A Review of Recent Developments and Applications of Compound Parabolic Concentrator-Based Hybrid Solar Photovoltaic/Thermal Collectors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Historical Perspective
3. Basic Construction and Classification of CPCs
3.1. Feasibility of CPC-Based Hybrid PVT Systems
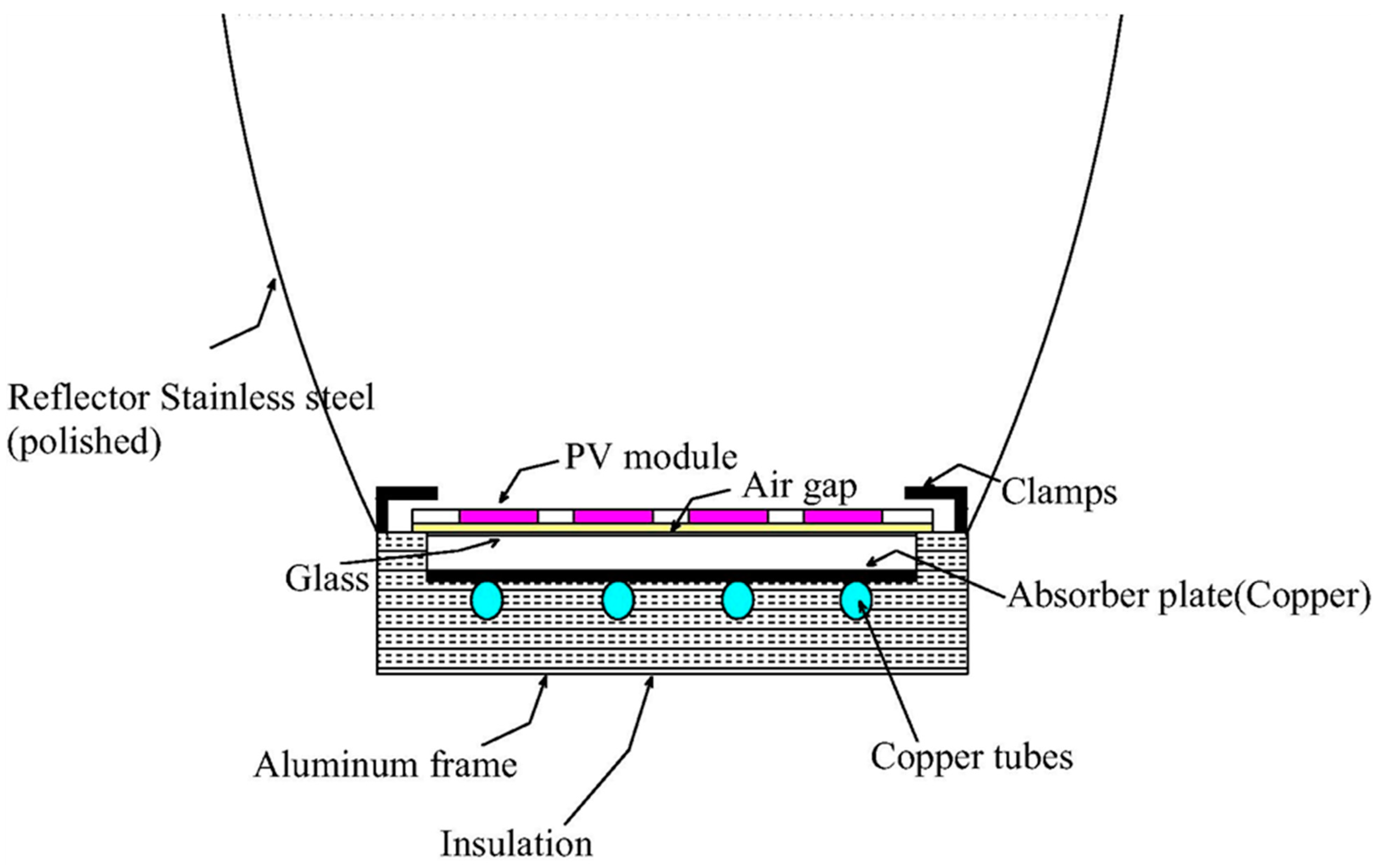
3.2. Performance Enhancement Using Phase Change Materials
4. Optical Performance Evaluation
5. Heat Exchanger Configurations for CPC-PVT Collectors
6. Applications of CPC-Based Hybrid Solar PVT Collectors
6.1. CPC-PVT Air Heating Collectors
6.2. Hybrid CPC-PVT Collectors Using Water as HTF
6.3. Rooftop and Building Façade Integrated CPC-PVT Systems
6.4. Special Applications Involving Hybrid CPC-PVT Collectors
7. Innovative Design Configurations
7.1. Hybrid CPC-PVT Collectors with Special CPC Designs
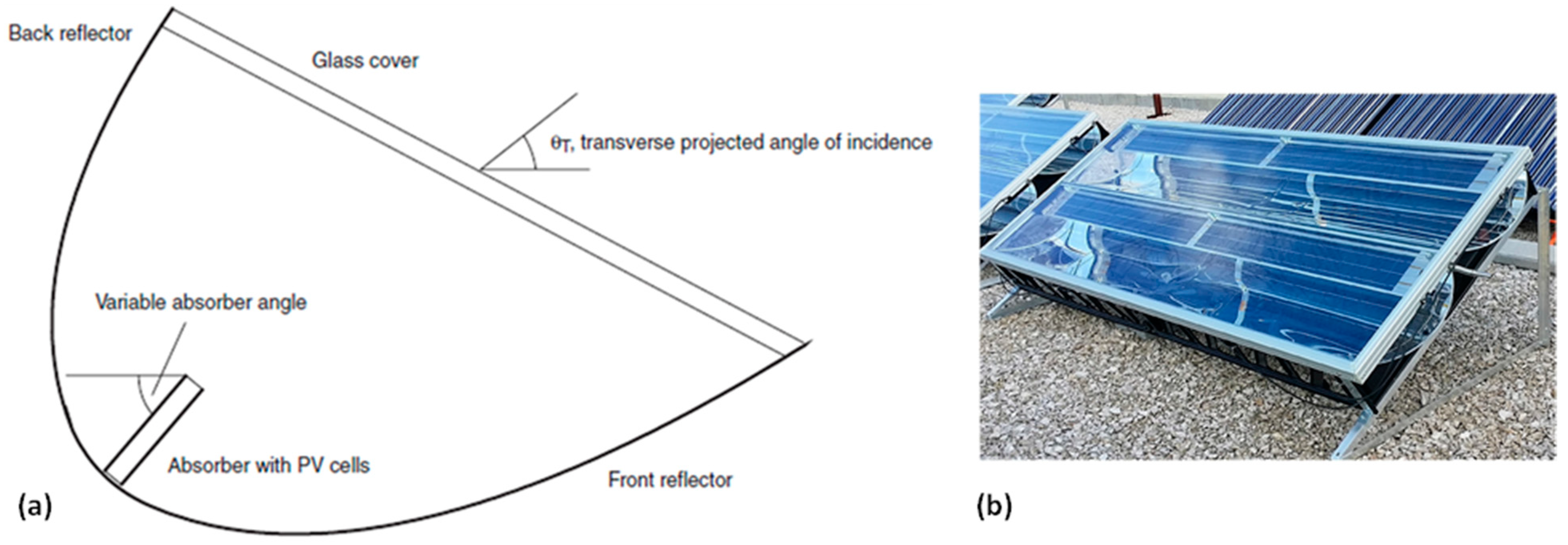
7.2. Bifacial Absorbers in CPC-PVT Collectors
7.3. Partially Covered Hybrid CPC-PVT Collectors
8. Observations and Future Prospects
8.1. Observations about Existing Systems
8.2. Recommendations for Prospective Systems
- A variety of CPC designs are available in the literature ranging from simple 2D troughs to more complex 3D geometries. Each design configuration has its own pros and cons. Optimization studies using efficient computational algorithms are required to be performed for the design optimization of existing designs. The parabolic shape of reflectors gives rise to non-uniform solar flux distribution at the receiver surface, which in turn causes a reduction in net outputs of CPC-based systems. Despite extensive research, the problem of non-uniform illumination has still not been fully solved and requires the attention of prospective researchers.
- The increased temperature of concentrated solar cells is responsible for lower electrical outputs of CPC-PVT systems. Air and water are currently being used as HTFs for removing the excess heat generated in the solar cells during the photovoltaic conversion process. With the development of nanofluids possessing superior thermophysical properties, the heat extraction process from concentrated solar cells can be accomplished more efficiently. Future research should focus on the thermal and electrical performance assessment of CPC-PVT systems using different nanofluids and diverse heat exchanger configurations.
