Influence of Rainfall Intensity and Slope on Runoff and Sediment Reduction Benefits of Fine Mesh Net on Construction Spoil Deposits
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Preparation of Soil and Fine Mesh Net
2.4. Rainfall Simulation and Data Analysis
3. Results
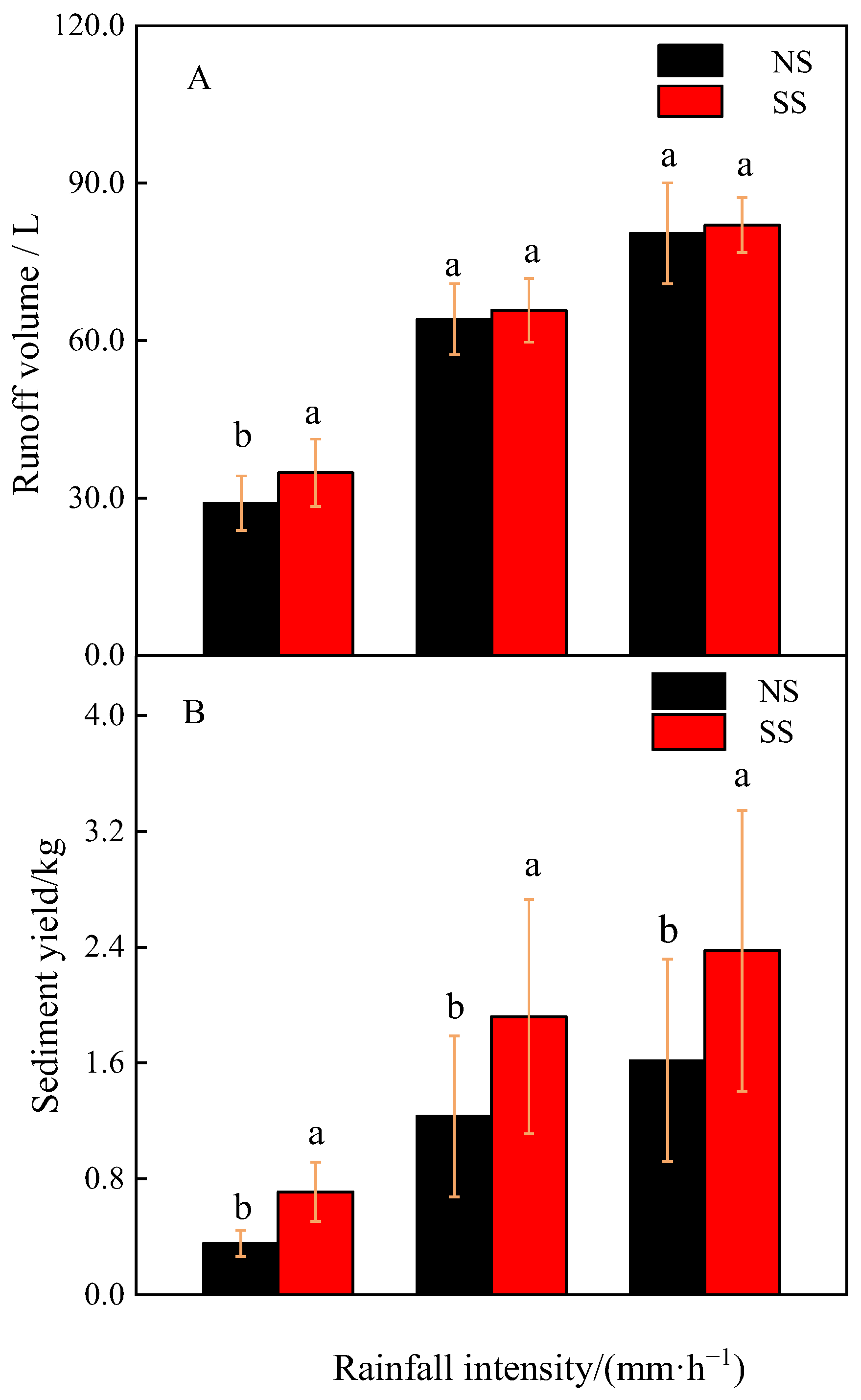
3.1. Sediment and Runoff Reduction Benefits of Fine Mesh Net
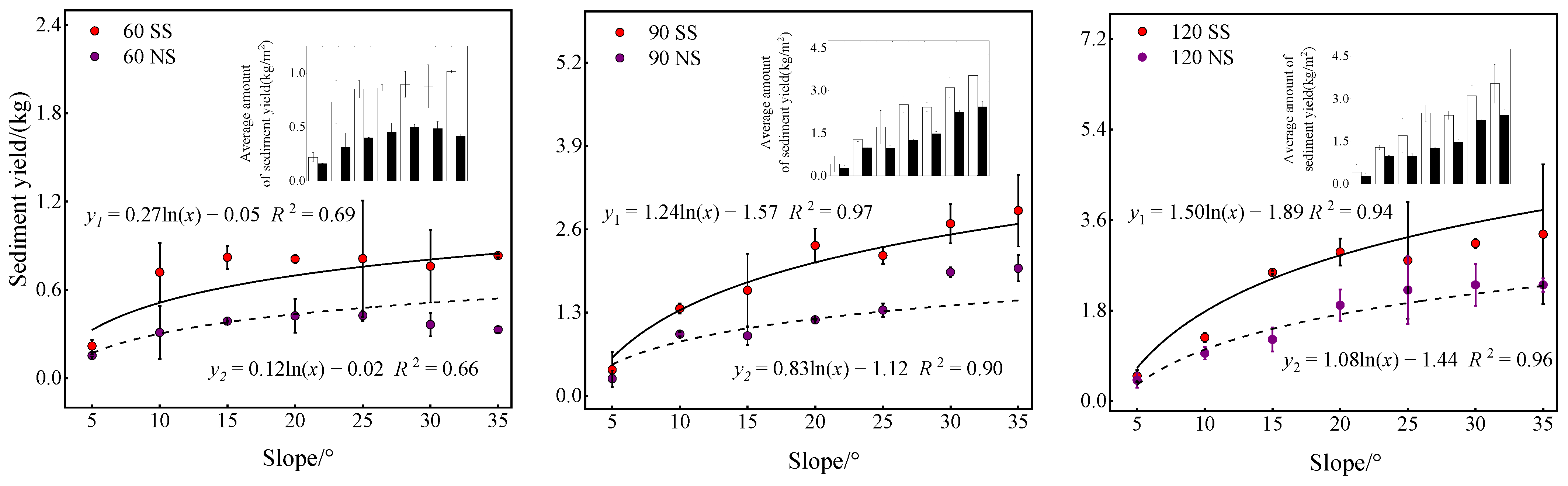
3.2. The Role of Fine Mesh Net in Relation to Slope Gradient
3.2.1. Relationship between Slope and Runoff
3.2.2. Relationship between Slope and Sediment
3.3. Fine Mesh Net Function in Relation to Rainfall Intensity
3.3.1. Relationship between Rainfall Intensity and Runoff
3.3.2. Relationship between Rainfall Intensity and Sediment
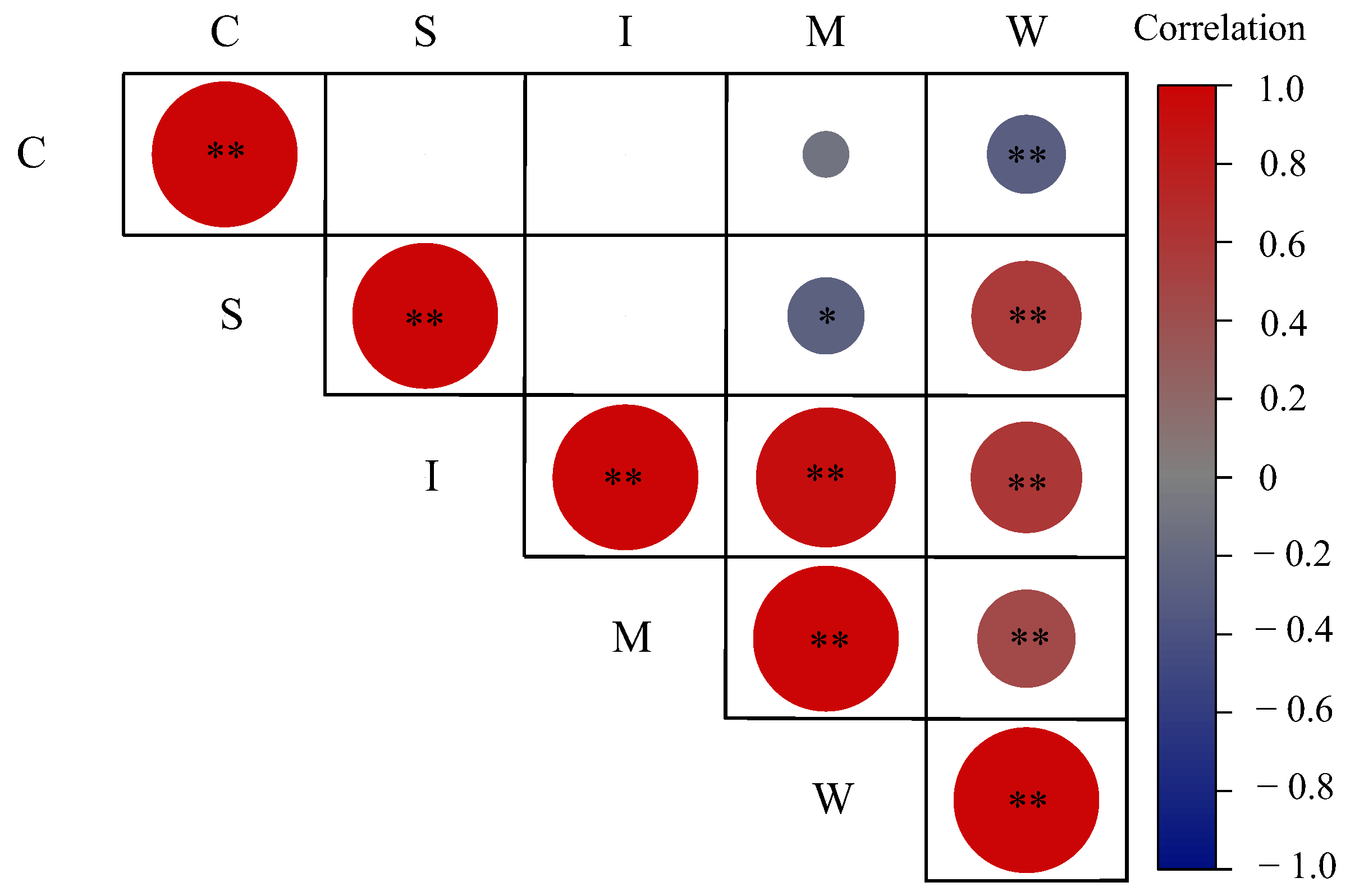
3.4. Comprehensive Analysis of Factors Influencing Soil Erosion
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Rainfall Intensity on Soil Erosion
4.2. Influence of Slope on Soil Erosion
4.3. Factors That Influence Runoff and Sediment Reduction Benefits of Fine Mesh Net
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, X.; Shi, D.; Jiang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. Runoff erosion process on different underlying surfaces from disturbed soils in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Catena 2014, 123, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tømmervik, H.; Johansen, B.; Høgda, K.A.; Strann, K.B. High-resolution satellite imagery for detection of tracks and vegetation damage caused by all-terrain vehicles (ATVs) in Northern Norway. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 23, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atucha, A.; Merwin, I.A.; Brown, M.G.; Gardiazabal, F.; Mena, F.; Adriazola, C.; Lehmann, J. Soil erosion, runoff and nutrient losses in an avocado (Persea americana Mill) hillside orchard under different groundcover management systems. Plant Soil 2012, 368, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, C.Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.H.; Gao, Y. The vegetation cover dynamics (1982–2006) in different erosion regions of the Yellow River Basin, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 23, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zeng, D.H.