Energy Consumption and Carbon Dioxide Production Optimization in an Educational Building Using the Supported Vector Machine and Ant Colony System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
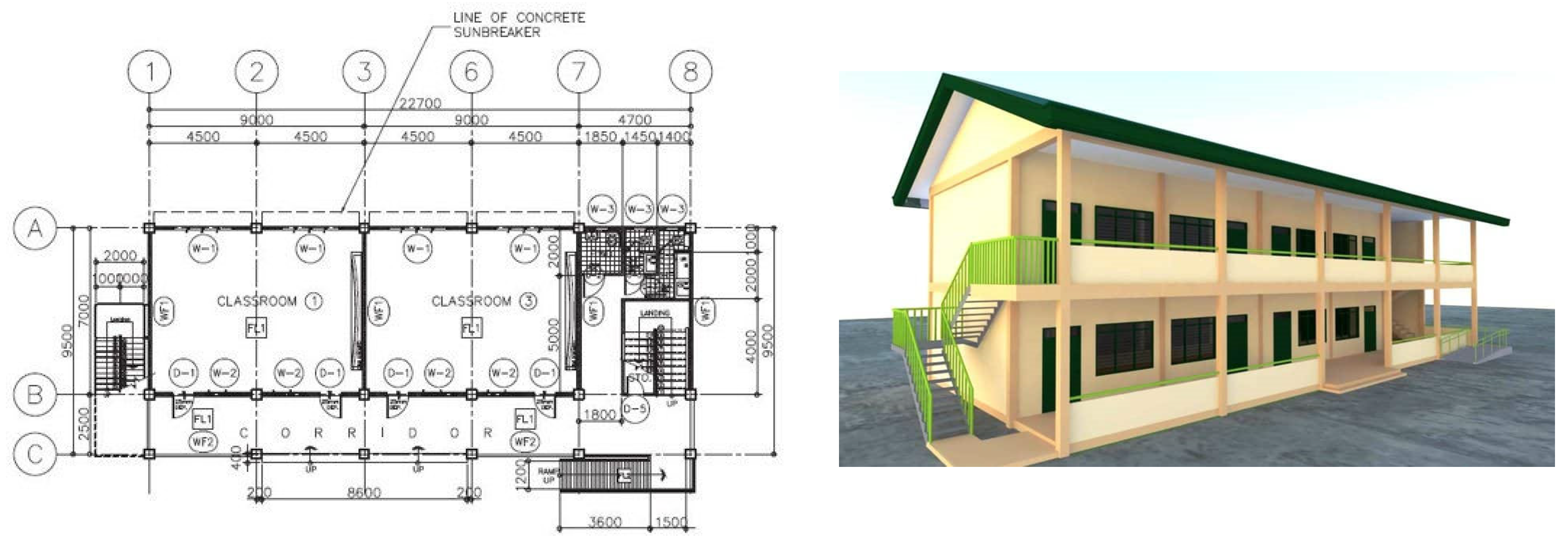
2.1. Case Study
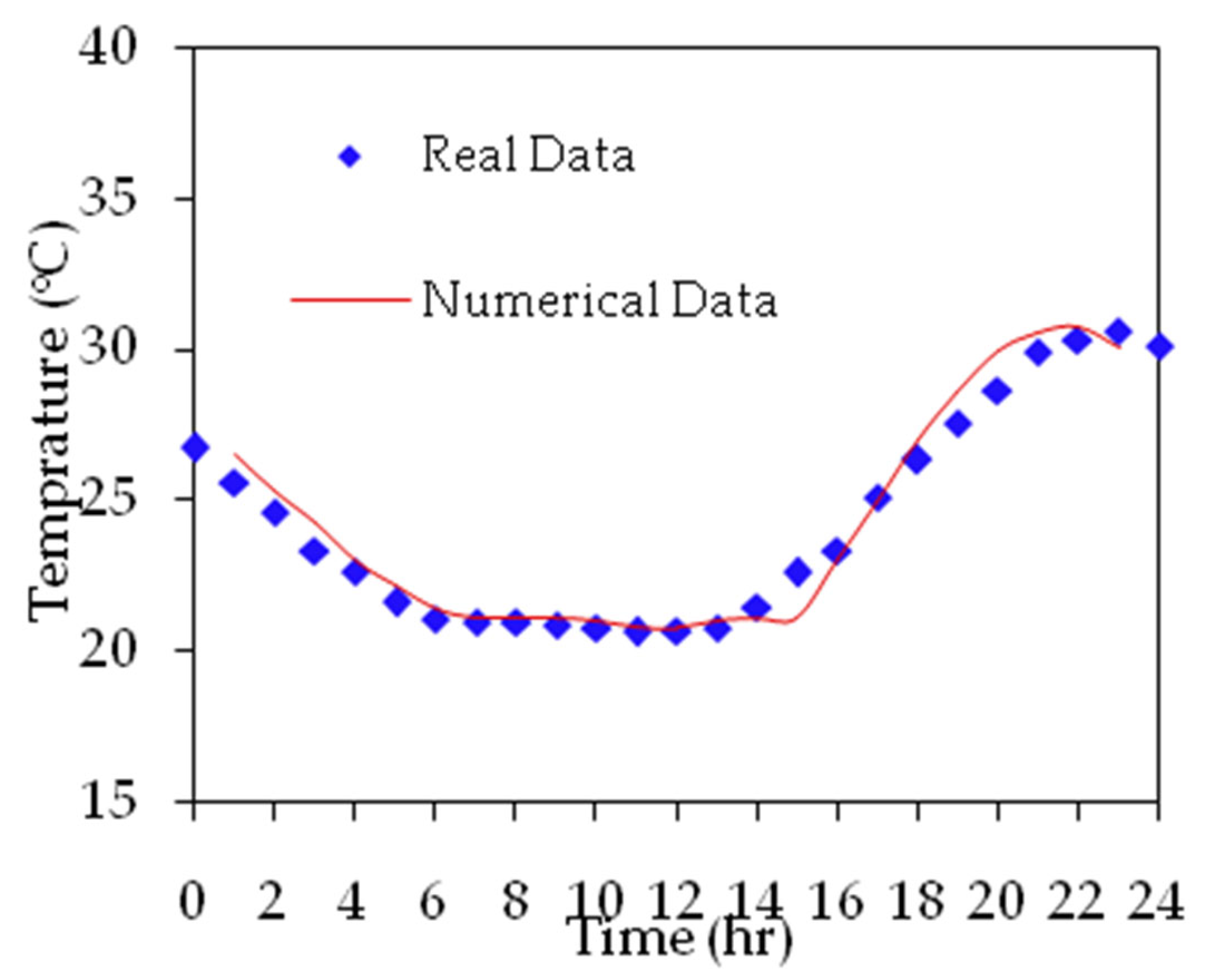
2.2. DesignBuilder Model Validation
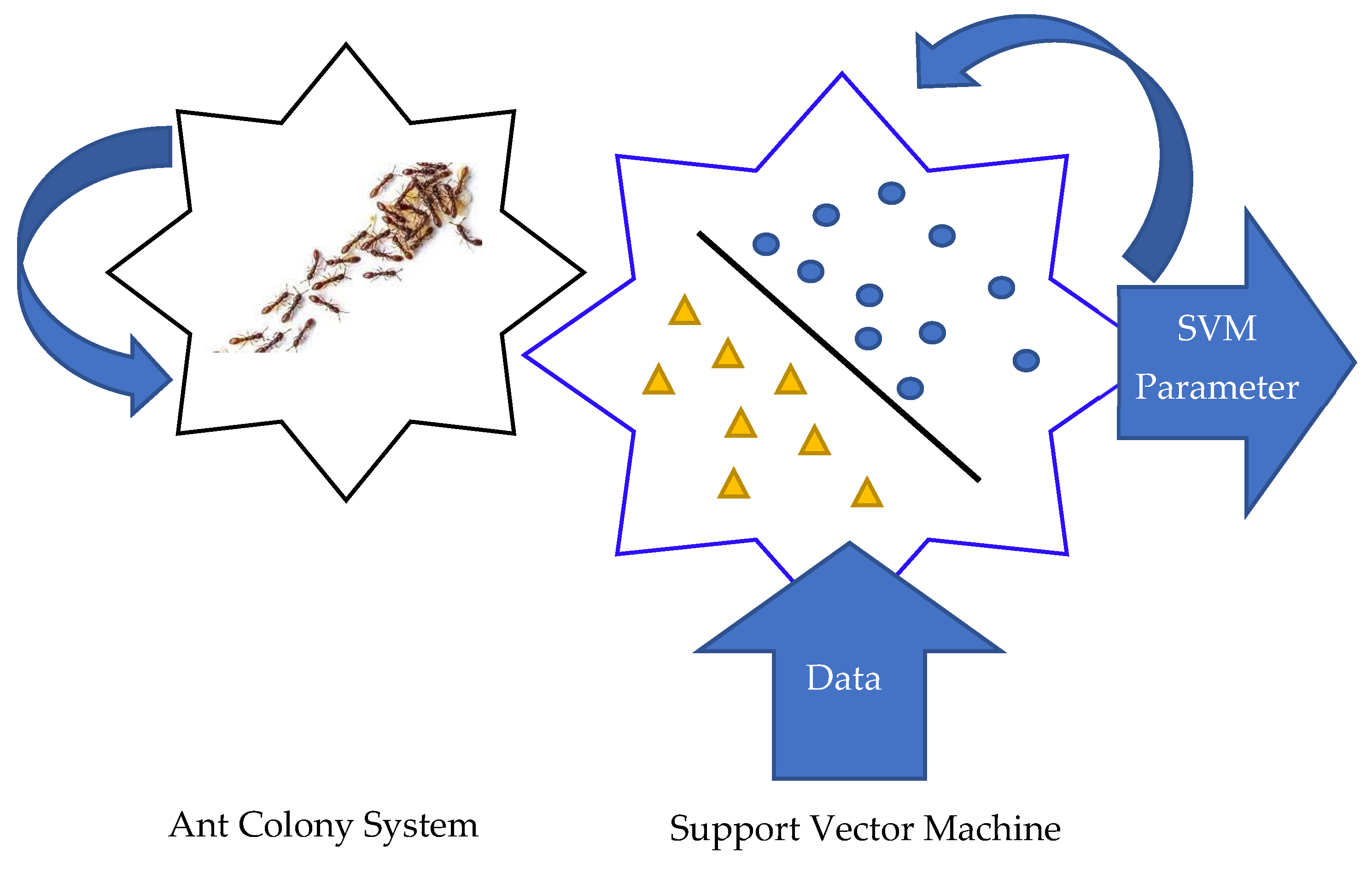
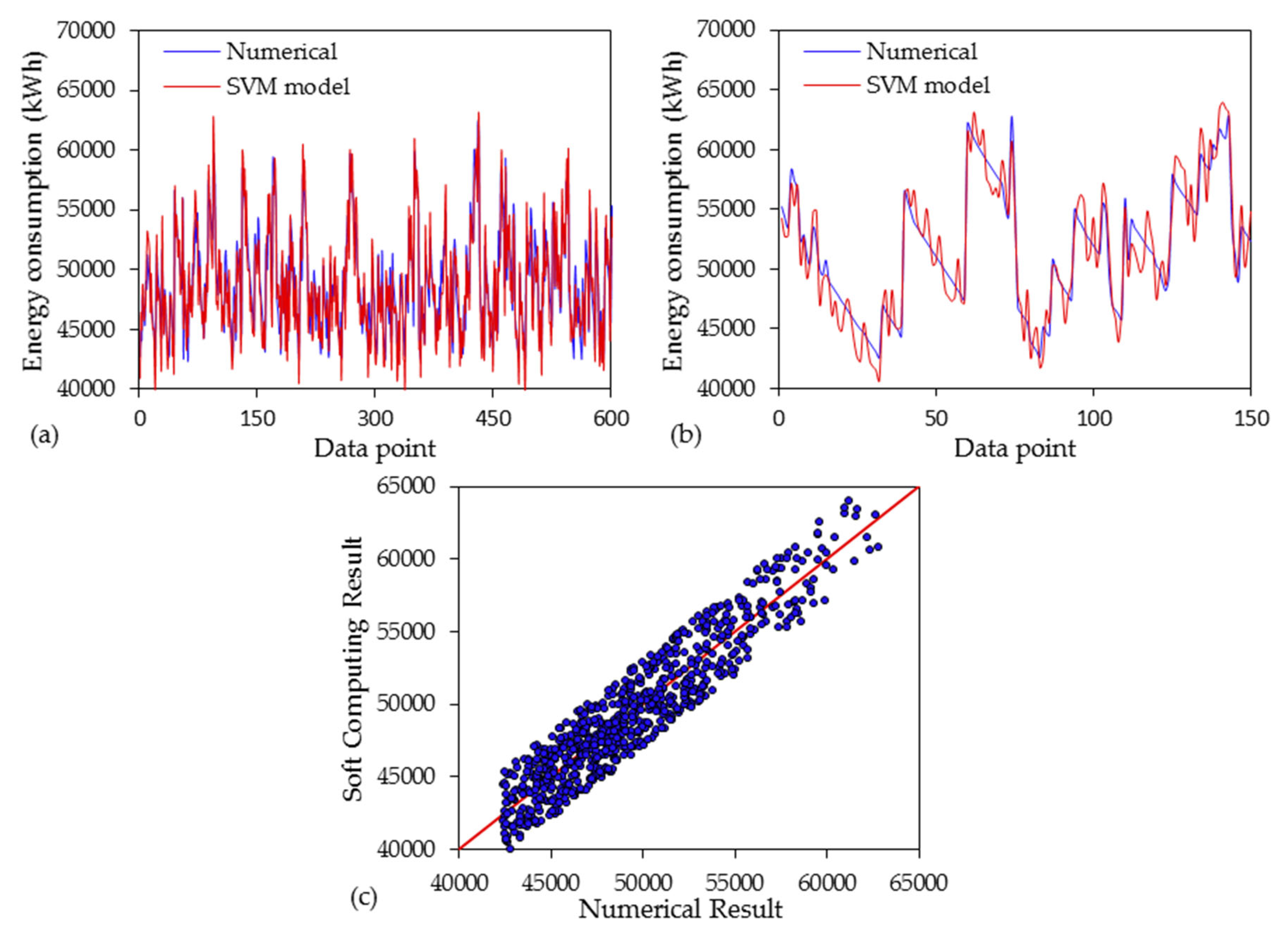
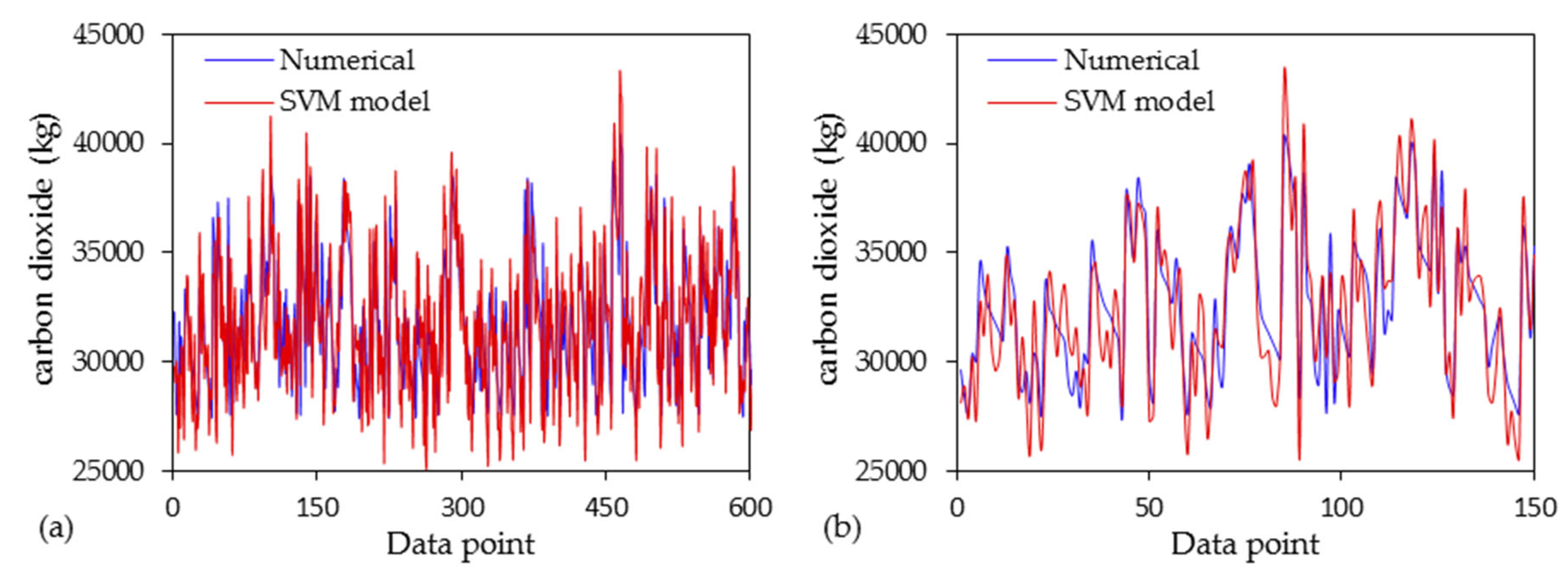
2.3. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
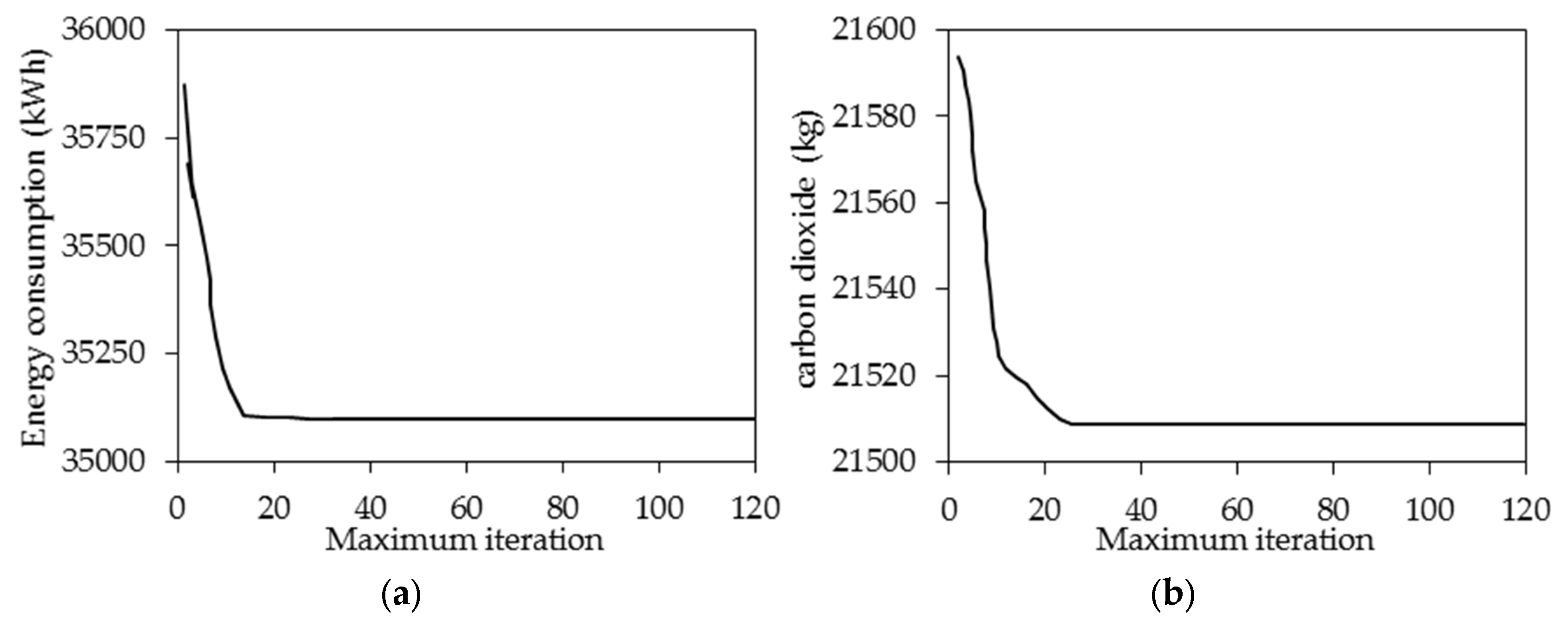
2.4. Ant Colony System (ACS)
3. Results and Discussion
4. Results of Optimization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| The pheromone value is on the edge that connects nodes i and j. | |
| Probability of moving from node i to unvisited node j by ant k. | |
| Innovative information to measure the ant’s field of view | |
| Parameters are controls that determine the importance ratio of the value of the ant’s field of view against the pheromone marker on the edge connecting node i and j. | |
| A random parameter uniformly distributed in [0, 1]. | |
| A constant threshold parameter in [0, 1] that determines the importance ratio of mining to exploration. |
References
- Molajou, A.; Afshar, A.; Khosravi, M.; Soleimanian, E.; Vahabzadeh, M.; Variani, H.A. A New Paradigm of Water, Food, and Energy Nexus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molajou, A.; Pouladi, P.; Afshar, A. Incorporating Social System into Water-Food-Energy Nexus. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 4561–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Sayyaadi, H.; Dehghani, S.; Hosseinzade, H. Designing a Solar Powered Stirling Heat Engine Based on Multiple Criteria: Maximized Thermal Efficiency and Power. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 75, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Doury, R.R.J.; Salem, T.K.; Nazzal, I.T.; Kumar, R.; Sadeghzadeh, M. A Novel Developed Method to Study the Energy/Exergy Flows of Buildings Compared to the Traditional Method. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 145, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Jashnani, H.; Chau, K.W.; Kumar, R.; Rosen, M.A. Carbon Dioxide Emissions Prediction of Five Middle Eastern Countries Using Artificial Neural Networks. Energy Sources A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 41, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, F.; Salehi Neyshabouri, S.A.; Yazdi, J.; Molajou, A.; Brysiewicz, A. A Novel Framework for Urban Flood Damage Assessment. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 1991–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, H.; Nejatian, N. Evaluation of the Climate Change Impact on the Intensity and Return Period for Drought Indices of SPI and SPEI (Study Area: Varamin Plain). Water Supply 2022, 22, 4373–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banan-Dallalian, M.; Shokatian-Beiragh, M.; Golshani, A.; Abdi, A. Use of a Bayesian Network for Storm-Induced Flood Risk Assessment and Effectiveness of Ecosystem-Based Risk Reduction Measures in Coastal Areas (Port of Sur, Sultanate of Oman). Ocean Eng. 2023, 270, 113662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayi, R.; Mohkam, M.; Seyednouri, S.R.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Sharifpur, M. Energy/Economic Analysis and Optimization of on-Grid Photovoltaic System Using CPSO Algorithm. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlmeir, J.; Buhl, H.U.; Fridgen, G.; Keller, R. The Energy Consumption of Blockchain Technology: Beyond Myth. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2020, 62, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruga, K.; Islam, M.M.; Jannat, A. Effects of COVID-19 on Indian Energy Consumption. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Hao, Y.; Xu, L.; Wu, H.; Ba, N. Digitalization and Energy: How Does Internet Development Affect China’s Energy Consumption? Energy Econ. 2021, 98, 105220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osobajo, O.A.; Otitoju, A.; Otitoju, M.A.; Oke, A. The Impact of Energy Consumption and Economic Growth on Carbon Dioxide Emissions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olu-Ajayi, R.; Alaka, H.; Sulaimon, I.; Sunmola, F.; Ajayi, S. Building Energy Consumption Prediction for Residential Buildings Using Deep Learning and Other Machine Learning Techniques. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, S.; Jia, G.; Li, H.; Li, W. Urban Heat Island Impacts on Building Energy Consumption: A Review of Approaches and Findings. Energy 2019, 174, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Dilkina, B.; Hubbs, J.; Zhang, W.; Guhathakurta, S.; Brown, M.A.; Pendyala, R.M. Machine Learning Approaches for Estimating Commercial Building Energy Consumption. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdeau, M.; Zhai, X.Q.; Nefzaoui, E.; Guo, X.; Chatellier, P. Modeling and Forecasting Building Energy Consumption: A Review of Data-Driven Techniques. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 48, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Hu, Z.Z.; Lin, J.R.; Zhang, Y.Y. A Framework for the Automatic Integration and Diagnosis of Building Energy Consumption Data. Sensors 2021, 21, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharghi, E.; Nourani, V.; Molajou, A.; Najafi, H. Conjunction of Emotional ANN (EANN) and Wavelet Transform for Rainfall-Runoff Modeling. J. Hydroinform. 2019, 21, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Kumar, R.; Assad, M.E.H.; Ngo, P.T.T. Applications of Machine Learning Methods in Modeling Various Types of Heat Pipes: A Review. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 146, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojtahedi, A.; Dadashzadeh, M.; Azizkhani, M.; Mohammadian, A.; Almasi, R. Assessing Climate and Human Activity Effects on Lake Characteristics Using Spatio-Temporal Satellite Data and an Emotional Neural Network. