Size Structure of Exploited Holothurian Natural Stocks in the Hellenic Seas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Commercial Holothurian Species
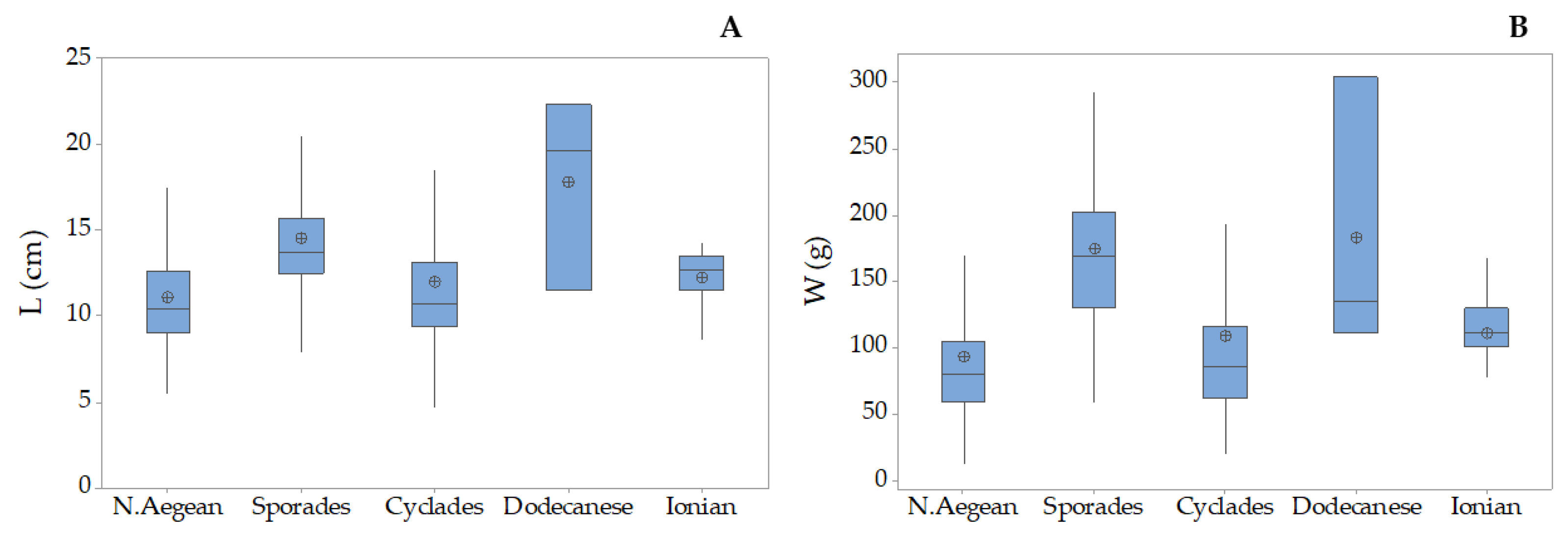
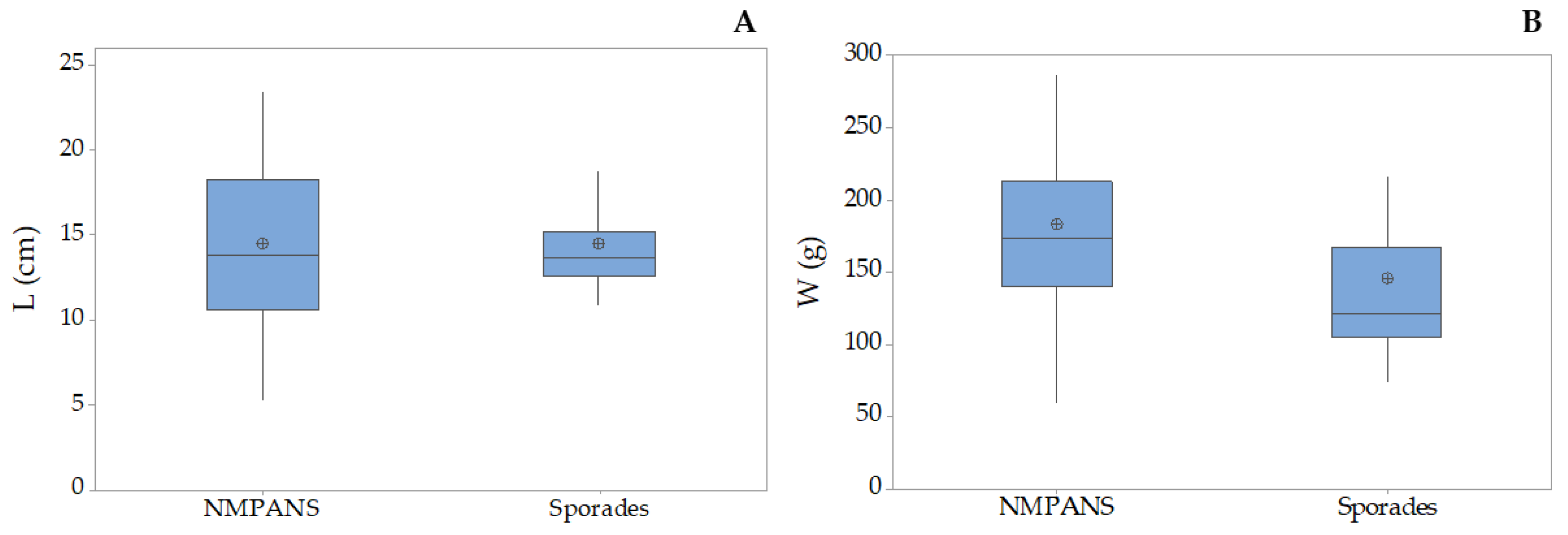
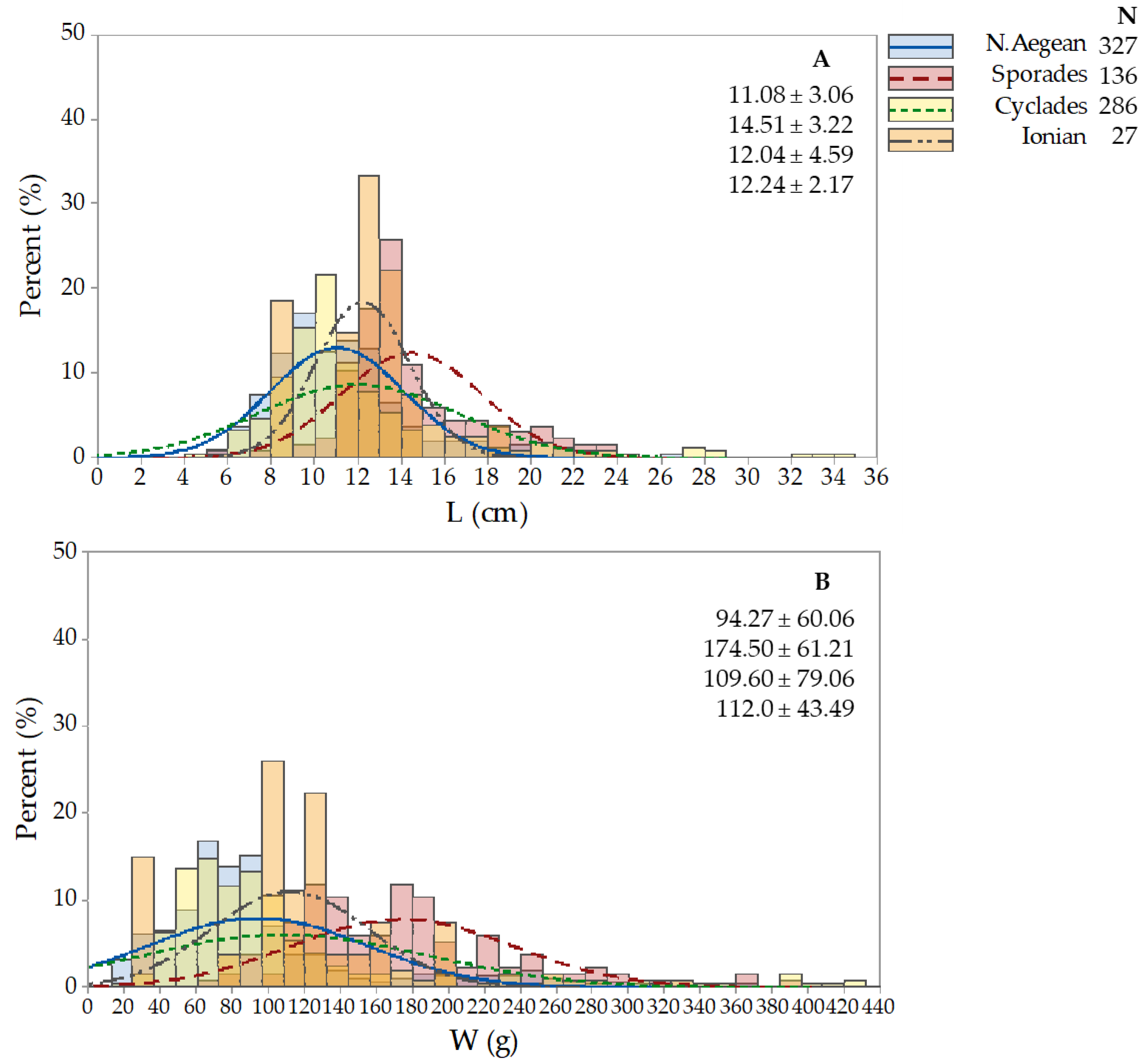
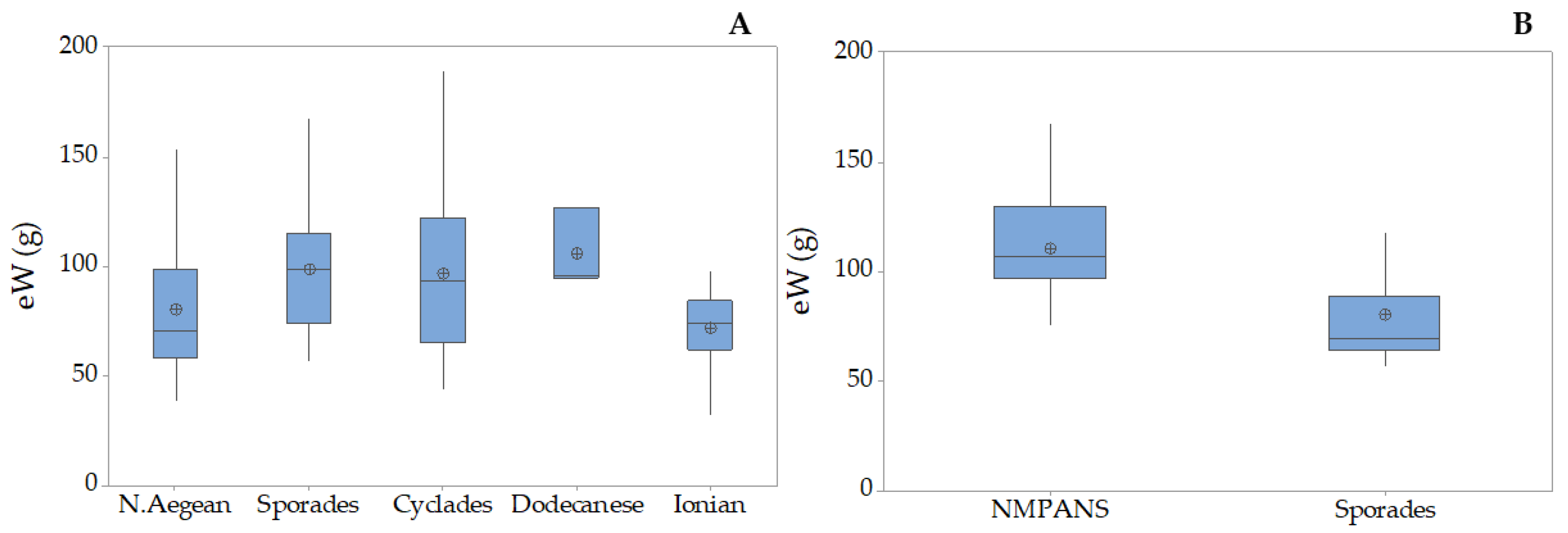
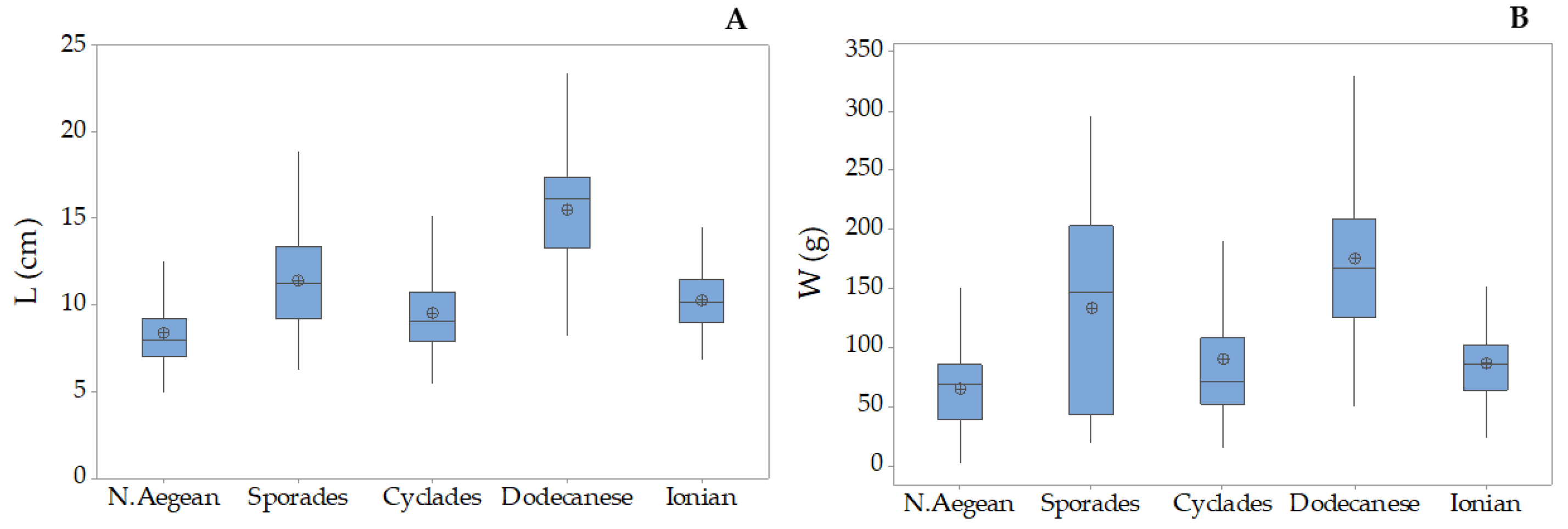
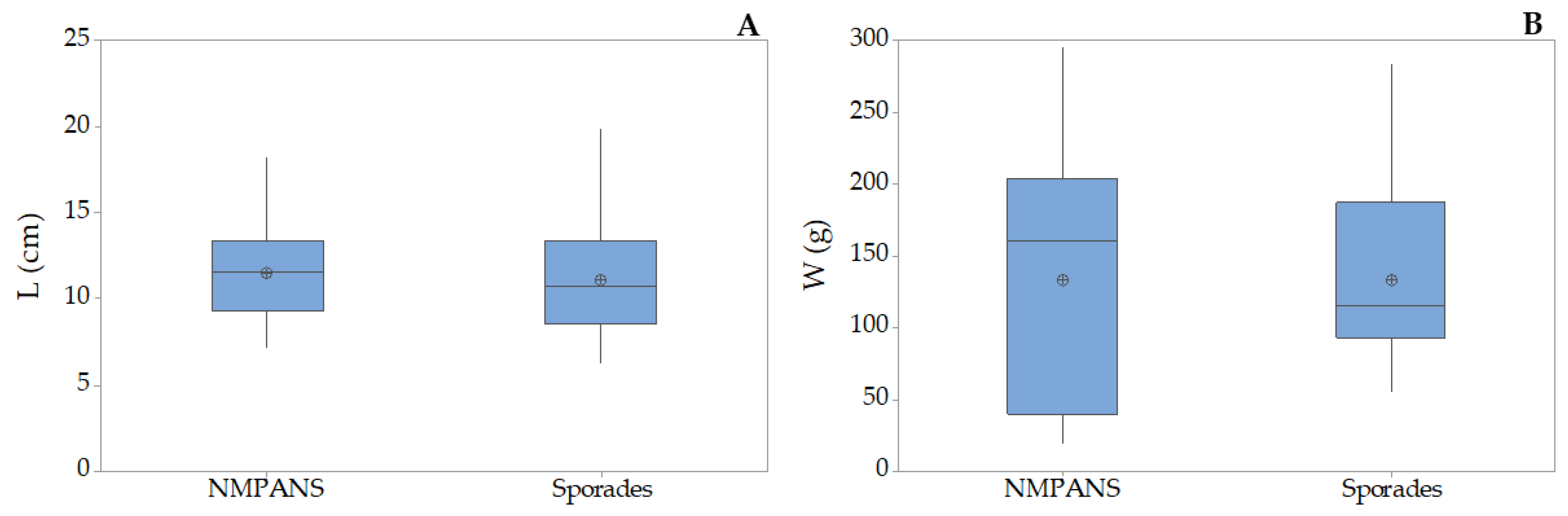
3.2. Holothuria tubulosa
3.3. Holothuria poli
3.4. Holothuria sanctori
3.5. Holothuria mammata
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, A.; Kerr, A.M.; Paulay, G.; Reich, M.; Wilson, N.G.; Carvajal, J.I.; Rouse, G.W. Molecular phylogeny of extant Holothuroidea (Echinodermata). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 111, 110–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motokawa, T. Skin of sea cucumbers: The smart connective tissue that alters mechanical properties in response to external stimuli. J. Aero Aqua Bio-Mech. 2019, 8, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wilkie, I.C.; Carnevalli, M.D.C. Morphological and physiological aspects of mutable collagenous tissue at the autotomy plane of the starfish Asterias rubens L. (Echinodermata, Asteroidea): An echinoderm paradigm. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toral-Granda, V.; Lovatelli, A.; Vasconcellos, M. Sea Cucumbers: A Global Review of Fisheries and Trade; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper, 516; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008; pp. 1–317. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, S.W.; Samyn, Y.; Conand, C. Commercially Important Sea Cucumbers of the World; FAO Species Catalogue for Fishery Purposes. No. 6; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012; pp. 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Vafidis, D.; Antoniadou, C. Holothurian fisheries in the Hellenic Seas: Seeking for sustainability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangestuti, R.; Arifin, Z. Medicinal and health benefit effects of functional sea cucumbers. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2018, 8, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Govan, H.; Wolff, M.; Purcell, S. Economic and other benefits of enforcing size limits in Melanesian sea cucumber fisheries. SPC Fish. Newsl. 2018, 155, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, C.; Foale, S.; Kinch, J.; Frijlink, S.; Lindsay, D.; Southgate, P.C. Socioeconomic impacts of a sea cucumber fishery in Papua New Guinea: Is there an opportunity for mariculture? Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 179, 104826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.W.; Williamson, D.H.; Ngaluafec, P. Chinese market prices of beche-de-mer: Implications for fisheries and aquaculture. Mar. Pol. 2018, 91, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conand, C.; Claereboudt, M.; Dissayanake, C.; Ebrahim, A.; Fernando, S.; Godvinden, R.; Lavitra, T.; Léopold, M.; Mmbaga, T.; Mulochau, T.; et al. Review of fisheries and management of sea cucumbers in the Indian Ocean. WIO J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 21, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.C.; Flemming, J.M.; Watson, R.; Lotzel, H.K. Rapid global expansion of invertebrate fisheries: Trends, drivers, and ecosystem effects. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggertsen, M.; Eriksson, H.; Slater, M.J.; Raymond, C.; dela Torre-Castro, M. Economic value of small-scale sea cucumber fisheries under two contrasting management regimes. Ecol. Soc. 2020, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.W.; Mercier, A.; Conand, C.; Hamel, J.