Organic Carbon Content in Fractions of Soils Managed for Soil Fertility Improvement in Sub-Humid Agroecosystems of Kenya
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Characteristics
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Soil Samples Collection
2.4. Rainfall Characteristics at the Experimental Site
2.5. Laboratory Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Organic Carbon Concentration in Soil Sampled at 0 to 5 cm Depth
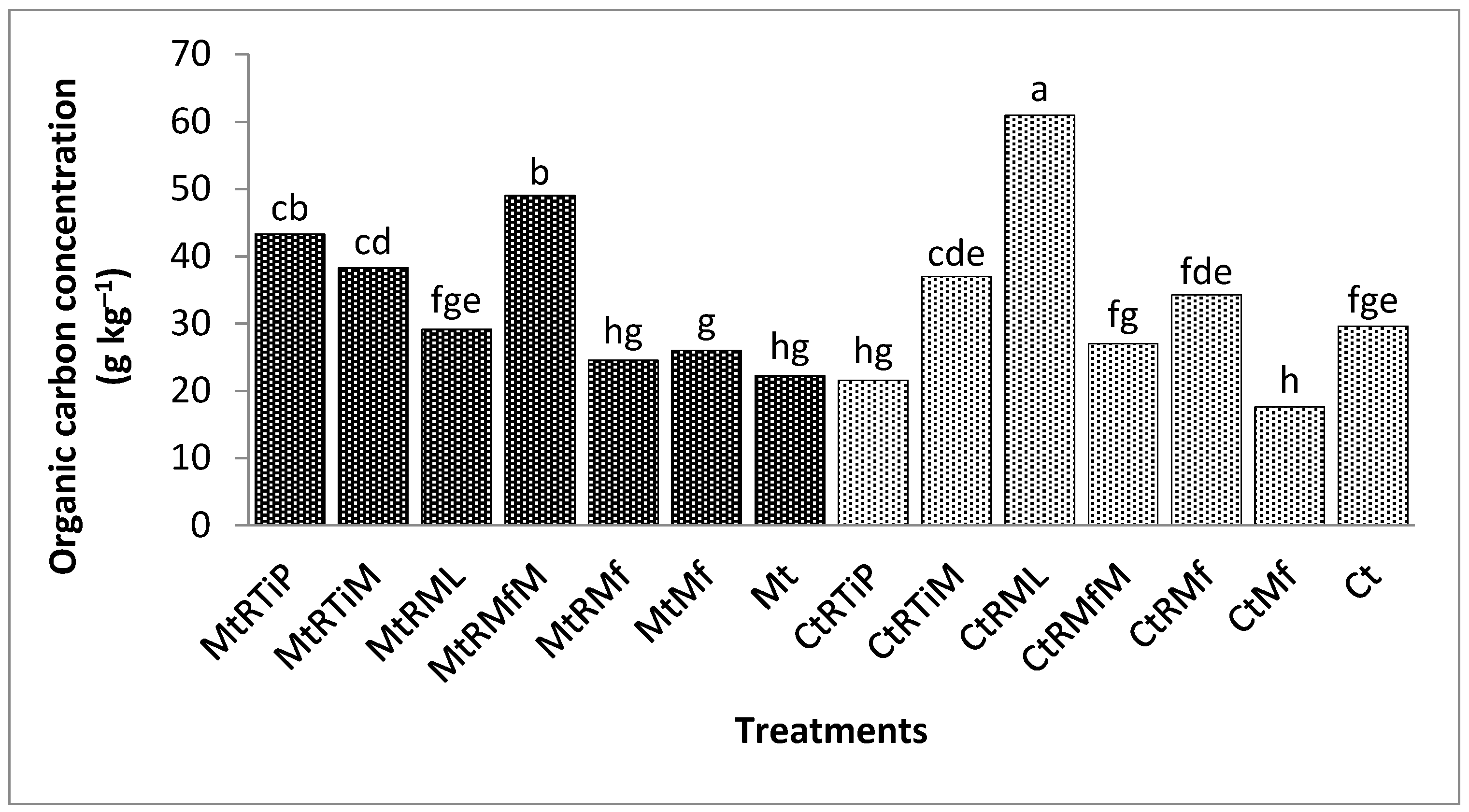
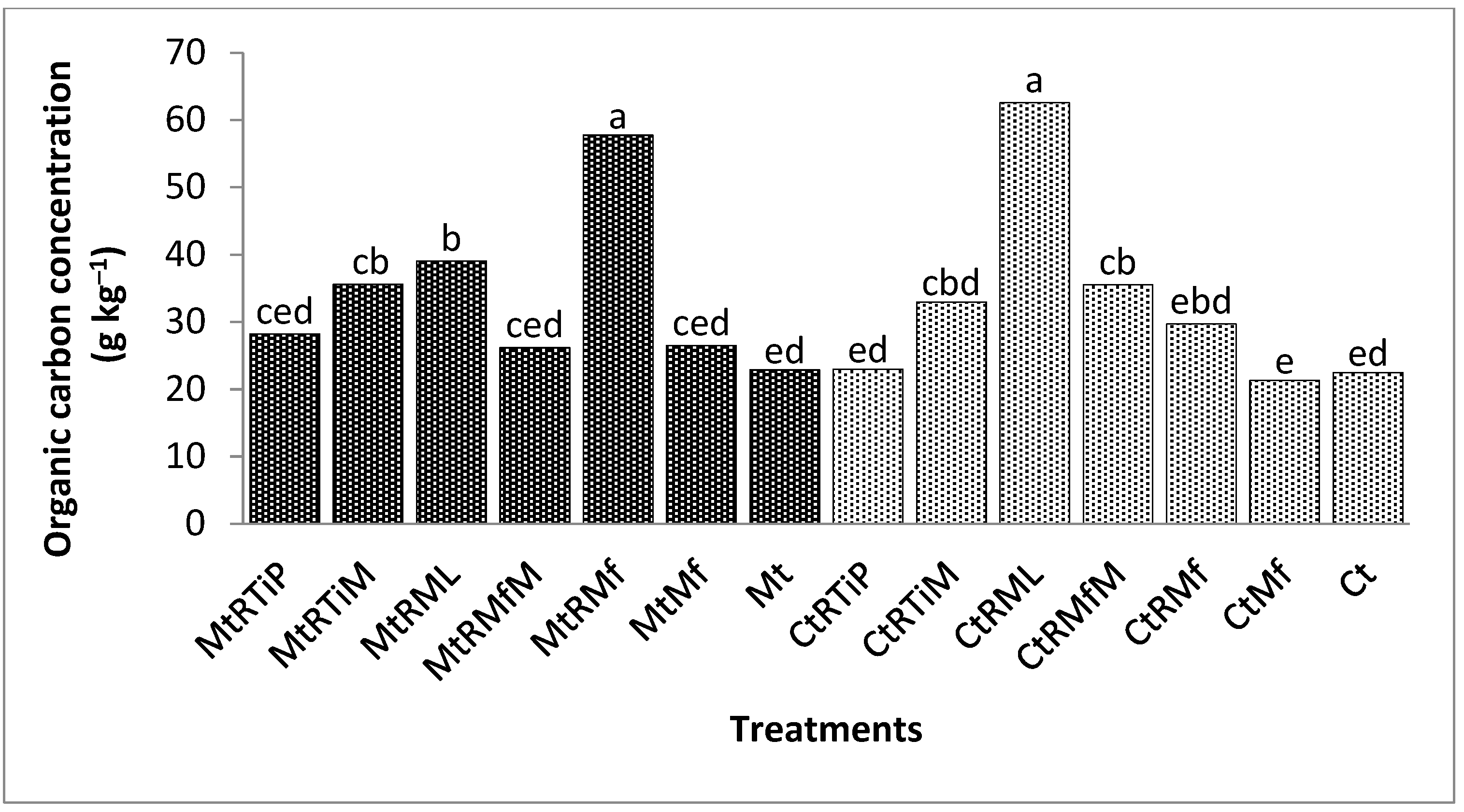
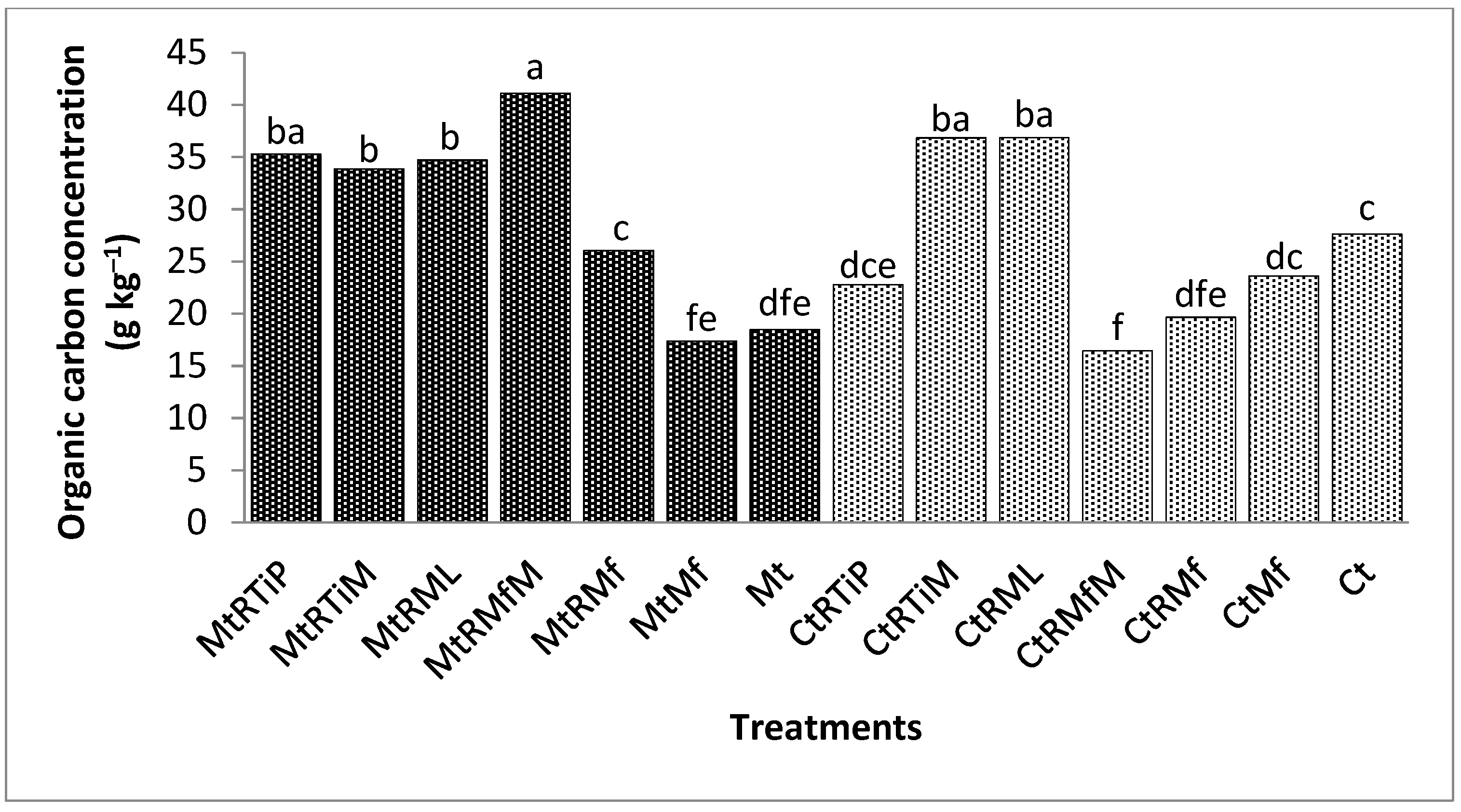
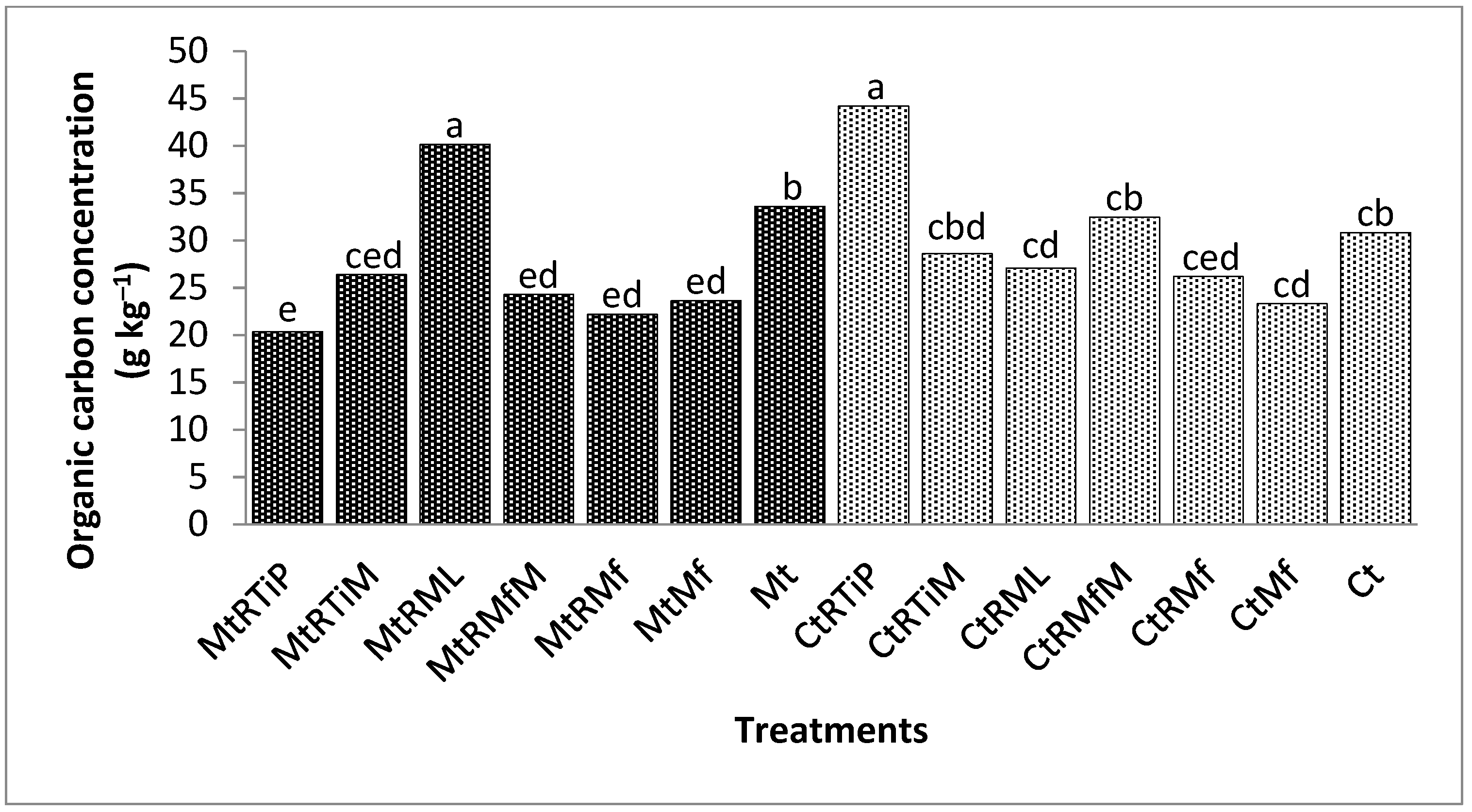
3.1.1. The Concentration of Organic Carbon in the 1.7 mm Fraction
3.1.2. Organic Carbon Concentration in the 500 µm Fraction
3.1.3. The Concentration of Organic Carbon in the 250 µm Fraction
3.1.4. The Concentration of Organic Carbon in the 90 µm Fraction
3.1.5. The Concentration of Organic Carbon in the 75 µm Fraction
3.2. Organic Carbon Concentration in Soils Sampled at 5 to 15 cm Depth
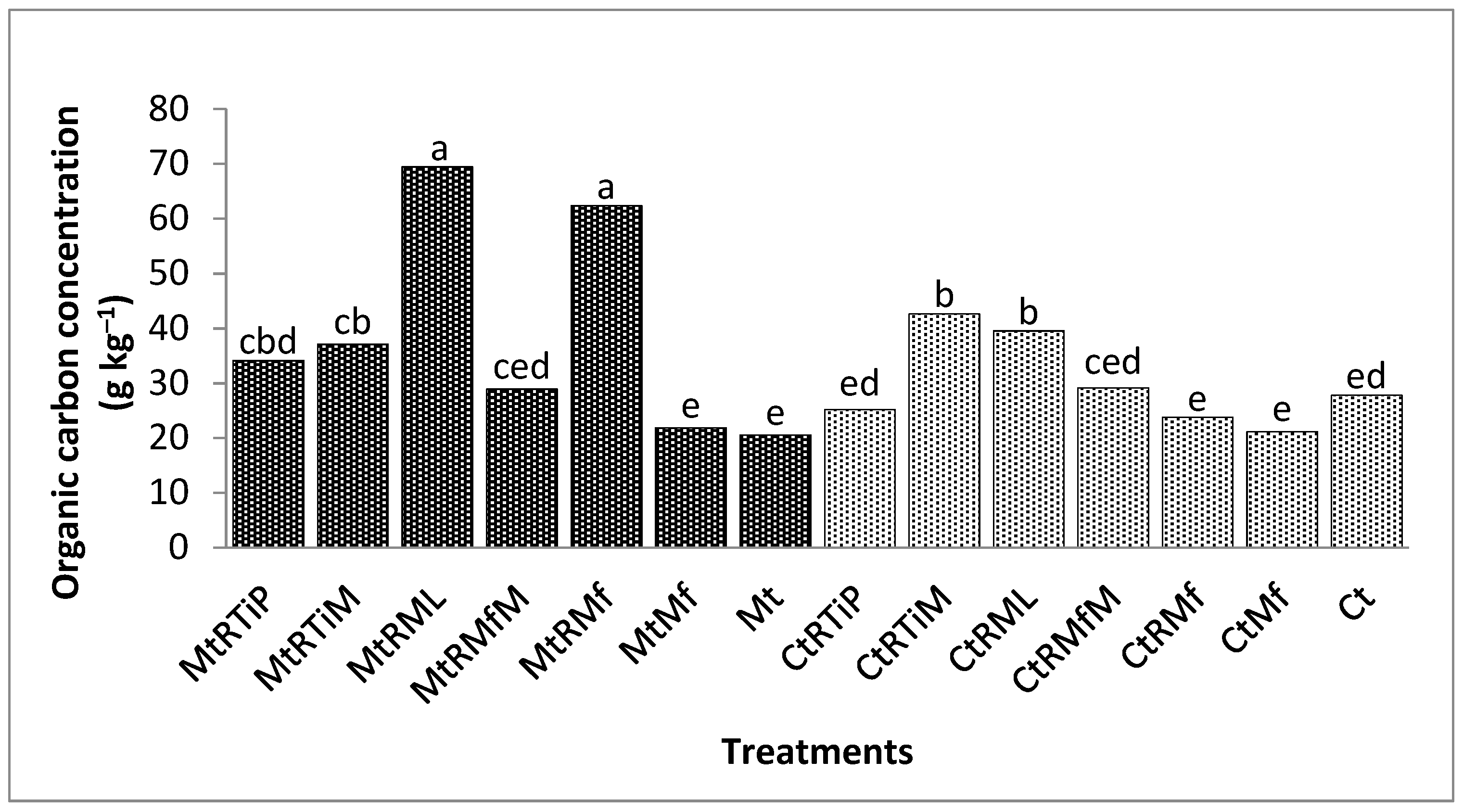
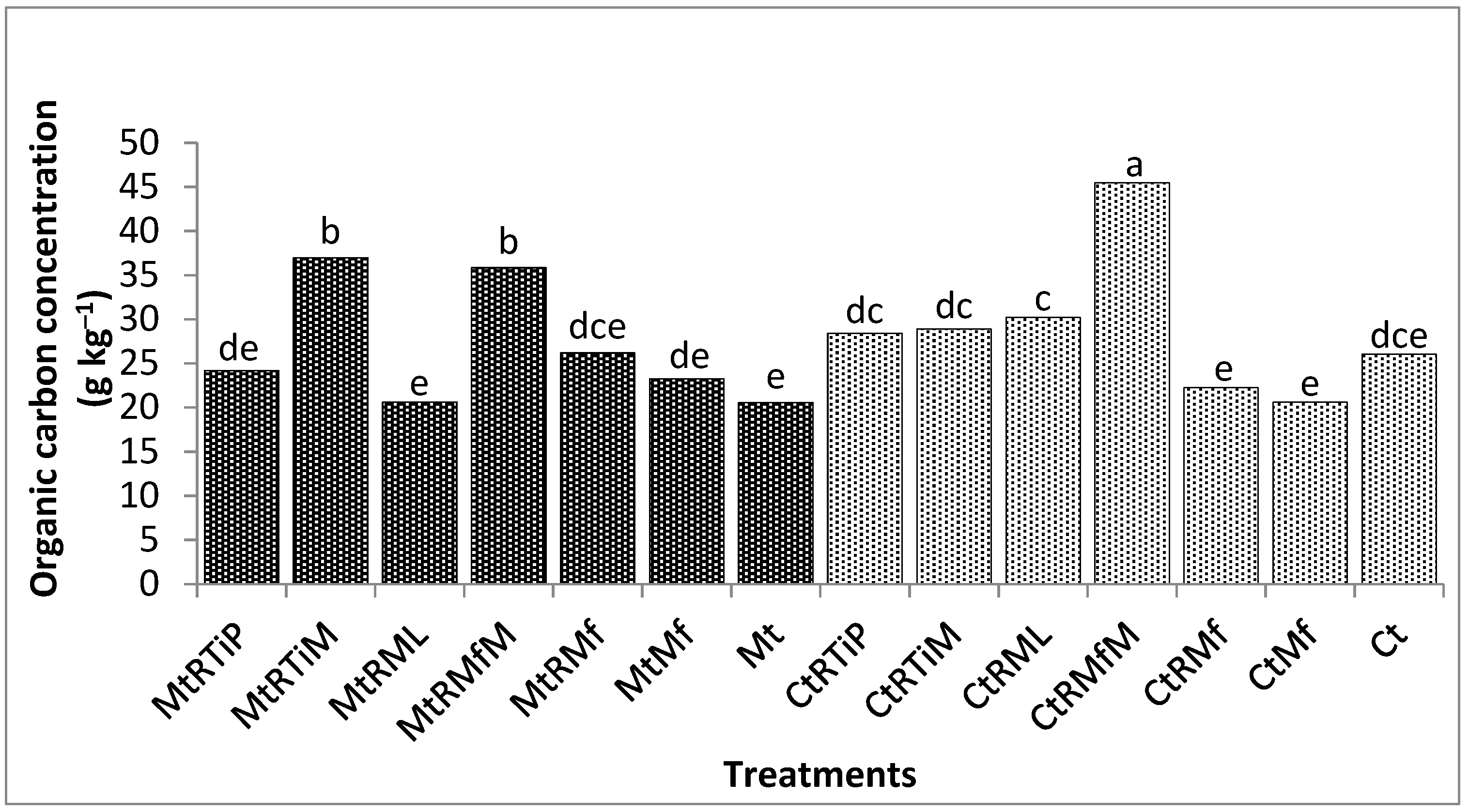
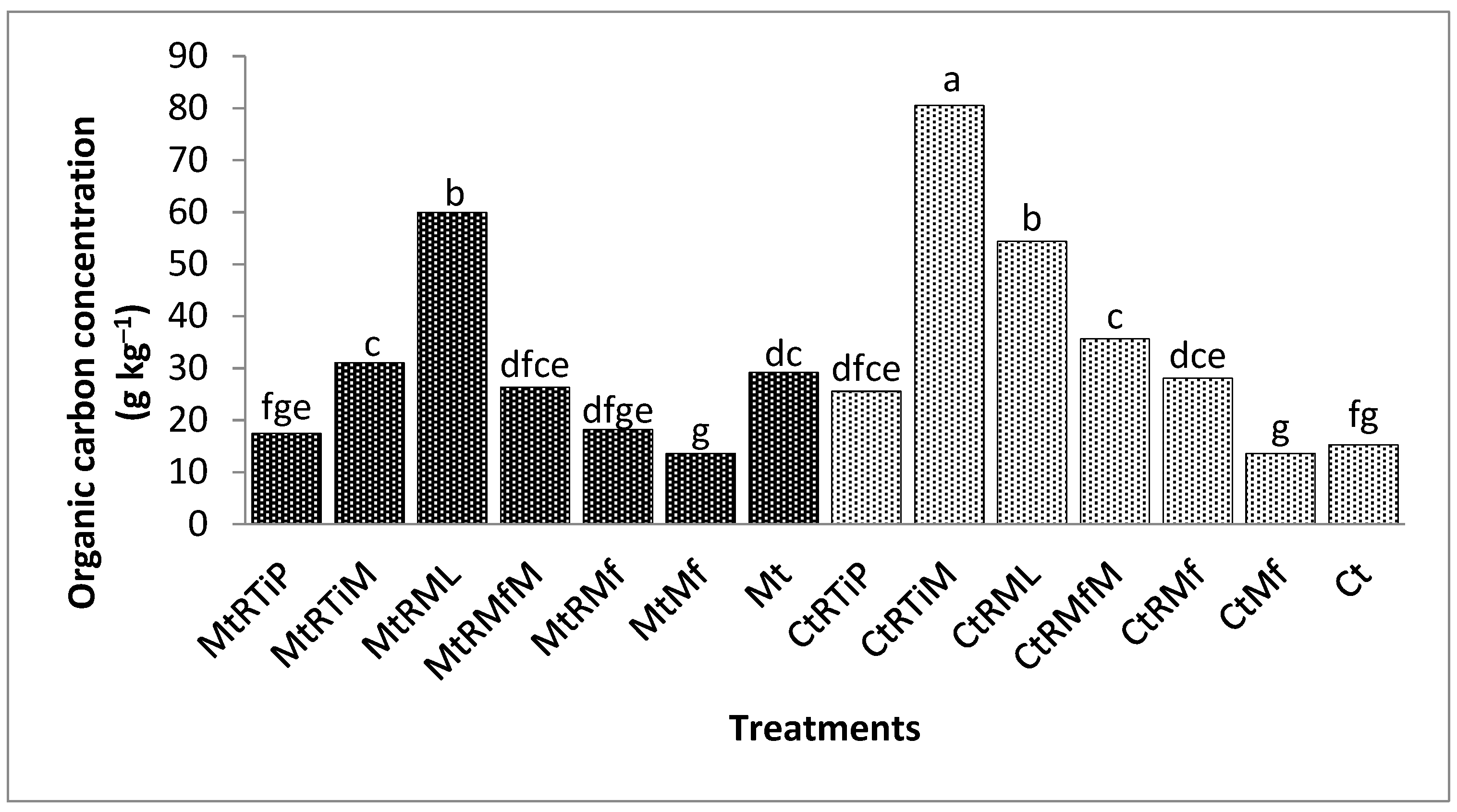
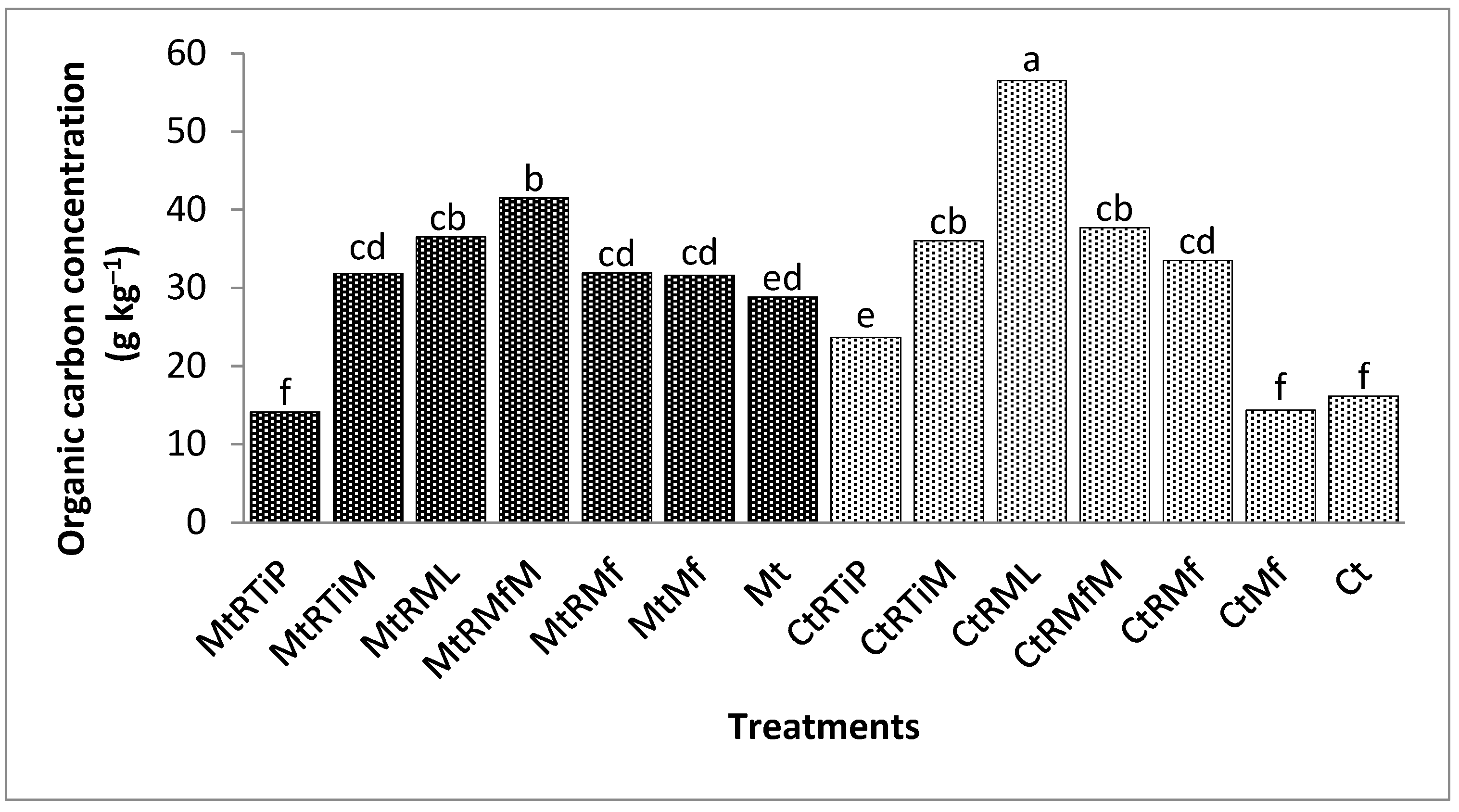
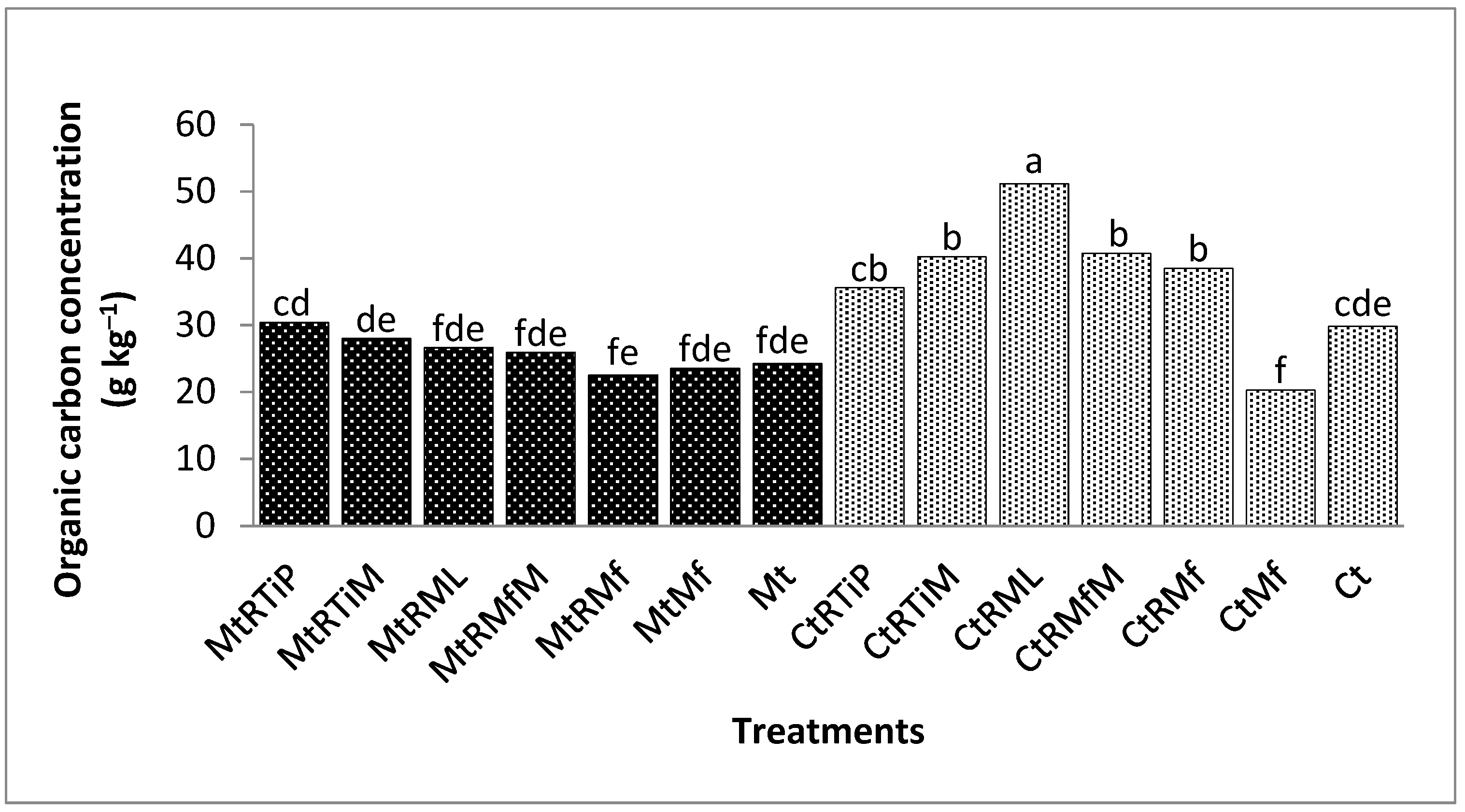
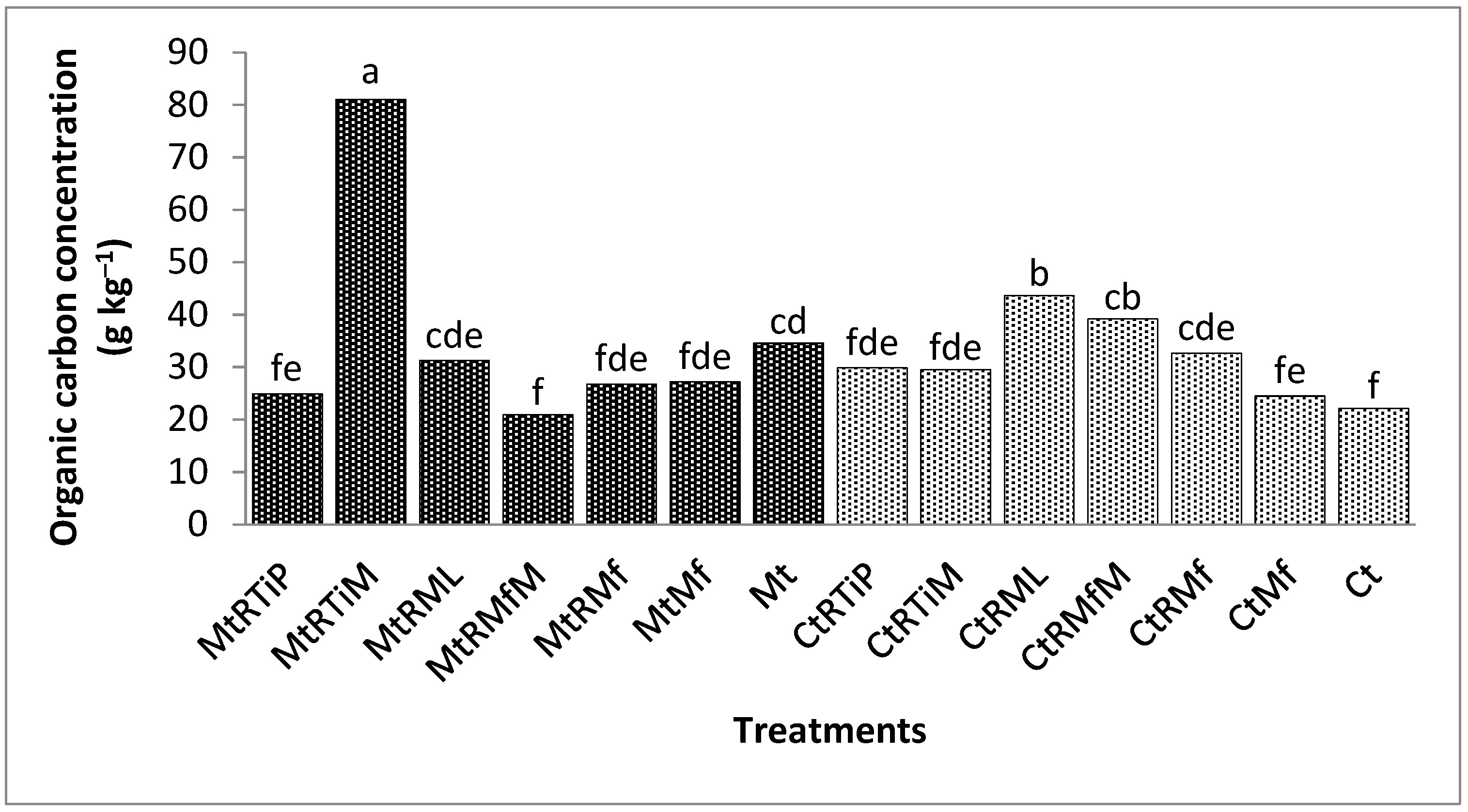
3.2.1. The Concentration of Organic Carbon in the 1.7 mm Fraction
3.2.2. The Concentration of Organic Carbon in the 500 µm Fraction
3.2.3. The Concentration of Organic Carbon in the 250 µm Fraction
3.2.4. The Concentration of Organic Carbon in the 90 µm Fraction
3.2.5. The Concentration of Organic Carbon in the 75 µm Fraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zingore, S.; Mutegi, J.; Agesa, B.; Tamene, L.; Kihara, J. Soil degradation in sub Saharan Africa and crop production options for soil rehabilitation. Better Crops 2015, 99, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Adekiya, A.O. Green manures and poultry feather effects on soil characteristics, growth, yield, and mineral contents of tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 257, 108721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walter, A.; Chris, J.; Kadambot, H.M.S. Addressing the yield gap in rainfed crops: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, W. Closing the gap between actual and potential yield of rainfed wheat. The impacts of environment, management and cultivar. Field Crop. Res. 2010, 116, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanyenji, G.M.; Oluoch-Kosura, W.; Onyango, C.M.; Ng’Ang’A, S.K. Prospects and constraints in smallholder farmers’ adoption of multiple soil carbon enhancing practices in Western Kenya. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, C.J.; Chemarum, A.K.; Vedeld, P.O.; Petursson, J.G. Old wine, new bottles? Investigating the differential adoption of ‘climate-smart’ agricultural practices in western Kenya. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 56, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibet, E.; Musafiri, C.M.; Kiboi, M.N.; Macharia, J.; Ng’Etich, O.K.; Kosgei, D.K.; Mulianga, B.; Okoti, M.; Zeila, A.; Ngetich, F.K. Soil Organic Carbon Stocks under Different Land Utilization Types in Western Kenya. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Eyre, J.X.; Wilkus, E.; de Voil, P.; Broad, I.; Rodriguez, D. 3D characterization of crop water use and the rooting system in field agronomic research. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 202, 107409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Li, N.; Zare, E.; Wang, J.; Triantafilis, J. Mapping cation exchange capacity using a quasi-3d joint inversion of EM38 and EM31 data. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 200, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githongo, M.; Kiboi, M.; Ngetich, F.; Musafiri, C.; Muriuki, A.; Fliessbach, A. The effect of minimum tillage and animal manure on maize yields and soil organic carbon in sub-Saharan Africa: A meta-analysis. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omenda, J.A.; Ngetich, K.F.; Kiboi, M.N.; Mucheru-Muna, M.W.; Mugendi, D.N. Soil organic carbon and acid phosphatase enzyme activity response to phosphate rock and organic inputs in acidic soils of central highlands of Kenya in maize. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2019, 30, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozlu, E.; Gozukara, G.; Acar, M.; Bilen, S.; Babur, E. Field-Scale Evaluation of the Soil Quality Index as Influenced by Dairy Manure and Inorganic Fertilizers. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merante, P.; Dibari, C.; Ferrise, R.; Sánchez, B.; Iglesias, A.; Lesschen, J.P.; Kuikman, P.; Yeluripati, J.; Smith, P.; Bindi, M. Adopting soil organic carbon management practices in soils of varying quality: Implications and perspectives in Europe. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.; Ning, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Lal, R. Crop yield and soil carbon responses to tillage method changes in North China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 163, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, T.; Bragazza, L.; Levasseur, C.; Libohova, Z.; Sinaj, S. Long-term soil organic carbon dynamics in temperate cropland-grassland systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 305, 107184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenu, C.; Angers, D.A.; Barré, P.; Derrien, D.; Arrouays, D.; Balesdent, J. Increasing organic stocks in agricultural soils: Knowledge gaps and potential innovations. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 188, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarecki, M.; Grant, B.; Smith, W.; Deen, B.; Drury, C.; VanderZaag Qian, A.; Yang B., J.; Wagner-Riddle, C. Long-term trends in corn yields and soil carbon under diversified crop rotations. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, A.; Xu, H.; Shao, X.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Murphy, D.V. Carbon and nitrogen mineralisation in relation to soil Particle-Size fractions after 32 years of chemical and manure application in a continuous cropping system. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152521. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Hu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Tao, B.; Meng, Y. Short-term responses of soil organic carbon and carbon pool man-agement index to different annual straw return rates in a rice–wheat cropping system. Catena 2015, 135, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaura, G.; Kiboi, M.; Mugwe, J.; Nicolay, G.; Bett, E.; Muriuki, A.; Musafiri, C.; Ngetich, F. Economic evaluation and socioeconomic drivers influencing farmers’ perceptions on benefits of using organic inputs technologies in Upper Eastern Kenya. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, E.; Kiboi, M.; Gian, N.; Muriuki, A.; Musafiri, C.; Ngetich, F. Uptake of integrated soil fertility management technologies in heterogeneous smallholder farms in sub-humid tropics. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.S.; Kim, K.H.; Das, S.; Uchimiya, M.; Jeon, B.H.; Kwon, E.; Szulejko, J.E. A review on the role of organic inputs in maintaining the soil carbon pool of the terrestrial ecosystem. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 167, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koishi, A.; Bragazza, L.; Maltas, A.; Guillaume, T.; Sinaj, S. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil organic matter quantity and quality in conventional cropping systems in Switzerland. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiboi, M.N.; Ngetich, K.F.; Mugendi, D.N.; Muriuki, A.; Adamtey, N.; Fliessbach, A. Microbial biomass and acid phosphomonoesterase activity in soils of the Central Highlands of Kenya Geoderma Regional. Geoderma Reg. 2018, 15, e00193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Hedlund, K.; Jackson, L.E.; Kätterer, T.; Lugato, E.; Thomsen, I.K.; Jørgensen, H.B.; Isberg, P.-E. How does tillage intensity affect soil organic carbon? A systematic review. Environ. Évid. 2017, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villamil, M.B.; Nafziger, E.D. Corn residues, tillage and nitrogen rate effects on soil properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 151, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alhameid, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Kumar, S.; Sexton, P.; Schumacher, T. Soil Organic Carbon Changes Impacted by Crop Rotational Diversity under No-Till Farming in South Dakota, USA. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogužas, V.; Mikučionienė, R.; Šlepetienė, A.; Sinkevičienė, A.; Feiza, V.; Steponavičienė, V.; Adamavičienė, A. Long-term effect of tillage systems, straw and green manure combinations on soil organic matter. Zemdirb. -Agric. 2015, 102, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabiri, V.; Raiesi, F.; Ghazavi, M.A. Six years of different tillage systems affected aggregate-associated SOM in a semi-arid loam soil from Central Iran. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 154, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchmann, H.; Haberhauer, G.; Kandeler, E.; Sessitsch, A.; Gerzabek, M. Effects of level and quality of organic matter input on carbon storage and biological activity in soil: Synthesis of a long-term experiment. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, H.S.; Datta, A.; Sharma, P.C.; Kumar, V.; Yadav, A.K.; Choudhary, M.; Choudhary, V.; Gathala, M.K.; Sharma, D.K.; Jat, M.L.; et al. Assessing soil properties and nutrient availability under conservation agriculture practices in a reclaimed sodic soil in cereal-based systems of North-West India. Ach. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanderman, J.; Creamer, C.; Baisden, W.T.; Farrell, M.; Fallon, S. Greater soil carbon stocks and faster turnover rates with increasing agricultural productivity. Soil 2017, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ercoli, L.; Masoni, A.; Mariotti, M.; Pampana, S.; Pellegrino, E.; Arduini, I. Effect of preceding crop on the agronomic and economic performance of durum wheat in the transition from conventional to reduced tillage. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 82, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercoli, L.; Schüßler, A.; Arduini, I.; Pellegrino, E. Strong increase of durum wheat iron and zinc content by field-inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at different soil nitrogen availabilities. Plant Soil 2017, 419, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, L.; Munkholm, L.J. Eleven Years’ effect of conservation practices for temperate sandy loams: II. Soil pore char-acteristics. J. Soil Sci. Ame. 2017, 81, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehy, J.; Regina, K.; Alakukku, L.; Six, J. Impact of no-till and reduced tillage on aggregation and aggregate-associated carbon in Northern European agro-ecosystems. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 150, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.; Solutions, L. Carbon Sequestration Potential on Agricultural Lands: A Review of Current Science and Available Practices; National Sustainable Agriculture Coalition: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Feng, W.; Luo, Y.; Baldock, J.; Wang, E. Soil organic carbon dynamics jointly controlled by climate, carbon inputs, soil properties and soil carbon fractions. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 4430–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, J.V.N.S.; Rao, C.S.; Srinivas, K.; Jyothi, C.N.; Venkateswarlu, B.; Ramachandrappa, B.K.; Dhanapal, G.N.; Ravichandra, K.; Mishra, P.K. Effect of ten years of reduced tillage and recycling of organic matter on crop yields, soil organic carbon and its fractions in Alfisols of semiarid tropics of southern India. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 156, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, G.; Pellegrino, E.; Moscatelli, M.C.; Ercoli, L. Long-term conservation tillage and nitrogen fertilisation effects on soil aggregate distribution, nutrient stocks and enzymatic activities in bulk soil and occluded micro-aggregates. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 196, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musafiri, C.M.; Macharia, J.M.; Kiboi, M.N.; Ng’etich, O.K.; Shisanya, C.A.; Okeyo, J.M.; Mugendi, D.N.; Okwuosa, E.A.; Ngetich, F.K. Soil greenhouse gas fluxes from maize cropping system under different soil fertility management technologies in Ken-ya. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 301, 107064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bationo, A.; Kihara, J.; Vanlauwe, B.; Waswa, B.; Kimetu, J. Soil organic carbon dynamics, functions and management in West African agro-ecosystems. Agric. Syst. 2007, 94, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tittonell, P.; Corbeels, M.; van Wijk, M.T.; Vanlauwe, B.; Giller, K.E. Combining organic and mineral fertilisers for integrated soil fertility management in smallholder farming systems of Kenya: Explorations using the Crop-Soil model FIELD. J. Agron. 2007, 100, 1511–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaetzold, R.; Schmidt, H.; Hornet, Z.B.; Shisanya, C.A. Natural Conditions and Farm Information. Eastern Province. In Farm Management Handbook of Kenya, 2nd ed.; Ministry of Agriculture/GTZ: Nairobi, Kenya, 2007; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Fertilizer Use Recommendation Project (FURP). Description of First Priority Trial Site in the Various Districts; Embu District Kenya National Agricultural Research Laboratories: Nairobi, Kenya, 1987; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Ngetich, K.F.; Diels, J.; Shisanya, C.A.; Mugwe, J.N.; Mucheru-Muna, M.; Mugendi, D.N. Effects of selected soil and water conservation techniques on runoff, sediment yield and productivity under sub-humid and semiarid conditions in Kenya. Catena 2014, 121, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tilman, D.; Lambers, H.; Zhang, F.S. Plant diversity and over yielding: Insights