Effects of Land Use Characteristics, Physiochemical Variables, and River Connectivity on Fish Assemblages in a Lowland Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodst
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Fish Sampling and Diversity Indices
2.3. Measured Environmental Variables
2.3.1. Local-Scale Physiochemical Variables
2.3.2. Land Use Characteristics
2.3.3. River Connectivity Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clustering River Connectivity Variables
3.2. Spatial Gradients of Physiochemical Variables among Connectivity Groups
3.3. Influence of River Connectivity on Fish Assemblages
3.4. Linking Environmental Variables to Fish Assemblages
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Heterogeneity of Environmental Variables
4.2. Connectivity Variables Slightly Influence Variations in Fish Assemblages
4.3. Upstream Land Use and Flow Velocity Play More Important Roles in Fish Assemblage Variance
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, Y.Z.; Xiang, X.Y.; Chu, L.; Zhan, Y.J.; Fu, C.Z. Influences of local habitat and stream spatial position on fish assemblages in a dammed watershed, the Qingyi Stream, China. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. 2011, 20, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.K.; Kang, Z.J.; Tao, J.; Liu, C.L.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.F. Hydrologic connectivity driven natural stream fish assemblages in mountain streams in the Yangtze River basin: Implications for stream fish conservation in monsoonal East Asia. Hydrobiologia 2017, 785, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.J.; Xu, Y.P.; Han, L.F. Impacts of human activities on the structural and functional connectivity of a river network in the Taihu Plain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2575–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.J.; Gao, Y.N.; Zhang, S.H. The impact of dams on the river connectivity of the two largest river basins in China. River Res. Appl. 2022, 38, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, J.P.; Manish, K.; Pandit, M.K. Elevational Gradients in Fish Diversity in the Himalaya, Water Discharge Is the Key Driver of Distribution Patterns. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Quintero, J.D.; Escobar, F.; Alvarado, F.; Villa-Navarro, F.A.; Jaramillo-Villa, Ú.; Maldonado-Ocampo, J.A. Variation in freshwater fish assemblages along a regional elevation gradient in the northern Andes, Colombia. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 2608–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Yan, Y.Z.; Zhu, R.; Zhou, K.; Chu, L. Spatial variations in fish assemblages within the headwater streams of the Wanhe watershed, A river network-based approach. J. Fish. Sci. China 2014, 21, 988–999. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela-Aguayo, F.; McCracken, G.R.; Manosalva, A.; Habit, E.; Ruzzante, D.E. Human-induced habitat fragmentation effects on connectivity, diversity, and population persistence of an endemic fish, Percilia irwini, in the Biobio River basin (Chile). Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, U.S.; Welcomme, R.L. An analysis of fish species richness in natural lakes. