The Impact of Housing Prices on Regional Innovation Capacity: Evidence from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
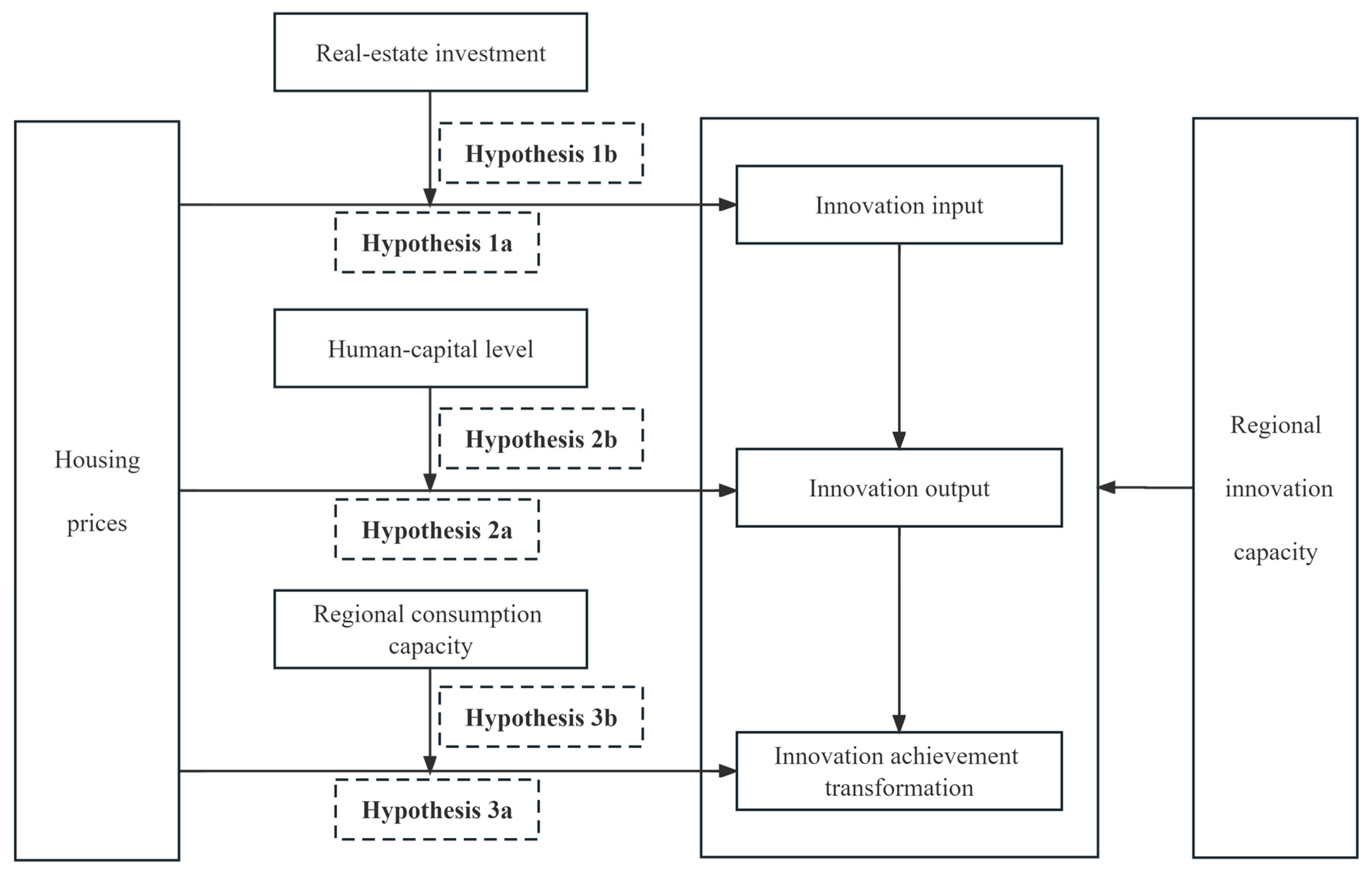
3. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypotheses
3.1. Innovation Input Stage
3.2. Innovation Output Stage
3.3. Innovation Achievement Transformation Stage
4. Research Design
4.1. Econometrics Model
4.2. Variable Description
4.3. Data Description
5. Econometrics Analysis and Discussion of Results
5.1. Benchmark Regression Results
5.2. Mechanism Testing
5.3. Heterogeneity Analysis
5.4. Robustness and Endogeneity Analysis
6. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
6.1. Research Findings
6.2. Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y. Investigation on technological innovation ability of enterprises of different ownership systems. Ind. Econ. Res. 2014, 69, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ding, W.; Zhao, X. Research on the relationship between relationship strength, absorptive capacity and innovation performance in enterprise innovation network. Nankai Bus. Rev. 2016, 19, 30–42. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Lin, G. Government Support, R&D Management and Technological Innovation Efficiency: An Empirical Analysis Based on China’s Industrial Industry. Manag. World 2014, 4, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Chen, Q.; Chen, H. Environmental regulation, technological innovation and business performance: An empirical analysis based on 37 industrial sectors. Res. Manag. 2017, 38, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Wu, G.; Lv, X. The Determinants of Regional Innovation Capability—Comment on the Regional Gap of Innovation Capability in China. China Soft Sci. Mag. 2010, 9, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Jiang, F. Collaborative Innovation, Spatial Correlation and Regional Innovation Performance. Econ. Res. J. 2015, 50, 174–187. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Tan, J.; Cai, X. The Impact of Housing Boom on Total Factor Productivity at Industrial Level: Micro Evidence from Chinese Industrial Enterprises Survey Data. Econ. Rev. 2017, 6, 22–37+121. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C. Dose Housing Price Impede Regional Innovation?-A Spatial Econometric Study of 285 Prefecture-level Cities in China. Mod. Financ. Econ. -J. Tianjin Univ. Financ. Econ. 2018, 38, 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Tan, J. House prices, liquidity effect and financial constraint. Ind. Econ. Res. 2015, 4, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lian, Y.; Zheng, J. Rising House Prices and Corporate Technology Innovation: Empirical Evidence from Chinese Listed Companies and Bond Companies. Acad. Res. 2017, 6, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Li, B. Study on the Effect of Urban Real Estate Value on Innovation Efficiency and Transmission Mechanisms. Soft Sci. 2020, 34, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Rong, Z. Housing Boom and Firm Innovation: Evidence from Industrial Firms in China. China Econ. Q. 2014, 13, 465–490. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, B. The Impact of Real Estate Investment on Enterprise Innovation in Industrial Enterprises: An Empirical Study Based on Data of Chinese Listed Companies. Res. Econ. Manag. 2014, 10, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Xin, F. Real Estate Hinders Innovation in China?—Based on the Explanation of Loan Term Structure in the Financial System. Manag. World 2016, 5, 64–80. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Cheng, X.; Gao, S. Does Real Estate Price Bubble Drive Out a Company’s R&D Activity?—The Evidence form GEM Company. Chin. Soft Sci. 2018, 12, 95–109. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, A.; Wang, T.; Wu, W. The Impact of Rising Housing Prices on Urban Innovation: Reevaluation Based on the Perspective of Industrial Structure Optimization. East China Econ. Manag. 