Endogeic Earthworms Avoid Soil Mimicking Metal Pollution Levels in Urban Parks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects and Housing
2.2. Artificial Soil Preparation
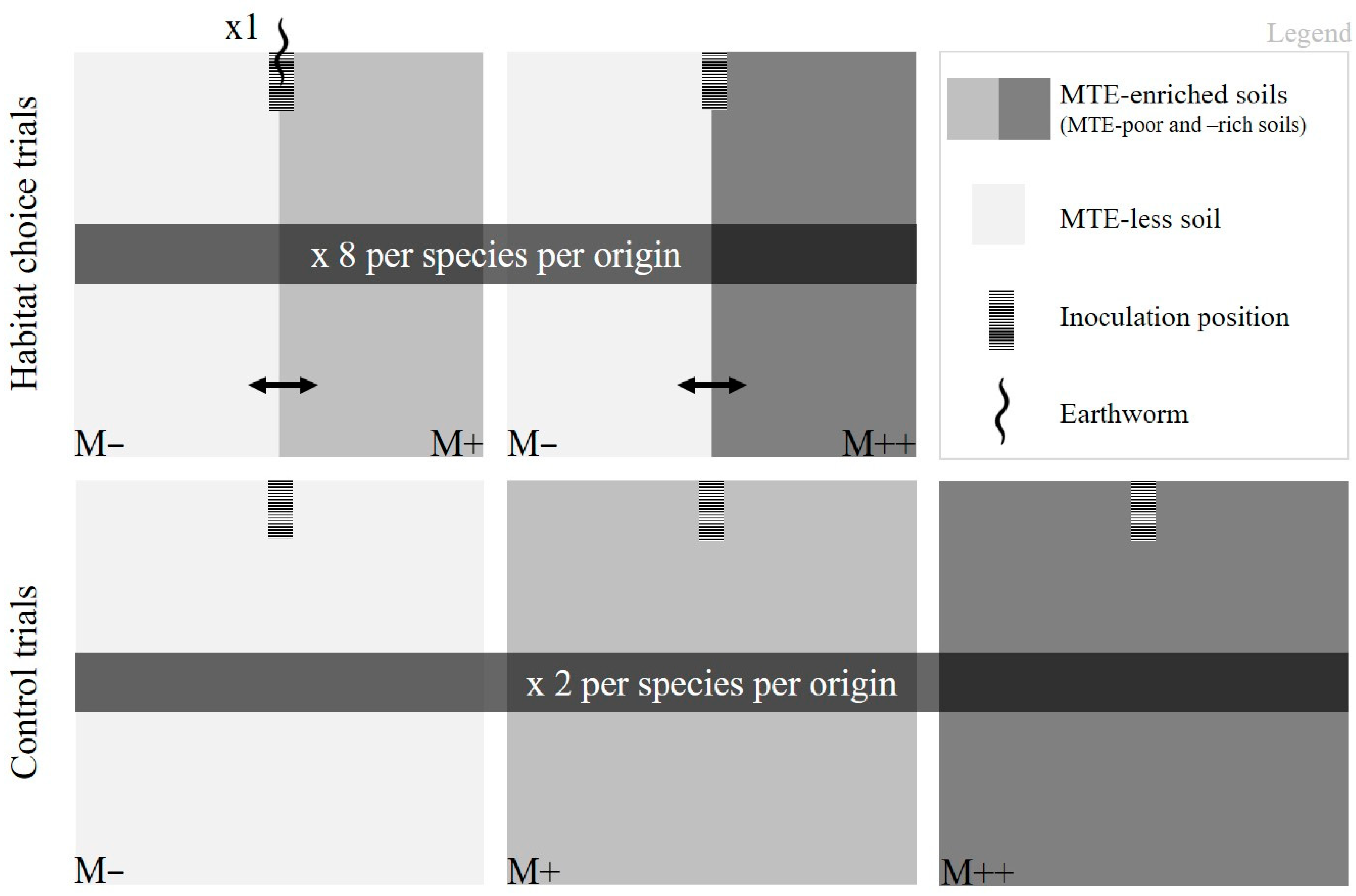
2.3. Terrarium Set-Up for Behavioral Trials
2.4. Trial Procedure: Movement and Body Mass Maintenance Measurements
2.5. Movement Analyses
2.6. MTE Analyses
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
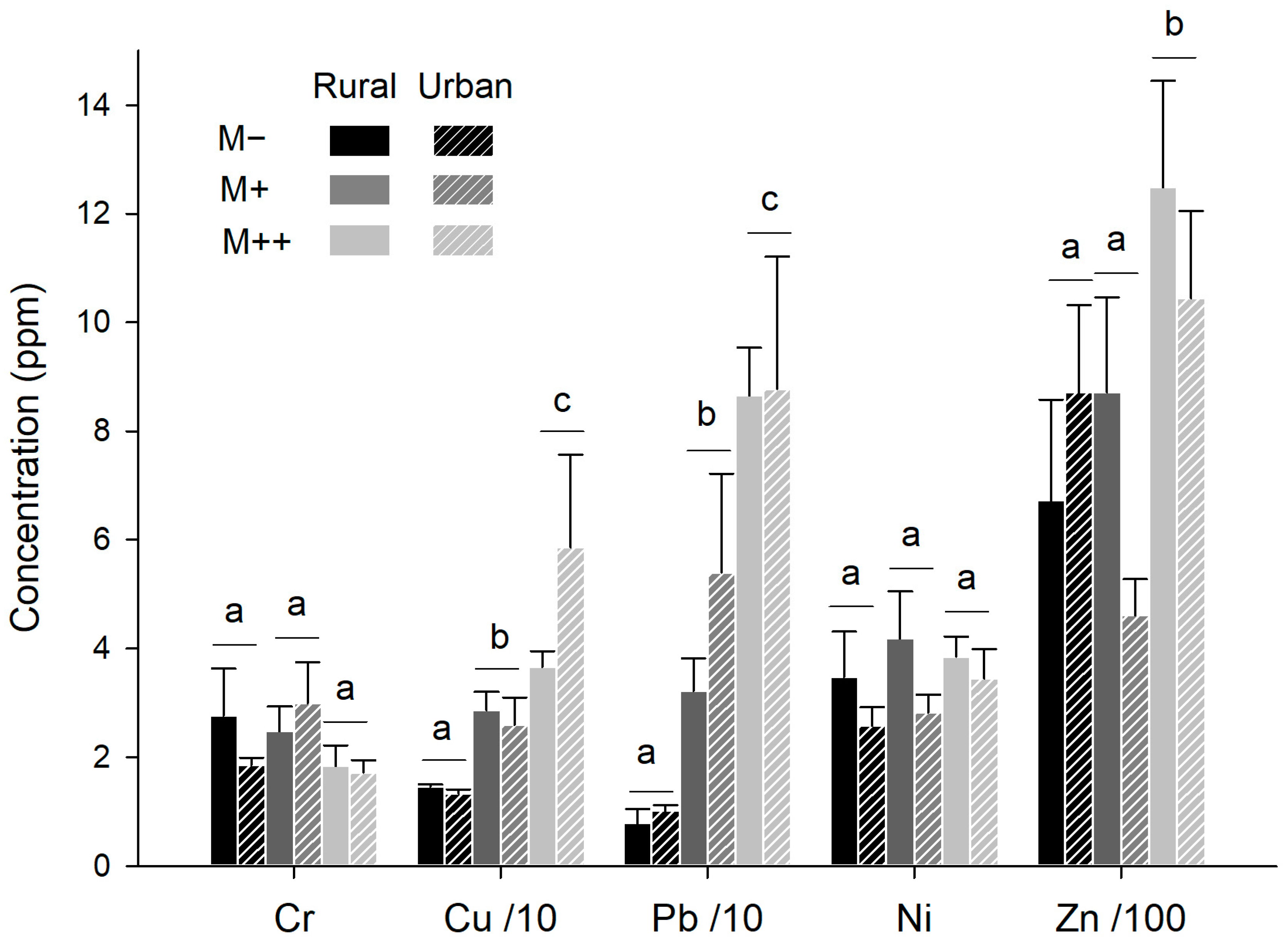
3.1. MTE Concentrations in Natural and Artificial Soils
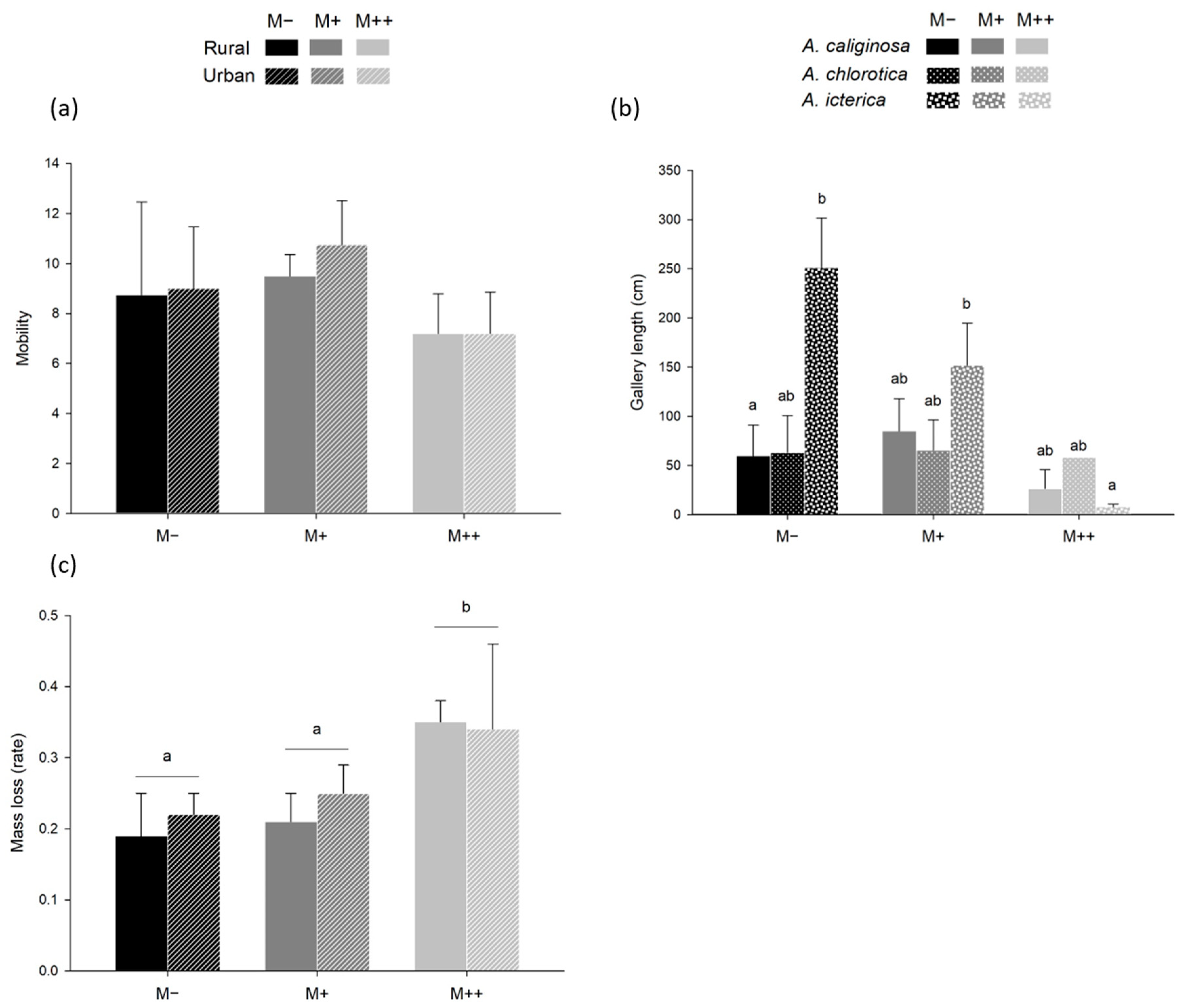
3.2. Space Occupation Homogeneity (Control Trials)
3.3. MTE-Induced Health Impairment (Control Trials)
3.4. MTE Accumulation in Earthworms (Control Trials)
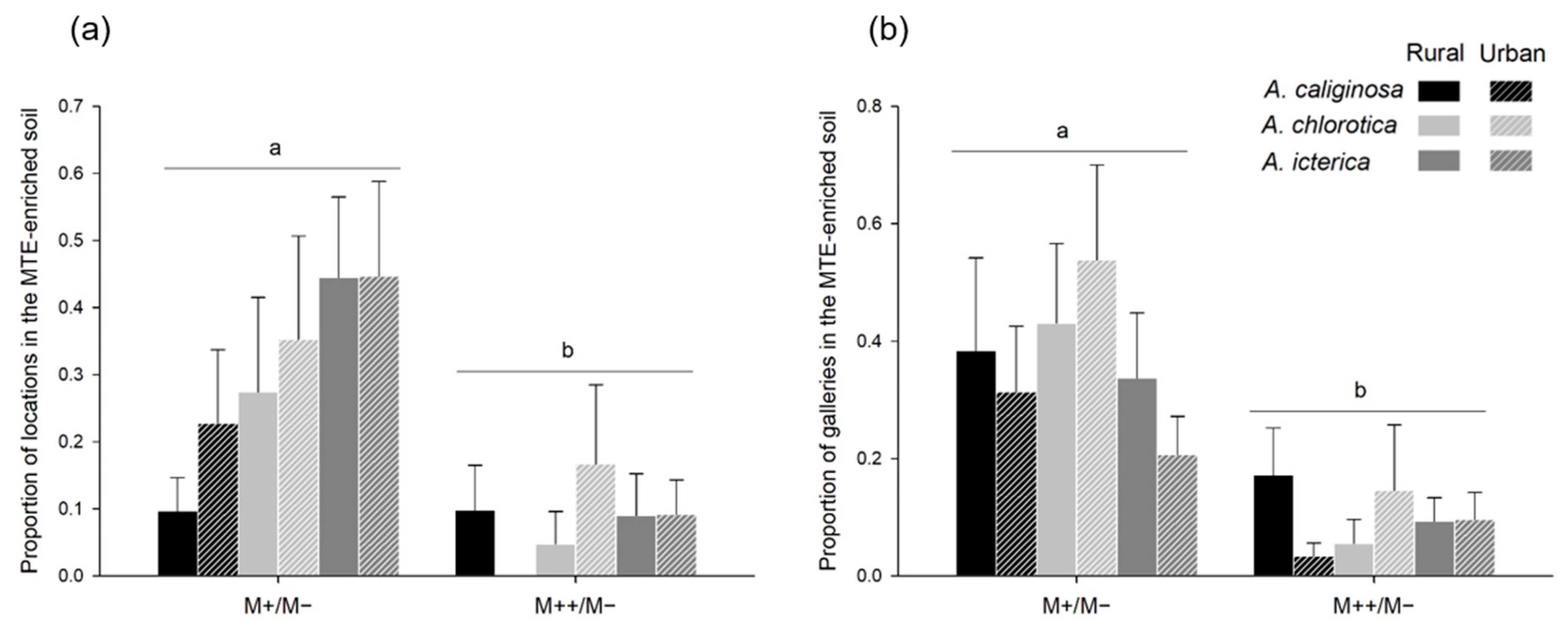
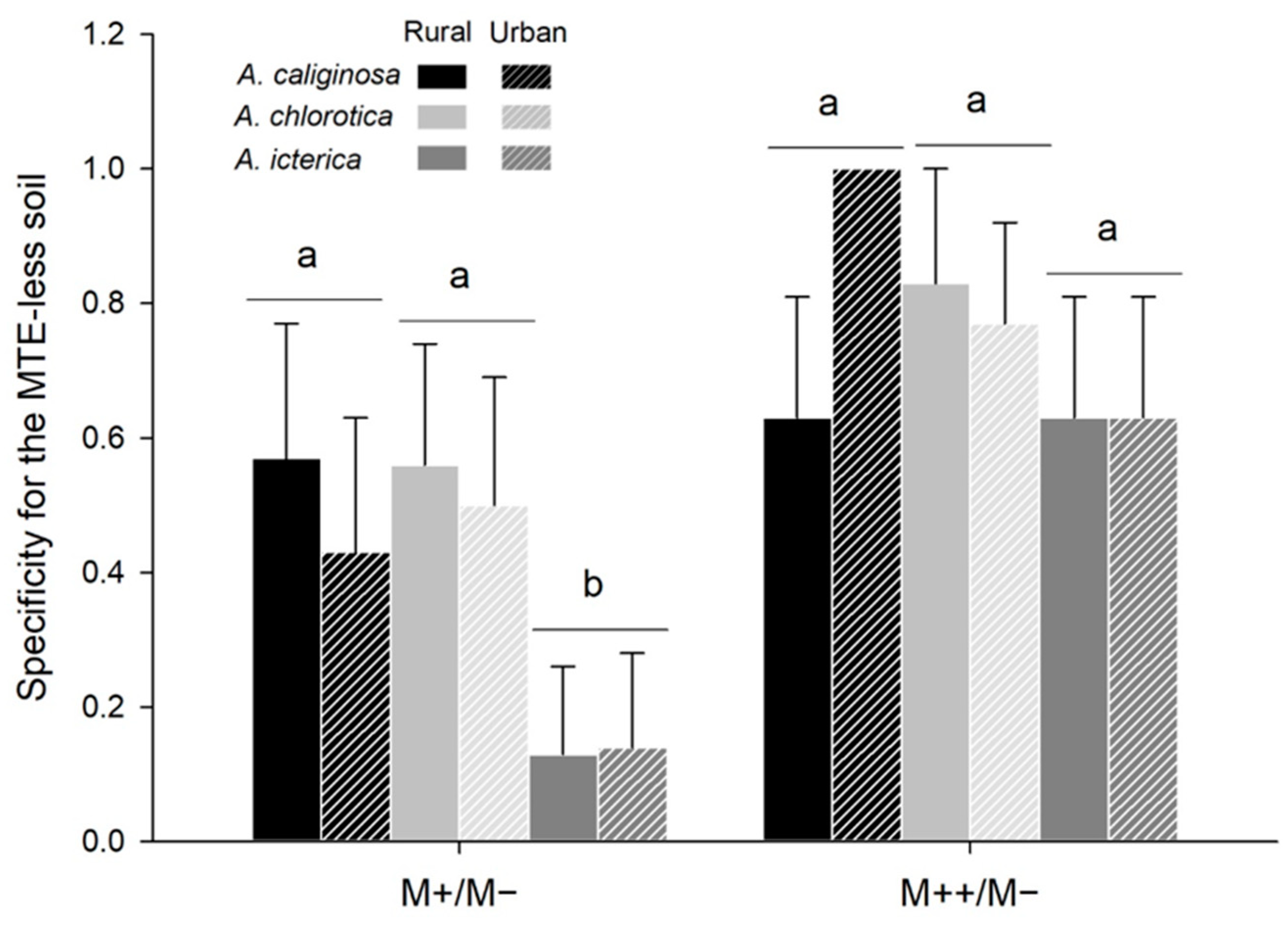
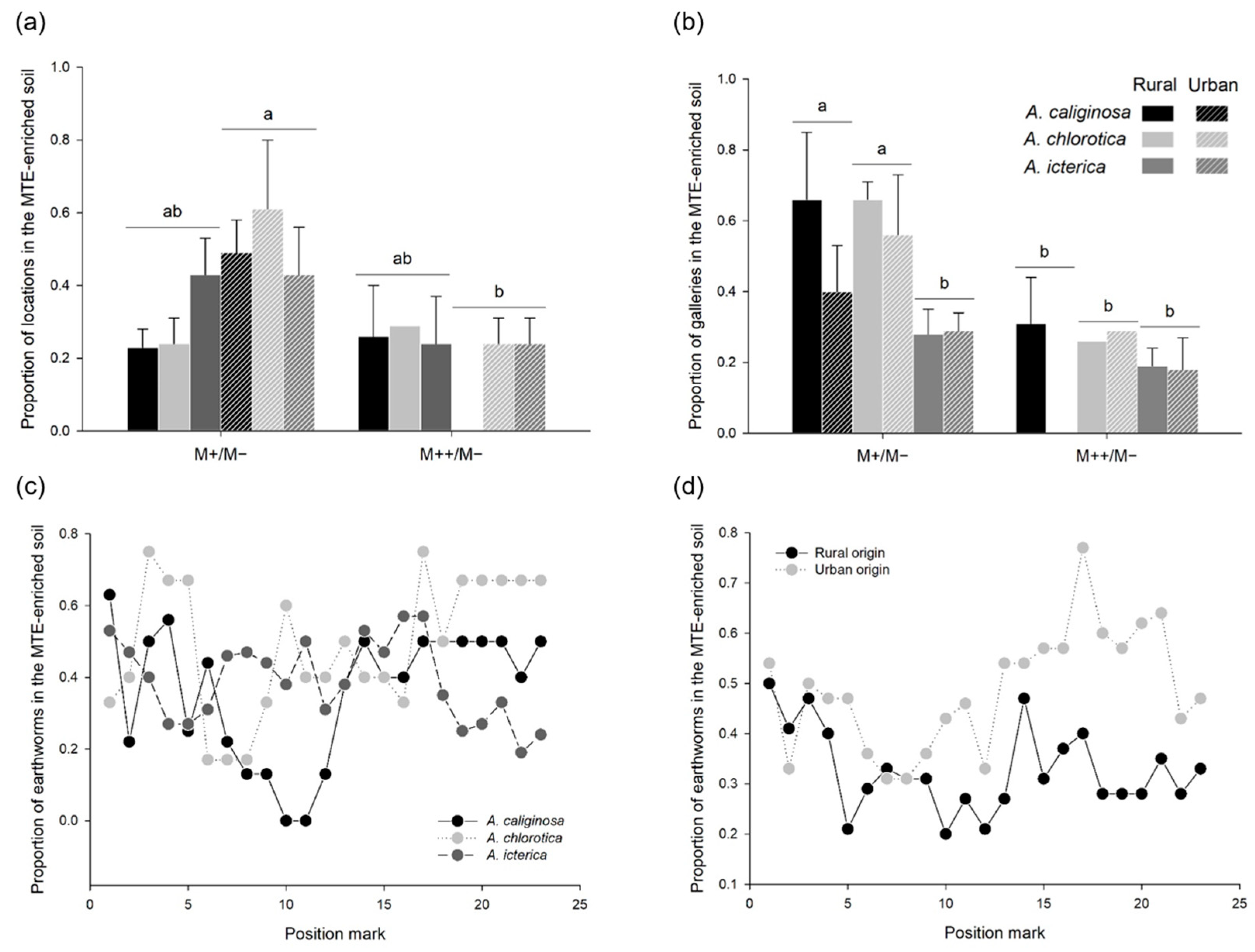
3.5. MTE-Linked Habitat Preference (Choice Trials)
4. Discussion
4.1. MTE Exposure Decreases Body Mass Maintenance
4.2. MTE Exposure Strongly Affects Habitat Preference
4.3. Response to MTE Exposure Only Slightly Differs between Species
4.4. Little Evidence of Evolutionary Divergence between Urban and Rural Populations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biasioli, M.; Barberis, R.; Ajmonemarsan, F. The Influence of a Large City on Some Soil Properties and Metals Content. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 356, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmone-Marsan, F.; Biasioli, M. Trace Elements in Soils of Urban Areas. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 213, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, K.E.; Marra, P.P. The Presence and Impact of Environmental Lead in Passerine Birds along an Urban to Rural Land Use Gradient. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 53, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.G.; Lawton, J.H.; Shachak, M. Organisms as Ecosystem Engineers. In Ecosystem Management; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 130–147. ISBN 978-0-387-94667-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.G.; Gutiérrez, J.L.; Byers, J.E.; Crooks, J.A.; Lambrinos, J.G.; Talley, T.S. A Framework for Understanding Physical Ecosystem Engineering by Organisms. Oikos 2010, 119, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, M.; Hodson, M.E.; Delgado, E.A.; Baker, G.; Brussaard, L.; Butt, K.R.; Dai, J.; Dendooven, L.; Peres, G.; Tondoh, J.E.; et al. A Review of Earthworm Impact on Soil Function and Ecosystem Services: Earthworm Impact on Ecosystem Services. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, G.; Tranvik, L. Critical Metal Concentrations for Forest Soil Invertebrates: A Review of the Limitations. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1989, 47, 381–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévêque, T.; Capowiez, Y.; Schreck, E.; Mombo, S.; Mazzia, C.; Foucault, Y.; Dumat, C. Effects of Historic Metal(Loid) Pollution on Earthworm Communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahmani, J.; Lavelle, P. Effects of Heavy Metal Pollution on Soil Macrofauna in a Grassland of Northern France. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2002, 38, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G.; Påhlsson, A.-M.B.; Bengtsson, G.; Bååth, E.; Tranvik, L. Heavy-Metal Ecology of Terrestrial Plants, Microorganisms and Invertebrates: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1989, 47, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Hopkin, S.P. Effects of Cadmium, Copper, Lead and Zinc on Growth, Reproduction and Survival of the Earthworm Eisenia Fetida (Savigny): Assessing the Environmental Impact of Point-Source Metal Contamination in Terrestrial Ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1994, 84, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Hopkin, S.P. Effects of Metal-Contaminated Soils on the Growth, Sexual Development, and Early Cocoon Production of the EarthwormEisenia Fetida, with Particular Reference to Zinc. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1996, 35, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhauser, E.F.; Loehr, R.C.; Milligan, D.L.; Malecki, M.R. Toxicity of Metals to the Earthworm Eisenia Fetida. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1985, 1, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gestel, C.A.M.; van Dis, W.A.; Dirven-van Breemen, E.M.; Sparenburg, P.M.; Baerselman, R. Influence of Cadmium, Copper, and Pentachlorophenol on Growth and Sexual Development of Eisenia Andrei (Oligochaeta; Annelida). Biol. Fertil. Soils 1991, 12, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gestel, C.A.M.; Dirven-Van Breemen, E.M.; Baerselman, R.; Emans, H.J.B.; Janssen, J.A.M.; Postuma, R.; Van Vliet, P.J.M. Comparison of Sublethal and Lethal Criteria for Nine Different Chemicals in Standardized Toxicity Tests Using the Earthworm Eisenia Andrei. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1992, 23, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lock, K.; Janssen, C.R. Effect of New Soil Metal Immobilizing Agents on Metal Toxicity to Terrestrial Invertebrates. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 121, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisessar, S. Effect of Heavy Metals on Microorganisms in Soils near a Secondary Lead Smelter. Water Air. Soil Pollut. 1982, 17, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, G.; Rundgren, S. Ground-Living Invertebrates in Metal-Polluted Forest Soils. Ambio 1984, 13, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Jones, O.A.H.; Dorne, J.-L.C.M.; Svendsen, C.; Swain, S.; Stürzenbaum, S.R. Systems Toxicology Approaches for Understanding the Joint Effects of Environmental Chemical Mixtures. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3725–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, M.L. Effects of Urbanization on Species Richness: A Review of Plants and Animals. Urban Ecosyst. 