Abstract
Growing global production leads to continuing generation of waste, part of which still ends its life cycle in landfills and dumps. Despite the efforts of waste reuse and recycling and waste self-degradation, existing and old landfills and dumps remain a huge challenge for the future. The majority of landfills can be identified as non-sanitary and can be designated as existing or former dumps, meaning hills or fields of abandoned garbage and degraded inert waste masses without any or with little aftercare maintenance. In contrast, the term ‘landfill’ refers to legally organized waste disposal sites created in a controlled manner, according to modern environmentally responsible standards. The paper gives a case study-based integrated assessment of closed and revitalized waste disposal sites that have undergone a functional change from ‘lost territories’ to primarily green space beneficial for society and the urban environment, in terms of ecosystem services estimation based on the criteria evaluation approach and monetary assessment of land assets value recovery potential. The chosen four case studies (in the United States, Australia, Poland and Estonia) serve as successful examples of a sustainable degraded site revitalization gateway indicating opportunities for accelerating land value through the prism of ecosystem services estimations and spatial planning criteria. Beneficial value of land assets after site revitalization is assessed in monetary terms.
1. Introduction
The progress of civilization and economic development are greatly based on demand and supply, accompanied by infinite production and servicing, leading to waste generation. For decades, the world has been facing global problems related to resource depletion, limited space for waste disposal, accumulated environmental pollution, and loss of valuable lands. About 11 million tons of various wastes are produced daily around the world [1]. Yearly, around 2 billion tons of municipal solid waste is generated globally, but its amount will increase to 3.4 billion tons per year by 2050 [2]. Despite the efforts of waste reuse and recycling and waste self-degradation, existing and old landfills and dumps remain a huge challenge in the future. Sustainable management involves proper site revitalization integrating resources extraction and return of the land to a state meeting the needs of society and the economy [3,4,5]. The EURELCO (European Enhanced Landfill Mining Consortium), an open quadruple helix network specifically working on landfill mining issues, in 2018 estimated that 500,000 landfills were located in Europe containing up to 80% of urban solid waste (the remaining 20% refers to specific industrial waste). Furthermore, the majority of these waste disposal sites were publicly owned, and only 20% were privately held. According to the Landfill Directive of 1999, last amended and consolidated in 2018 [6], the majority of landfills can be identified as non-sanitary and can be designated as existing or former dumps, meaning hills or fields of abandoned garbage and degraded inert waste masses without any or with little aftercare maintenance [7,8]. In contrast, the term ‘landfill’ refers to legally organized waste disposal sites created in a controlled manner according to modern environmentally responsible standards [5,6,9]. A rough assumption indicates that if Europe accounted for around 15% of the world economy in 2019, the number of non-sanitary dumps might range from 3 to 5 million sites globally. The largest of them can be mapped (Figure 1); however, this does not reveal the whole global waste disposal picture [7,10].
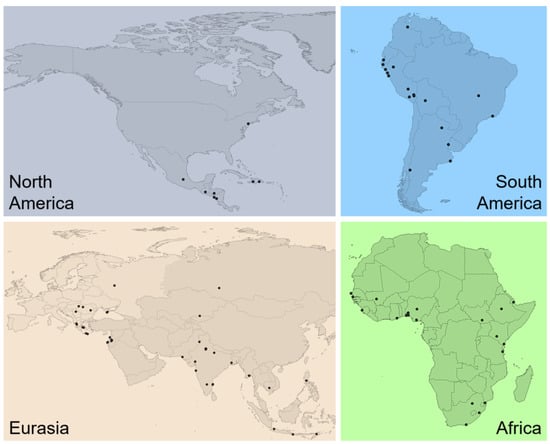
Figure 1.
Schematic mapping of the largest uncontrolled non-sanitary dumps worldwide, reflecting only documented sites; authors’ work after [10].
Notwithstanding, precise estimation of existing and former non-sanitary dumps is practically impossible, not only due to the various statistical approaches used for accounting but also because of historically undocumented, hidden disposal of waste and illegal mixing of various waste types—from municipal waste to industrial and even mining waste, not excluding traces of hazardous waste [4,11,12,13]. It is indisputable that large urbanized areas as well as wastelands pose increased risks of negative impacts on the environment including all its subjects—flora, fauna, soil, water and humans.
Status improvement and revitalization of degraded sites such as closed landfills and former dumps is an obligation that the past and present owe to future generations, and it should be supported by governments and municipalities. Waste management per se is not able to improve the status of abandoned waste disposal sites directly, but some approaches to landfill mining can be the right choice. At best, dumps are intended to be revitalized for the purpose of surrounding environmental improvement, adding societal value to degraded areas and maintaining public health [8,13,14,15,16]. Added value can be increased by material and energy recovery but, generally, only a small part of old or closed landfills and dumps deals with modern recycling and waste logistics centres nowadays [17,18,19,20].
The transition from a linear to a circular economy approach involves the identification and estimation of secondary material flows by constructing network models in accordance with the input–output analysis. It helps to increase productivity and environmental management perspectives and creates closed loops for resource circularity that are hugely significant for sustainable future development [21,22,23]. The circular economy concept was introduced by David Pearce in 1990 and is directly linked with industrial ecology. In a way, it means a type of open-ended system with the aim of reducing circulating matter and energy within the economic system, trying to fight against rising entropy [24,25]. Initially, the circularity referred mostly to material and energy loops either in space (areas) or abstract, less tangible matter and terms [26]. Lately, the discourse has been applied to eco-industrial parks and the implementation of circular economy ideas beyond direct material and energy flows, devoting greater attention to urban planning policies and management [27,28].
Revitalized landscapes do not consist just of substances and matter. The integrated landscape includes intangible elements such as ecosystems providing esthetic, social and spatial cognition potential and nature-regulating services for the surrounding inhabitants and public space users [29,30,31]. Notwithstanding, it is still meaningful to take into account land asset recovery, whether it is to be used in future in the interests of society for cultural, recreational, sports or industrial purposes, or in terms of more abstract values such as ecosystem restoration, bringing the benefits of improved ecosystem services favorable for society and the whole environment [4,29]. The largest difference between the evolution of natural and human-affected (residential, industrial or waste disposal sites, etc.) landscapes is that the latter includes an artificial concentration of materials and concentrated energy flows [32]. Smart management is necessary to reduce the excess of materials and energy leading to entropy increase. Even if the revitalization process is aimed at the long-term benefit of society and the environment, it might happen that the restructuring of a degraded site into a park or green space is not an absolute guarantee of public acceptance. Part of society realizes the benefits of site revitalization from the earlier ‘lost land’ stage; however, another part often retains a reserved attitude based on the assumption that revitalized areas pose hidden environmental and health threats that are just camouflaged [33]. Studies reveal that site transformation to green space is the most preferable revitalization manner, as the public attitude to this on average is relatively neutral [31]. Additionally, if the basic targets of revitalization are achieved successfully, other land use options beyond the creation of parks might become attractive in the future; even constructing residential areas on the edges of transformed landscape cells, which is especially meaningful for overpopulated areas [34,35].
The paper gives a case study-based integrated assessment of closed and revitalized waste disposal sites that have already undergone a functional change from ‘lost territories’ primarily to green space beneficial for society and the urban environment in terms of ecosystem services and land assets recovery. The chosen four case studies serve as successful examples of a sustainable degraded site revitalization gateway, indicating opportunities for improving land value through the prism of ecosystem services estimations and spatial planning criteria.