- A noticeable obstruction in the universal acceptance of concentrated solar systems is the comparatively higher upfront costs associated with these systems. Research studies using modern optimization techniques should be conducted with the sole intention of minimizing the cost functions of low concentrating PVT systems purposely designed for single-family houses and smaller multi-family apartment buildings. This will not only reduce the burden on the national grid but also provide a chance for exporting the surplus power to the grid network through net metering technology, resulting in a financial benefit to the consumers, which can potentially act as a motivational factor in multiplying the share of solar systems in the energy mix of a country.
9. Conclusions
- Most researchers used CPCs having geometric CR ˂ 5, whereby sun tracking was not required. However, due to low CR, the quality of heat generated by these systems was relatively lower. The produced heat energy was thus suitable only for low-temperature process heat and preheating applications.
- The CPC-PVT systems produced higher electrical and thermal outputs than equivalent nonconcentrating collectors. However, a trade-off often has to be made between electrical and thermal outputs in hybrid systems because an increment in one of the products is usually achieved at the cost of the other.
- A 3D CPC caused a higher concentration on the target surface than its 2D counterpart. However, the circular shape of 3D CPC resulted in higher losses.
- The PCM can be employed for the efficient removal and storage of heat energy in hybrid CPC-PVT collectors.
- Although expensive, active cooling techniques caused effective heat removal from solar cells and improved the systems’ performance.
- Bifacial absorbers were found to have more output per unit area of the absorber. However, more research studies are still required for the performance evaluation of bifacial absorbers in CPC-PVT systems.
- The CPC-PVT systems have found numerous applications in rooftop and building integrated systems for simultaneously producing heat and electricity.
