Abstract
With development, people around the world have become wealthier and live longer. At the same time, development can lead to growing inequalities within and between nations. This paper analyses inequalities related to disability and how they vary across countries by development level. Using internationally comparable data on disability inequalities in 40 countries, we assess disability inequalities through the use of regression analyses with a variety of development measures. Results support the hypothesis only partially: disability inequalities related to education, employment, and multidimensional poverty are found to be significantly larger in countries at higher levels of development. However, this is not the case for rates of access to water, sanitation, clean fuel, electricity, housing, and assets. These results, overall, hold when using different development and outcome indicators, and when focusing on specific subgroups of the population. The potential implications of these findings are discussed. Further research is needed to understand, for education and employment, the factors and processes that contribute to larger disability inequalities in countries at higher levels of development and what strategies might be pursued to reduce them.
1. Introduction
Human development is widely understood as expanding people’s capabilities [1]. With human development, people have been able to stay in school, live longer, and earn more. At the same time, development has sometimes contributed to growing inequalities within and between nations [2]. This paper analyses inequalities related to disability and explores whether they are larger at higher levels of human development.
The United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) has been ratified by 184 countries. The United Nations (UN) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), adopted by Heads of States in 2015 as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, aim to be inclusive so that “no one will be left behind” in processes of global development [3]. Despite such policy advances, research in the past decade or so has shown that persons with disabilities experience higher rates of poverty than those without disabilities, mainly due to “barriers in society such as discrimination, limited access to education and employment and lack of inclusion in livelihood and other social programmes” [4]. The poverty experienced by persons with disabilities tends to be multidimensional in nature, impacting areas such as education, employment, health, material wellbeing, and social inclusion [4]. While the links between poverty and disability have been analysed in depth conceptually as well as empirically [4,5,6], how such links may change with development requires further study [7,8]. Studies of the past decade suggest that there may be smaller differences between the levels of wellbeing of persons with and without disabilities in countries with low levels of development. This has been observed in the areas of employment [9], income poverty [4,10], and multidimensional poverty [8,11,12].
Groce and Kett coined the term “disability and development gap” to refer to the hypothesis that countries and communities may develop in such ways that persons with disabilities are left behind [13]. We test this hypothesis and examine factors contributing to the disability and development gap, such as potential exclusionary development processes.
Although the disability and development gap hypothesis was formulated almost a decade ago, there has been limited research to test it. Using, for the first time, internationally comparable data on the inequalities associated with disability in 40 low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), this study aims to analyse the disability and development gap using regression analyses with various development measures. The hypothesis is that there is an international disability and development gap in which inequalities between persons with and without disabilities are larger in countries at higher levels of development. This study uses the measure of disability recommended by the United Nations Principles and Recommendations for Population and Housing Censuses [14]. Survey questions need to cover at least the four essential domains of functional difficulties (seeing, hearing, walking, cognition) and may also cover two additional domains (selfcare, communication). Such a measure is consistent with interactional definitions of disability, in which disability results from an interaction between a person with a health condition and the environment in its many dimensions (e.g., physical, social, legal, policy). Such interactional definitions (e.g., by the WHO [15] and Mitra [16]) have developed as attempts to merge purely medical or social definitions of disability [17].
This study adds to the ongoing global assessment of disability related inequalities [4], with implications for the ongoing conversation regarding the inclusion of persons with disabilities in development policy as well as the determinants of disability.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Disability Gaps
We use nationally representative statistics on disability inequalities in 40 countries from the Disability Data Report [18]. The 40 countries under study are presented below in Table 1. The Disability Data Report was compiled based on nationally representative household surveys and censuses with internationally comparable questions on disability between the years 2009 and 2018.

Table 1.
Countries included in the study by region.