2. Methodology
2.1. Case Studies of Revitalized Sites
Four representative case studies of revitalized former waste disposal sites located in the United States (Freshkills Park), Australia (Sydney Olympic Park), Poland (Gorka Rogowska former landfill) and Estonia (Kudjape former landfill) were selected for the integrated assessment due to their successful functionality change to green space (Table 1).

Table 1.
Description of selected case studies—closed and revitalized waste disposal sites.
These case studies represent a beneficial transformation of large and medium waste disposal sites and land asset revitalization on a global scale. The cases were chosen carefully based on available information on their revitalization performance and the possibility of applying parameters to estimate ecosystem services recovery impact and real estate value predictions. Furthermore, the selected case study sites currently are open (or partly open) areas accessible to the public and were recently visited by the authors on-site (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Characteristic landscapes at the sites of the case studies: (a) Freshkills Park in 2016; (b) Sydney Olympic Park in 2018; (c) Gorka Rogowska in 2022; (d) Kudjape Park in 2022 (photos taken by the authors).
The cases are unique in their planning and revitalization management, with various sizes, locations, climate zones, geotechnical properties and disposed waste amounts and composition. Many former dumps face the problem of hazardous waste residues and related environmental pollution, which should be solved first of all. Most often, revitalization of closed waste disposal sites is implemented in a ‘closed to public’ manner, which was not the case for the selected case studies, where the sites were relatively quickly redeveloped and used immediately after revitalization. They faced legal restrictions, specific rules from authorities and a long and harsh process of obtaining permissions, planning, allocating monetary resources and implementation [6,7].
Usually, if the former degraded site covers a large territory, the scope of stakeholders includes governmental and municipal authorities, experts, construction and project planning companies, society, non-governmental organizations, as well as developers, managers and financial bodies. Therefore, the estimation of legal barriers and options to overstep them should follow in a proportional manner. It was considered that for the selected case studies, these barriers were overstepped and, instead of degraded and closed areas, society received functioning green space with opportunity for further development, but without a specific gap in time for monitoring and environmental margin of safety.
2.2. Estimation of Ecosystem Services’ Recovery Potential
The practices of ecosystem services’ estimation (ESE) and their recovery potential assessment are mostly based on the Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services (CICES) classification, dividing them into three main groups: provisioning, regulating and cultural services [53,54]. A similar classification is also provided by the Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB), the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA), and the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) expanding additional supporting ecosystem services [55,56,57]. The ESE approach is widely conducted in scope to map categories that supply or have potential to provide services valuable for human use and meet demands of what society requires [58]. ESE by quantification can be applied to various spatial (land cover, land use, landscape patterns) and temporal time scales based on vast types of methodologies, depending on the assessment purpose [59]. Ecosystem assessment and mapping can be a complex series of steps; the most used is the ecosystem services matrix approach (ESMA), arranging ESE dimension values in relative scores according to certain indicators [60,61]. Generally, the assessment methods are divided into three types: biophysical quantification [62], sociocultural valuation approach [63], economic quantification [64], and incorporation into the three-pillar sustainability concept (social, economic, environmental) [65].
Applied simplified approach of ESE to degraded site revitalization was based on the general methodology [53,54,55,56,57,58,59] of criteria evaluation according to available information on the case studies. In the performed case study evaluation (Table 2), the criteria were assessed as ‘more relevant’ (M) or ‘less relevant’ (L), meaning that they were not essential in the case of degraded site transformation to green space, but could be relevant for other revitalization projections. The significance of selected indications was assigned taking into account the suitability of the set of ecosystem services in the framework of degraded sites’ ecological and natural potential linked to economic, social, nature-related and revitalization-driven aspects. Criteria evaluation was based on certain methodological steps including assessment of targets, accessibility, public acceptance, complexity and revitalization implementation practice.

Table 2.
Criteria evaluation for ecosystem services estimation at former waste disposal sites transforming them to green space (M—more relevant, L—less relevant).
Referring to scientific publications, the ESE approach has not been widely used in degraded site revitalization planning processes. However, the methodology is able to provide a holistic overview and complex analysis of the major environmental, socioeconomic losses and benefits delivered for society and nature. For instance, modeling including ESE can be applied to supply scenarios supporting decision-making for site-specific restoration of quarries and brownfields [66,67], mine reclamation impact of ecosystem services supply in the long-term period on a regional level [68], involving stakeholders in the decision-making process of rejuvenating ecosystem services by reclaiming degraded land and brownfields [69,70], and raising the supply of ecosystem services in urban areas based on sustainable degraded site redevelopment [29,71]. The criteria-based evaluation for each case study was performed entirely by the authors using available information and documented facts, providing input data for the system-dynamic flow charts designed for each case study. The outcome flow charts were not weighted by the impact of importance, but the interaction between the challenging problems and solutions is shown.
2.3. Valuation of Land Assets
The process of former waste disposal site revitalization and functional redevelopment is very individual as every site has a specific history of waste dumping, various amounts and types of waste dumped, different landscapes, climatic conditions and geomorphology [43,50,52]. Green space, especially in urban areas, has a highly appreciable value but is difficult to assess in monetary terms. Esthetic, air and water quality improvements provided by green space are highly important merits for human welfare accompanied by recreational, leisure and cultural values, mostly evaluated by indirect means of economic analysis [57,69,72]. Among feasible approaches, market analysis can be applied if exact monetary gains need to be estimated, including the real estate pricing and municipality income from taxes paid by property and business owners, as well as spending coming from tourists [73,74]. Estimation can be based on generalized assumptions of direct and indirect gains for the real estate prices in step with health and welfare-related and social cohesion improvements that lead to lower expenditure on social care and inequality-related losses [30,75,76]. The assessment of revitalization projects includes the following aspects: (a) natural—geotechnical, geomorphological, ecosystem, pollution prevention and hydrological issues; (b) economic—land value, infrastructure and geographical location, future perspectives of land use; (c) social—opportunities for new jobs, recreation, cultural value and social acceptance. The case studies reveal former dump and landfill revitalization primarily achieved by transformation into green space but with further development perspectives. Selected case studies were evaluated based on the analysis of these three main aspects, valuing land as assets including real estate property tax, tourism and general welfare improvement potential, thus integrating direct and indirect assessments according to tangible and intangible benefits for society [77]. Projections were estimated by real estate property pricing evaluation for the vicinity area of case studies performed through the analysis of real estate websites [78,79,80,81,82,83,84] according to the pricing in December 2022. Monetary estimation is expressed in euros according to the timely currency exchange rate.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Green Space Reclaimed from the World’s Largest Dump: Freshkills Park
The largest documented dump in the world had been operating since the 1950s at its location in New York Staten Island, mainly in a landscape that was a salty marsh. The amount of waste gathered there from New York City and its vicinity was estimated at 26,300 metric tons of garbage every day. Waste dumping resulted in 136 million metric tons of solid waste spread over 931 ha [36]. An international revitalization design tender with the involvement of the community led to the idea of creating green space: Freshkills Park [36,37,38,39]. Analysis of this case revealed that the main concerns for residents and authorities were health and environmental issues, and only afterwards possible resource reuse and property prices gained significance. The main spatial intervention for dump reclamation to make the public park was performed by transformation through ecological renewal, applying methods often used in the ESE approach. Apart from defined main revitalization targets and results, co-benefits were reached to address local issues and respond to future ESE demands. Multiple effects of environmental, social, political and economic interests’ integration in the dump transformation process were identified (Figure 3). Regarding the ESE approach, obviously, a wide range of experts was involved, and local community consultations and information dissemination were performed to develop the revitalization masterplan [85,86] in line with the set of biophysical ESE implemented by indirect measurements (expert-based estimation), direct measurements (field observation, monitoring data) and sociocultural ESE realized by society’s involvement and detailed management plan analysis.