- The upcoming research should focus on designing and developing technically feasible and economically viable CPC-based PVT systems to fulfill future energy requirements through renewable resources.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PVT | Photovoltaic/thermal |
| CPC | Compound Parabolic Concentrator |
| ACPC | Asymmetric Compound Parabolic Concentrator |
| CCPC | Crossed Compound Parabolic Concentrator |
| AR-CCPC | Absorptive, Reflective Crossed Compound Parabolic Concentrator |
| ALCPC | Air-gap Lens-walled Compound Parabolic Concentrator |
| CHCT | Compound Hyperbolic trumpet |
| CR | Concentration Ratio |
| CCHP | Combined Cooling, Heating, and Power |
| LCPV | Low Concentrating Photovoltaic |
| LCPVT | Low Concentrating Photovoltaic/thermal |
| PCM | Phase Change Materials |
| ECPC | Elongated Compound Parabolic Concentrator |
| EMR | Eliminating Multiple Reflections |
| LEMR | Lowest Truncated—Eliminating Multiple Reflections |
| HEMR | Highest Truncated—Eliminating Multiple Reflections |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| HTF | Heat Transfer Fluid |
| TRNSYS | Transient System Simulation |
| SWCNT | Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes |
| MWCNT | Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes |
| ICE | Internal Combustion Engine |
| FEL | Following Electrical Load |
| FTL | Following Thermal Load |
| TEC | Thermo-ecological Cost |
| MaReCo | Maximum Reflector Collector |
| DNI | Direct Normal Irradiance |
References
- Kannan, N.; Vakeesan, D. Solar energy for future world—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calise, F.; Vanoli, L. Parabolic Trough Photovoltaic/Thermal Collectors: Design and Simulation Model. Energies 2012, 5, 4186–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, M.; Senthilkumar, T. Experimental demonstration of enhanced solar energy utilization in flat PV (photovoltaic) modules cooled by heat spreaders in conjunction with cotton wick structures. Energy 2015, 90, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Baredar, P.; Qureshi, U. Historical and recent development of photovoltaic thermal (PVT) technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Waeli, A.H.A.; Sopian, K.; Kazem, H.A.; Chaichan, M.T. Photovoltaic/Thermal (PV/T) systems: Status and future prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwania, S.; Agrawal, S.; Siddiqui, A.S.; Singh, S. Photovoltaic–thermal (PV/T) technology: A comprehensive review on applications and its advancement. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2019, 11, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Ko, B.; Nyari, E.A.; Park, S.; Kim, H.-J. Performance Evaluation of Photovoltaic Solar System with Different Cooling Methods and a Bi-Reflector PV System (BRPVS): An Experimental Study and Comparative Analysis. Energies 2017, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, D.-J.; Bhattarai, S.; Oh, J. Simulation and Model Validation of the Surface Cooling System for Improving the Power of a Photovoltaic Module. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2011, 133, 041012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Kotak, Y.; Muneer, T. Review on recent trend of solar photovoltaic technology. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2016, 34, 485–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, R.D.; van Dyk, E.E.; Vorster, F.J. The effect of the optical system on the electrical performance of III–V concentrator triple junction solar cells. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2016, 480, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renno, C.; Petito, F. Design and modeling of a concentrating photovoltaic thermal (CPV/T) system for a domestic application. Energy Build. 2013, 62, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, K.; Senthilarasu, S.; Mallick, T.K. Optics for concentrating photovoltaics: Trends, limits and opportunities for materials and design. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.A.; Striano, V.; Coppola, G. Volume Holographic Optical Elements as Solar Concentrators: An Overview. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freier, D.; Ramirez-Iniguez, R.; Jafry, T.; Muhammad-Sukki, F.; Gamio, C. A review of optical concentrators for portable solar photovoltaic systems for developing countries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.N.; Atheaya, D.; Tiwari, A. Review on Solar Thermal Power Concentrators. Open Access J. Photoenergy 2017, 1, 00016. [Google Scholar]
- Chemisana, D. Building Integrated Concentrating Photovoltaics: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, L.; Sarmah, N.; Luo, X.; Reddy, K.S.; Mallick, T.K. Opportunities and challenges in micro- and nano-technologies for concentrating photovoltaic cooling: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 20, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokeswaran, S.; Mallick, T.K.; Reddy, K.S. Design and analysis of dense array CPV receiver for square parabolic dish system with CPC array as secondary concentrator. Sol. Energy 2020, 199, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parupudi, R.V.; Singh, H.; Kolokotroni, M. Low Concentrating Photovoltaics (LCPV) for buildings and their performance analyses. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.I. Experimental Characterisation of Photovoltaic Modules with Cells Connected in Different Configurations to Address Nonuniform Illumination Effect. J. Renew. Energy 2019, 2019, 5168259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, J.J.; Iqbal, S.M.; Iniyan, S.; Goic, R. Enhanced electrical performance in a solar photovoltaic module using V-trough concentrators. Energy 2018, 148, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, F.; Nallagownden, P.A.L.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Akhter, J.; Alam, M.A.; Yusuf, M. Design and Parametric Analysis of Compound Parabolic Concentrator for Photovoltaic Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems (ICIAS), Virtual Congress, 13–15 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Winston, R. Principles of solar concentrators of a novel design. Sol. Energy 1974, 16, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, J.; Gilani, S.I.; Al-Kayiem, H.H.; Mehmood, M.; Ali, M.; Ullah, B.; Alam, M.A.; Masood, F. Experimental Investigation of a Medium Temperature Single-Phase Thermosyphon in an Evacuated Tube Receiver Coupled with Compound Parabolic Concentrator. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 754546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Nirmalathas, A.; Lim, C.; Skafidas, E. High-speed duplex optical wireless communication system for indoor personal area networks. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 25199–25216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keränen, K.; Mäkinen, J.-T.; Korhonen, P.; Juntunen, E.; Heikkinen, V.; Mäkelä, J. Infrared temperature sensor system for mobile devices. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 158, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xuan, Q.; Zhao, X.; Pei, G.; Ji, J.; Su, Y. A novel concentrating photovoltaic/daylighting control system: Optical simulation and preliminary experimental analysis. Appl. Energy 2018, 228, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Q.; Li, G.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, X.; Pei, G. The design, construction and experimental characterization of a novel concentrating photovoltaic/daylighting window for green building roof. Energy 2019, 175, 1138–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, N.-H.; Shin, S. Cost-effective optical fiber daylighting system using modified compound parabolic concentrators. Sol. Energy 2016, 136, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Su, Y.; Zheng, H.; Riffat, S. A study on use of miniature dielectric compound parabolic concentrator (dCPC) for daylighting control application. Build. Environ. 2014, 74, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgbemene, C.A.; Njoku, H.O.; Agbo, C.O.A. Investigation of Parametric Performance of the Hybrid 3D CPC/TEM System Due to Thermoelectric Irreversibilities. Front. Energy Res. 2018, 6, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgbemene, C.A.; Duffy, J.; Sun, H.; Onyegegbu, S.O. Electricity Generation from a Compound Parabolic Concentrator Coupled to a Thermoelectric Module. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2010, 132, 031015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduabuchi, C.C.; Mgbemene, C.A. Numerical Study of a Phase Change Material Integrated Solar Thermoelectric Generator. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 5917–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmim, A.; Merzouk, M.; Boukar, M.; Amar, M. Performance study of a box-type solar cooker employing an asymmetric compound parabolic concentrator. Energy 2012, 47, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Smith, S.; Xu, J.; Yu, X. Review of R&D progress and practical application of the solar photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 599–617. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, T.T. A review on photovoltaic/thermal hybrid solar technology. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, V.V.; Kaushik, S.C.; Tyagi, K.S. Advancement in solar photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) hybrid collector technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1383–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrazik, A.S.; Al-Sulaiman, F.A.; Saidur, R.; Ben-Mansour, R. A review on recent development for the design and packaging of hybrid photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) solar systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 95, 110–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamoudi, A.; Saaduddin, S.M.; Munir, A.B.; Muhammad-Sukki, F.; Abu-Bakar, S.H.; Yasin, S.H.M.; Karim, R.; Bani, N.A.; Mas’Ud, A.A.; Ardila-Rey, J.A.; et al. Using Static Concentrator Technology to Achieve Global Energy Goal. Sustainibility 2019, 11, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, O.Z.; Orhan, M.F. Concentrated photovoltaic thermal (CPVT) solar collector systems: Part I—Fundamentals, design considerations and current technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 1500–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, O.Z.; Orhan, M.F. Concentrated photovoltaic thermal (CPVT) solar collector systems: Part II—Implemented systems, performance assessment, and future directions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 1566–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshazarian, R.; Cuce, E.; Cuce, P.M.; Sher, F. Concentrating photovoltaic thermal (CPVT) collectors and systems: Theory, performance assessment and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamooshi, M.; Salati, H.; Egelioglu, F.; Faghiri, A.H.; Tarabishi, J.; Babadi, S. A Review of Solar Photovoltaic Concentrators. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014, 958521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jing, D.; Zhao, L.; Wei, J.; Guo, L. Concentrating PV/T Hybrid System for Simultaneous Electricity and Usable Heat Generation: A Review. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 869753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Xu, C.; Liao, Z.; Du, X.; Wei, G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. A review of concentrated photovoltaic-thermal (CPVT) hybrid solar systems with waste heat recovery (WHR). Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 1388–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Su, Y.; Zheng, H.; Pei, G.; Li, G.; Riffat, S. A review on the recent research progress in the compound parabolic concentrator (CPC) for solar energy applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 1272–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.I. Application of compound parabolic concentrators to solar photovoltaic conversion: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 4003–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gallagher, J.J. Nonimaging Optics in Solar Energy. Synth. Lect. Energy Environ. Technol. Sci. Soc. 2008, 2, 1–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, A. Review of modelling details in relation to low-concentration solar concentrating photovoltaic. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, T.K.; Eames, P.C.; Hyde, T.J.; Norton, B. The design and experimental characterisation of an asymmetric compound parabolic photovoltaic concentrator for building façade integration in the UK. Sol. Energy 2004, 77, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, M.S.; Nada, S.A.; Ookawara, S. Performance Evaluation of Photovoltaic panel Integrated with Compound Parabolic Concentrator (CPC) Installed in Hot Arid Area. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Sustainable Energy Technologies—SET 2015, Nottingham, UK, 25–27 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Masood, F.; Nallagownden, P.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Akhter, J.; Alam, M.A. A New Approach for Design Optimization and Parametric Analysis of Symmetric Compound Parabolic Concentrator for Photovoltaic Applications. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinterberger, H.; Winston, R. Principles of cylindrical concentrators for solar energy. Sol. Energy 1975, 17, 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Rabl, A. Optical and thermal properties of compound parabolic concentrators. Sol. Energy 1976, 18, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, F.; Nor, N.B.M.; Nallagownden, P.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Alam, M.A.; Yusuf, M.; Ali, M.; Akhter, J.; Mehmood, M. Dataset on the effect of receiver size and acceptance half-angle on the aperture width and height of compound parabolic concentrator for low-concentrating photovoltaic applications using RSM. Data Brief 2021, 39, 107630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudekar, A.S.; Jadhav, A.S.; Panse, S.V.; Joshi, J.B.; Pandit, A.B. Cost effective design of compound parabolic collector for steam generation. Sol. Energy 2013, 90, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.; Minano, J.C.; Benitez, P.G.; Bortz, W.N.S.J.C.; Shatz, N.; Bortz, J.C. Nonimaging Optics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rabl, A.; Sevcik, V.J.; Giugler, R.M.; Winston, R. Use of Compound Parabolic Concentrator for Solar Energy Collection, 3rd ed.; Argonne National Lab.: Lemont, IL, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Rabl, A.; Winston, R. Ideal concentrators for finite sources and restricted exit angles. Appl. Opt. 1976, 15, 2880–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, P.; Kandpal, T.; Mathur, S. Concentration characteristics of a two stage solar concentrator: Effect of primary mirror surface errors. Int. J. Energy Res. 1992, 16, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraidenraich, N.; Salcedo, I.H. Multimode analysis of compound parabolic concentrators with flat absorber. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 2891–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiruneh, A.T.; Ndlela, W.N.; Gadaga, T.H.; Debesay, T.; Heikkilä, J. A Four-Wing Compound Parabolic Concentrator (CPC) Design for Heating and Sanitization of Waste Products. J. Power Energy Eng. 2017, 5, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paul, D.I. Review of Mathematical Equations for the Design of Compound Parabolic Concentrating Solar Energy Collectors. Invertis J. Renew. Energy 2019, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabl, A. Comparison of solar concentrators. Sol. Energy 1976, 18, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanesco, I.; Lorenzo, E. Optimisation of an asymmetric static concentrator: The PEC—44D. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2002, 10, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, N.; Mallick, T.K. Optical efficiency study of PV Crossed Compound Parabolic Concentrator. Appl. Energy 2013, 102, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Collares-Pereira, M.; Gordon, J.; Rabl, A. Truncation of CPC solar collectors and its effect on energy collection. Sol. Energy 1985, 35, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhaddi, F.; Farahat, S.; Ajam, H.; Behzadmehr, A.; Mahdavi Adeli, M. An improved thermal and electrical model for a solar photovoltaic thermal (PV/T) air collector. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 2328–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preet, S. Water and phase change material based photovoltaic thermal management systems: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 791–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, J.J.; Iniyan, S.; Goic, R. Flat plate solar photovoltaic–thermal (PV/T) systems: A reference guide. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 62–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarracino, I.; Mellor, A.; Ekins-Daukes, N.J.; Markides, C.N. Dynamic coupled thermal-and-electrical modelling of sheet-and-tube hybrid photovoltaic/thermal (PVT) collectors. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 101, 778–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Lin, T.; Hung, W.; Sun, F. Performance evaluation of solar photovoltaic/thermal systems. Sol. Energy 2001, 70, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffat, S.B.; Cuce, E. A review on hybrid photovoltaic/thermal collectors and systems. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2011, 6, 212–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Guo, X.; Li, M. Design and performance study of a low concentration photovoltaic-thermal module. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 2199–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, K.; Chen, H.; Gao, D.; Guo, X. Thermal and electrical performance of low-concentrating PV/T and flat-plate PV/T systems: A comparative study. Energy 2019, 177, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahaidarah, H.M.; Tanweer, B.; Gandhidasan, P.; Ibrahim, N.; Rehman, S. Experimental and numerical study on non-concentrating and symmetric unglazed compound parabolic photovoltaic concentration systems. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atheaya, D.; Tiwari, A.; Tiwari, G.N. Experimental validation of a fully covered photovoltaic thermal compound parabolic concentrator system. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- al Imam, M.F.I.; Beg, R.A.; Rahman, M.S.; Khan, M.Z.H. Performance of PVT solar collector with compound parabolic concentrator and phase change materials. Energy Build. 2016, 113, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- al Imam, M.; Beg, M.R.A.; Rahman, M. Experimental Analysis on the Photovoltaic-Thermal Solar Collector with Compound Parabolic Concentrator Using Phase Change Material-Towards Solar Energy Utilization. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 13, 3964–3979. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Jia, Y.; Lin, Y.; Alva, G.; Fang, G. Numerical study of a novel miniature compound parabolic concentrating photovoltaic/thermal collector with microencapsulated phase change slurry. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 153, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, N.; Richards, B.S.; Mallick, T.K. Evaluation and optimization of the optical performance of low-concentrating dielectric compound parabolic concentrator using ray-tracing methods. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 3303–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanlou, Y.; Hashjin, T.T.; Ghobadian, B.; Najafi, G.; Mamat, R. A comprehensive review of Uniform Solar Illumination at Low Concentration Photovoltaic (LCPV) Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 1430–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, F.; Nallagownden, P.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Alam, M.A.; Ali, M.; Azeem, M. Design and Optical Performance Analysis of a Quasi-stationary Compound Parabolic Concentrator for Photovoltaic Applications. In Advances in Material Science and Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.M.; Yu, M.J.; Tang, R.S. A mathematical procedure to predict optical performance of CPCs. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 40, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, N.; Mallick, T.K.; McNeil, D.A. Optical characterisation of 3-D static solar concentrator. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 64, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, H.; Sellami, N.; Bahaidarah, H.; Mallick, T. Optical analysis of a CPC based CPV/T system for application in the kingdom of saudi arabia. In Proceedings of the 28th EU PVSEC2013, Paris, UK, 30 September–4 October 2013; pp. 653–657. [Google Scholar]
