Abstract
Styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) is currently the most widely used asphalt modifier. However, high-SBS-concentration high-viscosity modified asphalts (HVMA) are characterized by poor flow and storage instability. To make up for the lack of performance of traditional SBS-HVMA, a nano-based high-viscosity composite modified asphalt with excellent performance was developed. Since carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are nanomaterials, they are prone to agglomeration when added to the modified asphalt, and the dispersion effect is poor, which affects the modifier’s contribution rate. To better disperse CNTs in the modified asphalt, the nanomaterials were modified, and two new CNT additives were prepared by combining two polymers with CNTs. The appropriate ratio of these two new additives was selected to be further combined with SBS to obtain CNTs/SBS-HVMA. The flow characteristics and anti-aging properties of the three kinds of bitumen in different temperature ranges were studied by taking the common SBS-HVMA and Tafpack super (TPS) high-viscosity modified asphalts (TPS/SBS-HVMA) as comparison samples and by evaluating the road performance of a stone mastic asphalt (SMA-13) mixture. The storage stability, workable performance, rheological characteristics, and aging resistance of three high-viscosity asphalts were analyzed through a segregation test, dynamic viscosity analysis, Brookfield viscosity measurements, bending beam rheometer (BBR) tests, dynamic shear rheometer (DSR), and multiple stress creep recovery (MSCR) before and after short-term aging. The experimental results showed that CNT/SBS-HVMA exhibited good storage stability and workability. DSR measurements and other rheological tests revealed that TPS/SBS-HVMA had higher low-temperature flexibility than the other modified asphalts, while CNT/SBS-HVMA exhibited good high-temperature resistance, aging resistance, and deformation resistance. Through the verification of asphalt mixture performance, it was found that the high-temperature rutting resistance of CNTs/SBS-HVMA prepared by new CNT additives was 7% and 28% higher than those of SBS-HVMA and TPS/SBS-HVMA, respectively, but the low-temperature performance of CNT/SBS-HVMA was 5% lower than that of SBS-HVMA. This showed that CNT/SBS addition improved the high-temperature performance of the asphalt without a significant negative impact on the low-temperature performance of the asphalt.
1. Introduction
With increasing traffic, the proportion of large and heavy-duty vehicles on the road increases. This increase in the road surface load will affect the performance and service life of the road surface. To prevent the pavement from being damaged, it is necessary to manufacture a more durable asphalt binder. Numerous methods have been developed to improve the performance of asphalt binders, such as the use of additives. The most commonly used additives are polymers. Bitumen can be modified with polymers to form new materials [1]. Styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) is the most widely used asphalt modifier [2]. Mixing SBS with asphalt can result in the physical crosslinking of polystyrene blocks to form a three-dimensional (3D) network, while the polybutadiene mid-blocks provide material flexibility, thereby significantly improving the asphalt performance [3,4,5,6].
HVMA has high adhesion, which can improve the durability of asphalt materials, and has good wrapping properties, which can improve the aging resistance of asphalt materials. Usually, 60 °C viscosity is used as the key index to evaluate HVAM. Its main characteristics are high viscosity, low penetration, and high softening point. HVMA can be applied to permeable pavements [7,8,9]. Due to its high viscosity and strong adhesion to aggregates, it is widely used in high-performance pavement and steel bridge deck pavement. Many countries divide HVMA into two categories [10]: direct-throw HVMA and finished HVMA. Direct HVMA involves directly adding a high-viscosity modifier to aggregates and a matrix asphalt during the high-temperature mixing process using the shear force between the aggregates to disperse the modifier into the leakage; this method eliminates the preparation process of the modified asphalt, saving time and energy, but the performance of this modified asphalt is unstable. At present, the more common HVMAs on the market are Japan’s TPS-HVMA and high-content SBS-HVMA.
However, the large differences in density, polarity, and relative molecular mass [11,12] limit the compatibility between the asphalt and modifier phases in SBS-HVMA. Consequently, segregation easily occurs during production, transportation, and construction, and the SBS anti-aging performance is poor. Moreover, TPS-HVMA generally has some problems that are difficult to solve, namely, it is easy to segregate during thermal storage, the performance decays rapidly, and the viscosity of HVMA and the construction and workability aspects are difficult to balance. Zhang et al. [10] added SBS, a plasticizer, and a cross-linking agent to an asphalt to prepare HVMA and studied the effects of the modifiers on the structure and rheological behavior of the SBS-modified asphalt through asphalt rheological test. Qu et al. [13] prepared HVMA with modifiers such as SBS, rock pitch, and rubber powder; carried out a rotational viscosity test, DSR test, and BBR test; and found that the addition of modifiers can improve the high- and low-temperature properties of the asphalt and its mixture. Shi et al. [14] used SBS/c9 petroleum resin blends (SPR) as a high-viscosity asphalt modifier and compared it with the traditional modifier TPS; the results showed that the SPR modifier had good compatibility with asphalts in the production process, making SPR easier to disperse in asphalts with average particle size. Furthermore, its modification effect was better than that of TPS, and its production cost was lower than that of TPS-HVMA. According to relevant research, the addition of nanomaterials to modified asphalts can modify asphalts at the mesoscopic or microscopic level, significantly improve the high temperature stability and viscosity of asphalts, and significantly improve the aging resistance of asphalts. In recent years, the application of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in road asphalts has gradually attracted research interest. Although CNTs are expensive, several researchers have found that the composite modification of CNTs and SBS can reduce the cost and also improve the storage stability and aging resistance of SBS-HVMA [15,16,17,18,19]. Wang et al. [20] found that a CNTs/SBS asphalt binder exhibited better low-temperature performance than SBS-HVMA. Prabin Kumar Ashish [21] found that the CNT-modified asphalt binders were stable under high-temperature storage conditions. Ziari and Amirkhania found that adding sufficient CNTs can increase the modulus, physical properties, rutting resistance, and fatigue resistance of asphalt binders [22,23,24,25].
