Exploring the Carbon-Mitigation Effect of High-Speed Railway and Its Underlying Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
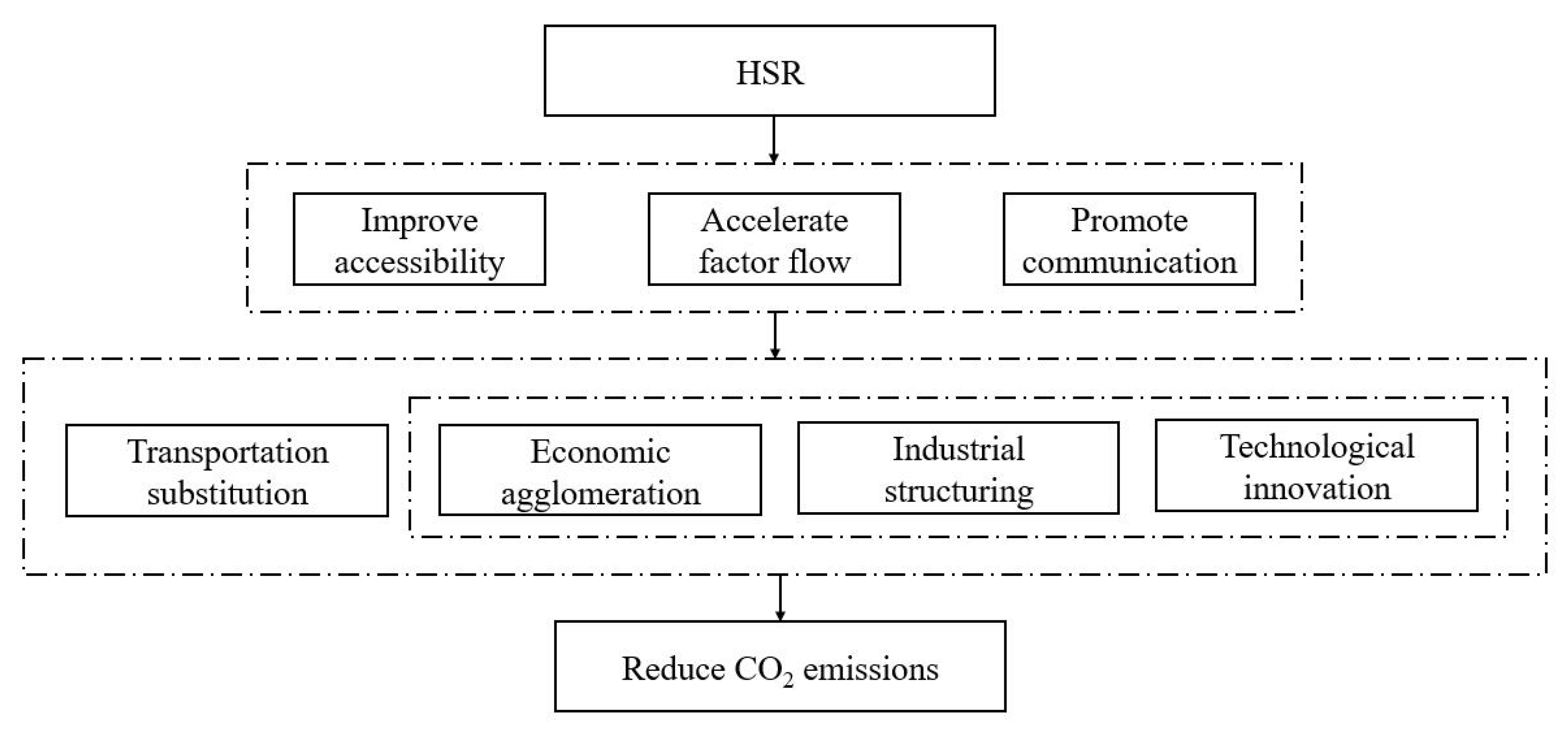
3. Theoretical Analysis
3.1. Transportation Substitution
3.2. Economic Agglomeration
3.3. Industrial Structuring
3.4. Technological Innovation
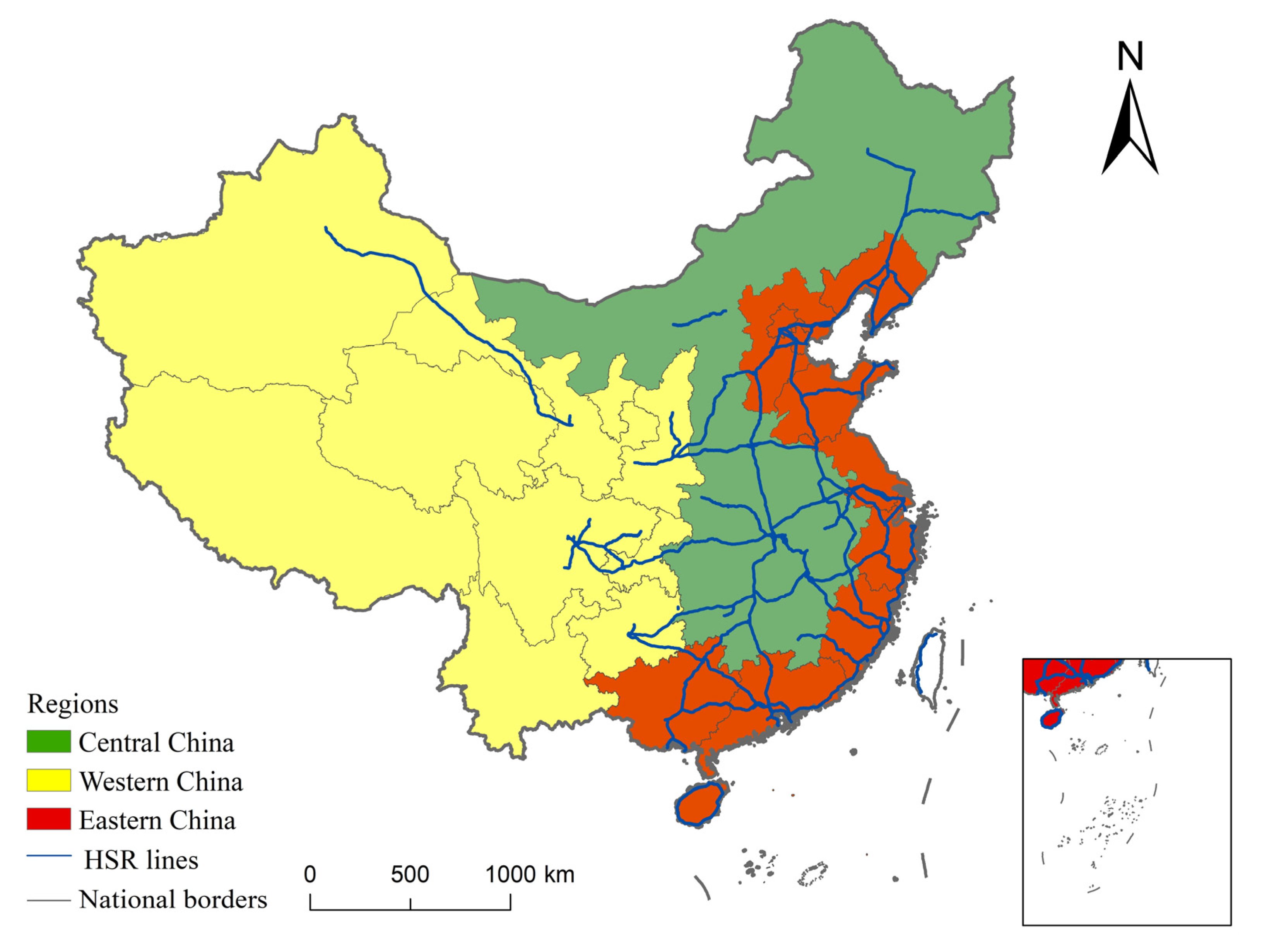
4. Data and Model
4.1. Data and Sample
4.2. Variable Selection
4.2.1. Dependent Variable
4.2.2. Key Independent Variable
4.2.3. Mediation Variables
4.2.4. Control Variables
4.3. Empirical Model
5. Empirical Analysis
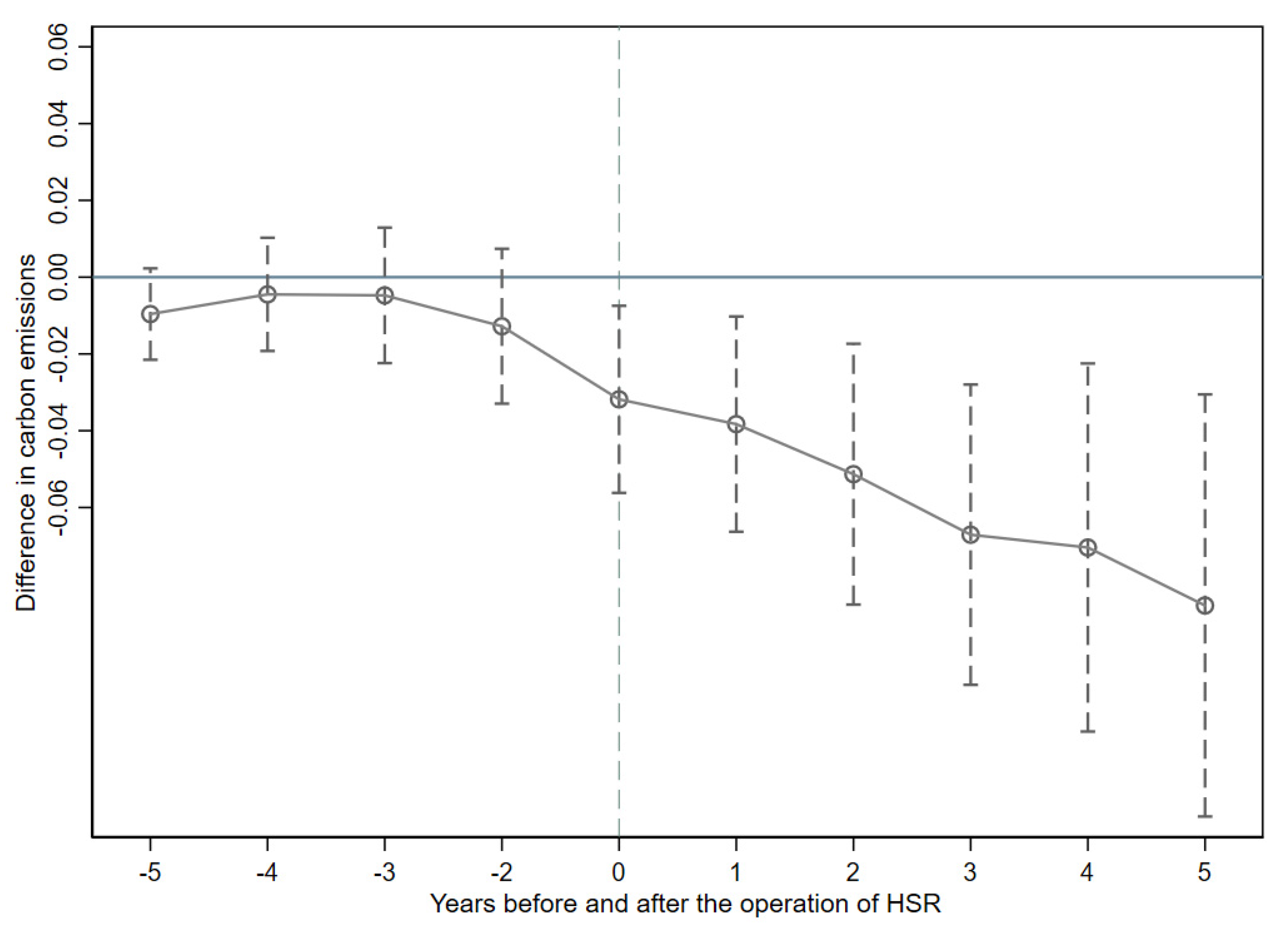
5.1. Parallel Trend Test
5.2. Benchmark Regression
5.3. Robustness Test
5.3.1. PSM-DID Method
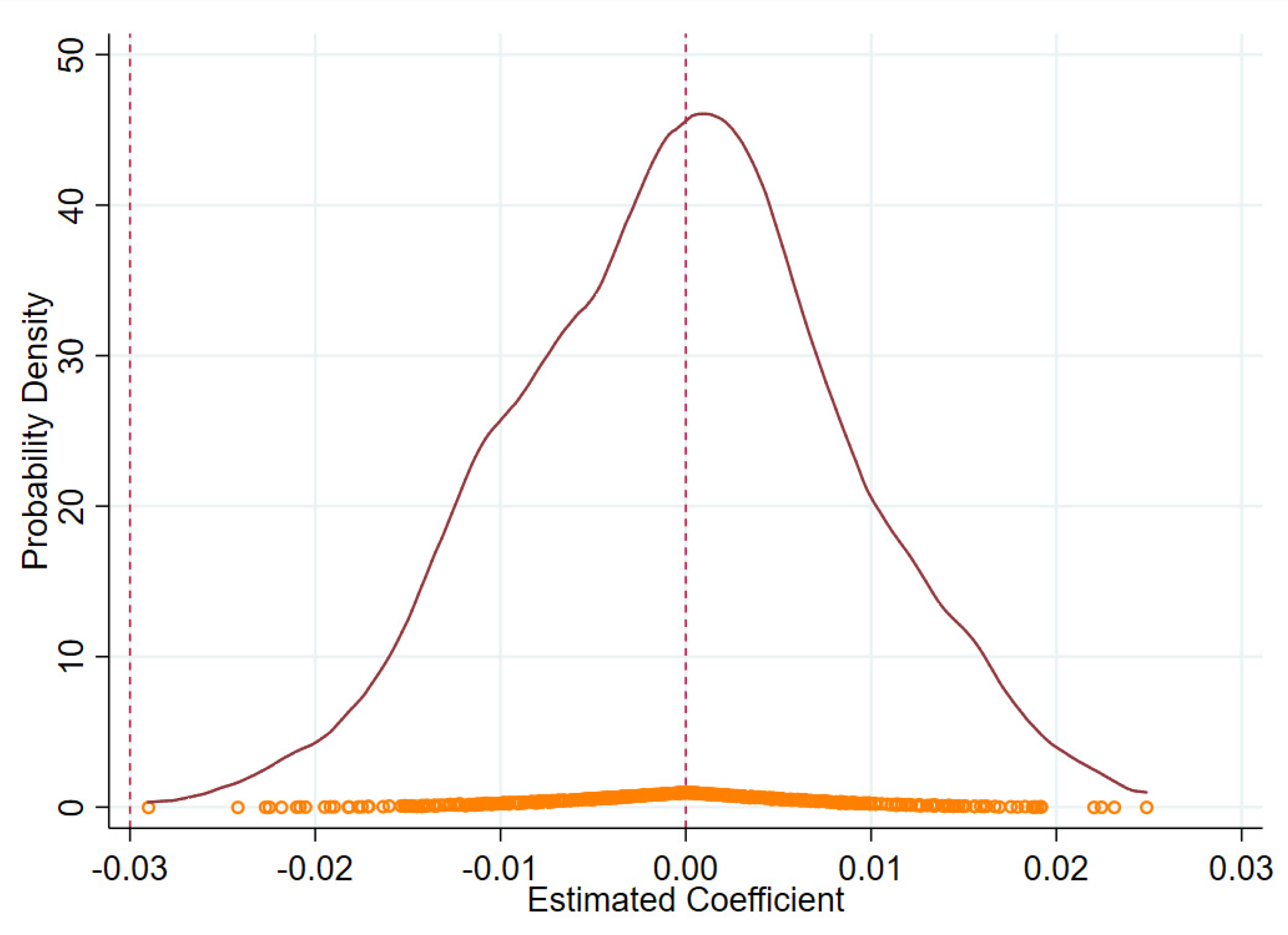
5.3.2. Placebo Test
5.4. Endogeneity Test
5.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
5.5.1. Regional Heterogeneity
5.5.2. Scale Heterogeneity
6. Mediation Analysis
6.1. Mediation Model
6.2. Bootstrap Method
7. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mora, C.; Spirandelli, D.; Franklin, E.C.; Lynham, J.; Kantar, M.B.; Miles, W.; Smith, C.Z.; Freel, K.; Moy, J.; Louis, L.V.; et al. Broad Threat to Humanity from Cumulative Climate Hazards Intensified by Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Li, J. Towards a Green World: How Do Green Technology Innovations Affect Total-Factor Carbon Productivity. Energy Policy 2019, 131, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Lin, B. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions during Urbanization: A Comparative Study between China and Japan. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Baležentis, T.; Tian, Z.; Shao, S.; Geng, Y.; Wu, R. Environmental Performance and Regulation Effect of China’s Atmospheric Pollutant Emissions: Evidence from “Three Regions and Ten Urban Agglomerations”. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2019, 74, 211–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, L.; Wang, Q. The Impact of Energy Efficiency on Carbon Emissions: Evidence from the Transportation Sector in Chinese 30 Provinces. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohring, H. Optimization and Scale Economies in Urban Bus Transportation. Am. Econ. Rev. 1972, 62, 591–604. [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, J.; Li, H.; Cui, J. High-Speed Rail’s Impact on Airline Demand and Air Carbon Emissions in China. Transp. Policy 2021, 109, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Xie, R.; Lu, Y.; Fang, J.; Liu, Y. The Effects of Urban Agglomeration Economies on Carbon Emissions: Evidence from Chinese Cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1096–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Tian, Z.; Yang, L. High Speed Rail and Urban Service Industry Agglomeration: Evidence from China’s Yangtze River Delta Region. J. Transp. Geogr. 2017, 64, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, A. High-Speed Rail and Industrial Developments: Evidence from House Prices and City-Level GDP in China. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2021, 149, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, A. Technology, International Trade, and Pollution from US Manufacturing. Am. Econ. Rev. 2009, 99, 2177–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Strauss, J.; Liu, L. A Panel Investigation of High-Speed Rail (HSR) and Urban Transport on China’s Carbon Footprint. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Xue, X.; Wang, Y. Spillover Effects of Railway and Road on CO2 Emission in China: A Spatiotemporal Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Z. Technology Advance and the Carbon Dioxide Emission in China—Empirical Research Based on the Rebound Effect. Energy Policy 2017, 101, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, S. Do the Coupling Effects of Environmental Regulation and R & D Subsidies Work in the Development of Green Innovation? Empirical Evidence from China. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, T.; Gao, J. The Effect of Emission Trading Policy on Carbon Emission Reduction: Evidence from an Integrated Study of Pilot Regions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Deng, J.; Ding, B. Correction to: Characteristics, Decoupling Effect, and Driving Factors of Regional Tourism’s Carbon Emissions in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 47094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westin, J.; Kågeson, P. Can High Speed Rail Offset Its Embedded Emissions? Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2012, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkic, G.; Balaban, O.; Tuydes-Yaman, H.; Celikkol-Kocak, T. An Assessment of the CO2 Emissions Reduction in High Speed Rail Lines: Two Case Studies from Turkey. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 746–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, T.; Rosa, E.A. Effects of Population and Affluence on CO2 Emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, R.; Zhan, L. Is Decoupling Economic Growth from Fuel Consumption Possible in Developing Countries?—A Comparison of China and India. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wee, B.; van den Brink, R.; Nijland, H. Environmental Impacts of High-Speed Rail Links in Cost–Benefit Analyses: A Case Study of the Dutch Zuider Zee Line. Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2003, 8, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirao, B.; Campa, J.L.; Casado-Sanz, N. Labour Mobility between Cities and Metropolitan Integration: The Role of High Speed Rail Commuting in Spain. Cities 2018, 78, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhu, G.; Ai, B.; Zhong, Z. A Survey on High-Speed Railway Communications: A Radio Resource Management Perspective. Comput. Commun. 2016, 86, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xin, Q. Transportation Infrastructure and Resource Allocation of Capital Market: Evidence from High-Speed Rail Opening and Company Going Public. China J. Account. Stud. 2020, 8, 272–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, J.; He, M. Does High-Speed Rail Promote Enterprises Productivity? Evidence from China. J. Adv. Transp. 2019, 2019, 1279489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, H. Can High-Speed Rail Improve Enterprise Capacity Utilization? A Perspective of Supply Side and Demand Side. Transp. Policy 2022, 115, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbués, P.; Baños, J.F.; Mayor, M. The Spatial Productivity of Transportation Infrastructure. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2015, 75, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Shao, S.; Yang, L. High-Speed Rail and CO2 Emissions in Urban China: A Spatial Difference-in-Differences Approach. Energy Econ. 2021, 99, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Jia, H. Does the Development of China’s High-Speed Rail Improve the Total-Factor Carbon Productivity of Cities? Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2022, 105, 103230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Gan, M.; Li, X.; Liu, X. Strategic Plan for China’s Air High-Speed Rail Express Freight Network and Its Carbon Reduction Potential. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 29110–29124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Dai, C.; Wei, Y. Does the Opening of High-Speed Railway Improve Air Quality? Evidence from China. Socioecon. Plann. Sci. 2022, 84, 101381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Graham, D.J.; Wong, M.S.C. Quantifying the Substitutability and Complementarity between High-Speed Rail and Air Transport. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2018, 118, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalate, D.; Bel, G.; Fageda, X. Competition and Cooperation between High-Speed Rail and Air Transportation Services in Europe. J. Transp. Geogr. 2015, 42, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, M. Impact of High-Speed Rail on Road Traffic and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, M.; Horvath, A. High-Speed Rail with Emerging Automobiles and Aircraft Can Reduce Environmental Impacts in California’s Future. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 034012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlfeldt, G.M.; Feddersen, A. From Periphery to Core: Measuring Agglomeration Effects Using High-Speed Rail. J. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 18, 355–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Kahn, M.E. China’s Bullet Trains Facilitate Market Integration and Mitigate the Cost of Megacity Growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1248–E1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.B.; Moxnes, A.; Ulltveit-Moe, K.H. Two-Sided Heterogeneity and Trade. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2018, 100, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, W.; Ma, D.; Zhang, C. Carbon Emissions and Optimal Scale of China’s Manufacturing Agglomeration under Heterogeneous Environmental Regulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhou, C.; Qin, C. No Difference in Effect of High-Speed Rail on Regional Economic Growth Based on Match Effect Perspective? Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2017, 106, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, X.; Derudder, B.; Zhong, Y.; Shen, W. Mapping Producer Services Networks in Mainland Chinese Cities. Urban Stud. 2015, 52, 3018–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y. High-speed Rails and City Economic Growth in China. J. Financ. Res. 2017, 449, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunmei, L.; Maosheng, D.; Xiliang, Z.; Jieting, Z.; Lingling, Z.; Guangping, H. Empirical Research on the Contributions of Industrial Restructuring to Low-Carbon Development. Energy Procedia 2011, 5, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiaoqing, Z.; Jianlan, R. The Relationship between Carbon Dioxide Emissions and Industrial Structure Adjustment for Shandong Province. Energy Procedia 2011, 5, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xiang, Q. Adjustment of Industrial Structure and the Potential Assessment of Energy Saving and Carbon Reduction. China Ind. Econ. 2014, 310, 44–56. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, P.; Kogut, B. Localization of Knowledge and the Mobility of Engineers in Regional Networks. Manag. Sci. 1999, 45, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Yin, S. Is Technological Innovation Effective for Energy Saving and Carbon Emissions Reduction? Evidence From China. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 83524–83537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, X. Collaborative Evolution of Regional Green Innovation System under the Influence of High-Speed Rail Based on Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 69101–69116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Meng, L.; Xing, L. Energy Technological Innovation and Carbon Emissions Mitigation: Evidence from China. Kybernetes 2022, 51, 982–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Luan, X.; Song, Y. The Impact of High-Tech Industry Agglomeration on Green Economy Efficiency—Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, P.-P.; Duranton, G.; Gobillon, L. Spatial Wage Disparities: Sorting Matters! J. Urban Econ. 2008, 63, 723–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Sun, W.; Yao, S.; Zheng, S. Does High-Speed Railway Reduce Air Pollution along Highways?