Study of the Spatio-Temporal Variation of Agricultural Sustainability at National and Provincial Levels in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Screening of SDGs for Agriculture Sustainability
2.2. Evaluation Index System for Agricultural Sustainable Development
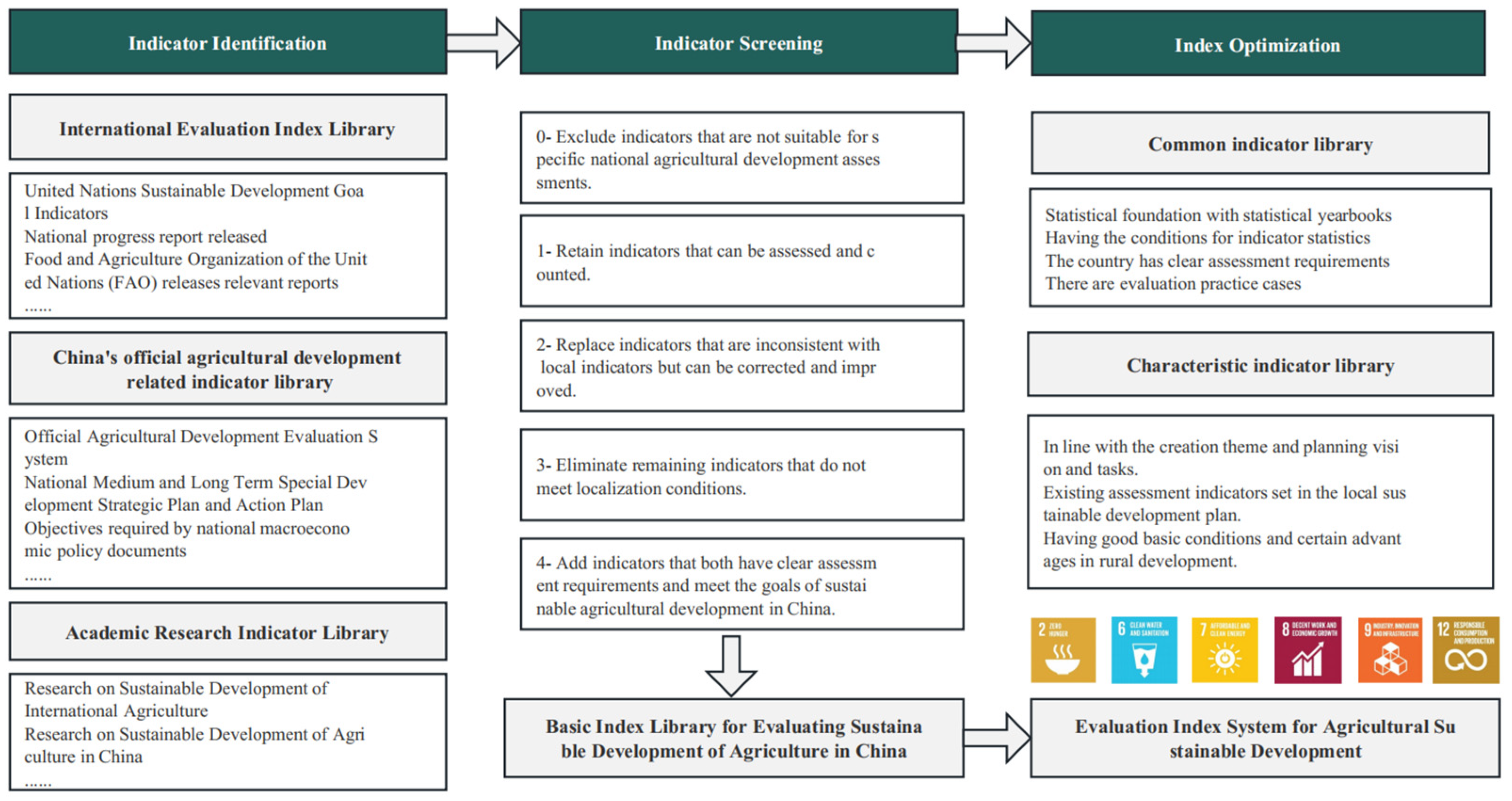
2.2.1. Scheme on Constructing the Evaluation Index System
2.2.2. Basic Indicator Library
2.2.3. Construction of Evaluation Index System
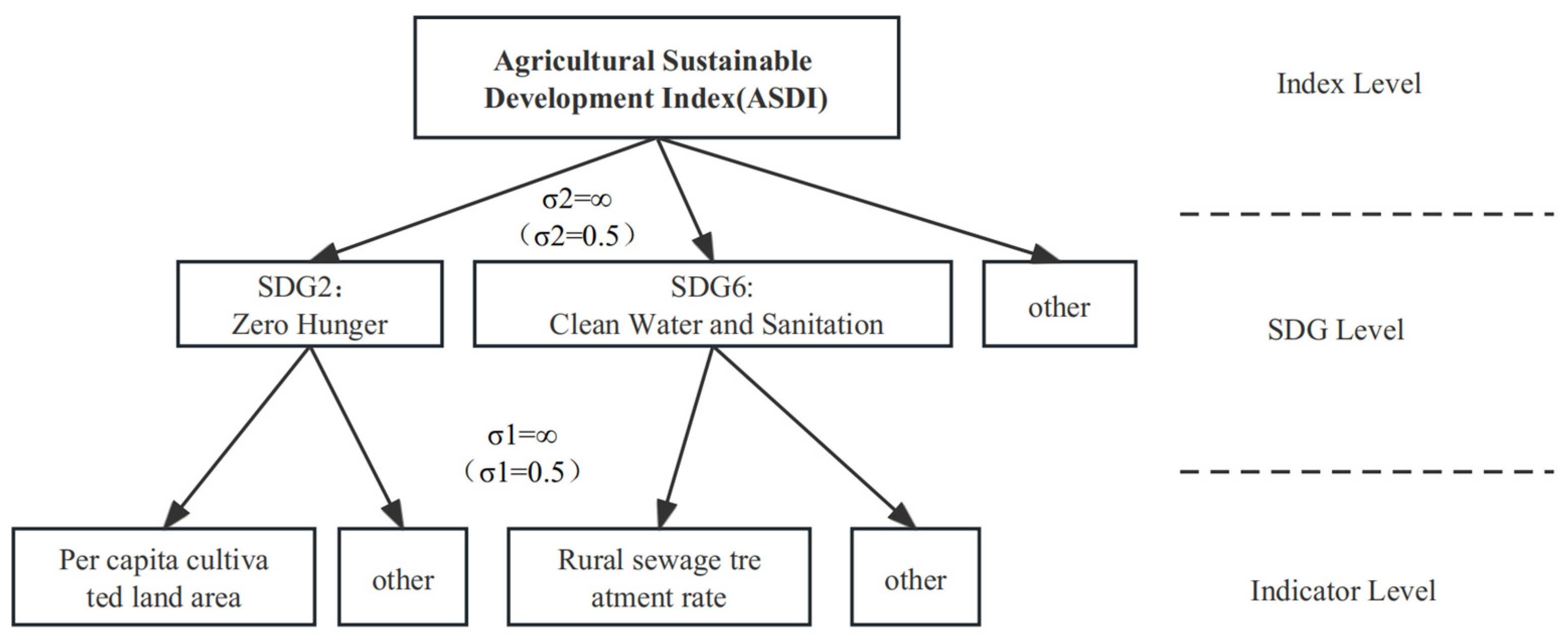
2.3. Evaluation and Analysis Methods
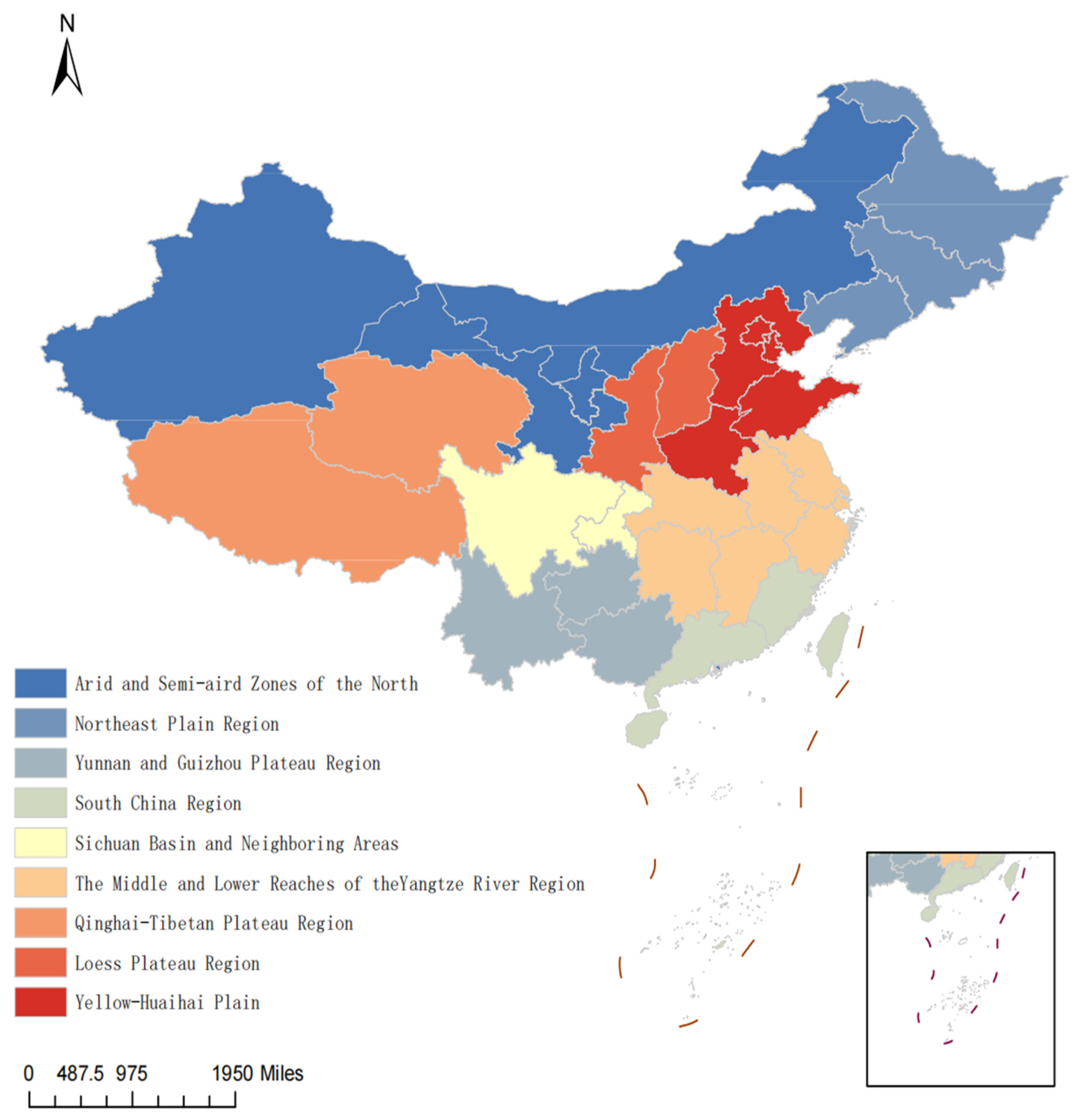
2.3.1. Data Sources
2.3.2. Normalization
2.3.3. Aggregation
3. Results
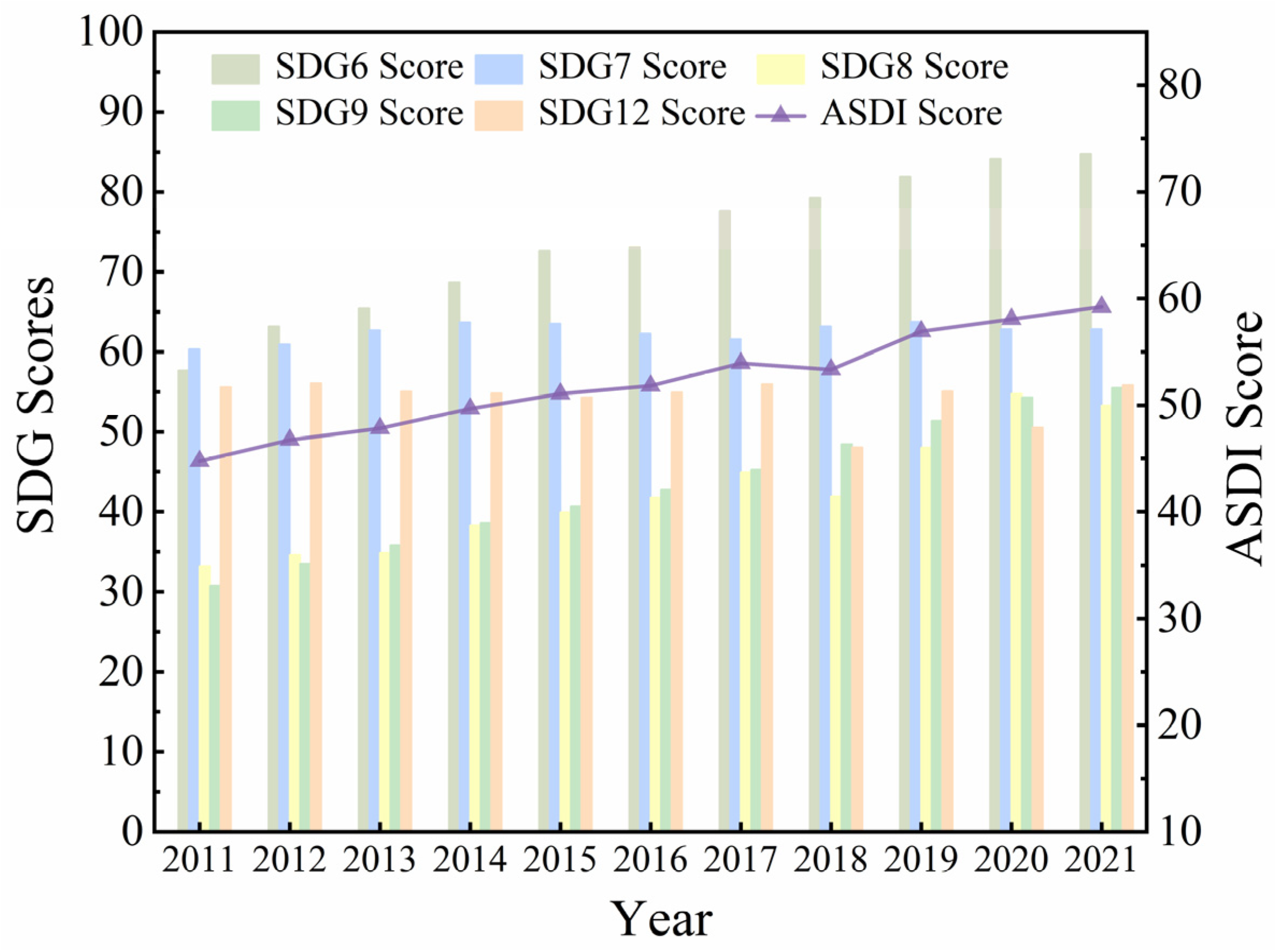
3.1. Agriculture-Related SDGs Assessment
3.1.1. Spatio-Temporal Evolution for Agriculture-Related SDGs
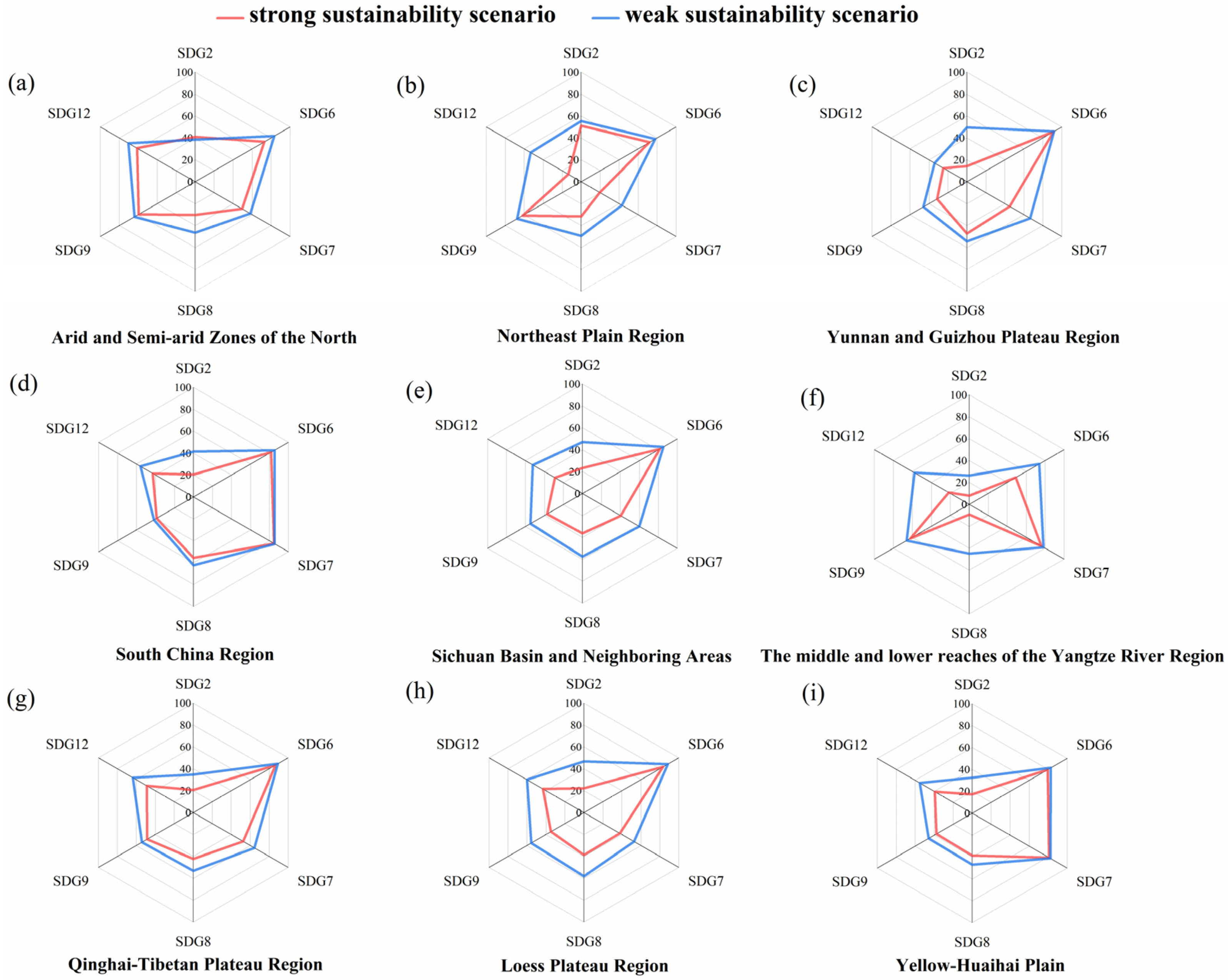
3.1.2. SDGs Sensitivity Analysis
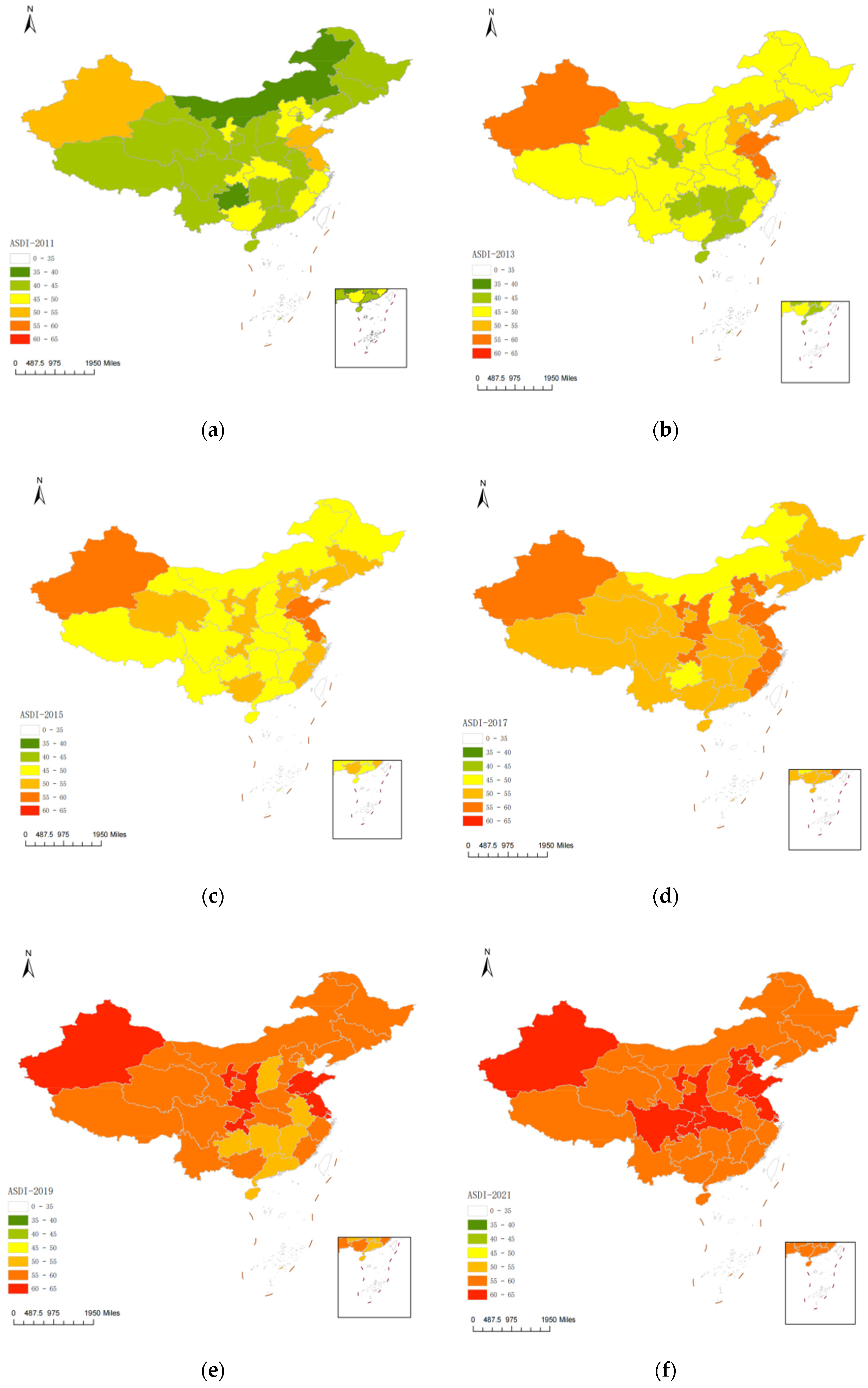
3.2. ASDI Assessment
3.2.1. Spatio-Temporal Evolution for ASDI
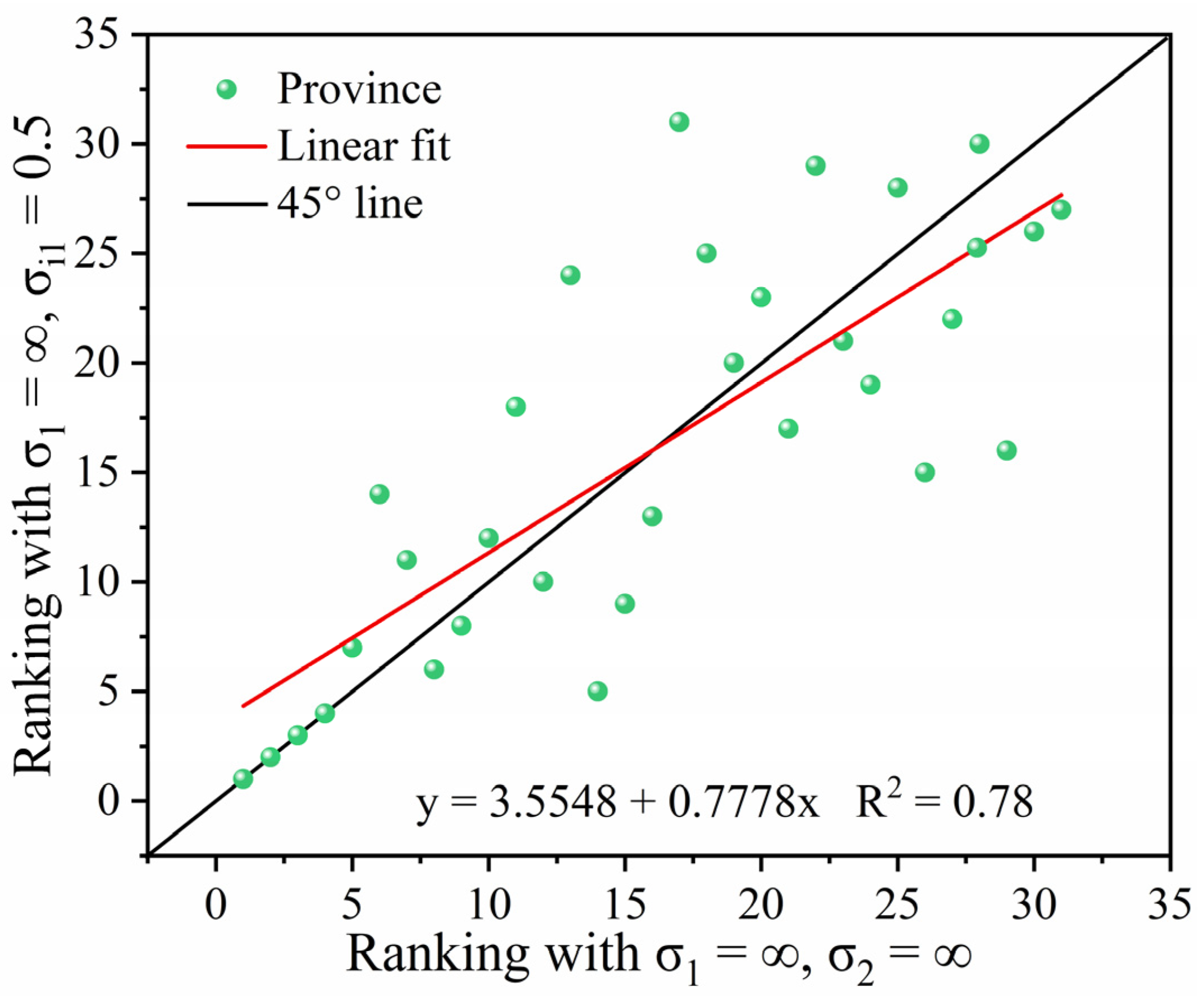
3.2.2. ASDI Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorward, A.; Kydd, J.; Morrison, J.; Urey, I. A Policy Agenda for Pro-Poor Agricultural Growth. World Dev. 2004, 32, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdei, K.N.; Esfahani, S.M.J.; Lebailly, P.; Dogot, T.; Van Passel, S.; Azadi, H. Environmental impact assessment and efficiency of cotton: The case of Northeast Iran. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 10301–10321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.W.; Mi, C.H.; Shi, R.G.; Yang, Y.Y. Hotspots and trends of agriculture sustainable development: Visualization analysis based on bibliometrics. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2022, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickens, C.; McCartney, M.; Tickner, D.; Harrison, I.J.; Pacheco, P.; Ndhlovu, B. Evaluating the Global State of Ecosystems and Natural Resources: Within and Beyond the SDGs. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.S.; Wu, C.J. Theories and Progress of Study on Sustainable Agriculture Development. Econ. Geogr. 2000, 20, 63168. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, K.S.; Nguyen, T.D.; Francois, J.R.; Ojha, S. Rural sustainability methods, drivers, and outcomes: A systematic review. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 31, 1226–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China’s Agenda 21: China’s White Paper on Population, Environment and Development in the 21st Century; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994.
- Liu, X.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Sui, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Herbert, S.J.; Ding, G. Soil degradation: A problem threatening the sustainable development of agriculture in Northeast China. Plant Soil Environ. 2010, 56, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, D.; Woodhouse, P.; Young, T.; Burton, M. Constructing a farm level indicator of sustainable agricultural practice. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 39, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.H.; Lv, C.H. Application of DPSIR Framework for Analyses of Sustainable Agricultural Developmen. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2004, 5, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Shah Moridi, R.; Kazemi, H.; Kamkar, B. Evaluation of Sustainable Agricultural Development in Golestan Province. J. Agric. Sci. Sustain. Prod. 2017, 27, 197–215. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.L.; Mao, X.B.; Mao, X.H.; Wang, J. Evaluation of Agricultural Sustainable Development Based on Resource Use Efficiency: Empirical Evidence from Zhejiang Province, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Gong, Q.X.; Yang, S. A Sustainable, Regional Agricultural Development Measurement System based on Dissipative Structure Theory and the Entropy Weight Method: A Case Study in Chengdu, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, Q.X. Sustainable Development of Agroecosystem in Hilly Ridge Areas of Loess Hills Based on Emergy: A Case of Yonghe County, Shanxi Province. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2018, 34, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, D.N.; Loof, R.; Paudyal, G.N. Environmental-economic decision-making in lowland irrigated agriculture using multi-criteria analysis techniques. Agric. Syst. 1999, 60, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golusin, M.; Ivanovic, O.M.; Teodorovic, N. The review of the achieved degree of sustainable development in South Eastern Europe-The use of linear regression method. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.G.; Williams, A.G.; Pearce, B.D. The energy efficiency of organic agriculture: A review. Renew. Agric Food Syst. 2015, 30, 280–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Yao, C.S.; Wang, G.X.; Bao, S.M. An integrated sustainable development approach to modeling the eco-environmental effects from urbanization. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezierska-Thöle, A.; Gwiaździńska-Goraj, M.; Dudzińska, M. Environmental, Social, and Economic Aspects of the Green Economy in Polish Rural Areas—A Spatial Analysis. Energies 2022, 15, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.L.; Zhao, Y.L.; Li, P. Assessment of agricultural water resources carrying capacity and analysis of its spatio-temporal variation in Henan Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 403, 136869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Kuang, Y.P. Evaluation, Regional Disparities and Driving Mechanisms of High-Quality Agricultural Development in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoleikhaie Sayyar, L.; Naderi Mahdei, K.; Shabanali Fami, H.; Motaghed, M. Developing and Analyzing the Agri-cultural Water Poverty Index in West Iran. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Song, Q.Q. The forecasting model research of rural energy transformation in Henan Province based on STIRPAT model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China, 2012–2022. In China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022; ISBN 978-7-5037-9950-1. (In Chinese)