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2002, 65, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, A.P.; Súarez, Y.R. Influence of local and landscape characteristics on the distribution and diversity of fish assemblages of streams in the Ivinhema River basin, Upper Paraná River. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2013, 25, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Jin, H.; Jeppesen, E.; Li, K.Y.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.D. Fish-mediated plankton responses to increased temperature in subtropical aquatic mesocosm ecosystems, Implications for lake management. Water Res. 2018, 144, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Prinzio, C.Y.; Casaux, R.J.; Miserendino, M.L. Effects of land use on fish assemblages in Patagonian low order streams. Ann. Limnol-Int. J. Lim. 2009, 45, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Tolonen, K.E.; Yin, H.B.; Gao, J.F.; Zhang, Z.M.; Li, K.Y. Substrate degradation and nutrient enrichment structuring macroinvertebrate assemblages in agriculturally dominated Lake Chaohu Basins, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.J.; Fang, Y.; Jawitz, J.W.; Yan, J.G.; Cui, B.S. River network connectivity and fish diversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.H.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.P.; Lu, M.; Lin, Z.X.; Gao, B. Dynamic impacts of changes in river structure and connectivity on water quality under urbanization in the Yangtze River Delta plain. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Wu, H.T.; Xu, L.; Kang, Y.J.; Lu, K.L.; Liu, D.D.; Han, D.D.; Xue, Z.S.; Yuan, Y.X.; Wang, W.F.; et al. Hydrological connectivity shapes multiple diversity facets of snail (Mollusca: Gastropoda) assemblages in freshwater floodplain wetlands. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodeles, A.A.; Galicia, D.; Miranda, R. A new method to include fish biodiversity in river connectivity indices with applications in dam impact assessments. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ferreras, A.M.; Leal, S.; Barquín, J.; Almodóvar, A. Patterns of genetic diversity of brown trout in a northern Spanish catchment linked to structural connectivity. Aquat. Sci. 2022, 84, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, M.L.C.; Smith, B.; Bird, B.; McMillan, S.; Pyron, M.; Hauswald, C. Hydrologic connectivity and land cover affect floodplain lake water quality, fish abundance, and fish diversity in floodplain lakes of the Wabash-White River basin. River Res. Appl. 2022, 38, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y.; Ishiyama, N.; Nakamura, F.; Shibata, H.; Fukuzawa, K.; Morimoto, J. Contribution of Hydrological Connectivity in Maintaining Aquatic Plant Communities in Remnant Floodplain Ponds in Agricultural Landscapes. Wetlands 2023, 43, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scordo, F.; Seitz, C.; Fiorenza, J.E.; Piccolo, M.C.; Perillo, G.M.E. Human impact changes hydrological connectivity in a Patagonian fluvial basin. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2023, 45, 101315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutes, R.B. Artificial wetlands and water quality improvement. Environ. Int. 2001, 26, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gido, K.B.; Dodds, W.K.; Eberle, M.E. Retrospective analysis of fish community change during a half-century of landuse and streamflow changes. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 970–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ji, J.; Shi, C. Water geochemistry of the Chaohu Lake Basin rivers, China: Chemical weathering and anthropogenic inputs. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, S379–S383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, C.R.; Leibowitz, S.G.; Autrey, B.C.; LeDuc, S.D.; Alexander, L.C. Hydrological, physical, and chemical functions and connectivity of non-floodplain wetlands to downstream waters, A review. J. Am. Water Resour. As. 2018, 54, 346–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.L.; Yeo, D.C.J.; Tan, H.H.; Fikri, A.H.; Ewers, R.M. Land-use change is associated with a significant loss of freshwater fish species and functional richness in Sabah, Malaysia. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 222, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Liang, X.S.; Zhang, T.Y.; Dong, J.X.; Wang, Y.; Qu, Y. Spatio-Temporal Evolution Patterns of Hydrological Connectivity of Wetland Biodiversity Hotspots in Sanjiang Plain between 1995 and 2015. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, U.S.; De Silva, S.S.; Nissanka, C. Evaluation of the robustness of predictive yield models based on catchment characteristics using GIS for reservoir fisheries in Sri Lanka. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2002, 9, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liermann, C.R.; Nilsson, C.; Robertson, J.; Ng, R.Y. Implications of Dam Obstruction for Global Freshwater Fish Diversity. BioScience 2012, 62, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mara, K.; Venarsky, M.; Stewart-Koster, B.; McGregor, G.B.; Schulz, C.; Kainz, M.; Marshall, J.; Bunn, S.E. Connectivity of fish communities in a tropical floodplain river system and predicted impacts of potential new dams. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P. Three-Gorges Dam, Risk to ancient fish. Science 2003, 302, 1149–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Zeng, Q.H.; Wang, J.H.; Hou, J.M.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.F.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y. Identification of hotspots of threatened inland fish species and regions for restoration based on longitudinal river connectivity. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouchlianitis, F.A.; Bobori, D.; Tsakoumis, E.; Sapounidis, A.; Kritikaki, E.; Ganias, K. Does fragmented river connectivity alter the reproductive behavior of the potamodromous fish Alburnus vistonicus? Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 4029–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá-Oliveira, J.C.; Isaac, V.J.; Ferrari, S.F. Fish community structure as an indicator of the long-term effects of the damming of an Amazonian river. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2015, 98, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrieu, K.G.; Pasternack, G.B.; Schwindt, S. Automated analysis of lateral river connectivity and fish stranding risks-Part 1: Review, theory and algorithm. Ecohydrology 2021, 14, e2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiroff, W.A.; Zak, D.R.; Lanser, C.M.; Wiley, M.J. Microbial community functional potential and composition are shaped by hydrologic connectivity in riverine floodplain soils. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffels, R.J.; Humphries, P.; Bond, N.R.; Price, A.E. Fragmentation of lateral connectivity and fish population dynamics in large rivers. Fish Fish. 2022, 23, 680–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, C.M. Hydrologic connectivity and the management of biological reserves, A global perspective. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.E. Fish assemblages in oxbow lakes relative to connectivity with the Mississippi River. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2005, 134, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, P.; Segurado, P.; Santos, J.M.; Pinheiro, P.; Ferreira, M.T. Does longitudinal connectivity loss affect the distribution of freshwater fish? Ecol. Eng. 2012, 48, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.F.; Cai, Y.J.; Xia, T.; Zhang, Z.M.; Yin, H.B.; Huang, Q. Aquatic Ecosystem Health of Lake Chaohu Basin; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Zhu, Q.; Li, Y.R.; Kang, B.; Chu, L.; Yan, Y.Z. Effects of low-head dams on fish assemblages in subtropical streams: Context dependence on species category and data type. River Res. Applic. 2019, 35, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, P.A.; Ibanez, C.; Moya, N.; Bigorne, R.; Camacho, J.; Goitia, E.; Hugueny, B.; Maldonado, M.; Rivero, M.; Tomanová, S.; et al. Local-scale species-energy relationships in fish assemblages of some forested streams of the Bolivian Amazon. C. R. Biol. 2007, 330, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datry, T.; Melo, A.S.; Moya, N.; Zubieta, J.; De la Barra, E.; Oberdorff, T. Metacommunity patterns across three Neotropical catchments with varying environmental harshness. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Version 4.14. 2023. Available online: https://www.nhm.uio.no/english/research/resources/past/ (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Paredes del Puerto, J.M.; Garcia, I.D.; Maiztegui, T.; Paracampo, A.H.; Capítulo, L.R.; Garcia de Souza, J.R.; Maroñas, M.E.; Colautti, D.C. Impacts of land use and hydrological alterations on water quality and fish assemblage structure in headwater Pampean streams (Argentina). Aquat. Sci. 2022, 84, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 27992.1; Water Depth finding equipment–Part 1: Hydrologic sounding rod. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pápista, É.; Ács, É.; Böddi, B. Chlorophyll-a determination with ethanol—A critical test. Hydrobiologia 2002, 485, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A.N. Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1957, 38, 913–920. [Google Scholar]
- Shreve, R.L. Statistical law of stream numbers. J. Geol. 1966, 74, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.A. Perspectives on the recent status of redfin pickerel in the Schuylkill River basin of southeast Pennsylvania. In Warmwater Workshop Proceedings, Esocid Management and Culture; Soderberg, R., Ed.; American Fisheries Society Northeast Division: Mansfield, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild, G.W.; Horwitz, R.J.; Nieman, D.A.; Boyer, M.R.; Knorr, D.F. Spatial variation and historical change in fish assemblages of the Schuylkill River drainage, southeast Pennsylvania. Am. Midl. Nat. 1998, 139, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, L.L.; Wiley, M.J. Influence of tributary spatial position on the structure of warmwater fish communities. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.B.; Hawley-Howard, J.; Pitt, A.L.; Wang, J.J.; Baldwin, R.F.; Chow, A.T. Water quality of small seasonal wetlands in the Piedmont ecoregion, South Carolina, USA, Effects of land use and hydrological connectivity. Water Res. 2015, 73, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.S.; Li, X.B.; Li, S.K.; Dang, D.L.; Li, X.; Lyu, X.; Li, M.Y.; Liu, S.Y. Mapping ecosystem services bundles for analyzing spatial trade-offs in inner Mongolia, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Smith, G.M. Analysing Ecological Data, Statistics for Biology and Health; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lemm, J.U.; Venohr, M.; Globevnik, L.; Stefanidis, K.; Panagopoulos, Y.; van Gils, J.; Posthuma, L.; Kristensen, P.; Feld, C.K.; Mahnkopf, J.; et al. Multiple stressors determine river ecological status at the European scale: Towards an integrated understanding of river status deterioration. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 1962–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. Version 2.5-7. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Van Groenigen, K.J.; Hungate, B.A.; Cao, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, R.W. A keystone microbial enzyme for nitrogen control of soil carbon storage. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaaq1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Q.; Bååth, E.; Pei, J.M.; Fang, C.M.; Nie, M. Temperature adaptation of soil microbial respiration in alpine, boreal and tropical soils: An application of the square root (Ratkowsky) model. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres-Neto, P.R.; Legendre, P.; Dray, S.; Borcard, D. Variation partitioning of species data matrices: Estimation and comparison of fractions. Ecology 2006, 87, 2614–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.J.; Heino, J. Different roles for geography, energy and environment in determining three facets of freshwater molluscan beta diversity at broad spatial scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Braak, C.; Smilauer, P. CANOCO: Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide, Software for Canonical Community Ordination Version 4.5; Microcomputer Power Ithaca: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Gao, J.F. Linking landscape structures and ecosystem service value using multivariate regression analysis, a case study of the Chaohu Lake Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, B.D.; Sagin, J.; Baulch, H.M.; Lindenschmidt, K.E.; Jardine, T.D. Influence of hydrological connectivity on winter limnology in floodplain lakes of the Saskatchewan River Delta, Saskatchewan. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 73, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenouillet, G.; Pont, D.; Hérissé, C. Within-basin fish assemblage structure, the relative influence of habitat versus stream spatial position on local species richness. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2004, 61, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.A.; Kraft, C.E. Stream fish assemblages in relation to landscape position and local habitat variables. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2005, 134, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansac-Tôha, F.M.; Meira, B.R.; Segovia, B.T.; Lansac-Tôha, F.A.; Velho, L.F.M. Hydrological connectivity determining metacommunity structure of planktonic heterotrophic flagellates. Hydrobiologia 2016, 781, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.L.; Li, P.W.; Li, Q.; Chu, L.; Wang, K.; Yan, Y.Z. Effects of land use on the β-diversity of fish assemblages in subtropical headwater streams, China. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2022, 31, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.S.; Pires, M.M.; Schulz, U.H. Influence of land-use classes on the functional structure of fish communities in southern Brazilian headwater streams. Environ. Manag. 2020, 65, 618–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueira, R.; Chapman, J.M.; Suski, C.D.; Cooke, S.J. The influence of watershed land use cover on stream fish diversity and size-at-age of a generalist fish. Environ. Int. 2016, 60, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.A.; Menninger, H.L.; Bernhardt, E. River restoration, habitat heterogeneity and biodiversity: A failure of theory or practice? Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D. Landscapes and riverscales: The influence of land use on streamecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.S. Hefei Water Conservancy Chronicles; Huangshan Publishing House: Hefei, China, 1997. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Q.; Zhou, Z.H.; Liu, D.Y.; Hu, Q.; Tang, W.H.; Zhou, M. Study on landscape pattern change of Chaohu basin based on land use change. Agric. Sci. J. Yanbian Univ. 2022, 44, 84–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Matono, P.; Sousa, D.; Ilhéu, M. Effects of land use intensification on fish assemblages in Mediterranean climate streams. Environ. Manag. 2013, 52, 1213–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, R.P.; Zuanon, J.; Mouillot, D.; Leal, C.G.; Hughes, R.M.; Kaufmann, P.R.; Villéger, S.; Pompeu, P.S.; Kasper, D.; de Paula, F.R.; et al. Disentangling the pathways of land use impacts on the functional structure of fish assemblages in Amazon streams. Ecography 2018, 41, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.E.; Bies, J.M.; Hann, D.A. Land use structures fish assemblages in reservoirs of the Tennessee River. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2015, 66, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
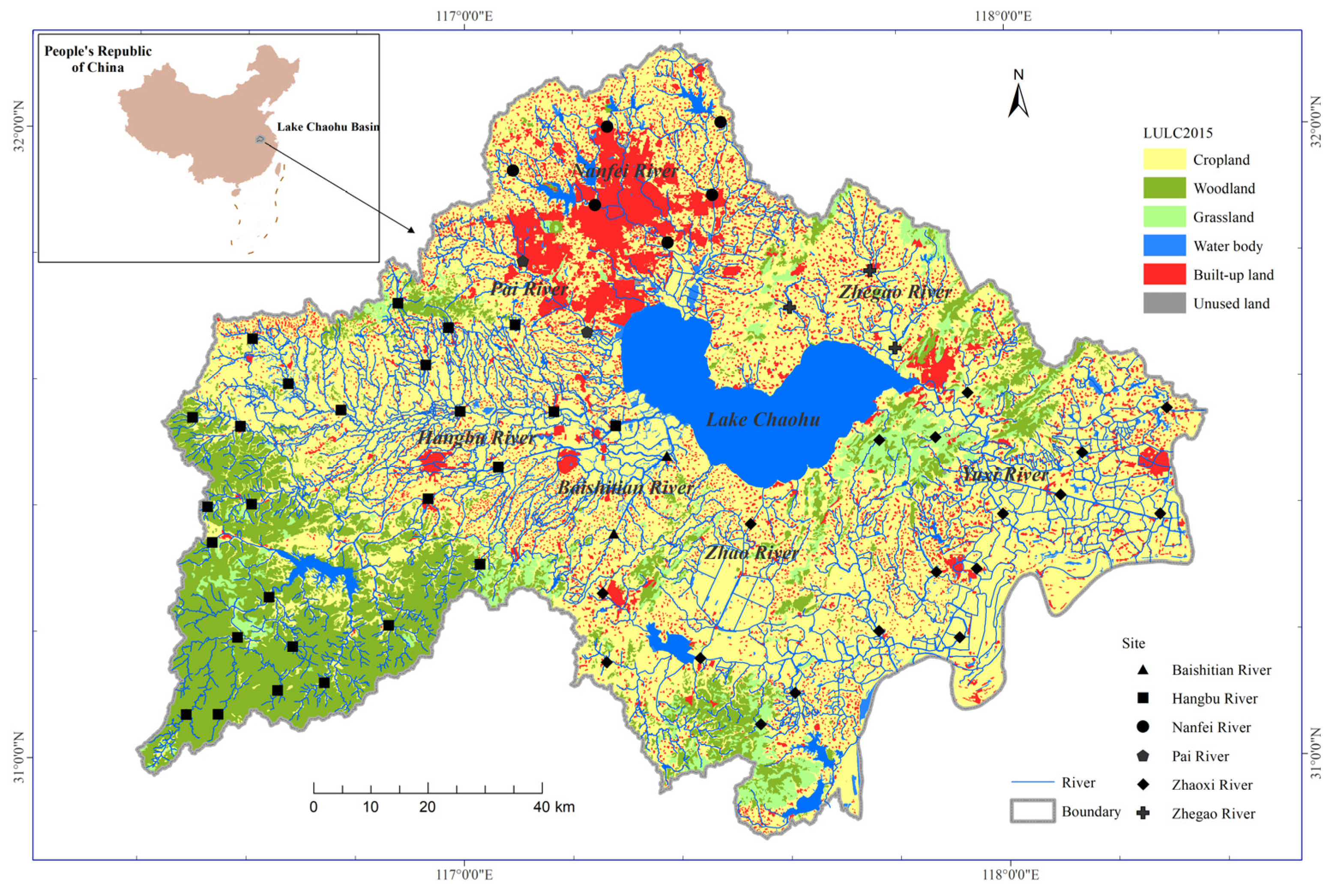
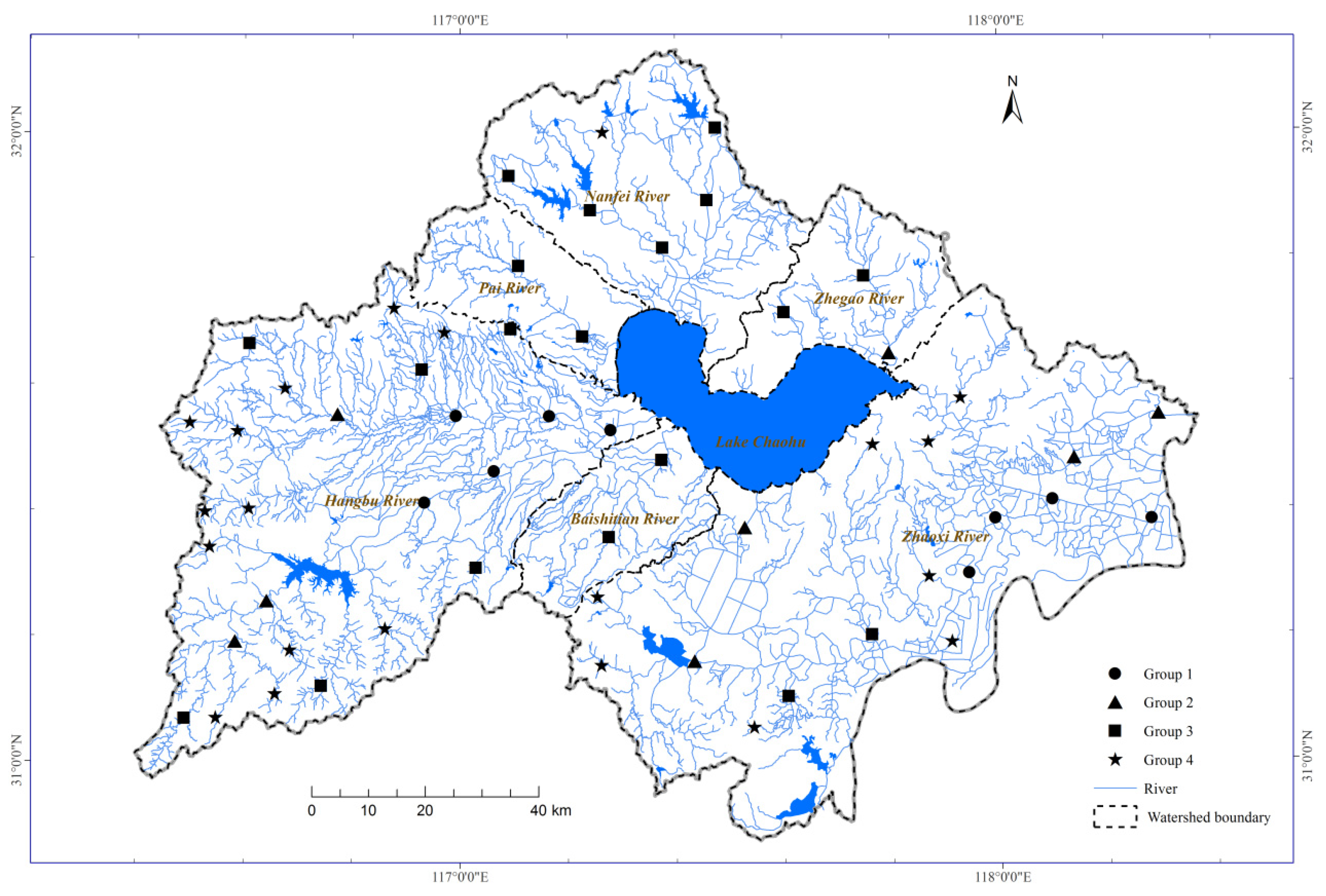
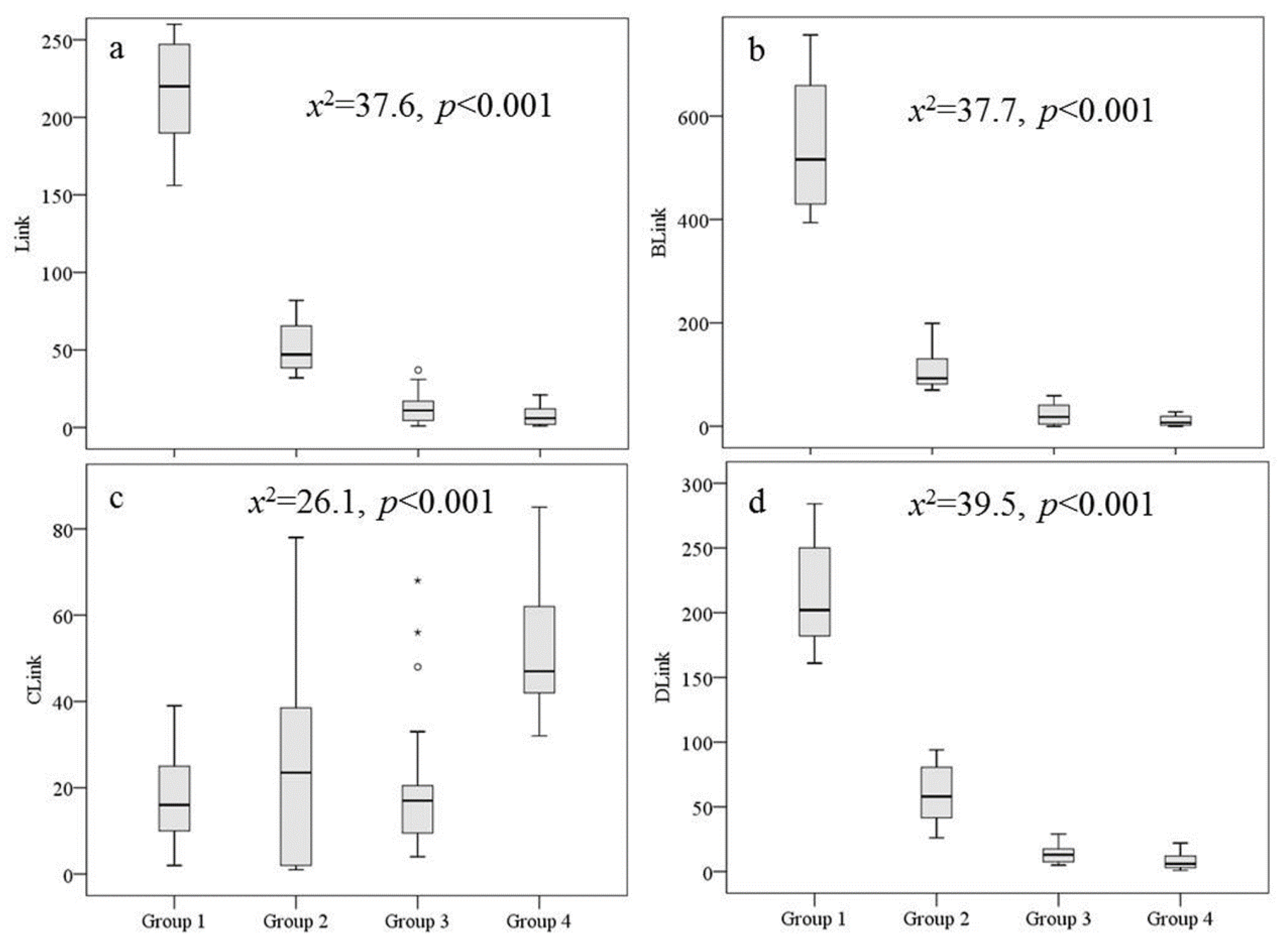


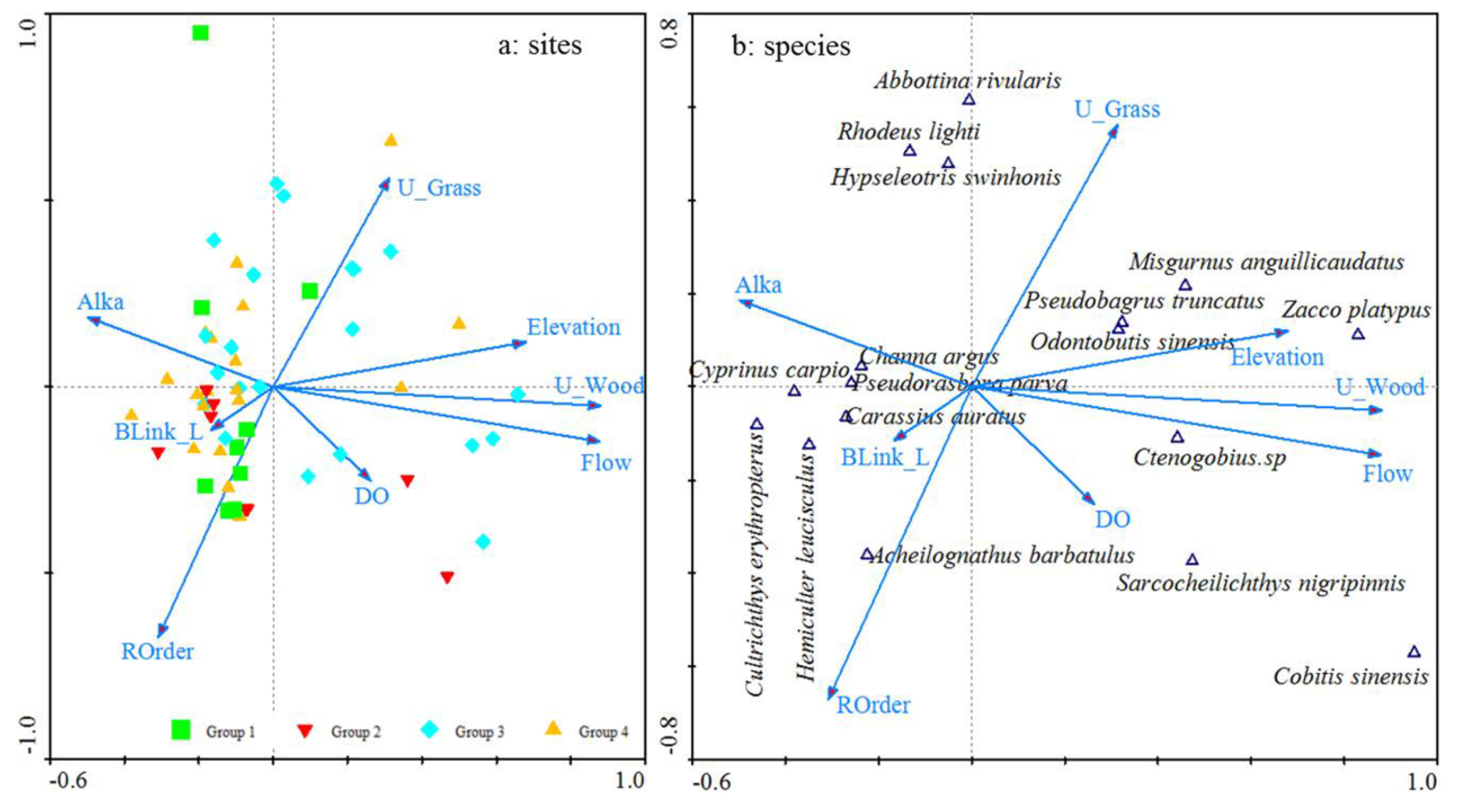
| Physicochemical Variables | River-Connectivity Group | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (n = 9) | Group 2 (n = 8) | Group 3 (n = 19) | Group 4 (n = 21) | ||
| ROrder | 4.67 (2–5) | 4.13(4–5) | 2.89 (1–4) | 2.43 (1–3) | <0.001 *** |
| Link | 250.22 (156–567) | 52 (32–82) | 12.89 (1–37) | 7.38 (1–21) | <0.001 *** |
| BLink_Lf | 279.56 (108–970) | 60.38 (5–119) | 13.68 (0–45) | 4.95 (0–16) | <0.001 *** |
| BLink_R | 353.22 (215–537) | 49.38 (26–84) | 10.21 (0–33) | 5.81 (0–18) | <0.001 *** |
| BLink | 632.78 (394–1423) | 109.75 (70–199) | 23.89 (0–59) | 10.76 (0–28) | <0.001 *** |
| CLink | 18 (2–39) | 25.88 (1–78) | 21.05 (4–68) | 53.05 (32–85) | <0.001 *** |
| DLink | 239.11 (161–499) | 60 (26–94) | 14.05 (5–29) | 8.1 (1–22) | <0.001 *** |
| Down_L (km) | 1290.5 (13.02–3911) | 1700.35 (63.37–6957) | 874.07 (10.9–7329) | 2016 (11.8–16,500) | 0.420 |