In this paper, two kinds of CNTs and SBS modifiers that underwent surface modification are used to prepare composite HVMA. The common SBS-HVMA and TPS/SBS-HVMA were used as comparison samples. In this study, the effect of CNTs on the performance of SBS-HVMA was studied via rheological experiments, and the pavement performance of the asphalt mixture was compared. The rheological and aging properties of three modified asphalts under different temperature ranges were studied. The general properties of bitumen were evaluated based on the softening point and kinematic viscosity. High-temperature flow characteristics were investigated using the Brookfield viscosity test. The rheological performance was studied with a dynamic shear rheometer (DSR) in the frequency sweep mode, and the main curve was established based on the CAM model. The high- and low-temperature performances were investigated using a multi-stress creep recovery (MSCR) test and bending beam rheometer (BBR) test, respectively. Finally, the pavement performance of a stone mastic asphalt (SMA-13) mixture was evaluated through the Hamburg rutting test and a low-temperature trabecular bending test. This study provided some new methods for obtaining HVMA.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Preparation of HVMA Samples
China Qilu 70# base asphalt was used as raw material. A Fluko high-speed shearing machine and mixer were used as the modified asphalt production equipment. The performance indicators of the base asphalt are shown in Table 1. Linear SBS (T6302) produced by PetroChina Dushanzi Petrochemical Company was used as the modifier. The composite-modified materials were TPS from Japan and a new type of CNT. A new twin-screw extrusion process was used to produce a masterbatch through melt blending, and a new carbon nanotube modifier was obtained. The crosslinking agent was a sulfur stabilizer.

Table 1.
Technical characteristics of A70# asphalt binders.
First, the base asphalt was heated at 160 °C to improve its fluidity. Then, SBS, TPS, and CNT modifiers were added to the asphalt, sheared at a high temperature in a high-speed shearing machine and mixer, and developed at a constant temperature. The shearing temperature and growth temperature were set at 175 °C ± 5 °C, the shearing machine speed was adjusted to 4000 r/min, the stabilizer was added after 1 h shearing, and, finally, the SBS-HVMA, TPS/SBS-HVMA, and CNT/SBS-HVMA were prepared in the mixer for 3 h at a constant temperature. The performance indicators of the three modified asphalts are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Performance indexes of modified asphalt.
Crushed basalt stone was used as aggregates, and the aggregate particle size was divided into three grades: 0–3 mm, 5–10 mm, and 10–15 mm. Finely ground limestone ore powder was used as fillers. The SMA-13 asphalt mixture gradation was designed according to the experimental design specification shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
SMA-13 Composite grading.
2.2. Thermal Storage Temperature Test
The asphalt segregation test was performed according to ASTM D 5–D 5976, and the samples from the upper and lower parts of the segregation tube were selected for a softening point test. The three kinds of asphalt were heated once every 24 h to measure their dynamic viscosity at 60 °C. The dynamic viscosity test was performed according to ASTM D 2170.
2.3. Workable Performance Test
The rotational viscosity test was performed according to ASTM D4402. The measurement temperatures were 100 °C, 120 °C, 135 °C, 155 °C, and 175 °C, respectively, and the rotor model was 27#. The high-temperature flow characteristics of the asphalt material were analyzed through the change of the viscosity–temperature relationship.
2.4. High-Temperature Rheological Test
2.4.1. Frequency Sweep Test
The frequency sweep test was performed on the three kinds of high-viscosity asphalt. The test temperature was 45 °C–75 °C, the interval temperature was 10 °C, and the reference temperature was 55 °C. Parallel plates of Φ25 mm were used; the plate spacing was 1 mm; and the frequency sweep range was 0.1–50 Hz. The DSR test was performed according to ASTM D 8189.
2.4.2. High-Temperature Performance Test
The test temperature was 60 °C, a Φ25 mm parallel plate was used, and the plate spacing was 1 mm. First, a stress of 0.1 kPa was applied for 1 s to creep deform the asphalt, then the asphalt was unloaded for 9 s to recover. This process was repeated for 10 cycles, followed by the application of a stress of 3.2 kPa, for a total of 20 cycles and a total duration of 200 s. The whole test was performed for 20 cycles, with a total duration of 200 s. The MSCR test was performed according to ASTM D 8239.
2.5. Low-Temperature Rheological Test
The low-temperature properties of asphalt were evaluated through the BBR test. The specimen preparation and instrument operation were performed in accordance with JTG E20-2011 [26] and American AASHTO M320–10 specifications. The selected test temperatures were −12 °C, −18 °C, and −24 °C, respectively.
2.6. Asphalt Mixture Performance Test
2.6.1. Hamburg Rutting Test
The temperatures of the test chamber and the water bath of the asphalt mixture were both 60 °C, the width of the test wheel was 47 mm, the wheel pressure was 0.7 MPa, and the loading rate was 52 ± 2 passes per minute. The test ended after ≥20,000 wheel rolling passes or when the rut depth was ≥12.5 mm.
