Sustainable and Green Synthesis of Carbon Nanofibers from Date Palm Residues and Their Adsorption Efficiency for Eosin Dye
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Alcohol
2.3. Preparation of CNFs
2.4. Batch Biosorption Experiments
2.5. Adsorption Capacity Analysis
2.6. Equilibrium Biosorption Isotherm Models
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Sorbents
3.2. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
3.3. Contact Time
3.4. Effect of Initial Dye Concentration
3.5. Effect of pH
3.6. Adsorption Isotherms
3.7. Kinetics of the Adsorption of ES-Y and ES-B onto CNFs
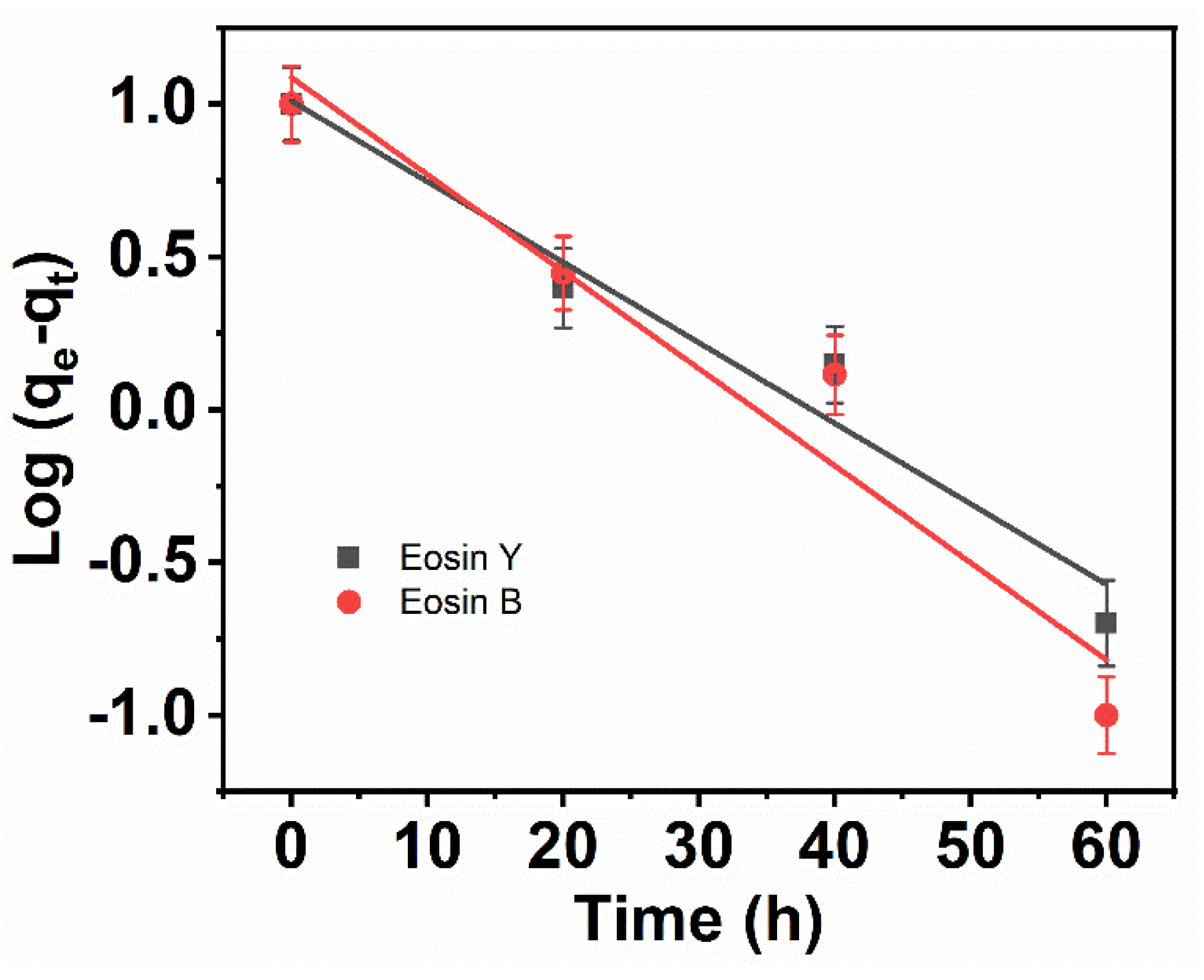
3.8. Pseudo-First Order
3.9. Pseudo-Second-Order Rate Model
3.10. The Waber-Morris Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Husain, M.; Khan, R.A. Date Palm Crop Yield Estimation a Framework. Int. J. Innov. Res. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2019, 7, 2347–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, M.; Al-Tamimi, A.; Cecchi, L.; Adessi, A.; Innocenti, M.; Balli, D.; Mulinacci, N. Phenolic compounds and polysaccharides in the date fruit (Phoenix dactylifera L.): Comparative study on five widely consumed Arabian varieties. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharawy, N.T.; AL-Mutarrafi, M.; Al-Ayafi, A. Different types of dates in Saudi Arabia and its most fungal spoilage and its most preservation methods. Int. J. Recent Sci. Res. 2019, 10, 35787–35799. [Google Scholar]
- Sukirno, S.; Husain, M.; Siswantoro, M.; Rasool, K.G.; Shaheen, F.A.; Salman, S.; Aldawood, A.S. Study on the Loss of Value of Khodari Date Fruit Infested by Almond Moth (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Fla. Èntomol. 2021, 103, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, K.Y.; Baidurah, S. Renewable biomass feedstocks for production of sustainable biodegradable polymer. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 27, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, T.I.M.; Alminderej, F.M.; El-Sayed, W.A.; Saleh, S.M.; Shalaby, A.S.G. Enhanced Optimization of Bioethanol Production from Palm Waste Using the Taguchi Method. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.E.; Bail, A.; Castillo, R.O.; Arízaga, G.G. Removal and Extraction of Carboxylic Acids and Non-ionic Compounds with Simple Hydroxides and Layered Double Hydroxides. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, A.P.; Kunhiraman, S.; Abdulhameed, S. Bioprocessing with cashew apple and its by-products. In Valorisation of Agro-industrial Residues—Volume II: Non-Biological Approaches; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 83–106. [Google Scholar]
