Environmental, Energy, and Techno-Economic Assessment of Waste-to-Energy Incineration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method and Data Source
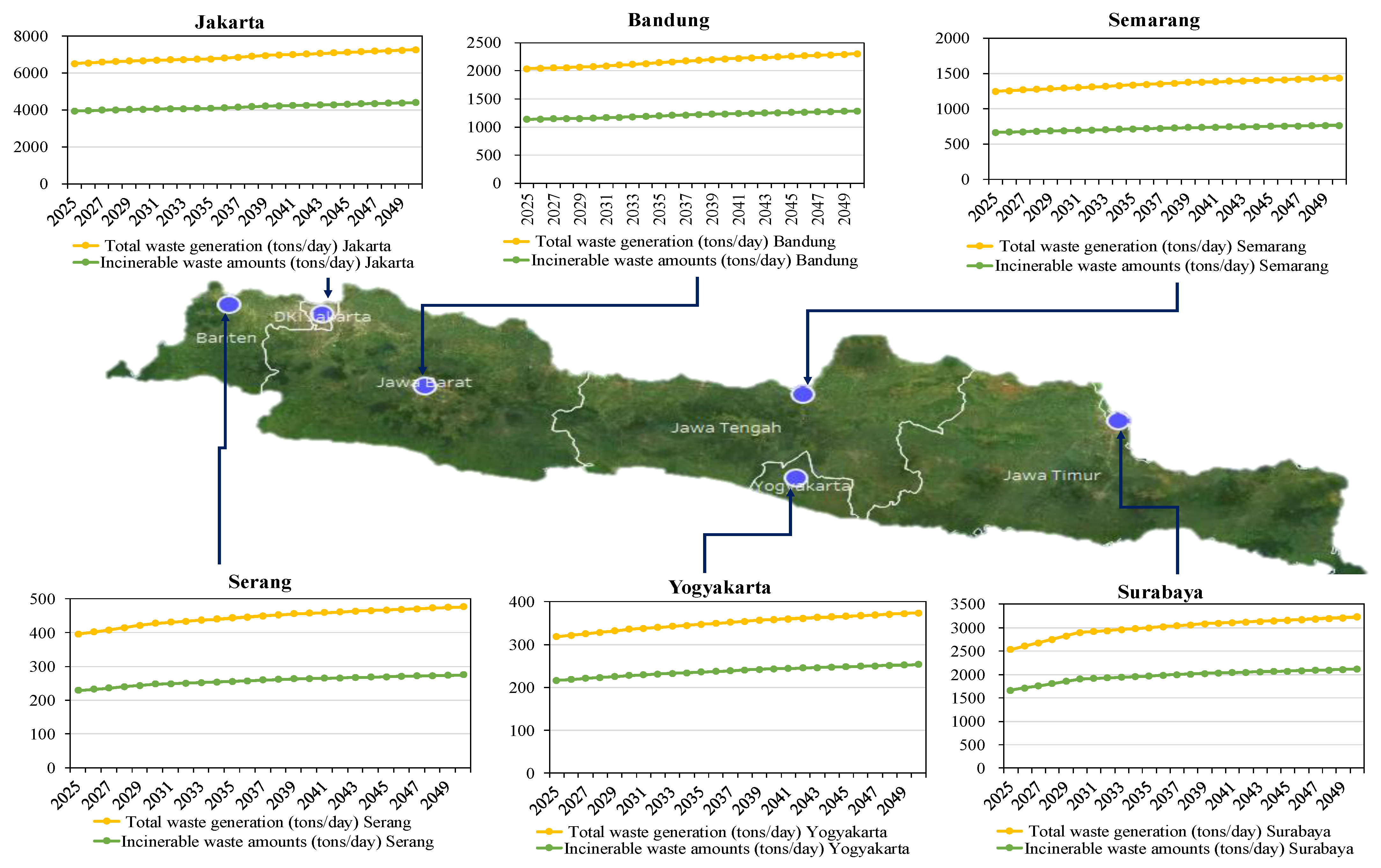
2.1. Brief Introduction of Java Island
2.2. Life Cycle Environmental Assessment and Emission Reduction Potential
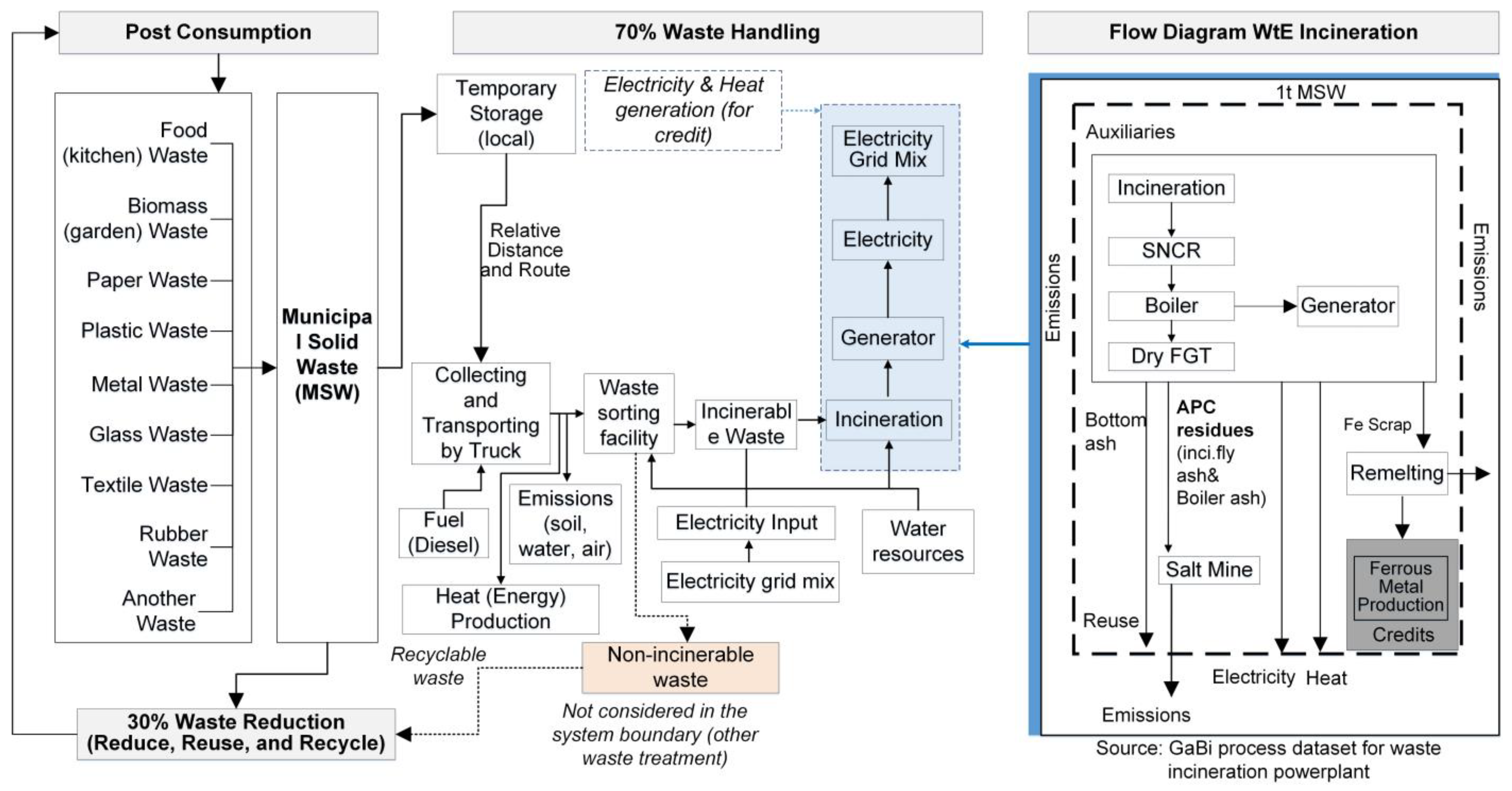
2.2.1. Goals, Functional Unit, and System Boundary
2.2.2. Life Cycle Inventory and Data Sources
2.2.3. Life Cycle Impact Assessment
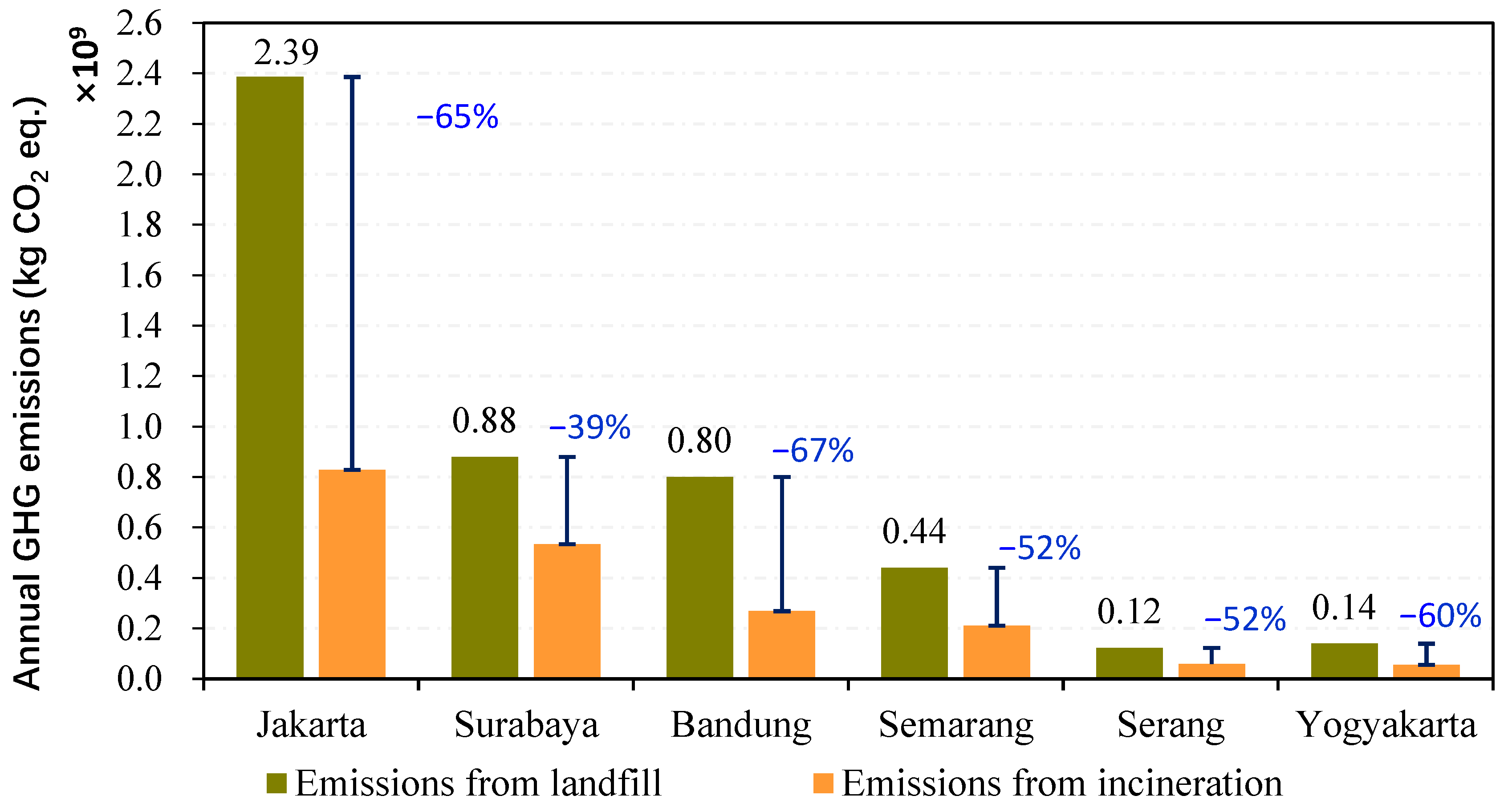
2.2.4. GHG Emission Reduction Potential from Incineration Compared with Landfill
2.3. Energy Recovery with the Dulong Approach
2.4. Techno-Economic Feasibility Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Life Cycle Environmental Impact Assessment
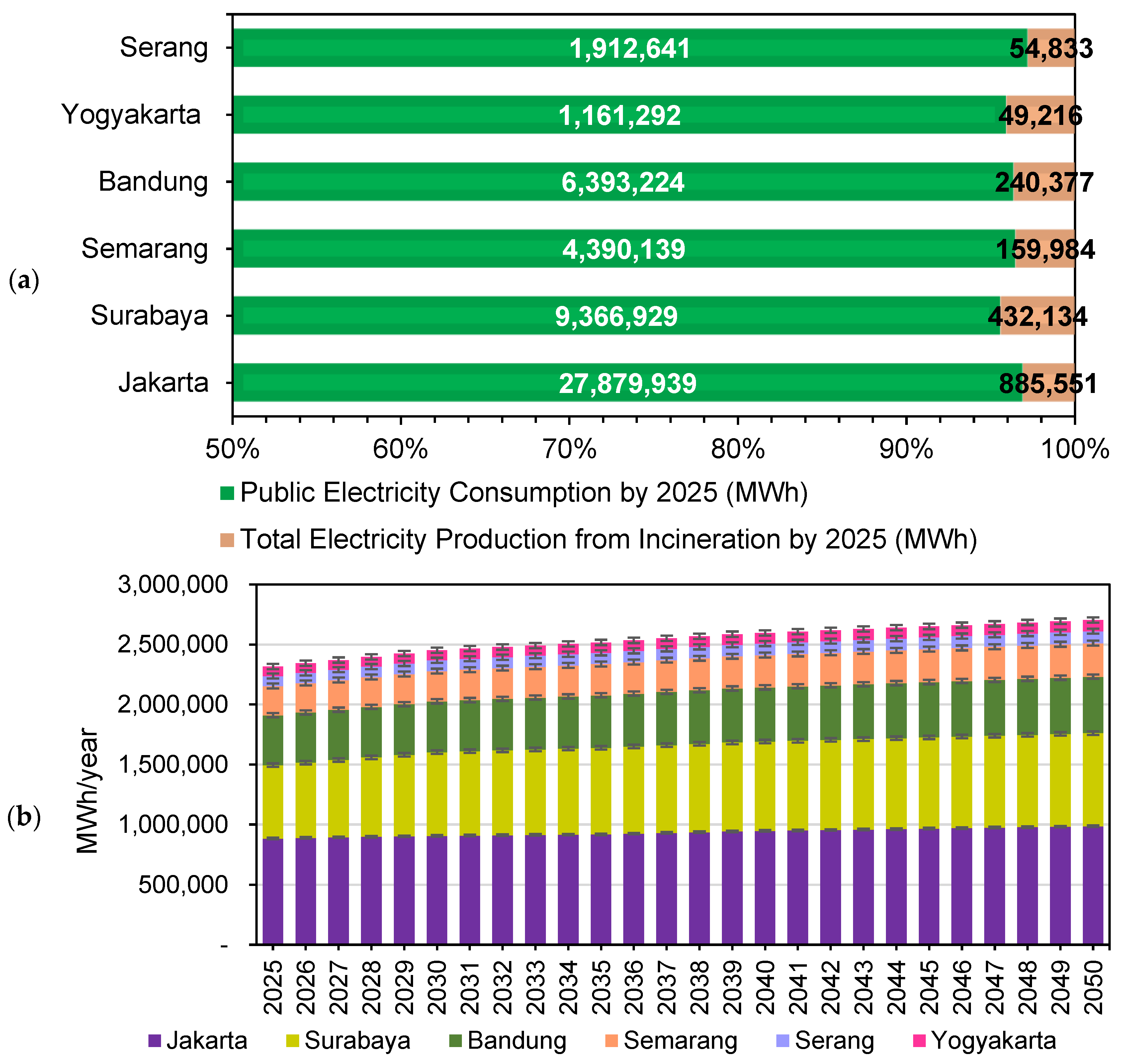
3.2. Electricity Generation Potential
3.3. Techno-Economic Analysis
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| WtE | Waste-to-energy |
| MSW | Municipal solid waste |
| LCA | Life cycle assessment |
| LCIA | Life cycle impact assessment |
| ADP | Abiotic depletion potential |
| AP | Acidification potential |
| EP | Eutrophication potential |
| FAETP | Freshwater aquatic ecotoxicity potential |
| GWP100 | Global warming potential, 100 years |
| HTP | Human toxicity potential |
| MAETP | Marine aquatic ecotoxicity potential |
| ODP | Ozone layer depletion potential |
| POCP | Photochemical ozone creation potential |
| TETP | Terrestrial ecotoxicity potential |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
| DDOC | Decomposable degradable organic carbon |
| MCF | Correction factor for methane |
| DOC | Degradable organic carbon (aerobic conditions) |
| OX | Oxidation factor |
| CE | Emissions from combustion |
| SW | Quantity of incinerated solid waste |
| DM | Dry matter content (partially wet weight) of waste |
| CF | Carbon fraction in dry matter (total carbon content) |
| FCF | Fossil carbon fraction |
| OF | Oxidation factor |
