1. Introduction
e-Learning has existed for a prolonged time in different parts of the world. However, e-Learning has been a distant dream in many developing countries. Unpredictably, the COVID-19 pandemic spread over the world. The governments of countries worldwide moved fast and decisively to protect their citizens from the health risks posed by the sickness and to reduce the number of people infected with it. Worldwide lockdowns and social distance regulations were implemented, and many physically demanding activities were put on hold. There was no possibility for education to be provided in a conventional manner, such as through physical classrooms, as educational institutions at all levels and in every region of the world were shut down, mirroring the course of events in many other fields’ endeavors. At that time, people worldwide started adopting and utilizing previously developed technology at an accelerated rate to lessen the impact of these worldwide limits. Educational establishments all around the globe have been under pressure to adopt innovative teaching methods and use emerging technologies; one such technology is e-Learning. The most significant and drastic adaptation and utilization of e-Learning occurred in developing countries during the COVID-19 period. These countries now utilize e-Learning at different educational levels and activities [
1,
2]. As time passed, the significance of e-Learning for students’ learning gains and academic advancement became increasingly crucial. This trend continued even after the COVID-19 period ended [
3,
4,
5].
The significance of e-Learning, its positive impact on students’ learning gains, the availability of educational opportunities, and the effect it has on complementing academic accomplishments are recognized and accepted in every region of the world. This is true because its significance is universally known and understood. On the other hand, the circumstance is different in Bangladesh. At every level of education in Bangladesh, the socio-economic situations of the students are very different. The parent’s financial position substantially impacts various issues relevant to the child’s access to educational opportunities. In addition, there is a wide disparity in the educational opportunities open to each person due to the inadequate application of social justice. In addition, the financial circumstances of many students are insufficient to allow them to acquire the necessary digital technology and services to use and benefit from the education provided through e-Learning [
6].
The digital divide has emerged as a consequence of the circumstance. In addition, many students do not have adequate knowledge of utilizing e-Learning since there is no unified educational curriculum focusing on it, and only a few expensive education curricula meet the requirements for teaching digital literacy. Consequently, students who lack digital literacy and cannot afford digital equipment and services cannot make full use of the learning and educational opportunities that have become available as a direct result of the advancements made in educational technology, such as e-Learning. As a consequence of this, it frequently has a negative impact on their academic achievements. Even though e-Learning has various records of positive effects on students’ learning gains and educational opportunities, students in Bangladesh of all educational levels are frequently unable to utilize these innovations to improve their academic performance. Primarily due to Bangladesh being home to a large number of obstacles. Due to this, there has been a considerable increase in the number of students across the country who choose not to continue their education or who take time off between school years as a direct result of the aftereffects of COVID-19, and the introduction of new educational technologies, such as e-Learning. In addition to the challenges already present in education due to e-Learning, there is also a dearth of programs for developing skills offered by both the government and educational institutions. Due to this, university students will be prevented from attaining their full potential and will be less prepared for employment, which is especially problematic today when technology-based skills are highly sought across the globe [
7,
8].
The relevance of e-Learning in education is growing daily, and it is abundantly clear that its significance will only grow to an even greater degree in the years to come. As a direct result, its influence on students’ academic progress will continue to grow. In this age of globalization, it is possible to consider this impact to be felt worldwide, and it will be experienced by every nation [
9,
10]. However, due to the wide range of socio-economic conditions and cultural norms worldwide, how each country acknowledges and addresses the problem may differ significantly. Such e-Learning advancements may have a negative impact on students’ learning gains, educational opportunities, and academic achievements in developing nations, such as Bangladesh, where access to digital technology and the internet is frequently regarded as a luxury. This is especially true for university students, who have been the most dependent on e-Learning advancements in recent years. In addition, while fully aware of the pre-existing conditions that include a lack of social justice, the digital gap, technological growth in education, and impediments to academic success in the country, the government has not yet taken any severe action.
Past literature has shown that there has been an accelerated adaptation and utilization of e-Learning in education and that it has many positive aspects. The literature also shows that for developing countries, such as Bangladesh, the full potential of e-Learning in education is hindered due to the diverse socio-economic conditions and the prevalence of the digital divide. Moreover, the existing literature showcases that e-Learning in education has caused a transformation in the delivery of education, which all cannot acquire due to socio-economic conditions and the digital divide. Hence, it can be said that e-Learning acts as a doubled edge sword for the academic achievements of university students in developing countries, such as Bangladesh. Additionally, the University Grant Commission of Bangladesh (UGC) hopes to emphasize more on the use of technology in higher educational institutes (HEIs). Hence, it is crucial to identify all the factors that might benefit and hinder the students learning and academic achievements [
11].