2.6.2. Low-Temperature Bending Beam Test
The bending test of the asphalt mixture was performed in accordance with JTG E20-2011 “Asphalt and Asphalt Mixture Test Regulations for Highway Engineering” T0715 [26]. The trabecular specimens were first incubated for 5 h in a −10 °C incubator, then tested at the same temperature at a loading rate of 50 mm/min. The test flow chart is shown in Figure 1
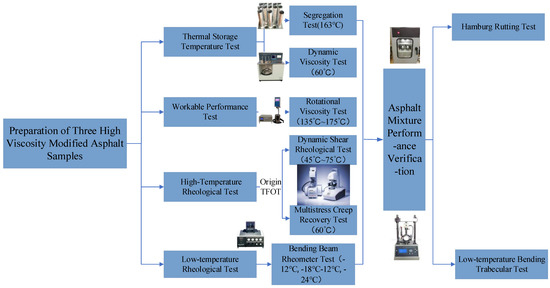
Figure 1.
Experimental design flowchart.
3. Results
3.1. Thermal Storage Temperature Test Result
The segregation softening point differences of the three asphalts are plotted in Figure 2a. Only the segregation softening point difference of CNT/SBS-HVMA was less than 2.5 °C and it remained unchanged with increasing segregation time, indicating that the modified asphalt had good storage stability. However, the softening point difference between the upper and lower parts of the commonly used SBS-HVMA and TPS/SBS-HVMA was greater than the 2.5 °C specification requirement. Among them, the softening point difference of SBS-HVMA was large, and severe segregation occurred. The softening point difference of TPS/SBS-HVMA reached the maximum on the sixth day of segregation, then gradually decreased, but was still higher than the specification requirements. This indicates that TPS/SBS-HVMA exhibited poor stability under long-term thermal storage, while CNT/SBS-HVMA exhibited good high-temperature storage stability.
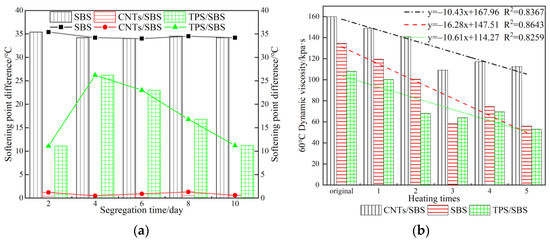
Figure 2.
Asphalt viscosity test: (a) segregation softening point difference of three modified asphalts; (b) viscosity decay of three modified asphalts.
Figure 2b plots the decay trend of the dynamic viscosities of the three modified asphalts after repeated heating. The dynamic viscosities of the three asphalts at 60 °C were greater than 20,000 Pa·s, which met the requirements of the current specification. The dynamic viscosities decreased as follows: CNT/SBS-HVMA (160,000 Pa·s) > SBS-HVMA (134,500 Pa·s) > TPS/SBS-HVMA (108,000 Pa·s), indicating that CNT/SBS-HVMA exhibited the strongest adhesion to aggregates under high-temperature conditions, and the highest high-temperature rutting resistance. After repeated heating, the viscosities of the three asphalts exhibited a downward trend, indicating that the modified asphalt was heated at a high temperature, the internal modifier was degraded, the glue system was damaged, and viscosity decreased. The correlation coefficient between the kinematic viscosity of SBS and the number of heating cycles was 0.8643, which was higher than those of CNT/SBS-HVMA and TPS/SBS-HVMA. This indicates that SBS-HVMA was more susceptible to performance attenuation under the influence of temperature, which affected the road performance of the asphalt mixture. The TPS/SBS-HVMA exhibited the best performance, followed by CNT/SBS-HVMA, but the difference between the performances of both asphalts was not significant.
3.2. Workability Test Result
The viscosity–temperature relationship of asphalt had a large influence on the service quality and process characteristics of asphalt pavement.
Figure 3a plots the viscosity–temperature relationship curves of the three asphalts. With increasing test temperature, the viscosity of the three asphalts gradually decreased, and the decreasing rate gradually decreased. Among the three asphalt materials, at a test temperature of approximately 100 °C, the asphalt viscosities decreased as follows: CNT/SBS-HVMA > SBS-HVMA > TPS/SBS-HVMA. At a test temperature of approximately 120 °C, the viscosities decreased as follows: SBS-HVMA > TPS/SBS-HVMA > CNT/SBS-HVMA, indicating that the viscosity of CNT/SBS-HVMA was higher at a lower temperature in the range of 100 °C–120 °C for the three kinds of high-viscosity asphalt. This trend extended to a lower temperature and was consistent with the kinematic viscosity at 60 °C, indicating that the asphalt had a higher high-temperature rutting resistance. At a test temperature between 120 °C and 175 °C, the viscosity of the three asphalts gradually decreased with increasing temperature, and the size relationship was consistent. The workability of the bituminous materials was evaluated at a viscosity of 135 °C in accordance with the Strategic Highway Research Program specification. Figure 3a shows that at a test temperature of 135 °C, the viscosities of CNT/SBS-HVMA, SBS-HVMA, and TPS-HVMA were 2.88, 4.38, and 3.85 Pa.s, respectively, and only the CNT viscosity at 135 °C and <3 Pa·s met the specification, owing to the high polarity of the hydroxylated II-CNTs, which reduced the viscosity of CNT/SBS-HVMA. At an ambient temperature lower than 100 °C, the viscosity of CNT/SBS-HVMA was high, the asphalt hardness was high, and the high-temperature rutting resistance of the road surface was good. At a construction temperature higher than 120 °C, the CNT/SBS-HVMA exhibited a low viscosity, good fluidity, and the best construction workability.
