Assessing the Impact of the Recent Unprecedented World Events on the Economic and Environmental Conditions of Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
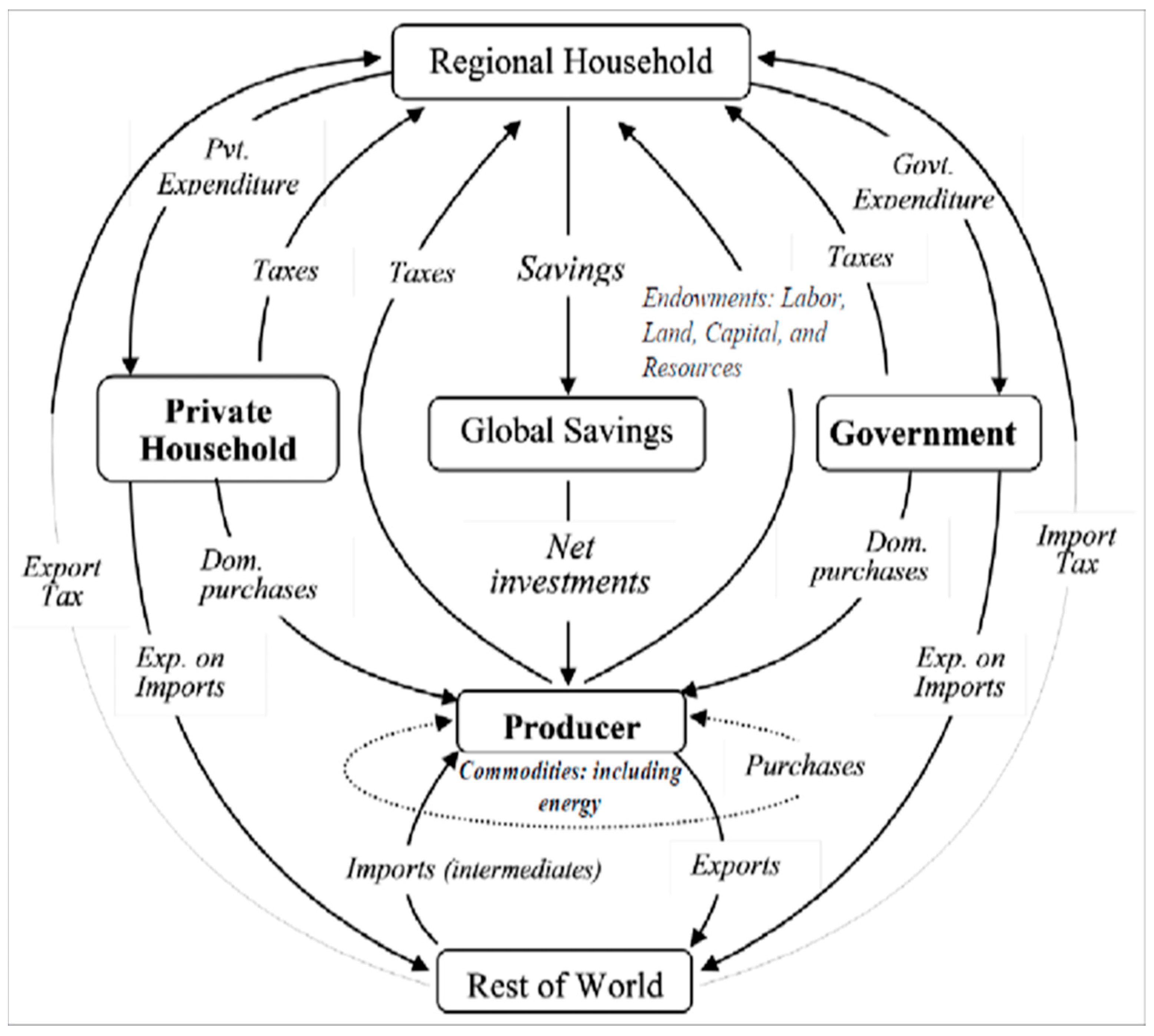
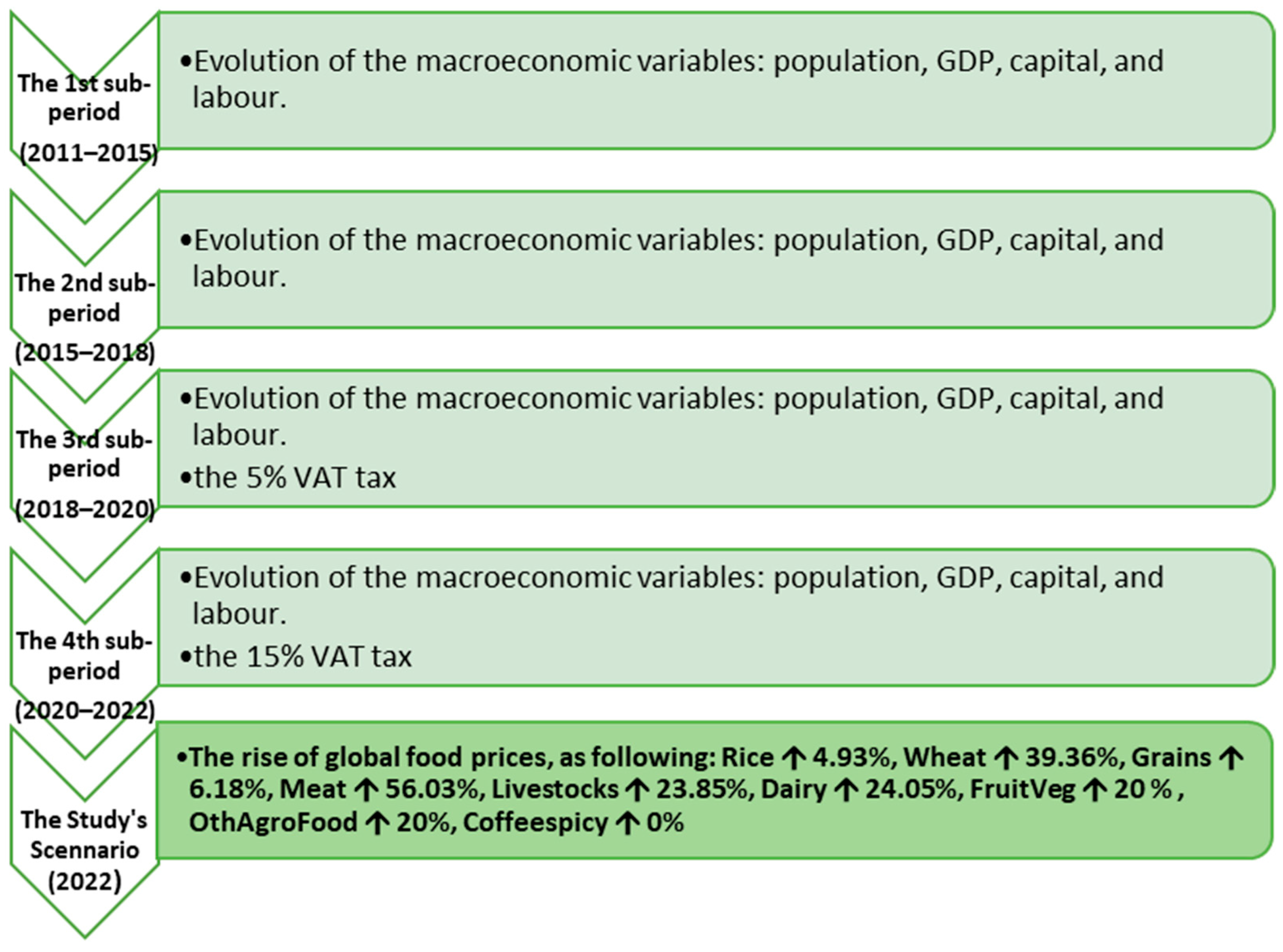
2. Methodology, Database, and Scenario Description
3. Results and Discussion
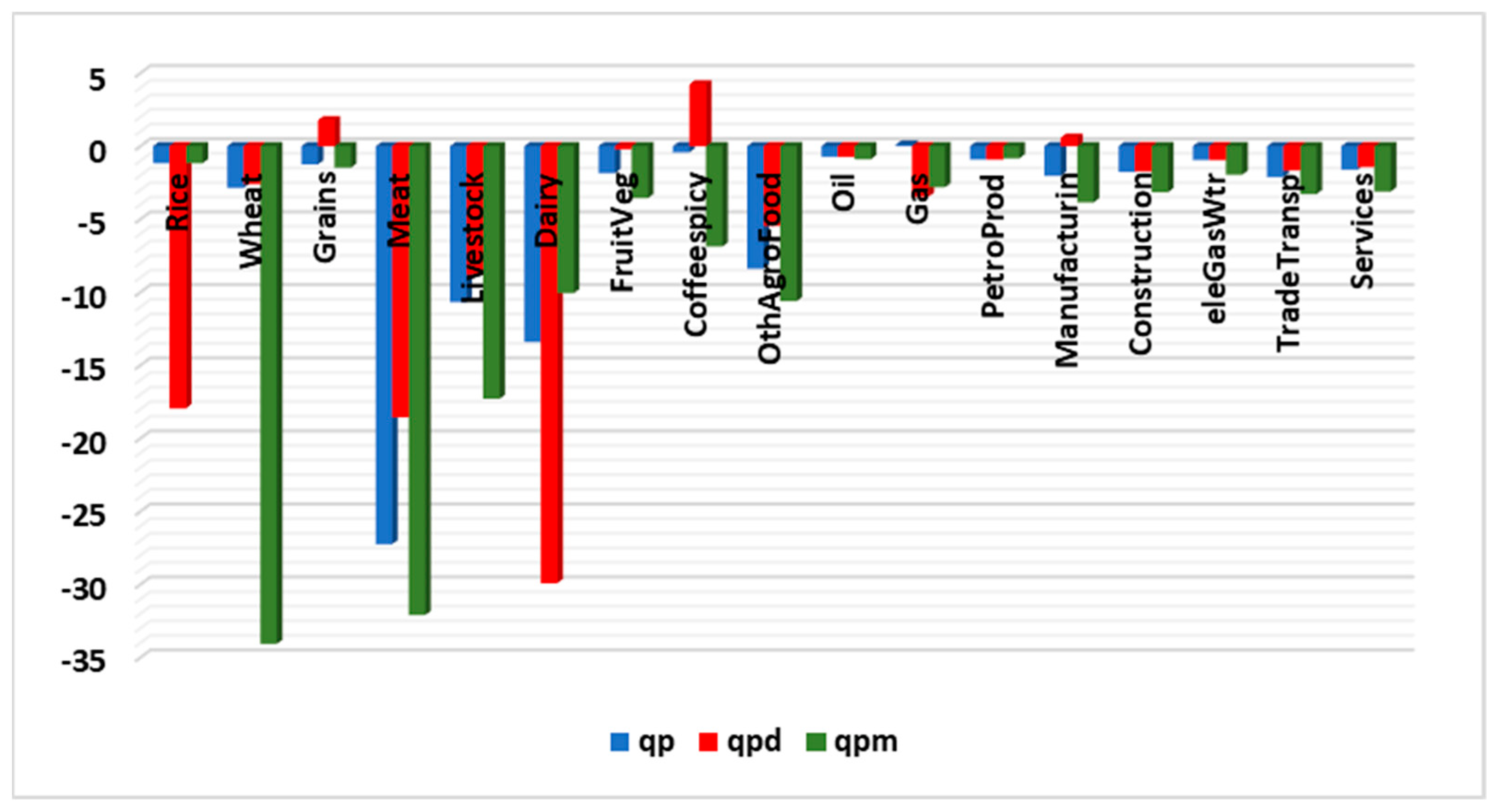
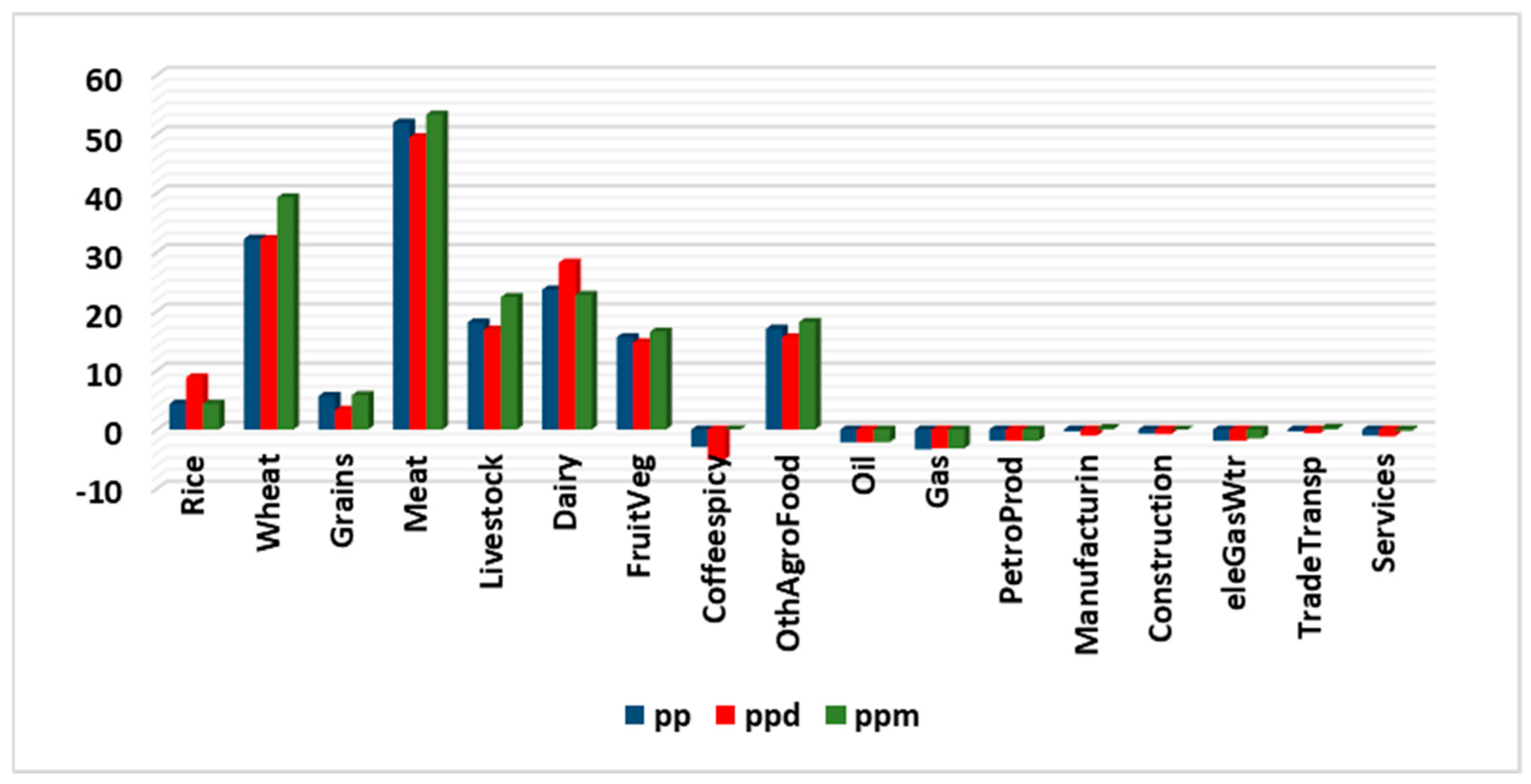
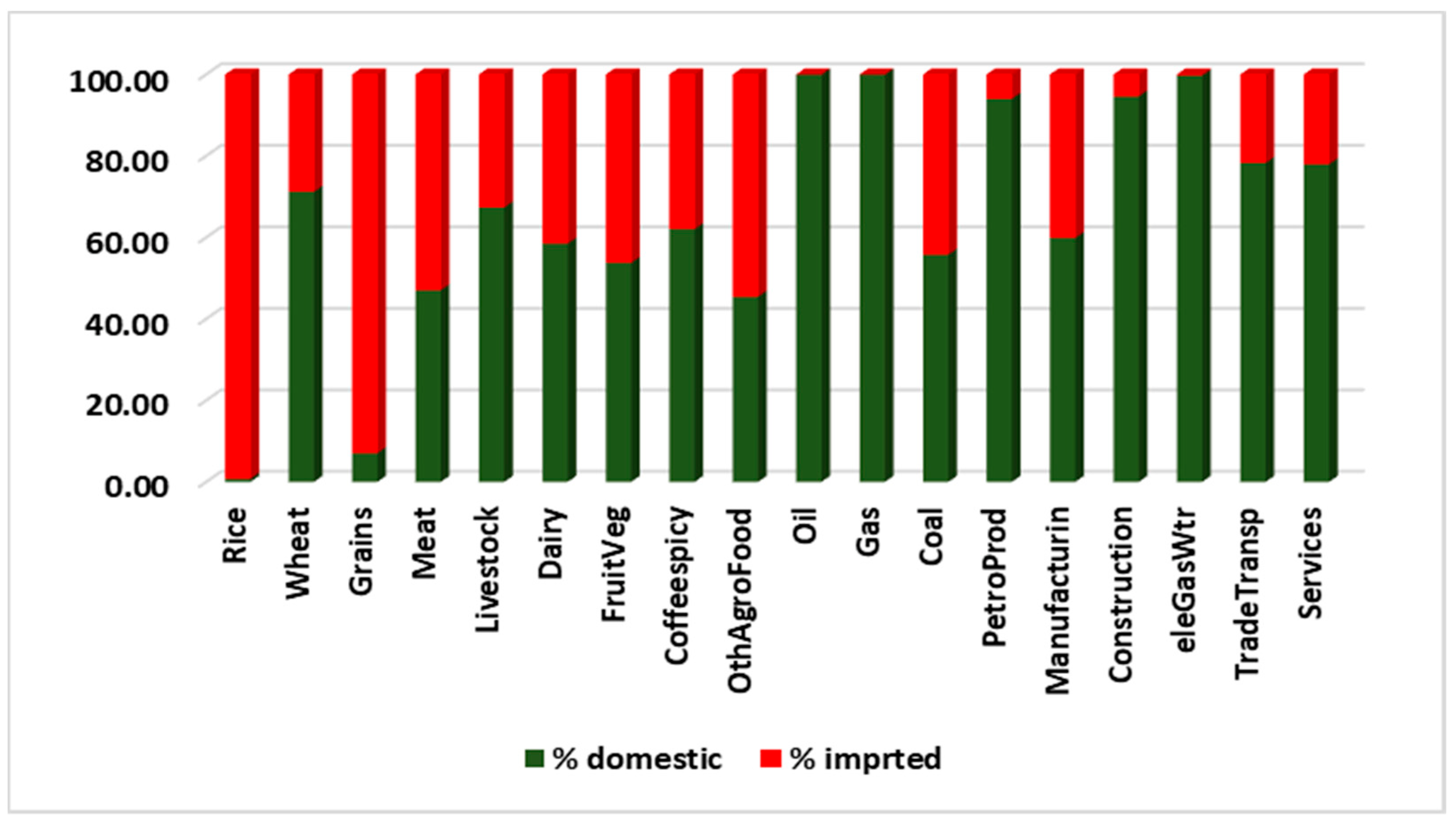
3.1. Economic Impacts
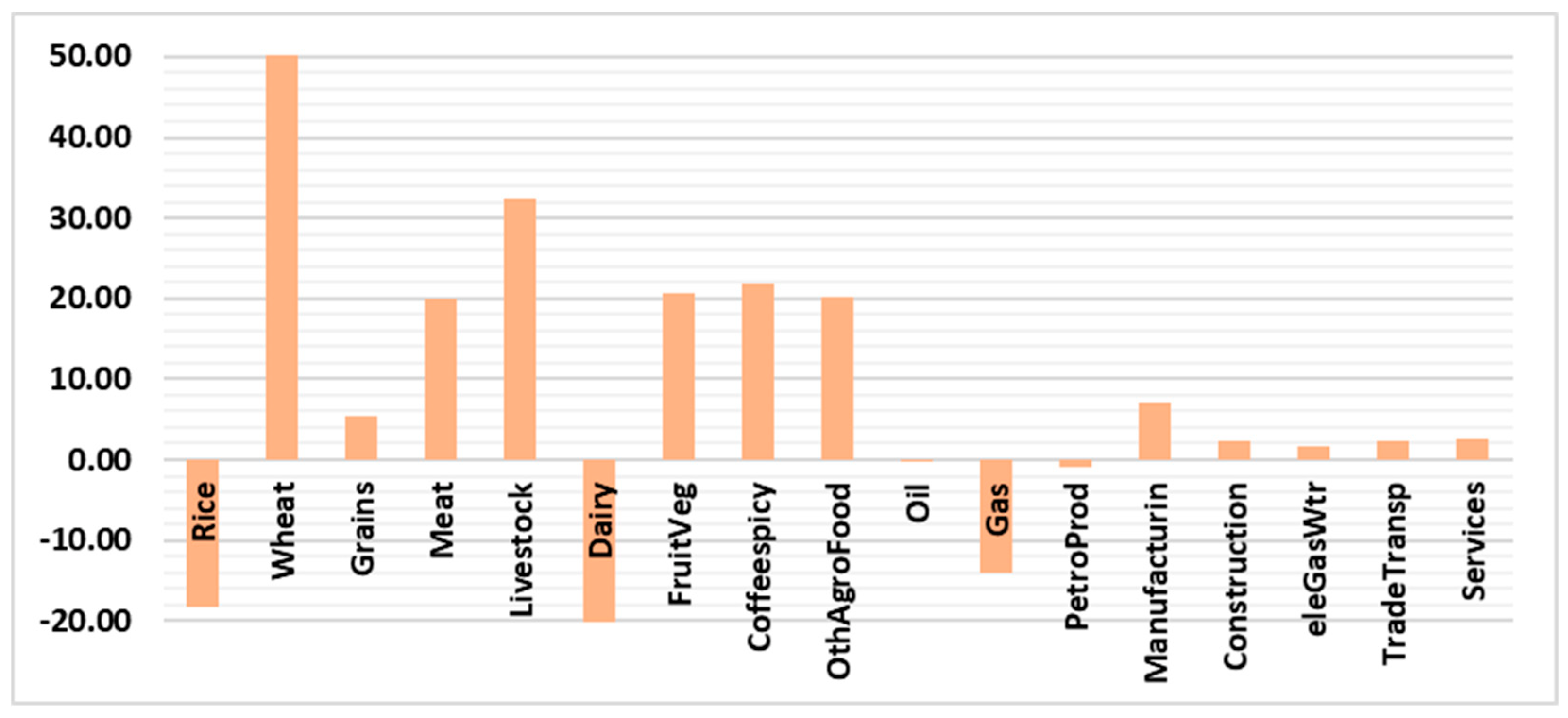
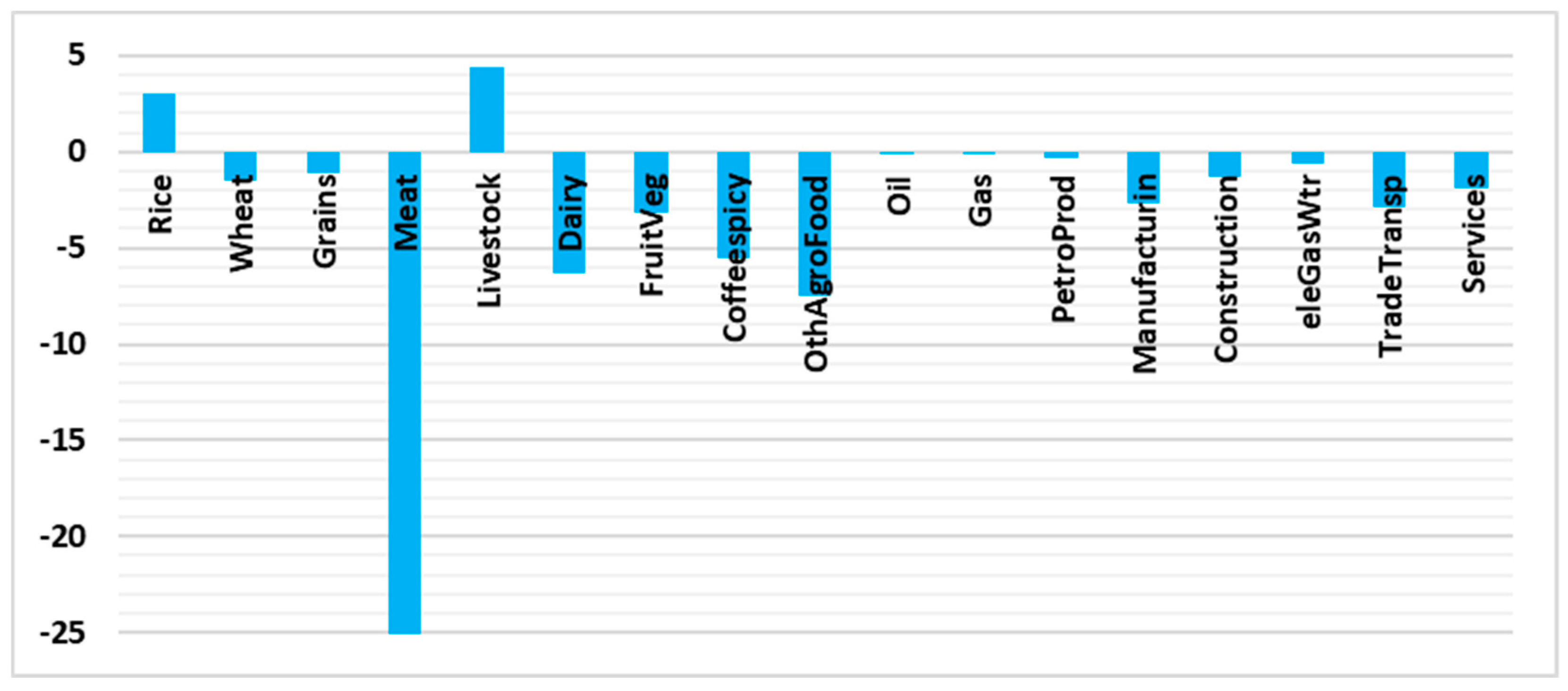
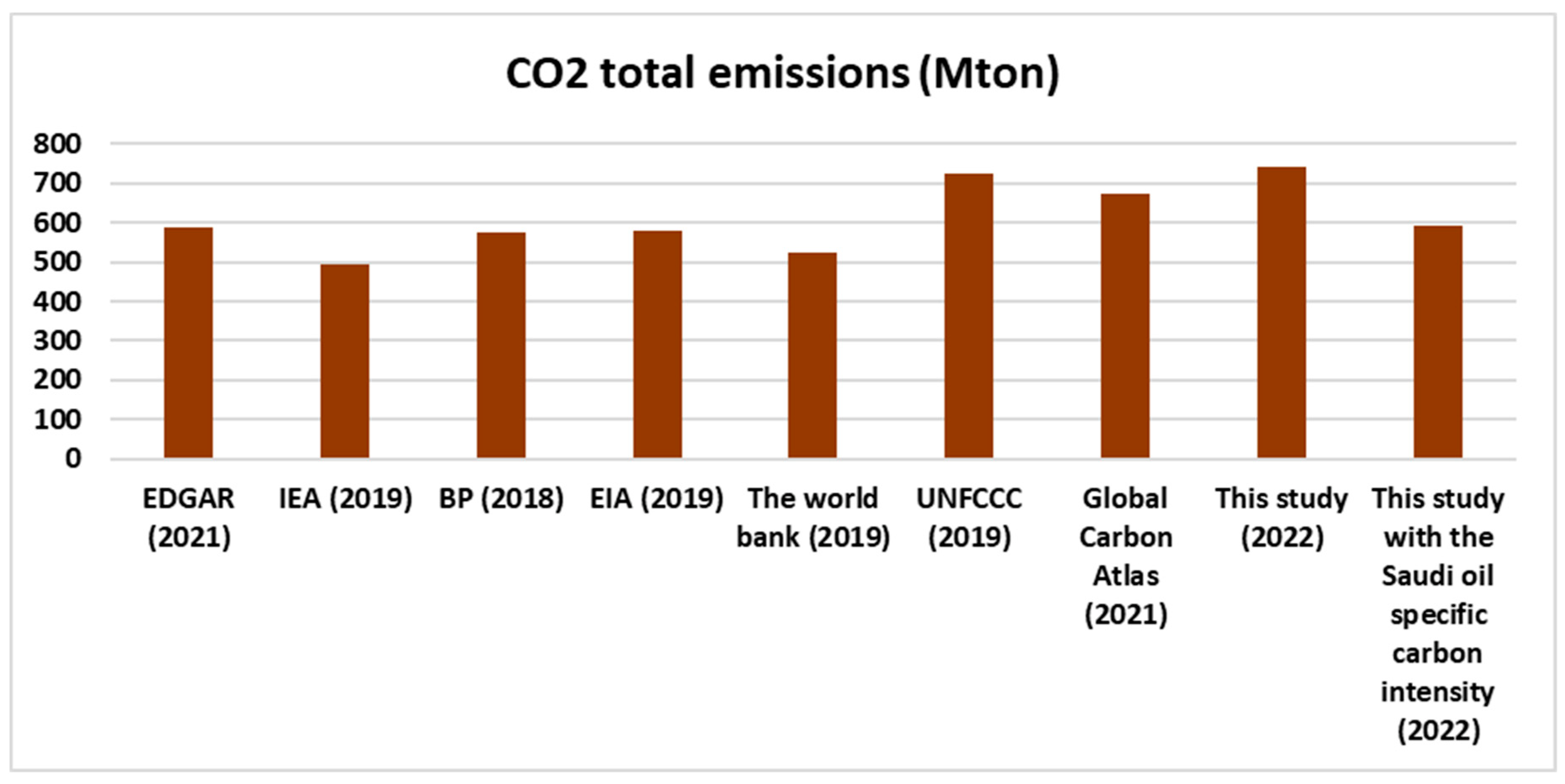
3.2. Impact on CO2 Emissions, Using the Input–Output Life Cycle Assessment Approach (IO-LCA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Development Programme. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Saudi_Vision 2030. 2016. Available online: https://www.vision2030.gov.sa/ (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Colussi, J.; Schnitkey, G.; Cabrini, S. Wheat Outlook after Five Months of War in Ukraine. Farmdoc Daily, 1 August 2022; p. 112. [Google Scholar]
