The Spatiotemporal Measurement of Coordinated Development of Resource-Environment-Economy Based on Empirical Analysis from China’s 30 Provinces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Research Methods
3.1. Indicator System Construction
3.2. Research Data and Processing
3.2.1. Research Data
3.2.2. Data Processing
3.3. Empowerment of Indicators
3.4. Evaluation Model Designing
3.4.1. Integrated Evaluation Function
3.4.2. Coupling Coordination Model
3.4.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Analysis of Time-Series Evolutionary
4.2. Analysis of Spatial Distribution Characteristics
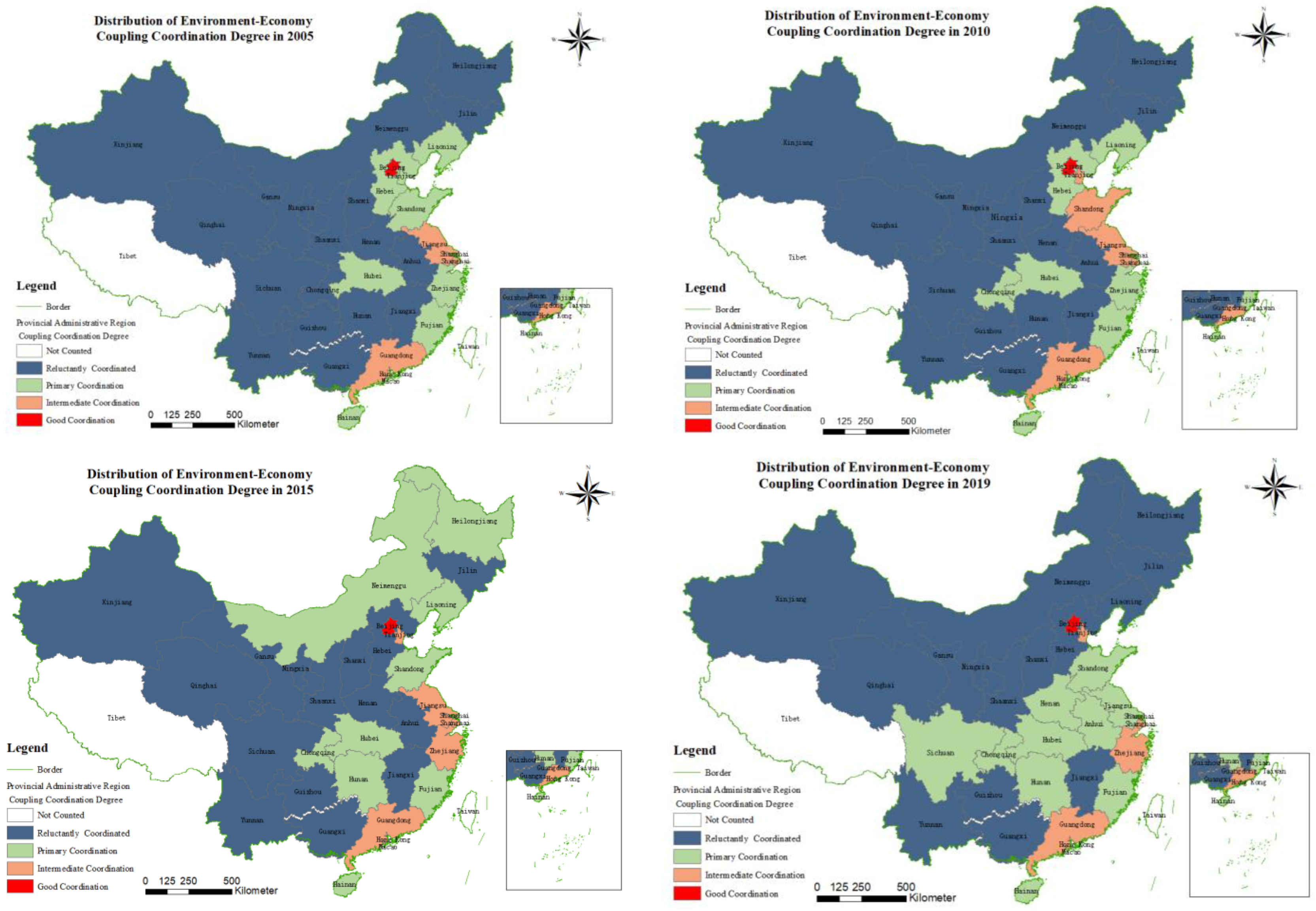
4.2.1. Analysis of the Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the Two Systems
4.2.2. Analysis of the Spatial Distribution Characteristics of the Three Systems
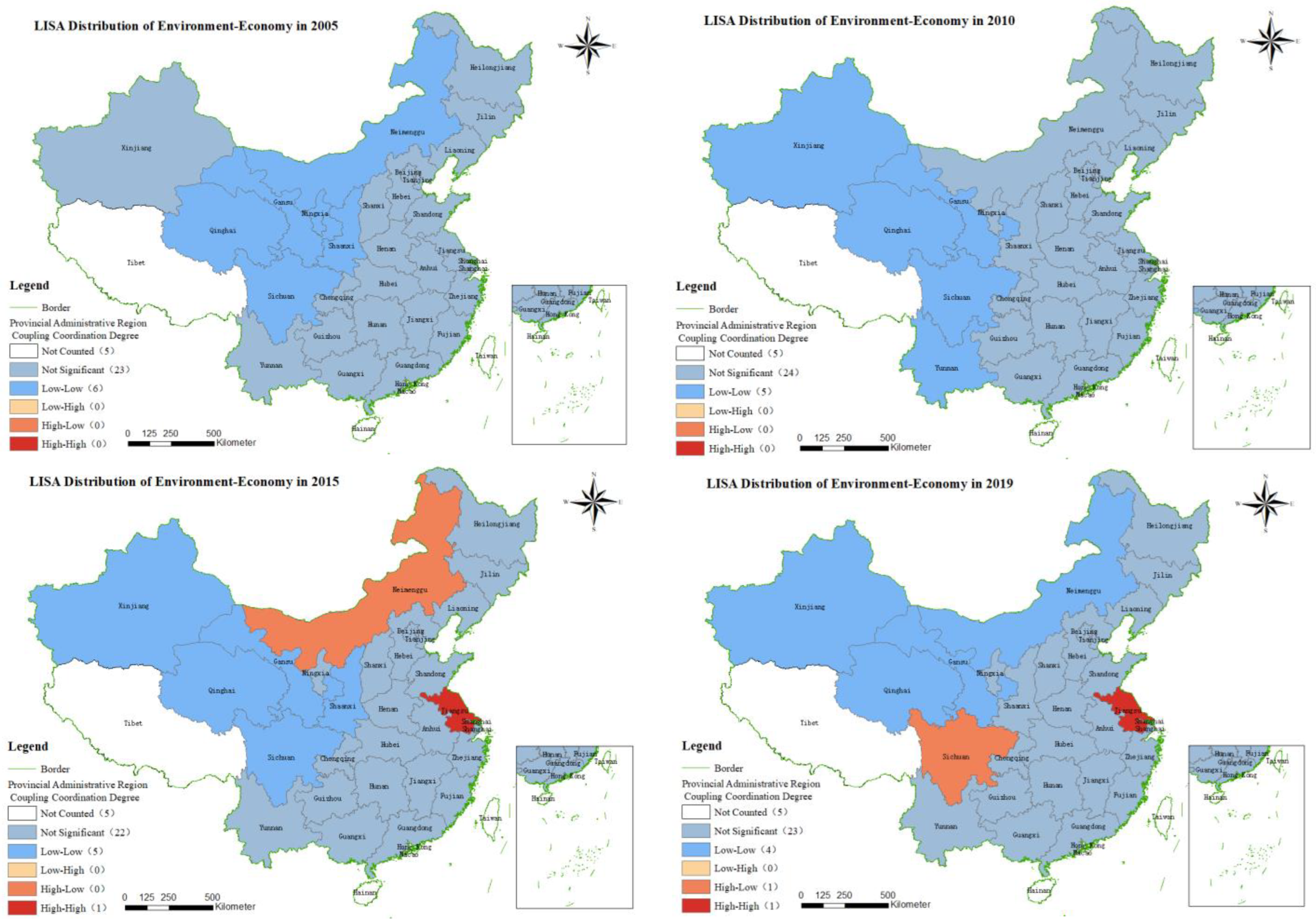
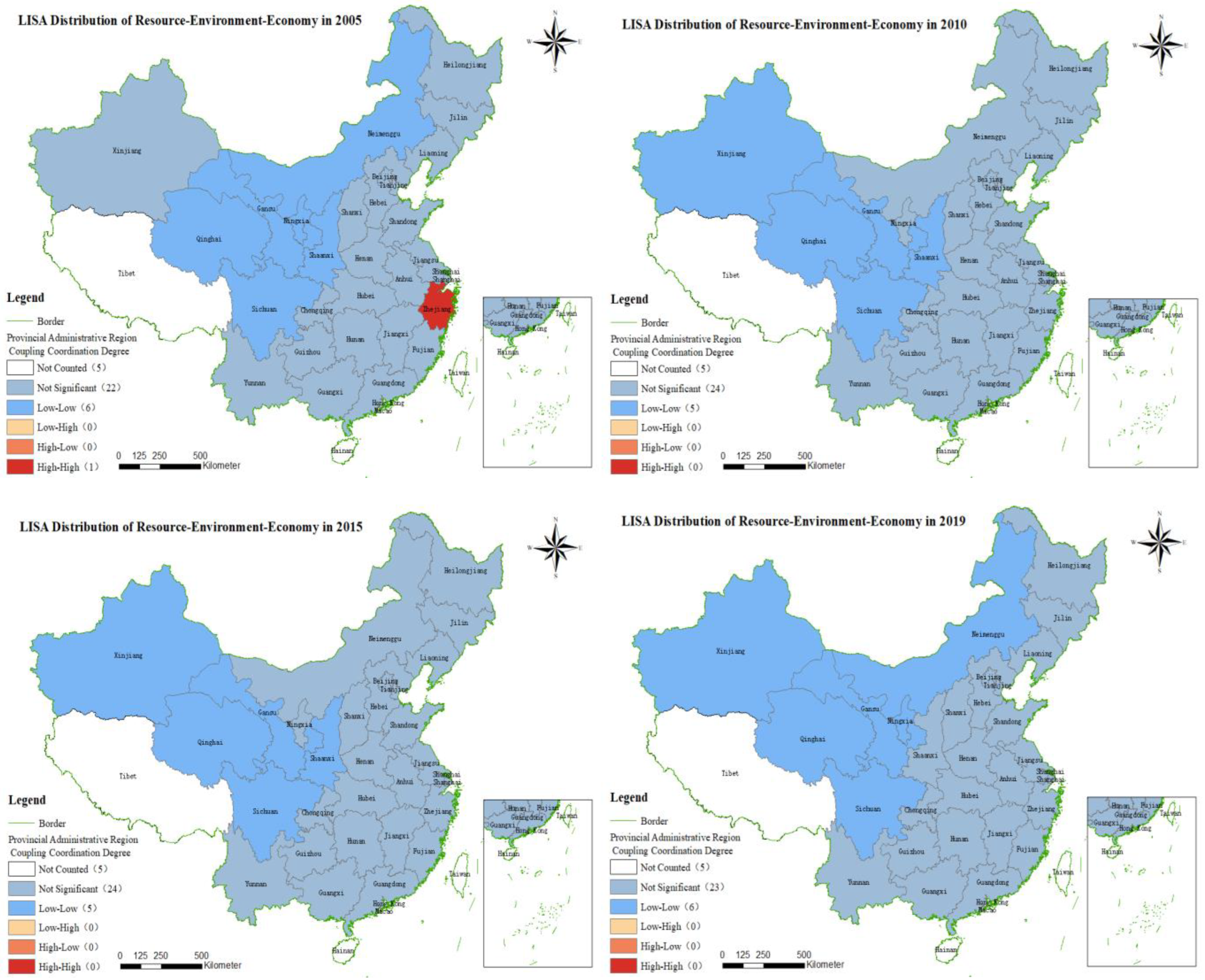
4.3. Spatial Correlation Analysis
4.3.1. Global Moran’s I Test
4.3.2. The LISA Diagram
5. Conclusions
6. Discussion and Policy Recommendations
6.1. Limitations
6.2. Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, J.; Wang, H. Economic structure, development policy and environmental quality: An empirical analysis of environmental Kuznets curves with Chinese municipal data. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 76, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Oh, D.-W. Economic growth and the environment in China: Empirical evidence using prefecture level data. China Econ. Rev. 2015, 36, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Garg, N.; Paudel, R. Environmental Degradation: Causes and Consequences. Eur. Res. 2014, 81, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, U.K.; Erdogan, S.; Ozkan, O. Is reducing fossil fuel intensity important for environmental management and ensuring ecological efficiency in China? J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Environmental pollution emissions, regional productivity growth and ecological economic development in China. China Econ. Rev. 2015, 35, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, U.K.; Kumar, A. The Influence of Hydropower and Coal Consumption on Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Comparison between China and India. Water 2021, 13, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Lin, B. Research on influencing factors of environmental pollution in China: A spatial econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, X. Investigation of a coupling model of coordination between urbanization and the environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 98, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement. Soc. Sci. Electron. Publ. 1991, 8, 223–250. [Google Scholar]
- Erdogan, S. Analyzing the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The role of disaggregated transport infrastructure investments. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, M.A.; Ozturk, I.; Bekun, F.V.; Khan, D. Modeling the dynamic linkage between financial development, energy innovation, and environmental quality: Does globalization matter? Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020, 30, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfred, B. Economic growth and the environment: Whose growth? Whose environment? World Dev. 1992, 20, 481–496. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Q.; Kou, D. Economic growth, energy structure transformation and carbon dioxide emissions-empirical analysis based on panel data. Res. Econ. Manag. 2020, 41, 19–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W. Environmental Kuznets Curve Test of Relationship between Economic Growth and Industrial Environmental Pollution: Based on the Yangtze River Economic Belt Provincial Panel Measurement Model. J. Nanjing Technol. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2020, 19, 64–72+112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Congregado, E.; Feria-Gallardo, J.; Golpe, A.A.; Iglesias, J. The environmental Kuznets curve and CO2 emissions in the USA. Environ Sci. Pollut. R. 2016, 23, 18407–18420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Monserrate, M.A.; Fernandez, M.A. An Environmental Kuznets Curve for N2O emissions in Germany: An ARDL approach. Nat. Resour. Forum. 2017, 41, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraby, T.; Bauch, C.T.; Anand, M. The environmental Kuznets curve fails in a globalized socio-ecological metapopulation: A sustainability game theory approach. Handb. Stat. 2018, 39, 315–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, D. Environmental Kuznets curves: A spatial econometric approach. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2006, 51, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantele, M.; Bal, P.; Kompas, T.; Hadjikakou, M.; Wintle, B. Equilibrium Modeling for Environmental Science: Exploring the Nexus of Economic Systems and Environmental Change. Earths Future 2021, 9, e2020EF001923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Nie, J.; Jahanger, A. An Evaluation of the Energy-Related Carbon Dioxide Emissions From China’s Light Sector to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals. Eval. Rev. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hou, J.; Jahanger, A.; Cao, X.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Radulescu, M.; Jiang, T. Decomposition analysis of China’s chemical sector energy-related CO2 emissions: From an extended SDA approach perspective. Energy Environ. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, M.; Nie, C.; Ke, L. Carrying capacity and coordinated development of ERE system in the coastal area of Bohai Sea. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 163–172. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.; Guo, X. Measuring the level of coordinated economic-resource-environmental development in the western region. Stat. Decis. 2019, 35, 124–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lin, W. Evaluation of Sustainable Development of Cities in Henan Province Based on Grey Correlation Analysis. Math. Pract. Theory 2019, 49, 18–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhong, C.; Jiang, T.; Li, X. Spatio-Temporal differentiation of regional coordinated development and its influencing factors in china. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; An, T.; Shen, J.; Zhang, K.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, R.; He, G.; Hynes, S.; Jattak, Z.U. Development of a land-sea coordination degree index for coastal regions of China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2022, 230, 106370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, C. Research on the effective route of ecological civilization construction in Yunnan Province based on System Dynamics. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2019, 29, 16–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Cheng, J.; Fang, C. Coordinated development of economy, resources and environment in the Yangtze River Economic Belt based on “Three Lines and One Order”. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 31, 163–173. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Chang, H.; Wang, Y. Dynamic evolution of provincial energy economy and environment coupling in China’s regions. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2017, 27, 60–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xing, L.; Xue, M.G.; Hu, M.S. Dynamic simulation and assessment of the coupling coordination degree of the economy-resource-environment system: Case of Wuhan City in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 230, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhan, J.; Wang, C.; Twumasi-Ankrah, M.J. Coupling coordination analysis and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between sustainable development and ecosystem services in Shanxi Province. China Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wu, F.; Chen, Y.X.; Qin, K.Y. Coupling coordination degree spatial analysis and driving factor between socio-economic and eco-environment in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.Q.; Lian, H.H.; Qin, Q.D. Spatial disparities of the coupling coordinated development among the economy, environment and society across China’s regions. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q. Coupling coordination degree measurement and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment—Empirical evidence from tropical and subtropical regions of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, N. The spatial and temporal evolution of coordinated ecological and socioeconomic development in the provinces along the Silk Road Economic Belt in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 47, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Guo, C. Empirical Analysis on Coordination Degree of China’s Energy, Economic and Environment(3E). J. Nanjing Univ. Financ. Econ. 2014, 186, 15–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wang, B.; Xu, J. The analysis on the areal difference of coordinating degree between regional economy and ecological environment-based on comprehensive evaluation method. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2014, 34, 36–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Wu, K.; Xu, Z. Spatial-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of coordination between economic and environmental development of three major urban agglomerations in China. Geogr. Res. 2020, 39, 272–288. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Decoupling analysis and influence factors between resource environment and economic growth in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 43–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhong, Q.; Qu, P.; Yin, Y.; Zuo, Y. Grey Forecasting Model of rural water environment quality based on web search information. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2020, 28, 222–230. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Tong, L.; Zhu, S.; Lu, Z. The coordinated development of economy and environment based on ARMA model in Shenyang Economic Zone. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2014, 34, 32–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, W.; Lu, L. An innovative digitization evaluation scheme for Spatio-temporal coordination relationship between multiple knowledge driven rural economic development and agricultural ecological environment—Coupling coordination model analysis based on Guangxi. J. Innov. Knowl. 2022, 7, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Khan, S.U.; Swallow, B.; Liu, W.; Zhao, M. Coupling coordination analysis of China’s water resources utilization efficiency and economic development level. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildirici, M.; Ersin, O.O. Economic growth and CO2 emissions: An investigation with smooth transition autoregressive distributed lag models for the 1800-2014 period in the USA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 200–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildirici, M.; Ersin, O. Markov-switching vector autoregressive neural networks and sensitivity analysis of environment, economic growth and petrol prices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 31630–31655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomal, M. Evaluation of coupling coordination degree and convergence behaviour of local development: A spatiotemporal analysis of all Polish municipalities over the period 2003–2019. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 71, 102992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, M.W.; Shahfahad; Talukdar, S.; Ishtiaq, M.; Rahman, A. Modelling built-up land expansion probability using the integrated fuzzy logic and coupling coordination degree model. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Tian, L.; Zhou, Y. Regional Energy–Economy–Environment Coupling Coordinated Development System Driven by Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutralization over 13 Cities in Jiangsu Province. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Jin, S.; Pang, M.; Lu, C. Research on the Spatial–Temporal Synthetic Measurement of the Coordinated Development of Population-Economy-Society-Resource-Environment (PESRE) Systems in China Based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Sustainability 2019, 11, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, M. A Data preprocessing Method in Dynamic Comprehensive Evaluation. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2020, 28, 162–169. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Ding, C.; Guo, Q.; Yang, L. Measurement and path selection of coupling and coordinated development of rural revitalization in Hunan Province. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 191–197. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.Y.; Liu, X.W.; Zhang, T.; Huang, P.; Tang, X.L.; Wang, Y.J. Comprehensive Measurement of the Coordinated Development of China’s Economic Growth, Energy Consumption, and Environmental Conservation. Energies 2022, 15, 6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhu, J.W.; Lou, K.L.; Yang, L. Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between urbanization and ecological environment in Shaanxi Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Q.; Pan, X.X.; Wang, Y.; Lei, S.Y. Evaluation and Analysis on Coupling Coordinated Development of Urban Resource, Environment and Economy in Jiangxi Province in China. Prog. Environ. Prot. Process. Resour. 