-F.; Toral-Granda, V.M.; Lovatelli, A.; Uthicke, S. Sea cucumber fisheries: Global analysis of stocks, management measures and drivers of overfishing. Fish. Fish. 2013, 14, 34–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conand, C.; Polidoro, B.; Mercier, A.; Gamboa, R.; Hamel, J.F.; Purcell, S. The IUCN Red List assessment of aspidochirotid sea cucumbers and its implications. SPC Beche-de-mer Inf. Bull. 2014, 34, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Wangüemert, M.; Domínguez-Godino, J.; Cánovas, F. The fast development of sea cucumber fisheries in the Mediterranean and NE Atlantic waters: From a new marine resource to its over-exploitation. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2018, 151, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Wangüemert, M.; Valente, S.; Henriques, F.; Domínguez-Godino, J.; Serrão, E. Setting preliminary biometric baselines for new target sea cucumbers species of the NE Atlantic and Mediterranean fisheries. Fish. Res. 2016, 179, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plagányi, E.E.; Murohy, N.; Skewes, T.; Dutra, L.X.C.; Dowling, N.; Fischer, M. Development of a data-poor harvest strategy for a sea cucumber fishery. Fish. Res. 2020, 230, 105635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Stern-Pirlot, A.; Winker, H.; Gascuel, D. Size matters: How single-species management can contribute to ecosystem-based fisheries management. Fish. Res. 2008, 92, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, J.; Zhoo, S.; Prasetyo, A.P. Soft bodies make estimation hard: Correlations among body dimensions and weights of multiple species of sea cucumbers. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2015, 66, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthicke, S.; Welh, D.; Benzie, J.A.H. Slow growth and lack of recovery in overfished holothurians on the Great Barrier Reef: Evidence from DNA fingerprints and repeated large-scale surveys. Conserv. Biol. 2004, 18, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhag, J.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Guo, L.; Ren, Y.; Qiao, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q. Transcriptome analysis of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) polian vesicles in response to evisceration. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 97, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazanidis, G.; Antoniadou, C.; Lolas, A.; Neofitou, N.; Vafidis, D.; Chintiroglou, C.; Neofitou, C. Population dynamics and reproduction of Holothuria tubulosa (Holothuroidea: Echinodermata) in the Aegean Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2010, 90, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShane, P.; Knuckey, I. A Review of Size Limits for the Queensland Sea Cucumber Fishery (East Coast); Fishwell Consulting: Queenscliff, Australia, 2022; 15p. [Google Scholar]
- Voultsiadou, E.; Dailianis, T.; Antoniadou, C.; Vafidis, D.; Dounas, C.; Chintiroglou, C. Aegean bath sponges: Historical data and current status. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2011, 19, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortonese, E. Fauna d’Italia. In Echinodermata; Calderini: Bologna, Italy, 1965; pp. 1–422. [Google Scholar]
- Bulteel, P.; Jangoux, M.; Coulon, P. Biometry, bathymetric distribution, and reproductive cycle of the holothuroid Holothuria tubulosa (Echinodermata) in Mediterranean seagrass beds. Mar. Ecol. 1992, 13, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, C.; Vafidis, D. Population structure of the traditionally exploited holothurian Holothuria tubulosa in the south Aegean Sea. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2011, 52, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Underwood, A.J. Experiment in Ecology: Their Logical Design and Interpretation Using Analysis of Variance; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 1–504. [Google Scholar]
