent applications to the State Intellectual Property Office, resulting in an added natural logarithmic value of 1. The ultimate ranking of green technology innovations in enterprises is determined by taking the natural logarithm, which represents the level of green technology innovation in enterprises’ lnPatent.
- (2)
- Key explanatory variable
This paper’s explanation revolves around corporate behavior linked to the overseas market (Ovse). At present, corporate behavior related to the overseas market is measured by whether the enterprise has overseas subsidiaries, associated companies, and other affiliated companies, and it is proposed in this practice to use dummy variables to measure the corporate behavior related to the overseas market. If the enterprise has an overseas-affiliated company for the first time during the sample period, the value of Ovse after this year is 1; otherwise, the value is 0. At the same time, enterprises with overseas affiliates in the first year of the sample period are excluded.
- (3)
- Control variable
To make it more reliable, this study also refers to the current research findings associated with the green transformation of companies and adds other control variables and correlates the governing behaviors to the regression model, for example, the asset/liability ratio, scale, listing age, growth ability, profitability, property rights, agency costs, capital intensity, equity concentration, and cash flow generated by operating activities. Table 1 shows the particular symbols and definitions, while the main variables are shown in Table 2 through descriptive statistics.

Table 2.
The descriptive statistics for the main variables.
3.3. Model Setting
The objective of this investigation is to determine whether corporate behavior related to the overseas market has impacts on the green transformation of enterprises. Corporate behavior related to the overseas market can be measured by the constructed indicator variables, so the problem of endogeneity can be well solved by using the DID method, and the econometric model is as follows:
Among them, is the green transformation of the enterprise, and is the dummy variable of whether the enterprise has an overseas-related state: If the enterprise i has an overseas affiliated company for the first time in year t during the sample period, then the value of the enterprise’s is 1 after t; otherwise, it is 0. is a series of control variables, represents the individual effect of the firm, denotes the time effect, and is the random perturbation term. is the coefficient of main concern, and if is significant and greater than 0, it means that the corporate behavior related to the overseas market can significantly promote the level of enterprise green transformation.
To find more elements of the behavior of firms associated with the foreign market that are related to promoting the green transformation of enterprises, we can use the mediating effect model widely used at present:
is possible mediating variable. When regressing Equations (2) and (3), if it is found that the coefficient is significant in Equation (2), it means that the corporate behavior related to the overseas market can have an impact on the mediating variable. In the event that the coefficient λ in Equation (3) is also important, it implies that the corporate behavior related to the overseas market can indeed influence the corporations in green transformation by the mediating variable Z, and the mediating effect is established. The model’s remaining variables have their meanings based on Equation (1). To investigate the diverse effects of enterprise characteristics on the relationship between green transformation and the behavior of companies involved in the foreign market, the following model is established:
In Equation (4), is the different characteristic variable of the firm, and τ is the coefficient of main concern. If the coefficient τ is significant, the impact of corporate behavior related to the overseas market on enterprises’ green transformation vary with , and Equation (1) is also associated with other variables.
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Baseline Regression Analysis
First, the benchmark regression was performed using Equation (1). The benchmark regression results shown in Table 3 demonstrate that the behavior related to the overseas market has the potential to encourage enterprises to perform better in green transformation, which is not just visible in the increased corporate investment for environmental protection but also in the increase in green technology innovation. After controlling for individual, time, and provincial effects at the same time, the estimated results yielded significance at the 5% level. From the analysis, it is obvious that if the pressure of environmental regulation is reduced by Chinese enterprises, more equipment should be upgraded, and more technology should be introduced, and in addition to this, technological innovation must also be adopted. The behavior related to the overseas market is a spontaneous business strategy choice of enterprises. On the one hand, when enterprises participate in international market competition, they will have to adapt to the stricter environmental standards and face higher requirements for environmental information disclosure. In this, they will increase their investment in environmental protection as a result of compliance pressure. On the other hand, behavior related to the overseas market can also help enterprises explore overseas markets, obtain overseas resources, and access more advanced green production methods and knowledge. In this process, the productivity of enterprises will increase, and the expected advantages of green behavior will be further enhanced. Therefore, the enthusiasm for accelerating green technology innovation can be further enhanced, which eventually leads to promoting enterprises’ green transformation.