- National Bureau of Statistic & Ministry of Ecological Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2012–2022. In China Statistical Yearbook on Environment; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021; ISBN 978-7-5230-0075-5. (In Chinese)
- Department of Rural Socio-Economic Surveys, National Statistical Office, 2012–2022. In China Agricultural Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021; ISBN 978-7-5037-9680-7. (In Chinese)
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China, 2012–2022. In China Energy Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2023; ISBN 978-7-5230-0106-6. (In Chinese)
- Population and Employment Statistics Division, National Statistical Office, 2012–2022. In China Population and Employment Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022; ISBN 978-7-5037-9915-0. (In Chinese)
- Shan, Y.; Guan, D.; Zheng, H.; Ou, J.; Li, Y.; Meng, J.; Mi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q. China CO2 emission accounts 1997–2015. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 170201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Guan, D.; Hubacek, K. China CO2 emission accounts 2016–2017. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.R.; Shan, Y.L.; Huang, Q.; Chen, H.L.; Wang, D.; Hubacek, K. Assessment to China’s Recent Emission Pattern Shifts. Earth’s Future 2021, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.L.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.W.H.; Shao, S.; Wang, P.; Guan, D.B. New provincial CO2 emission inventories in China based on apparent energy consumption data and updated emission factors. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.S.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhou, X.W.; Lai, C.G.; Chen, X.H. Trends in temperature extremes over nine integrated agricultural regions in China, 1961–2011. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2021, 129, 1279–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, J.; Schmidt-Traub, G.; Kroll, C.; Lafortune, G.; Fuller, G.W.F. The Sustainable Development Goals and COVID-19. In Sustainable Development Report 2020; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; Available online: https://www.sustainabledevelopment.report/reports/sustainable-development-report-2020/ (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Halpern, B.S.; Longo, C.; Scarborough, C.; Hardy, D.; Best, B.D.; Doney, S.C.; Katona, S.K.; McLeod, K.L.; Rosenberg, A.A.; Samhouri, J.F. Assessing the Health of the US West Coast with a Regional-Scale Application of the Ocean Health Index. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, J.G. Landscape sustainability science: Ecosystem services and human well-being in changing landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 999–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, H.E. On Wilfred Beckerman’s critique of sustainable development. Environ. Values 1995, 4, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickels, W.; Quaas, M.F.; Visbeck, M. How healthy is the human-ocean system? Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 044013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickels, W.; Dovern, J.; Hoffmann, J.; Quaas, M.F.; Schmidt, J.O.; Visbeck, M. Indicators for monitoring sustainable development goals: An application to oceanic development in the European Union. Earth’s Future 2016, 4, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, J.; Schmidt-Traub, G.; Kroll, C.; Durand-Delace, D.; Teksoz, K. SDG Index and Dashboards—Global Report; Bertelsmann Stiftung and Sustainable Development Solutions Network: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dovern, J.; Quaas, M.F.; Rickels, W. A comprehensive wealth index for cities in Germany. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafortune, G.; Fuller, G.; Moreno, J.; Schmidt-Traub, G.; Kroll, C. SDG Index and Dashboards Detailed Methodological Paper; Bertelsmann Stiftung and Sustainable Development Solutions Network: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Hou, Y.T.; Xin, F.; Mao, Z.; Xue, X.Z. Study of the spatio-temporal variation of environmental sustainability at national and provincial levels in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Appolloni, A.; Cavallaro, F.; D’Adamo, I.; Di Vaio, A.; Ferella, F.; Gastaldi, M.; Ikram, M.; Kumar, N.M.; Martin, M.A.; et al. Development Goals towards Sustainability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SDGs | Targets | IAEG-SDGs Indicators | Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDG2: Zero Hunger | Target 2.1 | INDICATORS 2.1.1 | Proportion of malnutrition among rural elderly |
| INDICATORS 2.1.2 | Per capita cultivated land area, Grain yield per hectare *, Comprehensive grain production capacity | ||
| / | Sampling inspection pass rate of edible agricultural products | ||
| Target 2.2 | INDICATORS 2.2.1 | Growth stunting rate among rural children under 5 years old | |
| INDICATORS 2.2.2 | Underweight rate among rural children under 5 years old * | ||
| / | The proportion of the rural population covered by the Government’s minimum subsistence allowance as a percentage of the rural population | ||
| Target 2.3 | INDICATORS 2.3.1 | Agricultural labor productivity | |
| INDICATORS 2.3.2 | Per capita disposable income of rural residents | ||
| Target 2.4 | INDICATORS 2.4.1 | Proportion of high-standard farmland | |
| / | Comprehensive utilization rate of straw, Comprehensive utilization rate of livestock and poultry manure | ||
| Target 2.5 | INDICATORS 2.5.1 | Number of livestock and poultry genetic resource breeding farms, protected areas, gene banks, Agricultural germplasm resources | |
| Target 2.a | INDICATORS 2.a.1 | Proportion of agriculture, forestry, and water expenditures in fiscal expenditures | |
| INDICATORS 2.a.2 | Central finance agricultural insurance premium subsidy ratio, Crop seed subsidy ratio, Proportion of direct subsidies to grain farmers, Comprehensive agricultural input subsidy ratio | ||
| Target 2.c | INDICATORS 2.c.1 | Grain and oil price index | |
| SDG6: Clean Water and Sanitation | Target 6.1 | INDICATORS 6.1.1 | Drinking water hygiene qualification rate in villages and towns, Rural piped water penetration |