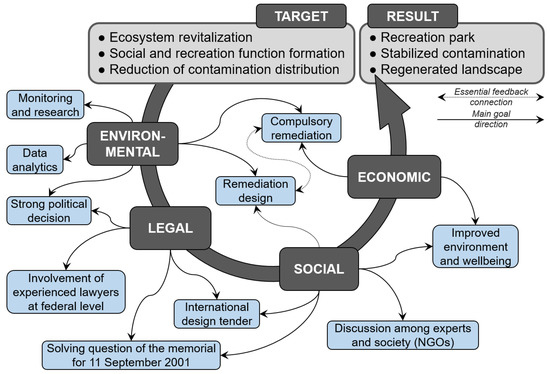
Figure 3.
From target to result through environmental, legal, social and economic challenges: revitalization of Freshkills Park site.
Regulating, maintaining and cultural interest regarding ESE have been strongly considered through site-specific traditional values [36,39]; for instance, pollutant filtration and sequestration by micro-organisms, algae and plants, hydrological cycle and water flow regulation, maintaining flora and fauna nursery populations and habitats, and esthetic experience involving symbolic future meaning. Generally, Freshkills Park is a representation of sustainable ESE trade-off management, at the same time gaining new ESE values, meaning and functions in society. Revitalization of this huge degraded territory to green space open for society is an impressive project not only on the country scale for the United States but also globally—it is the largest dump ever to have been revitalized with a financial budget exceeding USD 600 million [87]. When evaluating the dimensions of restored ecosystems, the project’s financial value and the impact of the final result on the socioeconomic development of the region, ESE was carried out very scrupulously in several project implementation stages and paid great attention to details. Recovery of the ESE sustainability was ensured by integrating public and environment-related interests with the methodologies used in ESE. The main driver of ecosystem revitalization and ecosystem services recovery anyway is political will, and in this case study there was also a strong public initiative.
Except for the impressive dimensions, projects comparable in measures of ESE revitalization cases and rejuvenation of ecosystem services include the Tehri Garhwal area in Uttarkhand (India) [69], belonging to a sensitive Himalayan ecosystem [88]. There, reclaiming of degraded land was achieved by the complex evaluation of ecosystem services, simultaneously applying a broad scale methodological approach involving multi-stakeholder consultations, and interventions were estimated to improve natural resource management, biodiversity recovery and carbon sequestration potential. Consequently, it can be assumed that scaling of projects is of importance, but not the limiting factor in ecosystem services evaluation in degraded site revitalization.
One must not forget that the Freshkills Park site is a special place regarding the tragedy of 11 September 2001 in New York due to the disposal of the Twins Towers’ debris there after its removal from Manhattan. An international design competition was initiated to find the most appropriate solution for transforming the dump into a green space with flourishing biodiversity, serving also as a memorial place for 11 September 2001, although some expressed worries about possible health, psychological and emotional issues [36,86,89]. Still, the discussion is open on what exactly should be the best landscape and sculptural design for finalizing the memorial place. Besides, the Freshkills Park project provides wide opportunities for sustainability, including ecosystem restoration and recreational, social and cultural functions as well as a plan for further monitoring and development [36,37,38].
3.2. From Dump to Olympic Dream: Sydney Olympic Park
Waste dumping leading to soil and water pollution in one of Australia’s largest cities began at the site currently known as Sydney Olympic Park in the 1950s, resulting in significant threats to the environment. More than half of the area (>300 ha) basically was industrial land with all the related consequences of dumping contaminated soil and industrial residuals on-site in the wetlands. Industrialization became more intense, as did municipal waste flows and dredging and dumping of filled soil from the Parramatta River in mangrove forests [40,41,42]. The site became neglected land in the 1980s, later followed by the urban renewal activities around Homebush Bay park, including the former Olympic City and new residential areas including the Sports Centre, the Australia Centre and the opening of Bicentennial Park [40,41,42,43,44,90].
Today Sydney Olympic Park represents an urban biodiversity hotspot, a contracted wetland system known as an ecosystem able to provide a wide range of regulation and cultural ESE in an urban area [41]. While defining revitalization targets and achieving results most beneficial to society, the ecosystem’s health and its condition and ability to provide locally demanded services were emphasized as the most important. At the initial stage, the revitalization process was managed by the life cycle assessment approach with the purpose of reducing the environmental impact of the fast-growing development [91]. Nowadays, the site involves a green space with ponds and a revitalized ecosystem. In the late 1990s, the ESE approach was not a widely used tool for spatial planning and decision-making processes although both methodological approaches, used for the same aim, can overlap, leading to strengthened results. Revitalization of the case study site from the ESE suitability indicated that biophysical assessment was done by a complex engineering process (expert-based estimations) using also simplified model-based tools such as restored land and property values (Figure 4). Targeted environmental legislation in favor of the ecosystem’s reconstruction resulted in significant biodiversity conservation potential, providing a range of ESE, mainly promoting pollutant filtration and sequestration processes in the wetlands, hydrological cycle and water flow regulation by freshwater systems, saltmarsh meadows and woodlands, maintaining pollination, flora and fauna populations and microclimate regulation by all types of habitat naturalization.
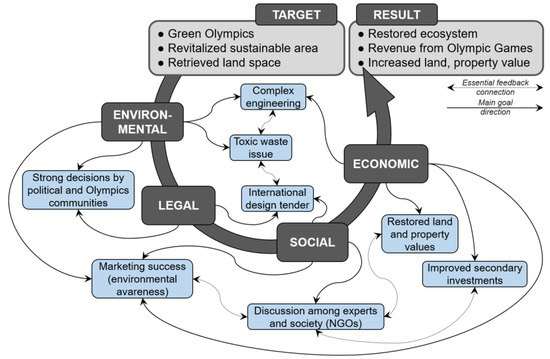
Figure 4.
From target to result through environmental, legal, social and economic challenges: revitalization of Sydney Olympic Park site.
Landscape reconstruction in terms of environmental management activities led to enriched visitor experiences and enabled recreational opportunities—active and passive interactions with nature, environmental education and esthetic experiences integrated into the urban environment. During the revitalization process, highly intensive interaction between ecosystem health and local economic stabilization and development potential was assured by the ESE economic assessment methods, such as direct market pricing and total economic value. The case of Sydney Olympic Park serves as a great example of returning ‘lost land’ to society and how the socioeconomic values of a place are increased by improving ecosystem conditions. During the revitalization of degraded territory at Sydney Olympic Park, nature rejuvenation was emphasized by wildlife habitat restoration. This resonates with other projects; for example, a quarry site restoration in terms of ESE in Arrabida Natural Park (Portugal) [92], where great emphasis was put on pollination as an ecosystem service enhancement using biophysical assessment methodologies resulting in accelerated biodiversity, consequently having positive impact on other ecosystem services.
Site revitalization in the case of Sydney Olympic Park was the largest remediation and degraded land recovery project in the history of Australia and Oceania. Currently, the site is unique with its world-class facilities, residential areas and facilities for sports, recreation and cultural events.