2013, 295–298, 2457–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Lu, F.X.; Qin, Y.C.; Zhou, Y.S.; Xie, Z.X. The Spatial Quantitative Evaluation and Coupling Coordination Degree of Urban Ecosystem Carrying Capacity: A Case Study of the Urban Agglomeration in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 15169–15190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Qin, F.; Zhai, Y.X.; Cao, H.P.; Zhang, R.; Cao, F.P. Evaluation of coordinated development of forestry management efficiency and forest ecological security: A spatiotemporal empirical study based on China’s provinces. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Lin, B.; Zhou, Y. Does financial structure promote energy conservation and emission reduction? Evidence from China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2021, 76, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Fan, C.; Zhong, M.; Cao, F.; Wang, G.; Cao, L. Evaluation of Habitat Suitability for Asian Elephants in Sipsongpanna under Climate Change by Coupling Multi-Source Remote Sensing Products with MaxEnt Model. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.K.; Han, Q.; Wu, K.X.; Xu, Z.T.; Liu, P. Spatial-temporal patterns and evolution characteristics of the coordinated development of industrial economy, natural resources and environment in China. Resour. Policy 2022, 75, 102463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, W.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, T. Spatiotemporal and driving forces of Ecological Carrying Capacity for high-quality development of 286 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.P.; Yi, X.; Pan, C.L.; Yang, B.M.; Li, Y. Analysis on the Temporal and Spatial Features of the Coupling and Coordination of Industrialization and Agricultural Green Development in China during 1990–2019. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.B.; Liu, W.; Yan, Y.A.; Liu, C.Y. A perspective of ecological civilization: Research on the spatial coupling and coordination of the energy-economy-environment system in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongoma, V.; Epule, T.E.; Brouziyne, Y.; Tanarhte, M.; Chehbouni, A. COVID-19 response in Africa: Impacts and lessons for environmental management and climate change adaptation. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Khan, S.U.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, M. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity, convergence and its impact factors: Perspective of carbon emission intensity and carbon emission per capita considering carbon sink effect. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 92, 106699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Shuai, C.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, S. Decoupling China’s economic growth from carbon emissions: Empirical studies from 30 Chinese provinces (2001–2015). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Zhang, N.; Ullah, K.; Gao, S. Enhancing Digital Innovation for the Sustainable Transformation of Manufacturing Industry: A Pressure-State-Response System Framework to Perceptions of Digital Green Innovation and Its Performance for Green and Intelligent Manufacturing. Systems 2022, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Systems | Tier 1 Indicators | Tier 2 Indicators | Code | Unit | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resource | Resource consumption | Total energy consumption | X1 | million tons of standard coal | - |
