The Relationship between the Built Environment and Climate Change: The Case of Turkish Provinces
Abstract
1. Introduction
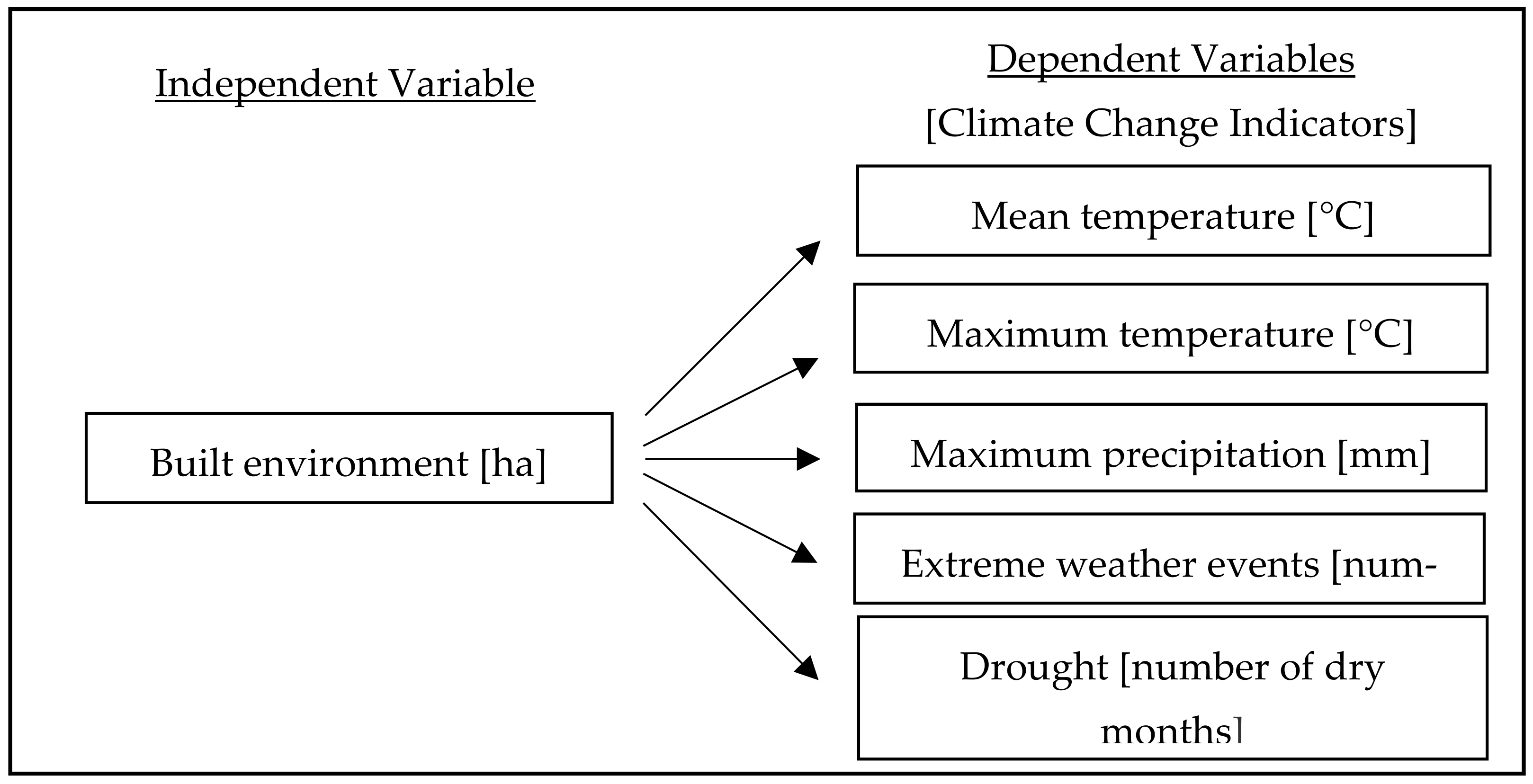
2. Data and Methodology
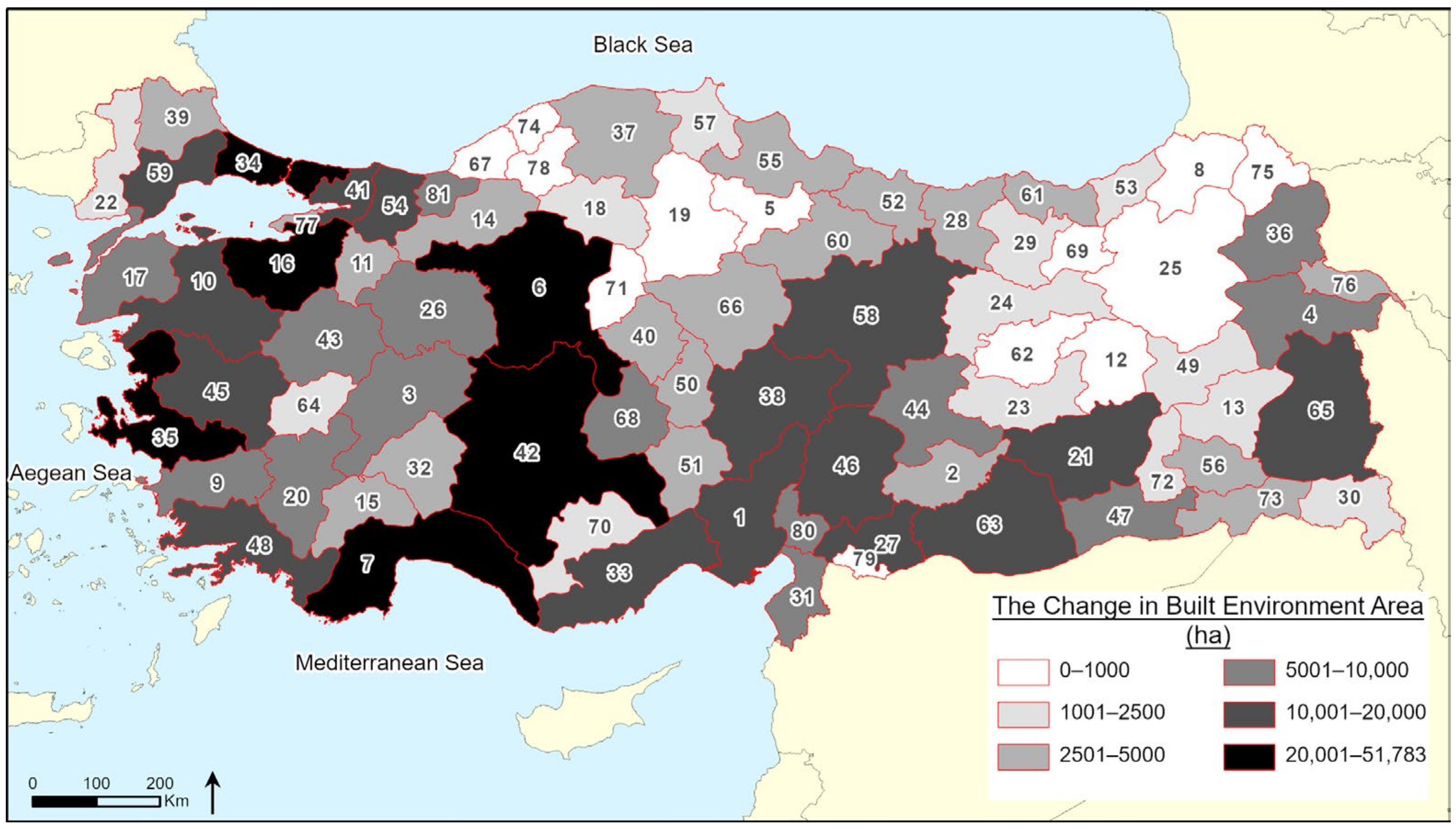
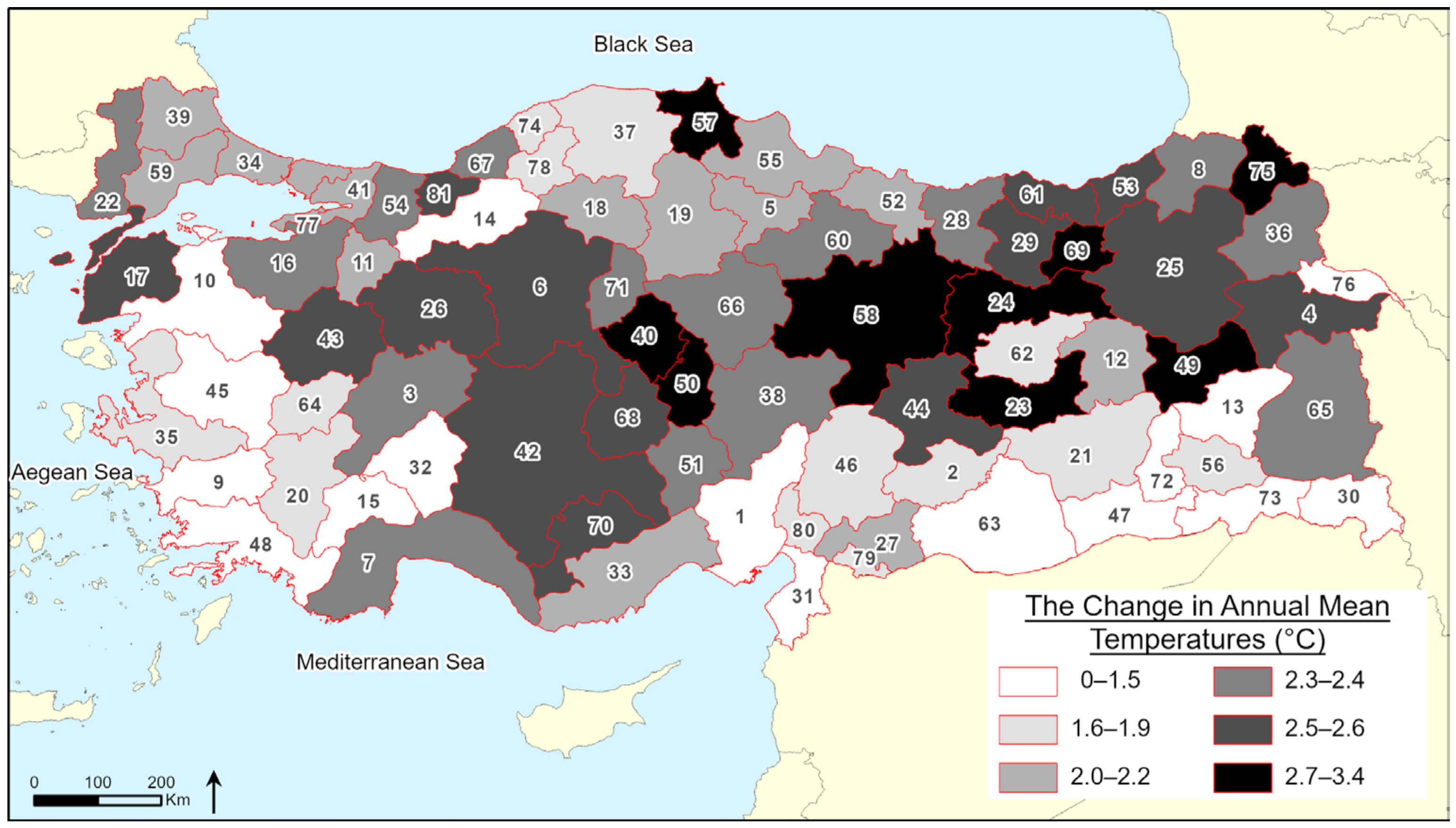
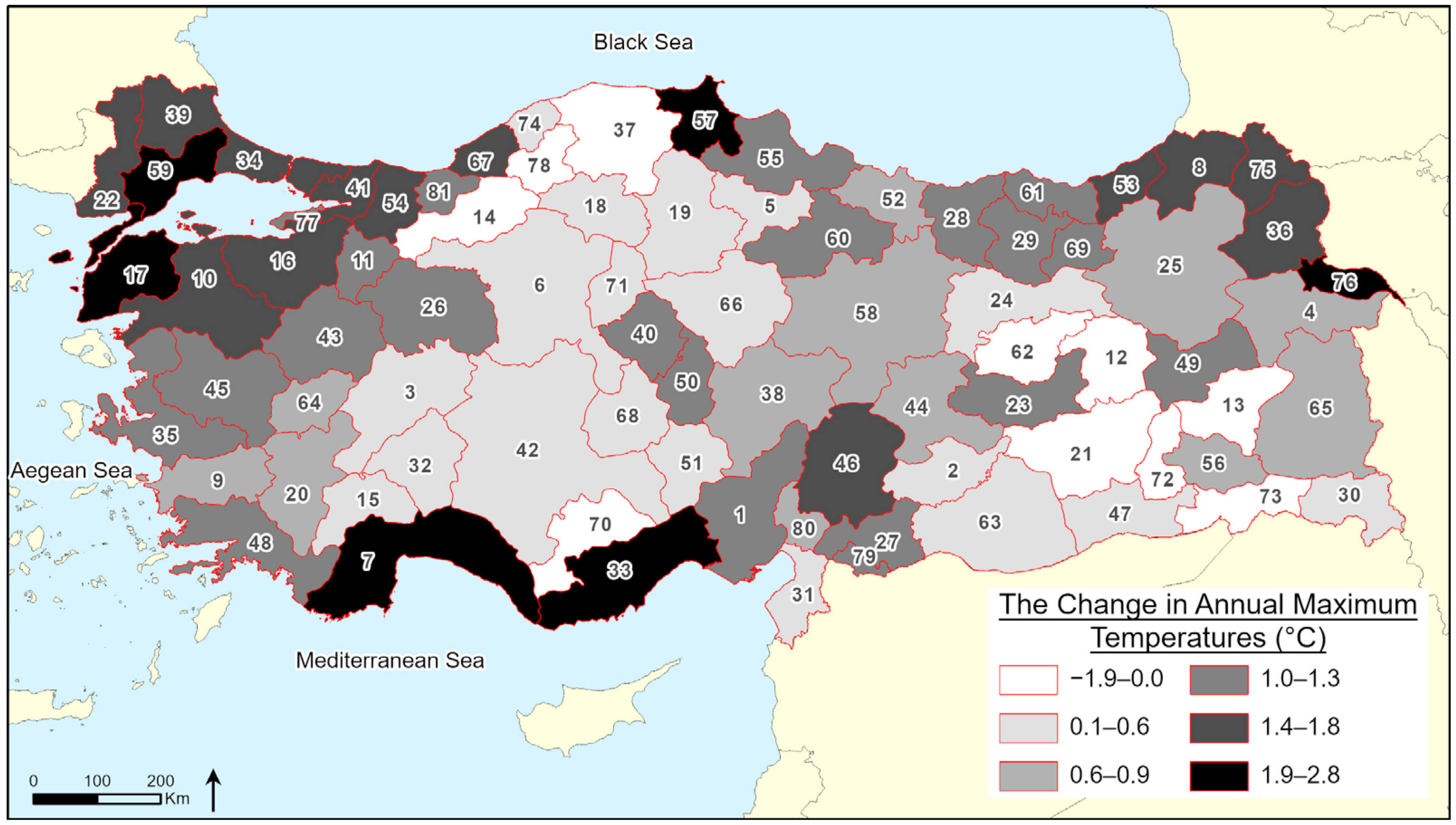
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dale, V.H. The relationship between land-use change and climate change. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilby, R.L. A review of climate change impacts on the built environment. Built Environ. 2007, 33, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Jing, W.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Geng, W.; Rong, T.; Shao, J.; Yang, J.; et al. Comprehensive assessment of the effect of urban built-up land expansion and climate change on net primary productivity. Complexity 2020, 2020, 8489025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T.R. The Ministry of Environment, Urbanization and Climate Change, Directorate of Environmental Impact Assessment, Permit and Inspection, Çevresel Göstergeler. (Yayın No. 49-1). 2020. Available online: https://ced.csb.gov.tr/cevresel-gostergeler-kitapcigi-i-82681 (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Resilience Alliance. Urban Resilience Research Prospectus. Resource Document. Resilience Alliance. 