The disability gap is the difference in an indicator between adults with and without disabilities, where disability is measured through self-reports of any functional difficulty in six domains: seeing, hearing, walking, cognition, self-care, and communication as per the United Nations guidelines on disability measurement [14] (pp. 206–210). For this study, a person is considered having any functional difficulty if a respondent answers either “some difficulty,” “at least a lot of difficulty,” or “cannot do at all” in at least one domain [18]. The indicators assessed in this study either reflect achievements or deprivations. For indicators that reflect achievements, the disability gap is the indicator for persons without disabilities minus that for persons with disabilities. For indicators that capture deprivations, i.e., multidimensional poverty headcount and less than primary school completion, the disability gap is the indicator for persons with disabilities minus that for persons without disabilities. The disability gap can be positive or negative: a positive disability gap reflects the disadvantage of persons with disabilities relative to persons without disabilities, while a negative disability gap reflects the reverse—persons with no disabilities are worse off relative to persons with disabilities.
Data on the disability gap is taken from Mitra and Yap [18]. Gaps are estimated for all adults as well as disaggregated across smaller subgroups of the population by sex, rural/urban location, and age. The indicators under consideration include the multidimensional poverty headcount and the components that go into its calculation: share of adults who have not completed primary school, employment population ratio (or employment rate), and standard of living indicators, i.e., adults in households with safely managed drinking water, safely managed sanitation services, clean cooking fuel, electricity, adequate housing, and adults in households owning assets. The multidimensional poverty measure captures an individual’s experience of deprivations in more than one dimension of wellbeing (e.g., education, health, employment, and standard of living). Its calculation follows the counting method by Alkire and Foster [20] as operationalized by Mitra and Yap [18]. An individual is considered multidimensionally poor if they experience more than one deprivation across four domains (educational attainment, employment status, health (water, sanitation), standard of living (clean fuel, electricity, adequate housing, owning assets)).
2.2. Development Variable
Development is measured with the Human Development Index (HDI), a continuous variable that ranges between 0 and 1, with values closer to 1 reflecting higher levels of development [21]. For each country, we use the HDI value for the same year as the data used to compute the disability gap. HDI measures three key dimensions of human development: a long and healthy life, knowledge, and a decent standard of living [22]. These dimensions are measured using life expectancy at birth, expected and mean years of schooling, and GNI per capita, respectively.
The hypothesis under consideration is whether the gap is larger in magnitude for countries with higher levels of development. We use ordinary least square regression analyses to consider the relationship between the disability gap and development levels.
We start with a regression model without any control variables and then add several country-level control variables as follows. The CRPD binary is a dummy variable equal to 1 if the CRPD was ratified before the dataset for that country was collected, 0 otherwise [23]. The constitutional provision variable is equal to 1 if the equality of persons with disabilities is constitutionally guaranteed and 0 if there are no specific provisions for the equality of persons with disabilities [24]. The anti-discrimination legislation control variable is equal to 1 if there is a disability-specific prohibition of workplace discrimination in at least one category (hiring processes, equal pay, or the provision of reasonable accommodation) and 0 otherwise [24]. The prevalence rate for any functional difficulty is the share of the adult population reporting having at least one functional difficulty [18]. While other control variables were considered for use in the analysis—such as the informal employment rate and the share of the population below age 15—these were found to be highly correlated with the development measures being used, with correlation coefficients of over 0.5. Importantly, the control variables above are not significantly correlated with our development measures.
As development is a multifaceted notion that has been defined and measured in a variety of ways, we use HDI in our main results as well as alternative measures of development: the natural log of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita; the share of employment in agriculture; and the share of the population in rural areas [25]. We also analyse alternative gap indicators as follows: the share of adults who have completed secondary school or higher, the youth idle rate (share of youths ages 15 to 24 years old who are neither enrolled in school nor employed), the share of adults in informal work, and the share of adults in households with a cell phone.
We conduct several sensitivity analyses. First, the regression model is applied to the disability gap for specific population subgroups by gender (men/women), area of residence (rural/urban), and age group (15 to 29/30 to 44/45 to 64/ 65+). Second, we use a different calculation of the gap to focus on the difference in an indicator between persons with no difficulty and those with at least a lot of difficulty (“At least a lot of difficulty” captures the number of people who reported having A lot of difficulty or Unable to do in at least one functional domain.)—as opposed to no difficulty and any level of difficulty in the main analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
Table 2 presents descriptive statistics for the indicators and control variables. Disability gaps are measures of gaps within each indicator. Larger numbers imply wider inequalities between populations, while the sign reflects which group is relatively disadvantaged.