3.3. Gorka Rogowska Landfill Transformation
Gorka Rogowska is a former landfill located in Lodz Voivodeship, situated in the central part of Poland, now partly transformed into green space open for recreational activities such as walking trails, picnic places and landscape viewpoints. The surrounding area is occupied by Lagiewnicki forest (1200 ha) serving as a promising place for aerial planning of semi-rural and urban infrastructure with excellent potential for single-family housing estates [45,46,47]. The former landfill, mainly consisting of construction waste, has much better geotechnical characteristics and stability than the dump sites filled with municipal waste. Gorka Rogowska former landfill site is officially approved by the authorities as a strategic area important as an additional recreation centre and city complex development in the future.
The potential development opportunities of the case study site that have been discussed so far emphasize the economic development of the urban environment. The ESE approach is a popular tool to estimate the most sustainable land cover transformation regarding economic development, especially for intensive construction.
The ESE regarding Gorka Rogowska consisted of using all environmental knowledge (any of the biophysical assessment methods) and sociocultural demand (GIS tools, management plan analysis), assessment of loads on the ecosystem by direct measurements (field observations, monitoring data, surveys and questionnaires) and analysis from the economic perspective (e.g., damage costs avoided method, replacement costs, MRC method, contingent valuation method (willingness to pay), benefits transfer method, hedonic pricing method). A similar evaluation of the development possibilities for the degraded area was carried out at former limestone quarries located in the province of Limburg (the Netherlands) [66], where the ESE implementation started with cooperation among the involved parties, successively evaluating the biophysical benefits and then translating them into monetary values via economic valuation methods.
However, the discussion and decision-making process for the Gorka Rogowska landfill transformation lacked a full range of stakeholder involvement from the initial stage (Figure 5). If Freshkills Park and Sydney Olympic Park serve as lessons for learning based on experience, possibly replicated in other degraded ecosystems’ wise reconstruction to provide sustainable future directions, then the Gorka Rogowska site is a significant part of the urban landscape indicating the need to involve local stakeholders in the development planning process and to create future scenarios by comprehensive ESE demand.
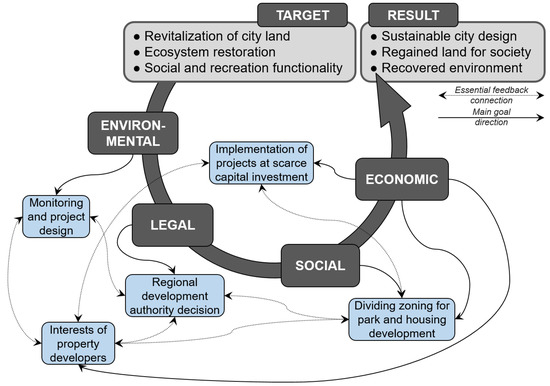
Figure 5.
From target to result through environmental, legal, social and economic challenges: revitalization of Gorka Rogowska former landfill site.
At the moment, the revitalization project of Gorka Rogowska is in a temporary stage consisting of assessing slope geomorphology on the landfill hill according to the landscape architecture projections. The hill is covered by natural but regularly maintained vegetation. The site is open to the public, but further development is suspended due to the lack of finances.
3.4. Kudjape Landfill: Serving Society and Science
The former Kudjape landfill is located in the western part of Estonia, in Saaremaa—the largest island of the West Estonian Archipelago in the Baltic Sea. Until the landfill closure in 2009, all the waste was just dumped in a heap without any proper sorting or treatment. It is estimated that about 200,000 m3 of waste was disposed of there. Initiation of the revitalization project at the Kudjape site was set as a mandatory obligation forced by the regulations of the European Union. Long discussions among authorities, engineers and environmental scientists led to the decision to perform landfill mining with the creation of an innovative material to cap the landfill’s surface properly. It was necessary because another cover material with low porosity, such as clay, was not available on the island, and material transportation over the sea was costly and environmentally unfriendly. The local regulation required the waste capping with a 1.5 m thick layer of secondary material derived from a fine fraction of waste. The cover material was obtained from approximately 80,000 m3 of waste after careful sorting and sieving by specific techniques, adding matured compost and regular soil [48,49,50,51,52].
In the case of Kudjape former landfill, environmental recovery was led primarily by cultural ESE demand, less taking into count the surrounding habitat type and relic ecosystem’s structure and function before the waste disposal site. Landscape biophysical analysis was performed using GIS tools, aiming to promote local ecosystem-based recreation opportunities to improve the esthetic landscape value and fully realize the ecosystem’s potential to provide services. For a far-reaching study to gain comprehensive data, it would be best additionally to apply integrated evaluation methodologies such as integrated valuation of ecosystem services and trade-offs, or artificial intelligence environment and sustainability tools to assess specific ecological processes of nature and society interaction and to design their connection as part of a flow network. In assessing Kudjape’s former landfill revitalization management, the process differences between Freshkills Park and Sydney Olympic Park’s revitalization emerge: improvement of regulation and maintenance ESE subsidiary values contribute to higher socioeconomic benefits (Figure 6). Recovery of the Kudjape site started the other way around, with initial adjustment of the ecosystem to promote socioeconomic landscape value; in the future are intended slow ecosystem naturalization processes to ensure non-specifically defined regulation ESE. The detailed ESE approach definitely provides comprehensive information on the development potential of a degraded area, taking into account the overall physical site characteristics, the public’s demand for ecosystem services, as well as the created anthropogenic load on the ecosystem. Another example is the urban brownfield revitalization conducted in the UK [29], indicating that trade-offs in ecosystem service demand can be a determining factor in the proper selection of the ecosystem restoration approach.
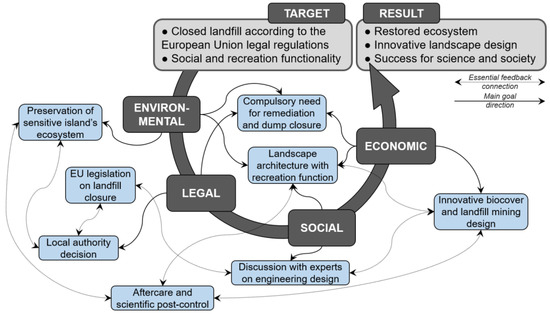
Figure 6.
From target to result through environmental, legal, social and economic challenges: revitalization of Kudjape former landfill site.
The design of the new Kudjape hill, after the beginning of the former landfill revitalization, was changed a few times to give a better shape for skiing, recreation and picnic areas as well as to make it a more interesting geomorphological landscape in a naturally flat area. The design of revitalization took in account three main things—technical needs, esthetics and sports facilities requirements. The final design was created to be safe for hobby sports and active leisure, friendly for families with children and serves as a much needed green space for society. For safety reasons related to more public places, the primary site was covered over by pure soil on top. The acceptance of the recreational areas by the public is being evaluated.
Assessment for scientific purposes at Kudjape is still continuing. Scientific research is being conducted on planted vegetation and methane monitoring; furthermore, a team of botanists and microbiologists had been performing a study at the site for almost a decade when the revitalization began. The objectives of this project, not big in size but in the Baltics region unique, included analyzing sustainable landfill mining opportunities, testing the long-term functionality performance of this innovative cover layer (in terms of landfill gas emission safety) and the response of planted vegetation and microbiota.