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.J.; Mao, R. Chemical and microbial properties in contaminated soils around a magnesite mine in northeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 23, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, K.; Dai, H.; Liang, Y. Modeling interrill erosion on unpaved roads in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 26, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilley, J.E.; Gee, G.W.; Bauer, A.; Willis, W.O.; Young, R.A. Runoff and erosion characteristics of surface-mined sites in western north Dakota. Trans. ASAE 1977, 20, 0697–0700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Tian, H. Dynamic processes of soil erosion by runoff on engineered landforms derived from expressway construction: A case study of typical steep spoil heap. Catena 2015, 128, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Schulze, M.; Rieke-Zapp, D.; Schlunegger, F. Rill development and soil erosion: A laboratory study of slope and rainfall intensity. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Tang, S.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H. Influences of sand cover on erosion processes of loess slopes based on rainfall simulation experiments. J. Arid. Land 2018, 10, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, K.H.; Lee, D.H.; Chung, S.R.; Jeong, G.C. Effect of rainfall intensity, soil slope and geology on soil erosion. J. Eng. Geol. 2014, 24, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, K.; Guo, Z. Runoff and soil erosion from highway construction spoil deposits: A rainfall simulation study. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2012, 17, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jing, S.; Zhang, H.; Huan, L.I.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.C. Runoff and sediment yield characteristics on waste soil and slag formed from railway construction in Jiaodong Peninsula region. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 32, 80–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, L.D. Universal soil loss equation. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1984; p. 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A.; Ziegler, A.D. Hillslope runoff and erosion as affected by rolled erosion control systems: A field study. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2839–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zheng, F.; Wen, L.; Han, Y.; Hu, W. Impacts of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on rill erosion processes at loessial hillslope. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, R.L.; Martin, G.L. Closure to “Effect of Unit Weight and Slope on Erosion”. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1971, 97, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Mondal, M.M. A review on jute geotextile—part 1. Ijret 2014, 3, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smets, T.; Poesen, J.