| Coal consumption | X2 | million tons | - | ||
| Natural gas consumption | X3 | billion cubic meters | - | ||
| Electricity consumption | X4 | billion kWh | - | ||
| Water consumption | X5 | billion cubic meters | - | ||
| Resource efficiency | Energy consumption elasticity factor | X6 | - | - | |
| Electricity consumption elasticity factor | X7 | - | - | ||
| Energy consumption per CNY 10,000 of GDP | X8 | tons of standard coal/CNY 10,000 | - | ||
| Electricity consumption per CNY 10,000 of GDP | X9 | kWh/million | - | ||
| Water consumption per CNY 10,000 of GDP | X10 | cubic meters/CNY 10,000 | - | ||
| Environment | Environmental pollution | Sulfur dioxide emissions | Y1 | ton | - |
| Industrial fume emissions | Y2 | ton | - | ||
| Industrial wastewater discharge | Y3 | million tons | - | ||
| Respirable particulate matter PM10 | Y4 | mg/m3 | - | ||
| Environmental quality | Greenery coverage | Y5 | % | + | |
| Green space per capita | Y6 | cubic meters per person | + | ||
| Integrated industrial solid waste volume | Y7 | million tons | + | ||
| Annual completed investment in industrial pollution control | Y8 | million | + | ||
| Harmless disposal rate of domestic waste | Y9 | % | + | ||
| Economy | Economy scale | GDP per capita | Z1 | billion | + |
| Total investment in fixed assets | Z2 | billion | + | ||
| Total retail sales of social consumer goods | Z3 | billion | + | ||
| Total imports and exports | Z4 | billion | + | ||
| General budget revenue of local finance | Z5 | billion | + | ||
| Economic quality | Ratio of urban to rural disposable income | Z6 | % | - | |
| Fixed asset input–output ratio | Z7 | % | + | ||
| Urbanization rate | Z8 | % | + | ||
| Economic structure | GDP percentage of tertiary sector | Z9 | % | + | |
| GDP percentage of industry | Z10 | % | - | ||
| Construction as a share of GDP | Z11 | % | - | ||
| Scientific research expenditure as a percentage of GDP | Z12 | % | + |
| No. | Coupling Coordination | Grade Stage | Type | Stage Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (0.0, 0.1] | Extreme disorders | Types of dysfunctional decline | Poorly developed inter-system coordination, complex systems in a dysfunctional decline stage |
| 2 | (0.1, 0.2] | Severe disorders | ||
| 3 | (0.2, 0.3] | Severe disorders | ||
| 4 | (0.3, 0.4] | Mild disorders | ||
| 5 | (0.4, 0.5] | On the verge of disorder | ||
| 6 | (0.5, 0.6] | Reluctantly coordinated | Type of coordinated development | The system begins to enter a phase of coordinated development and synergies between systems begin to develop |
| 7 | (0.6, 0.7] | Primary coordination | ||
| 8 | (0.7, 0.8] | Intermediate coordination | ||
| 9 | (0.8, 0.9] | Good coordination | ||
| 10 | (0.9, 1.0] | Quality coordination | Inter-system synergy development |
| Provinces | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.436 | 0.487 | 0.576 | 0.640 | 0.636 | 0.667 | 0.724 | 0.730 | 0.774 | 0.806 | 0.840 | 0.819 | 0.848 | 0.818 | 0.862 |
| Tianjin | 0.467 | 0.517 | 0.561 | 0.602 | 0.629 | 0.640 | 0.672 | 0.687 | 0.696 | 0.731 | 0.778 | 0.825 | 0.841 | 0.811 | 0.842 |