| Target 6.2 | INDICATORS 6.2.1 | The popularity rate of sanitary toilets in rural areas | |
| Target 6.3 | INDICATORS 6.3.1 | Rural sewage treatment rate | |
| INDICATORS 6.3.2 | The proportion of surface water quality reaching or better than Class III water bodies, Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) emissions from wastewater of 10,000 Yuan GDP in agriculture | ||
| Target 6.4 | INDICATORS 6.4.1 | Agricultural water efficiency | |
| INDICATORS 6.4.2 | Water consumption per 10,000 yuan of GDP, water resources development, and utilization rate | ||
| Target 6.6 | INDICATORS 6.6.1 | Water quality compliance rate of important rivers and lakes water functional areas | |
| Target 6.b | / | County Domestic Waste Disposal Rate, rural domestic waste harmless treatment rate | |
| SDG7: Affordable and Clean Energy | Target 7.1 | INDICATORS 7.1.1 | Agricultural electrification rate, annual per capita electricity consumption of rural residents |
| INDICATORS 7.1.2 | Gas penetration rate *, number of biogas digesters per rural household | ||
| Target 7.2 | INDICATORS 7.2.1 | Renewable energy power generation as a percentage of total power generation, The proportion of non-fossil energy in primary energy consumption | |
| Target 7.3 | INDICATORS 7.3.1 | Energy consumption of 10,000 yuan GDP in agriculture, Decline rate of energy consumption per unit of agricultural GDP | |
| / | Electricity consumption rate for agricultural production, Carbon emissions per capita from agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and water resources | ||
| SDG8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | Target 8.1 | INDICATORS 8.1.1 | Per capita GDP * (rural), Per capita GDP * (rural), Value added of primary sector as % of GDP, Share of primary sector output in GNP, Number of enterprises in the primary sector per unit of sown area |
| Target 8.2 | INDICATORS 8.2.1 | The ratio of agricultural product processing output value to total agricultural output value | |
| Target 8.3 | INDICATORS 8.3.1 | The overall employment rate of the rural labor force | |
| / | The proportion of the population returning home in the county, Rural labor supply intensity | ||
| Target 8.4 | INDICATORS 8.4.2 | Rural disposable income | |
| Target 8.5 | INDICATORS 8.5.2 | Registered urban unemployment rate *, Surveyed unemployment rate of rural migrants | |
| Target 8.6 | INDICATORS 8.6.1 | High-quality farmer training rate | |
| Target 8.8 | INDICATORS 8.8.1 | Deaths from work safety accidents per 100,000 people * | |
| Target 8.9 | INDICATORS 8.9.1 | The added value of tourism as a proportion of regional GDP | |
| / | The GDP of the tertiary industry as a percentage of the GDP of the region | ||
| Target 8.10 | INDICATORS 8.10.1 | County deposit-to-loan ratio | |
| / | Input–output ratio of rural fixed assets, Rural fixed assets input-output ratio, Agricultural insurance coverage | ||
| SDG9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure | Target 9.1 | INDICATORS 9.1.1 | Road area per capita in rural |
| INDICATORS 9.1.2 | Logistics distribution network density | ||
