Long-Term Anaerobic Digestion of Seasonal Fruit and Vegetable Waste Using a Leach-Bed Reactor Coupled to an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Bed Reactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Waste Mixtures and Composition
2.2. Mechanical FVW Pretreatment and Fractionation
2.3. Batch Anaerobic Digestion Assays
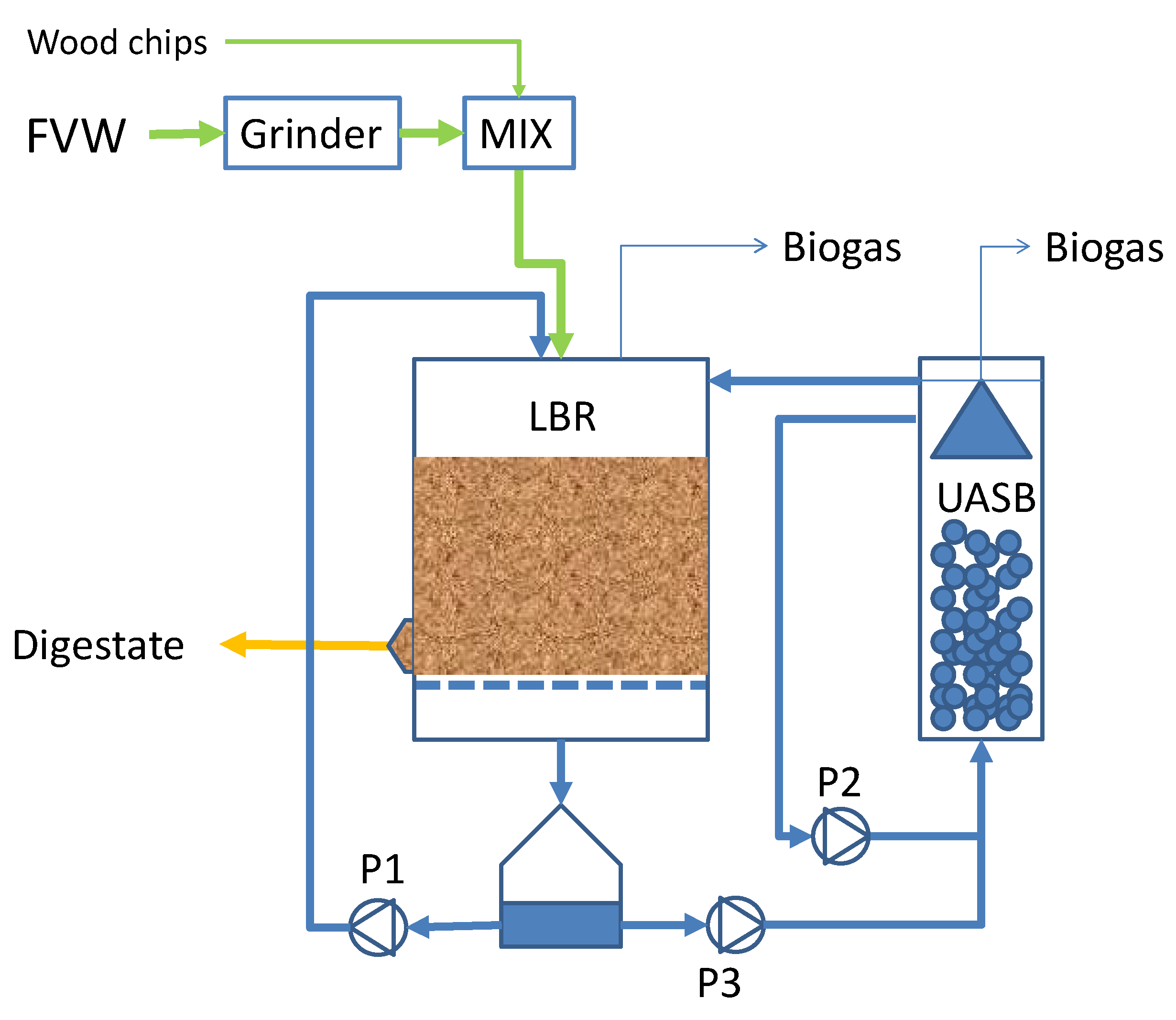
2.4. Bench-Scale Reactor Design and Operation
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results
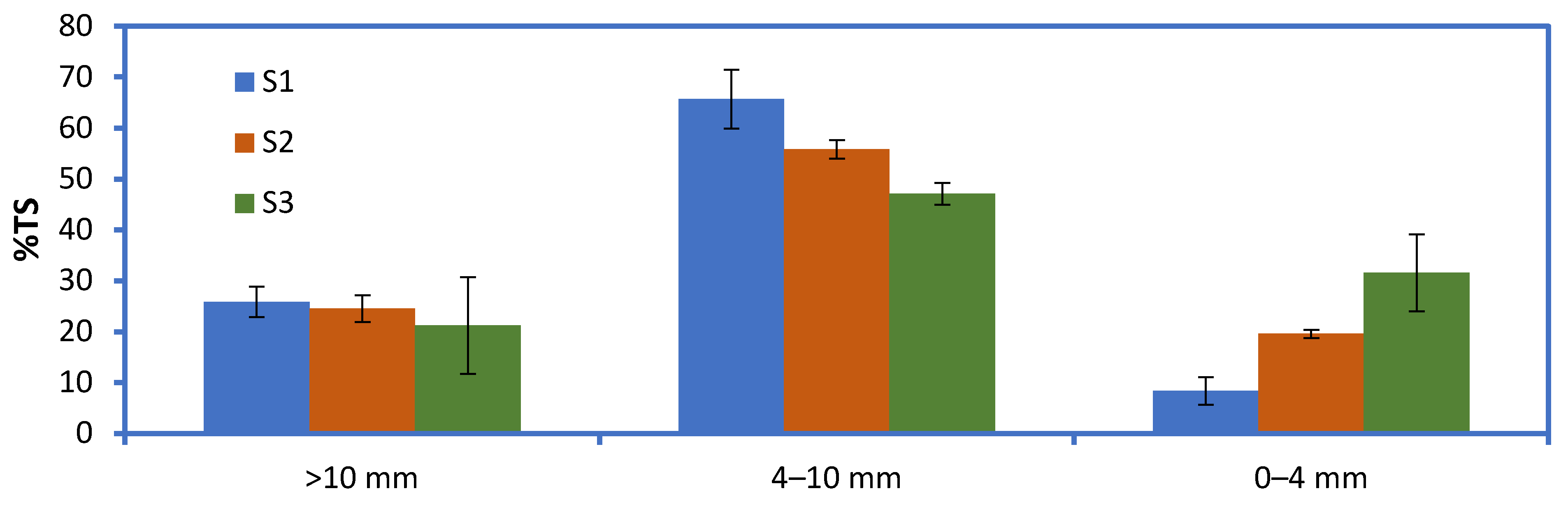
3.1. Fractionation of Seasonally Generated FVW
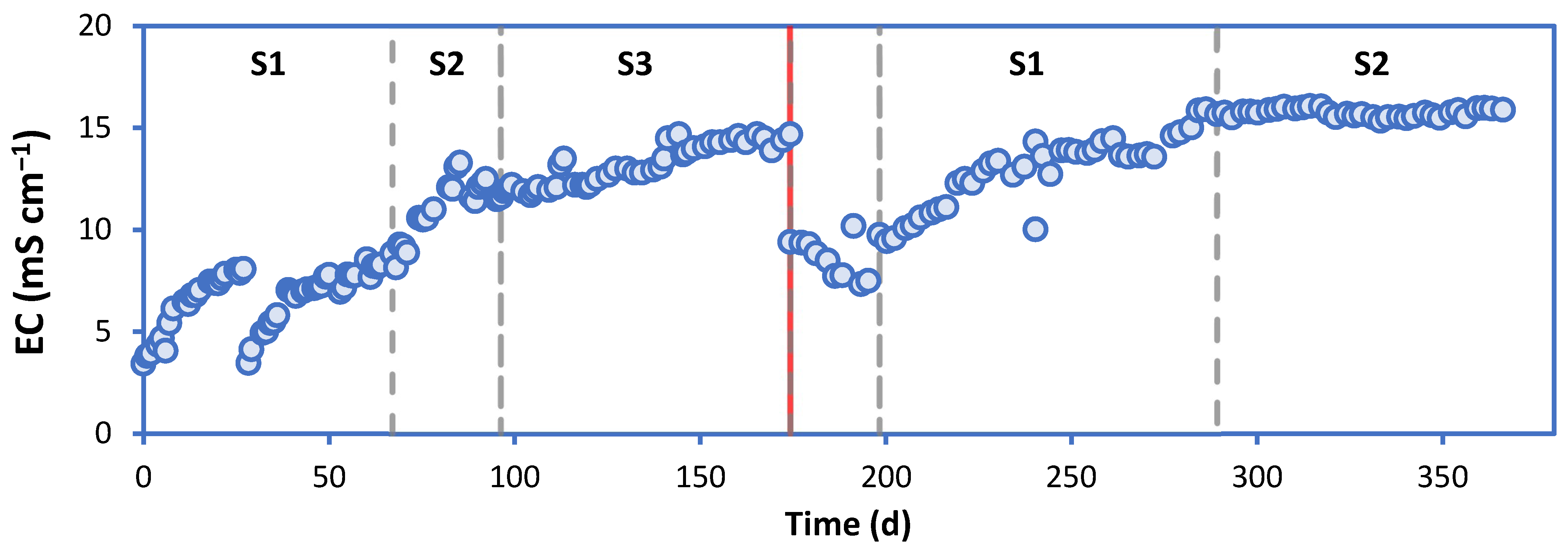
3.2. Performance of the LBR-UASB
4. Discussion
4.1. Composition and Methane Yield of Seasonally Generated FVW
4.2. Comparison of LBR/UASB with Conventional CSTR
| FVW Origin–Pretreatment | V (L) | T (°C) | VS in (g kg−1) | VS out (g kg−1) | RT (d) | OLR (g L−1 d−1) | YCH4 (L kg−1 VS) | VS r (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSTR | |||||||||
| Industry FVW–ground | 45 | 30 | 38 | nr | 20 | 2 | 370 | Nr | [37] |
| Market FVW–shredded | 4 | 35 | 65 | 18 | 22 | 3 | 420 | 72 | [33] |
| Market VW–ground 4–5 mm | 60 | 35 | 60–70 | Nr | 20 | 3 | 340 | 83 | [35] |
| Market FVW–ground 10 mm | 4 | 37 | 90 | Nr | 30 | 3 | 285 | Nr | [4] |
| Simulated VW–ground | 1.5 | 35 | 72 | 14 | 20 | 3–4 | 350 | 84 | [34] |
| Simulated FVW–ground 4 mm | 1.7 | 35 | 95 | Nr | est 100 | 1 | 254 | Nr | [18] |
| Simulated FVW–ground 10 mm | 1.7 | 35 | 100 | Nr | est 100 | 1 | 229 | Nr | [18] |
| Simulated FVW–ground 10 mm | 10 | 35 | 110 | 19 | 45 | 3.5 | 450 | 82 | [41] |
| LBR/UASB | |||||||||
| Simulated FVW–ground | 1.3 + 0.5 | 35 | 57 | Nr | 13 + 5 | 3 | 400 | 72 | [23] |
| Simulated FVW–ground 10 mm | 1.2 + 2.2 | 37 | 140 | 183 | 6 + 10 | 3.1 ± 0.7 | 360–375 | 83 | This study |
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Anaerobic digestion |
| BMP | Biochemical methane potential |
| COD | Total chemical oxygen demand |
| CSTR | Continuous stirred tank reactors |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| ECSB | External circulation sludge bed |
| FID | Flame ionization detector |
| FVR | Fruit-to-vegetable ratio |
| FVW | Fruit and vegetable wastes |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
| HRT | Hydraulic residence time |
| LBR | Leaching bed reactor |
| OLR | Organic loading rate |
| PFR | Plug-flow reactors |
| RT | Retention time |
| S1, S2, S3 | Season 1 (autumn/winter), Season 2 (spring), Season 3 (summer) |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| STP | Standard temperature and pressure conditions. |
| TCD | Thermal conductivity detector |
| TKN | Total Kjeldahl nitrogen |
| TS | Total solids |
| TSS | Total suspended solids |
| UASB | Upflow anaerobic sludge bed |
| VFA | Volatile fatty acids |
| VS | Volatile solids |
| VSS | Volatile suspended solids |
References