- Eddy, D.T.; Lotze, H.K.; Fulton, E.A.; Coll, M.; Ainsworth, C.H.; deAraújo, J.N.; Bulman, C.M.; Bundy, A.; Christensen, V.; Field, J.C.; et al. Ecosystem effects of invertebrate fisheries. Fish. Fish. 2017, 18, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Ignatiades, l. Phytoplankton in pelagic and coastal waters. In State of the Hellenic Marine Environment; Papathanasiou, E., Zenetos, A., Eds.; Hellenic Center for Marine Research Publications: Athens, Greece, 2005; pp. 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- Mezali, K.; Lebouazda, Z.; Slimane-Tamacha, F.; Soualili, D.L. Biometry, size structure and reproductive cycle of the sanded sea cucumbers Holothuria poli (Echinodermata, Holothuriidae) from the west Algerian coast. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2022, 66, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venâncio, E.; Félix, P.M.; Brito, A.C.; Azevedo e Silva, F.; Simões, T.; Sousa, J.; Mendes, S.; Pombo, A. Reproductive Biology of the Sea Cucumber Holothuria mammata (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea). Biology 2022, 11, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.G.; Garcia-Sanz, S.; Tuya, F. Reproductive biology of the sea cucumber Holothuria sanctori (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea). Sci. Mar. 2012, 76, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, V.; Giglioli, A.A.; Pusceddu, A.; Addis, P. Biology, ecology and management perspectives of overexploited depositfeeders sea cucumbers, with focus on Holothuria tubulosa (Gmelin, 1788). Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2021, 12, 9995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckner, A.W. Management and conservation strategies and practices for sea cucumbers. In The Proceedings of the Technical Workshop on the Conservation of Sea Cucumbers in the Families Holothuridae and Stichopodidae; Bruckner, A.W., Ed.; NOAA Technical Memorandum, NMFS-OPR 34; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2005; pp. 1–244. [Google Scholar]
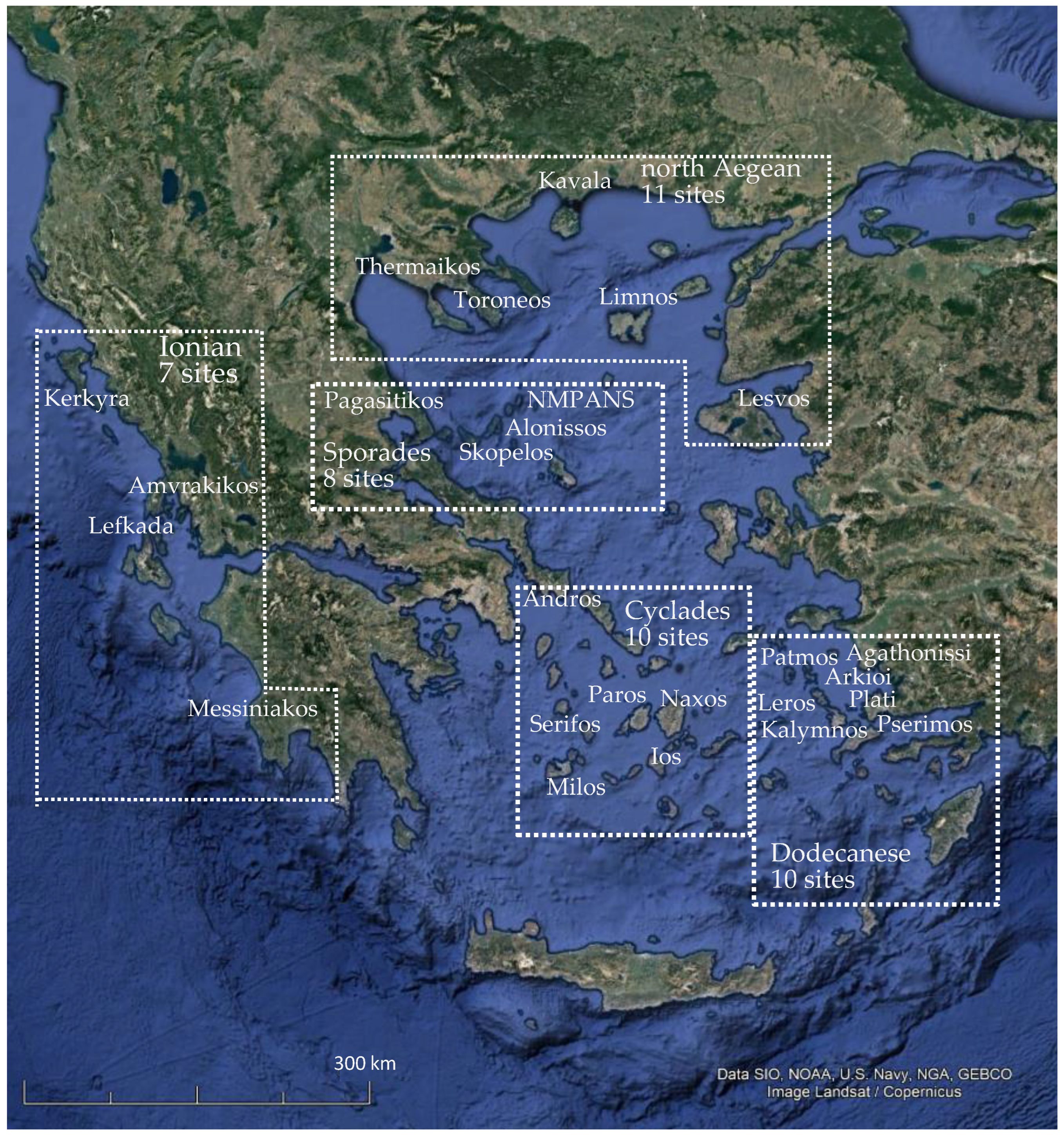
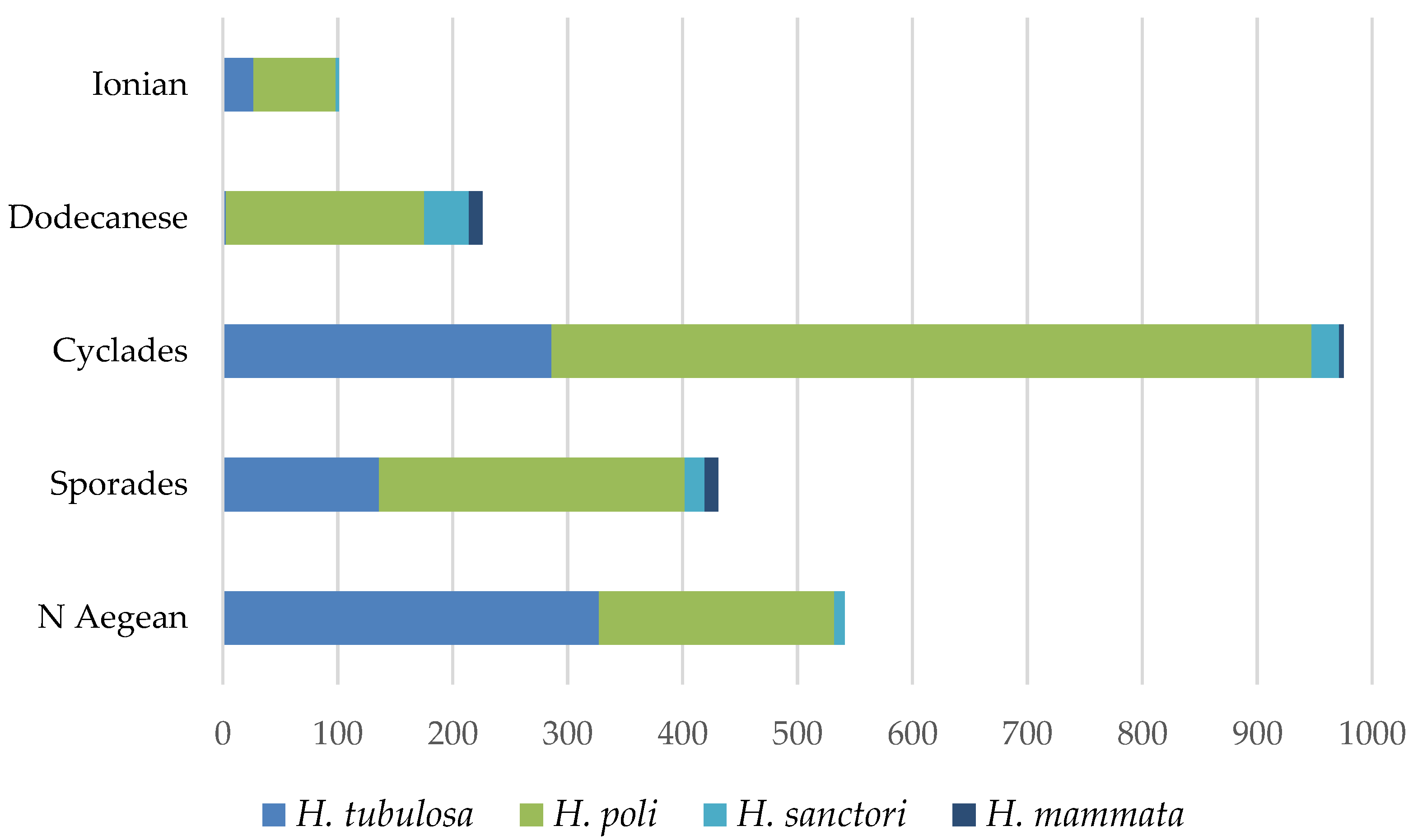