—Evidence from China. Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2020, 89, 102607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, W. Has the Opening of High-Speed Rail Reduced Urban Carbon Emissions? Empirical Analysis Based on Panel Data of Cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, B. Trade Integration, Market Size, and Industrialization: Evidence from China’s National Trunk Highway System. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2014, 81, 1046–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.; Kenny, D. The Moderator-Mediator Variable Distinction in Social Psychological Research: Conceptual, Strategic, and Statistical Considerations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Sresakoolchai, J.; Peng, J. Life Cycle Cost, Energy and Carbon Assessments of Beijing-Shanghai High-Speed Railway. Sustainability 2020, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Long, F.; Lu, P.; Ren, Y.; Chen, J. Life-Cycle Cost Model of High-Speed Railway Considering Carbon Emissions. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2023, 29, 05023006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Unit | Obs. | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE | megaton | 3962 | 2.874 | 0.807 | 0.425 | 4.71 |
| HSR | - | 3962 | 0.170 | 0.376 | 0.000 | 1.00 |
| TS | 104 person | 3962 | 10.369 | 2.842 | 0.020 | 19.50 |
| EA | 104 person/km2 | 3962 | 0.767 | 1.222 | 0.020 | 16.17 |
| IS | - | 3962 | 0.833 | 0.414 | 0.090 | 4.17 |
| TI | - | 3962 | 5.096 | 15.92 | 0.000 | 114.78 |
| PG | 104 yuan/person | 3962 | 2.290 | 1.826 | 0.010 | 9.87 |
| PD | 104 person/km2 | 3962 | 0.423 | 0.324 | 0.005 | 2.638 |
| SE | % | 3962 | 19.747 | 4.571 | 1.990 | 30.87 |
| ER | - | 3962 | 78.025 | 24.139 | 0.000 | 115.00 |
| IC | person/m2 | 3962 | 2.509 | 0.480 | −0.942 | 3.50 |
| FI | % | 3962 | 0.021 | 0.022 | 0.000 | 0.11 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSR | −0.0411 *** | −0.0452 *** | −0.0362 *** | −0.0408 *** | −0.0588 *** |
| (0.0056) | (0.0055) | (0.0055) | (0.0054) | (0.0217) | |
| PG | 0.0228 *** | 0.0244 *** | 0.0096 *** | ||
| (0.0048) | (0.0049) | (0.0020) | |||
| PG2 | −0.0017 *** | −0.0020 *** | −0.0002 *** | ||
| (0.0005) | (0.0005) | (0.0001) | |||