Table 2.
Descriptive statistics.
The disability gaps are largest for the multidimensional poverty headcount, less than primary school completion, and the employment population ratio, with their medians at 11, 20, and 8 percentage points, respectively. For safely managed drinking water, safely managed sanitation services, clean cooking fuel, access to electricity, adequate housing, and adults in households with assets, the disability gap is smaller, with medians at less than five percentage points, reflecting lower inequality between those with and without disabilities. For all indicators, except multidimensional poverty, headcount and less than primary school completion, the minimum value for the disability gap is negative, indicating that in some countries, persons with functional difficulties are better off than persons without.
The HDI ranges from a low of 0.43 to a high of 0.79 with a median of 0.60, reflecting a sample with a majority of countries with relatively low human development. Most of the countries under study have ratified the CRPD or have disability-specific prohibitions of workplace discrimination, but only a third have constitutional provisions on the equality of persons with disabilities. The median prevalence rate of functional difficulties stands at 12%, with a low of 4% and a high of 42%.
3.2. Main Results
Table 3 presents the main Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) estimates for the disability gap on HDI. Each cell represents the result of a separate regression, with column 1 regressing the disability development gap only on HDI (with no controls) and column 2 including the controls. The scatter plot and corresponding regression line of the disability gap in multidimensional poverty headcount and HDI with no controls, corresponding with Table 3, is presented in Figure 1.

Table 3.
Main regression for all adults.
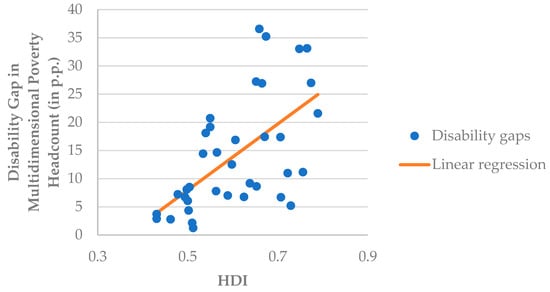
Figure 1.
Scatter plot and regression line of the disability gap in multidimensional poverty headcount and HDI.
We find that except for the gap in access to electricity, the direction and significance of the estimates are similar overall between the two columns. Referring to column 2, the HDI coefficient is positive and statistically significant at 55.86 for multidimensional poverty headcount. This means that if HDI increased by 0.1 (indicating a higher level of human development), there is an associated increase in the disability gap in the multidimensional poverty headcount of 5.6 percentage points (p.p.). We also find larger gaps for less than primary school and the employment population ratio, which translates to a 3 p.p. and 7 p.p. increase in the inequality, respectively, for every 0.1 increase in HDI. This implies that countries with higher levels of development have a worsening inequality (the gaps are larger) between populations without and with functional difficulty, with the latter at a disadvantage.
For the remaining indicators in Table 3, i.e., the standard of living indicators, only the indicator for the share of adults in households with clean fuel in column 2 has a statistically significant estimated coefficient of HDI at 13.63, though this is relatively lower than the indicators previously discussed. We do not find statistically significant coefficients for safely managed water, safely managed sanitation, access to electricity, adequate housing, and assets owned after adding the controls to our regression analysis.
In Table 4 we present the regression results for the control variables listed on the columns. Each row represents a separate regression. Our results show that estimated coefficients for the control variables are generally not statistically significant with a few exceptions. For instance, CRPD ratification is significantly correlated with a smaller disability gap for clean fuel but not for the other outcome variables. Surprisingly, having anti-discrimination legislation correlates with a significantly higher disability gap for less than primary school and access to clean water.

Table 4.
Regression of disability gaps on HDI with controls for all adults.
3.3. Alternative Development Indicators
We also consider alternative development indicators. The descriptive statistics are presented in Table 2. Table 5 presents the regression of disability gaps on alternative development indicators. Each cell gives the results of a separate regression of the disability gap on a development measure—either HDI, the share of employment in agriculture, the share of population in rural areas, or the natural log of GDP per capita—with the same control variables as the main regression. Each of the columns is associated with a different development indicator. Here, the negative and statistically significant coefficients for the share of employment in agriculture and the share of population in rural areas are consistent with our hypothesis.