| Up_L (km) | 1227.53 (131.1–5231) | 1504.04 (29.43–3930) | 997.75 (11.48–4852) | 1414.17 (13.11–4840) | 0.826 |
| LSS | 0.51 (0.05–0.99) | 0.55 (0.01–0.94) | 0.56 (0.04–0.98) | 0.46 (0.01–0.99) | 0.909 |
| Physicochemical Variables | River-Connectivity Group | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (n = 9) | Group 2 (n = 8) | Group 3 (n = 19) | Group 4 (n = 21) | ||
| pH | 8.39 (7.4–9.87) | 8.22 (6.93–9.87) | 8.25 (7.5–10.16) | 8.06 (7.23–9.19) | 0.619 |
| DO (mg/L) | 10.72 (6.14–18.22) | 9.82 (3.22–18.22) | 8.86 (0.85–13.45) | 9.86 (1.46–16.94) | 0.896 |
| EC (μs/cm) | 158.56 (69–221) | 185.75 (41–323) | 201.74 (33–576) | 191.9 (41–616) | 0.939 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 0.12 (0.05–0.17) | 0.14 (0.03–0.26) | 0.15 (0.03–0.4) | 0.14 (0.04–0.29) | 0.952 |
| Alka (mg/L) | 35.18 (0–59.36) | 40.99 (14.13–62.19) | 60.7 (19.79–115.89) | 44.82 (8.48–132.85) | 0.088 |
| Turb (NTU) | 14.22 (0.9–30.9) | 8.6 (0.9–20.4) | 21.78 (0.1–116.1) | 10.75 (0.3–34.8) | 0.414 |
| TN (mg/L) | 0.63 (0.09–2.11) | 0.52 (0.08–2.11) | 2.64 (0.17–15.85) | 0.60 (0.09–4.99) | 0.595 |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 0.49 (0.13–1.8) | 0.76 (0.06–2.74) | 0.14 (0.04–0.73) | 0.21 (0.04–1.04) | 0.082 |
| NO3−-N (mg/L) | 1.72 (0.66–2.7) | 1.94 (0.45–4.97) | 3.77 (0.57–17.87) | 1.70 (0.48–5.55) | 0.006 ** |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.06 (0.02–0.26) | 0.05 (0.01–0.24) | 0.20 (0.01–1.05) | 0.03 (0–0.06) | 0.013 * |
| PO43−-P (mg/L) | 0.11 (0.04–0.34) | 0.08 (0.02–0.34) | 0.41 (0.02–2.66) | 0.05 (0.01–0.11) | 0.020 * |
| DOC (mg/L) | 4.55 (3.03–7.59) | 5.13 (3.18–7.21) | 7.17 (2.34–16.81) | 4.72 (1.45–8.03) | 0.041 * |
| Elevation (m) | 22 (12–33) | 50.25 (18–123) | 57.63 (8–387) | 63.24 (7–159) | 0.023 * |
| Temp (°C) | 18.77 (15.99–25.25) | 17.83 (13.32–25.25) | 18.76 (10.96–25.89) | 17.85 (12.3–25.23) | 0.495 |
| Width (m) | 149.22 (40–320) | 61.38 (10–108) | 48.16 (4–240) | 20.67 (3–150) | <0.001 *** |
| Depth (m) | 4.12 (0.9–7) | 2.21 (0.8–4) | 1.98 (0.3–4) | 0.99 (0.3–5) | <0.001 *** |
| Flow (m/s) | 0.10 (0–0.2) | 0.19 (0–0.61) | 0.09 (0–0.51) | 0.18 (0–0.81) | 0.349 |
| Chl-a (μg/cm2) | 0.25 (0.03–0.71) | 0.17 (0.05–0.33) | 0.40 (0.05–1.79) | 0.31 (0.02–1.27) | 0.899 |
| Land Use and Land Cover | River-Connectivity Group | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (n = 9) | Group 2 (n = 8) | Group 3 (n = 19) | Group 4 (n = 21) | ||
| U_Grass | 0 (0–0) | 1.25 (0–9.98) | 1.49 (0–28.33) | 12.72 (0–86.32) | 0.018 * |
| U_Built | 9.18 (0–21.46) | 9.5 (0–13.93) | 21.56 (0–84.98) | 7.57 (0–54.3) | 0.080 |
| U_Crop | 78.21 (63.45–97.14) | 66.68 (27.34–90.72) | 62.83 (0–98.76) | 49.64 (0–97.25) | 0.127 |
| U_Wood | 1.39 (0–12.47) | 15.25 (0–61.85) | 10.83 (0–100) | 27.52 (0–100) | 0.002 ** |
| U_Water | 11.22 (0–31.16) | 7.32 (0–23.31) | 3.29 (0–39.3) | 2.54 (0–13.58) | 0.032 * |
| D_Grass | 0 (0–0) | 1.16 (0–6.84) | 1.31 (0–24.96) | 10.09 (0–57.22) | 0.094 |
| D_Built | 8.02 (0–28.55) | 9.76 (0–19.88) | 19.03 (0–99.24) | 8.15 (0–42.62) | 0.255 |
| D_Crop | 81.04 (62.05–94.97) | 66.53 (28.8–93.2) | 65.81 (0–98.6) | 53.95 (0–96.4) | 0.081 |
| D_Wood | 0 (0–0) | 12.98 (0–56.08) | 10.39 (0–100) | 24.87 (0–100) | 0.002 ** |
| D_Water | 10.95 (0–33.17) | 9.56 (0–35.79) | 3.31 (0–41.23) | 2.94 (0–13.15) | 0.031 * |
| T_Grass | 0 (0–0) | 1.29 (0–8.33) | 1.41 (0–26.81) | 10.16 (0–53.22) | 0.023 * |