| Target 9.4 | / | Agricultural mechanization rate | |
| Target 9.5 | INDICATORS 9.5.1 | The proportion of agricultural R&D investment, Research and development (R&D) expenditures as a proportion of regional GDP, Full-time equivalent of research and experimental development (R&D) personnel per 10,000 people *, Number of invention patents per 10,000 population * | |
| INDICATORS 9.5.2 | Proportion of agricultural technicians, Proportion of agricultural science and technology talents with a Bachelor’s degree or above | ||
| / | Agricultural science and technology progress contribution rate | ||
| Target 9.b | INDICATORS 9.b.1 | Number of agricultural high-tech enterprises per 100,000 people | |
| Target 9.c | INDICATORS 9.c.1 | Rural Internet penetration rate, The proportion of the agricultural digital economy in agricultural added value | |
| SDG12: Responsible Consumption and Production | Target 12.2 | INDICATORS 12.2.2 | Fertilizer application intensity, Pesticide application intensity, Agricultural mulch coverage rate |
| / | Agriculture, Forestry, Animal Husbandry and Fishery Gross Output Value Index, Rate of water-saving irrigation | ||
| Target 12.3 | INDICATORS 12.3.1 | Total loss rate of the entire grain industry chain | |
| Target 12.4 | INDICATORS 12.4.2 | Crop fertilizer utilization rate, Pesticide utilization rate | |
| Target 12.5 | INDICATORS 12.5.1 | Comprehensive utilization rate of agricultural waste, Comprehensive utilization rate of livestock and poultry manure, Comprehensive utilization rate of straw, Coverage rate of agricultural mulch | |
| Target 12.b | INDICATORS 12.b.1 | Leisure agriculture and rural tourism reception |
| No. | Goals | Indicators | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SDG2: Zero Hunger | Per capita cultivated land area | hectares |
| 2 | Agricultural labor productivity | RMB/person | |
| 3 | Grain yield per hectare * | kg/ha | |
| 4 | The proportion of the rural population covered by the Government’s minimum subsistence allowance as a percentage of the rural population | % | |
| 5 | SDG6: Clean Water and Sanitation | Rural piped water penetration | % |
| 6 | Rural sewage treatment rate | % | |
| 7 | Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) emissions from wastewater of 10,000 yuan GDP in agriculture | kg/million | |
| 8 | County Domestic Waste Disposal Rate | % | |
| 9 | SDG7: Affordable and Clean Energy | Energy consumption of 10,000 yuan GDP in agriculture | Tons of standard coal/$10,000 |
| 10 | Carbon emissions per capita from agriculture, forestry, fisheries, and water resources | tons/person | |
| 11 | Number of biogas digesters per rural household | Unit/household | |
| 12 | SDG8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | Number of enterprises in the primary sector per unit of sown area | Unit/hectares |
| 13 | Input-output ratio of rural fixed assets | % | |
| 14 | Share of primary sector output in GNP | % | |
| 15 | Rural disposable income | Yuan | |
| 16 | Value added of primary sector as % of GDP | - | |