| PD | 0.3374 *** | 0.3730 *** | 0.2798 *** | ||
| (0.0492) | (0.0500) | (0.0446) | |||
| SE | −0.0018 *** | −0.0019 *** | −0.0018 *** | ||
| (0.0006) | (0.0006) | (0.0006) | |||
| ER | −0.0003 ** | −0.0003 *** | −0.0003 *** | ||
| (0.0001) | (0.0001) | (0.0001) | |||
| IC | −0.0050 | −0.0064 * | −0.0046 | ||
| (0.0039) | (0.0039) | (0.0035) | |||
| FI | −0.2863 ** | −0.4909 *** | 0.0003 *** | ||
| (0.1431) | (0.1398) | (0.0000) | |||
| Constant | 2.8807 *** | 0.9898 *** | 2.8799 *** | 0.7895 *** | 2.0082 *** |
| (0.0018) | (0.2814) | (0.0018) | (0.2867) | (0.2897) | |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Year FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 3962 | 3962 | 3881 | 3881 | 3962 |
| Adj-R2 | 0.9864 | 0.9867 | 0.9871 | 0.9876 | 0.9884 |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk Wald F statistic | 288.048 | ||||
| Variable | Unmatched | Mean | Bias | t-Test | p > |t| | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matched | Treated | Control | (%) | Value | ||
| PG | U | 2.5830 | 2.1076 | 27.6 | 5.89 | 0.000 |
| M | 2.5830 | 2.6035 | −1.2 | −0.17 | 0.868 | |
| PD | U | 6.0098 | 5.7064 | 39.4 | 7.56 | 0.000 |
| M | 6.0098 | 6.0129 | −0.4 | −0.07 | 0.947 | |
| SE | U | 20.2870 | 19.6830 | 13.9 | 2.70 | 0.007 |
| M | 20.2870 | 20.3070 | −0.4 | −0.07 | 0.946 | |
| ER | U | 85.0640 | 76.8880 | 35.7 | 6.96 | 0.000 |
| M | 85.0640 | 83.9610 | 4.8 | 0.83 | 0.409 | |
| IC | U | 2.4549 | 2.5113 | −12.0 | −1.85 | 0.016 |
| M | 2.4549 | 2.4373 | 3.7 | 0.51 | 0.573 | |
| FI | U | 0.0195 | 0.0209 | −7.4 | −0.46 | 0.183 |
| M | 0.0195 | 0.0193 | 0.8 | 0.18 | 0.893 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSR × East | −0.0636 *** | ||||
| (0.0073) | |||||
| HSR × Mid | −0.0067 | ||||
| (0.0065) | |||||
| HSR × West | −0.0047 | ||||
| (0.0142) | |||||
| HSR × Large | −0.0466 *** | ||||
| (0.0056) | |||||
| HSR × Small | −0.0028 | ||||
| (0.0184) | |||||
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 3962 | 3951 | 3951 | 3962 | 3962 |
| Adj-R2 | 0.9868 | 0.9865 | 0.9865 | 0.9867 | 0.9865 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE | TS | CE | EA | CE | IS | CE | TI | CE | |
| HSR | −0.0452 *** | −0.1367 ** | −0.0444 *** | 0.0400 ** | −0.0438 *** | 0.0234 ** | −0.0442 *** | 9.6932 *** | −0.0244 *** |
