Population Growth Parameters of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) on Various Legume Seeds Reveal Potential Tolerance Traits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Seeds
2.2. Insect Rearing
2.3. Experiments
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Development of Immature Stages, Adult Longevity, and Lifespan
3.2. Survival Rate
3.3. Oviposition Period and Fecundity
3.4. Population Growth Parameters
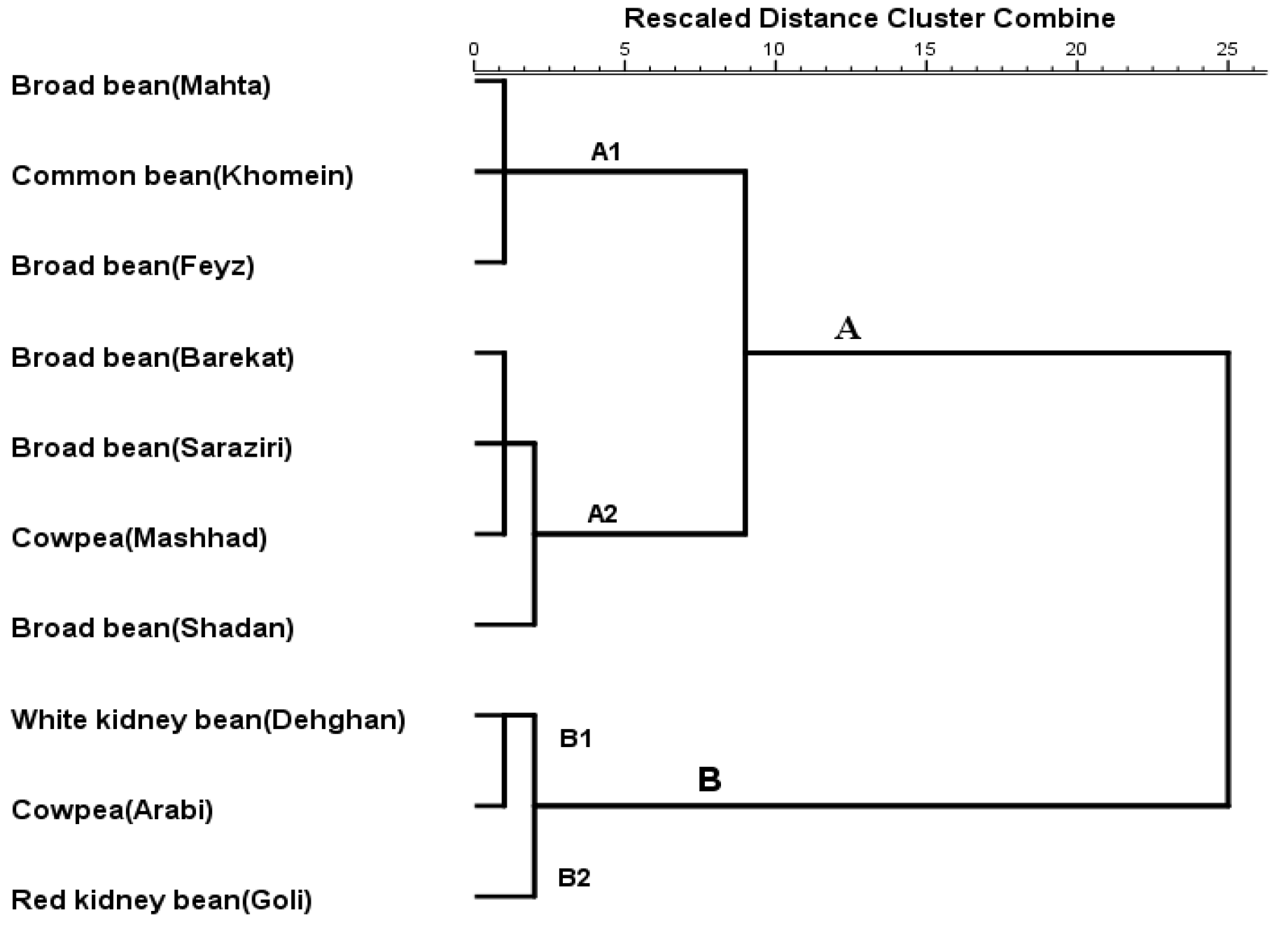
3.5. Cluster Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zalucki, M.P.; Furlong, M.J. Forecasting Helicoverpa populations in Australia: A comparison of regression-based models and a bioclimatic based modelling approach. Insect Sci. 2005, 12, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.F.; Baldin, E.L.; Specht, A.; Sosa-Gómez, D.R.; Roque-Specht, V.F.; Morando, R.; Paula-Moraes, S.V. Biotic potential and life table of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) from three Brazilian regions. Neotrop. Entomol. 2018, 47, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathipour, Y.; Babaei, M.; Bagheri, A.; Talebi, A.A.; Yazdanpanah, S. Demographic parameters of Helicoverpa armigera on ten corn hybrids-mediated artificial diets reveals striking differences. J. Crop Prot. 2021, 10, 363–374. [Google Scholar]
- Atashi, N.; Shishehbor, P.; Seraj, A.A.; Rasekh, A.; Hemmati, S.A.; Riddick, E.W. Effects of Helicoverpa armigera Egg Age on Development, Reproduction, and Life Table Parameters of Trichogramma euproctidis. Insects 2021, 12, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Gong, P.; Wu, K. Life table studies of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), on different host plants. Environ. Entomol. 2004, 33, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talekar, N.S.; Opena, R.T.; Hanson, P. Helicoverpa armigera management: A review of AVRDC’s research on host plant resistance in tomato. Crop Prot. 2006, 25, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemati, S.A.; Naseri, B.; Nouri Ganbalani, G.; Rafiee Dastjerdi, H.; Golizadeh, A. Effect of different host plants on nutritional indices of the pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera. J. Insect Sci. 2012, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Hemmati, S.A.; Habibpour, B. Evaluation of artificial diets based on different legume seeds on the nutritional physiology and digestive function of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2023, 113, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S. Management of Helicoverpa armigera: A review and prospectus for Pakistan. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2000, 3, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitt, G.P. The ecology of Heliothis species in relation to agroecosystems. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1989, 34, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemati, S.A.; Naseri, B.; Ganbalani, G.N.; Dastjerdi, H.R.; Golizadeh, A. Digestive proteolytic and amylolytic activities and feeding responses of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on different host plants. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironidis, G.K.; Savopoulou-Soultani, M. Development, survivorship, and reproduction of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) under constant and alternating temperatures. Environ. Entomol. 2014, 37, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, D.F. The corn earworm complex. Mem. Ent. Soc. Can. 1965, 97, 5–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, F.M. Analysis of the Spatio–temporal Distribution of Helicoverpa armigera Hb. In a Tomato Field using a Stochastic Approach. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 93, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongming, R.; Kunjun, W. Performances of the cotton boll worm, Helicoverpa armigera on different food plants. Kun chong xue bao. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2001, 44, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, J.H. Egg and larval survivorship of Carposina sasakii (Lepidoptera: Carposinidae) in apple and peach and their effects on adult population dynamics in orchards. Environ. Entomol. 2002, 31, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, I.F.; Baldin, E.L.L.; Specht, A.; Roque-Specht, V.F.; Morando, R.; Malaquias, J.V.; Paula-Moraes, S.V. Role of nutritional composition in the development and survival of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on artificial diet and natural hosts. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2021, 111, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, S.A.; Shishehbor, P.; Stelinski, L.L. Life Table Parameters and Digestive Enzyme Activity of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on Selected Legume Cultivars. Insects 2022, 13, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, A.; Fujisaki, K. Larval feeding preference and performance of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), on different flower parts of cosmos. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2010, 45, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babamir-Satehi, A.; Habibpour, B.; Aghdam, H.R.; Hemmati, S.A. Interaction between feeding efficiency and digestive physiology of the pink stem borer, Sesamia cretica Lederer (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), and biochemical compounds of different sugarcane cultivars. Arthropod Plant Interact. 2022, 16, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani Fard, S.; Hemmati, S.A.; Shishehbor, P.; Stelinski, L.L. Growth, consumption and digestive enzyme activities of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd) on various mung bean cultivars reveal potential tolerance traits. J. Appl. Entomol. 2022, 146, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woestmann, L.; Saastamoinen, M. The importance of trans-generational effects in Lepidoptera. Curr. Zool. 2016, 62, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, J.; Dunse, K.; Fox, J.; Evans, S.; Anderson, M. Biotechnological approaches for the control of insect pests in crop plants. In Pesticides-Advances in Chemical and Botanical Pesticides; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 269–308. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, O.L.; Rigden, D.J.; Melo, F.R.; Grossi-de-Sá, M.F. Plant α-amylase inhibitors and their interaction with insect α-amylases: Structure, function and potential for crop protection. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.E.; Barbosa, A.E.; Macedo, L.L.; Pitanga, J.C.; Moura, F.T.; Oliveira, A.S.; Moura, R.M.; Queiroz, A.F.; Macedo, F.P.; Andrade, L.B.; et al. Effect of trypsin inhibitor from Crotalaria pallida seeds on Callosobruchus maculatus (cowpea weevil) and Ceratitis capitata (fruit fly). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 43, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.P.; Casado-Filho, E.L.; Corrêa, A.S.; Farias, L.R.; Bloch, C.; Grossi de Sá, M.F.; Mendes, P.A.; Quirino, B.F.; Noronha, E.F.; Franco, O.L. Identification of an α-amylase inhibitor from Pterodon pubescens with ability to inhibit cowpea weevil digestive enzymes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4382–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatehouse, A.M.; Gatehouse, J.A. Identifying proteins with insecticidal activity: Use of encoding genes to produce insect-resistant transgenic crops. Pestic. Sci. 1998, 52, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabadi, M.; Franco, O.L.; Bandani, A.R. Plant proteinaceous alpha-amylase and proteinase inhibitors and their use in insect pest control. In New Perspectives in Plant Protection; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 229–246. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, A.D.H.; Luiz, A.J.; Campanhola, C. Statistical inference on associated fertility life table parameters using jackknife technique: Computational aspects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, R.I.; Walsh, W.A.; Kanehisa, D.; Jang, E.B.; Armstrong, J.W. Demography of four Hawaiian fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) reared at five constant temperatures. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1997, 90, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjou, J.; Naseri, B.; Hemati, S.A. Comparative performance of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on various host plants. J. Pest Sci. 2014, 87, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitt, G.P. Cotton pest management. Part 3. An Australian perspective. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1994, 39, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Arif, M.I.; Attique, M.R. Pyrethroid resistance of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Pakistan. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1997, 87, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranthi, K.R.; Jadhav, D.R.; Kranthi, S.; Wanjari, R.R.; Ali, S.S.; Russell, D.A. Insecticide resistance in five major insect pests of cotton in India. Crop Prot. 2002, 21, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorey, H.H.; Hale, R.L. Mass-rearing of the larvae of nine noctuid species on a simple artificial medium. J. Econ. Entomol. 