- Mitigation of Climate Change Climate Change 2022 Working Group III Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/05/uncertainty-guidance-note.pdf. (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Boylan, S.M.; Thow, A.M.; Tyedmers, E.K.; Malik, A.; Salem, J.; Alders, R.; Raubenheimer, D.; Lenzen, M. Using Input-Output Analysis to Measure Healthy, Sustainable Food Systems. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrobaish, W.S.; Vlerick, P.; Luning, P.A.; Jacxsens, L. Food safety governance in Saudi Arabia: Challenges in control of imported food. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, A.; Narayanan, B.; Mcdougall, R. An Overview of the GTAP 9 Data Base. JGEA 2016, 1, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munasinghe, M. Computable general equilibrium modelling applications. Sustain. Dev. Pract. 2010, 1, 269–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Lu, Q.; Ali, S.; Mohsin, M. How does hydropower energy asymmetrically affect environmental quality? Evidence from quantile-based econometric estimation. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Mohsin, M.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Does green finance counteract the climate change mitigation: Asymmetric effect of renewable energy investment and R&D. Energy Econ. 2022, 113, 106183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Information Administration (EIA). 2022. Available online: http://www.eia.gov/dnav/pet/pet_pri_spt_s1_a.htm (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Burfisher, M.E. Introduction to Computable General Equilibrium Models; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Corong, E.L.; Hertel, T.W.; Mcdougall, R.A.; Tsigas, M.E.; Van Der Mensbrugghe, D. The Standard GTAP Model, Version 7. JGEA 2017, 2, 1–119. [Google Scholar]
- Horridge, M. Chapter 5 GTAPAgg: Data Aggregation Program. 2015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jonathan-Horridge/publication/265409625_GTAPAgg_Data_Aggregation_Program/links/54d0cc720cf20323c219a9f0/GTAPAgg-Data-Aggregation-Program.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- The World Bank. 2022. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/ (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- The World Economic Forum. 2022. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/ (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Tsigas, M. ILO Statistics and the GTAP Labor Module. 