- Chandan; Dey, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Reddy, K.S.; Pesala, B. Optical and electrical performance investigation of truncated 3X non-imaging low concentrating photovoltaic-thermal systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 220, 113056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Pei, G.; Yang, M.; Ji, J.; Su, Y. Optical evaluation of a novel static incorporated compound parabolic concentrator with photovoltaic/thermal system and preliminary experiment. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 85, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wei, J.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Xi, Y.; Khalid, M. Investigation into effects of non-uniform irradiance and photovoltaic temperature on performances of photovoltaic/thermal systems coupled with truncated compound parabolic concentrators. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wei, J.; Zhang, L.; Xi, C.; Ding, R.; Wang, Z.; Khalid, M. A comprehensive study on the effects of truncation positions of the compound parabolic concentrator eliminating multiple reflections on the performances of concentrating photovoltaic and thermal system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 183, 116162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiqiang, L.; Gang, P.; Su, Y.; Xi, Z.; Jie, J. Preliminary study based on building-integrated compound parabolic concentrators (CPC) PV/thermal technology. Energy Procedia 2012, 14, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaaz, A.H.; Hasan, H.A.; Sopian, K.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Gaaz, T.S.; Al-Amiery, A.A. Outdoor Performance Analysis of a Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) Collector with Jet Impingement and Compound Parabolic Concentrator (CPC). Materials 2017, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaaz, A.H.; Sopian, K.; Gaaz, T.S. Study of the electrical and thermal performances of photovoltaic thermal collector-compound parabolic concentrated. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proell, M.; Osgyan, P.; Karrer, H.; Brabec, C.J. Experimental efficiency of a low concentrating CPC PVT flat plate collector. Sol. Energy 2017, 147, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Huang, J. Experimental investigation of a novel LCPV/T system with micro-channel heat pipe array. Renew. Energy 2018, 115, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, H.; Siviter, J.; Li, W.; Paul, M.C.; Montecucco, A.; Rolley, M.H.; Sweet, T.K.N.; Gao, M.; Mullen, P.A.; Fernandez, E.F.; et al. Conceptual design and performance evaluation of a hybrid concentrating photovoltaic system in preparation for energy. Energy 2018, 147, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Samie, M.M.A.; Ju, X.; Zhang, Z.; Adam, S.A.; Pan, X.; Xu, C. Three-dimensional numerical investigation of a hybrid low concentrated photovoltaic/thermal system. Energy 2020, 190, 116436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Guo, X. The comparison study between different battery and channel of the LCPV/T systems under concentration ratio 4. Energy 2020, 191, 116492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, J.; Gilani, S.I.; Al-kayiem, H.H.; Ali, M.; Masood, F. Characterization and stability analysis of oil-based copper oxide nanofluids for medium temperature solar collectors. Mater. Und Werkst. 2019, 50, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, J.; Gilani, S.I.; Al-Kayiem, H.H.; Ali, M.; Masood, F. Experimental evaluation of thermophysical properties of oil-based titania nanofluids for medium temperature solar collectors. Mater. Und Werkst. 2020, 51, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamnatou, C.; Vaillon, R.; Parola, S.; Chemisana, D. Photovoltaic/thermal systems based on concentrating and non-concentrating technologies: Working fluids at low, medium and high temperatures. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H.; Adhikari, R. Transient simulation of conventional hybrid photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) air heating collectors. Int. J. Energy Res. 1998, 22, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H.; Adhikari, R.S. Performance analysis of a hybrid photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) collector with integrated CPC troughs. Int. J. Energy Res. 1999, 23, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.Y.H.; Yatim, B.; Sopian, K.; Bakar, M.N.A. Performance analysis of a double-pass photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) solar collector with CPC and fins. Renew. Energy 2005, 30, 2005–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shi, M. Numerical study on optical and electric-thermal performance for solar concentrating PV/T air system. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2009, 52, 3514–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsafi, A.M.; Gandhidasan, P. Comparative study of double-pass flat and compound parabolic concentrated photovoltaic–thermal systems with and without fins. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 98, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayatizadeh, M.; Ajabshirchi, Y.; Sarhaddi, F.; Safavinejad, A.; Farahat, S.; Chaji, H. Thermal and Electrical Assessment of an Integrated Solar Photovoltaic Thermal (PV/T) Water Collector Equipped with a Compound Parabolic Concentrator (CPC). Int. J. Green Energy 2013, 10, 494–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proell, M.; Karrer, H.; Brabec, C.J.; Hauer, A. The influence of CPC reflectors on the electrical incidence angle modifier of c-Si cells in a PVT hybrid collector. Sol. Energy 2016, 126, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Patel, J. Photovoltaic thermal technology with compound parabolic concentrator. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2019, 43, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoglu, A.; Ozbey, U.; Torlaklı, H. Numerical investigation of concentrating photovoltaic/thermal (CPV/T) system using compound hyperbolic—trumpet, V-trough and compound parabolic concentrators. Renew. Energy 2020, 152, 1192–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Iqbal, S.M.; Reddy, K.S.; Pesala, B. Numerical modeling and performance assessment of elongated compound parabolic concentrator based LCPVT system. Renew. Energy 2021, 167, 199–216. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Pei, G.; Ji, J.; Su, Y. Outdoor overall performance of a novel air-gap-lens-walled compound parabolic concentrator (ALCPC) incorporated with photovoltaic/thermal system. Appl. Energy 2015, 144, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Paul, M.; Rolley, M.; Sweet, T.; Gao, M.; Baig, H.; Fernández, E.; Mallick, T.; Montecucco, A.; Siviter, J.; et al. A coupled optical-thermal-electrical model to predict the performance of hybrid PV/T-CCPC roof-top systems. Renew. Energy 2017, 112, 166–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronaki, I.P.; Nitsas, M.T. Experimental and theoretical performance investigation of asymmetric photovoltaic/thermal hybrid solar collectors connected in series. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 654–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Paul, M.; Baig, H.; Siviter, J.; Montecucco, A.; Mallick, T.; Knox, A. A three-point-based electrical model and its application in a photovoltaic thermal hybrid roof-top system with crossed compound parabolic concentrator. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 400–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Yun, H.; Yang, F. Simulating and experimental research on a low-concentrating PV/T triple-generation system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 199, 111942. [Google Scholar]
- Alamoudi, A.; Muhammad-Sukki, F.; Prabhu, R.; Sellami, N. Design of an absorptive reflective crossed CPC PV/T system. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2149, 050001. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, R.G.; Tiwari, G.N. Thermal and electrical performance evaluation of photo-voltaic thermal compound parabolic concentrator integrated fixed dome biogas plant. Renew. Energy 2020, 154, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Singh, H.P.; Sahota, L.; Arora, M.K.; Arya, R.; Singh, S.; Jain, A.; Singh, A. Performance and cost analysis of photovoltaic thermal (PVT)-compound parabolic concentrator (CPC) collector integrated solar still using CNT-water based nanofluids. Desalination 2020, 495, 114595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Lior, N.; Li, W. Energy, exergy and environmental analysis of a hybrid combined cooling heating and power system integrated with compound parabolic concentrated-photovoltaic thermal solar collectors. Energy 2019, 185, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Bu, Y. Experimental study on a flash tank integrated with low concentrating PV/T (FT-LCPVT) hybrid system for desalination. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 159, 113874. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, C.; Gao, Y. Thermo-ecological cost assessment and optimization for a hybrid combined cooling, heating and power system coupled with compound parabolic concentrated-photovoltaic thermal solar collectors. Energy 2019, 176, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; Håkansson, H.; Karlsson, B. Electrical and thermal characterization of a PV-CPC hybrid. Sol. Energy 2007, 81, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseriyan, P.; Gorouh, H.A.; Gomes, J.; Cabral, D.; Salmanzadeh, M.; Lehmann, T.; Hayati, A. Numerical and Experimental Study of an Asymmetric CPC-PVT Solar Collector. Energies 2020, 13, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, P.; Fernandes, J.F.P.; Torres, J.P.N.; Branco, P.J.C.; Fernandes, C.; Gomes, J. From Sweden to Portugal: The effect of very distinct climate zones on energy efficiency of a concentrating photovoltaic/thermal system (CPV/T). Sol. Energy 2019, 188, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, D.; Costeira, J.; Gomes, J. Electrical and Thermal Performance Evaluation of a District Heating System Composed of Asymmetric low concentration PVT Solar Collector Prototypes. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Solar Energy for Buildings and Industry (ISES EuroSun), Rapperswil, Switzerland, 10–13 September 2018; pp. 755–763. [Google Scholar]
- Solarus AB Products. Available online: https://solarus.com/en/producten-pvt-panelen/ (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- Wang, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Khalid, M. Design and performance study on a large-scale hybrid CPV/T system based on unsteady-state thermal model. Sol. Energy 2019, 177, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Lemus, R.; Vega, R.; Kim, T.; Kimm, A.; Shephard, L.E. Bifacial solar photovoltaics—A technology review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 1533–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, A.; Luque, A.; Eguren, J.; del Alamo, J. 50 Per cent more output power from an albedo-collecting flat panel using bifacial solar cells. Sol. Energy 1982, 29, 419–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- João, G.; Davidsson, H.; Christian, G.; Stefan, M.; Karlsson, B. Testing bifacial PV cells in symmetric and asymmetric concentrating CPC collectors. Engineering 2013, 5, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripanagnostopoulos, Y.; Yianoulis, P.; Papaefthimiou, S.; Zafeiratos, S. CPC solar collectors with flat bifacial absorbers. Sol. Energy 2000, 69, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adsten, M.; Helgesson, A.; Karlsson, B. Evaluation of CPC-collector designs for stand-alone, roof- or wall installation. Sol. Energy 2005, 79, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, R.; Gomes, J.; Cabral, D.; Eleyele, A.; Lança, M. Evaluation of Symmetric C-PVT Solar Collector Designs with Vertical Bifacial Receivers. In Proceedings of the SWC/SHC 2019. Solar World Congress 2019, Santiago, Chile, 4–7 November 2020; pp. 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, D.; Karlsson, B.O. Electrical and thermal performance evaluation of symmetric truncated C-PVT trough solar collectors with vertical bifacial receivers. Sol. Energy 2018, 174, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, D.; Gomes, J.; Karlsson, B. Performance evaluation of non-uniform illumination on a transverse bifacial PVT receiver in combination with a CPC geometry. Sol. Energy 2019, 194, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarus Sunpower. Available online: https://www.f6s.com/solarussunpower (accessed on 13 April 2022).