1965, 58, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, J.R. Insect biodemography. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2001, 46, 79–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, L. The intrinsic rate of natural increase of an insect population. J. Anim. Ecol. 1948, 17, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwood, T.R.E.; Henderson, P.A. Absolute population estimates by sampling a unit of soil or litter habitat: Extraction techniques. In Ecological Methods, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Science: Malden, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 213–241. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, J.S.; Ingersoll, C.G.; McDonald, L.L.; Boyce, M.S. Estimating uncertainty in population growth rates: Jackknife vs. bootstrap techniques. Ecology 1986, 67, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lenteren, J.C.V.; Noldus, L.P.J.J. Whitefly-plant relationships: Behavioural and ecological aspects. In Whiteflies: Their Bionomics, Pest Status and Management; Intercept: Andover, UK, 1990; Volume 47, p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Fathipour, Y.; Baghery, F.; Bagheri, A.; Naseri, B. Development, reproduction and life table parameters of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on five main host plants. J. Crop Prot. 2020, 9, 551–561. [Google Scholar]
- Alami, S.; Naseri, B.; Golizadeh, A.; Razmjou, J. Age-stage, two-sex life table of the tomato looper, Chrysodeixis chalcites (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), on different bean varieties. Arthropod-Plant Inter. 2014, 8, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Ge, F.; Zhu, S.; Parajulee, M.N. Effect of cotton variety on development and reproduction of Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae) and its predator Propylaea japonica (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2004, 97, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, B.; Fathipour, Y.; Moharramipour, S.; Hosseininaveh, V. Life table parameters of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lep: Noctuidae) on different soybean cultivars. J. Entomol. Soc. Iran 2009, 29, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, S.; Fathipour, Y.; Talebi, A.A.; Naseri, B. Evaluation of canola cultivars for resistance to Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) using demographic parameters. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahnejad-Mojarrad, N.; Goldasteh, S.; Rafiei-Karahroodi, Z.; Vafaei Shoushtari, R. Response of the Cotton Bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to Different Semi-Artificial Diets. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 19, 1303–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Kumral, N.A.; Kovanci, B.; Akbudak, B. Life tables of the olive leaf moth, Palpita unionalis (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), on different host plants. J. Biol. Environ. Sci. 2007, 1, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Shishehbor, P.; Hemmati, S.A. Investigation of secondary metabolites in bean cultivars and their impact on the nutritional performance of Spodoptera littoralis (Lep.: Noctuidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2022, 112, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