2013. Available online: www.gtap.agecon.purdue.edu (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- The Saudi General Authority of Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.sa/en/814 (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Pearson, K.; Horridge, M.; Corong, E. Hands-On Computing with RunGTAP and WinGEM to Introduce GTAP and Gempack. 2010. Available online: http://www.copsmodels.com/gempack.htm (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- World Food Price Index. 2022. Available online: https://tradingeconomics.com/world/food-price-index (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Macrotrends—The Long Term Perspective on Markets. Available online: https://www.macrotrends.net/futures/ (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Pearson, K.R.; Hertel, T.W.; Horridge, J.M. AnalyseGE: Software Assisting Modellers in the Analysis of Their Results; Center for Global Trade Analysis, Purdue University: Lafayette, IN, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson, C.T.; Lave, L.B.; Matthews, H.S. Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Goods and Services an Input-Output Approach; Routledge: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tuomas, J. Mattila Use of Input–Output Analysis in LCA. In Life Cycle Assessment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lenzen, M. Double-counting in life cycle calculations. J. Ind. Ecol. 2008, 12, 583–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabernard, L.; Pfister, S.; Oberschelp, C.; Hellweg, S. Growing environmental footprint of plastics driven by coal combustion. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Ran, C.; Mu, M. Is burden responsibility more effective? A value-added method for tracing worldwide carbon emissions. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 181, 106889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen-Olsen, K.; Owen, A.; Hertwich, E.G.; Lenzen, M. Effects of sector aggregation on CO2 multipliers in multiregional input–output analyses. Econ. Syst. Res. 2014, 26, 284–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masnadi, M.S.; El-Houjeiri, H.M.; Schunack, D.; Li, Y.; Englander, J.G.; Badahdah, A.; Monfort, J.C.; Anderson, J.E.; Wallington, T.J.; Bergerson, J.A.; et al. Global carbon intensity of crude oil production. Science 2018, 361, 851–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Guan, D.; Wei, W.; Davis, S.J.; Ciais, P.; Bai, J.