Effort to Mitigate Volatile Fatty Acid Inhibition by Using Mixed Inoculum and Compost for the Degradation of Food Waste and the Production of Biogas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
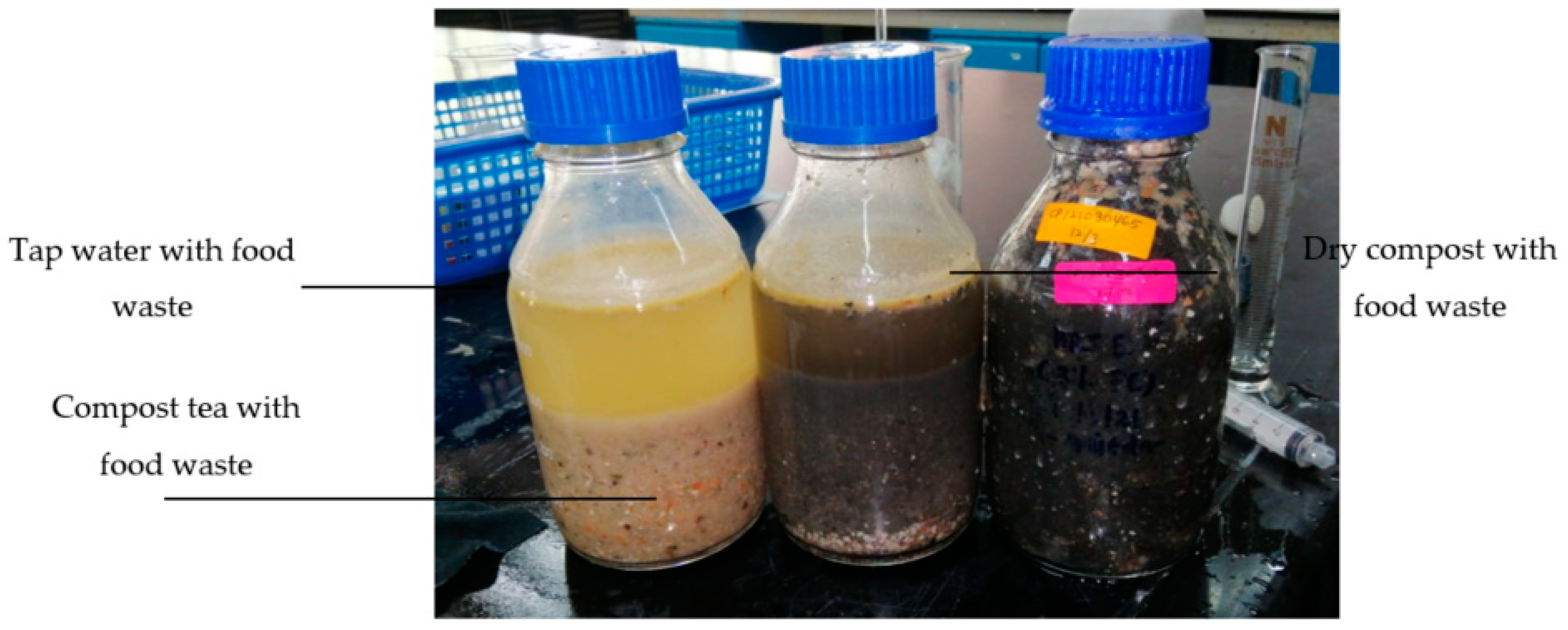
2.2. Effect of pH Buffering of Substrate Composting
2.3. Substrate Preparations and Pre-Fermentation
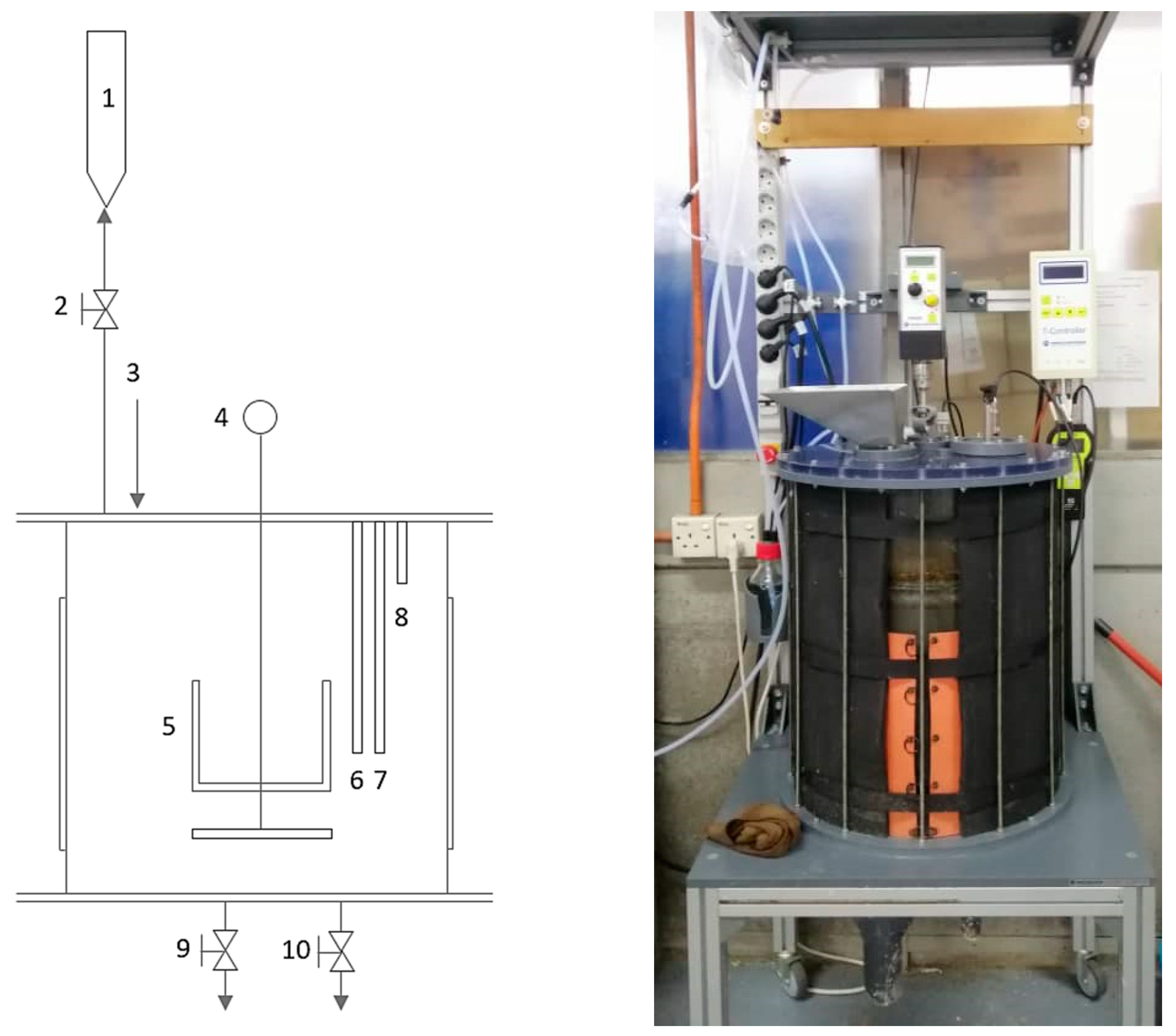
2.4. Setup and Operation of the Anaerobic Reactor
2.5. Analytical Methzod for Methane Yield and Substrate Parameters
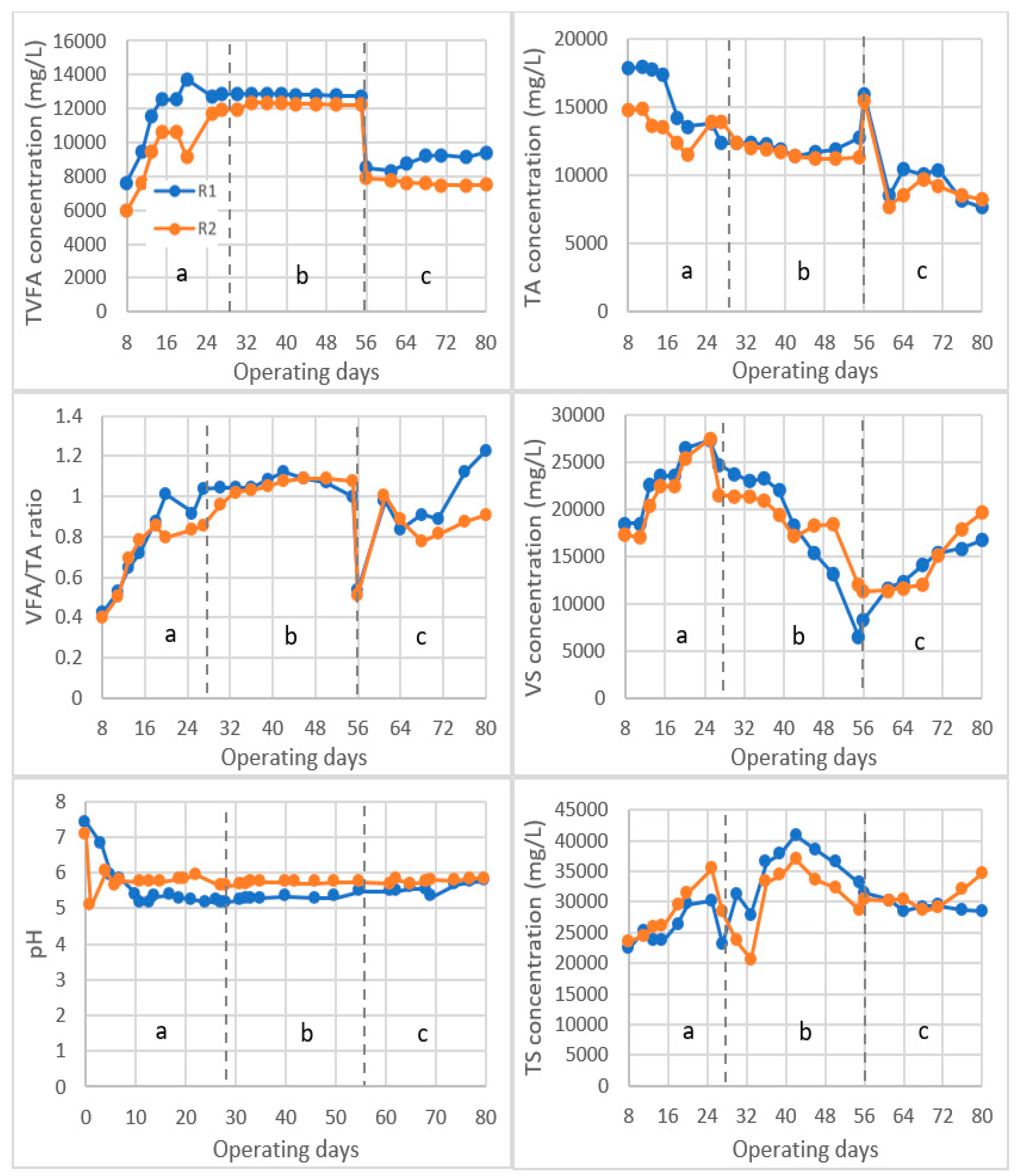
3. Results and Discussion
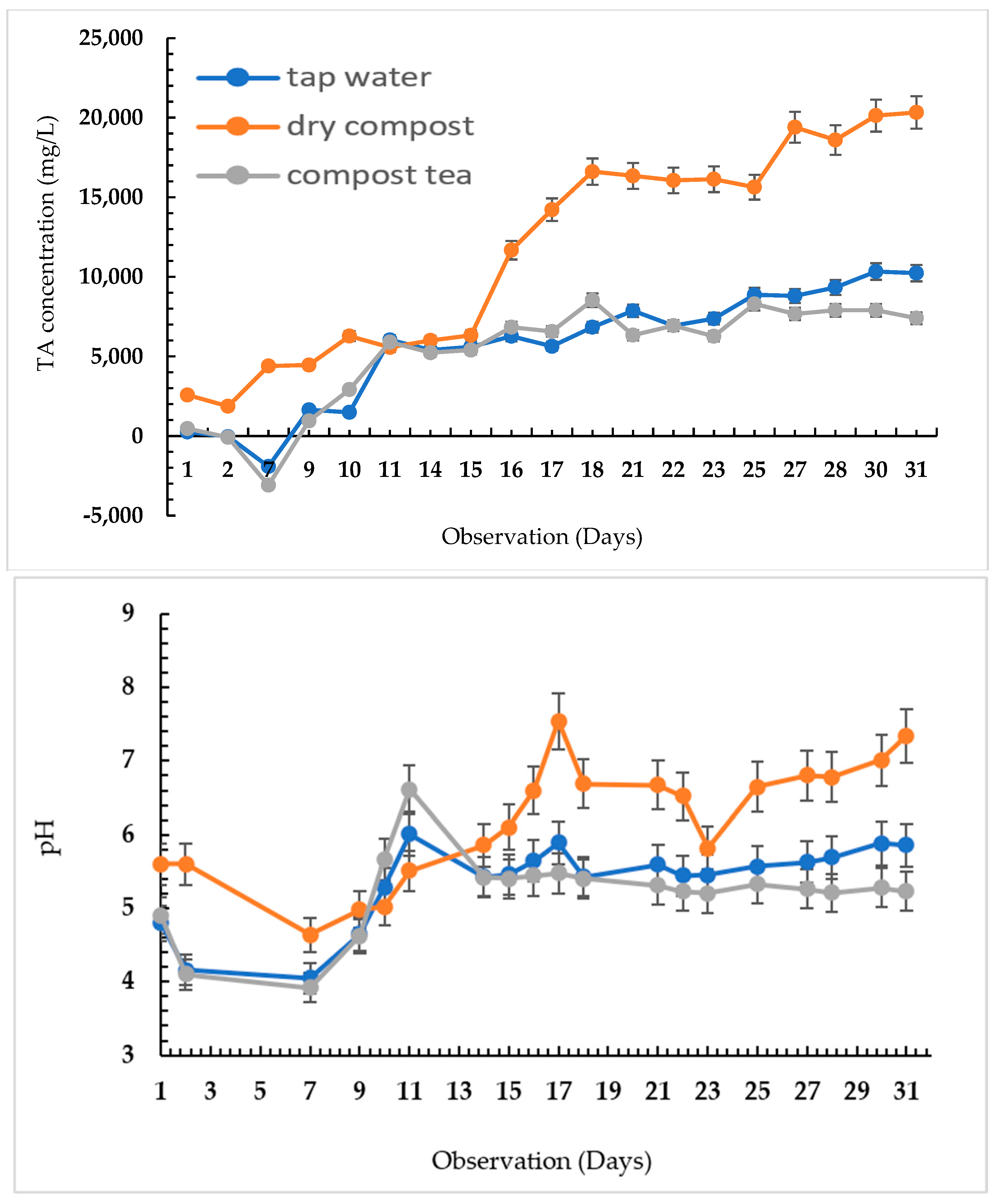
3.1. pH Value and TA Concentrations during the Composting
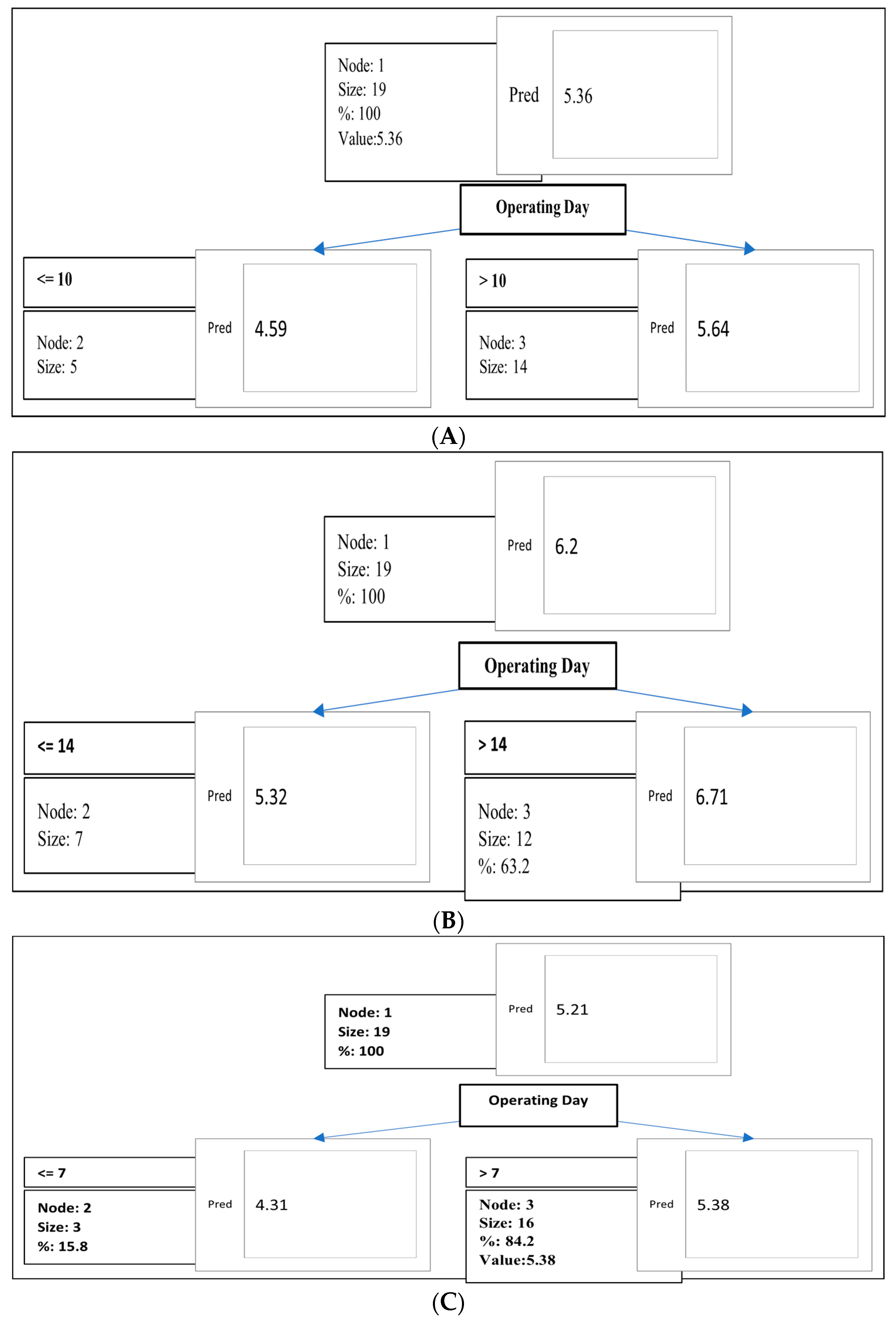
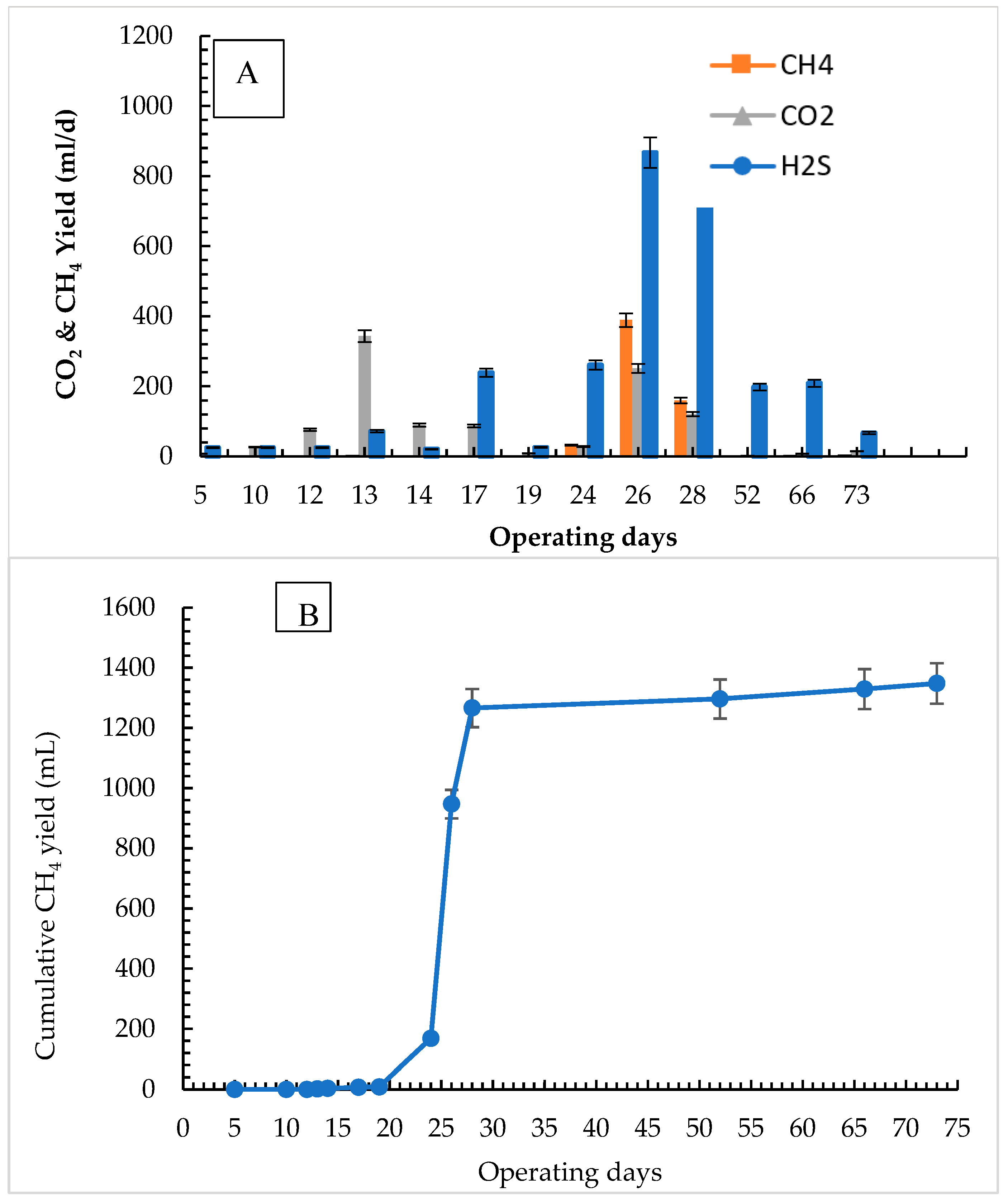
3.2. Methane Yield for Food Waste Digestion with Mixed Inoculum
3.3. Enumeration of Bacteria on Substrate with SCOBY and Kombucha Inoculum
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hashim, A.A.; Kadir, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Halim, S.; Sarani, N.A.; Hassan, M.I.H.; Hamid, N.J.A.; Hashar, N.N.H.; Hissham, N.F.N. Overview on food waste management and composting practice in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 6–9 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Yu, M.; Zhang, X.; Song, N.; Chang, Q.; Gao, M.; Sonomoto, K. Effect of ethanol pre-fermentation and inoculum-to-substrate ratio on methane yield from food waste and distillers’ grains. Appl. Energy 2015, 155, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniveloo, K.; Amran, M.A.; Norhashim, N.A.; Mohamad-Fauzi, N.; Peng-Hui, F.; Hui-Wen, L.; Kai-Lin, Y.; Jiale, L.; Chian-Yee, M.G.; Jing-Yi, L.; et al. Food waste composting and microbial community structure profiling. Processes 2020, 8, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, B.Y. Changes in major components of tea fungus metabolites during prolonged fermentation. J. Appl. Microbiol 2000, 89, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trovatti, E.; Serafim, L.S.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Neto, C.P. Gluconacetobacter sacchari: An efficient bacterial cellulose cell-factory. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, A.J.; O’Sullivan, O.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Sequence-based analysis of the bacterial and fungal compositions of multiple kombucha (tea fungus) samples. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Son, S.M.; Pyon, J.H.; Park, J.Y. Performance comparison between mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic reactors for treatment of palm oil mill effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 165, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, R.C.; Sullivan, D.M. Determining the pH buffering capacity of compost via titration with dilute sulfuric acid. Waste Biomass Valorization 2014, 5, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, L.; Scherer, P. Impact of bioaugmentation by compost on the performance and ecology of an anaerobic digester fed with energy crops. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2931–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thummes, K.; Schäfer, J.; Kämpfer, P.; Jäckel, U. Thermophilic methanogenic Archaea in compost material: Occurrence, persistence and possible mechanisms for their distribution to other environments. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 30, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, Y.Y.; Chou, K.W.; Norli, I. Strategies for improving biogas production of palm oil mill effluent (POME) anaerobic digestion: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2993–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Gong, X. Anaerobic cultivation of waste activated sludge to inoculate solid state anaerobic co-digestion of agricultural wastes: Effects of different cultivated periods. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demichelis, F.; Tommasi, T.; Deorsola, F.A.; Marchisio, D.; Fino, D. Effect of inoculum origin and substrate-inoculum ratio to enhance the anaerobic digestion of organic fraction municipal solid waste (OFMSW). J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 351, 131539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgewater, L.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jayabalan, R.; Malbaša, R.V.; Lončar, E.S.; Vitas, J.S.; Sathishkumar, M. A review on kombucha tea-microbiology, composition, fermentation, beneficial effects, toxicity, and tea fungus. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesaro, A.; Naddeo, V.; Amodio, V.; Belgiorno, V. Enhanced biogas production from anaerobic codigestion of solid waste by sonolysis. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2012, 19, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patowary, D.; West, H.; Clarke, M.; Baruah, D.C. Biogas Production from Surplus Plant Biomass Feedstock: Some Highlights of Indo-UK R&D Initiative. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, K.Y. Establishment and Stabilization of pH in Container Root Substrate; North Carolina State University ProQuest Dissertations Publishing: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nasef, M.A.; Shaban, K.A.; Abd El-Hamid, A.F. Effect of Compost, Compost Tea and Bio-Fertilizer Application on Some Chemical Soil Properties and Rice Productivity Under Saline Soil Condition. J. Agric. Chem. Biotechnol. 2009, 34, 2609–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Grandvalet, C.; Verdier, F.; Martin, A.; Alexandre, H.; Tourdot-Maréchal, R. Microbial Dynamics between Yeasts and Acetic Acid Bacteria in Kombucha: Impacts on the Chemical Composition of the Beverage. Foods 2020, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, E. H2S removal from biogas using bioreactors: A review. Int. J. Energy Environ. 2015, 6, 479–498. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Yu, M.; Song, N.; Xu, B.; Gao, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q. Effect of ethanol pre-fermentation on organic load rate and stability of semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, Q.; Yu, M.