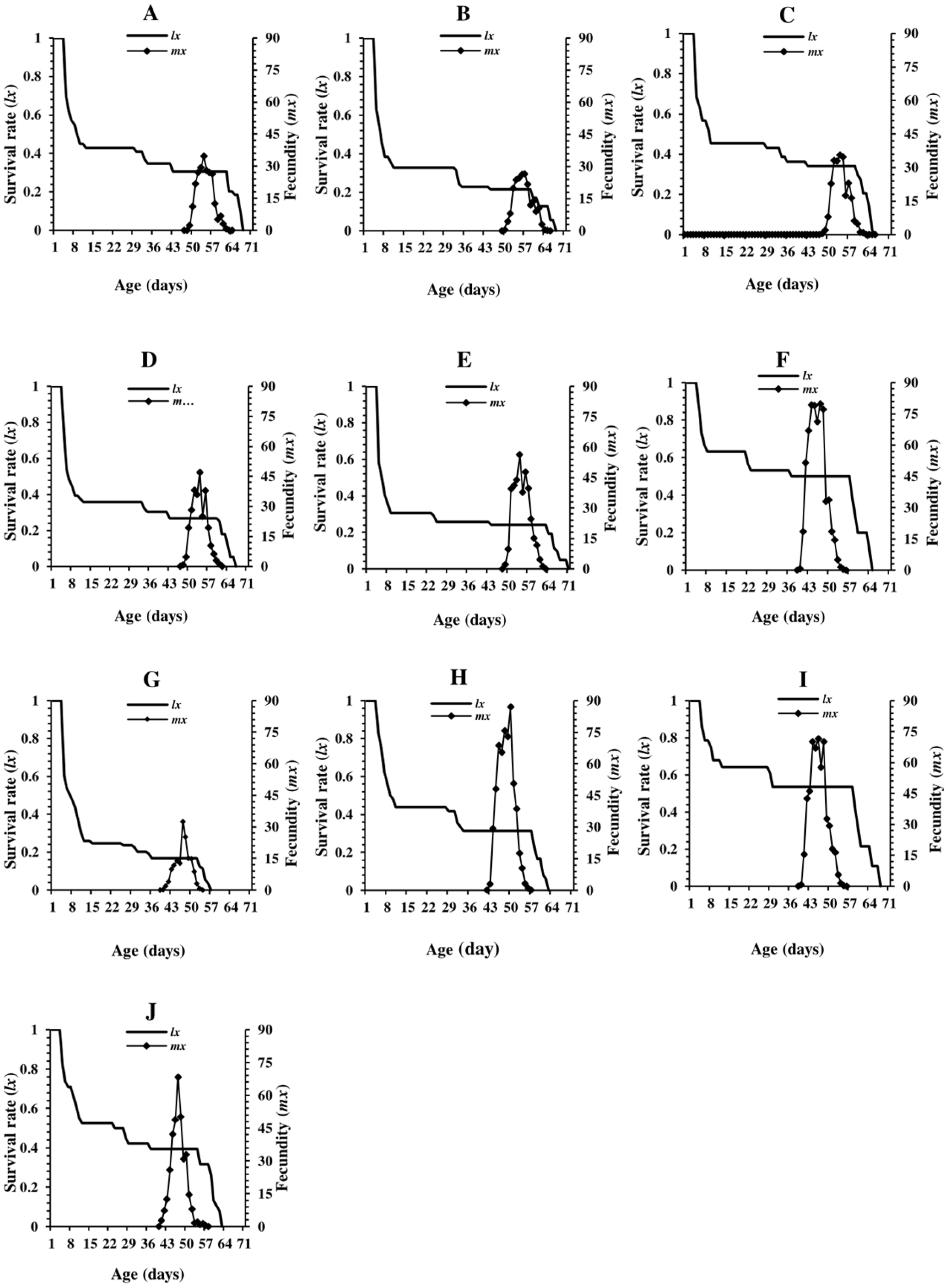
| Host (Cultivars) | Incubation Period (Days) | Larval Period (Days) | Pre-Pupal Period (Days) | Pupal Period (Days) | Development Time (Days) | Longevity (Days) | Whole Lifespan (Days) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Male | Female | ||||||
| Broad bean (Barekat) | 3.46 ± 0.02b | 20.32 ± 0.26b | 3.43 ± 0.10a | 15.97 ± 0.15ab | 43.13 ±0.27c | 17.72 ±0.31de | 19.83 ± 0.40bcd | 61.00 ± 0.54bcd | 62.64 ± 0.55ab |
| Broad bean (Mahta) | 3.68 ± 0.03a | 21.5 ± 0.22a | 3.33 ± 0.08a | 16.48 ± 0.13a | 44.82 ± 0.24a | 16.93 ± 0.49ef | 18.11 ± 0.36d | 62.20 ± 0.64abc | 62.11 ± 0.57ab |
| Broad bean (Saraziri) | 3.18 ± 0.03c | 20.53 ± 0.22b | 3.49 ± 0.10a | 16.12 ± 0.12ab | 43.13 ± 0.23c | 19.05 ± 0.39cd | 18.73 ± 0.28cd | 62.25 ± 0.59abc | 61.73 ± 0.58abc |
| Broad bean (Feyz) | 3.14 ± 0.03c | 20.92 ± 0.25ab | 3.24 ± 0.07a | 16.18 ± 0.13ab | 43.44 ± 0.29bc | 20.80 ± 0.38abc | 19.28 ± 0.37bcd | 64.17 ± 0.59a | 62.78 ± 0.48ab |
| Broad bean (Shadan) | 3.23 ± 0.03c | 21.08 ± 0.24ab | 3.41 ± 0.09a | 15.6 ± 0.17bc | 43.31 ± 0.28c | 19.73 ± 0.56bcd | 21.00 ± 0.50b | 63.10 ± 0.85ab | 64.28 ± 0.55a |
| White kidney bean (Dehghan) | 2.76 ± 0.03e | 16.16 ± 0.15e | 2.5 ± 0.07b | 14.31 ± 0.13e | 35.76 ± 0.21f | 20.75 ± 0.46abc | 23.32 ± 0.52a | 56.60 ± 0.56e | 59.00 ± 0.63cd |
| Common bean (Khomein) | 3.26 ± 0.03c | 21.61 ± 0.22a | 3.57 ± 0.09a | 16.18 ± 0.15ab | 44.62 ± 0.27ab | 15.63 ± 0.33f | 16.00 ± 0.32e | 60.66 ± 0.35bcd | 60.76 ± 0.48bcd |
| Red kidney bean (Goli) | 2.86 ± 0.03de | 18.6 ± 0.25c | 2.41 ± 0.08b | 15.11 ± 0.13cd | 38.89 ± 0.34d | 20.00 ± 0.48bc | 19.45 ± 0.33bcd | 58.72 ± 0.62de | 58.35 ± 0.79d |
| Cowpea (Arabi) | 2.78 ± 0.04de | 17.04 ± 0.12de | 2.48 ± 0.08b | 14.66 ± 0.15de | 36.94 ± 0.21ef | 21.29 ± 0.55ab | 23.60 ± 0.51a | 58.65 ± 0.67de | 60.30 ± 0.60bcd |
| Cowpea (Mashhad) | 2.9 ± 0.03d | 17.75 ± 0.18cd | 2.47 ± 0.08b | 14.38 ± 0.13e | 37.38 ± 0.29e | 22.30 ± 0.53a | 20.64 ± 0.40bc | 59.50 ± 0.76cd | 58.18 ± 0.56d |
| Host (Cultivars) | APOP (Days) | TPOP (Days) | Oviposition Period (Days) | Fecundity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | Total | ||||
| Broad bean (Barekat) | 3.27 ± 0.153bc | 46 ± 0.455b | 13.13 ± 0.35a | 72.14 ± 2.21de | 942.27 ± 37.18cd |
| Broad bean (Mahta) | 4.6 ± 0.363a | 49.1 ± 0.47a | 10.27 ± 0.581b | 60.41 ± 3efg | 598.33 ± 24.66e |
| Broad bean (Saraziri) | 3.87 ± 0.133ab | 47.27 ± 0.447ab | 11.6 ± 0.434ab | 75.93 ± 2.92cd | 871.4 ± 30.91d |
| Broad bean (Feyz) | 3.8 ± 0.107b | 47.53 ± 0.343ab | 11.73 ± 0.384ab | 55.86 ± 2.48fg | 645.8 ± 21.07e |
| Broad bean (Shadan) | 3.2 ± 0.107bc | 46.17 ± 0.416b | 12.8 ± 0.2a | 87.62 ± 2.09bc | 1118.13 ± 22.1b |
| White kidney bean (Dehghan) | 2.6 ± 0.131cd | 37.6 ± 0.277d | 13 ± 0.365a | 99.57 ± 4.04ab | 1292.33 ± 49.44a |
| Common bean (Khomein) | 2.87 ± 0.133cd | 47.1 ± 0.493ab | 11.93 ± 0.358ab | 48.86 ± 1.59g | 584.73 ± 23.28e |