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Hubacek, K.; Marland, G.; et al. Reduced carbon emission estimates from fossil fuel combustion and cement production in China. Nature 2015, 524, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EDGAR—Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research. CO2 Emissions of All World Countries. 2022. Available online: https://edgar.jrc.ec.europa.eu/report_2022#emissions_table (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- International Energy Agency, Saudi Arabia. 2020. Available online: https://www.iea.org/countries/saudi-arabia (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- bp. bp Statistical Review of World Energy. 2020. Available online: www.bp.com/statisticalreview (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- The U.S. Energy Information Administration Saudi Arabia Emissions. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/international/data/country/SAU/other-statistics/emissions-by-fuel (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- The World Bank Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions. 2020. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EN.ATM.CO2E.KT?end=2019&locations=SA&start=2015 (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What Climate Commitments Has Saudi Arabia submitted? 2020. Available online: https://www.climatewatchdata.org/countries/SAU?end_year=2019&start_year=1990 (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Global Carbon Atlas. Fossil Fuels Emissions. 2021. Available online: http://www.globalcarbonatlas.org/en/CO2-emissions (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Dandres, T.; Gaudreault, C.; Tirado-Seco, P.; Samson, R. Assessing non-marginal variations with consequential LCA: Application to European energy sector. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 3121–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Regions | Sectors | Factors of Production |
|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | Rice | Land |
| Rest of World (ROW) | Wheat | Unskilled labour |
| Grains | Skilled labour | |
| Meat | Capital | |
| Livestock | Natural resources | |
| Dairy | ||
| FruitVeg (vegetables, fruit, nuts) | ||
| Coffeespicy (coffee, spices, and seeds) | ||
| OthAgroFood (other agriculture, forestry, fish, and food) | ||
| Oil | ||
| Gas | ||
| Coal | ||
| PetroProd (refined petroleum products) | ||
| Manufacturin (manufacturing) | ||
| Construction | ||
| eleGasWtr (electricity, gas distribution, and water) | ||
| TradeTransp (trade and transportation) | ||
| Services (other services) |
| Real GDP | Nominal GDP | yp | ypev | DTBAL (US$ Million) | EV (US$ Million) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KSA | −0.39 | −1.27 | −0.93 | −1.93 | −10,440.76 | −23,344.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almutairi, K.; Alahmadi, R. Assessing the Impact of the Recent Unprecedented World Events on the Economic and Environmental Conditions of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021610
Almutairi K, Alahmadi R. Assessing the Impact of the Recent Unprecedented World Events on the Economic and Environmental Conditions of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021610
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmutairi, Kamel, and Ramzi Alahmadi. 2023. "Assessing the Impact of the Recent Unprecedented World Events on the Economic and Environmental Conditions of Saudi Arabia" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021610
APA StyleAlmutairi, K., & Alahmadi, R. (2023). Assessing the Impact of the Recent Unprecedented World Events on the Economic and Environmental Conditions of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability, 15(2), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021610