2021, 35, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, H. The Influence Mechanism and Policy Optimization of Real Estate Market Development on Scientific and Technological Innovation. Chongqing Soc. Sci. 2019, 12, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, J.; Wang, P. Sectoral Bubbles, Misallocation, and Endogenous Growth. J. Math. Econ. 2014, 53, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, S. Urban Housing Prices, Purchase Restriction Policy and Technological Innovation. China Ind. Econ. 2017, 6, 98–116. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Shi, D. High Housing Prices and Enterprise Innovation: Crowding in or Crowding out? -Measurement and Calculation Based on Bilateral Stochastic Frontier Model. China Soft Sci. 2019, 9, 150–165. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.T.; Birkinshaw, J. The innovation value chain. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2007, 85, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Ganotakis, P.; Love, J.H. The innovation value chain in new technology-based firms: Evidence from the UK. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2012, 29, 839–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongze, Y.; Liu, D. The Effect of the Space Outflow of China’s Regional Innovation and the Effect of the Outflow of Value Chanins:A Study, from the Perspective of the Innovative Value Chain, on the Model of the Panel of Multidimentsional Space. Manag. World 2013, 7, 6–20+70+187. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Liu, D.; Liang, T. Research on the Effect of Innovation Input of China’s Large Enterprises on Regional Industrial Evolution. Sci. Sci. Manag. S T 2016, 37, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yang, S. Fiscal Decentralization, Government Innovation Preferences and Regional Innovation Efficiency. Manag. World 2018, 34, 29–42+110+193–194. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, B.H. The financing of research and development. Oxf. Rev. Econ. Policy 2002, 18, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, R.E.; Petersen, B.C. Capital Market Imperfections, High-Tech Investment, and New Equity Financing. Econ. J. 2002, 112, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, R.K. New product introductions and failures under uncertainty. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2006, 23, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Distorted Investment under Chinese Style Decentralization. Econ. Res. J. 2017, 52, 137–152. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C. The fundamental institutions of China’s reforms and development. J. Econ. Lit. 2011, 49, 1076–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S. The cost effect and investment effect of real estate price on the technological innovation output of company: An empirical analysis of A-share listed companies. J. Chongqing Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 26, 34–49. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Huang, S.; Ouyang, D. Can rising real estate prices drive economic growth? China Econ. Q. 2018, 17, 1079–1102. [Google Scholar]
- An, T.; Fang, Y.; Ludovik, A. Chinese Manufacturing Firms: Barriers to Technological Innovation and Countermeasures. Econ. Theory Bus. Manag. 2005, 07, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sjaastad, L.A. The costs and returns of human migration. J. Political Econ. 1962, 70, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.Y.; Cocco, J.F. How do house prices affect consumption? Evidence from micro data. J. Monet. Econ. 2007, 54, 591–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Y. Rising house prices, multi-home decisions and the savings rate of Chinese urban residents. Econ. Res. J. 2015, 50, 100–113. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Qian, Z.; Guo, J. Does Real Estate Drive China’s Economic Cycle? Econ. Res. J. 2015, 50, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, T.; Huang, Y. Demand-Induced Innovation: Evidence from the Chinese Household Appliance Industry. Bus. Manag. J. 2021, 43, 25–43. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, C.K.Y.; Tse, C.Y. Flipping in the housing market. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2017, 76, 232–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beracha, E.; He, Z.; Wintoki, M.B.; Xi, Y. On the relation between innovation and housing prices—A metro level analysis of the US market. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2022, 65, 622–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.C.Y.; Leung, C.K.Y.; Chen, S. Corporate real estate holding and stock returns: Testing alternative theories with international listed firms. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2022, forthcoming. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, T.; Chen, D.; Hu, L. On the Housing Price, Population Size and Urban Innovation Capacity in Yangtze River Delta Region. J. Tongji Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 32, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Jiang, X. How Does the Rise of House Prices Affect the Ability of Urban Innovation and Development?—An Empirical Analysis based on the Data of 283 Prefecture-level Cities in China. World Econ. Pap. 2021, 05, 86–102. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D. Land Resource Misallocation and City Innovation Capacity: Based on Chinese City-level Panel Data Analysis. China J. Econ. 2020, 7, 86–112. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z. The Anti-driving Effect of Land Supply Restriction on Enterprise Innovation: Evidence Based on Micro-data. J. Lanzhou Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2021, 49, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S.; Tan, L.; Yang, H. Yangtze River Delta Integration, Regional Housing Price Difference and Industrial Agglomeration—Empirical Analysis Based on the Panel of Prefecture Level Cities in Yangtze River Delta. Inq. Into Econ. Issues 2021, 12, 46–61. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Xue, C.; Feng, Y.; Hu, L. Fiscal Decentralization, Local Government Debt and Regional Innovation. Stat. Decis. 2022, 38, 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y. Government Preferences, Fiscal Decentralization, and Regional Digital Innovation. Stat. Decis. 2022, 38, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg, M.; Eklöf, M.; Fredriksson, P.; Jofre-Monseny, J. Estimating preferences for local public services using migration data. Urban Stud. 2012, 49, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; He, J.; Ma, R. How housing prices affect labor migration? Econ. Res. J. 2017, 52, 155–170. [Google Scholar]
| Innovation Stage | Variable Type | Variable Name | Obs | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent variable | lnhp | 480 | 8.46 | 0.61 | 7.36 | 10.33 | |
| Innovation input stage | Dependent variable | lnrdf | 480 | 14.12 | 1.50 | 10.32 | 17.04 |
| Controlled variables | lnpergdp | 480 | 10.40 | 0.68 | 8.92 | 11.91 | |
| fin | 480 | 2.90 | 1.11 | 1.29 | 8.13 | ||
| lnrevp | 480 | 0.34 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 1.36 | ||
| lnrdp | 480 | 10.87 | 1.20 | 7.82 | 13.28 | ||
| lntetra | 480 | 4.03 | 1.73 | 0.50 | 8.15 | ||
| Mechanism variable | lnreinv | 480 | 7.14 | 1.18 | 4.04 | 9.39 | |
| Innovation output stage | Dependent variable | lnperinpapp | 480 | 1.20 | 0.90 | 0.10 | 4.10 |
| Controlled variables | lnpergdp | 480 | 10.40 | 0.68 | 8.92 | 11.91 | |
| lnpersci | 480 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.18 | ||
| lnstud | 480 | 4.09 | 0.81 | 1.65 | 5.37 | ||
| urate | 480 | 0.54 | 0.14 | 0.25 | 0.94 | ||