| Hebei | 0.450 | 0.462 | 0.532 | 0.588 | 0.615 | 0.671 | 0.674 | 0.688 | 0.719 | 0.775 | 0.817 | 0.822 | 0.850 | 0.842 | 0.883 |
| Shanxi | 0.453 | 0.474 | 0.548 | 0.644 | 0.660 | 0.642 | 0.655 | 0.688 | 0.713 | 0.736 | 0.781 | 0.808 | 0.778 | 0.781 | 0.824 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.530 | 0.507 | 0.587 | 0.646 | 0.676 | 0.681 | 0.682 | 0.705 | 0.743 | 0.794 | 0.805 | 0.836 | 0.823 | 0.796 | 0.803 |
| Liaoning | 0.532 | 0.560 | 0.565 | 0.605 | 0.628 | 0.656 | 0.666 | 0.711 | 0.732 | 0.744 | 0.771 | 0.774 | 0.822 | 0.821 | 0.818 |
| Jilin | 0.481 | 0.519 | 0.569 | 0.590 | 0.603 | 0.627 | 0.620 | 0.648 | 0.678 | 0.721 | 0.759 | 0.824 | 0.824 | 0.827 | 0.864 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.406 | 0.435 | 0.509 | 0.578 | 0.613 | 0.659 | 0.687 | 0.683 | 0.742 | 0.762 | 0.795 | 0.814 | 0.809 | 0.845 | 0.860 |
| Jiangsu | 0.465 | 0.475 | 0.568 | 0.616 | 0.596 | 0.627 | 0.663 | 0.695 | 0.726 | 0.762 | 0.800 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 0.861 | 0.864 |
| Shanghai | 0.469 | 0.529 | 0.560 | 0.602 | 0.651 | 0.626 | 0.641 | 0.683 | 0.673 | 0.739 | 0.732 | 0.790 | 0.819 | 0.844 | 0.861 |
| Zhejiang | 0.410 | 0.427 | 0.453 | 0.502 | 0.565 | 0.573 | 0.598 | 0.685 | 0.689 | 0.758 | 0.809 | 0.827 | 0.839 | 0.848 | 0.911 |
| Anhui | 0.540 | 0.525 | 0.551 | 0.568 | 0.570 | 0.580 | 0.602 | 0.640 | 0.670 | 0.708 | 0.729 | 0.805 | 0.846 | 0.853 | 0.856 |
| Fujian | 0.546 | 0.513 | 0.549 | 0.584 | 0.621 | 0.595 | 0.554 | 0.665 | 0.683 | 0.661 | 0.749 | 0.778 | 0.788 | 0.786 | 0.821 |
| Jiangxi | 0.509 | 0.499 | 0.537 | 0.627 | 0.652 | 0.674 | 0.669 | 0.710 | 0.724 | 0.731 | 0.754 | 0.770 | 0.820 | 0.842 | 0.848 |
| Shandong | 0.432 | 0.489 | 0.529 | 0.592 | 0.620 | 0.643 | 0.686 | 0.732 | 0.756 | 0.805 | 0.792 | 0.846 | 0.882 | 0.866 | 0.861 |
| Hubei | 0.496 | 0.508 | 0.561 | 0.595 | 0.600 | 0.621 | 0.609 | 0.640 | 0.698 | 0.719 | 0.742 | 0.832 | 0.844 | 0.854 | 0.861 |
| Henan | 0.434 | 0.441 | 0.499 | 0.530 | 0.566 | 0.575 | 0.613 | 0.660 | 0.677 | 0.732 | 0.747 | 0.825 | 0.849 | 0.849 | 0.883 |
| Hunan | 0.431 | 0.510 | 0.560 | 0.593 | 0.615 | 0.639 | 0.635 | 0.670 | 0.703 | 0.733 | 0.784 | 0.803 | 0.834 | 0.827 | 0.861 |
| Guangdong | 0.344 | 0.395 | 0.468 | 0.557 | 0.586 | 0.615 | 0.647 | 0.706 | 0.741 | 0.737 | 0.808 | 0.838 | 0.861 | 0.869 | 0.877 |
| Guangxi | 0.462 | 0.498 | 0.544 | 0.585 | 0.637 | 0.627 | 0.689 | 0.730 | 0.752 | 0.775 | 0.818 | 0.847 | 0.858 | 0.830 | 0.868 |
| Hainan | 0.568 | 0.540 | 0.556 | 0.603 | 0.638 | 0.659 | 0.672 | 0.724 | 0.754 | 0.775 | 0.757 | 0.816 | 0.834 | 0.798 | 0.801 |
| Chongqing | 0.411 | 0.421 | 0.550 | 0.633 | 0.626 | 0.667 | 0.694 | 0.724 | 0.771 | 0.754 | 0.795 | 0.813 | 0.850 | 0.868 | 0.868 |
| Sichuan | 0.481 | 0.507 | 0.559 | 0.603 | 0.577 | 0.615 | 0.637 | 0.674 | 0.711 | 0.742 | 0.762 | 0.794 | 0.824 | 0.841 | 0.858 |
| Gansu | 0.473 | 0.495 | 0.507 | 0.564 | 0.606 | 0.601 | 0.607 | 0.650 | 0.675 | 0.701 | 0.728 | 0.830 | 0.791 | 0.793 | 0.858 |
| Ningxia | 0.542 | 0.533 | 0.558 | 0.592 | 0.619 | 0.688 | 0.639 | 0.703 | 0.739 | 0.797 | 0.770 | 0.860 | 0.819 | 0.823 | 0.827 |
| Shaanxi | 0.544 | 0.544 | 0.570 | 0.604 | 0.650 | 0.678 | 0.682 | 0.688 | 0.714 | 0.729 | 0.768 | 0.766 | 0.777 | 0.807 | 0.831 |
| Qinghai | 0.564 | 0.558 | 0.585 | 0.557 | 0.607 | 0.626 | 0.679 | 0.695 | 0.681 | 0.739 | 0.764 | 0.816 | 0.791 | 0.800 | 0.837 |