| 17 | SDG9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure | Agricultural mechanization rate | % |
| 18 | Percentage of agricultural technicians | % | |
| 19 | Road area per capita in rural | square meter | |
| 20 | Internet penetration | % | |
| 21 | SDG12: Responsible Consumption and Production | Fertilizer application intensity | kg/ha |
| 22 | Pesticide application intensity | kg/ha | |
| 23 | Agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fisheries gross output index | % | |
| 24 | Rate of water-saving irrigation | % | |
| 25 | Coverage rate of agricultural mulch | % |
| Provinces | Year | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
| Beijing | 45.36 | 47.46 | 48.29 | 50.19 | 49.27 | 51.21 | 53.59 | 52.38 | 55.75 | 55.89 | 60.29 |
| Tianjin | 42.17 | 44.70 | 46.40 | 47.47 | 51.58 | 51.32 | 53.28 | 51.10 | 54.28 | 55.60 | 56.91 |
| Hebei | 46.76 | 48.72 | 51.59 | 52.92 | 53.57 | 55.15 | 56.53 | 55.97 | 58.09 | 59.76 | 61.12 |
| Shanxi | 41.60 | 43.29 | 45.18 | 47.86 | 48.19 | 48.67 | 49.61 | 48.32 | 51.76 | 54.77 | 55.67 |
| Inner Mongolia | 39.66 | 43.44 | 45.29 | 46.00 | 47.97 | 48.30 | 47.55 | 51.96 | 56.23 | 55.20 | 56.15 |
| Liaoning | 44.75 | 47.67 | 50.72 | 50.04 | 53.55 | 52.85 | 54.52 | 53.17 | 57.30 | 57.52 | 59.21 |
| Jilin | 44.15 | 47.26 | 48.85 | 49.48 | 51.29 | 51.12 | 53.17 | 50.16 | 55.96 | 55.11 | 56.07 |
| Heilongjiang | 41.75 | 44.88 | 45.38 | 48.13 | 49.42 | 51.01 | 53.45 | 53.92 | 56.40 | 55.08 | 57.89 |
| Shanghai | 48.35 | 50.00 | 52.67 | 55.20 | 54.12 | 54.26 | 57.69 | 58.42 | 60.47 | 59.50 | 61.51 |
| Jiangsu | 52.77 | 54.15 | 55.01 | 56.55 | 57.80 | 58.19 | 59.75 | 59.95 | 61.85 | 64.44 | 64.95 |
| Zhejiang | 48.70 | 50.38 | 49.70 | 52.06 | 52.98 | 54.05 | 55.64 | 53.84 | 56.24 | 58.15 | 58.47 |
| Anhui | 43.24 | 45.59 | 45.57 | 46.83 | 48.06 | 49.08 | 51.66 | 51.41 | 54.70 | 55.80 | 57.50 |
| Fujian | 45.92 | 47.04 | 49.38 | 51.50 | 52.32 | 54.04 | 55.36 | 53.69 | 56.47 | 59.28 | 59.97 |
| Jiangxi | 44.09 | 45.39 | 44.93 | 46.44 | 48.29 | 49.01 | 51.37 | 51.01 | 54.62 | 55.59 | 57.15 |
| Shandong | 51.62 | 53.27 | 55.22 | 56.85 | 58.18 | 59.29 | 59.15 | 59.34 | 60.70 | 62.29 | 64.41 |
| Henan | 44.44 | 46.01 | 45.63 | 47.34 | 48.86 | 50.15 | 53.09 | 52.79 | 57.19 | 58.58 | 58.78 |
| Hubei | 47.84 | 46.83 | 45.89 | 47.00 | 49.58 | 51.00 | 53.97 | 53.21 | 57.58 | 57.50 | 60.41 |
| Hunan | 42.96 | 45.09 | 44.93 | 46.42 | 47.45 | 48.50 | 52.13 | 51.18 | 53.80 | 54.84 | 56.49 |
| Guangdong | 41.70 | 42.03 | 43.82 | 47.55 | 47.61 | 49.63 | 52.42 | 49.10 | 52.33 | 54.59 | 55.28 |
| Guangxi | 47.25 | 49.43 | 48.23 | 49.42 | 50.93 | 51.93 | 54.19 | 52.88 | 57.12 | 56.93 | 57.59 |
| Hainan | 40.09 | 42.97 | 44.86 | 47.96 | 48.22 | 49.62 | 50.50 | 48.76 | 54.29 | 54.57 | 56.09 |
| Chongqing | 45.81 | 47.56 | 47.33 | 52.38 | 53.58 | 55.13 | 58.28 | 54.88 | 61.16 | 64.20 | 64.14 |
| Sichuan | 44.20 | 46.58 | 46.28 | 47.78 | 49.40 | 50.77 | 54.06 | 53.64 | 57.77 | 59.40 | 60.04 |
| Guizhou | 38.43 | 41.63 | 40.55 | 43.14 | 45.76 | 46.15 | 49.22 | 49.55 | 54.93 | 57.04 | 57.86 |
| Yunnan | 43.43 | 46.33 | 46.51 | 47.74 | 48.57 | 49.11 | 52.46 | 51.26 | 56.61 | 56.61 | 57.49 |