| Mechanism variable | lnperrdp | 480 | 2.78 | 0.79 | 1.10 | 4.97 | |
| Innovation achievement transformation stage | Dependent variable | lnnewincp | 480 | 6.43 | 0.64 | 4.42 | 9.58 |
| Controlled variables | lnpergdp | 480 | 10.40 | 0.68 | 8.92 | 11.91 | |
| lnstud | 480 | 4.09 | 0.81 | 1.65 | 5.37 | ||
| industr | 480 | 0.89 | 0.06 | 0.70 | 1.00 | ||
| lnperroad | 480 | 3.36 | 2.19 | 0.51 | 14.20 | ||
| unem | 480 | 3.48 | 0.67 | 1.37 | 4.60 | ||
| Mechanism variable | consui | 480 | 0.37 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.51 | |
| (1) Innovation Input Stage | (2) Innovation Output Stage | (3) Innovation Achievement Transformation Stage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnhp | −0.21 *** (−3.20) | −0.48 *** (−4.26) | −0.91 *** (−4.18) |
| Observations | 480 | 480 | 480 |
| R-squared | 0.73 | 0.22 | 0.65 |
| Controlled variables | Y | Y | Y |
| Provincial fixed effect | Y | Y | Y |
| Year fixed effect | Y | Y | Y |
| (1) Innovation Input Stage | (2) Innovation Output Stage | (3) Innovation Achievement Transformation Stage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnhp | −0.21 *** (−3.21) | −0.36 *** (−3.78) | −0.79 *** (−3.59) |
| inter1 | −0.04 *** (−3.15) | ||
| inter2 | 0.34 *** (8.56) | ||
| inter3 | 3.91 *** (4.59) | ||
| Observations | 480 | 480 | 480 |
| R-squared | 0.74 | 0.39 | 0.67 |
| Controlled variables | Y | Y | Y |
| Provincial fixed effect | Y | Y | Y |
| Year fixed effect | Y | Y | Y |
| (1) Eastern Region Innovation Output Stage | (2) Eastern Region Innovation Achievement Transformation Stage | (3) Central Region Innovation Output Stage | (4) Western Region Innovation Input Stage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnhp | −0.79 *** (−4.53) | −0.83 *** (−2.94) | −0.97 *** (−3.76) | −0.25 ** (−2.51) |
| Observations | 176 | 176 | 128 | 176 |
| R-squared | 0.30 | 0.58 | 0.51 | 0.74 |
| Controlled variables | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Provincial fixed effect | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Year fixed effect | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| (1) Innovation Input Stage | (2) Innovation Output Stage | (3) Innovation Achievement Transformation Stage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnhp | −0.18 *** (−2.70) | −0.27 ** (−1.98) | −0.09 *** (−3.22) |
| Observations | 480 | 480 | 480 |
| R-squared | 0.70 | 0.30 | 0.57 |
| Controlled variables | Y | Y | Y |
| Provincial fixed effect | Y | Y | Y |
| Year fixed effect | Y | Y | Y |
| (1) Innovation Input Stage | (2) Innovation Output Stage | (3) Innovation Achievement Transformation Stage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| L.lnhp | −0.1669 *** (−2.59) | −0.4185 *** (−3.82) | −0.7795 *** (−3.51) |
| Observations | 450 | 450 | 450 |
| R-squared | 0.75 | 0.21 | 0.67 |
| Controlled variables | Y | Y | Y |
| Provincial fixed effect | Y | Y | Y |
| Year fixed effect | Y | Y | Y |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Lyu, P.; Jin, C. The Impact of Housing Prices on Regional Innovation Capacity: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11868. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511868
Li J, Lyu P, Jin C. The Impact of Housing Prices on Regional Innovation Capacity: Evidence from China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11868. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511868
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jianlong, Ping Lyu, and Chen Jin. 2023. "The Impact of Housing Prices on Regional Innovation Capacity: Evidence from China" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11868. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511868
APA StyleLi, J., Lyu, P., & Jin, C. (2023). The Impact of Housing Prices on Regional Innovation Capacity: Evidence from China. Sustainability, 15(15), 11868. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511868