2008, 11, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupp, M.J.; Shrewsbury, P.M.; Herms, D.A. Ecology of Herbivorous Arthropods in Urban Landscapes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.W. Temporal Variation, Habitat Selection and Community Structure. Oikos 1990, 59, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, J.B.; Danielson, B.J.; Pulliam, H.R. Ecological Processes That Affect Populations in Complex Landscapes. Oikos 1992, 65, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogren, C.L.; Trumble, J.T. The Impacts of Metals and Metalloids on Insect Behavior. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2010, 135, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukkari, T.; Haimi, J. Avoidance of Cu- and Zn-Contaminated Soil by Three Ecologically Different Earthworm Species. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 62, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukkari, T.; Aatsinki, M.; Väisänen, A.; Haimi, J. Toxicity of Copper and Zinc Assessed with Three Different Earthworm Tests. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 30, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, C.J.; Piearce, T.G.; Meharg, A.A.; Semple, K.T. Survival and Behaviour of the Earthworms Lumbricus Rubellus and Dendrodrilus Rubidus from Arsenate-Contaminated and Non-Contaminated Sites. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonte, D.; Van Dyck, H.; Bullock, J.M.; Coulon, A.; Delgado, M.; Gibbs, M.; Lehouck, V.; Matthysen, E.; Mustin, K.; Saastamoinen, M.; et al. Costs of Dispersal. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 290–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global Change and the Ecology of Cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, J.; Bestion, E.; Jacob, S.; Travis, J.; Legrand, D.; Baguette, M. Evolution of Dispersal Strategies and Dispersal Syndromes in Fragmented Landscapes. Ecography 2017, 40, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, J.; Singh, S.