2007. Available online: http://www.resalliance.org/1610.php (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Pielke, R.A.; Marland, G.; Betts, R.A.; Chase, T.N.; Eastman, J.L.; Niles, J.O.; Niyogi D dutta, S.; Running, S.W. The influence of land-use change and landscape dynamics on the climate system: Relevance to climate-change policy beyond the radiative effect of greenhouse gases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2002, 360, 1705–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelsohn, R.; Dinar, A. Land use and climate change interactions. Annu. Rev. Resour. Econ. 2009, 1, 309–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, Z. İklim Değişikliği Tatlı Su Kaynakları ve Türkiye (Climate Change, Fresh Water Resources and Türkiye); Su Vakfı: Istanbul, Turkiye, 2009. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- House-Peters, L.A.; Chang, H. Modeling the impact of land use and climate change on neighborhood-scale evaporation and nighttime cooling: A surface energy balance approach. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 103, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.O.; Krumhardt, K.M.; Zimmermann, N.E. The effects of land use and climate change on the carbon cycle of Europe over the past 500 years. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.X.; Pla, F.; Latorre-Carmona, P.; Myint, S.W.; Caetano, M.; Kieu, H.V. Characterizing the relationship between land use land cover change and land surface temperature. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 124, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doelman, J.C.; Stehfest, E.; Tabeau, A.; van Meijl, H.; Lassaletta, L.; Gernaat, D.E.H.J.; Hermans, K.; Harmsen, M.; Daioglou, V.; Biemans, H.; et al. Exploring