- Arnaoutakis, G.E.; Marques-Hueso, J.; Ivaturi, A.; Fischer, S.; Goldschmidt, J.C.; Krämer, K.W.; Richards, B.S. Enhanced energy conversion of up-conversion solar cells by the integration of compound parabolic concentrating optics. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 140, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atheaya, D.; Tiwari, A.; Tiwari, G.N.; Al-Helal, I.M. Analytical characteristic equation for partially covered photovoltaic thermal (PVT) compound parabolic concentrator (CPC). Sol. Energy 2015, 111, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atheaya, D.; Tiwari, A.; Tiwari, G.N. Exergy analysis of photovoltaic thermal (PVT) compound parabolic concentrator (CPC) for constant collection temperature mode. Sol. Energy 2016, 135, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atheaya, D.; Tiwari, A.; Tiwari, G.N.; Al-Helal, I.M. Performance evaluation of inverted absorber photovoltaic thermal compound parabolic concentrator (PVT-CPC): Constant flow rate mode. Appl. Energy 2016, 167, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.; Tiwari, G.N. Energetic and exergetic analysis of N partially covered photovoltaic thermal-compound parabolic concentrator (PVT-CPC) collectors connected in series. Sol. Energy 2016, 137, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.; Tiwari, G.N. Exergy and carbon credits for series connected N photovoltaic thermal-compound parabolic concentrator (PVT-CPC) collector: At constant outlet temperature. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Res. Technol. 2017, 6, 678–696. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, D.; Sherwani, A.F.; Atheaya, D.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, N. Thermodynamic analysis of Organic Rankine cycle driven by reversed absorber hybrid photovoltaic thermal compound parabolic concentrator system. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.B.; Bansal, G.; Prasad, H.; Mallick, A.; Kumar, N.; Sharma, S.K. Sensitivity Analysis of N Undistinguishable Photovoltaic Thermal Compound-Parabolic-Concentrator Collectors (Partly Covered, 50%) Integrated Single-Slope Solar Distiller Unit. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2021, 143, 021003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Tiwari, G.N. Effect of cooling condensing cover on the performance of N-identical photovoltaic thermal-compound parabolic concentrator active solar still: A comparative study. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2018, 9, 473–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraj, M.; Mahmood, S.M.; Khan, M.E.; Azhar, M.; Tiwari, G.N. Effect of N-Photovoltaic thermal integrated parabolic concentrator on milk temperature for pasteurization: A simulation study. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 2153–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, V.; Tripathi, R.; Tiwari, G.N.; Al-Helal, I.M. Electrical and thermal energy assessment of series connected N partially covered photovoltaic thermal (PVT)-compound parabolic concentrator (CPC) collector for different solar cell materials. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 128, 1611–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Ref | Type of CPC | CR | Receiver/Solar Cells | Methodology | Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Efficiency | Electrical Efficiency | |||||
| [91] | Symmetric 2D | 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3 | Single-crystalline silicon solar cells with a U-type pipe pasted on the backside | Steady-state thermal-electrical modeling | 67.6% | 12.6% |
| [92] | Symmetric 2D | - | 36 polycrystalline silicon solar cells of 156 × 156 mm with nozzles connected at the back for jet impingement cooling | Experimental | 84% | 14.5% |
| [95] | Symmetric 2D | 4.00 | Silicon solar cells pasted on Al plate connected to microchannel heat pipe array | Experimental | 54.48% | 14.49% |
| [96] | 3D CCPC | 3.60 | LGBC silicon solar cells directly bonded to a conductive heat exchanger | Numerical modeling, Indoor experiments | - | 16% |
| [97] | Symmetric 2D | 2.40 | Polycrystalline silicon cells pasted on an Al absorber sheet | 3D numerical modeling | 48.84% | 7.12% |
| [98] | Symmetric 2D | 4.00 | Monocrystalline silicon solar panel bonded with three different cooling channels (i) glass channel (GC), (ii) aluminum channel (AC) and (iii) heat pipe (HP) | Experimental | 73% (GC) 66% (AC) 51% (HP) | 12.5% (HP) 11.21% (AC) 9.92% (GC) |
| [107] | Symmetric 2D | 2.00 | Polycrystalline silicon | Numerical modeling | 51.46% | 9.6% |
| [109] | Symmetric 2D | 3.00 | Transparent solar cells | Experimental | 53.92% | 13.52% |
| [111] | ECPC | 2.50 | 315 W commercial solar panel | Numerical and experimental | 40% | 12.5% |
| [112] | ALCPC | 2.40 | Two sets of 36 series connected PV cells bonded with Cu pipe cooling channel | Simulation/Experiment | 52% | 6.6% |
| [116] | Symmetric 2D | 4.00 | Monocrystalline silicon solar cells bonded with Al cooling channel | Simulation/Experimental | 69% | 10% |
| [118] | MaReCo | 1.52 | A parallel combination of two strings of 38 series connected silicon cells on both sides of the receiver | CFD modeling | 52% | 13.3% |
| [119] | EMR-CPC | 4.00 | 20 series-connected 156 × 78 mm polycrystalline silicon solar cells | Steady-state and unsteady state thermal modeling | 55% | 13% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masood, F.; Nor, N.B.M.; Nallagownden, P.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Saidur, R.; Alam, M.A.; Akhter, J.; Yusuf, M.; Mehmood, M.; Ali, M. A Review of Recent Developments and Applications of Compound Parabolic Concentrator-Based Hybrid Solar Photovoltaic/Thermal Collectors. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5529. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095529
Masood F, Nor NBM, Nallagownden P, Elamvazuthi I, Saidur R, Alam MA, Akhter J, Yusuf M, Mehmood M, Ali M. A Review of Recent Developments and Applications of Compound Parabolic Concentrator-Based Hybrid Solar Photovoltaic/Thermal Collectors. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5529. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095529
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasood, Faisal, Nursyarizal Bin Mohd Nor, Perumal Nallagownden, Irraivan Elamvazuthi, Rahman Saidur, Mohammad Azad Alam, Javed Akhter, Mohammad Yusuf, Mubbashar Mehmood, and Mujahid Ali. 2022. "A Review of Recent Developments and Applications of Compound Parabolic Concentrator-Based Hybrid Solar Photovoltaic/Thermal Collectors" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5529. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095529
APA StyleMasood, F., Nor, N. B. M., Nallagownden, P., Elamvazuthi, I., Saidur, R., Alam, M. A., Akhter, J., Yusuf, M., Mehmood, M., & Ali, M. (2022). A Review of Recent Developments and Applications of Compound Parabolic Concentrator-Based Hybrid Solar Photovoltaic/Thermal Collectors. Sustainability, 14(9), 5529. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095529