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M.; Singh, M. Adaptation Strategies of Plants against Heavy Metal Toxicity: A Short Review. Biochem. Pharmacol. Open Access 2015, 04, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Heavy Metal Tolerance in Plants: Role of Transcriptomics, Proteomics, Metabolomics, and Ionomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posthuma, L.; Van Straalen, N.M. Heavy-Metal Adaptation in Terrestrial Invertebrates: A Review of Occurrence, Genetics, Physiology and Ecological Consequences. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1993, 106, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.J.; Kille, P.; Stürzenbaum, S.R. Microevolution and Ecotoxicology of Metals in Invertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, T.K.S.; Roelofs, D.; van Straalen, N.M. Molecular Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Tolerance and Evolution in Invertebrates. Insect Sci. 2009, 16, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroni, G.; Wise, J.; Young, J.E.; Otto, E. Metallothionein Gene Duplications and Metal Tolerance in Natural Populations of Drosophila Melanogaster. Genetics 1987, 117, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rożen, A. Effect of Cadmium on Life-History Parameters in Dendrobaena Octaedra (Lumbricidae: Oligochaeta) Populations Originating from Forests Differently Polluted with Heavy Metals. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeby, A.; Richmond, L. Adaptation by an Urban Population of the Snail Helix Aspersa to a Diet Contaminated with Lead. Environ. Pollut. 1987, 46, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouché, M.B. Lombriciens de France: Écologie et Systématique; Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique: Paris, France, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, R.W.; Gerard, B.M. Earthworms: Keys and Notes for the Identification and Study of the Species; No. 31 of the Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series); Kermack, D.M., Barnes, R.S.K., Eds.; The Linnean Society of London and The Estuarine and Brackish-Water Biological