SSP land-use dynamics using the IMAGE model: Regional and gridded scenarios of land-use change and land-based climate change mitigation. Glob. Environ. Change 2018, 48, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, C.A.; Sellers, P.J.; Shukla, J. Amazonian deforestation and regional climate change. J. Clim. 1991, 4, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, R.E.; Kennedy, P. Impacts on regional climate of Amazon deforestation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 1947–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.H.; Foley, J.A. Combined effects of deforestation and doubled atmospheric co2 concentrations on the climate of Amazonia. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielke, R.A. Land use as climate change. Science 2005, 310, 1625–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, D. The implications of population growth and urbanization for climate change. Environ. Urban. 2009, 21, 545–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienow, A.; Kantakumar, L.N.; Ghazaryan, G.; Dröge-Rothaar, A.; Sticksel, S.; Trampnau, B.; Thonfeld, F. Modelling the spatial impact of regional planning and climate change prevention strategies on land consumption in the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Area 2017–2030. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 217, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, A.J.; de Noblet-Ducoudré, N.; Cruz, F.T.; Davin, E.L.; Bonan, G.B.; Brovkin, V.; Claussen, M.; Delire, C.; Ganzeveld, L.; Gayler, V.; et al. Uncertainties in climate responses to past land cover change: First results from the LUCID intercomparison study. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L14814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, D.; Kemper, T.; Pesaresi, M.; Corbane, C. Built-up area and population density: Two Essential Societal Variables to address climate hazard impact. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 90, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonck, M.-L.; Demuzere, M.; Hooyberghs, H.; Beck, C.; Cyrys, J.; Schneider, A.; Dewulf, R.; Van Coillie, F. The potential of local climate zones maps as a heat stress assessment tool, supported by simulated air temperature data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 178, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA-Environment Protection Agency. Climate Change Indicators in The United States (Fourth Edition). 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2021-02/documents/climate_indicators_2016.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Rovers, V.; Bosch, P.; Albers, R. Final Report Climate Proof Cities 2010–2014. 2014. Available online: https://klimaatadaptatienederland.nl/en/themes-sectors/themes/climate-change/ (accessed on 23 May 2021).
- EEA-European Environment Agency. Europe’s Changing Climate Hazards-An Index-Based Interactive EEA Report. 2021. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/downloads/163297bf75d54a45a1dcbe5d8ce1d9fe/1637331959/climate-hazards-indices.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2021).