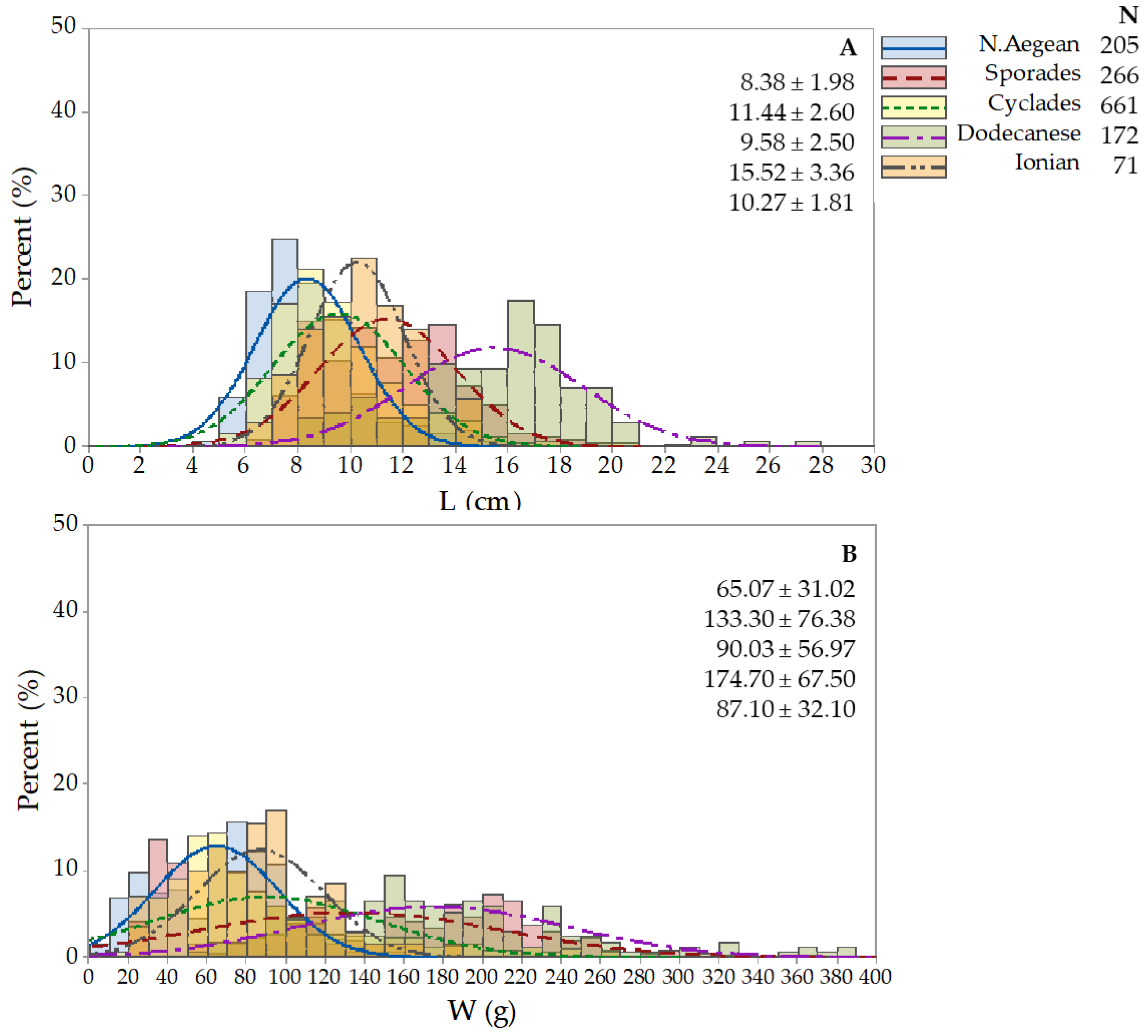
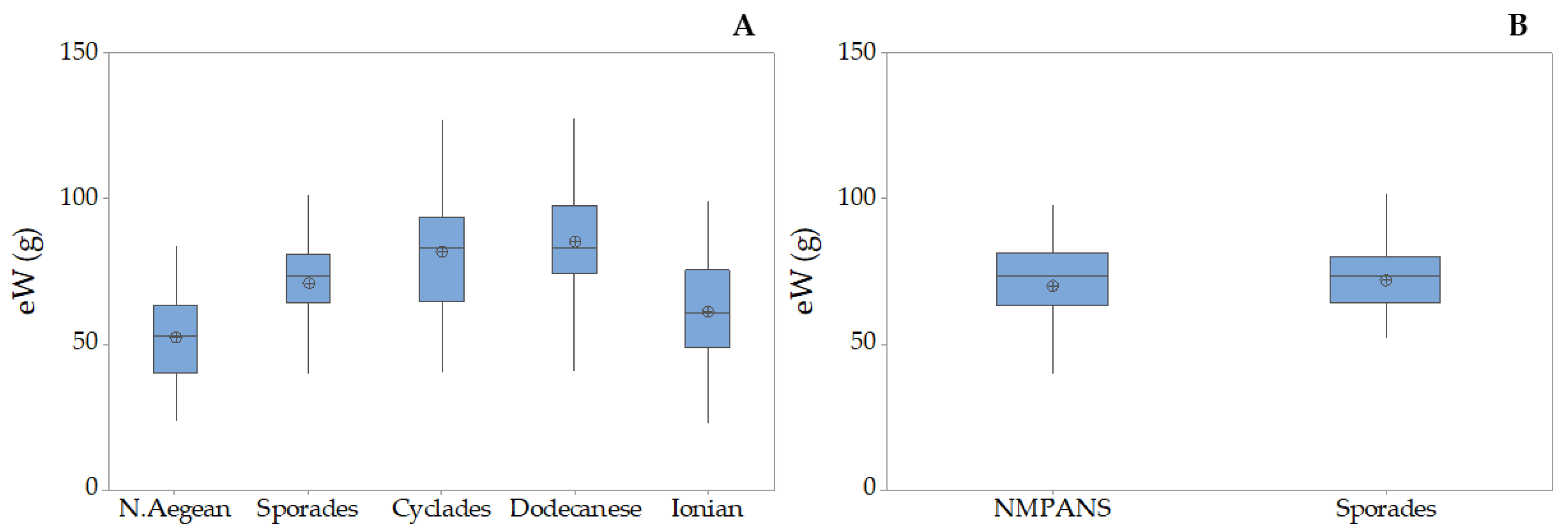
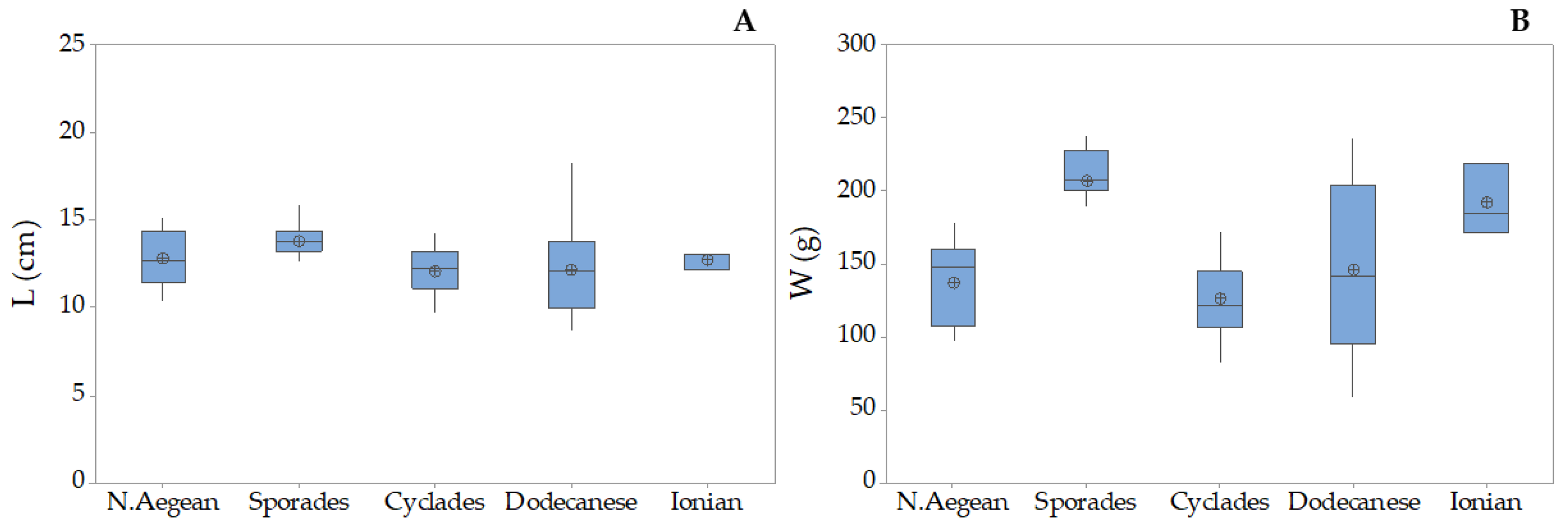
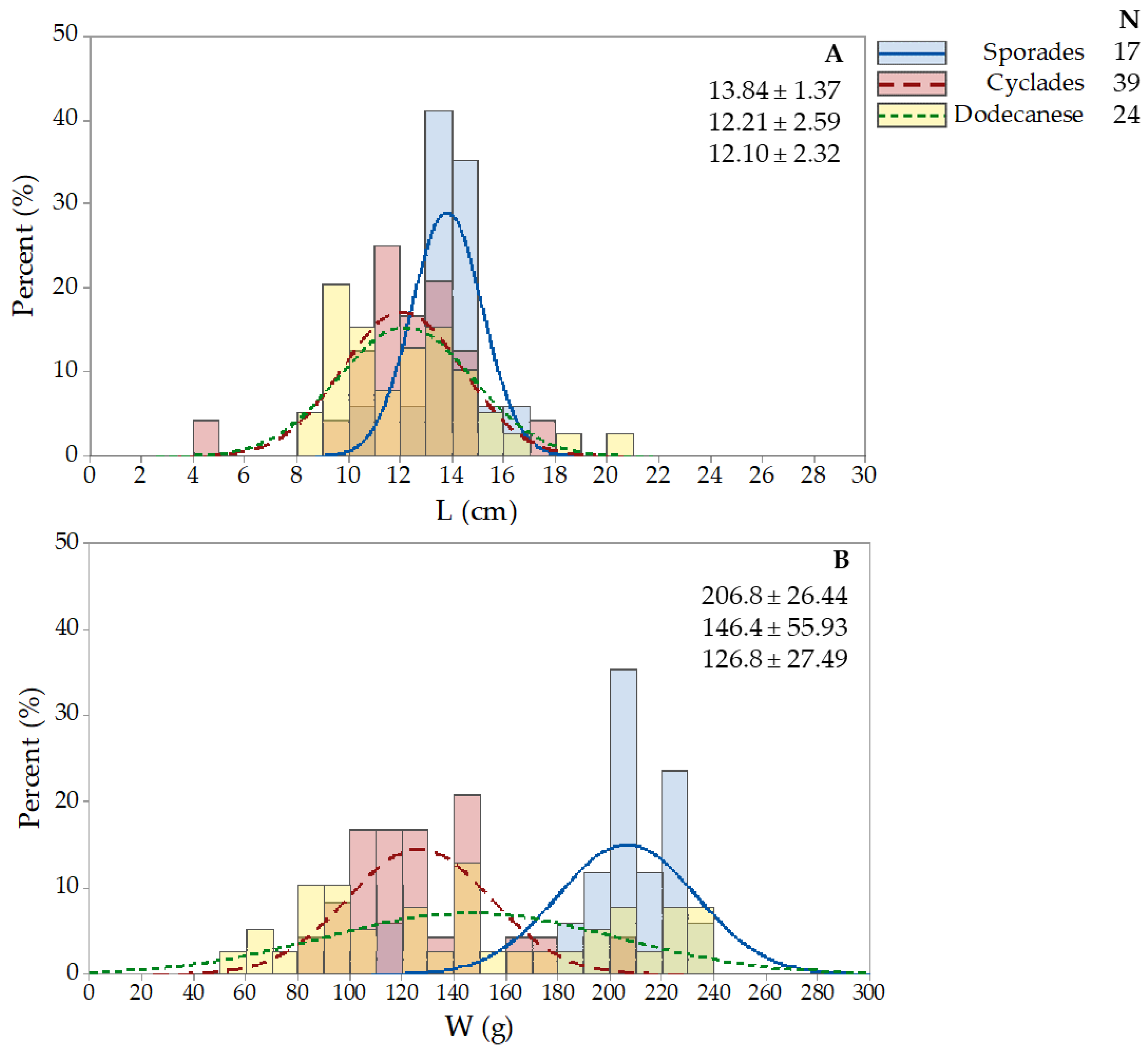
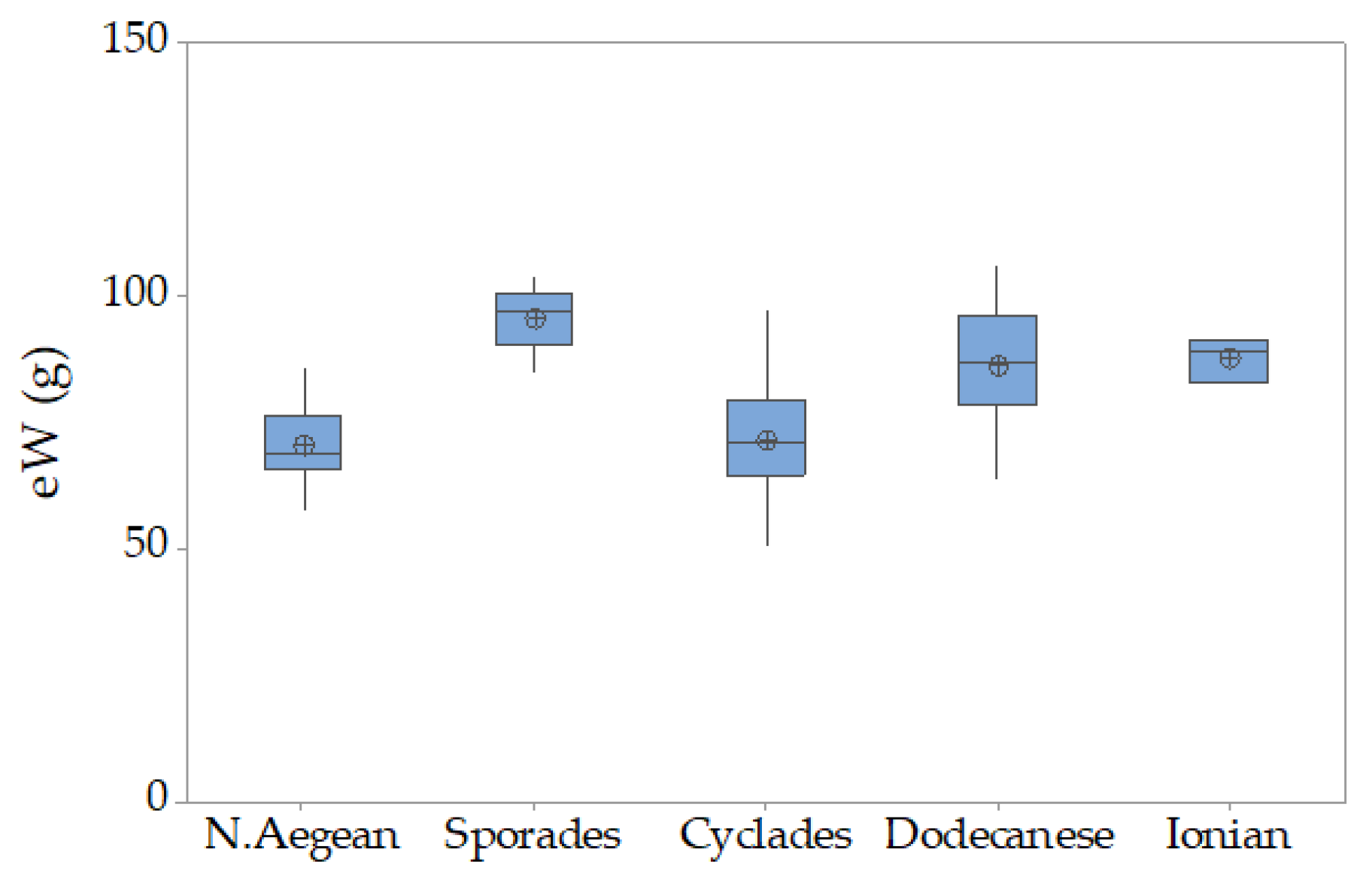
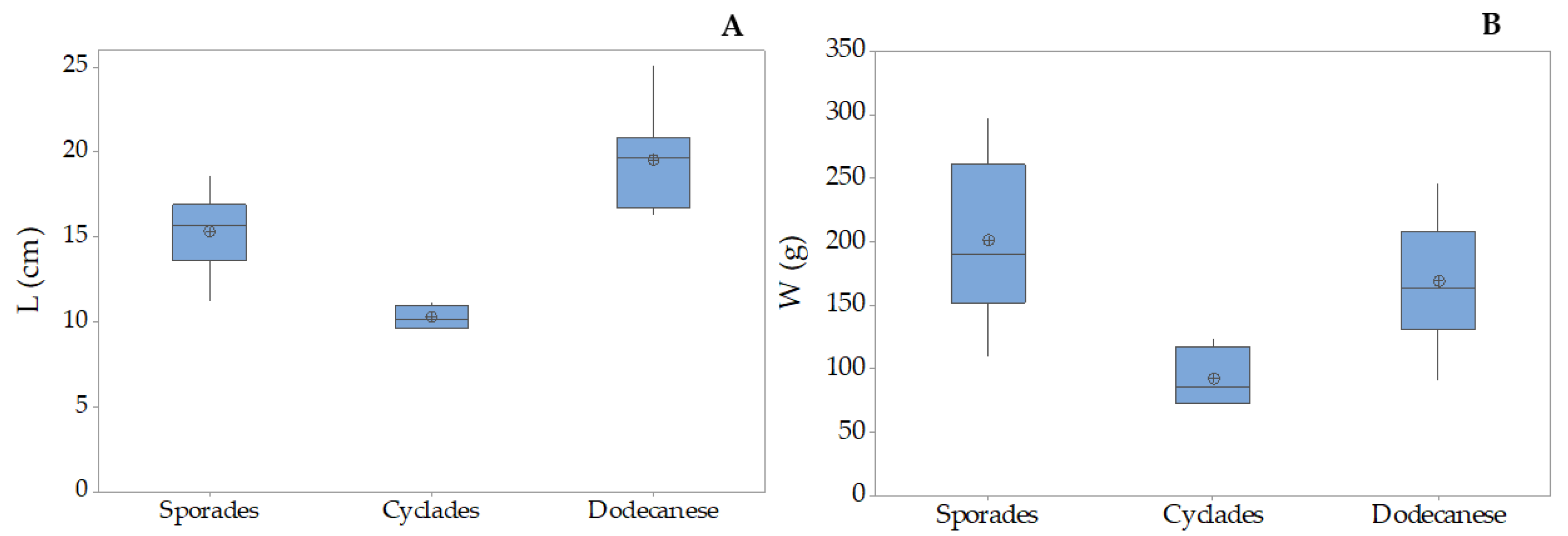
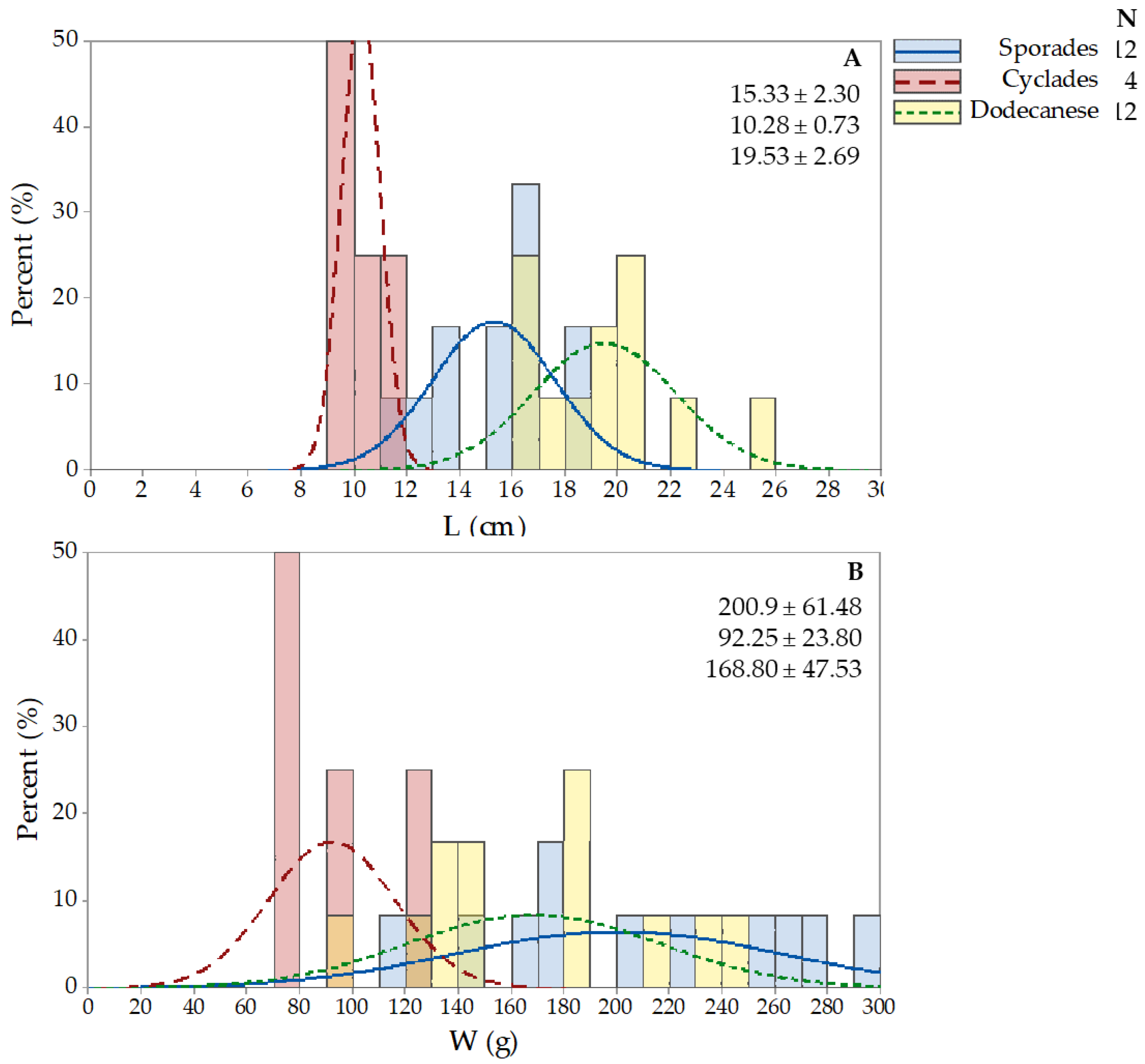
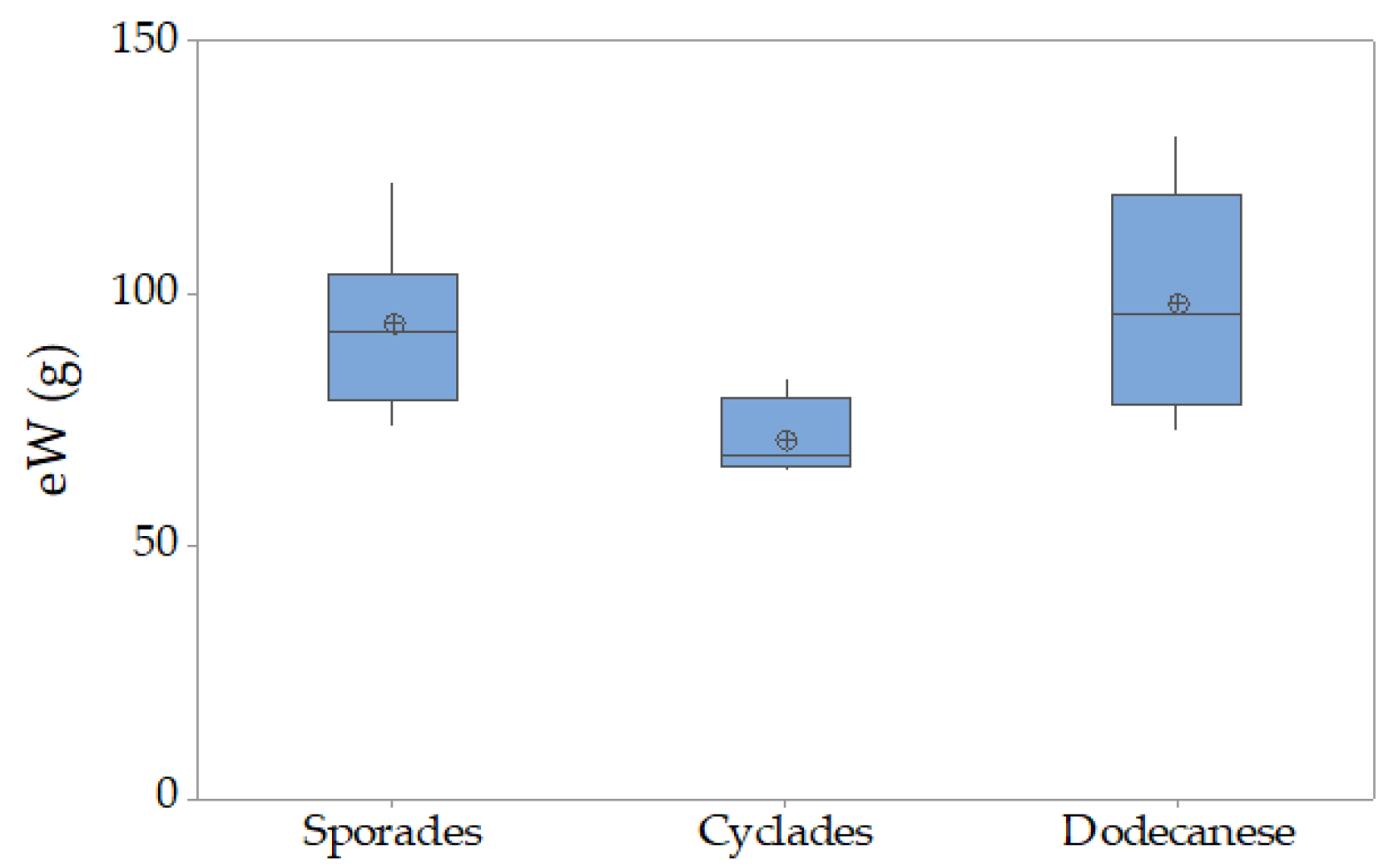
| Holothurians fisheries grounds in the Hellenic Seas | Location | Toponym | Station Longitude/Latitude | N/eN | ||||
| H.t. | H.p. | H.s. | H.m. | |||||
| North Aegean (April 2022) | Kavala Gulf | Agiasma | 40°52.276′ N 24°36.347′ E | 7 | 12/10 | |||
| Nea Peramos | 40°50.268′ N 24°20.040′ E | 10 | 15 | |||||
| Thermaikos Gulf | NeaMoudania | 40°13.770′ N 23°17.555′ E | 221/20 | 49 | ||||
| Potidea | 40°11.572′ N 23°19.209′ E | 41/20 | 90/20 | 2/2 | ||||
| Toroneos Gulf | Nea Fokea | 40°8.440′ N 23°23.238′ E | 1 | 3/3 | ||||
| Gerakini | 40°15.962′ N 23°26.551′ E | 29/20 | 1/1 | |||||
| Limnos | Plaka | 40°1.062′ N 25°26.820′ E | 5 | 7 | 2/2 | |||
| Kotsina | 39°56.999′ N 25°17.646′ E | 3 | 5 | 1/1 | ||||
| Moudros | 39°52.476′ N 25°14.712′ E | 6 | 12/10 | |||||
| Lesvos | Kalloni | 39°9.356′ N 26°12.159′ E | 3 | 10 | ||||
| Geras | 39°2.524′ N 26°31.241′ E | 2 | 5 | |||||
| Sporades (May 2019) | Kyra Panagia * | Planitis | 39°20.823′ N 24°04.495′ E | 88/20 | 115/15 | 9/9 | ||
| Ag. Petros | 39°18.929′ N 24°03.469′ E | 11 | 37 | |||||
| Alonissos ** | Gerakas | 39°16.441′ N 23°57.045′ E | 10/10 | 46/5 | 2/2 | |||
| Peristera | 39°11.825′ N 23°58.522′ E | 3 | 5 | 1/1 | 8/8 | |||
| Skopelos | Skala | 39°7.718′ N 23°44.369′ E | 3/3 | 15/5 | 5/5 | 4/4 | ||
| Pagasitikos Gulf | Nies | 39°6.949′ N 22°55.946′ E | 15/10 | 24/10 | ||||
| Traxili | 39°9.504′ N 23°6.050′ E | 10 | ||||||
| Akti Petras | 39°9.199′ N23°11.633′ E | 7/7 | 14/5 | |||||
| Cyclades islands (June 2021) | Andros | Palaiopoli | 37°48.675′ N 24°49.587′ E | 3 | ||||
| Paros | Naoussa | 37°8.416′ N 25°13.688′ E | 57/10 | 64/5 | 2 | |||