Table 3.
The benchmark regression result.
In order to guarantee the reliability of statistics, changes to the sample (high-polluting enterprises and other enterprises) should be controlled as time goes by so as to ensure the impacts of the green transformations before using this model. Consequently, constructing a DID model requires one of the key factors that conforms to the parallel trend assumption. In the parallel trend chart (Figure 2), 0 indicates the first year in which the company had an overseas affiliate during the sample period, −1 indicates the year before the firm first had an overseas affiliate during the sample period, and so on. Before the establishment of overseas-affiliated companies, comparing the experimental group and the control group, it is evident that there was no difference between the two groups in regards to environmental investment and the development of green technology. However, after the establishment of overseas-affiliated companies, there were significant differences between two groups. Furthermore, it was found out that green technology innovation is not progressing in a timely manner. In the first and second years of the establishment of overseas-affiliated companies of enterprises, green technology innovation was significantly promoted, but over time, it gradually became more advanced. In addition, the companies that made a commitment to protecting the environment in the year of the establishment of their overseas-affiliated companies increased.
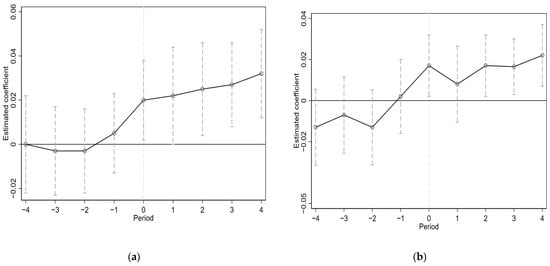
Figure 2.
(a) The interpreted variable is EPI; (b) the interpreted variable is lnPatent.
4.2. Placebo Test
Moreover, a placebo test was also applied in this research so as to enhance the credibility of the experiment, showing that the influence only lies in the corporate behavior and not in any other elements or factors that cannot be observed. In order to verify the assumption, the tests were replicated more than a thousand times, the results of which can be seen in Figure 3. It includes the dispersed distribution of corresponding p-value, estimation coefficients of control variables, and probability density distribution. It can be seen that the coefficient estimates for the experimental group with random distribution are mostly not significant at the 5% confidence level and are centrally distributed around 0. Thus, other non-observed missing variables do not interfere with the increase in enterprises’ green transformation caused by involvement in the overseas market.
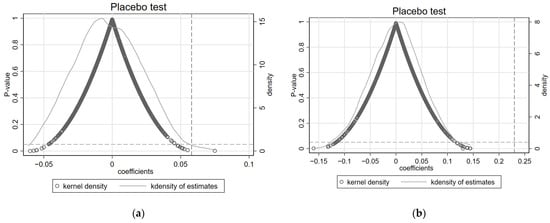
Figure 3.
(a) Placebo test of corporate behavior related to the overseas market on EPI. (b) Placebo test of corporate behavior related to the overseas market on lnPatent.
4.3. Robustness Tests
- (1)
- Consider the self-selection bias
PSM was applied in this research to overcome possible sample self-selection bias. The matching success samples were saved according to the scores after the propensity score matching, and the regression analysis was carried out by Equation (1). The Table 4 shows that, at a level of 10%, corporate environmental protection investments are impacted significantly by corporate behavior related to the overseas market, while the impact of corporate behavior related to the overseas market on the creation of green technology is significant at the level of 5%. Therefore, behavior related to the overseas market can achieve the green transformation, and the benchmark regression conclusion is robust.

Table 4.
PSM-DID estimation results.