| (0.0055) | (0.0643) | (0.0055) | (0.0201) | (0.0055) | (0.0113) | (0.0055) | (0.6596) | (0.0053) | |
| TS | 0.0063 *** | ||||||||
| (0.0021) | |||||||||
| EA | −0.0353 *** | ||||||||
| (0.0057) | |||||||||
| IS | −0.0436 *** | ||||||||
| (0.0115) | |||||||||
| TI | −0.0022 *** | ||||||||
| (0.0002) | |||||||||
| Control | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| City FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time FE | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 3962 | 3962 | 3962 | 3962 | 3962 | 3962 | 3962 | 3962 | 3962 |
| Adj-R2 | 0.9867 | 0.8767 | 0.9868 | 0.9196 | 0.9870 | 0.8244 | 0.9868 | 0.6747 | 0.9873 |
| Variable | Indirect | Effect | Z Value | p > |Z| | Normal-Based [95% Conf. Interval] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct | Lower | Upper | ||||
| TS | I | 0.1400 | 1.97 | 0.049 | 0.0005 | 0.2795 |
| D | 14.4993 | 14.30 | 0.000 | 12.5124 | 16.4862 | |
| EA | I | 0.0933 | 8.65 | 0.000 | 0.7218 | 0.1145 |
| D | 0.4686 | 16.41 | 0.000 | 0.4127 | 0.5246 | |
| IS | I | 0.0141 | 2.79 | 0.005 | 0.0042 | 0.0240 |
| D | 0.5584 | 19.04 | 0.000 | 0.5001 | 0.6159 | |
| TI | I | 0.2843 | 16.12 | 0.000 | 0.2497 | 0.3189 |
| D | 0.2776 | 9.25 | 0.000 | 0.2188 | 0.3364 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.Y.; Yip, T.L. Exploring the Carbon-Mitigation Effect of High-Speed Railway and Its Underlying Mechanism. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12725. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712725
Gao Y, Zhang Y, Wang KY, Yip TL. Exploring the Carbon-Mitigation Effect of High-Speed Railway and Its Underlying Mechanism. Sustainability. 2023; 15(17):12725. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712725
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yake, Yawei Zhang, Kelly Yujie Wang, and Tsz Leung Yip. 2023. "Exploring the Carbon-Mitigation Effect of High-Speed Railway and Its Underlying Mechanism" Sustainability 15, no. 17: 12725. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712725
APA StyleGao, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, K. Y., & Yip, T. L. (2023). Exploring the Carbon-Mitigation Effect of High-Speed Railway and Its Underlying Mechanism. Sustainability, 15(17), 12725. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712725