| Red kidney bean (Goli) | 2.6 ± 0.19cd | 41.6 ± 0.77c | 11.67 ± 0.41ab | 105.94 ± 4.93a | 1230.2 ± 62.25ab |
| Cowpea (Arabi) | 2.67 ± 0.126cd | 39.23 ± 0.358d | 13.13 ± 0.363a | 82.62 ± 2.86cd | 1075.33 ± 25.34bc |
| Cowpea (Mashhad) | 2.4 ± 0.131d | 39.53 ± 0.386cd | 12.4 ± 0.567a | 68.75 ± 3.72def | 826.8 ± 26.27d |
| Host (Cultivars) | R0 | r (day−1) | T (day) | DT (day) | Λ (day−1) | GRR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broad bean (Barekat) | 72.378 ± 8.097g | 0.080 ± 0.001e | 53.799 ± 0.097d | 8.709 ± 0.023c | 1.080 ± 0.001d | 236.451 ± 22.442g |
| Broad bean (Mahta) | 41.976 ± 4.542h | 0.066 ± 0.001g | 56.419 ± 0.102a | 10.465 ± 0.053a | 1.070 ± 0.001e | 206.376 ± 17.279h |
| Broad bean (Saraziri) | 81.396 ± 8.208f | 0.080 ± 0.001e | 54.673 ± 0.012b | 8.615 ± 0.005d | 1.080 ± 0.001d | 240.001 ± 19.622g |
| Broad bean (Feyz) | 73.931 ± 5.172g | 0.079 ± 0.001e | 54.462 ± 0.011c | 8.772 ± 0.005c | 1.080 ± 0.001d | 276.089 ± 36.641f |
| Broad bean (Shadan) | 90.485 ± 10.128e | 0.082 ± 0.001d | 54.859 ± 0.005b | 8.44 ± 0.002e | 1.090 ± 0.001c | 374.002 ± 35.528d |
| White kidney bean (Dehghan) | 310.326 ± 27.847a | 0.124 ± 0.001a | 46.232 ± 0.009h | 5.585 ± 0.003h | 1.130 ± 0.001a | 620.652 ± 28.693a |
| Common bean (Khomein) | 26.159 ± 3.073i | 0.069 ± 0.001f | 47.577 ± 0.006f | 10.103 ± 0.008b | 1.070 ± 0.001e | 155.412 ± 11.439i |
| Red kidney bean (Goli) | 178.32 ± 16.645c | 0.106 ± 0.001b | 48.955 ± 0.006e | 6.547 ± 0.005g | 1.110 ± 0.001b | 570.625 ± 31.062b |
| Cowpea (Arabi) | 291.999 ± 31.491b | 0.123 ± 0.001a | 46.337 ± 0.011h | 5.658 ± 0.002h | 1.130 ± 0.001a | 545.066 ± 35.917c |
| Cowpea (Mashhad) | 138.094 ± 12.296d | 0.104 ± 0.001c | 47.37 ± 0.013g | 6.664 ± 0.003f | 1.110 ± 0.001b | 350.959 ± 29.722e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jafari, H.; Habibpour, B.; Hemmati, S.A.; Stelinski, L.L. Population Growth Parameters of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) on Various Legume Seeds Reveal Potential Tolerance Traits. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7502. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097502
Jafari H, Habibpour B, Hemmati SA, Stelinski LL. Population Growth Parameters of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) on Various Legume Seeds Reveal Potential Tolerance Traits. Sustainability. 2023; 15(9):7502. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097502
Chicago/Turabian StyleJafari, Hasan, Behzad Habibpour, Seyed Ali Hemmati, and Lukasz L. Stelinski. 2023. "Population Growth Parameters of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) on Various Legume Seeds Reveal Potential Tolerance Traits" Sustainability 15, no. 9: 7502. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097502
APA StyleJafari, H., Habibpour, B., Hemmati, S. A., & Stelinski, L. L. (2023). Population Growth Parameters of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) on Various Legume Seeds Reveal Potential Tolerance Traits. Sustainability, 15(9), 7502. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097502