| Tibet | 42.53 | 44.09 | 45.33 | 47.67 | 49.52 | 49.91 | 50.52 | 52.25 | 55.34 | 56.56 | 57.37 |
| Shaanxi | 44.13 | 45.78 | 49.51 | 51.83 | 53.10 | 54.30 | 56.78 | 56.84 | 60.03 | 63.81 | 64.20 |
| Gansu | 40.03 | 41.78 | 44.37 | 47.22 | 49.73 | 50.08 | 52.62 | 50.82 | 56.91 | 57.40 | 59.30 |
| Qinghai | 41.81 | 43.64 | 48.12 | 49.20 | 50.65 | 51.08 | 53.63 | 53.53 | 57.00 | 59.60 | 58.33 |
| Ningxia | 49.02 | 51.42 | 50.76 | 52.42 | 54.75 | 54.63 | 57.15 | 57.53 | 60.02 | 61.86 | 61.43 |
| Xinjiang | 53.03 | 54.58 | 56.55 | 57.46 | 58.97 | 56.67 | 58.50 | 60.38 | 61.94 | 62.87 | 63.61 |
| Provinces | ASDI (σ1 = ∞, σ2 = ∞) | ASDI (σ1 = ∞, σ2 = 0.5) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score | Rank | Score | Rank | |
| Beijing | 59.10 | 10 | 54.01 | 12 |
| Tianjin | 58.46 | 25 | 50.01 | 28 |
| Hebei | 60.47 | 8 | 56.95 | 6 |
| Shanxi | 55.48 | 30 | 50.13 | 26 |
| Inner Mongolia | 55.46 | 27 | 50.42 | 22 |
| Liaoning | 58.84 | 14 | 57.42 | 5 |
| Jilin | 55.21 | 29 | 53.42 | 16 |
| Heilongjiang | 56.14 | 18 | 49.31 | 25 |
| Shanghai | 60.61 | 6 | 53.75 | 14 |
| Jiangsu | 64.11 | 1 | 62.29 | 1 |
| Zhejiang | 56.41 | 16 | 53.92 | 13 |
| Anhui | 55.78 | 21 | 53.40 | 17 |
| Fujian | 57.60 | 12 | 54.26 | 10 |
| Jiangxi | 56.01 | 24 | 52.76 | 19 |
| Shandong | 62.91 | 2 | 60.41 | 2 |
| Henan | 56.75 | 15 | 54.88 | 9 |
| Hubei | 58.79 | 9 | 57.17 | 8 |
| Hunan | 54.67 | 26 | 53.28 | 15 |
| Guangdong | 52.71 | 31 | 49.89 | 27 |
| Guangxi | 54.79 | 20 | 48.22 | 23 |
| Hainan | 52.32 | 28 | 45.76 | 30 |
| Chongqing | 62.78 | 4 | 58.10 | 4 |
| Sichuan | 58.11 | 11 | 52.74 | 18 |
| Guizhou | 57.39 | 19 | 53.08 | 20 |
| Yunnan | 54.99 | 22 | 46.91 | 29 |
| Tibet | 57.46 | 23 | 50.39 | 21 |
| Shaanxi | 62.21 | 3 | 57.85 | 3 |
| Gansu | 59.18 | 13 | 50.04 | 24 |
| Qinghai | 56.03 | 17 | 42.94 | 31 |
| Ningxia | 62.35 | 7 | 54.52 | 11 |
| Xinjiang | 62.58 | 5 | 55.71 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, X.; Xin, S.; Shao, C.; Yang, F.; Long, Y. Study of the Spatio-Temporal Variation of Agricultural Sustainability at National and Provincial Levels in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15959. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215959
Zhan X, Xin S, Shao C, Yang F, Long Y. Study of the Spatio-Temporal Variation of Agricultural Sustainability at National and Provincial Levels in China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(22):15959. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215959
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Xuesong, Shuqi Xin, Chaofeng Shao, Feng Yang, and Yuhan Long. 2023. "Study of the Spatio-Temporal Variation of Agricultural Sustainability at National and Provincial Levels in China" Sustainability 15, no. 22: 15959. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215959
APA StyleZhan, X., Xin, S., Shao, C., Yang, F., & Long, Y. (2023). Study of the Spatio-Temporal Variation of Agricultural Sustainability at National and Provincial Levels in China. Sustainability, 15(22), 15959. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152215959