| FC | Consumption of fuel |
| NCV | Net calorific value |
| EF | Emission factor |
| EC | Electricity consumption for WtE |
| RE | Reductions between emissions from landfill and incineration |
| HV | Heating value |
| EPnet | Net electricity generated potential |
| EPcapita | Electricity consumption per capita |
| NPV | Net present value |
| IRR | Internal rate of return |
| LCoE | Levelized cost of electricity |
| r | Discount rate |
References
- Zhang, C.; Dong, H.; Geng, Y.; Liang, H.; Liu, X. Machine learning based prediction for China’s municipal solid waste under the shared socioeconomic pathways. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastjerdi, B.; Strezov, V.; Kumar, R.; He, J.; Behnia, M. Comparative life cycle assessment of system solution scenarios for residual municipal solid waste management in NSW, Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Dong, H. Uncover Cost-Benefit Disparity of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration in Chinese Provinces. Sustainability 2020, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC User Manual Estimation Tool for Greenhouse Gas (GHG). Emissions from Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Management in a Life Cycle Perspective; IGES: Hayama, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Asian Development Bank. Summary of Indonesia’s Energy Sector Assessment; Asian Development Bank: Manila, Philippines, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cudjoe, D.; Acquah, P.M. Environmental impact analysis of municipal solid waste incineration in African countries. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Xue, R.; Gao, G.; Zhang, R. Life cycle assessment of environmental impact on municipal solid waste incineration power generation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 65435–65446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, R.M.; Kumar, D.; Alappat, B.J. A technique to quantify incinerability of municipal solid waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 140, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.J.d.V.B.d.; dos Santos, I.F.S.; Mensah, J.H.R.; Goncalves, A.T.T.; Barros, R.M. Incineration of municipal solid waste in Brazil: An analysis of the economically viable energy potential. Renew. Energy 2020, 149, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, M.; Siddiqi, A.; Narayanamurti, V. Stochastic cost-benefit analysis of urban waste-to-energy systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 224, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, A.; Haraguchi, M.; Narayanamurti, V. Urban waste to energy recovery assessment simulations for developing countries. World Dev. 2020, 131, 104949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarasinghe, K.; Wijayatunga, P.D.C. Techno-economic feasibility and environmental sustainability of waste-to-energy in a circular economy: Sri Lanka case study. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2022, 68, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastjerdi, B.H.; Strezov, V.; Kumar, R.; Behnia, M. Economic feasibility and sustainability assessment of residual municipal solid waste management scenarios in NSW, Australia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-García, P.E.; Camarillo-López, R.H.; Carrasco-Hernández, R.; Fernández-Rodríguez, E.; Legal-Hernández, J.M. Technical and economic analysis of energy generation from waste incineration in Mexico. Energy Strateg. Rev. 2020, 31, 100542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pinegar, L.; Immonen, J.; Powell, K.M. Conversion of food waste to renewable energy: A techno-economic and environmental assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 385, 135741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.M.; Shahid, S.; Nawaz, M.I.; Mustafa, J.; Iftekhar, S.; Ahmed, I.; Tabraiz, S.; Bontempi, E.; Assad, M.; Ghafoor, F.; et al. Waste to energy feasibility, challenges, and perspective in municipal solid waste incineration and implementation: A case study for Pakistan. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2024, 18, 100595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachim, T.A. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Pengolahan Sampah Secara Termal (Studi Kasus: TPA Benowo, Kota Surabaya). Inst. Teknol. Sepuluh Nop. 2017, 144, 141581. Available online: https://repository.its.ac.id/43075/1/3313100063-Undergraduate_Theses.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Gunamantha, M.; Fandeli, C.; Tandjung, S.D.; Sarto, S. Life cycle assessment of solid waste management options: Case study of the Kartamantul regions, D.I.Yogyakarta province. J. Mns. Lingkung. 2010, 17, 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Sudibyo, H.; Majid, A.I.; Pradana, Y.S.; Budhijanto, W.; Deendarlianto; Budiman, A. Technological evaluation of municipal solid waste management system in Indonesia. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudibyo, H.; Pradana, Y.S.; Budiman, A.; Budhijanto, W. Municipal solid waste management in Indonesia—A study about selection of proper solid waste reduction method in, D.I. Yogyakarta Province. Energy Procedia 2017, 143, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Indonesia. Total Population Projection Result by Province and Gender (Thousand People), 2018–2020; Statistics Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021.
- Sharma, A.; Ganguly, R.; Gupta, A.K. Life cycle assessment of municipal solid waste generated from hilly cities in India—A case study. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xayachak, T.; Haque, N.; Lau, D.; Emami, N.; Hood, L.; Tait, H.; Foley, A.; Pramanik, B.K. White spill: Life cycle assessment approach to managing marine EPS litter from flood-released pontoons. Chemosphere 2023, 337, 139400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Dong, H.; Geng, Y.; Fujii, M. Life cycle cost–benefit efficiency of food waste treatment technologies