from belowground facilitation of in-tercropping in agriculture. New Phyt. 2014, 203, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantappiè, M.; L’Abate, G.; Costantini, E.A.C. Factors influencing soil organic carbon stock variations in Italy during the last three decades. In Land Degradation and Desertification: Assessment, Mitigation and Remediation; Zdruli, P., Pagliai, M., Kapur, S., Cano, A.F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 435–466. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, R.; Seddaiu, G.; Orsini, R.; Steglich, E.; Roggero, P.P.; Francaviglia, R. Soil carbon dynamics and crop productivity as influenced by climate change in a rainfed cereal system under contrasting tillage using EPIC. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Elliott, E.T. Particulate Soil Organic-Matter Changes across a Grassland Cultivation Sequence. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods, 5.3; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Jing Tian, J.; Meersmans, J.; Fang, H.; Yang, H.; Lou, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Yi Zhou, Y.; Blagodatskaya, E.; et al. Functional soil organic matter fractions in response to long-term fertilisation in upland and paddy systems in South China. Catena 2018, 162, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cong, W.-F.; Hoffland, E.; Li, L.; Six, J.; Sun, J.-H.; Bao, X.-G.; Zhang, F.-S.; Van Der Werf, W. Intercropping enhances soil carbon and nitrogen. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinamhodzi, L.; Murwira, H.K.; Nyamangara, J. Effect of cotton—cowpea intercropping on C and N mineralisation patterns of residue mixtures and soil. Soil Res. 2009, 47, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.-F.; Van Ruijven, J.; Mommer, L.; De Deyn, G.; Berendse, F.; Hoffland, E. Data from: Plant species richness promotes soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in grasslands without legumes. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, B.S.; Singh, K.; Dheri, G.S.; Kumar, B. Carbon sequestration and soil carbon pools in a rice–wheat cropping system: Effect of long-term use of inorganic fertilisers and organic manure. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 128, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, S.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W. Stability and saturation of soil organic carbon in rice fields: Evidence from a long-term fertilisation experiment in subtropical China. J. Soils. Sediments 2013, 13, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Boot, C.M.; Denef, K.; Paul, E. The Microbial Efficiency-Matrix Stabilization (MEMS) framework integrates plant litter decomposition with soil organic matter stabilisation: Do labile plant inputs form stable soil organic matter? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasche, F.; Musyoki, M.K.; Röhl, C.; Muema, E.K.; Vanlauwe, B.; Cadisch, G. Lasting influence of biochemically contrasting organic inputs on abundance and community structure of total and proteolytic bacteria in tropical soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 74, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, S.S.; Nyborg, M.; Solberg, E.D.; McConkey, B.; Dyck, M.; Puurveen, D. Long-term straw management and N fer-tiliser rate effects on quantity and quality of organic C and N and some chemical properties in two contrasting soils in Western Canada. Biol. Fert. Soils. 2011, 47, 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Chen, H.; Gong, Y.; Yang, H.; Fan, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effect of 15years of manure and mineral fertilisers on enzyme activities in particle-size fractions in a North China Plain soil. Euro. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 60, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; He, P.; Qiu, S.; Jia, L.; Liu, M.; Jin, J.; Johnston, A.M. Long-term effects of potassium fertilisation and straw return on soil potassium levels and crop yields in north-central China. Field. Crop. Res. 2014, 169, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinola, B.; Salami, A. Effect of Herbicides Application on the Management of Tithonia in Maize (Zea mays). Greener J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 6, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montemurro, F.; Fiore, A.; Campanelli, G.; Tittarelli, F.; Ledda, L.; Canali, S. Organic Fertilization, Green Manure, and Vetch Mulch to Improve Organic Zucchini Yield and Quality. HortScience 2013, 48, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; He, Z.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, H.; Endale, D.M.; Schomberg, H.H. Water extractable soil organic carbon and ni-trogen affected by tillage and manure application. Soil Sci. 2011, 176, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellin, J.; Erenstein, O.; Beuchelt, T.; Camacho, C.; Flores, D. Maize stover use and sustainable crop production in mixed crop–livestock systems in Mexico. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 153, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urquiaga, S.; Alves, B.J.R.; Jantalia, C.P.; Boddey, R.M. Aplicación de técnicas de 13C en estudios de secuestro de carbono en el suelo. In IsoTopos Estables en Agroecosistemas Ampliacio ´n de Actas de las pri Meras Jornadas Argentinas Sobre el Empleo de iso ´topos Estables en Agroeco Sistemas Bahı ´a Blanca; Lázzari, M.A., Videla, C., Eds.; 2007; pp. 91–105. Available online: https://ediuns.com.ar/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/interior-isotopos.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2022).