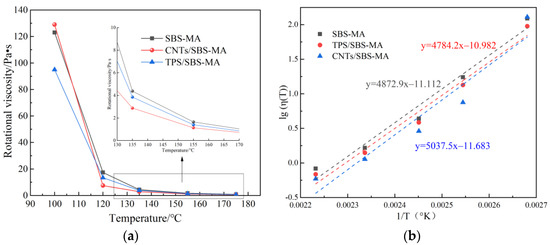
Figure 3.
Variation in high-temperature fluidity of three kinds of asphalt and activation energy calculation: (a) viscosity–temperature relationship curves of the three asphalts; (b) activation energy calculation.
The flow activation energy E reflects the temperature dependence of the material. At a constant material parameter A, the higher the activation energy, the higher the sensitivity of the material to temperature [27,28,29]. In asphalt, the lower the temperature, the higher the activation energy; the higher the temperature, the smaller the activation energy. As the test temperature was higher than the glass temperature of the asphalt (usually <0 °C), the activation energy can be considered a constant value. The activation energy of different asphalts can be obtained from Figure 3b and Equation (1) fitting (see Table 4).
where Eη is the activation energy; η(T) is the viscosity (Pa·s) at temperature T; K is the material constant; and R = 8.314 J/(mol·K) is the universal gas constant.

Table 4.
Calculation results of the activation energy of asphalt viscous flow.
The x [logarithm value of viscosity lg(η(T))] has a linear relationship with y (reciprocal 1/T of temperature). The slope of the straight line reflects the sensitivity of viscosity to temperature, and its magnitude can reflect the Eη of the viscous flow (i.e., Eη difference). CNT/SBS-HVMA exhibited the largest Eη (i.e., 96.454 kJ/mol), and TPS-HVMA exhibited the smallest Eη (i.e., 91.604 kJ/mol), but the Eη values of the three asphalts were similar (Table 4). This shows that the energy barrier that CNTs/SBS-HVMA needs to overcome to flow was slightly larger than those of SBS-HVMA and TPS/SBS-HVMA, and CNTs/SBS-HVMA required a higher temperature to flow. In contrast, TPS/SBS-HVMA had a relatively low Eη value and could flow at lower temperatures.
3.3. High-Temperature Rheological Test Result
3.3.1. Frequency Sweep Experiment
According to the time–temperature equivalence principle, the three kinds of high-viscosity asphalts were subjected to frequency sweep experiments using a DSR. According to the Christensen–Anderson–Marastanu model and the William–Landau–Ferry equation, the main curves of G* and δ were established (Figure 4).
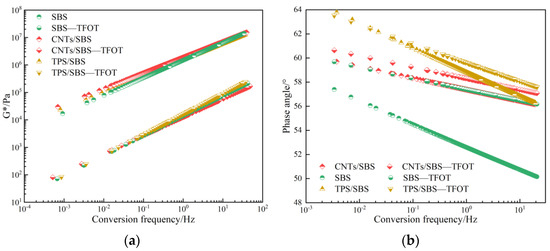
Figure 4.
Frequency sweep master curve: (a) G* master curve; (b) δ master.
According to the principle of time–temperature equivalence, the reference temperature was selected, and the shift factor was calculated. The parameters measured at different temperatures and frequencies were coupled into a smooth curve, which is called the master curve. Then, the Christensen–Anderson–Marastanu model was used to fit the main curve. The mathematical expression is shown as follows [30,31]:
where is the complex modulus of the equilibrium state; is the complex modulus of the glassy state; fc is the elastic threshold or crossover frequency reported by the National Cooperative Highway Research Program; f′ is frequency and is the function temperature and displacement; fc′ is the viscous limit threshold; k and me are the shape parameter and the rheological parameter, respectively; δm is the maximum value of the asphalt mixture; fd is the frequency at phase angle δm; Rd and md are the same as k and me; I is a constant parameter; αT is the shift factor; T is the loading period at a certain temperature; c1 and c2 represent the test constants, and c1 × c2 ≈ 900; T0 is the reference temperature; and T is the experimental temperature.
Figure 4a shows that the composite shear modulus of various asphalts gradually increased with increasing loading frequency. With increasing frequency, the loading time became increasingly shorter, material deformation was smaller, and stiffness was greater. The modulus was also higher; thus, the higher the complex shear modulus, the stronger the asphalt resistance to loading. The three asphalts before aging in the high-temperature and low-frequency region were compared. CNT/SBS-HVMA exhibited the largest G*, indicating that it exhibited a stronger resistance to deformation under high temperature and low-speed driving. This is attributable to the large aspect ratio of CNT/SBS-HVMA, which acts as a reinforcement between the asphalt and the modifier, making the asphalt system more stable at high temperatures [32]. In the low-temperature and high-frequency region, the G* main curves of the three high-viscosity asphalts basically overlap and the moduli were similar. TPS/SBS-HVMA exhibited the smallest G*, indicating that the cracking resistance of TPS/SBS-HVMA materials under low-temperature and fast-driving conditions was good. The low-temperature performance was slightly better than those of the other two high-viscosity asphalts.