3.5. Integrating Recovery of Land Assets and Ecosystem Services
The discussion on land assets’ potential needs to be determined in the framework. On one hand, land assets and land cover are significant from the ESE approach, but on the other hand, land as a real estate platform for future development means assets recover and value increases after a degraded site is revitalized. Implementation of a full-scale revitalization project at a dump, landfill, mining site or other degraded area requires efforts mainly to decrease or eliminate environmental and health threats and, if possible, regain the economic value of assets from recovered (excavated) or reused (in construction/demolition and mining waste option) material [16,19,31,57]. Real estate has undoubted significance either for commercial or public sector interests. Land per se can produce value in the form of goods and services. Its value varies within the range of estimates of future productivity and might be based on calculation-based assessments, historical data-based predictions or also subjective speculations [77]. The value of the land as an asset commonly exceeds the value of its contents in scaling large degraded areas utilized by the mining industry, where remains of depleted ores might be significant as well as deposits situated deeper in the ground and available for extraction in the future [16,50,93]. Revitalization and operational costs of degraded sites are very high; therefore, evaluation including a full set of gains from an environmental perspective, valorization potential of recovered land (future public parks and industrial zones), additional (new type) sanitary landfill space, recovery of esthetic landscapes and revitalization of ecosystem services have to be included in the estimation [94]. Urban regeneration of degraded sites, including abandoned dumps and landfills, besides taking into account many other aspects has to analyze social acceptance, which is significant in promoting the rise of the value of suburbs and degraded areas. Transformation, when coupled with the circular economy approach, promotes a tremendously great choice of options for how these areas may serve society and site-specific decision-making processes might lead to better scenarios and higher land asset values [95]. Integrating the recovery of land assets and ecosystem services leads to long-lasting and more sustainable results for the environment and society. Table 3 indicates attributed parameters for integrated assessment regarding the selected case studies according to site-specific choice of applied methods, project progress and success to achieve the set of revitalization targets, the scope of influences and scaled significance. It is obvious that sociocultural assessment is undoubtedly of high importance in all cases in terms of both ESE and land assets value estimation.

Table 3.
Criteria-based ecosystem services impact on land assets value evaluation for the selected case studies (A—applicable, N—not applicable).
Basically, the real estate potential estimation, meaning the value of the land whether it is degraded, contaminated or legally restricted to be used for broader purposes from the ecological point of view, is dependent on fundamental analysis of market trading transactions in the selected area. As the land assets never relate to short-term investments, the legal issues may be disregarded and revitalization expenses may be subtracted from the land value. That can lead to accumulated wealth in the future if the land is used for multiple purposes. Property buying and selling transactions at the very moment may give an insight into how much the land would cost if remediated and legal and/or ecological restrictions are taken away. However, in most cases, abandoned dump sites need to undergo remediation anyway; therefore, the calculation requires a comparison of the options for remediation technologies and planning the risks of legal obstacles for the reuse of the land in the nearest future [96,97]. After the analysis of case studies, four main directions of gained benefits from landfill revitalization were distinguished—economic, environmental, esthetic and legal (Figure 7). They may serve as a basis in the universalization of potential pros and cons assessment if a revitalization project is planned to be performed, whether the degraded site is large or medium-sized.
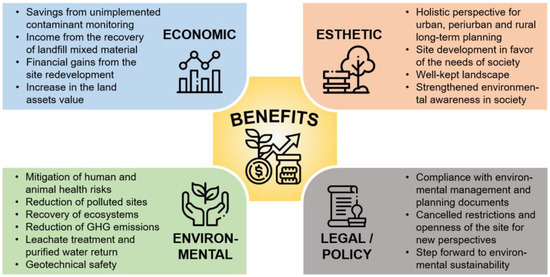
Figure 7.
The directions of benefits gained from landfill and dump revitalization.
The contemporary context of landfills and dumps situated in (or close to) cities and towns with urban growth potential offers promising solutions if the optimal way for site revitalization is found. The conditions of dumps and site-specific geographical/geomorphological peculiarities define the possible reuse and reform possibilities according to the applicability, feasibility and landscape design principles. If these sites are unused, they are burdens to society and their surroundings require special attention from authorities as well as restrictions to the public. However, excessive control leads to unnecessary bureaucracy when revitalization initiatives are planned and project developers show interest in investing. This leads to duality and so-called ‘territories of the possible’ [98]. The complex infrastructure of urban areas requires an individual approach, architectural integration and deep practical understanding in the assessment of physical parameters related to soil and environmental chemistry.
Reclamation usually is intended to regain land as an asset, and in case of further reuse for various purposes, the interpretation by designers and planners leads to the decision of whether to make the landscape green and visually interesting in terms of geomorphology (parks and recreation sites), practical and easy for infrastructure building while at the same time reducing environmental impacts (industry parks, road systems) or practically regaining the space for the new material to be landfilled, if the space is still needed for the recycling industry and some part of active landfilling remains [98]. The existing landscape always has to be assessed in the scope of urban planning, and the holistic approach must be applied. Reclamation of space is question number one if the landscape is reformed leading to new contemporary functions of space. Transformation is part of a larger outlook and strategy plans for the industry and community [16,50,98].
The value of restored land was estimated according to the timely data on real estate pricing in case study areas as well as analyzing similar approaches of green space value determination [30,73,74,75,76]. The analysis (Table 4) revealed that in the case of large-size restored dump sites, the proportion of real estate tax benefit is significantly higher as well as having a direct touristic benefit for the economy. In the case of medium-sized dumps such as Gorka Rogowska and Kudjape, more indirectly estimated benefits prevail regarding the health and welfare improvement for the residents in the vicinity and local benefits of esthetic and recreational value. Here might be added the point of discussion regarding the valuation of social cohesion and ecosystem restoration benefits for the environment, but this part is left out of the hedonic calculation and is analyzed further. The important aspect is not to mix the property’s potential value with the property tax amount improvements, because land as an asset in metropolitan and even average-sized cities and suburbs is immense. The analysis was targeted to the improvement of the economic benefits indirectly enhanced through establishing green space in absolutely degraded areas, which pose significant environmental threats that can be calculated from a monetary aspect. This part was excluded because of variability of local political and legislator decisions.

Table 4.
Analysis of real estate value integrating achieved benefits related to regained touristic attractiveness, welfare issues and direct use of land in the case study sites; expressed in euros based on the data of December 2022 [78,79,80,81,82,83,84].
The estimation from the improvement of land as an asset revealed that for large-sized revitalized dump sites, the greatest value was attributed to direct use, tourist business development benefits and pure hedonic property tax improvement benefits for the country itself. Here, the improvement in business activities was not analyzed that would arise from a revitalized and esthetic landscape free from legal restrictions in the future. On the regional scale from medium-sized dump sites, the proportional value of gains is much higher through indirect benefits. On the other hand, it can be considered as a clear benefit estimated in countable monetary values (as estimated for selected cases in Table 4), as in the so-called ‘zero scenario’ equal to ‘no action performed’, the real estate, direct use value as well as tourism virtually do not exist and the latter one is banned in most cases. The monetary calculations provided in this study indicate the amounts for the improvement of situation in real estate market, tourism and recreation as well as direct use value increase if taking ‘zero scenario’ as the base. Depending on the calculation approach, it could be assumed that the value might be even negative if revitalization is not implemented due to the mandatory maintenance regarding leachate drainage, monitoring of emissions and other specific reasons, such as fear of the broader spread of environmental pollution and issues regarding the armies of birds common at dumpsites. Thus, the valuation performed in this study indicates clear benefits even when excluding ESE and social cohesion.