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Q.; Sakai, K. Effects of digestate recirculation on a two-stage anaerobic digestion system, particularly focusing on metabolite correlation analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 251, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, P.; Hultman, J.; Paulin, L.; Auvinen, P.; Romantschuk, M. Bacterial diversity at different stages of the composting process. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicaksono, A.; Rahmawan, A.; Hawali Abdul Matin, H.; Gumilang Kencana Wardani, L.; Djoko Kusworo, T.; Sumardiono, S. The effect of pretreatment using sodium hydroxide and acetic acid to biogas production from rice straw waste. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 22–25 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N.; Yu, M.; Wang, Q.; Song, N.; Che, S.; Wu, C.; Sun, X. Effect of Ethanol and Lactic Acid Pre-fermentation on Putrefactive Bacteria Suppression, Hydrolysis, and Methanogenesis of Food Waste. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 2982–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, W.; James, D.; Clay, F. The Physiology and Biochemistry of Prokaryotes. In The Physiology and Biochemistry of Prokaryotes, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 383–403. [Google Scholar]
- Avery, L.M.; Anchang, K.Y.; Tumwesige, V.; Strachan, N.; Goude, P.J. Potential for Pathogen reduction in anaerobic digestion and biogas generation in Sub-Saharan Africa. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 70, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.R.; Lang, N.L.; Cheung, K.H.M.; Spanoudaki, K. Factors controlling pathogen destruction during anaerobic digestion of biowastes. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Properties | Value |
| Maximum OLR | 5 g-VS·L−1·d−1 |
| C:N ratio | 18.00 for R1, 17.08 for R2, and 17.05 for feedstock |
| Mixing | 60 rpm for 15 min every 2 h |
| Temperature | 37 °C |
| Initial pH | 7.4 for R1 and 7.03 for R2 |
| Parameters | Method | Apparatus and Instruments |
|---|---|---|
| pH and TA | APHA (Method 4500-H+. Electrometric, Method 2320 B. Titration) | HACH sension3 pH meter |
| TS and VS | APHA (Method 2540 B and 2540 E. Gravimetric) | Binder oven and Carbolite muffle furnace |
| TVFA | APHA (Method 5560 C. Distillation) | Rotary evaporator and titration set |
| VFA composition | APHA (Method 5560 D. GC-FID) | Shidmadzu GC-2010 Plus |
| Biogas composition | Handheld biogas analyzer | MRU instruments Optima 7 biogas |
| Biogas yield | Water displacement method | Measuring cylinder and beaker |
| C:N ratio | CHNS elemental analyzer | Perkin Elmer 2400 Series II |
| Sample | Weight (mg) | Carbon % | Hydrogen % | Nitrogen % | Sulfur % | Others % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feedstock | 1.951 | 46.04 | 6.92 | 2.70 | 0.59 | 43.75 |
| R1 | 2.163 | 24.31 | 2.19 | 1.35 | 0.30 | 71.85 |