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Fullen, M.A.; Subedi, M.; Booth, C.A.; Paterson, D.G. Evaluation of biological geotextiles for reducing runoff and soil loss under various environmental conditions using laboratory and field plot data. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Gu, W.; Dai, Q.; Makoto, S.; Liu, Y. Effectiveness of geotextile mulches for slope restoration in semi-arid northern China. Catena 2014, 116, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickson, R.J. Controlling sediment at source: An evaluation of erosion control geotextiles. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Smets, T.; Fullen, M.A.; Poesen, J.; Booth, C.A. Effectiveness of geotextiles in reducing runoff and soil loss: A synthesis. Catena 2010, 81, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auget, J. Advances in statistical methods for the health sciences: Applications to cancer and AIDS studies, genome sequence analysis, and survival analysis. Technometrics 2007, 49, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zheng, F.; Jia, L.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, F.; Zhang, J. Interactive effects of raindrop impact and groundwater seepage on soil erosion. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zheng, F.; Li, G.; Bian, F.; An, J. The effects of raindrop impact and runoff detachment on hillslope soil erosion and soil aggregate loss in the Mollisol region of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 161, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mügler, C.; Ribolzi, O.; Janeau, J.L.; Rochelle-Newall, E.; Latsachack, K.; Thammahacksa, C.; Valentin, C. Experimental and modelling evidence of short-term effect of raindrop impact on hydraulic conductivity and overland flow intensity. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, L.D.; Foster, G.R.; Nikolov, S. Effect of flow rate and canopy on rill erosion. Trans. ASAE 1975, 18, 0905–0911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.L.; Tang, K.L.; Zhang, C.E. Study of rainfall kinetic energy impact on rill erosion of sloping fields. Yellow River 1995, 7, 22–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Gu, R.X.; Ni, J.P. Research of runoff, sediment and nutrient loss characteristics on bare slopes in an engineering construction area under artificially simulated rainfall. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 31, 33–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Poesen, J.W. The influence of slope angle on infiltration rate and Hortonian overland flow. Geomorphology 1984, 49, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeau, J.L.; Bricquet, J.P.; Planchon, O.; Valentin, C. Soil crusting and infiltration on steep slopes in northern Thailand. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 54, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beullens, J.; Van de Velde, D.; Nyssen, J. Impact of slope aspect on hydrological rainfall and on the magnitude of rill erosion in Belgium and northern France. Catena 2014, 114, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalibová, J.; Petrů, J.; Jačka, L. Impact of rainfall intensity on the hydrological performance of erosion control geotextiles. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methacanon, P.; Weerawatsophon, U.; Sumransin, N.; Prahsarn, C.; Bergado, D.T. Properties and potential application of the selected natural fibers as limited life geotextiles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liang, X.; Wu, F. Soil surface roughness change and its effect on runoff and erosion on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Arid. Land 2013, 6, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iserloha, T.; Riesa, J.B.; Arnáezb, J.; Boix-Fayosc, C.; Butzena, V.; Cerdàd, A.; Echeverríae, M.T.; Fernández-Gálvezf, J.; Fisterg, W.; Geißler, C.; et al. European small portable rainfall simulators: A comparison of rainfall characteristics. Catena 2013, 110, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GB 5725-2009; Safety Mesh. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese)
- Shi, Q.H.; Wang, W.L.; Guo, M.M.; Bai, Y.; Deng, L.Q.; Li, Y.L. Runoff and sediment yielding process on red soil engineering accumulation containing gravels by a simulated rainfall experiment. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 2673–2680. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.; Wang, L.H.; Wu, F.Q. Effect of soil crust strength on erosion under different rainfall intensity. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 141–146. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, R.A. Rolled erosion control systems for hillslope surface protection: A critical review, synthesis and analysis of available data. I. Background and formative years. Land Degrad. Dev. 1998, 9, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, R.; Wu, F. Effect of tillage on soil erosion before and after rill development. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2506–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Midha, V.K. Influence of slope angle and rainfall intensity on the runoff erosion control performance of woven geomesh. J. Nat. Fibers 2017, 16, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.A.; Li, Y.Y. Experimental study on characteristics of water transformation on slope land. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 4, 48–53. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Shi, Z.H.; Wang, J.; Fang, N.F.; Wu, G.L.; Zhang, H.Y. Rainfall kinetic energy controlling erosion processes and sediment sorting on steep hillslopes: A case study of clay loam soil from the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 512, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.M.; Zhang, D.Q.; Cai, C.F.; Wilson, G.V.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, J.G. Exploring rainfall kinetic energy induced erosion behavior and sediment sorting for a coarse-textured granite derived soil of south China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 208, 104915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Liu, B.; Liu, H.; Xu, L. The effect of slope on interrill erosion at short slopes. Catena 2011, 84, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.F.; Zheng, F.L.; Lu, J.; An, J. Effects of rainfall and topographyon soil erosion processes of black soil hillslope. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2014, 46, 147–154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.L.; Li, Y.T.; Song, L. Influence of gradient of on stability of soil slope containing roots. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 16, 2350–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xin, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, W. Effects of slope and rainfall intensity on runoff and soil erosion from furrow diking under simulated rainfall. Catena 2019, 177, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Govindaraju, R.S. Role of slope on infiltration: A review. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.H.; Pan, Y.H.; Cheng, X.; Cui, S.F. Influence of slope and rainfall intensity on infiltration characteristics of Lou Soil. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 42, 1040–1044. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.X.; Lu, C.J.; Chen, D.; Guo, Y.S.; Wang, Y. Effects of rainfall intensities and slope gradients on runoff and sediment yield on bare iron tailings sand slope. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 33, 23–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Cao, W.H.; Chen, D. Study on relationship between soil erosion and land slope. J. Sediment Res. 1998, 43, 38–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu, Y.; Kato, H.; Zhu, B.; Wang, T.; Yang, F.; Rakwal, R.; Onda, Y. Effects of slope gradient on runoff from bare-fallow purple soil in China under natural rainfall conditions. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.Y.; Zafrullah, S.N.R.M.; Ismail, I.Z.; Ching, K.Y. Effects of water on breakdown characteristics of polyethylene composites. J. Electrost. 2018, 96, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.; Little, M.S.; Watts, J. The role of the interphase in the environmental failure of adhesive joints. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 4543–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A.; Ziegler, A.D. Effectiveness of coir-based rolled erosion control systems in reducing sediment transport from hillslopes. Appl. Geogr. 2007, 27, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Fang, Q.; Hou, R.; Wu, F. Effect of rainfall intensity and duration on soil erosion on slopes with different microrelief patterns. Geoderma 2021, 396, 115085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, E.; Liu, G.; Jia, Y.; Dan, C.; AbdElbasit, M.A.M.; Liu, C.; Gu, J.; Shi, H. Effects of raindrop impact on the resistance characteristics of sheet flow. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SL773—2018; Guidelines for Measurement and Estimation of Soil Erosion in Production and Construction Projects. Water Power Press: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese)
- Zhang, K.L.; Shu, A.P.; Xu, X.L.; Yang, Q.K.; Yu, B. Soil erodibility and its estimation for agricultural soils in China. J. Arid. Environ. 2008, 72, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
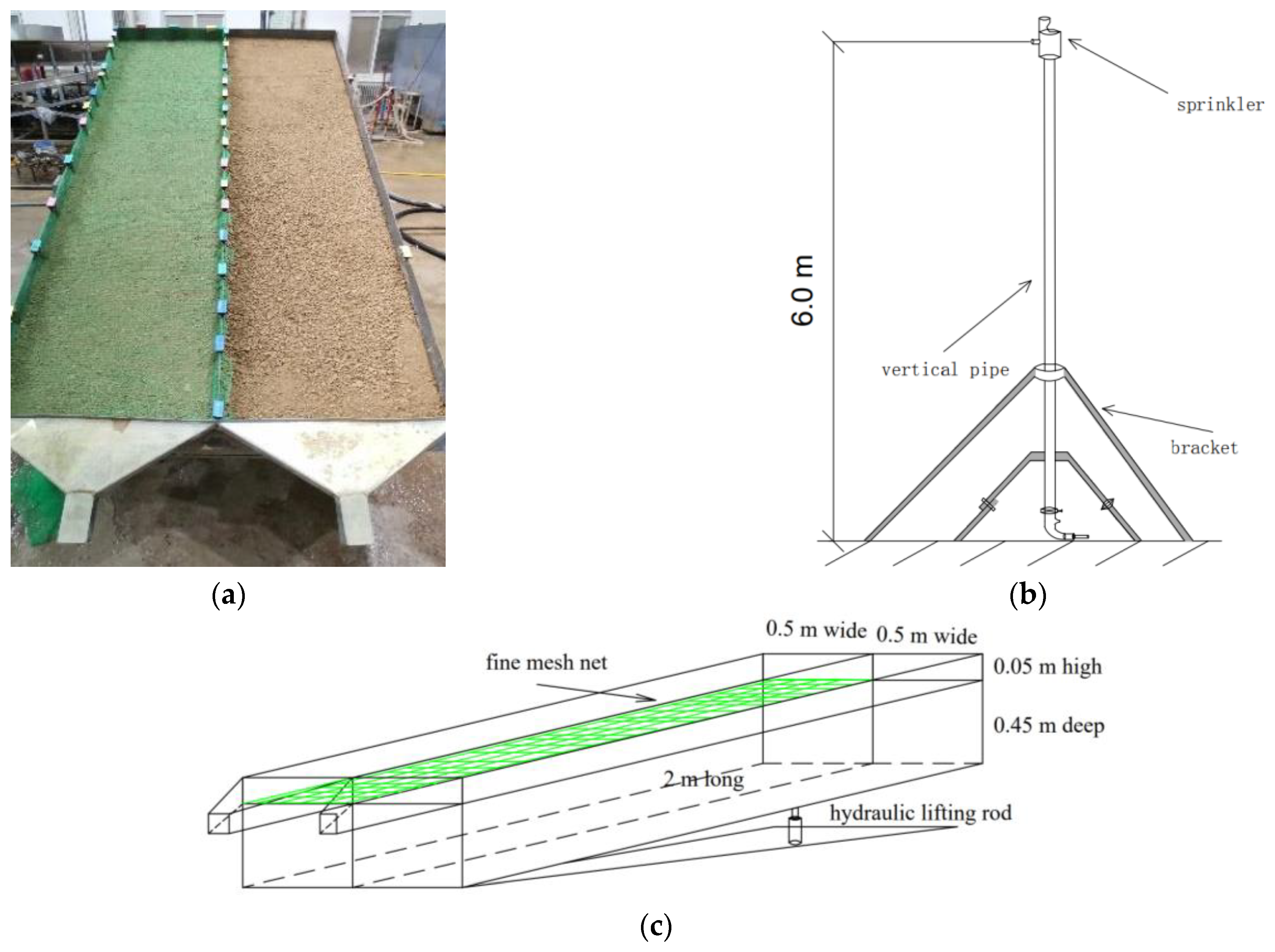

| Soil Type | Particle Size Composition/% | Organic Matter (%) | Rock (%) | Ammonium-N (g/kg) | Nitrate-N (g/kg) | Available K (g/kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay < 0.002 mm | Silt 0.002–0.05 mm | Sand > 0.05 mm | ||||||
| Clay loam | 5.14 | 85.01 | 9.85 | 7.3 | 0 | 36 | 4 | 60 |
| Item | Treatment | Maximum | Minimum | Mean | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Runoff volume (L) | SS | 88.63 | 25.26 | 60.85 | 20.47 | 33.64 |
| NS | 92.25 | 16.18 | 57.65 | 23.03 | 39.95 | |
| Sediment yield (kg) | SS | 3.32 | 0.22 | 1.67 | 1.02 | 61.08 |
| NS | 2.31 | 0.16 | 1.07 | 0.74 | 69.16 | |
| RRB (%) | - | 22.99 | 0.41 | 5.26 | 8.04 | 91.47 |
| SRB (%) | - | 59.16 | 16.67 | 35.93 | 12.06 | 31.90 |
| Slope Gradient | Runoff Volume | Sediment Yield | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | |
| 5° | 0.01 | 0.98 | 4.95 | 0.03 |
| 10° | 0.15 | 0.90 | 9.60 | 0.00 |
| 15° | 0.25 | 0.62 | 27.45 | 0.00 |
| 20° | 0.14 | 0.71 | 19.89 | 0.00 |
| 25° | 0.29 | 0.59 | 18.13 | 0.00 |
| 30° | 0.01 | 0.95 | 12.27 | 0.01 |
