Far-Field Influences Shadow the Effects of a Nuclear Power Plant’s Discharges in a Semi-Enclosed Bay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methods
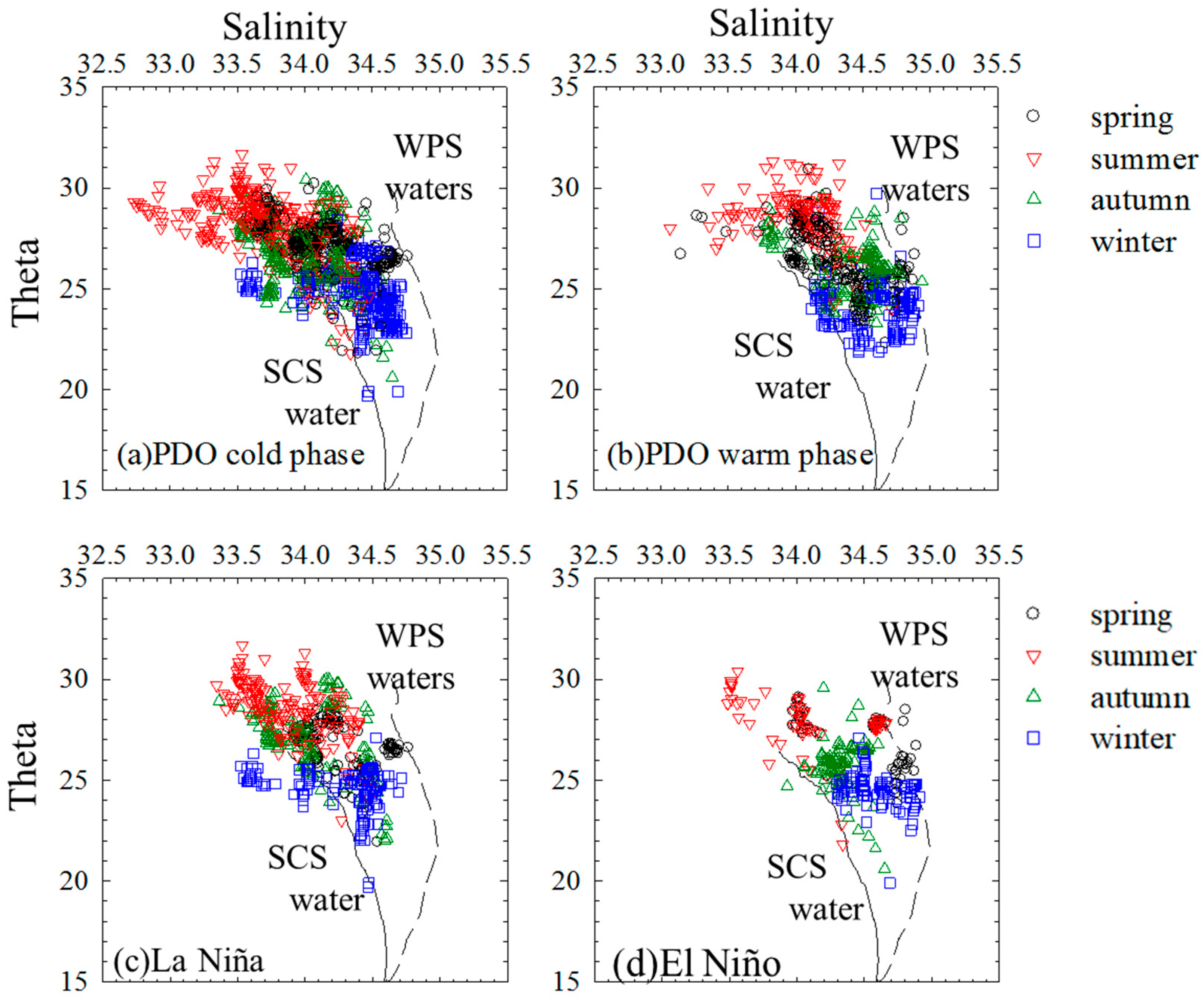
3. Dynamics of the Study Area
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Osterberg, C.L. Nuclear power wastes and the ocean. In Wastes in the Ocean; Duedall, I.W., Kester, D.R., Park, P.K., Ketchum, B.H., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1985; Volume 4, pp. 127–162. [Google Scholar]
- GESAMP. Report of the Twelfth Session; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Sixth Assessment Report: Climate Change 2023; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-T.A.; Yu, S.; Huang, T.-H.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Lui, H.-K. Temperature and secchi disk depth increase more rapidly in the subpolar Bering/Okhotsk Seas than in the subtropical South China Sea. Water 2023, 15, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Shiah, F.-K.; Lee, H.-J.; Li, K.-Y.; Meng, P.-J.; Kao, S.-J.; Tseng, Y.-F.; Chung, C.-L. Phytoplankton and bacterioplankton biomass, production and turnover in a semi-enclosed embayment with spring tide induced upwelling. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 304, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Lin, J.; Zheng, B. Effects of thermal discharge from coastal nuclear power plants and thermal power plants on the thermocline characteristics in sea areas with different tidal dynamics. Water 2019, 11, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Wang, Y.-S. Modeling the ecosystem response of the semi-closed Daya Bay to the thermal discharge from two nearby nuclear power plants. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 736–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Chao, S.-Y.; Fan, K.-L.; Wang, Y.-H.; Liang, N.-K. Tidally induced upwelling in a semi-enclosed basin: Nan Wan Bay. J. Oceanogr. 1997, 53, 467–480. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.-J.; Chao, S.-Y.; Liu, K.