in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 4935–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menikpura, N.; Sang-Arun, J. User Manual Estimation Tool for Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions from Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Management in a Life Cycle Perspective, 2nd ed.; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies: Kanagawa, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Menikpura, S.N.M.; Sang-Arun, J.; Bengtsson, M. Assessment of environmental and economic performance of Waste-to-Energy facilities in Thai cities. Renew. Energy 2016, 86, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.; Hamdan, S.; Shabib, A. Development of a dynamic optimization framework for waste management systems. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibikunle, R.A.; Titiladunayo, I.F.; Akinnuli, B.O.; Dahunsi, S.; Olayanju, T. Estimation of power generation from municipal solid wastes: A case Study of Ilorin metropolis, Nigeria. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibikunle, R.A.; Titiladunayo, I.F.; Lukman, A.F.; Dahunsi, S.; Akeju, E. Municipal solid waste sampling, quantification and seasonal characterization for power evaluation: Energy potential and statistical modelling. Fuel 2020, 277, 118122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, F.; Damanhuri, T.P. Kajian komposisi, karakteristik, dan potensi daur ulang sampah di TPA Cipayung, Depok. J. Tek. Lingkung. 2011, 17, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasek, A.D.; Gultom, K.W.; Suwono, A. Feasibility of recovering energy from municipal solid waste to generate electricity. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2013, 45, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Public Works and Public Housing of the Republic of Indonesia. WtE Thermal Technology Based Combustion (Incineration) Process. Badan Pengembangan Sumber Daya Manusia; Kementerian Pekerjaan Umum dan Perumahan Rakyat: Bandung, Indonesia, 2018.