| T_Built | 8.44 (0–22.94) | 9.78 (0–18.71) | 19.89 (0–89.66) | 8.07 (0–44.31) | 0.179 |
| T_Crop | 79.72 (64.61–95.73) | 66.37 (27.91–92.15) | 64.58 (0–98.68) | 52.92 (0–96.73) | 0.098 |
| T_Wood | 1.1 (0–9.87) | 14.44 (0–59.59) | 10.7 (0–100) | 26.07 (0–100) | 0.001 *** |
| T_Water | 10.75 (0–32.06) | 8.12 (0–27.88) | 3.37 (0–40.12) | 2.78 (0–12.98) | 0.045 * |
| Fish Taxa Richness and Diversity Indices | River-Connectivity Group | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (n = 9) | Group 2 (n = 8) | Group 3 (n = 19) | Group 4 (n = 21) | ||
| Number of taxa | 6.89 (3–13) | 6.13 (4–11) | 7.53 (1–14) | 5.48 (1–12) | 0.119 |
| Total number of individuals | 53.67 (12–142) | 46.25 (10–110) | 89.11 (1–455) | 44 (1–122) | 0.114 |
| Shannon-Wiener index | 0.63 (0.25–0.92) | 0.7 (0.47–0.9) | 0.57 (0.33–1) | 0.68 (0.32–1) | 0.099 |
| Buzas and Gibson’s evenness | 1.11 (0.6–1.59) | 1.16 (0.67–1.77) | 1.14 (0–1.71) | 0.95 (0–1.9) | 0.482 |
| Margalef’s richness index | 0.72 (0.42–0.95) | 0.78 (0.53–0.92) | 0.66 (0.29–0.82) | 0.72 (0.17–0.96) | 0.159 |
| Berger-Parker dominance index | 0.54 (0.29–0.83) | 0.46 (0.32–0.77) | 0.55 (0.29–1) | 0.56 (0.19–1) | 0.625 |
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | |
| Group 1 | 0.696 | 0.320 | 0.104 | |
| Group 2 | −0.042 | 0.390 | 0.048 * | |
| Group 3 | 0.029 | 0.004 | 0.006 ** | |
| Group 4 | 0.100 | 0.127 | 0.160 |
| Fish Taxa Richness and Diversity Indices | River-Order Group | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st-Order (n = 3) | 2nd-Order (n = 14) | 3rd-Order (n = 19) | 4th-Order (n = 12) | 5th-Order (n = 9) | ||
| Number of taxa | 4.67 (3–6) | 7 (1–13) | 5.89 (1–10) | 7.58 (4–14) | 6 (3–10) | 0.492 |
| Total number of individuals | 30.67 (5–55) | 46.5 (1–142) | 63.58 (1–122) | 96.08 (10–455) | 40.67 (12–92) | 0.236 |
| Shannon-Wiener index | 0.78 (0.66–0.96) | 0.68 (0.25–1) | 0.58 (0.32–1) | 0.59 (0.33–0.9) | 0.7 (0.39–0.92) | 0.149 |
| Buzas and Gibson’s evenness | 1.01 (0.68–1.24) | 1.11 (0–1.9) | 0.93 (0–1.71) | 1.22 (0.67–1.77) | 1.13 (0.6–1.59) | 0.649 |
| Margalef’s richness index | 0.84 (0.77–0.96) | 0.74 (0.46–0.93) | 0.62 (0.17–0.87) | 0.72 (0.53–0.92) | 0.77 (0.42–0.95) | 0.089 |
| Berger-Parker dominance index | 0.44 (0.4–0.5) | 0.52 (0.19–1) | 0.62 (0.29–1) | 0.5 (0.33–0.77) | 0.5 (0.29–0.83) | 0.415 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Cai, Y. Effects of Land Use Characteristics, Physiochemical Variables, and River Connectivity on Fish Assemblages in a Lowland Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215960
Zhang Z, Gao J, Cai Y. Effects of Land Use Characteristics, Physiochemical Variables, and River Connectivity on Fish Assemblages in a Lowland Basin. Sustainability. 2023; 15(22):15960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215960
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhiming, Junfeng Gao, and Yongjiu Cai. 2023. "Effects of Land Use Characteristics, Physiochemical Variables, and River Connectivity on Fish Assemblages in a Lowland Basin" Sustainability 15, no. 22: 15960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215960
APA StyleZhang, Z., Gao, J., & Cai, Y. (2023). Effects of Land Use Characteristics, Physiochemical Variables, and River Connectivity on Fish Assemblages in a Lowland Basin. Sustainability, 15(22), 15960. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215960