- THCA (Turkish Healthy Cities Association). COP24 Special Report, Sağlık ve İklim Değişikliği. 2020. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/276405/9786057496713-tur.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- NAS (National Adaptation Strategy). National Climate Adaptation Strategy. 2016. Available online: https://nas-adaptatietool.nl/ (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- EEA-European Environment Agency. National and Transnational Climate Atlases in Europe. 2021. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/europes-changing-climate-hazards-1/national-and-transnational-climate-atlases/view (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Brovkin, V.; Boysen, L.; Arora, V.K.; Boisier, J.P.; Cadule, P.; Chini, L.; Claussen, M.; Friedlingstein, P.; Gayler, V.; van den Hurk, B.J.J.M.; et al. Effect of anthropogenic land-use and land-cover changes on climate and land carbon storage in CMIP5 projections for the twenty-first century. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 6859–6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülbaz, S.; Kaya, Y.E.; Alhan, C.M.K. Düşük etkili kentleşme uygulamalarının yüzeysel akışa etkisi: İstanbul üniversitesi avcılar kampüsü örneği (The Impact of LID Implementation on Surface Runoff: Case Study of Istanbul University, Avcılar Campus). İklim Değişikliği Ve Çevre 2018, 3, 45–50. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Gao, H.; Cuo, L. Effects of urbanization and climate change on peak flows over the San Antonio River Basin, Texas. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 2371–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüeso, D.; Evans, J.P.; Fita, L.; Bormann, K.J. Temperature response to future urbanization and climate change. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 2183–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, S.; Watson, J.E.M.; Salazar, A.; Thatcher, M.; McAlpine, C.A. The impact of urbanization and climate change on urban temperatures: A systematic review. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Ge, E.; Liu, X.; Liao, W.; Luo, M. Urbanization effects on heat waves in Fujian Province, Southeast China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 210, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Yang, X.; Cao, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y. Effects of urbanization on regional extreme-temperature changes in China, 1960–2016. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, O. Mersin ilindeki kentsel büyümenin yer yüzey sıcaklığı üzerine etkisinin araştırılması (Investigation of the effect of urban expansion on surface temperature in Mersin city). Geomatik 2021, 6, 69–76. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Sodhi, N.S.; Peh, K.S.