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.J. Energy Consumption Prediction and Diagnosis of Public Buildings Based on Support Vector Machine Learning: A Case Study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.; Khan, W.; Katic, K.; Maassen, W.; Zeiler, W. Accuracy of Different Machine Learning Algorithms and Added-Value of Predicting Aggregated-Level Energy Performance of Commercial Buildings. Energy Build. 2020, 209, 109705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.; Chapelle, O. Bounds on Error Expectation for Support Vector Machines. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 2013–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.H.; Chen, W.J.; Liu, L.M.; Deng, N.Y. Laplacian Unit-Hyperplane Learning from Positive and Unlabeled Examples. Inf. Sci. 2015, 314, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Xie, X.; Huang, L.; Pang, W.; Coghill, G.M. An Efficient V-Minimum Absolute Deviation Distribution Regression Machine. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 85533–85551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bi, C.; Jiang, X. Revisiting Transductive Support Vector Machines with Margin Distribution Embedding. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2018, 152, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouaddi, K.; Benadada, Y.; Mhada, F.Z. Ant Colony System for Dynamic Vehicle Routing Problem with Overtime. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2018, 9, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.C.; Roddick, J.F.; Pan, J.S. Ant Colony System with Communication Strategies. Inf. Sci. 2004, 167, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, E.K.; Omar, A.H.; Elsayed, K.E. Smart Solution for STSP Semantic Traveling Salesman Problem via Hybrid Ant Colony System with Genetic Algorithm. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2020, 13, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajpal, Y.; Abad, P. An Ant Colony System (ACS) for Vehicle Routing Problem with Simultaneous Delivery and Pickup. Comput. Oper. Res. 2009, 36, 3215–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Zhan, Z.H.; Deng, J.D.; Li, Y.; Gu, T.; Zhang, J. An Energy Efficient Ant Colony System for Virtual Machine Placement in Cloud Computing. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2018, 22, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, E.A.; Ahmed, S.E.; Song, Y.; Nathoo, F.S. Ant Colony System Optimization for Spatiotemporal Modelling of Combined EEG and MEG Data. Entropy 2021, 23, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Tan, H.; Tzempelikos, A. The Effect of Reflective Coatings on Building Surface Temperatures, Indoor Environment and Energy Consumption—An Experimental Study. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Annual Values | Jakarta, Sumatra, Indonesia |
|---|---|
| Daytime maximum temperature | 31.70 °C |
| Daily low temperature | 23.60 °C |