Table 5.
Regression of disability gaps on other development indicators with controls for all adults.
For GDP per capita, positive coefficients reflect higher levels of GDP, indicating that higher levels of development correlate with larger disability gaps. Starting with multidimensional poverty, the coefficients for the share of employment in agriculture and the share of population in rural areas are −0.20 and −0.18, respectively. In other words, a decrease by 10 percentage points for all adults in the share of employment in agriculture or of population in rural areas is associated with an increase in the disability gap in multidimensional poverty headcount by 1.99 or 1.77 percentage points, respectively. The coefficients for all alternate indicators of development are significant and in the expected direction for multidimensional poverty, less than primary school completion, and the employment population ratio; that is, with higher levels of development by any of the considered measures, we can expect to see larger disability gaps in these areas. Of the considered development indicators, the coefficients are generally largest for the share of employment in agriculture, at −0.20, −0.17, and −0.22, for multidimensional poverty, less than primary school completion, and employment population ratio, respectively.
For the standard of living indicators, results vary across development indicators. For instance, the estimated coefficients for safely managed water and safely managed sanitation indicators are not statistically significant. Meanwhile, for electricity, there is a significant correlation between the disability gap and development for the share of employment in agriculture and the share of the population in rural areas, but not for HDI and GDP per capita.
We also assessed different measures of education, employment, and standard of living than those included in the main regression. We find a significant correlation between the gap in the rate of at least secondary school completion and development, regardless of the development indicator. For employment, we considered youth idle rate and informal work. For both indicators, the coefficient of the development variable is significant and in the expected direction for HDI and GDP but not for the other two development measures. The gap in the share of the population is households with cell phones is not significantly associated with any of the development measures.
Surprisingly, the coefficients for the share of employment in agriculture and share of population in rural areas are positive and statistically significant for the share of adults in households with electricity, at 0.05 and 0.04, respectively, indicating that the disability gap in rates of access to electricity is smaller in countries with higher levels of development.
3.4. Sensitivity Analyses
3.4.1. Subgroup Analysis
Appendix A Table A1 presents the regression of disability gaps on HDI, with controls, across various subgroups of the population. Each column gives the results associated with a particular sample of adults (e.g., all adults, women, men).
For the multidimensional poverty headcount, less than primary school completion rate, and the employment population ratio, the significant correlation holds across subgroups. The results for clean fuel are less uniform, being significant for all subgroups, except residents of urban areas, ages 15 to 29, and ages 65 and older. For asset ownership, a significant correlation is found only for adults ages 30 and older. For males and residents of urban areas, the coefficient for electricity is negative and statistically significant, suggesting that the gap is larger in countries with lower levels of human development. However, this result does not hold once we focus on different subgroups of the population.
3.4.2. Alternative Method of Gap Calculation: At Least a Lot of Difficulty vs. No Difficulty
Appendix A Table A2 presents descriptive statistics for the disability gaps when using the alternative method of gap calculation: we redefined the disability threshold to those who responded with “A lot of difficulty” or “Unable to do” in at least one of the functional domains, as recommended by the Washington Group on Disability Statistics, and recalculated the gaps. The sample size drops from 40 to 35 countries when using this method of calculation because some countries do not have a graded answer scale for functional difficulties, and therefore the distinction between some and at least a lot of difficulty cannot be made. Using this alternative method of calculation, we find that the disability gaps have higher medians, maxima, and minima compared with the descriptive statistics reported in Table 2. The standard deviations are also slightly larger, indicating a greater degree of variance in the considered gaps. The median prevalence rate of at least a lot of functional difficulties stands at 3.83%, with a low of 0.82% and a high of 12.17%. This is a noticeable reduction from the 12% median prevalence rate of any functional difficulties in the original sample of 40 countries.