- Galantini, J.A.; Suñer, L. Soil organic matter fractions: Analysis of Argentine soils. Agriscientia 2008, XXV, 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Benke, M.B.; Li, C.; Larney, F.J.; Beauchemin, K.A.; McAllister, T.A. Nitrogen transformations and greenhouse gas emissions during composting of manure from cattle fed diets containing corn dried distiller’s grains with solubles and con-densed tannins. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2011, 166–167, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udom, B.E.; Ogunwole, J.O. Soil organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus distribution in stable aggregates of an Ultisol under contrasting land use and management history. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhongaray, G.; Alvarez, R.; De Paepe, J.; Caride, C.; Cantet, R. Land use effects on soil carbon in the Argentine Pampas. Geoderma 2012, 192, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, M.A.; Pereira, M.W.; Vázquez, E.V.; Lado, M.; González, A.P. Depth distribution of soil organic carbon in an Oxisol under different land uses: Stratification indices and multifractal analysis. Geoderma 2017, 287, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margenot, A.J.; Paul, B.K.; Sommer, R.R.; Pulleman, M.M.; Parikh, S.J.; Jackson, L.E.; Fonte, S.J. Can conservation agriculture improve phosphorus (P) availability in weathered soils? Effects of tillage and residue management on soil P status after 9 years in a Kenyan Oxisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 166, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyawade, S.O.; Karanja, N.K.; Gachene, C.K.K.; Gitari, H.I.; Schulte-Geldermann, E.; Parker, M.L. Short-term dynamics of soil organic matter fractions and microbial activity in smallholder potato-legume intercropping systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 142, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherine, N.K. Long-term land management effects on soil properties and microbial populations in a maize-bean rota-tion at Kabete, Kenya. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 5, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, L.; Han, X. Impact of long-term Application of manure, crop residue, and mineral fer-tiliser on organic carbon pools and crop yields in a Mollisol. J. Soil Sediments 2014, 14, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Weijian, Z.W.; Yu, X.; Huang, Q. Effects of long-term fertilisation on corn productivity and its sustainability in an Ultisol of southern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 138, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, F.; Khan, I.; Ashraf, U.; Shahzad, T.; Hussain, S.; Shahid, M.; Abid, M.; Ullah, S. Effects of organic and inorganic manures on maize and their residual impact on soil physico-chemical properties. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Zhang, W.; Cong, R. Long-term fertilization effects on organic carbon fractions in a red soil of China. Catena 2014, 113, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Lou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Fang, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, M.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Response of soil organic matter fractions and composition of microbial community to long-term organic and mineral fertilisation. Biol. Fert. Soils. 2017, 53, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, S.Z.; Li, X.G.; Chen, Z.M.; Li, X.H.; Song, J.R.; Guggenberger, G. Long-term fertilisation and manuring effects on physically separated soil organic-matter pools under continuous wheat cropping at a rainfed semiarid site in China. J. Plant Nutri. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 689–697. [Google Scholar]
- Habte, M.; Gebrekidan, H.; Haile, W. Decomposition and nutrient release of selected green manure species at different stages of growth on Alisols at Areka, Southern Ethiopia. Int. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2013, 1, 30–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yao, P.; Zhao, N.; Liu, N.; Zhai, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, D.; Cao, W.; et al. Coupling life-cycle assessment and the RothC model to estimate the carbon footprint of green manure-based wheat production in China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 607–608, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolás, C.; Hernandez, T.; García, C. Organic amendments as strategy to increase organic matter in particle-size fractions of a semi-arid soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 57, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozlu, E.; Arriaga, F.J.; Bilen, S.; Gozukara, G.; Babur, E. Carbon Footprint Management by Agricultural Practices. Biology 2022, 11, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, C.; Blanco-Canqui, H.; DeClerck, F.; Gatere, L.; Grace, P. Conservation agriculture and ecosystem services: An overview. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 187, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endris, S. Combined Application of Phosphorus Fertilizer with Tithonia Biomass Improves Grain Yield and Agronomic Phosphorus Use Efficiency of Hybrid Maize. Int. J. Agron. 2019, 2019, 6167384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Francis, C.A.; Galusha, T.D. Does organic farming accumulate carbon in deeper soil profiles in the long term? Geoderma 2017, 288, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerzabek, M.H.; Haberhauer, G.; Kirchmann, H. Soil organic matter pools and carbon-13 natural abundances in parti-cle-size fractions of a long-term agricultural field experiment receiving organic amendments. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.K.; Vanlauwe, B.; Ayuke, F.; Gassner, A.; Hoogmoed, M.; Hurisso, T.; Koala, S.; Lelei, D.; Ndabamenye, T.; Six, J.; et al. Medium-term impact of tillage and residue management on soil aggregate stability, soil carbon and crop productivity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chessman, S.; Thierfelder, C.; Eash, N.; Kassie, G.; Frossard, E. Soil carbon stocks in conservation agriculture systems of Southern Africa. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 156, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, T.B.D.; Slater, B.K.; Corbalá, R.T.; Shaffer, J.M. Assessment of long-term tillage practices on physical prop-erties of two Ohio soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 186, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatments | Abbreviations |
|---|---|
| Conventional tillage + maize residues + inorganic fertilizer | CtRMf |
| Conventional tillage + maize residues + Tithonia diversifolia + goat manure | CtRTiM |
| Conventional tillage + maize residues + Inorganic fertilizer + goat manure | CtRMfM |
| Conventional tillage + maize residues + Tithonia diversifolia + phosphate rock (Minjingu) | CtRTiP |
| Conventional tillage + maize residues + goat manure + legume intercrop (Dolichos Lablab) | CtRML |
| Conventional tillage + sole inorganic fertilizer | CtMf |
| Conventional tillage (no inputs) | 1 Ct |
| Reduced tillage + maize residues + inorganic fertilizer | MtRMf |
| Reduced tillage + maize residues + Tithonia diversifolia + goat manure | MtRTiM |
| Reduced tillage + maize residues + inorganic fertilizer + goat manure | MtRMfM |
| Reduced tillage + maize residues + Tithonia diversifolia + phosphate rock (Minjingu) | MtRTiP |
| Reduced tillage + maize residues + goat manure + legume intercrop (Dolichos Lablab) | MtRML |
| Reduced tillage + sole inorganic fertilizer | MtMf |
| Reduced tillage (no inputs) | 2 Mt |
| LR 1 16 | SR 2 16 | LR17 | SR17 | LR18 | SR18 | LR19 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onset date | 3 April 2016 | 25 October 2016 | 22 March 2017 | 20 October 2017 | 3 March 2018 | 18 August 2018 | 28 March 2019 |
| Cessation date | 29 June 2016 | 31 December 2016 | 30 May 2017 | 4 January 2018 | 6 June 2018 | 18 January 2019 | 1 June 2019 |
| Season’s length | 88 | 68 | 70 | 77 | 96 | 154 | 66 |
| Seasonal rainfall(mm) | 879 | 385 | 341 | 571 | 1047 | 606 | 377 |
| 5–10 days | 2 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 11–15 days | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 1 |
| >15 days | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Number of dry spells | 6 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Githongo, M.; Kiboi, M.; Muriuki, A.; Fliessbach, A.; Musafiri, C.; Ngetich, F.K. Organic Carbon Content in Fractions of Soils Managed for Soil Fertility Improvement in Sub-Humid Agroecosystems of Kenya. Sustainability 2023, 15, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010683
Githongo M, Kiboi M, Muriuki A, Fliessbach A, Musafiri C, Ngetich FK. Organic Carbon Content in Fractions of Soils Managed for Soil Fertility Improvement in Sub-Humid Agroecosystems of Kenya. Sustainability. 2023; 15(1):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010683
Chicago/Turabian StyleGithongo, Miriam, Milka Kiboi, Anne Muriuki, Andreas Fliessbach, Collins Musafiri, and Felix K. Ngetich. 2023. "Organic Carbon Content in Fractions of Soils Managed for Soil Fertility Improvement in Sub-Humid Agroecosystems of Kenya" Sustainability 15, no. 1: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010683
APA StyleGithongo, M., Kiboi, M., Muriuki, A., Fliessbach, A., Musafiri, C., & Ngetich, F. K. (2023). Organic Carbon Content in Fractions of Soils Managed for Soil Fertility Improvement in Sub-Humid Agroecosystems of Kenya. Sustainability, 15(1), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010683