| Water temperature | 28.20 °C |
| Humidity | 83% |
| Precipitation | 2584 mm |
| Rain days | 152.4 days |
| Hours of sunshine | 1789 h |
| Building Elements | Materials | Heat Transfer Coefficient (W/m2.k) | Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Existing | |||
| Reinforced concrete girder | Mosaic | 1.456 | 22 |
| Plaster | 45 | ||
| Waterproofing | 45 | ||
| Concrete | 105 | ||
| Block | 250 | ||
| Plaster | 45 | ||
| Brick wall | 2.650 | 220 | |
| Optimal | |||
| Concrete Slab | Bituminous waterproofing | 1.520 | 32 |
| Plaster | 25 | ||
| Lightweight concrete | 40 | ||
| Concrete | 250 | ||
| Plaster | 20 | ||
| Concrete wall | Lightweight concrete | 2.291 | 125 |
| Plaster | 22 | ||
| Roof insulation | Polystyrene | 0.750 | 35 |
| Polystyrene | 0.645 | 40 | |
| Wall insulation | Polystyrene | 0.844 | 35 |
| Polystyrene | 0.541 | 40 | |
| Double-glazed glass | Two layers of glass | 1.562 | 8 |
| Argon gas Two layers of | 3 | ||
| Window triple glass | transparent glass | 0.656 | 4 |
| Low emissivity glass | 1 | ||
| Krypton gas | 15 | ||
| Output | Stage | Statistical Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | R2 | RMSE | ||
| Energy consumption | Train | 0.921 | 0.874 | 904 (kWh) |
| Test | 0.882 | 0.824 | 1012 (kWh) | |
| CO2 | Train | 0.901 | 0.831 | 1129 (kg) |
| Test | 0.863 | 0.799 | 1076 (kg) | |