-H.; Brook, B.W. Global evidence that deforestation amplifies flood risk and severity in the developing world. Glob. Change Biol. 2007, 13, 2379–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Franczyk, J. Climate Change, land-use change, and floods: Toward an integrated assessment: Climate change, land-use change, and floods. Geogr. Compass 2008, 2, 1549–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Leng, G.; Su, J.; Ren, Y. Comparison of urbanization and climate change impacts on urban flood volumes: Importance of urban planning and drainage adaptation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Gao, T.; Luo, M.; Ge, E.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ning, G. Contribution of urbanization to the changes in extreme climate events in urban agglomerations across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruç, S.; Yücel, İ.; Yılmaz, A. İklim Değişikliği, Ekstrem Yağışlar ve Etkileri: Etimesgut, Ankara Örneği (Climate Change, Extreme Rainfall and Its Effects: The Case of Etimesgut, Ankara). In Proceedings of the 10. Ulusal Hidroloji Kongresi, Muğla, Turkiye, 9–12 October 2019. (In Turkish). [Google Scholar]
- Kadıoğlu, M. Sellere dirençli kent oluşturmanın adımları (Steps to build a flood resilience city). Şehir ve Toplum 2018, 10, 77–89. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Kazancı, G. İklim Değişikliğine Uyum Kapsamında Akıllı Kentlerin Rolü: Muğla Metropoliten Alanı Üzerine Bir Değerlendirme (The Role of Smart Cities Under the Adaptation into Climate Change: An Evaluation on Mugla Metropolitan Area); Yüksek Lisans Tezi; İstanbul Teknik Üniversitesi: Istanbul, Turkiye, 2019. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Karacan, G. Kentsel Iklim Değişikliği Kapsamında Sera Gazı Azaltım Stratejileri; Ankara Örneği (Greenhouse Gas Reduction Strategies In The Context of Urban Climate Change; Case of Ankara); Yüksek Lisans Tezi; Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi: Isparta, Turkiye, 2020. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Onur, A.C.; Tezer, A. Ecosystem services based spatial planning decision making for adaptation to climate changes. Habitat Int. 2015, 47, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, O. İklim Değişirken Kent ve Kentleşme (City and Urbanization as the Climate Changes). In Proceedings of the 2023 Türkiye’si Sempozyumu, Ankara, Turkiye, 26–28 April 2018. (In Turkish). [Google Scholar]