-K.; Huang, S.-J.; Gong, G.-C. Tidal effects on circulation in and near the East China Sea. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2014, 25, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Lee, H.J.; Zheng, Q.; Lai, J.W.; Su, F.C.; Ho, C.R. Tide-Induced periodic sea surface temperature drops in the coral reef area of Nanwan Bay, southern Taiwan. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2019JC015226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C. The impact of tidal straining and advection on the stratification in a partially mixed estuary. Water 2023, 15, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, K.S.; Leu, M.-Y.; Wang, J.-T.; Chang, C.-M.; Chen, C.-C.; Meng, P.-J. A continuous, real-time water quality monitoring system for the coral reef ecosystems of Nanwan Bay, Southern Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-T.A.; Liu, C.-T.; Chuang, W.; Yang, Y.; Shiah, F.-K.; Tang, T.; Chung, S. Enhanced buoyancy and hence upwelling of subsurface Kuroshio waters after a typhoon in the southern East China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2003, 42, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.A. The Kuroshio intermediate water is the major source of nutrients on the East China Sea continental shelf. J Oceanol. Acta 1996, 19, 523–527. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, S.-Y.; Boicourt, W.C.; Wang, H.V. Three-layered circulation in reverse estuaries. Cont. Shelf Res. 1996, 16, 1379–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.C.; Jiang, Y.M.; Tan, T.H.; Chang, K.H.; Shao, K.C.; Huang, C.C.; Chu, T.C.; Fan, K.L.; Yeh, H.Y. Ecological Study of the Nuclear Power Plant, Southern TAIWAN. XIV, The Fourteen’s Annual Report (July 1992 to June 1993); Academia Sinica: Taipei, Taiwan, 1993; 136p. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. State of the Climate: Global Climate Report for 2022. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/monitoring/monthly-report/global/202213 (accessed on 18 January 2023).
