The Role of Beneficial Microorganisms in Soil Quality and Plant Health
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Relation between Soil and Plant Health
3. Microorganisms as Biofertilizers
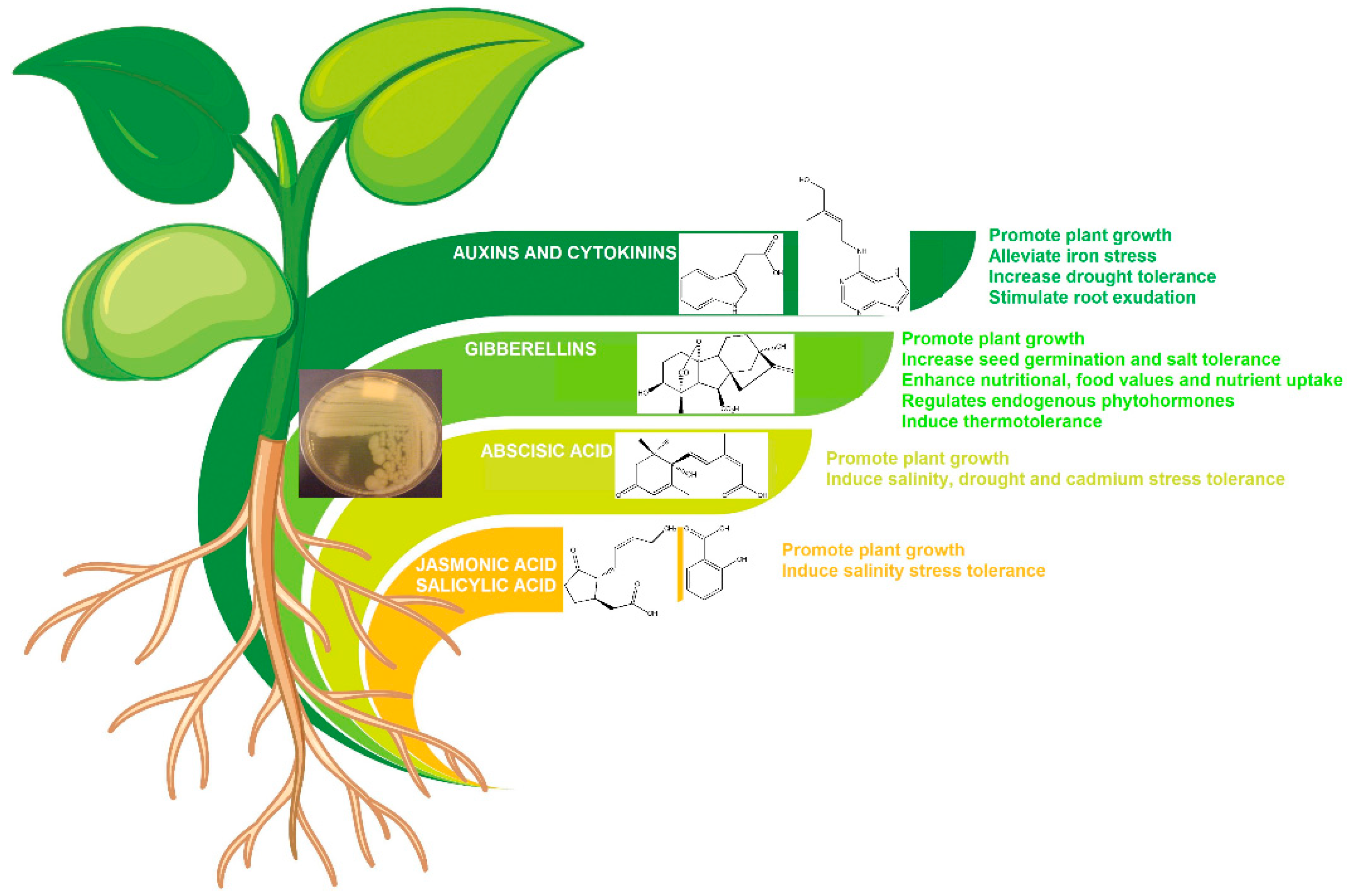
4. Bacillus spp. Beneficial for Plants
5. Practical Implications of This Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sansinenea, E. Application of biofertilizers: Current worldwide status. In Biofertilizers. Volume 1: Advances in Bio-Inoculants; Rakshit, A., Meena, V.S., Parihar, M., Singh, H.B., Singh, A.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; pp. 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Mendoza, J.L.; Sangoquiza-Caiza, C.A.; Campaña-Cruz, D.F.; Yánez-Guzmán, C.F. Use of Biofertilizers in Agricultural Production. In Technology in Agriculture; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/online-first/76918 (accessed on 27 April 2022).