- Ji, C.; Kong, C.X.; Mei, Z.L.; Li, J. A Review of the Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Waste. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 183, 906–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavi, S.; Kramer, L.E.; Gomes, L.P.; Miranda, L.A.S. Biogas Production from Co-Digestion of Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste and Fruit and Vegetable Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 228, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, M.; Ahmed, S.; Kumar, A. Anaerobic Digestion (AD) of Fruit and Vegetable Market Waste (FVMW): Potential of FVMW, Bioreactor Performance, Co-Substrates, and Pretreatment Techniques. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 3573–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwiges, T.; Frare, L.M.; Lima Alino, J.H.; Triolo, J.M.; Flotats, X.; Silva de Mendonça Costa, M.S. Methane Potential of Fruit and Vegetable Waste: An Evaluation of the Semi-Continuous Anaerobic Mono-Digestion. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, B.K.; Jash, T. Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion of Vegetable Market Waste Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste and Development of Improved Technology for Phase Separation in Two-Phase Reactor. Waste Manag. 2016, 58, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozhiarasi, V.; Speier, C.J.; Rose, P.M.B.; Mondal, M.M.; Pragadeesh, S.; Weichgrebe, D.; Srinivasan, S.V. Variations in Generation of Vegetable, Fruit and Flower Market Waste and Effects on Biogas Production, Exergy and Energy Contents. J. Mater. Cycles Waste 2019, 21, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papirio, S.; Trujillo-Reyes, Á.; di Perta, S.; Kalogiannis, A.; Kassab, G.; Khoufi, S.; Sayadi, S.; Frunzo, L.; Esposito, G.; Fermoso, F.G.; et al. Exploring the Biochemical Methane Potential of Wholesale Market Waste from Jordan and Tunisia for a Future Scale-Up of Anaerobic Digestion in Amman and Sfax. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 13, 3887–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmi, T.; Dewiandratika, M.; Damanhuri, E. An Environmental and Economic Comparison of Fruit and Vegetable Waste Treatment in the Traditional Markets. Int. J. GEOMATE 2018, 15, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.; Spångberg, J. Carbon Footprint and Energy Use of Food Waste Management Options for Fresh Fruit and Vegetables from Supermarkets. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Peña, E.I.; Parameswaran, P.; Kang, D.W.; Canul-Chan, M.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Anaerobic Digestion and Co-Digestion Processes of Vegetable and Fruit Residues: Process and Microbial Ecology. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9447–9455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arhoun, B.; Villen-Guzman, M.; Gomez-Lahoz, C.; Rodriguez-Maroto, J.M.; Garcia-Herruzo, F.; Vereda-Alonso, C. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Mixed Sewage Sludge and Fruits and Vegetable Wholesale Market Waste: Composition and Seasonality Effect. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehiyoun, A.R.; Sharifi, M.; Di Maria, F.; Zilouei, H.; Aghbashlo, M. Effect of Substituting Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste with Fruit and Vegetable Wastes on Anaerobic Digestion. J. Mater. Cycles Waste 2019, 21, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, L.; Whyte, P.; Zintl, A.; Gordon, S.; Markey, B.; de Waal, T.; Cummins, E.; Nolan, S.; O’flaherty, V.; Abram, F.; et al. A Small Study of Bacterial Contamination of Anaerobic Digestion Materials and Survival in Different Feed Stocks. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Cai, F.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, G. Compositional Components and Methane Production Potential of Typical Vegetable Wastes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 54177–54186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjaya, A.P.; Cahyanto, M.N.; Millati, R. Mesophilic Batch Anaerobic Digestion from Fruit Fragments. Renew. Energy 2016, 98, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, A.T.; Babel, S. Utilization of Green Waste from Vegetable Market for Biomethane Production: Influences of Feedstock to Inoculum Ratios and Alkalinity. J. Mater. Cycles Waste 2019, 21, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwiges, T.; Frare, L.; Mayer, B.; Lins, L.; Mi Triolo, J.; Flotats, X.; de Mendonça Costa, M.S.S. Influence of Chemical Composition on Biochemical Methane Potential of Fruit and Vegetable Waste. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Reyes, Á.; Serrano, A.; Cubero-Cardoso, J.; Fernández-Prior, Á.; Fermoso, F.G. Does Seasonality of Feedstock Affect Anaerobic Digestion? Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouallagui, H.; Ben Cheikh, R.; Marouani, L.; Hamdi, M. Mesophilic Biogas Production from Fruit and Vegetable Waste in a Tubular Digester. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 86, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouallagui, H.; Haouari, O.; Touhami, Y.; Ben Cheikh, R.; Marouani, L.; Hamdi, M. Effect of Temperature on the Performance of an Anaerobic Tubular Reactor Treating Fruit and Vegetable Waste. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 2143–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouallagui, H.; Touhami, Y.; Ben Cheikh, R.; Hamdi, M. Bioreactor Performance in Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Wastes. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Math-Alvarez, J.; Viturtia, A.; Llabrés-Luengo, P.; Cecchi, F. Kinetic and Performance Study of a Batch Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Wastes. Biomass Bioenergy 1993, 5, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viturtia, A.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Cecchi, F. Two-Phase Continuous Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Wastes. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 1995, 13, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, W.F.; Stuckey, D.C.; Healy, J.B., Jr.; Young, L.Y.; McCarty, P.L. Bioassay for monitoring biochemical methane potential and anaerobic toxicity. Water Res. 1979, 13, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Petersen, S.P.; Ahring, B.K. Effects of Lipids on Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion and Reduction of Lipid Inhibition upon Addition of Bentonite. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1990, 33, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environmental Federation: Washington DC, USA, 1999.