- (2)
- Eliminate the interference of relevant samples
This study concentrates on the influence of behavior related to the overseas market on enterprises’ innovation in investing in green technology and protecting the environment. However, in fact, the sample includes environmental protection and energy conservation companies. Through effective operation of the firms, the amount of money invested in protecting the environment was increased, and the enterprises improved their green innovation level, contrary to the hypothesis that behavior related to the overseas market promotes green transformation for firms. According to the research results, to avoid the consequences of the previous factors, the research sample was excluded from the samples of enterprises whose main business involves environmental protection, recycling, new energy, and other industries, and regression was carried out by Equation (1). Table 5 shows that enterprises are investing significantly in environmental protection and green technology creation, with a 5% level of investment. Therefore, behavior related to the overseas market can definitely ameliorate the green transformation for firms, indicating that the above conclusions are robust.

Table 5.
The regression result that excludes interfering samples.
- (3)
- Industry adjustments for the explained variables
Considering that there may be great differences for corporations from various industries in relation to the advancement of green technology and investing in environmental protection, it may have an impact on the research conclusions. Therefore, for excluding this effect, the explained variables were adjusted for the industry mean. The specific method was to first calculate the mean values of corporate investment in environmental protection and innovation in green technology by industry and year and then subtract the mean of the corresponding industry/year from the original value of the explained variables to obtain the industry mean-adjusted corporate environmental investment (Adj-EPI) and green innovation index (Adj-lnPatent) and regress to Equation (1). The regression results in Table 6 demonstrate that after taking into account the explained variables, the estimation results are still very significant; that is, the behavior related to the overseas market can promote the corporate green transformation.

Table 6.
The regression result that adjusts the industry for the explained variables.
4.4. Mechanism Regression
Furthermore, to investigate the ways in which overseas market behavior affects the green transformation of enterprises, this study conducted mechanism regression. According to the theoretical assumptions above, the impact mechanism can be divided into two aspects. The first is firm productivity (Tfp_lp), which refers to the method of figuring out the total productivity factor of the companies mentioned. With the implementation of the global strategy and the continuous enhancement of environmental regulations, enterprises in high-polluting industries have seen a gradual increase in compliance costs. Behavior related to the overseas market enables the acquisition of cutting-edge green technology patents or the learning of more cutting-edge environmental protection technologies, so they may enhance the productivity of enterprises and the expected benefits of green behaviors, which will further increase their enthusiasm for advancing green technology creation activities. The second channel is the corporate environmental responsibility awareness index (Envres), which is determined by the annual environmental responsibility score within the score assigned to corporate social responsibility of www.hexun.com. If the score is higher, it means the company has more awareness of environmental responsibility. In the Table 7 and Table 8, the mechanism test regression results are presented, where the result for corporate investment of environmental protection is in Table 7, and Table 8 is the regression result for corporate green technology creation.

Table 7.
The impact mechanism of corporate environmental protection investment.

Table 8.
The impact mechanism of green technology innovation.
The regression coefficients of overseas associations for corporate productivity and corporate environmental responsibility awareness indicators are significantly positive, as displayed in Table 7 and Table 8, which show that overseas associations can significantly improve corporate productivity and corporate environmental responsibility awareness. In addition, in Table 7, after introducing both overseas correlation intermediary variables and dummy variables, it can be found that the influencing mechanism of the behavior related to the overseas market on the corporate innovation of green technology and investment of environmental protection is different. After adding overseas correlation dummy variables and intermediary variables, the findings indicate that boosted awareness of corporate environmental responsibility can result in a significant advance in corporate investment for environmental protection, but the increase in enterprise productivity is insignificant for the increase in corporate investment for environmental protection. On the other hand, in Table 8, after taking dummy variables and intermediary variables into the model with overseas correlation, green technology innovation is significantly impacted by corporate environmental responsibility awareness and productivity improvements, and the 5% significance level indicates significant positive results. According to the findings, the basis for the innovation of green technology in enterprises and investment in environmental protection are different, so the mechanisms and approaches of behavior related to the overseas market for the realization of enterprises’ green transformation are different.