Similar quantifications and qualitative research for brownfield revitalization projects has been performed, for example, in Antwerp (Belgium) [71]. The Nature Value Explorer tool was used for estimations of benefits and losses for green infrastructure such as green corridors and their geomorphology that links the urban periphery to nature reserves. The green infrastructure that provides ESE versus the value of recreation benefits has shown the domination of the latter. Such case studies raise the problematic nature of dualism for existing ESE and economic benefit analysis; the comparison might become more accurate and reliable in future advanced analyses that would include deeper structured approach of environmental social governance [99].
Regarding the improvement of ecosystem services, additional calculations would lead to even more positive results as even with direct calculation it is possible to estimate the value of every clean cubic meter (treatment costs or substitution) of soil, treatment costs for water from leachate and washed-out pollutants with consequent environmental damage. In such large-scale activities, necessary from the legal aspect, the benefits can possibly be added directly without the remediation costs as the processes are inevitable due to political decisions. Regarding social cohesion, a more detailed analysis of any local (regional) society voluntary activity is needed, meaning that every volunteer working hour with its added value might be considered as an additional benefit.
The described case studies with their implementation management, economic evaluation and ESE aspects can serve as know-how and learning materials for the future. A combined approach that joins all environmental social governance aspects as well as policy framework reflects how revitalization of degraded sites can be achieved despite various obstacles that can be taken into account for future projects at state, regional or municipal scale. Such projects implementing wasteland transformation into green space cannot be developed only under scientific or environmental social governance standards. The economic benefit for business stakeholders, enthusiasm of implementers and lenience of policy makers should be integrated and act as catalysts. Just obligations or restrictions will not lead to beneficial result for the society. Uncoordinated and disintegrated actions result in vast resources spent on formal remediation but future land use still remains restricted with monitoring a necessity, fences around the remediated land and unattractive dome-type landscapes. Therefore, active involvement of society with bottom-up initiatives should be engaged, offering a role for the thinking, voting and acting stakeholder to contribute.
4. Conclusions
The revitalization of dumps and landfills must be focused on benefiting three main pillars: society, environment and economy. Transformation of degraded sites such as dumps and landfills into green space definitely improves urban land quality and induces new patterns in a circular economy’s practical implementation. -Environmental requirements for a revitalized ecosystem must be balanced with the necessities of newly acquired space from the point of view of landscape architecture and further economic use. Public and economic thinking should be directed beyond hedonic and tangible aspects by working on the return of lost land to society and nature-degraded areas creating new functions and adding the beneficial potential of ecosystem regeneration and new infrastructure.
The benefits of large-sized former dump revitalization projects are the following: (1) pure direct property value increase; (2) direct income benefits from taxes and business development; (3) significantly improved land value in vicinities; (4) environmental awareness strengthening on a worldwide scale. For medium-sized revitalization projects on the regional and local scale the benefits can be ranged as: (1) improved ecosystem services (quality of water, soil, air); (2) better health and welfare for residential population; (3) improved recreational opportunities for the local population.
The roadmap for future revitalization projects of former waste disposal sites, first of all, requires taking the right political decisions based on sustainable development goals. In this way, the legal barriers can be overstepped and the will of authorities to improve the environmental situation and look at the problem from a wider perspective for the future can be consolidated. Significant is the ‘triple helix’ approach of collaboration among authorities, business stakeholders and society with the one aim: restored ecosystem and better quality of life. The thing to remember is that ecosystem and public health is the weightiest component in the equation, and with the growing urbanization and greater need for green space, this aspect will only increase in value. The analyzed case studies indicate that holistic revitalization brings not only a comprehensive overview and contribution to sustainable development but ensures long-term benefits according to today’s growing environmental requirements to a wide range of stakeholders at one time. This means that, at the beginning of future revitalization projects of former waste disposal sites, the answers to questions as to ‘whether’, ‘to what extent’, ‘dimensions of funding capacity’ or ‘expanse of economic return’ should be based on full-scale ESE: biophysical, sociocultural and economic quantification of ecosystem services’ supply flows, potential, demand and impact of use in different time-frame dimensions; thus, providing answers to questions of strengths and weaknesses to prevent controversial spatial development decisions. The role of society in bottom-up initiatives, and its voice, should be significantly enlarged.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.V.-G., J.B. and M.F.-K.; methodology, J.B., M.F.-K., V.R., I.G. and K.S.; validation, E.H., M.K. (Maris Krievans), H.A.A. and M.Z.; formal analysis, J.B., M.F.-K., E.H., H.A.A. and M.Z.; investigation, Z.V.-G., J.B., M.F.-K. and K.S.; resources, M.W., I.G. and M.K. (Mait Kriipsalu); data curation, Z.V.-G., V.R. and A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.V.-G., J.B. and M.F.-K.; writing—review and editing, Z.V.-G., J.B., M.F.-K. and V.R.; visualization, Z.V.-G., M.K. (Maris Krievans) and A.G.; supervision, M.W. and M.K. (Mait Kriipsalu); project administration, J.B. and M.W.; funding acquisition, J.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
J.B. acknowledges the support received within the PASIFIC program “GeoReco” project funding provided by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program within the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No.847639 and the Ministry of Education and Science (Poland). H.A.A. acknowledges collaboration with the Environmental Research Centre (CRE) at Badji Mokhtar Annaba University (Algeria) and the Research and Study Laboratory in Planning and Urbanism (LREAU) at the University of Science and Technology Houari Boumediene (USTHB) (Algeria).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- The World Counts. Waste. Available online: https://www.theworldcounts.com/challenges/planet-earth/waste (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- The World Bank. Trends in Solid Waste Management. Available online: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/what-a-waste/trends_in_solid_waste_management.html (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Johansson, N.; Krook, J.; Eklund, M. Transforming dumps into gold mines. Experiences from Swedish case studies. Environ. Innov. Soc. 2012, 5, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlakovs, J.; Kriipsalu, M.; Klavins, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Vincevica-Gaile, Z.; Stenis, J.; Jani, Y.; Mykhaylenko, V.; Denafas, G.; Turkadze, T.; et al. Paradigms on landfill mining: From dump site scavenging to ecosystem services revitalization. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 123, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.T.; Geysen, D.; Tielemans, Y.; Van Passel, S.; Pontikes, Y.; Blanpain, B.; Quaghebeur, M.; Hoekstra, N. Enhanced Landfill Mining in view of multiple resource recovery: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 55, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Directive 1999/31/EC of 26 April 1999 on the Landfill of Waste. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1999, 182, 1–19. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A01999L0031-20180704 (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- EURELCO. Data Launched on the Landfill Situation in the EU-28. Available online: https://eurelco.org/2018/09/30/data-launched-on-the-landfill-situation-in-the-eu-28/#:~:text=The%20figure%20for%20the%20total,the%20Landfill%20Directive%20(1999) (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Malinauskaite, J.; Jouhara, H.; Czajczyńska, D.; Stanchev, P.; Katsou, E.; Rostkowski, P.; Thorne, R.J.; Colón, J.; Ponsá, S.; Al-Mansour, F.; et al. Municipal solid waste management and waste-to-energy in the context of a circular economy and energy recycling in Europe. Energy 2017, 141, 2013–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogland, W.; Marques, M.; Nimmermark, S. Landfill mining and waste characterization: A strategy for remediation of contaminated areas. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2004, 6, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waste Atlas. Available online: http://www.atlas.d-waste.com/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Facts and Figures on the European Union Economy. Available online: https://european-union.europa.eu/principles-countries-history/key-facts-and-figures/economy_en (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Vanheusden, B. Recent development in European policy regarding brownfield remediation. Environ. Pract. 