- Alminderej, F.M.; Hamden, Z.; El-Ghoul, Y.; Hammami, B.; Saleh, S.M.; Majdoub, H. Impact of Calcium and Nitrogen Addition on Bioethanol Production by S. cerevisiae Fermentation from Date By-Products: Physicochemical Characterization and Technical Design. Fermentation 2022, 8, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.-D.; Nghiem, N. Recent Developments and Current Status of Commercial Production of Fuel Ethanol. Fermentation 2021, 7, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamden, Z.; El-Ghoul, Y.; Alminderej, F.M.; Saleh, S.M.; Majdoub, H. High-Quality Bioethanol and Vinegar Production from Saudi Arabia Dates: Characterization and Evaluation of Their Value and Antioxidant Efficiency. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Saini, A. Lignocellulosic Ethanol Production from a Biorefinery Perspective; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shao, M.; Chen, X.; Yu, W.; Liu, X.; Qian, Y. Large-Scale Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes by an Ethanol Thermal Reduction Process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 8088–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.-X.; Liu, C.-C.; Wu, G.-H.; Chen, X.-M.; Chen, X. Palladium nanoparticles deposit on multi-walled carbon nanotubes and their catalytic applications for electrooxidation of ethanol and glucose. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 112, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Hossain, M.; Wycisk, R.; Pintauro, P.N. Poly(phenylene sulfonic acid)-expanded polytetrafluoroethylene composite membrane for low relative humidity operation in hydrogen fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2022, 535, 231375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, M.M.; El-Nasr, A.A. Adsorption of cationic dye (methylene blue) from water using polyaniline nanotubes base. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 14377–14383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, H.G.; Gilani, A.G.; Sangashekan, M. Tie-line data for the aqueous solutions of phenol with organic solvents at T=298.2K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013, 58, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.B. Health and environmental hazards of synthetic dyes. Textile Review Magazine, 15 May 2013. pp. 12–17.