- Kalogiannis, A.; Vasiliadou, I.A.; Spyridonidis, A.; Diamantis, V.; Stamatelatou, K. Biogas Production from Chicken Manure Wastes Using an LBR-CSTR Two-Stage System: Process Efficiency, Economic Feasibility, and Carbon Dioxide Footprint. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 2952–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yan, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, C.; Liu, G. Bio-Energy Conversion Performance, Biodegradability, and Kinetic Analysis of Different Fruit Residues during Discontinuous Anaerobic Digestion. Waste Manag. 2016, 52, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotto di Perta, E.; Cesaro, A.; Pindozzi, S.; Frunzo, L.; Esposito, G.; Papirio, S. Assessment of Hydrogen and Volatile Fatty Acid Production from Fruit and Vegetable Waste: A Case Study of Mediterranean Markets. Energies 2022, 15, 5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyridonidis, A.; Vasiliadou, I.A.; Akratos, C.S.; Stamatelatou, K. Performance of a Full-Scale Biogas Plant Operation in Greece and Its Impact on the Circular Economy. Water 2020, 12, 3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korai, M.S.; Mahar, R.B.; Uqaili, M.A. The Seasonal Evolution of Fruit, Vegetable and Yard Wastes by Mono, Co and Tri-Digestion at Hyderabad, Sindh Pakistan. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Reyes, Á.; Serrano, A.; Pérez, A.G.; Peces, M.; Fermoso, F.G. Impact of Monoterpenes in the Stability of the Anaerobic Digestion of Mediterranean Wholesale Market Waste. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zuo, J.; Gan, L.; Li, P.; Liu, F.; Wang, K.; Chen, L.; Gan, H. Effects of Mixture Ratio on Anaerobic Co-Digestion with Fruit and Vegetable Waste and Food Waste of China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.J. Strategies for Stable Anaerobic Digestion of Vegetable Waste. Renew. Energy 2012, 44, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sun, J.; Cao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Ran, Y. Recovery of Unstable Digestion of Vegetable Waste by Adding Trace Elements Using the Bicarbonate Alkalinity to Total Alkalinity Ratio as an Early Warning Indicator. Biodegradation 2019, 30, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Mei, Z.; Ren, H.; Cao, Q.; Yan, Z. Instability Mechanisms and Early Warning Indicators for Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Vegetable Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanath, P.; Sumithra Devi, S.; Nand, K. Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Processing Wastes for Biogas Production. Bioresour. Technol. 1992, 40, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglione, D.; Lotti, T.; Ficara, E.; Malpei, F. Inhibition on Anammox Bacteria upon Exposure to Digestates from Biogas Plants Treating the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste and the Role of Conductivity. Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag-Demirer, S.; Demirer, G.N. Post-Anaerobic Treatability and Residual Biogas Potential of Digestate. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshwari, K.V.; Lata, K.; Pant, D.C.; Kishore, V.V.N. A Novel Process Using Enhanced Acidification and a UASB Reactor for Biomethanation of Vegetable Market Waste. Waste Manag. Res. 2001, 19, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, R.; Torrijos, M.; Sousbie, P.; Lugardon, A.; Steyer, J.P.; Delgenes, J.P. Single-Phase and Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Comparison of Start-Up, Reactor Stability and Process Performance. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


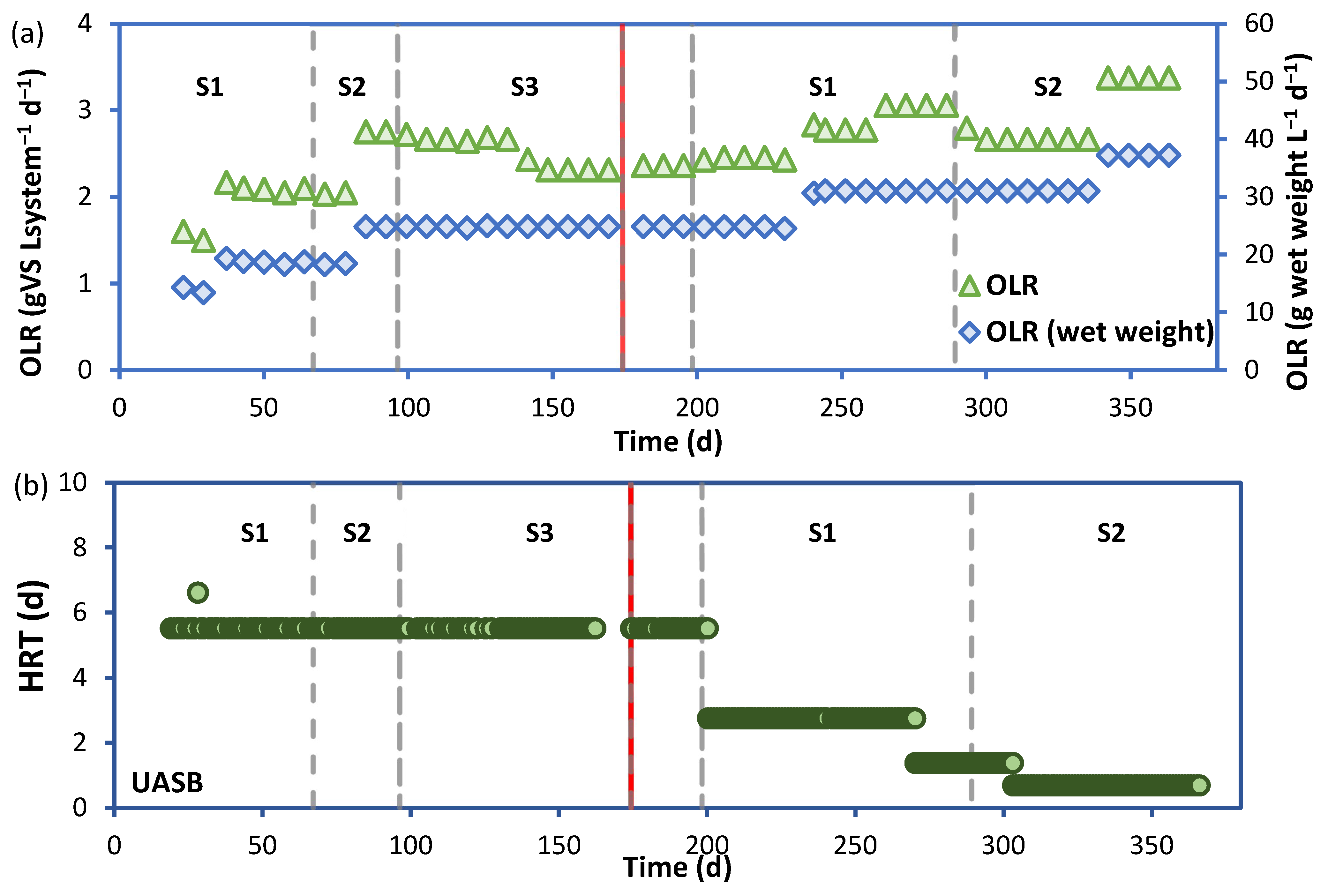
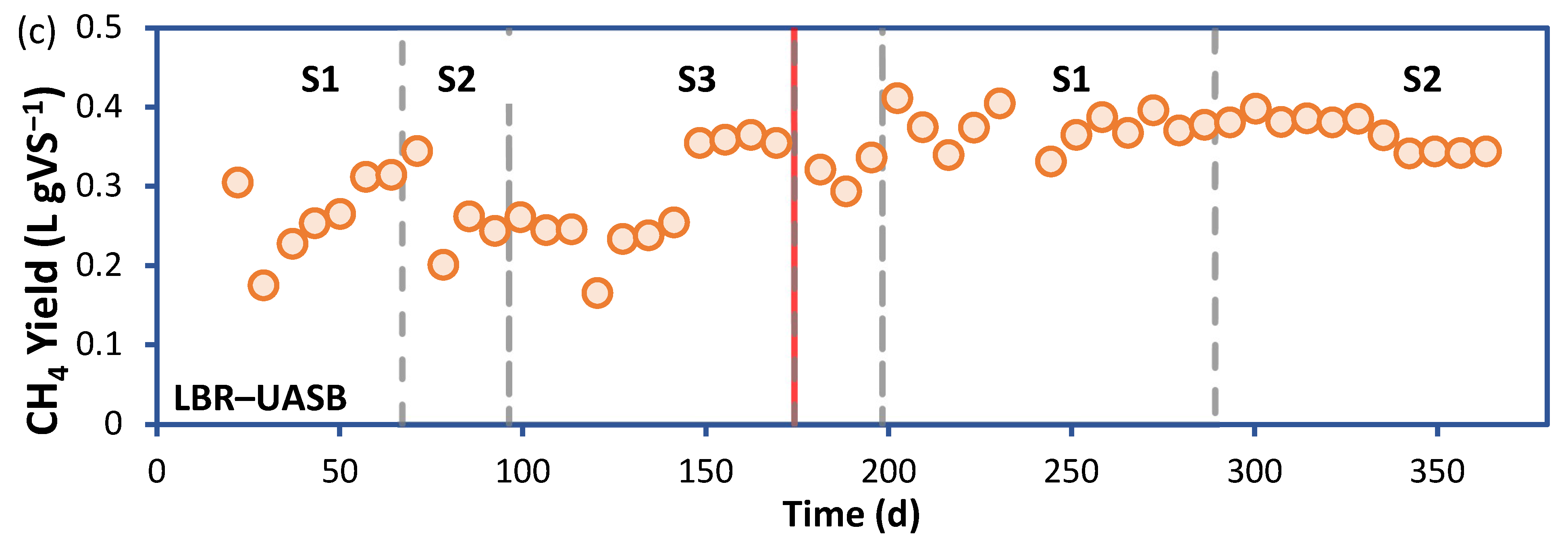
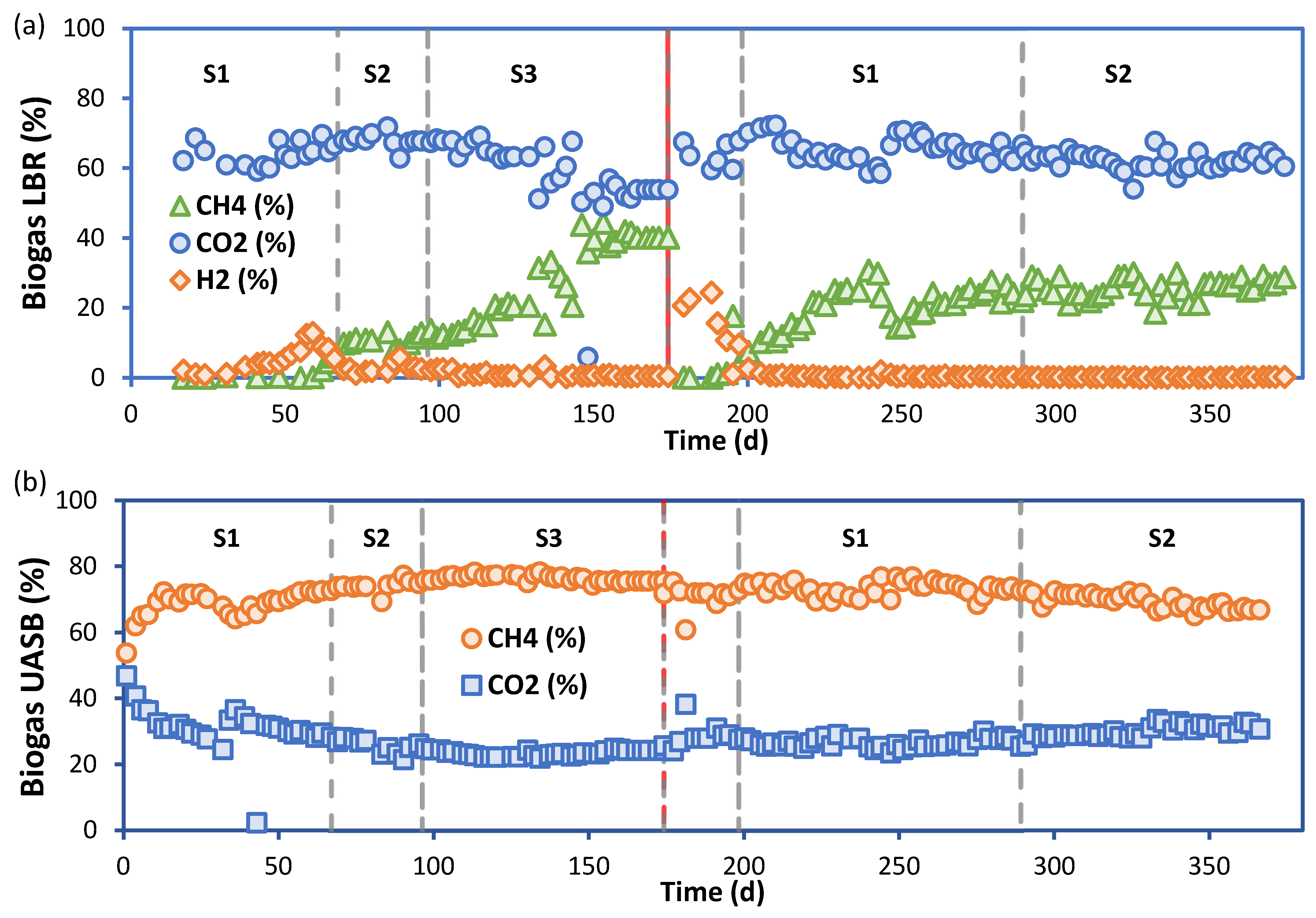
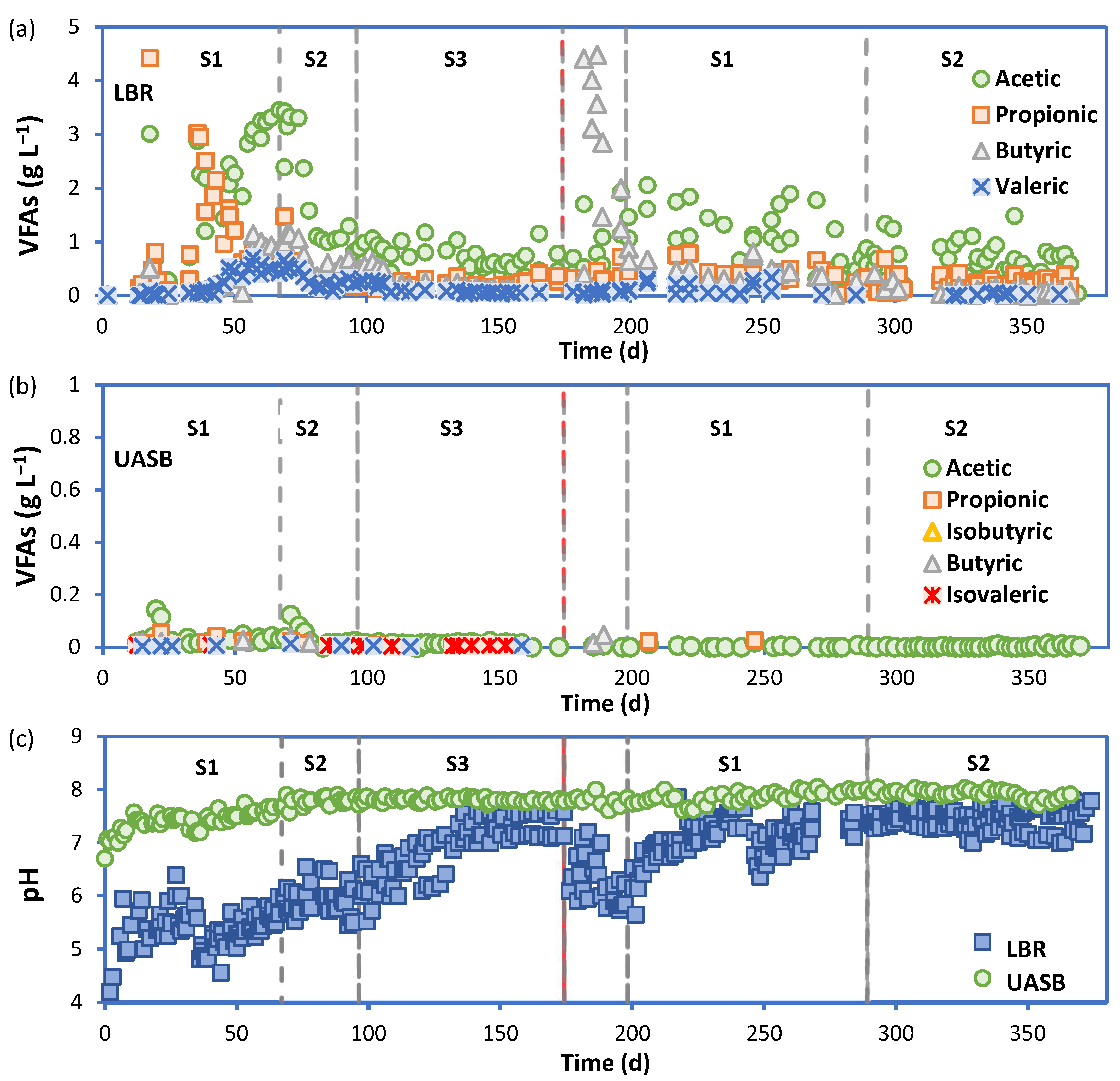
| Parameter | 0–4 mm | 4–10 mm | 0–10 mm (0–4 + 4–10 mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autumn/Winter (S1) | |||
| FM distribution (%ww *) | 24 | 76 | 100 |
| TS (g kg−1) | 30 ± 1 | 82 ± 2 | 77 ± 0 |
| VS (g kg−1) | 27 ± 0 | 71 ± 0 | 64 ± 1 |
| BMP (L kg VS−1) | 387 ± 32 | 473 ±17 | 429 ± 13 |
| COD (g kg VS−1) | 1196 ± 17 | 1340 ± 24 | 1396 ± 18 |
| TKN (g kg VS−1) | 28 ± 1 | 24 ± 1 | 29 ± 1 |
| Spring (S2) | |||
| FM distribution (%ww *) | 46 | 54 | 100 |