4.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
- (1)
- Distinguish the form of ownership of listed companies
Next, Equation (4) was used to explore the heterogeneity of the impact of the behavior related to the overseas market on corporate green technology innovation under the difference of corporate ownership. Enterprise ownership (Owner) is represented by the dummy variable introduced here. The value of “Owner” is 1 when the state has ownership of the enterprise; otherwise, it is 0. The term Owner_Ovse was generated and then regressed by the interactive variable of enterprise ownership (Owner) and the overseas association indicator variable (Ovse) after they were combined in a dummy variable. From the regression results (Table 9), after controlling for the impact of both the individual and time effects, the coefficient that preceded Owner_Ovse had a significance level of 1%. Regardless of whether the variable being discussed is the creation of green technology or investing in environmental protection for corporations, the influence of corporate behavior related to the overseas market on the improvement of the green transformation ability is more noticeable in the enterprises that are controlled by the state, and hypothesis 3 is found valid.

Table 9.
The regression result that distinguishes the ownership form of listed companies.
- (2)
- Further evaluation based on the motivation behind corporate environmental governance
By increased corporate awareness of the environment, engaging in overseas markets can have a significant impact for heavily polluting enterprises in regards to their investments in environmental protection and the innovation of green technology, according to research data. In addition, behavior related to the overseas market will give enterprises the chance to gain knowledge about concepts of green production and management and advance methods of protecting the environment to motivate businesses to foster the act of green technology innovation. To investigate the various motivations and modes of environmental governance in greater depth, the study divided the samples as follows: one group that has good business performance and has an ROI that exceeds the median (H-ROA) and one group with poor business performance (L-ROA) according to industry and annual standards. By distinguishing enterprises by different business performance, the impact of behavior related to the overseas market for corporations on green transformation was examined. Table 10 exhibits the regression outcomes that take into account the motivation behind corporate environmental governance. It also demonstrates the fact that behavior related to the overseas market can significantly improve the high-performing firms with investments in environmental protection and green technology innovation, and the regression results have a significance level of 5%. However, the corporate behavior related to the overseas market does not improve low-performing companies’ creation of the green technology. This suggests that high-performing firms’ green transformation is more evident due to the behavior related to the overseas market, and hypothesis 4 is proven valid.

Table 10.
The regression result considering the advantage-creation motivation of corporate green transformation.
The reason may be that, in the face of international competition, companies may face more compliance pressure to meet environmental standards and requirements for environmental information disclosure when their business performance is not good enough. Therefore, they tend to choose environmental protection investment, which is characterized by relatively low difficulty and relatively faster results. Enterprises with good business performance and relatively strong competitiveness will actively seek green transformation motivated by creating advantages. Therefore, such enterprises have a significantly higher enthusiasm for participating in green technology innovation activities.
5. Discussion
The research conducted in this paper used the DID model based on the data from Chinese companies on the A-share list between 2011 and 2019. Table 3 depicts the benchmark regression outcomes, which suggest that enterprises can promote their green transformation through behavior related to the overseas market. This can be easily found in the increase both in protection but also in innovations. In order to prove the research credibility, PSM was also used to remove the obstacles of some potential influencing factors such as the insure sample themselves and exclude the research sample whose main business involved environmental protection, recycling, new energy, and other green industries. Table 4 and Table 5 display the results. Furthermore, the regression results that adjust the industry for the explained variables are shown in Table 6. It is possible to indicate the credibility of the findings above all of the estimation results. Furthermore, Table 7 and Table 8 show the regression results. One depicts the results regarding environment protection investment, while the other shows the results from the perspective of the process of promoting green technology innovation.
When corporations increase their environmental protection investment, they need to pay attention to their own environmental management. Companies will be forced to take on more environmental responsibilities in a host country when they “go global”. And when facing the competition pressure in the international market, China’s enterprises tend to deal with stricter environmental information disclosure requirements and higher environmental standards. Therefore, high-polluting enterprises in China will take the initiative to seek their own development after increasing their awareness of environmental protection so as to increase protection investment. Therefore, the increase in the corporate investment in the overseas market is mostly in improving awareness based on compliance requirements. To improve green technology innovation, enterprises need to have more advanced technological innovation capabilities while paying attention to their own environmental behavior. The behavior related to the overseas market is a vital method for enterprises to continuously acquire overseas resources and explore international markets. By their behavior related to the overseas market, enterprises are able to acquire the resources necessary for green technology innovation. In light of the increasing pressure on environmental regulations, cost reduction and total factor productivity improvement can be achieved, which encourages the advancement of green technology innovation. Therefore, behavior related to the overseas market is very effective for strengthening enterprises to enhance their investments in environmental protection and for exploring and investigating the method of spontaneous green technology innovation.