- Ortiz, A.; Sansinenea, E. Recent advancements for microorganisms and their natural compounds useful in agriculture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansinenea, E. Bacillus spp.: As plant growth-promoting bacteria. In Secondary Metabolites of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizomicroorganisms: Discovery and Applications; Singh, H.B., Keswani, C., Reddy, M.S., Sansinenea, E., García-Estrada, C., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2019; pp. 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, R.; Ali, S.; Amara, U.; Khalid, R.; Ahmed, I. Soil beneficial bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion: A review. Ann. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 579–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, R.; Peukert, M.; Succurro, A.; Koprivova, A.; Kopriva, S. The Role of Soil Microorganisms in Plant Mineral Nutrition-Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prakash, J.; Mishra, S. Role of beneficial soil microbes in alleviating climatic stresses in plants. In Microbiome Under Changing Climate; Kumar, A., Singh, J., Romanholo-Ferreira, L.F., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2022; pp. 29–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Bano, A.; Curá, J.A. Role of Beneficial Microorganisms and Salicylic Acid in Improving Rainfed Agriculture and Future Food Safety. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Rakshit, A.; Al-Turki, A.I.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Datta, R. Connecting Bio-Priming Approach with Integrated Nutrient Management for Improved Nutrient Use Efficiency in Crop Species. Agriculture 2021, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, M. Biopesticides: An effective and environmental friendly insect pests inhibitor line of action. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Res. Tech. 2015, 1, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Magdoff, F.; Van Es, H. Building Soils for Better Crops Ecological Management for Healthy Soils, 4th ed.; SARE, USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021.
- Laishram, J.; Saxena, K.G.; Maikhuri, R.K.; Rao, K.S. Soil Quality and Soil Health: A Review. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2012, 38, 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.; Qu, P.; Wei, Z. Impacts of crop residues on soil health: A review. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2021, 33, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Abrol, V. Tillage Effects on Soil Health and Crop Productivity: A. Review. In Crop Production Technologies; Sharma, P., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; Available online: http://www.intechopen.com/books/crop-production-technologies/tillage-effects-on-soil-health-and-cropproductivity-a-review (accessed on 25 April 2022).
- Liu, Z.; Jiao, X.; Lu, S.; Zhu, C.; Zhai, Y.; Guo, W. Effects of winter irrigation on soil salinity and jujube growth in arid regions. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alori, E.T.; Adekiya, A.O.; Adegbite, K.A. Impact of Agricultural Practices on Soil Health. In Soil Health, Soil Biology; Giri, B., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baweja, P.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, G. Fertilizers and Pesticides: Their Impact on Soil Health and Environment. In Soil Health, Soil Biology; Giri, B., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanarella, L.; Pennock, D.J.; McKenzie, N.; Badraoui, M.; Chude, V.; Baptista, I.; Mamo, T.; Yemefack, M.; Aulakh, M.S.; Yagi, K.; et al. World’s soils are under threat. Soil 2016, 2, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Pawar, K. A review on soil health and fertility management in organic agriculture through green manuring. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 3213–3217. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasniayzare, S.K.; Sedaghathoor, S.; Dahkaei, M.N.P. Effect of biofertilizer application on growth parameters of Spathiphyllum illusion. Am. Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2012, 12, 669–673. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, D.V.; Kumar, M.; Rani, K. Biofertilizer Application in Horticultural Crops. In Microorganisms for Green Revolution, Microorganisms for Sustainability; Panpatte, D.G., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2017; Volume 6, pp. 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.K.; The, C.-Y. Impact of Biofertilizers on Horticultural Crops. In Biofertilizers: Study and Impact; Inamuddin, I., Ahamed, M.I., Boddula, R., Rezakazemi, M., Eds.; Scrivener Publishing LLC–Wiley: Salem, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 39–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husson, O.; Sarthou, J.P.; Bousset, L.; Ratnadass, A.; Schmidt, H.P.; Kempf, J.; Husson, B.; Tingry, S.; Aubertot, J.N.; Deguine, J.P.; et al. Soil and plant health in relation to dynamic sustainment of Eh and pH homeostasis: A. review. Plant. Soil 2021, 466, 391–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, S.N.; Das, A. Biofertilizers: A sustainable approach for pulse production. In Legumes for Soil Health and Sustainable Management; Meena, R.S., Das, A., Yadav, G.S., Lal, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente Cantó, C.; Simonin, M.; King, E.; Moulin, L.; Bennett, M.J.; Castrillo, G.; Laplaze, L. An extended root phenotype: The rhizosphere, its formation and impacts on plant fitness. Plant J. 2020, 103, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basu, A.; Prasad, P.; Das, S.N.; Kalam, S.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Reddy, M.S.; El Enshasy, H. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) as Green Bioinoculants: Recent Developments, Constraints, and Prospects. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshru, B.; Mitra, D.; Khoshmanzar, E.; Myo, E.M.; Uniyal, N.; Mahakur, B.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Panneerselvam, P.; Boutaj, H.; Alizadeh, M.; et al. Current scenario and future prospects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: An economic valuable resource for the agriculture revival under stressful conditions. J. Plant. Nutr. 2020, 43, 3062–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarekegn, M.M.; Salilih, F.Z.; Ishetu, A.I. Microbes used as a tool for bioremediation of heavy metal from the environment, Cogent Food. Agric. 2020, 6, 1783174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasusi, O.A.; Cruz, C.; Babalola, O.O. Agricultural sustainability: Microbial biofertilizers in rhizosphere management. Agriculture 2021, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, D.; Ansari, M.W.; Sahoo, R.K.; Tuteja, N. Biofertilizers function as key player in sustainable agriculture by improving soil fertility, plant tolerance and crop productivity. Microb. Cell Factories 2014, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, G.; Parihar, S.S.; Ahirwar, N.K.; Snehi, S.K.; Singh, V. Plant growth promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): Current and future prospects for development of sustainable agriculture. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2015, 7, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.C.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Hashem, A.; AbdAllah, E.F.; Wu, Q.S. Mycorrhizal Fungal Diversity and Its Relationship with Soil Properties. Camellia Oleifera Agric. 2021, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagne, N.; Ngom, M.; Djighaly, P.I.; Fall, D.; Hocher, V.; Svistoonoff, S. Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on plant growth and performance: Importance in biotic and abiotic stressed regulation. Diversity 2020, 12, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Djebaili, R.; Pellegrini, M.; Mahakur, B.; Sarker, A.; Chaudhary, P.; Khoshru, B.; Gallo, M.D.; Kitouni, M.; Barik, D.P.; et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis: Plant growth improvement and induction of resistance under stressful conditions. J. Plant. Nutr. 2021, 44, 1993–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itelima, J.U.; Bang, W.J.; Onyimba, I.A. A review: Biofertilizer; a key player in enhancing soil fertility and crop productivity. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 2, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, A.K.; Kumar, M.; Chakdar, H.; Anuroopa, N.; Bagyaraj, D.J. Bacillus species in soil as a natural resource for plant health and nutrition. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yousuf, J.; Thajudeen, J.; Rahiman, M.; Krishnankutty, S.P.; Alikunj, A.; Abdulla, M.H. Nitrogen fixing potential of various heterotrophic Bacillus strains from a tropical estuary and adjacent coastal regions. J. Basic Microbiol. 2017, 57, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.; Sansinenea, E. Succinic Acid Production as Secondary Metabolite from Bacillus megaterium ELI24. Nat. Prod. J. 2020, 10, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, M.; Rais, A.; Hassan, M.N.; Hafeez, F.Y. Root Associated Bacillus sp. improves growth, yield and zinc translocation for basmati rice (Oryza sativa) varieties. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.; Gonzalez-Andres, F. Bacillus as a source of phytohormones for use in agriculture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 8629–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xun, W.; Zhang, N.; Feng, H.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Participating mechanism of a major contributing gene ysnE for auxin biosynthesis in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokan, A.; Veselova, S.; Benkovskaya, G.; Maksimov, I. Endophytic strain Bacillus subtilis 26D increases levels of phytohormones and repairs growth of potato plants after Colorado potato beetle damage. Plants 2021, 10, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poveda, J. Use of plant-defense hormones against pathogen diseases of postharvest fresh produce. Physiol. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2020, 111, 101521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anckaert, A.; Arguelles-Arias, A.; Hoff, G.; Calonne-Salmon, M.; Declerck, S.; Ongena, M. The use of Bacillus spp. as bacterial biocontrol agents to control plant disease. In Microbial Bioprotectants for Plant Disease Management; Kohl, J., Ravensberg, W., Eds.; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2021; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Cui, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, W. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens L-1 for biocontrol of Pear Ring Rot. Hortic. Plant. J. 2017, 3, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pršić, J.; Ongena, M. Elicitors of plant immunity triggered by beneficial bacteria. Front. Plant. Sci. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, A.; Tabassum, B.; Fathi Abd Allah, E. Bacillus subtilis: A plant-growth promoting rhizobacterium that also impacts biotic stress. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, A.; Gómez, I.; Porta, H.; García-Gómez, B.I.; Rodriguez-Almazan, C.; Pardo, L.; Soberón, M. Evolution of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry toxins insecticidal activity. Microb. Biotechnol. 2013, 6, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.; Sansinenea, E. Bacillus thuringiensis based biopesticides for integrated crop management. In Biopesticides. Volume 2. Advances in Bio-Inoculants; Rakshit, A., Meena, V., Abhilash, P.C., Sarma, B.K., Singh, H.B., Fraceto, L., Parihar, M., Kumar, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.J.; Zhu, H.J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Peng, Y.F.; Chen, X.P. Safety Assessment of Bacillus thuringiensis Insecticidal Proteins Cry1C and Cry2A with a Zebrafish Embryotoxicity Test. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4336–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, P.H.; Kostov, K.; Damgaard, C.F. The effect of Bt crops on soil invertebrates: A systematic review and quantitative meta-analysis. Transgenic Res. 2020, 29, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarte, J.N.; Valacco, M.P.; Moreno, S.; Salerno, G.L.; Berón, C.M. Molecular characterization of a Bacillus thuringiensis strain from Argentina, toxic against Lepidoptera and Coleoptera, based on its whole-genome and Cry protein analysis. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 183, 107563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitter, E.K.; Tosi, M.; Obregón, D.; Dunfield, K.E.; Germida, J.J. Rethinking Crop Nutrition in Times of Modern Microbiology: Innovative Biofertilizer Technologies. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spraker, J.E.; Luu, G.T.; Sanchez, L.M. Imaging mass spectrometry for natural products discovery: A review of ionization methods. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, L.; Peters, B.M.; Li, B.; Chen, D.; Xu, Z.; Shirtliff, M.E. Complete genome sequence and bioinformatics analyses of Bacillus thuringiensis strain BM-BT15426. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 108, 55.e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakimovicha, A. mSphere of Influence: The rise of artificial intelligence in infection biology. mSphere 2019, 4, e00315-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
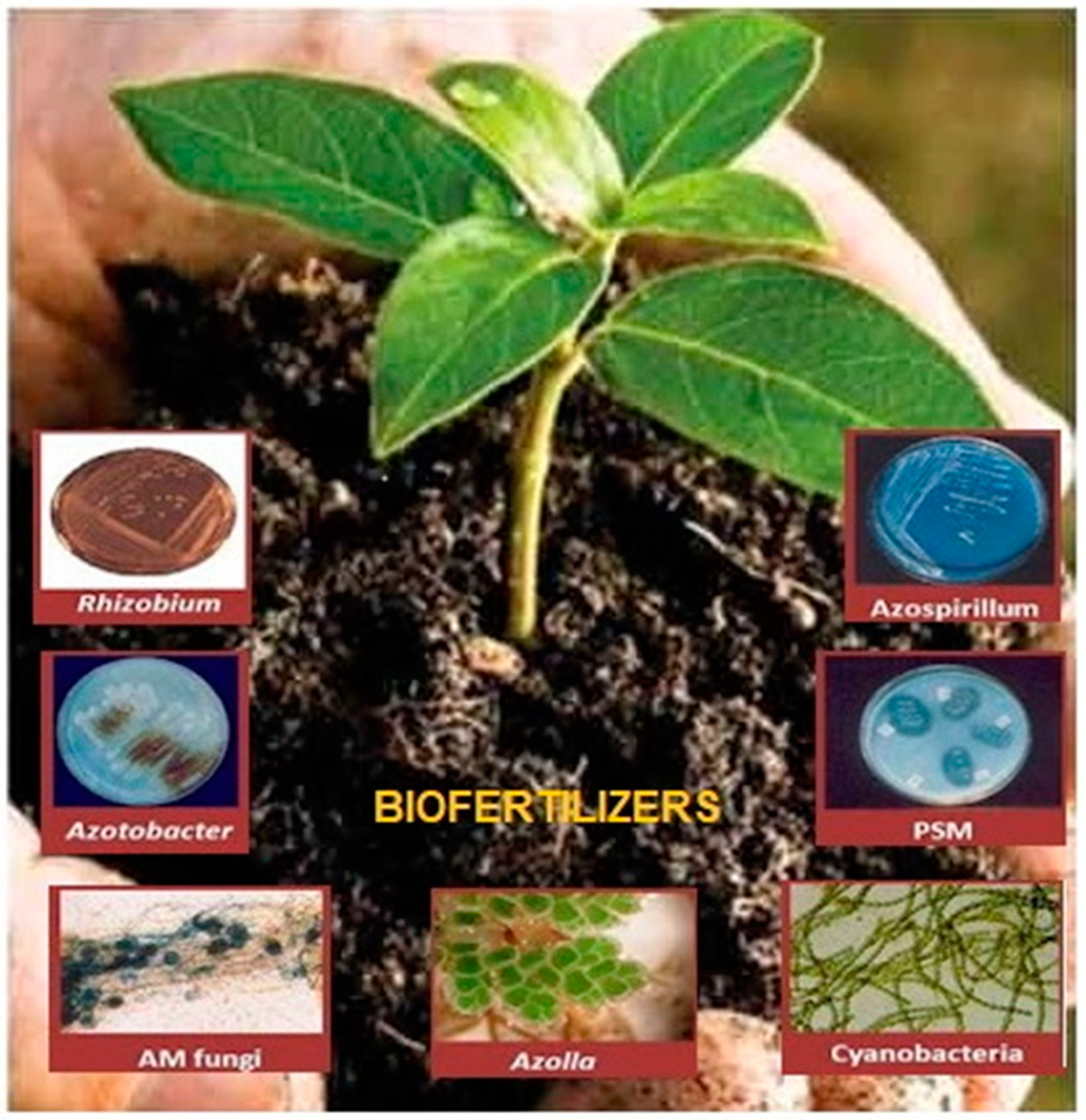


| Microbial Biofertilizers and Biopesticides | |
|---|---|
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
| Microorganism | Action | Brand Name | Producer |
|---|---|---|---|
| B. amyloliquefaciens | Fungicide | Serifel Integral Taegro Companion Maxxx Serenade Amylo-X Aveo | BASF Ag products Syngenta Group pH Douglass Plant Health Bayer CropScience LP Certis Valent BioSciences |
| B. pumilus | Fungicide | Ballad plus Sonata AS YieldShield | Bayer CropScience LP |
| B. sphaericus | Insecticide | VectoLex | Valent BioSciences |
| B. subtilis | Fungicide | Kodiak Cillus Biotilis | Bayer CropScience LP Green Biotech, Korea Agri Life |
| B. thuringiensis var. aizawai | Insecticide | XenTari Agree Turex Solbit | Valent BioSciences Certis Green Biotech, Korea |
| B. thuringiensis var. israelensis | Insecticide | Bactimos Teknar VectoBac VectoMax Aquabac Bacticide BTI granules | Valent BioSciences Becker Microbial Biotech Int’l Clarke Mos. Cont. |
| B. thuringiensis var. kurstaki | Insecticide | Dipel Foray Cordalene Lipel Sp Lipel Biolep BMP 123 Baturad Belthirul Deliver Delfin Condor Crymax Javelin WG Lepinox WG Turex Turicide Safer BTK Rapax Lepinox plus | Valent BioSciences Agrichem Som Phytopharma Agri Life Biotech international Becker microbial Agrindustrial S.A. Probelte S.A. Certis Woodstream Canada Ecogen/Intrachem |
| B. thuringiensis var. tenebrionis | Insecticide | Novodor | Valent BioSciences |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz, A.; Sansinenea, E. The Role of Beneficial Microorganisms in Soil Quality and Plant Health. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5358. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095358
Ortiz A, Sansinenea E. The Role of Beneficial Microorganisms in Soil Quality and Plant Health. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5358. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095358
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz, Aurelio, and Estibaliz Sansinenea. 2022. "The Role of Beneficial Microorganisms in Soil Quality and Plant Health" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5358. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095358
APA StyleOrtiz, A., & Sansinenea, E. (2022). The Role of Beneficial Microorganisms in Soil Quality and Plant Health. Sustainability, 14(9), 5358. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095358