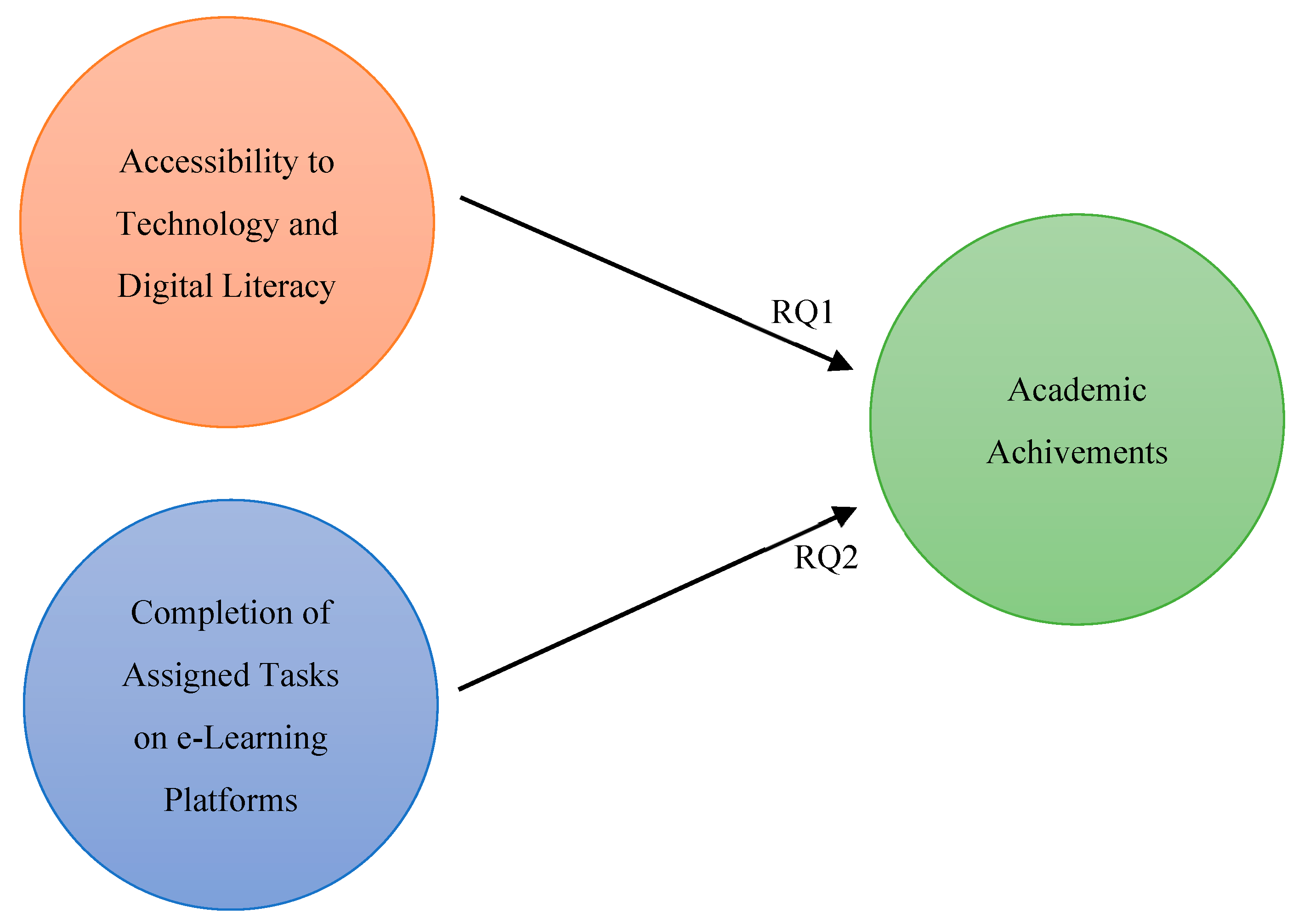
Moreover, most of the previous works have only focused on the positive sides of e-Learning in developing countries. Rarely has there been any prior work on how e-Learning in education has affected students’ academic achievements, particularly university students in developing countries. Hence, this has created a knowledge gap. Therefore, this study aims to fill the knowledge void, utilizing the technological determinism theory and the reflective theory of education. Moreover, the study intends to find responses to the following research questions:
- RQ1:
To what extent do university students’ access to technological devices and the digital divide affect e-Learning?
- RQ2:
To what extent do university students consider technological advancement, such as e-Learning, adversely affects their academic achievements?
7. Discussion and Recommendations
The prevailing inequality and poverty, which have been plaguing Bangladesh despite its applaudable development, are well known. Moreover, these predicaments have resulted in a lack of social justice and a digital divide. Considering these factors, many previous studies and reports have stated the lack of access to technological devices, fast and stable internet connection, and persistent digital literacy in many parts of the country. Moreover, these issues have been cited to be due to the country’s financial problems and other non-financial and infrastructural factors. These have created unfavorable conditions for students of all levels in Bangladesh. These issues have been widely reported by Kabir et al. (2021), Kabir et al. (2021), Saleh et al. (2022), and Progga et al. (2020), among many others [
41,
42,
43,
44]. However, the previous works have not covered or focused on how or to what extent these factors affect e-Learning for university students in Bangladesh. From the data collected by this study, it can be seen that 47.6% of the students reported not having any technological devices for accessing e-Learning, which is nearly half of the total students.