| TS (g kg−1) | 38 ± 1 | 92 ± 4 | 68 ± 0 |
| VS (g kg−1) | 35 ± 0 | 77 ± 3 | 64 ± 2 |
| BMP (L kg VS−1) | 360 ± 8 | 480 ± 7 | 406 ± 4 |
| COD (g kg VS−1) | 1221 ± 16 | 1512 ± 15 | 1280 ± 19 |
| TKN (g kg VS−1) | 23 ± 2 | 24 ± 1 | 26 ± 1 |
| Summer (S3) | |||
| FM distribution (%ww *) | 61 | 39 | 100 |
| TS (g kg−1) | 45 ± 2 | 88 ± 2 | 72 ± 2 |
| VS (g kg−1) | 41 ± 2 | 81 ± 2 | 66 ± 2 |
| BMP (L kg VS−1) | 441 ± 17 | 527 ± 21 | 426 ±10 |
| COD (g kg VS−1) | 1533 ± 25 | 1439 ± 14 | 1354 ± 24 |
| TKN (g kg VS−1) | 16 ± 1 | 18 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 |
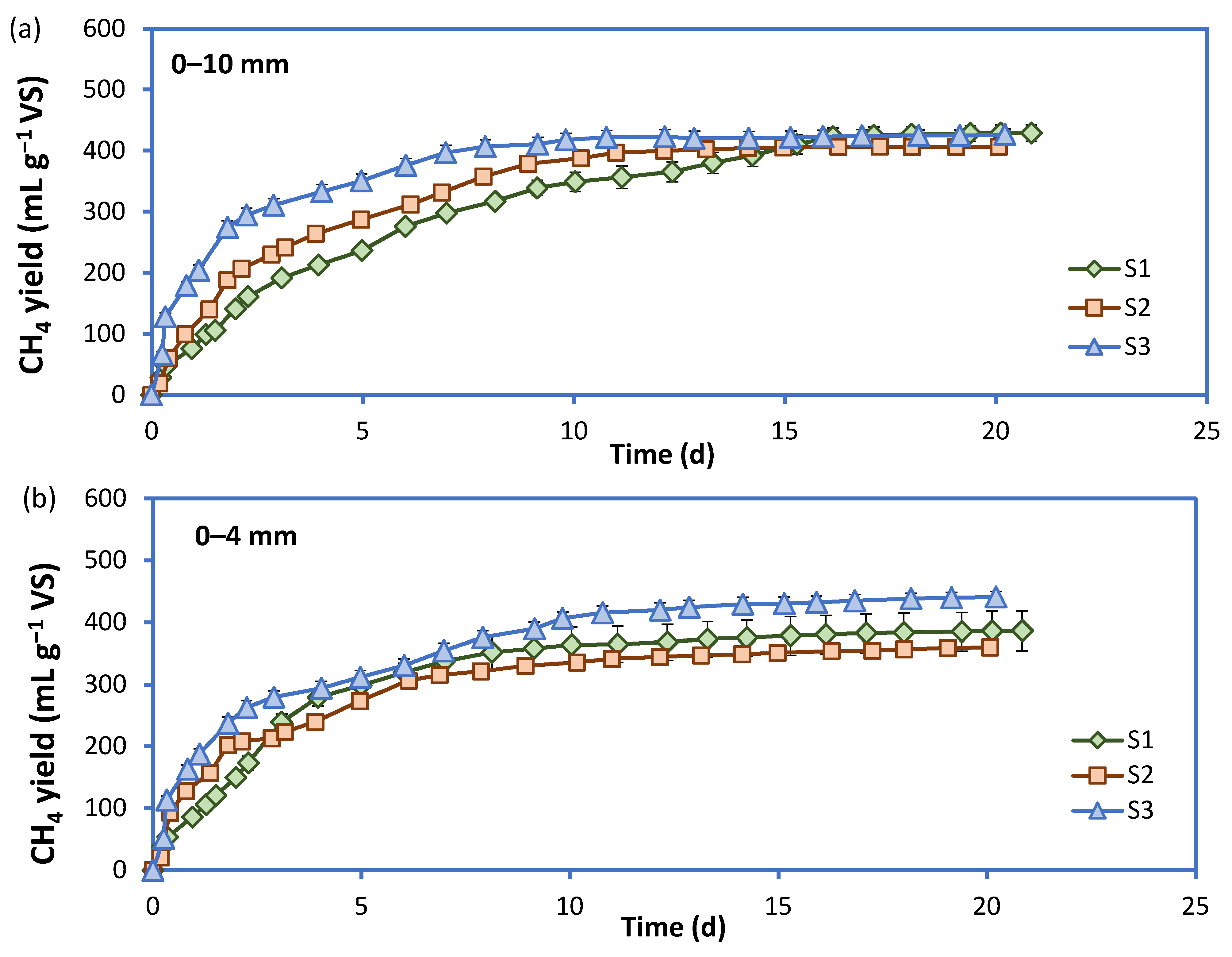
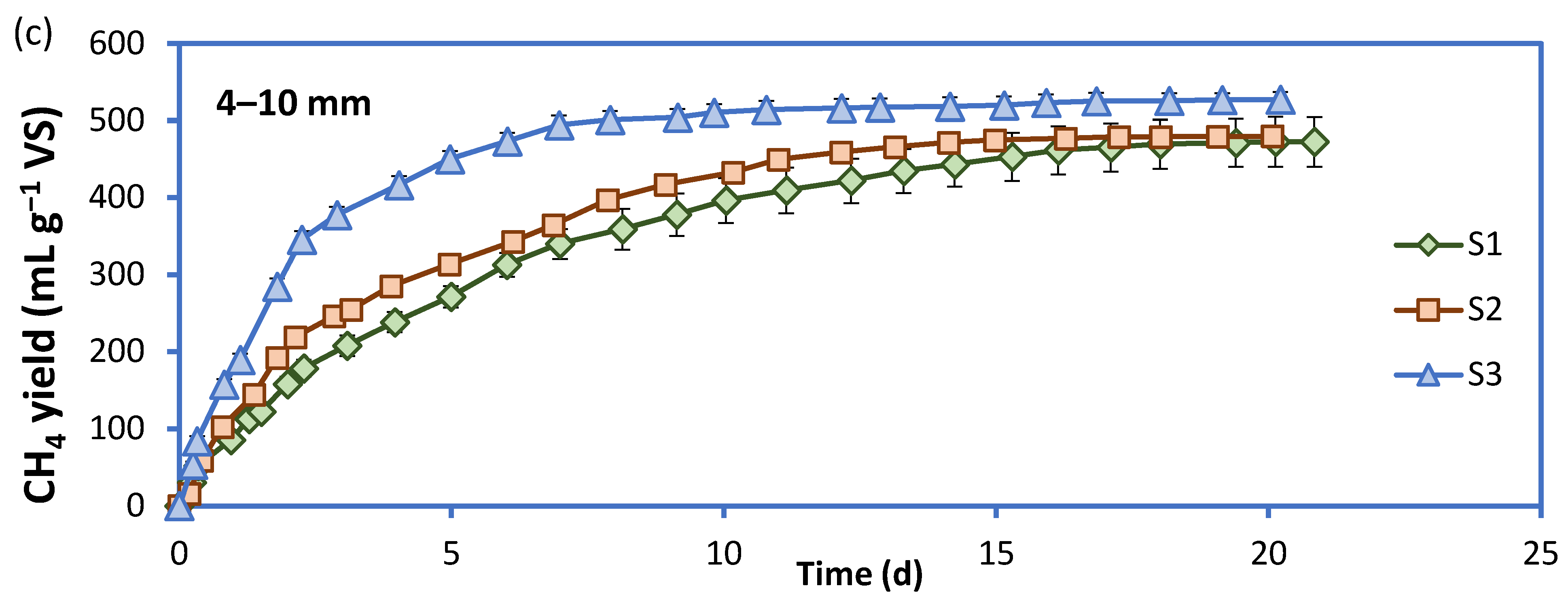
| Fractions | BMPexp (L kg−1 VS) | BMPmax (L kg−1 VS) | k (d−1) | χ2 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autumn/Winter (S1) | |||||
| 0–10 mm | 429 ± 13 | 453 ± 4 | 0.169 ± 0.005 | 221 | 0.989 |
| 0–4 mm | 387 ± 32 | 386 ± 4 | 0.285 ± 0.005 | 431 | 0.975 |
| 4–10 mm | 473 ± 17 | 482 ± 4 | 0.178 ± 0.004 | 197 | 0.992 |
| Spring (S2) | |||||
| 0–10 mm | 406 ± 4 | 407 ± 2 | 0.286 ± 0.006 | 135 | 0.992 |
| 0–4 mm | 360 ± 8 | 349 ± 3 | 0.387 ± 0.015 | 341 | 0.971 |
| 4–10 mm | 480 ± 7 | 486 ± 3 | 0.233 ± 0.005 | 183 | 0.993 |
| Summer (S3) | |||||
| 0–10 mm | 426 ± 10 | 415 ± 3 | 0.557 ± 0.022 | 454 | 0.971 |
| 0–4 mm | 441 ± 17 | 419 ± 5 | 0.387 ± 0.022 | 932 | 0.945 |