Association: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Manta, D.S.; Angelone, M.; Bellanca, A.; Neri, R.; Sprovieri, M. Heavy Metals in Urban Soils: A Case Study from the City of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 300, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zheng, N.; Tang, L.; Ji, X.; Li, Y. Effect of soil pH and organic matter content on heavy metals availability in maize (Zea mays L.) rhizospheric soil of non-ferrous metals smelting area. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Ali, S.; Zhang, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Qiu, B.; Wu, F.; Zhang, G. The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobet, G.; Pages, L.; Draye, X. A Novel Image-Analysis Toolbox Enabling Quantitative Analysis of Root System Architecture. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R.V. Least-Squares Means: The R Package Lsmeans. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 69, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monchanin, C.; Devaud, J.-M.; Barron, A.B.; Lihoreau, M. Current Permissible Levels of Metal Pollutants Harm Terrestrial Invertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, C.N.; Butt, K.R.; Cheynier, K.Y.-M. Assessment of Avoidance Behaviour by Earthworms (Lumbricus Rubellus and Octolasion Cyaneum) in Linear Pollution Gradients. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 124, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sivakumar, S. Effects of Metals on Earthworm Life Cycles: A Review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Z.; Alexander, D.; Ali, J.; Unrine, J.; Shoults-Wilson, W.A. Chemosensory Cues Alter Earthworm (Eisenia Fetida) Avoidance of Lead-Contaminated Soil: Chemosensory and Earthworm Avoidance. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Weeks, J.M.; Van Gestel, C.A.M. A Summary of Eleven Years Progress in Earthworm Ecotoxicology. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverack, M.S. Tactile and Chemical Perception in Earthworms —I. Responses to Touch, Sodium Chloride, Quinine and Sugars. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1960, 1, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverack, M.S. Tactile and Chemical Perception in Earthworms —II. Responses to Acid PH Solutions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1961, 1, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, G.L.; Kaushik, A.; Kaushik, N.K.; Solomon, K.R.; Steele, T.; Scroggins, R.P. Use of an Avoidance-Response Test to Assess the Toxicity of Contaminated Soils to Earthworms. Adv. Earthworm Ecotoxicol. 1998, 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.-C.; Bonten, L.T.C. Bioavailability Pathways Underlying Zinc-Induced Avoidance Behavior and Reproduction Toxicity in Lumbricus Rubellus Earthworms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourie, F.; Reinecke, S.A.; Reinecke, A.J. The Determination of Earthworm Species Sensitivity Differences to Cadmium Genotoxicity Using the Comet Assay. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 67, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, D.J.; Van den Brink, P.J. Using Biological Traits to Predict Species Sensitivity to Toxic Substances. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 67, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, A.; Todeschini, R.; Vighi, M. Sensitivity Assessment of Freshwater Macroinvertebrates to Pesticides Using Biological Traits. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 336–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, C.D. Absorption, Distribution, and Excretion of Toxicants. In Casarett & Doull’s Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poisons; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 50–87. [Google Scholar]
- Langdon, C.J.; Hodson, M.E.; Arnold, R.E.; Black, S. Survival, Pb-Uptake and Behaviour of Three Species of Earthworm in Pb Treated Soils Determined Using an OECD-Style Toxicity Test and a Soil Avoidance Test. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 138, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, M.L. Urbanization, Biodiversity, and Conservation. BioScience 2002, 52, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.T.J.; Munshi-South, J. Evolution of Life in Urban Environments. Science 2017, 358, eaam8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdem, C.; Fouet, C.; Gamez, S.; White, B.J. Pollutants and Insecticides Drive Local Adaptation in African Malaria Mosquitoes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Ferrari, M.C.O.; Harris, D.J. Evolution and Behavioural Responses to Human-Induced Rapid Environmental Change: Behaviour and Evolution. Evol. Appl. 2011, 4, 367–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cr | Cu | Pb | Ni | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M− | 5.5 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 5.5 | 38.8 ± 6.3 | BDL | 12.5 ± 12.5 |
| M+ | 6.2 ± 0.4 (5.0) | 42.0 ± 3.0 (50.0) | 154.3 ± 9.8 (150.0) | 2.9 ± 2.8 (7.5) | 106.0 ± 7.0 (122.5) |
| M++ | 7.1 ± 0.1 (10.0) | 69.5 ± 7.5 (100.0) | 243.8 ± 28.8 (300.0) | 7.9 ± 0.0 (15.0) | 189.5 ± 12.5 (245.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chatelain, M. Endogeic Earthworms Avoid Soil Mimicking Metal Pollution Levels in Urban Parks. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11513. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511513
Chatelain M. Endogeic Earthworms Avoid Soil Mimicking Metal Pollution Levels in Urban Parks. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11513. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511513
Chicago/Turabian StyleChatelain, Marion. 2023. "Endogeic Earthworms Avoid Soil Mimicking Metal Pollution Levels in Urban Parks" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11513. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511513
APA StyleChatelain, M. (2023). Endogeic Earthworms Avoid Soil Mimicking Metal Pollution Levels in Urban Parks. Sustainability, 15(15), 11513. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511513