Moreover, 57.3% reported not having any internet access. While the rest who did say having access to the internet again noted that 73.5% did not have a fast and stable internet connection. Furthermore, from the interviews, it was noticed that due to these existing factors, students had difficulties correctly accessing, utilizing, and learning from the e-Learning activities and tasks offered by their university. Hence, it could be said that to a great extent, university students’ access to technological devices and the digital divide affects e-Learning in Bangladesh.
Similarly, it is also known through various previous studies that the lack of social justice and the digital divide have affected a student’s academic achievements. Most of the earlier works have primarily focused on how a lack of social justice results in a lack of school choice. Hence, limiting the curriculum, quality of education, and accessibility to education by a student due to the socio-economic condition of the parents and other factors [
45,
46,
47]. Moreover, few other works have also focused on how the digital divide has influenced students’ academic achievements [
48,
49]. However, to what extent do university students consider technological advancement, such as e-Learning, adversely affects university students’ academic achievements in Bangladesh is a topic that has never been focused on before by previous works. From this study’s collected data, it can be seen that 68.4% of the students now have to use e-Learning activities and tasks; 94.5% have to submit tasks or complete activities through the e-Learning platforms for grading, which near to all the students who participated in this study; and 59.2% reported they have once failed to submit their tasks or complete the activity on time on the e-Learning platform.
Moreover, based on data analysis, it was found that there was a high positive correlation between a lack of technological devices and digital literacy, with academic achievements being negatively impacted due to e-Learning. Together with the numerical data, the interviews stated similar facts. Most students indicated that they found it challenging to complete the tasks or activities on the e-Learning platform with utmost diligence due to various predicaments, resulting in a bad grade or negative academic outcome for them. Therefore, for the second research question, it can also be said that, to a great extent, university students consider technological advancement, such as e-Learning, to adversely affects their academic achievements.
However, many previous works have stated e-Learning positively impacts students at various levels [
50,
51,
52]. Paradoxically, the students who participated in the study also agreed to some extent regarding the benefits of e-Learning. However, they mentioned the barriers that have limited e-Learning benefits and sometimes cause drawbacks to students [
53]. Based on these findings, it could be said that e-Learning is a doubled-edge sword for the academic achievements of university students in Bangladesh and other developing countries.
Recommendations
As the government of Bangladesh and other education-related offices are pushing for the digitalization and use of technology in education, the following suggestions and actions could help reduce the existing obstacles and mitigate the adverse effects of e-Learning:
First and foremost, the digital divide needs to be closed. This can be done by the government offering financial assistance through subsidies and public-private partnerships. The goal is to make digital devices and uninterrupted internet connections more accessible and affordable for college students.
Second, there needs to be an increase in the percentage of people who are literate in digital technology. This can be accomplished by fostering the growth of students’ soft skills by providing training by educational institutions and other organizations.
Third, students must have access to affordable, uninterrupted, and fast internet connections. The government, internet service providers, and cellular service providers all need to work together to make this a reality for students because it is the second most crucial factor in making effective use of technological advancements in education.
In conclusion, the existing educational curriculum must be modernized to guarantee the appropriate implementation of e-Learning in education. Teachers need the proper training to acquire the knowledge they need to maximize the benefits of these advancements. These recommendations will, one can only hope, ensure that the full potential of technological achievements in education and the academic achievements of university students is realized.
9. Conclusions
Amid the global health crisis, when it was physically challenging to carry out education delivery given the prevailing circumstances, technology emerged as essential for continuing education delivery. Although technology has been around for a considerable amount of time, its application, adaptation, and development have all accelerated dramatically during the period. e-learning, which was previously difficult to implement, is now within reach due to technological advancements. This is a significant change from the situation just a few years ago. Additionally, the development of technology was responsible for making the delivery of education and the dissemination of knowledge genuinely borderless. This was made possible by e-Learning. Students and academics worldwide were allowed to participate in webinars and world-class educational materials without the inconvenience of having to travel far from their homes. The development of e-Learning in education has made this outcome conceivable. It is impossible to dispute that e-Learning advances have positively impacted expanding educational opportunities and enhancing academic standards. In many regions of the world, a sizeable percentage of the population still regards access to technology and education as a luxury. The advancement of e-Learning in education has resulted in a more uneven distribution of educational opportunities and learning gains for many living in such locations.
Similarly, the application of e-Learning in educational settings in Bangladesh cannot reach its full potential. It is becoming a barrier to students’ academic achievement for various reasons, including the existing lack of social justice and the digital divide. Still, there are also several other reasons. To make sure that educational institutions in Bangladesh can make the most of the opportunities presented by e-Learning, the government of Bangladesh and all of the critical stakeholders in the country need to take immediate action and remove these barriers quickly as they can.