- Rangabhashiyam, S.; Anu, N.; Selvaraju, N. Sequestration of dye from textile industry wastewater using agricultural waste products as adsorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Huang, H.; Hu, H.-Y.; Li, Q. Removal potential of anti-estrogenic activity in secondary effluents by coagulation. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2562–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gou, J. Magnetic graphene oxides as highly effective adsorbents for rapid removal of a cationic dye rhodamine B from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 7254–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wang, Y. Removal of acid red 88 by a magnetic graphene oxide/cationic hydrogel nanocomposite from aqueous solutions: Adsorption behavior and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 63922–63932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, A. Adsorption characteristics of graphene oxide as a solid adsorbent for aniline removal from aqueous solutions: Kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism studies. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, S52–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menk, J.D.J.; Nascimento, A.I.S.D.; Leite, F.G.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Jozala, A.F.; de Oliveira Junior, J.M.; Chaud, M.V.; Grotto, D. Biosorption of pharmaceutical products by mushroom stem waste. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangashekan, M.; Asan, S.; Gilani, H.G. Investigation of Eosin B Removal from Aqueous Solution Employing Combined Graphene Oxide Adsorption and Zinc Oxide Coagulation Processes. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nagar, D.A.; Massoud, S.A.; Ismail, S.H. Removal of some heavy metals and fungicides from aqueous solutions using nano-hydroxyapatite, nano-bentonite and nanocomposite. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 7695–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, A.; Li, Y.; Mandal, B.; Kang, S.G.; Hur, S.H.; Chung, J.S. Selective adsorption of organic dyes on graphene oxide: Theoretical and experimental analysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 464, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Wilson, L.D.; Morin-Crini, N. Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, C.; Hou, B.; Wang, Y.; Hao, C.; Wu, J. Carbon composite lignin-based adsorbents for the adsorption of dyes. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wan, D.; Chen, J.; Xiao, S. Adsorption of toxic dye Eosin Y from aqueous solution by clay/carbon composite derived from spent bleaching earth. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.S. Chemical Food Safety Issues in the United States: Past, Present, and Future. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8161–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Deng, X.; Tan, K. An eosin Y-based “turn-on” fluorescent sensor for detection of perfluorooctane sulfonate. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 150, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallig, M.A.; Bolon, B.; Haschek, W.M.; Rousseaux, C.G. (Eds.) Fundamentals of Toxicologic Pathology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlidis, M.; Stupp, T.; Naskar, R.; Cengiz, C.; Thanos, S. Retinal Ganglion Cells Resistant to Advanced Glaucoma: A Postmortem Study of Human Retinas with the Carbocyanine Dye DiI. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 5196–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.F.; Kawaguchi, S.; Kamaya, A.; Ohshita, M.; Kabasawa, K.; Iwama, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Tsuda, S. The comet assay with 8 mouse organs: Results with 39 currently used food additives. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2002, 519, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.D.; Henderson, R.F.; Marshall, T.C.; Cheng, Y.S.; Dutcher, J.S.; Pickrell, J.A.; Mauderly, J.L.; Hahn, F.F.; Banas, D.A.; Seiler, F.A.; et al. The inhalation toxicity of two commercial dyes: Solvent yellow 33 and solvent green 3. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1987, 8, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.F.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Human exposure to chemical mixtures: Challenges for the integration of toxicology with epidemiology data in risk assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 103, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Jhare, D.; Mittal, J. Adsorption of hazardous dye Eosin Yellow from aqueous solution onto waste material De-oiled Soya: Isotherm, kinetics and bulk removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 179, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, A.; Oturan, M.A.; Oturan, N.; Şahin, Y. Removal of Acid Orange 7 from water by electrochemically generated Fenton’s reagent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albadri, A.E.; Aissa, M.A.B.; Modwi, A.; Saleh, S.M. Synthesis of Mesoporous Ru-ZnO@ g-C3N4 Nanoparticles and Their Photocatalytic Activity for Methylene Blue Degradation. Water 2023, 15, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; Albadri, A.E.; Aissa, M.A.B.; Modwi, A. Fabrication of Mesoporous V2O5@ g-C3N4 Nanocomposite as Photocatalyst for Dye Degradation. Crystals 2022, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Adeniyi, A.G. A comprehensive review of water quality monitoring and assessment in Nigeria. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, A.T. Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Uluozlu, O.D.; Sari, A.; Tuzen, M.; Soylak, M. Biosorption of Pb(II) and Cr(III) from aqueous solution by lichen (Parmelina tiliaceae) biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2972–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Fu, J. Magnetic hollow poly (cyclotriphosphazene-co-4, 4′-sulfonyldiphenol)-Fe3O4 hybrid nanocapsules for adsorbing Safranine T and catalytic oxidation of 3, 3′, 5, 5′-tetramethylbenzidine. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, R.; Talesh, S.S.A. Enhancement of ultrasound-assisted degradation of Eosin B in the presence of nanoparticles of ZnO as sonocatalyst. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 51, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.M.; McKinney, D.L.; Sigmund, W.M. Enhanced nanocatalysts. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2012, 73, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhlesi, B.; Leikin, J.B.; Murray, P.; Corbridge, T.C. Adult toxicology in critical carea: Part II: Specific poisonings. Chest 2003, 123, 897–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshidi, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K.; Ghaedi, A.; Hajati, S.; Goudarzi, A.; Alipanahpour, E. Highly efficient simultaneous ultrasonic assisted adsorption of brilliant green and eosin B onto ZnS nanoparticles loaded activated carbon: Artificial neural network modeling and central composite design optimization. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 153, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, M.; Ansari, A.; Nejad, P.A.; Ghaedi, A.; Vafaei, A.; Habibi, M.H. Artificial neural network and Bees Algorithm for removal of Eosin B using Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticle-activated carbon: Isotherm and Kinetics study. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fugetsu, B. A novel adsorbent obtained by inserting carbon nanotubes into cavities of diatomite and applications for organic dye elimination from contaminated water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Chung, S.; Oh, G.; Seo, T.S. Three-Dimensional Graphene Oxide Nanostructure for Fast and Efficient Water-Soluble Dye Removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D.; Rajabi, M.; Moradi, O.; Najafi, F.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Kinetics and thermodynamics of malachite green dye adsorption from aqueous solutions on graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.-H.; Zhang, X.-R.; Zeng, G.-M.; Gong, J.-L.; Niu, Q.-Y.; Liang, J. Simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and ionic dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite as an adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, E.; Afsin, B. Investigation of a basic dye adsorption from aqueous solution onto raw and pre-treated bentonite surfaces. Dye. Pigment. 2008, 76, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janoš, P.; Buchtova, H.; Rýznarová, M. Sorption of dyes from aqueous solutions onto fly ash. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4938–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alminderej, F.M.; Younis, A.M.; Albadri, A.E.; El-Sayed, W.A.; El-Ghoul, Y.; Ali, R.; Mohamed, A.M.; Saleh, S.M. The superior adsorption capacity of phenol from aqueous solution using Modified Date Palm Nanomaterials: A performance and kinetic study. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.C. Uma Optimization of Parameters for Adsorption of Methylene Blue on a Low-Cost Activated Carbon. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, J.; Jhare, D.; Vardhan, H.; Mittal, A. Utilisation of bottom ash as a low-cost sorbent for the removal and recovery of a toxic halogen containing dye eosin yellow. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 4508–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, C.A. Applicability of the various adsorption models of three dyes adsorption onto activated carbon prepared waste apricot. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yang, L. The adsorption of basic dyes from aqueous solution on modified peat–resin particle. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.V.; Porkodi, K. Batch adsorber design for different solution volume/adsorbent mass ratios using the experimental equilibrium data with fixed solution volume/adsorbent mass ratio of malachite green onto orange peel. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 74, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Queiroz, G.A.; Rabelo, A.G.S.; de Melo Santos, S.K. Characterization and optimization of production process of alcoholic fermentation of pineapple. Rev. Eletrôn. Gest. Educ. Tecnol. Ambient. 2019, 23, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Albadri, A.; Ben Aissa, M.A.; Modwi, A.; Saleh, S.M. High Poisonous Cd Ions Removal by Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 Nanocomposite: Description and Adsorption Mechanism. Inorganics 2023, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, M.B.; Aghababazadeh, R.; Arabi, H.; Mirhabibi, A. In situ fabrication of carbon nanotube–MgAl2O4 nanocomposite powders through hydrogen-free CCVD. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Nurul, S.; Schmitt, H.; Sutton, N.B.; Murk, T.A.; Blokland, M.H.; Rijnaarts, H.H.; Langenhoff, A.A. Evaluation of attenuation of pharmaceuticals, toxic potency, and antibiotic resistance genes in constructed wetlands treating wastewater effluents. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Min, K. Removal of phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions by iosorption onto Acacia leucocephala bark powder: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2011, 56, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.M.; Nafea, E.M.A.; Mosleh, Y.Y.I.; Hefnawy, M.S. Low-cost biosorbent (Lemnagibba L.) for the removal of phenol from aqueous media. J. Mediterr. Ecol. 2016, 14, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yapar, S.; Ozbudak, V.; Dias, A.; Lopes, A. Effect of adsorbent concentration to the adsorption of phenol on hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium-bentonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 121, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, M.; Mutare, E.; Chigondo, F.; Nyamunda, B.C. Removal of phenol from aqueous solution by adsorption on yeast, saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int. J. Recent Res. Appl. Stud. 2012, 11, 486–494. [Google Scholar]
- Younis, A.M.; Nafea, E.M.A. Heavy metals and nutritional composition of some naturally growing aquatic macrophytes of Northern Egyptian Lakes. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, S.; Younis, A.; Ali, R.; Elkady, E. Phenol removal from aqueous solution using amino modified silica nanoparticles. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, D.; Bruland, G.L.; Torrance, B.S.; Upchurch, V.G.; MacKay, A.A. pH-dependent ciprofloxacin sorption to soils: Interaction mechanisms and soil factors influencing sorption. Geoderma 2009, 151, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Chen, W.; Zheng, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, D. Adsorption of Sulfonamide Antibiotics to Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11608–11613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Pan, B.; Xing, B. Norfloxacin Sorption and Its Thermodynamics on Surface-Modified Carbon Nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Duan, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, D. Adsorption of Hydroxyl- and Amino-Substituted Aromatics to Carbon Nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6862–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Pan, B.; Wu, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Peng, H.; Wu, D.; Ning, P. Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole on functionalized carbon nanotubes as affected by cations and anions. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2616–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G. β-cyclodextrin functionalized graphene oxide: An efficient and recyclable adsorbent for the removal of dye pollutants. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2015, 9, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.M.; Elkady, E.M.; Saleh, S.M. Novel eco-friendly amino-modified nanoparticles for phenol removal from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30694–30705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Aissa, M.A.; Modwi, A.; Albadri, A.E.; Saleh, S.M. Dependency of Crystal Violet Dye Removal Behaviors onto Mesoporous V2O5-g-C3N4 Constructed by Simplistic Ultrasonic Method. Inorganics 2023, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiciklas, I.; Onjia, A.; Raičević, S.; Janaćković, Đ.; Mitrić, M. Factors influencing the removal of divalent cations by hydroxyapatite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Townsend, T.G.; Mazyck, D.; Boyer, T.H. Equilibrium and intra-particle diffusion of stabilized landfill leachate onto micro- and meso-porous activated carbon. Water Res. 2012, 46, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Adsorbent. | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | n | KF | R2 | |
| ES-Y | 168.634 | 0.0323 | 0.995 | 1.7449 | 10.3767 | 0.951 |
| ES-B | 165.017 | 0.0209 | 0.998 | 1.6899 | 8.30001 | 0.941 |
| CNFs | Experimental Value qe (mg g−1) | First-Order | Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | qe | R2 | K2 | qe | R2 | ||
| ES-Y | 9.2 | 0.0264 | 10.242 | 0.970 | 0.0102 | 9.5247 | 0.994 |
| ES-B | 9.1 | 0.0318 | 12.242 | 0.958 | 0.0077 | 9.3327 | 0.991 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alminderej, F.M.; Albadri, A.E.A.E.; El-Ghoul, Y.; El-Sayed, W.A.; Younis, A.M.; Saleh, S.M. Sustainable and Green Synthesis of Carbon Nanofibers from Date Palm Residues and Their Adsorption Efficiency for Eosin Dye. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10451. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310451
Alminderej FM, Albadri AEAE, El-Ghoul Y, El-Sayed WA, Younis AM, Saleh SM. Sustainable and Green Synthesis of Carbon Nanofibers from Date Palm Residues and Their Adsorption Efficiency for Eosin Dye. Sustainability. 2023; 15(13):10451. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310451
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlminderej, Fahad M., Abuzar E. A. E. Albadri, Yassine El-Ghoul, Wael A. El-Sayed, Alaa M. Younis, and Sayed M. Saleh. 2023. "Sustainable and Green Synthesis of Carbon Nanofibers from Date Palm Residues and Their Adsorption Efficiency for Eosin Dye" Sustainability 15, no. 13: 10451. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310451
APA StyleAlminderej, F. M., Albadri, A. E. A. E., El-Ghoul, Y., El-Sayed, W. A., Younis, A. M., & Saleh, S. M. (2023). Sustainable and Green Synthesis of Carbon Nanofibers from Date Palm Residues and Their Adsorption Efficiency for Eosin Dye. Sustainability, 15(13), 10451. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310451