| Paroikia | 37°5.549′ N 25°8.244′ E | 47 | 60/5 | 4/4 | ||||
| Alyki | 36°58.508′ N 25°7.363′ E | 67/10 | 96/15 | 2 | 3/3 | |||
| Piso Livadi | 37°0.414′ N 25°15.185′ E | 49 | 4/4 | |||||
| Naxos | Plaka | 37°2.357′ N 25°21.555′ E | 21/20 | 2/2 | ||||
| Kastraki | 37°0.419′ N 25°21.529′ E | 15 | 5/4 | |||||
| Ios | Skala | 36°43.241′ N 25°16.022′ E | 22/20 | 67/20 | 1 | 1/1 | ||
| Milos | Arkoudes | 36°46.235′ N 24°24.961′ E | 19 | 27 | 4/4 | |||
| Serifos | Livadi | 37°8.201′ N 24°31.910′ E | 2 | 47/20 | 2/2 | |||
| Dodecanese (December 2019) | Agathonissi | Ag.Georgios | 37°27.456′ N 26°59.548′ E | 1/1 | 24/10 | |||
| Skala | 37°27.356′ N 26°58.009′ E | 1 | ||||||
| Arkoi | Marathi | 37°21.989′ N 26°43.588′ E | 14/10 | |||||
| Patmos | Sapsila | 37°18.797′ N 26°33.570′ E | 25 | |||||
| Groikos | 37°18.069′ N 26°33.815′ E | 85/20 | ||||||
| Leros | Xirokampos | 37°6.335′ N 26°52.387′ E | 1/1 | 2 | 3 | 9/9 | ||
| Kalymnos | Telendos | 36°59.716′ N 26°55.408′ E | 2 | |||||
| Therma | 36°56.313′ N 26°59.267′ E | 12/10 | 3/3 | |||||
| Pserimos | Vathi | 36°56.153′ N 27°9.249′ E | 1/1 | 2 | 19/10 | |||
| Plati | 36°56.728′ N 27°5.573′ E | 3 | ||||||
| Ionian (April 2022) | Amvrakikos Gulf | Aktio | 38°56.134′ N 20°44.625′ E | 8/5 | ||||
| Ag. Nikolaos | 38°52.472′ N 20°45.804′ E | 15/15 | ||||||
| Messiniakos Gulf | Mantineia | 36°58.916′ N 22°8.705′ E | 7 | |||||
| Sagiada Bay | Sagiada | 39°36.900′ N 20°8.849′ E | 18/10 | |||||
| Kerkyra | Peleka | 39°34.434′ N 19°48.840′ E | 4 | 2/2 | ||||
| Lefkada | Vassiliki | 38°37.135′ N 20°35.819′ E | 5 | 1/1 | ||||
| Nydri | 38°42.356′ N 20°42.979′ E | 14/10 | ||||||
| Relation | Model | a | b | r | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eW/L | eW = aLb | 10.30 | 0.79 | 0.70 | 49.83 | −allometry (b < 3) |
| eW/W | eW = a + bW | 33.11 | 0.33 | 0.94 | 90.23 | −allometry (b < 1) |
| Relation | Model | a | b | r | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eW/L | eW = aLb | 8.76 | 0.82 | 0.73 | 54.54 | −allometry (b < 3) |