2009, 11, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelgaitė, A.; Liobikienė, G. Waste problem in European Union and its influence on waste management behaviours. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.C.; Teixeira, N.M. Assessment of municipal waste in a circular economy: Do European Union countries share identical performance? Clean. Waste Syst. 2022, 3, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, E.; Osiński, P.; Podlasek, A.; Markiewicz, A.; Winkler, J.; Vaverková, M.D. Geoenvironmental approaches in an old municipal waste landfill reclamation process: Expectations vs reality. Soils Found. 2023, 63, 101273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlakovs, J.; Kriipsalu, M.; Vincevica-Gaile, Z.; Grinfelde, I.; Grinberga, L. Material recovery and revitalisation of landfills: Multitasking approach striving to ‘beyond the zero waste’. SGEM Int. Multidiscip. Sci. GeoConf. 2021, 21, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaartinen, T.; Sormunen, K.; Rintala, J. Case study on sampling, processing and characterization of landfilled municipal solid waste in the view of landfill mining. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 55, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, N.; Krook, J.; Eklund, M.; Berglund, B. An integrated review of concepts and initiatives for mining the technosphere: Towards a new taxonomy. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 55, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehme, K.-M.; Kriipsalu, M. Full-scale project—From landfill to recreational area. Detritus 2018, 1, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekdar, A.V. Sustainable solid waste management: An integrated approach for Asian countries. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Savaget, P.; Bocken, N.M.P.; Hultink, E.J. The Circular Economy—A new sustainability paradigm? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Bi, J.; Moriguichi, Y. The circular economy: A new development strategy in China. J. Ind. Ecol. 2006, 10, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomponi, F.; Moncaster, A. Circular economy for the built environment: A research framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 143, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.S. An introductory note on the environmental economics of the circular economy. Sustain. Sci. 2007, 2, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Gómez, A.M.; González, F.A.; Bárcena, M.M. Smart eco-industrial parks: A circular economy implementation based on industrial metabolism. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieder, M.; Rashid, A. Towards circular economy implementation: A comprehensive review in context of manufacturing industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 115, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Fujita, M.; Dai, M.; Geng, Y.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Ohnishi, S. Towards preventative eco-industrial development: An industrial and urban symbiosis case in one typical industrial city in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 114, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winans, K.; Kendall, A.; Deng, H. The history and current applications of the circular economy concept. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washbourne, C.-L.; Goddard, M.A.; Le Provost, G.; Manning, D.A.C.; Manning, P. Trade-offs and synergies in the ecosystem service demand of urban brownfield stakeholders. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 42, 101074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gies, E. The Health Benefits of Parks: How Parks Keep Americans and Their Communities Fit and Healthy; The Trust for Public Land: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2006; 26p. [Google Scholar]
- De Sousa, C.A. Unearthing the benefits of brownfield to green space projects: An examination of project use and quality of life impacts. Local Environ. 2006, 11, 577–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liwarska-Bizukojc, E. The conceptual model of an eco-industrial park based upon ecological relationships. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowen, A.J.; Confer, J.J. The relationship between perceptions, distance, and socio-demographic characteristics upon public use of an urban park “in-fill”. J. Park Recreat. Adm. 2003, 21, 58–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Klenosky, D.B. Residents’ perceptions and attitudes toward waste treatment facility sites and their possible conversion: A literature review. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 20, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogland, W.; Burlakovs, J.; Mutafela, R.; Jani, Y. From glass dump to phytoremediation park. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 390, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenosky, D.B.; Snyder, S.A.; Vogt, C.A.; Campbell, L.K. If we transform the landfill, will they come? Predicting visitation to Freshkills Park in New York City. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 167, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NYC GovParks. Freshkills Park. Available online: https://www.nycgovparks.org/park-features/freshkills-park/about-the-site (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Freshkills Park. Students Learn About Water Quality at Freshkills Park. Available online: http://freshkillspark.org/blog/students-learn-about-water-quality-at-freshkills-park (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Steiner, F. Frontiers in urban ecological design and planning research. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M. The sustainable and entrepreneurial park? Contradictions and persistent antagonisms at Sydney’s Olympic Park. Urban Geogr. 2013, 34, 657–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcovich, K.; O’Meara, J. An Olympic legacy: Green and golden bell frog conservation at Sydney Olympic Park 1993–2006. Aust. Zool. 2008, 34, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.; McNeill, D. The redevelopment of Olympic sites: Examining the legacy of Sydney Olympic park. Urban Stud. 2012, 49, 1625–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Kirkwood, N.; Maksimović, Č.; Zheng, X.; O’Connor, D.; Jin, Y.; Hou, D. Nature based solutions for contaminated land remediation and brownfield redevelopment in cities: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Xu, B. Olympic effects on reshaping urban greenspace of host cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 230, 104615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długoński, A.; Dushkova, D. The hidden potential of informal urban greenspace: An example of two former landfills in post-socialist cities (central Poland). Sustainability 2021, 13, 3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długoński, A. Recreational development of old landfill: The case study of Górka Rogowska landfill in Łódź city, Poland. Detritus 2018, 2, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukaszkiewicz, J.; Fortuna-Antoszkiewicz, B.; Długoński, A.; Wiśniewski, P. From the heap to the park—Reclamation and adaptation of degraded urban areas for recreational functions in Poland. Sci. Rev. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 664–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczala, F.; Mehdinejad, M.H.; Lääne, A.; Orupõld, K.; Bhatnagar, A.; Kriipsalu, M.; Hogland, W. Leaching characteristics of the fine fraction from an excavated landfill: Physico-chemical characterization. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2017, 19, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Kaczala, F.; Burlakovs, J.; Kriipsalu, M.; Hogland, M.; Hogland, W. Hunting for valuables from landfills and assessing their market opportunities: A case study with Kudjape landfill in Estonia. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlakovs, J.; Kaczala, F.; Vincevica-Gaile, Z.; Rudovica, V.; Orupõld, K.; Stapkevica, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Kriipsalu, M.; Hogland, M.; Klavins, M.; et al. Mobility of metals and valorization of sorted fine fraction of waste after landfill excavation. Waste Biomass Valor. 2016, 7, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehme, K.-M.; Tamm, T.; Orupõld, K.; Kriipsalu, M. A study on methane degradation layer extracted from landfill mining. Proc. Linnaeus Eco-Tech 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón Márquez, A.J.; Cassettari Filho, P.C.; Rutkowski, E.W.; de Lima Isaac, R. Landfill mining as a strategic tool towards global sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Notte, A.; D’Amato, D.; Mäkinen, H.; Paracchini, M.L.; Liquete, C.; Egoh, B.; Geneletti, D.; Crossman, N.D. Ecosystem services classification: A systems ecology perspective of the cascade framework. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CICES. Towards a Common Classification of Ecosystem Services. Available online: https://cices.eu/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030. Bringing Nature Back into Our Lives. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/resource.html?uri=cellar:a3c806a6-9ab3-11ea-9d2d-01aa75ed71a1.0001.02/DOC_1&format=PDF (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Sukhdev, P.; Wittmer, H.; Miller, D. The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB): Challenges and Responses. In Nature in the Balance: The Economics of Biodiversity; Helm, D., Hepburn, C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecosystems and Human Wellbeing. Synthesis. Available online: https://www.millenniumassessment.org/documents/document.356.aspx.