| R2 | 1.863 | 49.02 | 9.19 | 2.87 | 0.81 | 38.11 |
| Independent Variables | Dependent Variables | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Presence of kombucha | pH | 0.000 |
| TA | 0.138 | |
| TVFA | 0.003 | |
| TS | 0.403 | |
| VS | 0.947 | |
| VFA/TA | 0.524 | |
| Addition of compost | pH | R1 = 0.002, R2 = 0.043 |
| TA | R1 = 0.021, R2 = 0.021 | |
| TVFA | R1 = 0.001, R2 = 0.001 | |
| TS | R1 = 0.021, R2 = 0.643 | |
| VS | R1 = 0.083, R2 = 0.021 | |
| VFA/TA | R1 = 0.165, R2 = 0.002 | |
| Presence of kombucha * Addition of compost | pH | 0.129 |
| TA | 0.951 | |
| TVFA | 0.000 | |
| TS | 0.036 | |
| VS | 0.936 | |
| VFA/TA | 0.350 |
| Samples | Gram Stain Test | Shape | Elevation | Form | Margin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCOBY | Gram +ve | bacilli | Convex | Circular | Entire (even) |
| Kombucha | No colony found | ||||
| Food waste | Gram +ve | bacilli | Convex | Circular | Entire (even) |
| Food waste, kombucha, SCOBY | Gram −ve | rod | Flat | Circular | Undulate (wavy) |
| Gram −ve | rod | Convex | Circular | Entire (even) | |
| Food waste, SCOBY | Gram −ve | rod | Flat | Circular | Undulate (wavy) |
| Gram −ve | rod | Convex | Circular | Entire (even) | |
| Fermented food waste, kombucha, SCOBY | Gram −ve | rod | Flat | Circular | Undulate (wavy) |
| Gram −ve | rod | Convex | Circular | Entire (even) | |
| Gram +ve | Cocco- rod/rod | Convex | Punctiform | Entire (even) | |
| Fermented food waste, SCOBY | Gram −ve | rod | Flat | Circular | Undulate (wavy) |