| eW/W | eW = a + bW | 35.09 | 0.24 | 0.89 | 80.61 | −allometry (b < 1) |
| Relation | Model | a | b | r | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eW/L | eW = aLb | 20.82 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 28.77 | −allometry (b < 3) |
| eW/W | eW = a + bW | 40.07 | 0.25 | 0.88 | 78.33 | −allometry (b < 1) |
| Relation | Model | a | b | r | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eW/L | eW = aLb | 20.17 | 0.54 | 0.67 | 43.83 | −allometry (b < 3) |
| eW/W | eW = a + bW | 48.33 | 0.26 | 0.83 | 68.07 | −allometry (b < 1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vafidis, D.; Antoniadou, C.; Apostologamvrou, C.; Voulgaris, K.; Varkoulis, A.; Giokala, E.; Lolas, A.; Roditi, K. Size Structure of Exploited Holothurian Natural Stocks in the Hellenic Seas. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13483. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813483
Vafidis D, Antoniadou C, Apostologamvrou C, Voulgaris K, Varkoulis A, Giokala E, Lolas A, Roditi K. Size Structure of Exploited Holothurian Natural Stocks in the Hellenic Seas. Sustainability. 2023; 15(18):13483. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813483
Chicago/Turabian StyleVafidis, Dimitris, Chryssanthi Antoniadou, Chrysoula Apostologamvrou, Konstantinos Voulgaris, Anastasios Varkoulis, Efthymia Giokala, Alexios Lolas, and Kyriakoula Roditi. 2023. "Size Structure of Exploited Holothurian Natural Stocks in the Hellenic Seas" Sustainability 15, no. 18: 13483. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813483
APA StyleVafidis, D., Antoniadou, C., Apostologamvrou, C., Voulgaris, K., Varkoulis, A., Giokala, E., Lolas, A., & Roditi, K. (2023). Size Structure of Exploited Holothurian Natural Stocks in the Hellenic Seas. Sustainability, 15(18), 13483. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813483