- Abdallah, M.; Arab, M.; Shabib, A.; El-Sherbiny, R.; El-Sheltawy, S. Characterization and sustainable management strategies of municipal solid waste in Egypt. Clean. Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, A.U. Comparative study of municipal solid waste treatment technologies using life cycle assessment method. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartika Wibowo, A.P. Pemodelan Kebutuhan Listrik Indonesia Terkait Pencapaian Sasaran Kebijakan Energi Nasional. J. Politeknosains 2017, 16, 50–60. Available online: http://download.garuda.kemdikbud.go.id/article.php?article=3318285&val=29117&title=Pemodelan%20Kebutuhan%20Listrik%20Indonesia%20Terkait%20Pencapaian%20Sasaran%20Kebijakan%20Energi%20Nasional (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Andersson, E.R. Economic Evaluation of Ergonomic Solutions: Part I-Guidelines for the Practitioner; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Keshavarz, A. CCHP Evaluation Criteria. In Combined Cooling, Heating and Power—Decision-Making, Design and Optimization; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, M.; Shanableh, A.; Shabib, A.; Adghim, M. Financial feasibility of waste to energy strategies in the United Arab Emirates. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics Indonesia. BI Rate 2021; Badan Pusat Statistik: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021.
- Cook, M. Project cash flow. In Developments in Petroleum Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 133–205. [Google Scholar]
- Timilsina, G.R. Demystifying the Costs of Electricity Generation Technologies; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ragheb, M. A Handbook for Onshore and Offshore Wind Turbines. In Wind Energy Engineering; Elsevier Inc.: London, UK, 2017; pp. 537–555. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, T.; Mowers, M.; Eurek, K. Competitiveness Metrics for Electricity System Technologies; National Renewable Energy Lab.: Golden, CO, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.S.; McCulloch, M.D. Levelized cost of electricity for solar photovoltaic and electrical energy storage. Appl. Energy 2017, 190, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Finance. Carbon Tax as an Instrument for Controlling Climate Change; Ministry of Finance: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021.
- Ministry of Finance. Committed to Overcoming Climate Change, Law on Harmonization of Tax Regulations (RUU HPP) Regulates the Imposition of Carbon Tax; Ministry of Finance: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021.
- The Indonesia Directorate General of Taxes. Pajak Karbon dan Pigouvian Tax. Available online: https://www.pajak.go.id/id/artikel/pajak-karbon-dan-pigouvian-tax (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Liamsanguan, C.; Gheewala, S.H. LCA: A decision support tool for environmental assessment of MSW management systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toniolo, S.; Mazzi, A.; Garato, V.G.; Aguiari, F.; Scipioni, A. Assessing the “design paradox” with life cycle assessment: A case study of a municipal solid waste incineration plant. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 91, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Teixeira, C.A.; Rouboa, A. Environmental analysis of waste-to-energy-a Portuguese case study. Energies 2018, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswani, H.K.; Azapagic, A. Assessing the environmental sustainability of energy recovery from municipal solid waste in the, U.K. Waste Manag. 2016, 50, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaya, W.; Gheewala, S.H. Life cycle assessment of MSW-to-energy schemes in Thailand. J. Clean. Prod. 2007, 15, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, S.; Tonini, D.; Christensen, T.H.; Scharff, H. Landfilling of waste: Accounting of greenhouse gases and global warming contributions. Waste Manag. Res. 2009, 27, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, M.R.; Aramaki, T.; Hanaki, K. Comparison of the environmental impact of incineration landfilling in São Paulo City as determined by, L.C.A. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2004, 41, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broun, R.; Sattler, M. A comparison of greenhouse gas emissions and potential electricity recovery from conventional and bioreactor landfills. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2664–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.H.; Damgaard, A.; Astrup, T.F. Waste to Energy: The carbon perspective. Waste Manag. World 2015, 24–28. Available online: https://orbit.dtu.dk/files/127630218/2015_Christensen_et_al_Waste_to_energy_the_carbon_perspective_postprint.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2015).