| Xinjiang | 0.518 | 0.484 | 0.573 | 0.588 | 0.661 | 0.676 | 0.687 | 0.671 | 0.673 | 0.706 | 0.740 | 0.796 | 0.830 | 0.839 | 0.831 |
| Yunnan | 0.478 | 0.485 | 0.549 | 0.580 | 0.632 | 0.647 | 0.647 | 0.677 | 0.720 | 0.759 | 0.796 | 0.828 | 0.841 | 0.854 | 0.883 |
| Guizhou | 0.488 | 0.468 | 0.483 | 0.584 | 0.604 | 0.630 | 0.633 | 0.665 | 0.717 | 0.751 | 0.791 | 0.805 | 0.818 | 0.838 | 0.872 |
| Mean-value | 0.479 | 0.493 | 0.544 | 0.592 | 0.619 | 0.637 | 0.652 | 0.688 | 0.715 | 0.746 | 0.776 | 0.814 | 0.828 | 0.831 | 0.853 |
| Coupling Coordination Level | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reluctantly coordinated | Xinjiang, Ningxia, Shanxi | Guizhou, Xinjiang, Qinghai, Gansu | Gansu, Xinjiang | Xinjiang |
| Primary coordination | Jilin, Hubei, Shandong, Hunan, Jiangxi, Anhui, Heilongjiang, Hebei, Guangxi, Sichuan, Henan, Chongqing, Shaanxi, Yunnan, Qinghai, Inner Mongolia, Guizhou, Gansu | Shanxi, Henan, Yunnan, Guangxi, Ningxia, Sichuan, Inner Mongolia, Anhui, Hebei, Shaanxi, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Hunan, Jiangxi, Liaoning, Hubei | Hunan, Hubei, Heilongjiang, Chongqing, Liaoning, Anhui, Jilin, Shandong, Guangxi, Inner Mongolia, Sichuan, Hebei, Jiangxi, Shaanxi, Yunnan, Henan, Guizhou, Shanxi, Ningxia, Qinghai | Hunan, Anhui, Chongqing, Henan, Shandong, Jiangxi, Sichuan, Heilongjiang, Guangxi, Liaoning, Jilin, Shaanxi, Yunnan, Hebei, Shanxi, Guizhou, Inner Mongolia, Gansu, Ningxia, Qinghai |
| Intermediate coordination | Guangdong, Tianjin, Jiangsu, Fujian, Zhejiang, Hainan, Liaoning | Tianjin, Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Fujian, Hainan, Shandong, Chongqing | Tianjin, Zhejiang, Guangdong, Hainan, Fujian, Jiangsu | Tianjin, Zhejiang, Guangdong, Hubei, Fujian, Hainan, Jiangsu |
| Good coordination | Beijing, Shanghai | Beijing, Shanghai | Beijing, Shanghai | Beijing, Shanghai |
| 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I Index | 0.475 | 0.459 | 0.452 | 0.432 |
| Z-value | 4.172 | 4.114 | 4.015 | 3.891 |
| p-value | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I Index | 0.488 | 0.489 | 0.469 | 0.447 |
| Z-value | 4.253 | 4.313 | 4.166 | 3.973 |
| p-value | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y. The Spatiotemporal Measurement of Coordinated Development of Resource-Environment-Economy Based on Empirical Analysis from China’s 30 Provinces. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6995. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086995
Wang H, Lu X, Guo Q, Zhang Y. The Spatiotemporal Measurement of Coordinated Development of Resource-Environment-Economy Based on Empirical Analysis from China’s 30 Provinces. Sustainability. 2023; 15(8):6995. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086995
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hongqiang, Xiaochang Lu, Qiujing Guo, and Yingjie Zhang. 2023. "The Spatiotemporal Measurement of Coordinated Development of Resource-Environment-Economy Based on Empirical Analysis from China’s 30 Provinces" Sustainability 15, no. 8: 6995. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086995
APA StyleWang, H., Lu, X., Guo, Q., & Zhang, Y. (2023). The Spatiotemporal Measurement of Coordinated Development of Resource-Environment-Economy Based on Empirical Analysis from China’s 30 Provinces. Sustainability, 15(8), 6995. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086995