- Giuliani, S.; Bellucci, L.G.; Nhon, D.H. The coast of Vietnam: Present status and future challenges for sustainable development. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 415–435. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; He, X.; Yu, S.; Chen, C.-T.A. Changes in the ecological environment of the marginal seas along the Eurasian continent from 2003 to 2014. Sustainability 2018, 10, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Lou, Z.-P.; Sun, C.-C.; Sun, S. Ecological environment changes in Daya Bay, China, from 1982 to 2004. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-S. Effects of the operating nuclear power plant on marine ecology and environment-A case study of Daya Bay in China. In Nuclear Power–Deployment, Operation and Sustainability; InTech: Wellington, New Zealand, 2011; pp. 255–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-R. Interannual modulation of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) on the low-latitude western North Pacific. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 110, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Cheng, Y.; Gong, F. Long-term changes and factors that influence changes in thermal discharge from nuclear power plants in Daya Bay, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kester, D.R.; Wang, Z.; Lian, J.; Kawamura, H. AVHRR satellite remote sensing and shipboard measurements of the thermal plume from the Daya Bay, nuclear power station, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tang, D.; Yao, L.; Chen, P.; Jia, X.; Li, C. Long-term water temperature variations in Daya Bay, China using satellite and in situ observations. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2010, 21, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yin, S.; Wu, C.; Ma, W.; Hou, H.; Xu, J. Remote sensing monitoring of thermal discharge in Daya Bay nuclear power station based on HJ-1 infrared camera. In Proceedings of the Ocean Remote Sensing and Monitoring from Space, Beijing, China, 15–16 October 2014; pp. 182–187. [Google Scholar]







| Nanwan Bay | Daya Bay * | |
|---|---|---|
| Location | 120.8° E, 21.9° N | 114.7° E, 22.6° N |
| Size | 38 km2 | 600 km2 |
| Deepest depth | 120 m | 21 m |
| Size of power plants | 951 MWe | 1688 MWe |
| Power plants began operating | May 1984 | August 1993 |
| Shape of bay | Large opening Bowl-like | Small opening Vase-like |
| Internal tides | Strong | None |
| Extent of thermal plume | 1 km (1.0 °C higher) | 10 km (1.0 °C higher) |
| Rate of T increase | 0.026/yr (1986–2022) | 0.079/yr (1982–2004) |
| Item | Normal Operation (1) | Under Maintenance (2) | (1)–(2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Season | St. 24 | Other Stations * | St. 24 | Other Stations * | St. 24 | Other Stations * | |
| Spring (March~May) | 28.3 ± 1.1, n = 19 | 27.0 ± 1.2, n = 108 | 27.7 ± 1.7, n = 15 | 27.1 ± 1.4, n = 84 | 0.7 ± 0.5 °C | −0.1 ± 0.2 °C | |
| Summer (June~August) | 30.6 ± 1.3, n = 27 | 29.2 ± 0.7, n = 152 | - | - | - | - | |
| Autumn (September~November) | 28.7 ± 1.5, n = 20 | 27.2 ± 1.1, n = 112 | 27.2 ± 1.6, n = 12 | 26.5 ± 1.6, n = 66 | 1.5 ± 0.6 °C | 0.7 ± 0.2 °C | |
| Winter (December~February) | 25.8 ± 1.6, n = 25 | 24.2 ± 1.1, n = 141 | 25.1, n = 1 | 24.8 ± 0.3, n = 6 | 0.7 ± 0.3 °C | −0.6 ± 0.2 °C | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-T.; Jan, S.; Chen, M.-H.; Liu, L.-L.; Huang, J.-F.; Yang, Y.-J. Far-Field Influences Shadow the Effects of a Nuclear Power Plant’s Discharges in a Semi-Enclosed Bay. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119092
Chen C-T, Jan S, Chen M-H, Liu L-L, Huang J-F, Yang Y-J. Far-Field Influences Shadow the Effects of a Nuclear Power Plant’s Discharges in a Semi-Enclosed Bay. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):9092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119092
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chen-Tung (Arthur), Sen Jan, Meng-Hsien Chen, Li-Lian Liu, Jung-Fu Huang, and Yiing-Jang Yang. 2023. "Far-Field Influences Shadow the Effects of a Nuclear Power Plant’s Discharges in a Semi-Enclosed Bay" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 9092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119092
APA StyleChen, C.-T., Jan, S., Chen, M.-H., Liu, L.-L., Huang, J.-F., & Yang, Y.-J. (2023). Far-Field Influences Shadow the Effects of a Nuclear Power Plant’s Discharges in a Semi-Enclosed Bay. Sustainability, 15(11), 9092. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119092