As discussed above, the present research distinguishes the ownership and performance of corporations, and Table 9 and Table 10 depict the result of the regression. It is more evident that a green transition is being promoted when it comes to state-owned enterprises’ behavior in the overseas market compared to non-state-owned enterprises. Moreover, enterprises with better performance have the motivation to create a competitive advantage, and it is more evident that enterprises’ green technology innovation is influenced by behavior related to the overseas market.
Nevertheless, the research does have certain constrains. This paper distinguishes enterprises’ green transformation into two aspects: The first is the environmental protection investment, and the second is green technology innovation. However, there are other ways to measure enterprises’ green transformation, which are not included in this research. Furthermore, there is the possibility that there is a correlation between investing in environmental protection and innovation in green technology from enterprises. However, in this research, we consider these two approaches as individual channels to discuss.
6. Conclusions
With the pressure of environmental regulation changing with the international situation, “going out” has become a strategic choice for more enterprises. The study of enterprises’ behavior in the foreign market is of great significance in determining whether their efforts to promote the development of green enterprises will involve increasing their investments in environmental protection and green technology innovation. The green transformation of corporations is influenced by their behavior in the overseas market and its influencing mechanism, which can be fully examined by using the DID model and using the data from China’s high-polluting enterprises listed in the A-share market from 2011 to 2019. At the same time, we distinguished two different types of ownership of enterprises and detailed the different motivations of corporate behavior related to the overseas market to promote the enterprises’ green transformation.
The research shows that the behavior related to the overseas market can increase enterprises’ investments in environmental protection and promote the development of green technology, thereby realizing the acceleration of enterprises’ green transformation. In addition, there are differences in mechanisms and approaches between these two aspects. Only by improving the corporate environmental responsibility awareness can the investment in them be increased, while the increase in corporate innovation in green technology not only requires higher awareness of environmental responsibility but also requires enterprises to learn management concepts about green development. Furthermore, we conclude that enterprises with relatively low business performance tend to choose corporate environmental protection investment, which is characterized by relatively low difficulty and more quickly meets the requirements of environmental standards and environmental information disclosure. Meanwhile, enterprises that perform better in business are more willing to examine the inherent worth of green technology innovation and decide on a course of action for promoting innovation technology for environment through behavior related to the overseas market. In addition, due to the high resource and capital requirements necessary for the innovation of green technology innovation, the influence of behavior related to the overseas market in improving the ability of enterprises for green transformation is particularly important in state-owned enterprises.
The current research into the impact of overseas market-related behavior on the facilitation of enterprises’ green transformation provides some useful suggestions. First of all, enterprises should actively “go global” in combination with their own situation and modifications to the international situation. At present, the restructuring of the global industrial chain, supply chain, and value chain is accelerating; the global production network is gradually moving towards regionalization; and the trade plate trend is also constantly strengthening. China needs to expand overseas markets and strengthen the harmony of local and overseas trade industrial and supply chains. Enterprises in China’s high-polluting industries also urgently need to accelerate their integration into the supply, industrial, and value chains of the world and strive to improve their ability to allocate factor resources and lay out market networks in the international market. Secondly, close attention should be paid to the transformation process itself not only by the government but also by non-state-owned enterprises in order to accelerate the realization of green development. Supervision and punishment of high-polluting industries for violating environmental requirements should be strengthened, and economic development should not be carried out by sacrificing environment quality and damaging the balance of the environment. Thirdly, entrepreneurial guidance and support from the government for companies that are actively going overseas is necessary. Enterprises will face higher environmental standards and stricter environmental information disclosure requirements after going overseas. On the one hand, the government ought to assume its fundamental roles, exhibit its necessary status, and swiftly intervene in establishing standardized practices for disclosing