The aged CNT/SBS-HVMA exhibited the largest G* in the high-temperature and low-frequency region, indicating that the aged CNT/SBS-HVMA exhibited the best high-temperature performance. Similarly, in the low-temperature and high-frequency region, the CNTs exhibited a smaller G* than SBS-HVMA and TPS/SBS-HVMA, indicating that the aged CNT/SBS-HVMA exhibited the highest low-temperature crack resistance, followed by SBS-HVMA, then TPS/SBS-HVMA. However, the low-temperature performance gap between the three asphalt was small.
The G* values of the three high-viscosity asphalts before and after aging and the related road performances were compared. CNT/SBS-HVMA exhibited a reinforcing role at high temperatures and improved high-temperature performance, particularly after a short period. After aging, the performance decayed slowly. In addition, aging prevented the loss of light components and reduced the low-temperature damage to the asphalt.
The phase angle can characterize the viscoelasticity ratio of the asphalt material. If the δ value in the high-frequency region is small, the viscous component will be small, which will affect the low-temperature crack resistance of the road surface during high-speed driving. If the δ value in the low-frequency region is large, the viscous component will also be large, which will affect the road surface resistance during low-speed driving and deformability. With increasing temperature, the viscous component increased, and the elastic component decreased. With increasing frequency, the phase angles of the three modified asphalts before and after aging gradually decreased. With increasing frequency and decreasing temperature, the elastic ratio of the three asphalts gradually increased, and the viscosity continuously decreased. Therefore, the resistance to permanent deformation gradually increased.
The phase angles of the three asphalts before aging were compared. The δ value gradually increased with reducing frequency, but with the increasing δ for the three high-viscosity asphalts, the “slopes” of the straight line were different. The main curves of SBS-HVMA and TPS/SBS-HVMA were nearly parallel, and their slopes were both larger than that of CNT/SBS-HVMA. CNT/SBS addition reduced the δ of HVMA in the high-temperature and low-frequency region and increased the δ value in the low-temperature and high-frequency region, which was beneficial to the reduction of the viscous component of asphalt at high temperature and increased the viscous component of asphalt at low temperatures (i.e., high-temperature rutting resistance and low-temperature cracking resistance) [3,4].
After the asphalt was aged, the phase angles of the three asphalts gradually increased with reducing frequency (i.e., from a low temperature to a high temperature), but the original asphalt exhibited a different trend. The slopes of the main curves of the phase angles of the aged asphalts were not much different, and the slopes of the curves of the original asphalts were smaller than those of the aged asphalts. During the aging process of asphalt, the light components were continuously volatilized, and asphalt sensitivity to temperature decreased. In the high-temperature and low-frequency region, the aged TPS/SBS-HVMA exhibited the largest δ value, indicating that TPS/SBS-HVMA exhibited the largest viscous component among the asphalts at high temperature, and its high-temperature rutting resistance was lower than those of the other two high-viscosity asphalts. The magnitude relationship of the phase angle main curve after aging in the low-temperature and high-frequency region was the same as that in the high-temperature and low-frequency region, but the values of the three main curves were relatively close, indicating that in the low-temperature and high-frequency state, the low-temperature properties of the three high-viscosity asphalts were similar. The addition of CNT/SBS to HVMA had little effect on the low-temperature performance of the asphalt.
3.3.2. High-Temperature Performance
The average creep recovery of asphalts in each cycle is calculated according to the following formulas:
where R is percent recovery; Jnr is non-recoverable creep compliance; γp is peak strain; γnr is residual strain; γ0 is initial strain; and τ is creep shear stress.
The average non-recoverable creep compliance values within ten creep recovery cycles under two stress levels of 0.1 and 3.2 kPa were expressed as Jnr 0.1 and Jnr 3.2, respectively. The corresponding stress sensitivity index Jnr-diff is expressed as follows:
Figure 5 shows the creep recovery curves of the three HVMAs under stress conditions of 0.1 and 3.2 kPa before and after aging. Under different stress conditions, the cumulative strain increased with the loading time. The asphalt strain at a stress of 3.2 kPa was higher than that at a stress of 0.1 kPa. Before and after aging, the strain of TPS/SBS-HVMA was the largest under both stress conditions, and the strain of CNTs/SBS-HVMA was the smallest. This shows that TPS/SBS-HVMA exhibited high asphalt flow deformation, which was unfavorable for the high-temperature rutting resistance of asphalt pavements. Under the low-stress conditions, the strains of TPS/SBS-HVMA and SBS-HVMA after aging were significantly reduced, while the strain of CNTs/SBS-HVMA was more stable. The addition of CNTs/SBS to HVMA reduced the cumulative strain of the modified asphalt and improved its high-temperature deformation resistance, and the improvement effect of the high-temperature deformation resistance under low-stress loading conditions was more prominent.