| 35° | 1.40 | 0.24 | 5.83 | 0.02 |
| Variable | Treatment | W(M) = a·S + b·I + c·M(W) + d | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | d | F | R2 | p | ||
| W | NS | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | −1.89 ± 0.30 | 44.28 | 0.78 | 0.00 |
| SS | 0.11 ± 0.01 | −0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | −2.47± 0.39 | 50.97 | 0.80 | 0.00 | |
| M | NS | −0.80 ± 0.15 | 0.79 ± 0.06 | 2.52 ± 2.16 | −1.38 ± 5.81 | 190.37 | 0.94 | 0.00 |
| SS | −0.86 ± 0.11 | 0.68 ± 0.05 | 4.01 ± 1.10 | 10.21 ± 4.07 | 276.68 | 0.96 | 0.00 | |
| P1 | P2 | P3 | W1 | W2 | W3 | M1 | M2 | M3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1 | 1.000 ** | 1.000 ** | −0.443 * | −0.812 ** | −0.739 ** | 0.776 ** | 0.850 ** | 0.858 ** |
| P2 | 1 | 1.000 ** | −0.443 * | −0.812 ** | −0.739 ** | 0.776 ** | 0.850 ** | 0.858 ** | |
| P3 | 1 | −0.443 * | −0.812 ** | −0.739 ** | 0.776 ** | 0.850 ** | 0.858 ** | ||
| W1 | 1 | 0.806 ** | 0.692 ** | 0.086 | −0.291 | −0.162 | |||
| W2 | 1 | 0.827 ** | −0.429 * | −0.659 ** | −0.585 ** | ||||
| W3 | 1 | −0.432 * | −0.703 ** | −0.464 * | |||||
| M1 | 1 | 0.786 ** | 0.794 ** | ||||||
| M2 | 1 | 0.771 ** | |||||||
| M3 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Gao, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Cao, B.; Chen, L.; Xue, D.; Wang, J. Influence of Rainfall Intensity and Slope on Runoff and Sediment Reduction Benefits of Fine Mesh Net on Construction Spoil Deposits. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5288. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095288
Liu C, Wang K, Gao L, Sun Y, Yang Q, Cao B, Chen L, Xue D, Wang J. Influence of Rainfall Intensity and Slope on Runoff and Sediment Reduction Benefits of Fine Mesh Net on Construction Spoil Deposits. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5288. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095288
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chao, Kanghong Wang, Linhai Gao, Yarong Sun, Qinxia Yang, Bozhao Cao, Lin Chen, Dong Xue, and Jian Wang. 2022. "Influence of Rainfall Intensity and Slope on Runoff and Sediment Reduction Benefits of Fine Mesh Net on Construction Spoil Deposits" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5288. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095288
APA StyleLiu, C., Wang, K., Gao, L., Sun, Y., Yang, Q., Cao, B., Chen, L., Xue, D., & Wang, J. (2022). Influence of Rainfall Intensity and Slope on Runoff and Sediment Reduction Benefits of Fine Mesh Net on Construction Spoil Deposits. Sustainability, 14(9), 5288. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095288