- Malakahmad, A.; Abualqumboz, M.S.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Abunama, T.J. Assessment of carbon footprint emissions and environmental concerns of solid waste treatment and disposal techniques; case study of Malaysia. Waste Manag. 2017, 70, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aracil, C.; Haro, P.; Fuentes-Cano, D.; Gómez-Barea, A. Implementation of waste-to-energy options in landfill-dominated countries: Economic evaluation and GHG impact. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources. Indonesia Energy Outlook; Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2019.
- Abd Kadir, S.A.S.; Yin, C.Y.; Rosli Sulaiman, M.; Chen, X.; El-Harbawi, M. Incineration of municipal solid waste in Malaysia: Salient issues, policies and waste-to-energy initiatives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhász, L. Comparing Net Present Value and Internal Rate of Return. Econ. Sociol. 2011, 4, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Cost-Benefit Analysis: Evaluation Criteria (Or: “Stay Away from the IRR”); The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources. Kajian Penyediaan dan Pemanfaatan Migas, Batubara, EBT dan Listrik (Study on Supply and Utilization of Oil and Gas, Coal, Electricity, and Renewable Energy); Center for Energy and Mineral Resources Data and Information Technology, Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2017.
- Indonesia Statistics. Indonesia Population Projection 2015–2045 Result of SUPAS 2015 (Revised Edition); Indonesia Statistics: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2018.
- Statistic Indonesia. Environment Statistics of Indonesia: Water and Environment; Badan Pusat Statistik Republik Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2020.
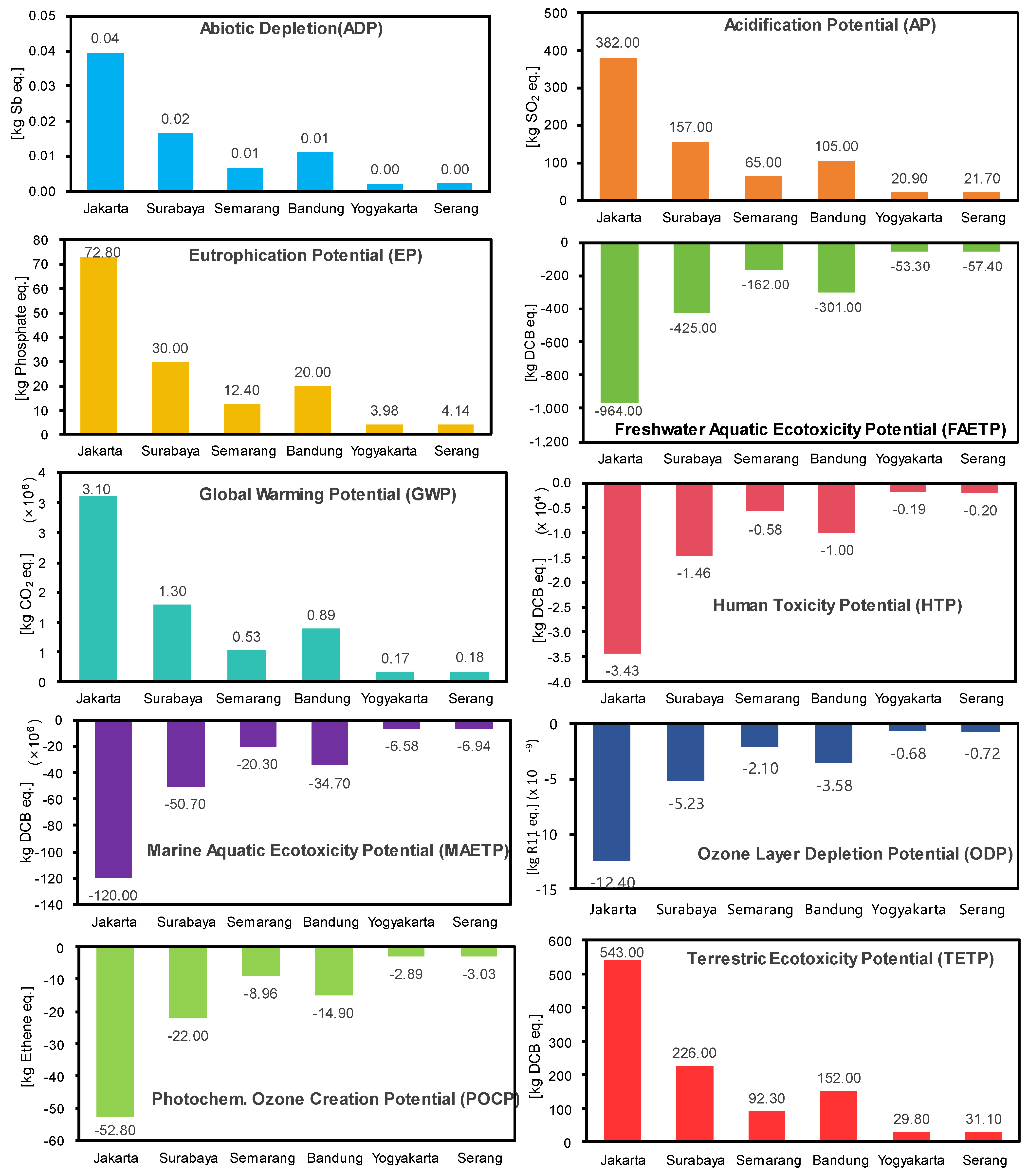
| ADP Elements (kg Sb eq.) | AP (kg SO2 eq.) | EP (kg Phosphate eq.) | FAETP (kg DCB eq.) | GWP100 (kg CO2 eq.) | |
| Total MSW in Java | 7.8 × 10−2 | 7.5 × 102 | 1.4 × 102 | −2.0 × 103 | 6.2 × 106 |
| 1 ton of MSW | 9.9 × 10−6 | 9.6 × 10−2 | 1.8 × 10−2 | −2.5 × 10−1 | 7.8 × 102 |
| HTP (kg DCB eq.) | MAETP (kg DCB eq.) | ODP (kg R11 eq.) | POCP (kg Ethene eq.) | TETP (kg DCB eq.) | |