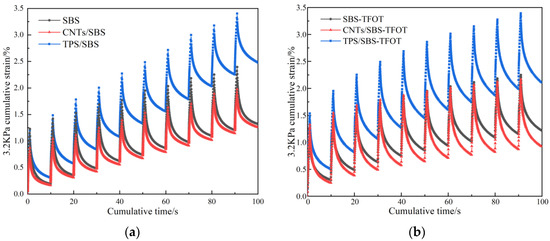
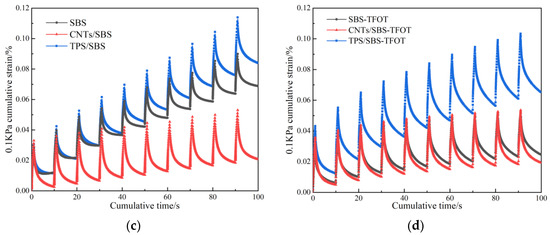
Figure 5.
Creep and recovery curves under two stress conditions before and after aging for three asphalt samples: (a) 3.2 kPa-origin; (b) 0.1 kPa-origin; (c) 3.2 kPa-TFOT; (d) 0.1 kPa-TFOT.
The MSCR test results before and after the aging of the three modified asphalts were analyzed, as shown in Figure 6a,b. R is the strain recovery rate. The higher the R value, the smaller the permanent deformation of the asphalt after stress unloading, and the smaller the possibility of rutting on the road surface. Jnr is the irrecoverable creep compliance. The smaller the Jnr, the smaller the irrecoverable residual strain of the asphalt after stress unloading, indicating that the rutting depth of the pavement was smaller [33]. Under both stress conditions, the strain recovery rate of CNTs/SBS-HVMA before and after aging was higher than those of SBS-HVMA and TPS/SBS-HVMA. The addition of CNTs to asphalt significantly improved the high-temperature rutting resistance of asphalt. The Jn analysis of the three asphalts showed that the Jnr value of the asphalt generally increased with increasing stress, indicating that the shear stress had an effect on the high-temperature deformation resistance of the asphalt. The Jnr values of the three asphalts after aging all increased, indicating that the light components of the asphalt volatilized during the aging process, and the viscous flow ability between the colloids decreased. The Jnr values of CNTs/SBS-HVMA at both strains before and after aging were smaller than those of the other two asphalts, indicating that CNTs functioned as a short fiber reinforcement and anchor between the SBS molecules, increased the bond strength of the asphalt system, and improved its high-temperature rutting resistance.
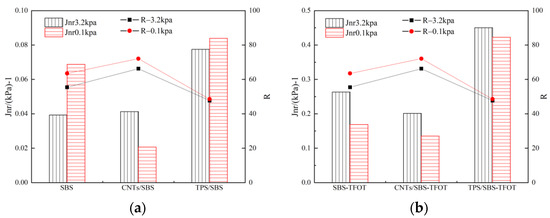
Figure 6.
R and Jnr before and after aging for three asphalt samples: (a) before aging; (b) after aging.
3.4. Low-Temperature Rheological Test Result
The creep stiffness modulus S and the rate of change m of the stiffness modulus with time were through a bending beam creep test (Figure 7). The greater the stiffness modulus S of the asphalt, the stronger the brittleness of the asphalt, and the higher the susceptibility of the asphalt to cracking and failure. The smaller the S value, the higher the low-temperature flexibility of the asphalt and the higher its low-temperature crack resistance. As the creep rate m of the asphalt increased and the temperature decreased, the shrinkage strain produced by the material reduced the stiffness modulus S of the asphalt, thereby reducing the tensile stress and the possibility of asphalt cracking.
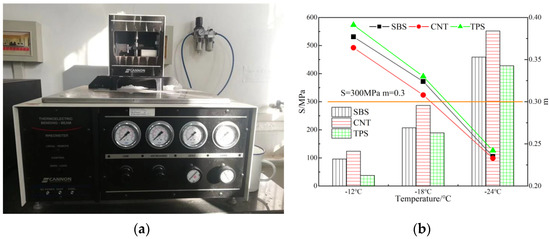
Figure 7.
Flexural creep stiffness test: (a) Bending beam rheometer BBR; (b) experimental results for three asphalts.
Generally, the higher the stiffness modulus S of the asphalt, the higher the brittleness of the asphalt, and the higher the susceptibility of the asphalt to cracking failure. The smaller the S value of the asphalt, the higher the low-temperature flexibility of the asphalt, and the higher its low-temperature crack resistance. Creep rate was characterized by the stress relaxation ability of the asphalt at low temperatures. At the same test temperature, the smaller the S value, the higher the creep rate, and the better the low-temperature performance of the asphalt. The test results are shown in Figure 7. With decreasing test temperature, the stiffness modulus of the three kinds of asphalts increased, and the creep rates decreased. With decreasing temperature, the asphalt specimen became hard and brittle, the stress relaxation performance decreased, and the low-temperature crack resistance of the asphalt declined. The Strategic Highway Response Program limits the creep stiffness S of the asphalt material to within 300 MPa and considers that a larger m value corresponds to better performance, and the m value should not be less than 0.30 (Figure 7b). TPS/SBS-HVMA exhibited the best low-temperature performance, followed by SBS-HVMA, then CNTs/SBS-HVMA (Figure 7). At the low temperatures of −12 °C and −18 °C, the three kinds of asphalt met the requirements of S ≤ 300 MPa and creep rate m ≥ 0.3. The CNT addition improved the high-temperature performance of the modified asphalt without significantly reducing its low-temperature performance.
3.5. Asphalt Mixture Performance Test Result
According to the evaluation requirements of the high-temperature stability of asphalt pavements, two indicators rutting depth and creep slope were used to characterize the stability of asphalt pavements. Using the test data curve with a relatively long straight line, the relationship between the rut depth and loading times is linearly regressed to obtain [34].