| max_it | q0 | β | α | ρ | k | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 120 | 0.6 | 0.79 | 0.98 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 2 | 5 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anupong, W.; Muda, I.; AbdulAmeer, S.A.; Al-Kharsan, I.H.; Alviz-Meza, A.; Cárdenas-Escrocia, Y. Energy Consumption and Carbon Dioxide Production Optimization in an Educational Building Using the Supported Vector Machine and Ant Colony System. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043118
Anupong W, Muda I, AbdulAmeer SA, Al-Kharsan IH, Alviz-Meza A, Cárdenas-Escrocia Y. Energy Consumption and Carbon Dioxide Production Optimization in an Educational Building Using the Supported Vector Machine and Ant Colony System. Sustainability. 2023; 15(4):3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043118
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnupong, Wongchai, Iskandar Muda, Sabah Auda AbdulAmeer, Ibrahim H. Al-Kharsan, Aníbal Alviz-Meza, and Yulineth Cárdenas-Escrocia. 2023. "Energy Consumption and Carbon Dioxide Production Optimization in an Educational Building Using the Supported Vector Machine and Ant Colony System" Sustainability 15, no. 4: 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043118
APA StyleAnupong, W., Muda, I., AbdulAmeer, S. A., Al-Kharsan, I. H., Alviz-Meza, A., & Cárdenas-Escrocia, Y. (2023). Energy Consumption and Carbon Dioxide Production Optimization in an Educational Building Using the Supported Vector Machine and Ant Colony System. Sustainability, 15(4), 3118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043118