| Gram −ve | bacilli | Convex | Circular | Entire (even) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shyan, L.L.; Mat Nanyan, N.S.; Ismail, N.; Al-Gheethi, A.; T. Nguyen, H.-H.; Vo, D.-V.N.; El Enshasy, H.A. Effort to Mitigate Volatile Fatty Acid Inhibition by Using Mixed Inoculum and Compost for the Degradation of Food Waste and the Production of Biogas. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021185
Shyan LL, Mat Nanyan NS, Ismail N, Al-Gheethi A, T. Nguyen H-H, Vo D-VN, El Enshasy HA. Effort to Mitigate Volatile Fatty Acid Inhibition by Using Mixed Inoculum and Compost for the Degradation of Food Waste and the Production of Biogas. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021185
Chicago/Turabian StyleShyan, Lai Llih, Noreen Suliani Mat Nanyan, Norli Ismail, Adel Al-Gheethi, Hong-Ha T. Nguyen, Dai-Viet N. Vo, and Hesham Ali El Enshasy. 2023. "Effort to Mitigate Volatile Fatty Acid Inhibition by Using Mixed Inoculum and Compost for the Degradation of Food Waste and the Production of Biogas" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021185
APA StyleShyan, L. L., Mat Nanyan, N. S., Ismail, N., Al-Gheethi, A., T. Nguyen, H.-H., Vo, D.-V. N., & El Enshasy, H. A. (2023). Effort to Mitigate Volatile Fatty Acid Inhibition by Using Mixed Inoculum and Compost for the Degradation of Food Waste and the Production of Biogas. Sustainability, 15(2), 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021185