environmental information and enhancing the quality of enterprises’ information disclosure; in contrast, they should connect enterprises with the resources to help them integrate the resources and innovation base of their original overseas enterprises or obtain the required product innovation resources and learn new technologies through overseas markets to achieve reverse technology spillover effects in order to enhance their green technology innovation capabilities. Through theoretical exploration, this study extends the understanding of the impact mechanism and provides empirical insights into how corporate behaviors tied to the overseas market affect their green transformation, providing an important reference for promoting the green and sustainable development of enterprises and promoting China’s green and low-carbon development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L. and Q.Z.; methodology, Z.L.; software, Z.L.; validation, Z.L.; formal analysis, Z.L. and Q.Z.; investigation, Z.L.; resources, Z.L.; data curation, Z.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.L. and Q.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.L. and Q.Z.; visualization, Z.L.; supervision, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by [Major projects of China Social Science Foundation] grant number [18VSJ036, 21ZDA115].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks are given to those who participated in the writing of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, C.H. An environmental perspective extends market orientation: Green innovation sustainability. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020, 29, 3123–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Kumar, A.; Upadhyay, A. How do green knowledge management and green technology innovation impact corporate environmental performance? Understanding the role of green knowledge acquisition. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 32, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, Y. Paths and Constraining Factors of Green Finance in Promoting High-Quality Development of Export Enterprises. Intertrade 2023, 9, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Wang, F.; Song, G.; Liu, L. Digital Transformation on Enterprise Green Innovation: Effect and Transmission Mechanism. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Zhou, J.K.; Li, Y. Corporate behavior related to the overseas market and green technology innovation under the dual circulation development pattern. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2023, 33, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lanoie, P.; Laurent-Lucchetti, J.; Johnstone, N.; Ambec, S. Environmental Policy, Innovation and Performance: New Insights on the Porter Hypothesis. J. Econ. Manag. Strategy 2011, 20, 803–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.M.; Zhang, L. Environmental Regulation, Economic Opening and China’s Industrial Green Technology Process. Econ. Res. J. 2014, 9, 34–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kafouros, M.I.; Buckley, P.J.; Clegg, J. The Effects of Global Knowledge Reservoirs on the Productivity of Multinational Enterprises: The Role of International Depth and Breadth. Res. Policy 2012, 41, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phene, A.; Almeida, P. Innovation in Multinational Subsidiaries: The Role of Knowledge Assimilation and Subsidiary Capabilities. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2008, 39, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaltegger, S.; Wagner, M. Sustainable Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Innovation: Categories and Interactions. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2011, 20, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.B.; Yang, M.; Chen, L. How Do Environmental Technology Standards Affect the Green Transition of China’s Manufacturing Industry-A Perspective from Technological Transformation. China Ind. Econ. 2021, 9, 118–136. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.C.; Zhang, W.G.; Bi, Q. The Study on the Backward Forcing Effect of Environmental Tax on Corporate Green Transformation. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2019, 7, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Ding, S.; Zhao, X. China’s Green Finance Policy, Financing Costs, and Green Transformation of Enterprises: From the Perspective of the Central Bank’s Collateral Policy. Finac. Res 2021, 12, 75–95. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Can the Green Finance Policy Force the Green Transformation of High-polluting Enterprises? A Quasi-natural Experiment Based on “Green Credit Guidelines”. Energy Econ. 2022, 114, 106265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.H.; Jiang, Y.B. The Influence of Environmental Regulation on the Behavior of Enterprise Environmental Governance: Based on a Quasi-Natural Experiment of New Environmental Protection Law. Bus. Manag. J. 2019, 41, 54–72. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Song, L.N.; Zhu, Y.S.; Liu, C.H. Does Green Finance Promote the Green Transformation of China’s Manufacturing Industry? Sustainability 2023, 15, 6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, N.; Strange, R.; Zucchella, A. Stakeholder Pressures, EMS Implementation, and Green Innovation in MNC Overseas Subsidiaries. Int. Bus. Rev. 2018, 27, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.M.; Han, Y.H. How can Local Manufacturing Enterprises Achieve Luxuriant Transformation in Green Innovation? A Multi-case Study Based on Attention-based View. J. Manag. World 2022, 38, 76–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.Z.