| 4–10 mm | 527 ± 21 | 520 ± 2 | 0.434 ± 0.010 | 220 | 0.992 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalogiannis, A.; Diamantis, V.; Eftaxias, A.; Stamatelatou, K. Long-Term Anaerobic Digestion of Seasonal Fruit and Vegetable Waste Using a Leach-Bed Reactor Coupled to an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Bed Reactor. Sustainability 2024, 16, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010050
Kalogiannis A, Diamantis V, Eftaxias A, Stamatelatou K. Long-Term Anaerobic Digestion of Seasonal Fruit and Vegetable Waste Using a Leach-Bed Reactor Coupled to an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Bed Reactor. Sustainability. 2024; 16(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010050
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalogiannis, Achilleas, Vasileios Diamantis, Alexandros Eftaxias, and Katerina Stamatelatou. 2024. "Long-Term Anaerobic Digestion of Seasonal Fruit and Vegetable Waste Using a Leach-Bed Reactor Coupled to an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Bed Reactor" Sustainability 16, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010050
APA StyleKalogiannis, A., Diamantis, V., Eftaxias, A., & Stamatelatou, K. (2024). Long-Term Anaerobic Digestion of Seasonal Fruit and Vegetable Waste Using a Leach-Bed Reactor Coupled to an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Bed Reactor. Sustainability, 16(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010050