| Total MSW in Java | −6.9 × 104 | −2.4 × 108 | −2.5 × 10−8 | −1.0 × 102 | 1.1 × 103 |
| 1 ton of MSW | −8.7 × 100 | −3.0 × 104 | −3.1 × 10−12 | −1.3 × 10−2 | 1.4 × 10−1 |
| Parameters | Jakarta | Surabaya | Semarang | Bandung | Yogyakarta | Serang |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investment (USD) | 61,248,526 | 25,871,957 | 10,370,912 | 17,683,719 | 3,363,300 | 3,545,005 |
| Operation and maintenance costs (USD/Year) | 39,743,488 | 16,788,025 | 6,729,570 | 11,474,769 | 2,517,241 | 2,300,314 |
| Revenues average (USD/Year) | 28,704,337 | 20,594,349 | 5,920,753 | 7,241,727 | 1,437,873 | 2,215,221 |
| NPV (USD) | 412,713,825 | 314,367,028 | 87,425,059 | 100,810,802 | 19,964,096 | 32,986,878 |
| IRR (%) * | 36.61 | 55.91 | 43.54 | 30.68 | 29.92 | 45.62 |
| IRR (%) ** | 37.25 | 56.37 | 44.09 | 31.53 | 29.92 | 46.19 |
| LCoE (USD/kWh) *** | 0.047 | 0.036 | 0.043 | 0.049 | 0.051 | 0.041 |
| LCoE (USD/kWh) **** | 0.046 | 0.036 | 0.042 | 0.049 | 0.050 | 0.041 |
| GHG reduction economical value (USD/Year) ***** | 2,069,037 | 267,584 | 254,636 | 701,211 | 103,744 | 70,121 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, J.; Mustafa, A.B.; Liu, M.; Huang, G.; Shang, N.; Liu, X.; Wei, K.; Wang, P.; Dong, H. Environmental, Energy, and Techno-Economic Assessment of Waste-to-Energy Incineration. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104140
Zeng J, Mustafa AB, Liu M, Huang G, Shang N, Liu X, Wei K, Wang P, Dong H. Environmental, Energy, and Techno-Economic Assessment of Waste-to-Energy Incineration. Sustainability. 2024; 16(10):4140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104140
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Jincan, Ade Brian Mustafa, Minwei Liu, Guori Huang, Nan Shang, Xi Liu, Kexin Wei, Peng Wang, and Huijuan Dong. 2024. "Environmental, Energy, and Techno-Economic Assessment of Waste-to-Energy Incineration" Sustainability 16, no. 10: 4140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104140
APA StyleZeng, J., Mustafa, A. B., Liu, M., Huang, G., Shang, N., Liu, X., Wei, K., Wang, P., & Dong, H. (2024). Environmental, Energy, and Techno-Economic Assessment of Waste-to-Energy Incineration. Sustainability, 16(10), 4140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104140