- Stone, B. Land use as climate change mitigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9052–9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotharkar, R.; Bagade, A. Evaluating urban heat island in the critical local climate zones of an Indian city. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 169, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezer, A.; Kazancı, G. İklim değişikliğine uyum konusunda öne çıkan mekânsal planlama kriterleri (Spatial planning criteria for adaptation to climate change). Mimar. Ve Mühendis Derg. 2019, 31, 90–94. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Büttner, G.; Kosztra, B.; Maucha, G.; Pataki, R.; Kleeschulte, S.; Hazeu, G.; Vittek, M.; Schröder, C.; Littkopf, A. Copernicus Land Monitoring Service CORINE Land Cover-User Manual; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kozstra, B.; Büttner, G.; Hazeu, G.; Arnold, S. Updated CLC Illustrated Nomen-Clature Guidelines; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017; pp. 1–124. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/user-corner/technical-library/corine-land-cover-nomenclature-guidelines/docs/pdf/CLC2018_Nomenclature_illustrated_guide_20190510.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Mirza, M.M.Q. Climate change and extreme weather events: Can developing countries adapt? Clim. Policy 2003, 3, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, D.G.; Gulledge, J. Extreme Weather and Climate Change: Understanding the Link, Managing the Risk; Pew Center on Global Climate Change: Arlington, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stott, P. How climate change affects extreme weather events. Science 2016, 352, 1517–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993. [Google Scholar]
- European Comission. Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI). European Drought Observatory Indicator Factsheet; European Comission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sonmez, F.K.; Komuscu, A.U.; Erkan, A.; Turgu, E. An analysis of spatial and temporal dimension of drought vulnerability in Turkey using the standardized precipitation index. Nat. Hazards 2005, 35, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehnia, N.; Alizadeh, A.; Sanaeinejad, H.; Bannayan, M.; Zarrin, A.; Hoogenboom, G. Estimation of meteorological drought indices based on AgMERRA precipitation data and station-observed precipitation data. J. Arid. Land. 2017, 9, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO—World Meteorological Organization. Standardized Precipitation Index User Guide; (WMO-No. 1090); WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Caloiero, T.; Veltri, S.; Caloiero, P.; Frustaci, F. Drought analysis in Europe and in the Mediterranean basin using the standardized precipitation index. Water 2018, 10, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahane, L.H. Regression Basics, 2nd ed.; Sage Publication: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky, H.; Christopoulos, A. Fitting Models to Biological Data Using Linear and Nonlinear Regression: A Practical Guide to Curve Fitting, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Peck, E.A.; Vining, G.G. Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.S.; McCabe, G.P.; Craig, B.A. Introduction to the Practice of Statistics, 8th ed; W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Casson, R.J.; Farmer, L.D. Understanding and checking the assumptions of linear regression: A primer for medical researchers. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2014, 42, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Y.D. Institutions, extreme weather, and urbanization in the Greater Mekong Region. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2019, 109, 1317–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, R.C.; Gallo, K.P.; Loveland, T.R. Influences of specific land use/land cover conversions on climatological normals of near-surface temperature. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D14113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, B. Fundamentals of Biostatistics, 8th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
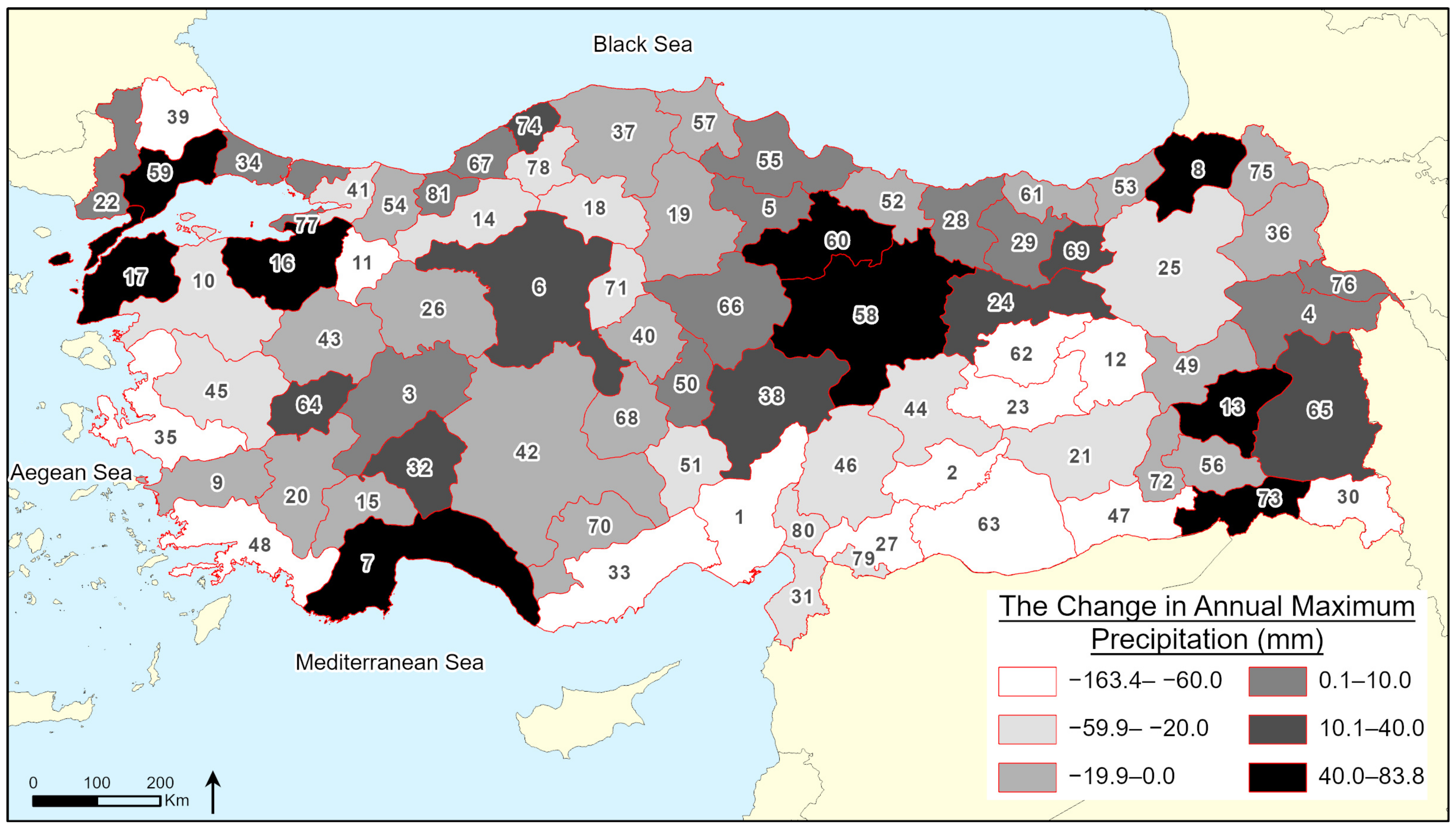
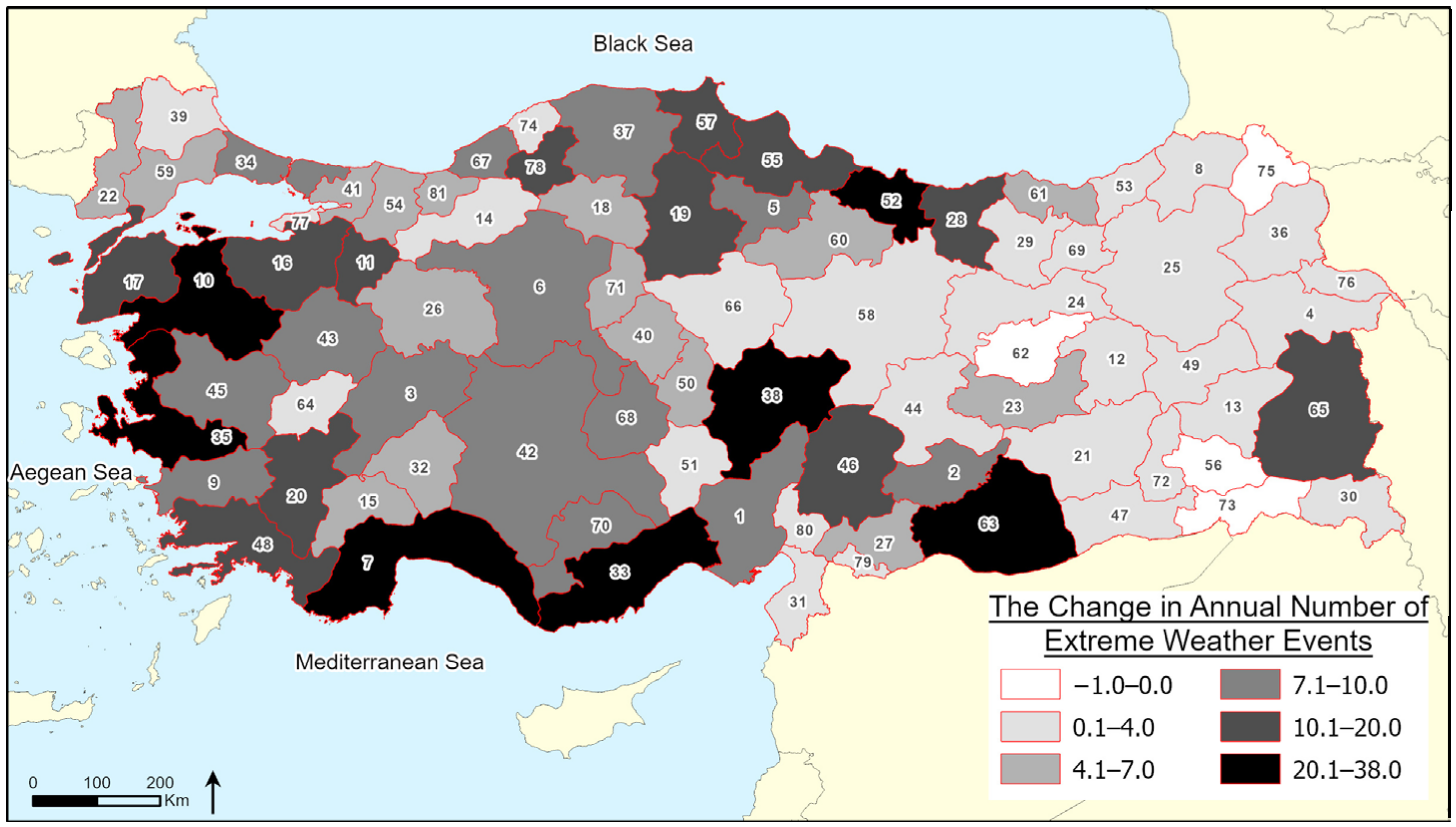
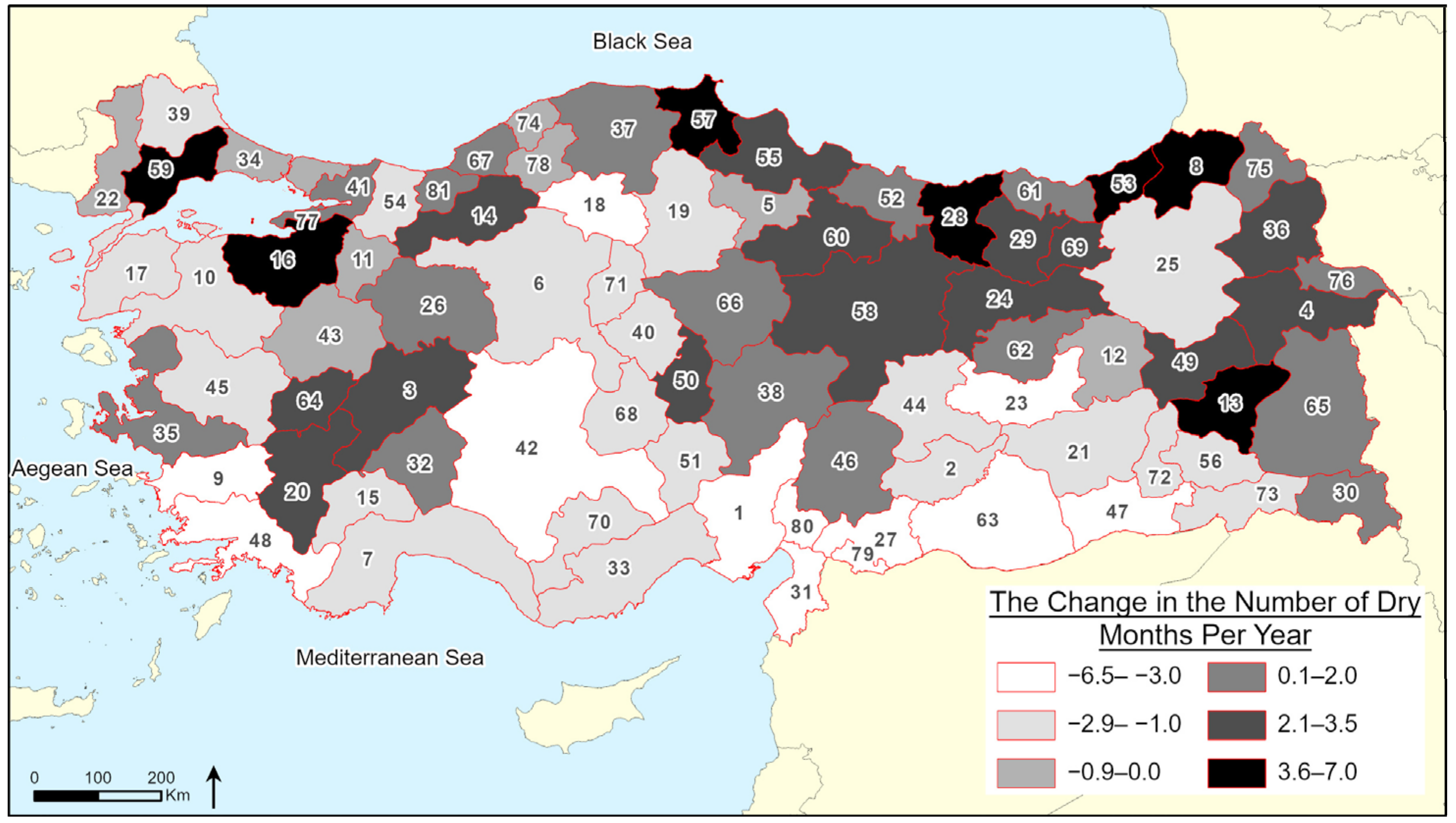
| SPI | Classification |
|---|---|
| 2.0 or higher | Exceptionally moist |
| 1.60 to 1.99 | Extremely moist |
| 1.30 to 1.59 | Very moist |
| 0.80 to 1.29 | Moderately moist |
| 0.51 to 0.79 | Abnormally moist |
| 0.50 to −0.50 | Normal |
| −0.51 to −0.79 | Abnormally dry |
| −0.80 to −1.29 | Moderately dry |
| −1.30 to −1.59 | Very dry |
| −1.60 to −1.99 | Extremely dry |
| −2.0 or lower | Exceptionally dry |
| Dependent Var. | Annual Mean Temperature | Annual Maximum Temperature | Annual Maximum Precipitation | Annual Number of Extreme Weather Events | Number of Dry Months per Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent Var. | ||||||
| Built Environment | R2 = 0.009 Sig = 0.420 | R2 = 0.063 Sig = 0.029 | R2 = 0.008 Sig = 0.435 | R2 = 0.158 Sig = 0.000 | R2 = 0.023 Sig = 0.196 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bektaş, Y.; Sakarya, A. The Relationship between the Built Environment and Climate Change: The Case of Turkish Provinces. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021659
Bektaş Y, Sakarya A. The Relationship between the Built Environment and Climate Change: The Case of Turkish Provinces. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021659
Chicago/Turabian StyleBektaş, Yasin, and Adem Sakarya. 2023. "The Relationship between the Built Environment and Climate Change: The Case of Turkish Provinces" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021659
APA StyleBektaş, Y., & Sakarya, A. (2023). The Relationship between the Built Environment and Climate Change: The Case of Turkish Provinces. Sustainability, 15(2), 1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021659