The low-temperature bending failure strain of the modified asphalt mixture in the severe cold region in winter should be ≥3000 με, and the higher the bending strain at failure, the higher the low-temperature crack resistance [35].
The analysis of the data from the Hamburg rutting test (Table 5) and the Hamburg rutting curve (Figure 8) revealed that the rutting depths of the three high-viscosity asphalt mixtures after 20,000 rolling cycles were small, and there was no significant peeling curve, indicating that the three kinds of asphalt mixtures had a relatively low rut depths, good high-temperature stability, and resistance to water damage. As shown in the table, the maximum rutting depths of the three asphalt mixtures increased as follows: SBS-HVMA < CNTs/SBS-HVMA < TPS/SBS-HVMA; however, the rutting depths of CNTs/SBS-HVMA and SBS-HVMA were almost the same. As shown in the rutting curves, the rutting depth and creep slope of TPS/SBS-HVMA were larger than those of SBS-HVMA and CNTs/SBS-HVMA. The creep slope represents the slope of the curve in the creep stage and reflects the deformation rate of the asphalt mixture in the creep stage under combined hydrothermal and loading conditions. The smaller the creep slope value, the lower the deformation rate and the higher the high-temperature stability [36]. The creep slope of CNTs/SBS-HVMA was smaller than those of SBS-HVMA and TPS/SBS-HVMA by 5% and 28%, respectively, indicating that CNTs/SBS-HVMA exhibited the highest high-temperature rutting resistance under the same conditions.

Table 5.
Hamburg Rutting Test Results.
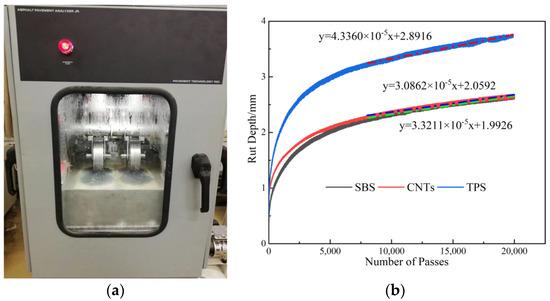
Figure 8.
Hamburg rut test: (a) APA Pavement Analyzer; (b) Asphalt Mix Hamburg Rutting Curve.
Among the three modified asphalts, TPS/SBS exhibited the highest failure strain, followed by SBS-HVMA, then CNTs/SBS (Table 6). The TPS-modified asphalt mixture exhibited the highest low-temperature cracking resistance, which was higher than those of SBS-HVMA and CNTs/SBS-HVM. The failure strain value of CNTs/SBS-HVMA εB was 5% lower than that of SBS-HVMA, indicating that CNT addition had a slight impact on the low-temperature performance of the asphalt; as the CNT addition increased the stiffness modulus of the asphalt mixture, which affected its stress relaxation ability in a low-temperature environment, thereby reducing the low-temperature crack resistance of the mixture, but it had a little effect on its failure strain [35]. The CNT-modified abstract still met the requirements for a low-temperature bending strain. This showed that CNT addition improved the high-temperature performance of asphalt, but had little effect on the low-temperature performance, and the mixture still had a good low-temperature crack resistance.

Table 6.
Low temperature bending test results.
4. Conclusions
To make up for the lack of performance of traditional SBS-HVMA, a high-viscosity composite modified asphalt with excellent performance was developed. CNTs/SBS-HVMA were prepared by combining two surfaces modified by CNT and SBS modifiers, and the most common, SBS-HVMA and TPS-HVMA, were used as comparison samples. The macroscopic properties, flow characteristics, high- and low-temperature properties, and asphalt mixture properties were studied, and the following main conclusions were drawn:
- (1)
- The analysis of the segregation softening point and viscosity test revealed that CNTs/SBS-HVMA had higher storage stability and better workability than the other two asphalts.
- (2)
- DSR frequency sweep and MSCR tests revealed that CNT addition improved the anti-aging performance of SBS-HVMA, played a short fiber reinforcement role between the asphalt and the SBS, increased the bond strength of the asphalt system, and enhanced the high-temperature deformation resistance of the asphalt.
- (3)
- BBR and low-temperature trabecular bending rheological tests revealed that CNT addition had little effect on the low-temperature properties and improved the high-temperature properties of the asphalt. The asphalt and asphalt mixture still exhibited good low-temperature crack resistance.