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, W.C. Does digitalization promote green technology innovation in resource-based enterprises? Stud. Sci. Sci 2022, 40, 332–344. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Jin, S. Can Enterprises in China Achieve Sustainable Development through Green Investment? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-J.; Shen, Q.; Geng, Y.; Li, D.-Y. Does Overseas Investment Raise Corporate Environmental Protection? Evidence from Chinese A-List Companies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Xia, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D. Environmental Regulation, Government R&D Funding and Green Technology Innovation: Evidence from China Provincial Data. Sustainability 2018, 10, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Li, Z.; Drakeford, B. Do the Green Credit Guidelines Affect Corporate Green Technology Innovation? Empirical Research from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, R.Y.K.; Lai, J.W.M.; Kim, N. Strategic Motives and Performance Implications of Proactive Versus Reactive Environmental Strategies in Corporate Sustainable Development. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 31, 2127–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazalin, N.; Mahmood, M. Toward Sustainable Development: Board Characteristics, Country Governance Quality, and Environmental Performance. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 3569–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neary, J.P. Cross-border Mergers as Instruments of Comparative Advantage. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2007, 74, 1229–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Impact of FDI on energy efficiency: An analysis of the regional discrepancies in China. Nat. Hazards 2017, 85, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojnik, J.; Ruzzier, M. What Drives Eco-innovation? A Review of an Emerging Literature. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2016, 19, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, R. The Value Creation Effect of “Environmental Supervision” from the Perspective of Enterprise Green Innovation: A Quasi-experimental Study Based on Environmental Interviews. Sci. Res. Manag. 2021, 42, 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- Stiebale, J. Cross-border M&As and Innovative Activity of Acquiring and Target Firms. J. Int. Econ. 2016, 99, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, C.; Kittler, M. Removing environmental market failure through support mechanisms: Insight from green star-ups in the British, French and German energy sectors. Small Bus. Econ. 2019, 52, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Geng, Y.; Lai, K. Barriers to promoting Eco-industrial parks development in China: Perspectives from senior officials at national industrial parks. J. Ind. Ecol 2015, 19, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liao, G.; Li, Z. Loaning scale and government subsidy for promoting green innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 144, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkinshaw, J.; Lingblad, M. Intrafirm Competition and Charter Evolution in the Multibusiness Firm. Organ. Sci. 2005, 16, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, D.; Montresor, S.; Schubert, T.; Vezzani, A. Multinationality, R&D and productivity: Evidence from the top R&D investors worldwide. Int. Bus. Rev. 2017, 26, 405–416. [Google Scholar]
- Dawkins, C.; Fraas, J.W. Coming Clean: The Impact of Environmental Performance and Visibility on Corporate Climate Change Disclosure. J. Bus. Ethics 2011, 100, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.W.; Li, Y.H. How Resource Alignment Moderates the Relationship Between Environmental Innovation Strategy and Green Innovation Performance. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2018, 33, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Kong, L.S.; Ciabuschi, F. Reverse Innovation Transfer in Chinese MNCs: The Role of Political Ties and Headquarters. J. Int. Manag. 2021, 27, 100829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Li, L.Z. An empirical study on the impact of green finance and green policies on the green transformation of entity enterprises. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2023, 33, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.C.; Shao, C.H.; Li, J.J. Green technology innovation and financial development: Do environmental regulation and innovation output matter? Energy Econ. 2021, 98, 105237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Xu, Y.Y.; Hao, Y.; Wu, H.T.; Xue, Y. What is the role of telecommunications infrastructure construction in green technology innovation? A firm-level analysis for China. Energy Econ. 2021, 103, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Q. Top management team faultlines, green technology innovation and firm financial performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.L.; Liu, X.; Qiu, J.L.; Shen, Y. Can Green M&A of Heavy Polluting Enterprises Achieve Substantial Transformation under the Pressure of Media. China Ind. Econ. 2019, 371, 174–192. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, K.; Nadeem, M.; Pandey, R. Do Capital Markets Reward Corporate Climate Change Actions? Evidence from the Cost of Debt. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 32, 3417–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, A.; Chandran VG, R.; Rajaghantham, D. Exploring SME Environmental Behaviour and Practice: The Case of Malaysia. Dev. Policy Rev. 2023, 41, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lu, J.R.; Ju, T. Formalism or Substantialism: Research on Green Innovation under Soft Market Supervision of ESG Rating. Nankai Bus. Rev. 2023, 26, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Ji, G.; Zhou, H. Environmental Will, Environmental Behavior and Knowledge Sharing: An Empirical Study Based on Resource-Based Enterprises. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 5833–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morck, R.; Yeung, B.; Zhao, M. Perspectives on China’s outward foreign direct investment. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2008, 39, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.B.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J.; Rasheed, A. Influence of FDI on environmental pollution in selected Arab countries: A spatialeconometric analysis perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res 2020, 27, 28222–28246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhan, D.; Li, J. Does foreign direct investment affect environmental pollution in China’s cities? A spatial econometric perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, H.; Sun, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Li, W. Does Environmental Regulation Promote Corporate Green Innovation? Empirical Evidence from Chinese Carbon Capture Companies. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrone, P.; Fosfuri, A.; Gelabert, L. Necessity as the Mother of Green Inventions: Institutional Pressures and Environmental Innovations. Strateg. Manag. J. 2013, 34, 891–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Wang, F. Does FDI bring environmental knowledge spillovers to developing countries? The role of the local industrialstructure. Environ. Resour. Econ 2018, 71, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafindadi, A.A.; Muye, I.M.; Kaita, R.A. The effects of FDI and energy consumption on environmental pollution in predominantly resource-based economies of the GCC. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2018, 25, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S.; Qayyum, U.; Majeed, T. FDI and environmental degradation: The role of political institutions in South Asian countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32544–32553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Martinsson, G.; Thomann, C. Can Environmental Policy Encourage Technical Change? Emissions Taxes and R&D Investment in Polluting Firms. Rev. Financ. Stud 2022, 35, 4518–4560. [Google Scholar]
- Leiter, A.M.; Parolini, A.; Winner, H. Environmental Regulation and Investment: Evidence from European Industry Data. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, P.; Bastola, U. Foreign direct investment, income, and environmental pollution in developing countries: Panel data analysis of Latin America. Energy Econ. 2017, 64, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujabal, P.; Sethi, N.; Padhan, P.C. ICT, foreign direct investment and environmental pollution in major Asia Pacific countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res 2021, 28, 42649–42669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildirici, M.; Gokmenoglu, S.M. The impact of terrorism and FDI on environmental pollution: Evidence from Afghanistan, Iraq, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, Syria, Somalia, Thailand and Yemen. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 81, 106340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, L.; Poncet, S. Environmental Policy and Exports: Evidence from Chinese Cities. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2014, 68, 296–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Hamilton, T. What is Driving Corporate Social and Environmental Responsibility in China: An Evaluation of Legacy Effects, Organizational Characteristics, and Transnational Pressures. Geoforum 2020, 110, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allet, M.; Huddon, M. Green microfinance: Characteristics of microfinance institutions involved in environmental management. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 126, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Wu, T. Does Environmental Credit Rating Promote Green Innovation in Enterprises? Evidence from Heavy Polluting Listed Companies in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, L.; Gonzalez, F.; Ruiz, I. The impact of FDI on CO2 emissions in Latin America. Oxf. Dev. Stud. 2013, 41, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albulescu, C.T.; Tiwari, A.K.; Yoon, S.M.; Kang, S.H. FDI, income, and environmental pollution in Latin America: Replication and extension using panel quantiles regression analysis. Energy Econ. 2019, 84, 104504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demena, B.A.; Afesorgbor, S.K. The effect of FDI on environmental emissions: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Energy Policy 2020, 138, 111192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, H.; Ren, S. How do FDI and technical innovation affect environmental quality? Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7835–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).