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Wang, Z.; Fu, B.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Li, Y. Ecosystem service assessments across cascade levels: Typology and an evidence map. Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 57, 101472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhard, M.; Banko, G.; Malak, D.M.; Santos-Martín, F. Mapping Ecosystem Types and Conditions. In Mapping Ecosystem Services; Burkhard, B., Maes, J., Eds.; Pensoft: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2017; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagne, C.S.; Roche, P.; Müller, F.; Burkhard, B. Ten years of ecosystem services matrix: Review of (r)evolution. One Ecosyst. 2020, 5, e51103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, P.K.; Campagne, S. Are expert-based ecosystem services scores related to biophysical quantitative estimates? Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihervaara, P.; Mononen, L.; Santos, F.; Adamescu, M.; Cazacu, C.; Luque, S.; Geneletti, D.; Maes, J. Biophysical Quantification. In Mapping Ecosystem Services; Burkhard, B., Maes, J., Eds.; Pensoft: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2017; pp. 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholte, S.S.K.; van Teeffelen, A.J.A.; Verburg, P.H. Integrating socio-cultural perspectives into ecosystem service valuation: A review of concepts and methods. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 114, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häyhä, T.; Franzese, P.P. Ecosystem services assessment: A review under an ecological-economic and systems perspective. Ecol. Model. 2014, 289, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvis, B.; Mao, Y.; Robinson, D. Three pillars of sustainability: In search of conceptual origins. Sustain. Sci. 2017, 14, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilker, J.; Rusche, K.; Benning, A.; MacDonald, M.A.; Blaen, P. Applying ecosystem benefit valuation to inform quarry restoration planning. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 20, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolosz, B.W.; Athanasiadis, I.N.; Cadisch, G.; Dawson, T.P.; Giupponi, C.; Honzák, M.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; Marvuglia, A.; Mojtahed, V.; Ogutu, K.B.Z.; et al. Conceptual advancement of socio-ecological modelling of ecosystem services for re-evaluating Brownfield land. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 33, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, E.; Subramani, T.; Karunanidhi, D. Integrated approach of ecosystem services for mine reclamation in a clustered mining semi-urban region of South India. Urban Clim. 2022, 45, 101246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, L.S.; Maikhuri, R.K.; Bahuguna, Y.M.; Jugran, A.K.; Maletha, A.; Jha, N.K.; Phondani, P.C.; Dhyani, D.; Pharswan, D.S.; Chamoli, S. Rejuvenating ecosystem services through reclaiming degraded land for sustainable societal development: Implications for conservation and human wellbeing. Land Use Policy 2022, 112, 105804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueffel, C.; Haase, D.; Priess, J.A. Mapping ecosystem services on brownfields in Leipzig, Germany. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 30, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Valck, J.; Beames, A.; Liekens, I.; Bettens, M.; Seuntjens, P.; Broekx, S. Valuing urban ecosystem services in sustainable brownfield redevelopment. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 35, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J.; Crane, D.E.; Stevens, J.C. Air pollution removal by urban trees and shrubs in the United States. Urban For. Urban Green. 2006, 4, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, J.L. The Proximate Principle: The Impact of Parks, Open Space and Water Features on Residential Property Values and the Property Tax Base, 2nd ed.; National Recreation and Park Association: Ashburn, VA, USA, 2004; 203p. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, S.; Crompton, J.L. The impact of greenways on property values: Evidence from Austin, Texas. J. Leis. Res. 2005, 37, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedimo-Rung, A.L.; Mowen, A.J.; Cohen, D.A. The significance of parks to physical activity and public health: A conceptual model. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2005, 28, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnik, P.; Welle, B. Measuring the Economic Value of a City Park System; The Trust of the Public Land: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2009; 28p. [Google Scholar]
- Pagourtzi, E.; Assimakopoulos, V.; Hatzichristos, T.; French, N. Real estate appraisal: A review of valuation methods. J. Prop. Invest. Financ. 2003, 21, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Property Shark. Staten Island Real Estate Market Trends. Available online: https://www.propertyshark.com/mason/market-trends/residential/nyc/staten-island (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Realtor. New York, NY Real Estate and Homes for Sale. Available online: https://www.realtor.com/realestateandhomes-search/New-York_NY (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Open Agent. Sydney Property Market News. Available online: https://www.openagent.com.au/suburb-profiles/sydney-property-market (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Real Estate. Real Estate and Property for Sale in Sydney Olympic Park. Available online: https://m.realestate.com.au/buy/in-sydney+olympic+park,+nsw+2127/list-1 (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Gratka. Real Estate Portal of Poland. Available online: https://gratka.pl/nieruchomosci/mieszkania/lodz (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Nieruchomosci. Real Estate Portal of Poland. Available online: https://lodz.nieruchomosci-online.pl/mieszkania,sprzedaz/ (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Kinnisvaraportaal. Real Estate Portal of Estonia. Available online: https://www.kv.ee/en/search?deal_type=1&county=11 (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Oudes, D.; Stremke, S. Climate adaptation, urban regeneration and brownfield reclamation: A literature review on landscape quality in large-scale transformation projects. Landsc. Res. 2020, 45, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithsonian Magazine. The Transformation of Freshkills Park from Landfill to Landscape. Available online: https://www.smithsonianmag.com/arts-culture/the-transformation-of-freshkills-park-from-landfill-to-landscape-75931143/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Bloomberg. The Wild Comeback of New York’s Legendary Landfill. Available online: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2017-02-17/freshkills-park-once-a-legendary-landfill-now-a-haven (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Gupta, A.K.; Negi, M.; Nandy, S.; Kumar, M.; Singh, V.; Valente, D.; Petrosillo, I.; Pandey, R. Mapping socio-environmental vulnerability to climate change in different altitude zones in the Indian Himalayas. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNN. A Landfill in Their Backyard. Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/interactive/2020/09/us/september-11-cancer-rates-fresh-kills/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Punter, J. Urban design in central Sydney 1945–2002: Laissez-Faire and discretionary traditions in the accidental city. Prog. Plan. 2005, 63, 11–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myer, A.; Chaffee, C. Life-cycle analysis for design of the Sydney Olympic Stadium. Renew. Energy 1997, 10, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.; Oliveira, A.; Caeiro, E.; Miralto, O.; Parrinha, M.; Sampaio, A.; Silva, C.; Mira, A.; Sagueiro, P.A. Insect pollination services in actively and spontaneously restored quarries converge differently to natural reference ecosystem. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zee, D.J.; Achterkamp, M.C.; de Visser, B.J. Assessing the market opportunities of landfill mining. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecina, V.; Juřička, D.; Galiová, M.V.; Kynický, J.; Baláková, L.; Brtnický, M. Polluted brownfield site converted into a public urban park: A place providing ecosystem services or a hidden health threat? J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 291, 112669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Spina, L. Urban Regeneration Strategies According to Circular Economy: A Multi-Criteria Decision Aiding Approach. In New Metropolitan Perspectives (NMP). Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Calabrò, F., Della Spina, L., Piñeira Mantiñán, M.J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 482, pp. 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Corgel, J.; Shin, S. Estimating net operating income growth for modeling U.S. apartment property capitalization rates. J. Real Estate Portf. Manag. 2014, 20, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, J.; Ling, D.C.; Naranjo, A. Commercial real estate valuation: Fundamentals versus investor sentiment. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2009, 38, 5–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddau, G.M.; Marotta, A.; Sanna, G. Abandoned landscape project design. City Territ. Archit. 2020, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schädler, S.; Morio, M.; Bartke, S.; Rohr-Zänker, R.; Finkel, M. Designing sustainable and economically attractive brownfield revitalization options using an integrated assessment model. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).