- (4)
- The Hamburg rutting test revealed that the high-temperature rutting resistance of CNTs/SBS-HVMA was 7% and 28%, respectively, higher than those of SBS-HVVMA and TPS/SBS-HVMA, respectively. This shows that CNT addition improved the high-temperature performance of the asphalt mixture while reducing the amount of modifier in SBS-HVMA.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C. and T.Z.; Methodology, Z.H.; Software, Z.H. and Z.Y.; Validation, T.Z.; Investigation, Z.H. and Z.Y.; Resources, H.W. and Z.Y.; Data curation, J.C., Z.H. and H.W.; Writing—original draft, Z.H.; Writing—review & editing, H.W.; Supervision, H.W. and T.Z.; Project administration, J.C.; Funding acquisition, J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kiselev, A.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. The effect of two-phase mixing on the functional and mechanical properties of TPS/SBS-modified porous asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Geng, J.; Xia, C.; He, L.; Liu, Z. A review of phase structure of SBS modified asphalt: Affecting factors, analytical methods, phase models and improvements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 294, 123610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, K.; Fan, Y. Rheological characterization of storage stable SBS-modified asphalts. Polym. Test. 2002, 21, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Isacsson, U. Rheological characterization of styrene-butadiene-styrene copolymer modified bitumens. Constr. Build. Mater. 1997, 11, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, A.; McNally, T. Polystyrene and asphaltene micelles within blends with a bitumen of an SBS block copolymer and styrene and butadiene homopolymers. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2003, 281, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, F.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Ge, J.; Wang, H.; Qiu, W.; Feng, W. 4D Printed untethered self-propelling soft robot with tactile perception: Rolling, racing, and exploring. Matter 2021, 4, 3313–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tan, Y.; Meng, L. Application study on high modulus asphalt concrete in bridge pavement. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 243–249, 4244–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, L.; Guo, M.; Zhang, L. Influence of crumb rubber and tafpack super on performances of SBS modified porous asphalt mixtures. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 20, S196–S216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuo, G.; Yuzhi, L.; Ping, Z. Research on road performance of SBS and TPS composite modified asphalt mixture. Sino-Foreign Highw. 2013, 33, 216–218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Hu, C. Preparation and properties of high viscosity modified asphalt. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Xin, X.; Fan, W.; Wang, H.; Ren, S.; Shi, J. Effects of polymerized sulfur on rheological properties, morphology and stability of SBS modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zani, L.; Giustozzi, F.; Harvey, J. Effect of storage stability on chemical and rheological properties of polymer-modified asphalt binders for road pavement construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Gao, Y.; Yao, H.; Cao, D.; Pei, G.; He, B.; Duan, K.; Zhou, W. Preparation and Performance Analysis of High-Viscosity and Elastic Recovery Modified Asphalt Binder. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 6070685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, P.; Fan, W.; Yang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Ouyang, J. Facile preparation and application performance evaluation of SBS/C9 petroleum resin blends as modifier for high viscosity asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, A.; Ziari, H.; Amini, A. Influence of carbon nanotubes on performance properties and storage stability of SBS modified asphalt binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Dong, Z.J.; Tan, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.Y. Effect of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the performance of styrene–butadiene–styrene copolymer modified asphalt. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsantilis, L.; Dalmazzo, D.; Baglieri, O.; Santagata, E. Effect of SBS molecular structure on the rheological properties of ternary nanomodified bituminous binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 222, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Yao, Z.; Shi, J.; Liang, M.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yao, K. Rheological properties, microstructure and aging resistance of asphalt modified with CNTs/PE composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, F.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, W. Graphene-based chiral liquid crystal materials for optical applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 7, 2146–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yue, M.; Xiong, Y.; Yue, J. Experimental study on mechanism, aging, rheology and fatigue performance of carbon nanomaterial/SBS-modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashish, P.K.; Singh, D. High- and Intermediate-Temperature Performance of Asphalt Binder Containing Carbon Nanotube Using Different Rheological Approaches. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 30, 04017254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziari, H.; Farahani, H.; Goli, A.; Galooyak, S.S. The investigation of the impact of carbon nano tube on bitumen and HMA performance. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 2102–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziari, H.; Rahim-of, K.; Fazilati, M.; Goli, A.; Farahani, H. Evaluation of different conditions on the mixing bitumen and carbon nano-tube. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2012, 12, 12–53. [Google Scholar]
- Amirkhanian, A.N.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Evaluation of high temperature rheological characteristics of asphalt binder with carbon nano particles. J. Test. Eval. 2010, 39, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Amirkhanian, A.N.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Characterization of unaged asphalt binder modified with carbon nano particles. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2011, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- JTG E20-2011; Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Zhang, D.; Birgisson, B.; Luo, X.; Onifade, I. A new short-term aging model for asphalt binders based on rheological activation energy. Mater. Struct. 2019, 52, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.R.M.; You, Z.; Yang, X.; Heiden, P.A. Quantification of physicochemical properties, activation energy, and temperature susceptibility of foamed asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 153, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Lin, T.; Zhu, X.; Cao, L. Calculation and evaluation of activation energy as a self-healing indication of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 95, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lin, J.T.; Pang, L.; Lei, M.; Jenkins, K.; Wu, S.P. Study on the Viscoelastic Performance of Asphalt Mixture Based on Dynamic Modulus. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 753–755, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Cui, H.Z.; Wang, W.L. Visco-Elasticity of Asphalt Mixture under Broad Temperature and Frequency. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 838–841, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.; Ahmad, N.; Nasir, M.A.; Hafeez, M.; Rafi, J.; Zaidi, S.B.A.; Haroon, W. Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) in Asphalt Binder: Homogeneous Dispersion and Performance Enhancement. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, A.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. Research on high temperature performance of asphalt pavement on in-service expressway based on Hamburg rutting test. Zhongwai Highw. 2020, 40, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, X.B.; Li, X.M.; Wei, D.B. Research on Rubber/SBS Modified Asphalt by MSCR Test. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 557–559, 1066–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.J.; Chen, H.B.; Zhang, J.Y. Research on Crack Resistance Evaluation of Asphalt Mixture at Low Temperature. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 753–755, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Y.; Tan, Y.Q.; Dong, Y.M.; Li, E.G. Rutting Resistance Property of Warm Recycled Asphalt Mixture. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 204–208, 3749–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).