Table A3 is similar to Table 5, now using this different method for calculating the disability gap. Compared with Table 5, the results hold for HDI and GDP per capita. They are more sensitive to changes in the development indicators used, with none of the disability gaps having significant coefficients for share of employment in agriculture and share of the population in rural areas, perhaps due to a smaller sample size.
The coefficients of the development indicators are significant and in the expected direction only for multidimensional poverty, less than primary school completion, employment population ratio, asset ownership, at least secondary school completion, and the youth idle rate. We also find that the coefficients in this table are generally larger: for multidimensional poverty, for example, the coefficient for HDI is 72.42 compared to 55.86 when using the previous method of disability gap calculation. Of the considered development indicators, the coefficients are generally largest for HDI, at 72.42, 36.62, and 85.68 for multidimensional poverty, less than primary school completion, and employment population ratio, respectively. For standard of living indicators, clean fuel, adequate housing, informal work, and cell phone ownership, the estimated coefficients for each of the development indicators are not statistically significant.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Development may lead to growing inequalities within countries. Using unique internationally comparable data on disability inequalities, this paper analyses the inequalities related to disability and how they vary across countries at different levels of development. Our results suggest that countries with higher levels of development tend to have larger inequalities between persons with and without disabilities in the areas of multidimensional poverty, educational attainment, and employment. The results hold when using different development measures, outcome indicators, an alternative calculation of the disability gap, and when focusing on specific subgroups of the population. However, no clear pattern emerges for standard of living indicators (e.g., housing), perhaps due to good living conditions being achieved universally—or nearly universally—as countries develop. Based on our results, the disability and development gap hypothesis is not confirmed for any of the standard of living indicators, with the exception of access to clean fuel. Moreover, the rate of access to electricity is the only area in which there are consistent significant results in the opposite direction of our hypothesis, indicating that the disability gap is smaller in countries with higher levels of development.
This study has limitations. First, the range of indicators is limited and the sample size of 40 countries is small, preventing the analysis of subgroups of countries by region or development level. Second, our cross-country approach using regression analysis provides an association, and does not causally identify the impact of development on the disability gap.
Nonetheless, this study offers the first cross-country study of the disability and development gap hypothesis. The results provide partial support of the disability and development gap, a potential pattern pointed out and a term coined almost a decade ago [8,9,13]. It remains unclear exactly what factors may contribute to this gap and what strategies might be pursued to most effectively lead to its reduction. Processes of development may impact inclusion practices as well as the onset of disability itself due to changes in healthcare access, disease environments, premature mortality among persons with disabilities, and the type of work most commonly performed, among other factors.
It is interesting that the strongest and most consistent evidence of the gap can be found when considering individual wellbeing—in the areas of education and employment—as opposed to the indicators measuring wellbeing at the household level (e.g., access to electricity). In addition, for some of the indicators in which the disability and development gap is not clearly identifiable—the rate of access to electricity being a prime example—the rates of achievement for many middle-income countries are very close to 100% of the population, resulting in disability gaps of zero percentage points. That is, the disability and development gap hypothesis does not hold when higher development can be expected to lead to universal achievement for the indicator in question, as is the case with several of the standard of living indicators under consideration.
In recent years, increased attention has been dedicated to the question of how the inclusion of persons with disabilities in development efforts should be achieved as well as to the assessment of existing development policies in terms of disability inclusion. Our results are in line with advocacy efforts for development policies to include clear goals for disability inclusion and indicators to assess the success of those goals [4,26]. In line with the CRPD and the Sustainable Development Agenda 2030, along with the risk of a disability and development gap, there is a need to adopt a disability-inclusive vision of human development and for human development to be achieved for all. Our results suggest that as a country develops, policies, specifically in relation to education and employment, need to be implemented to narrow and, eventually, close the gaps between persons with and without disabilities.
The study also has possible implications regarding the inclusion of persons with disabilities in development policy and the allocation of development aid based on a country’s development status: if development, and not inequalities, remain the primary criterion for aid eligibility [27], the existence of a disability and development gap for education and development, as found in this study, would indicate that the growing inequalities faced by persons with disabilities for some domains of wellbeing are a source of concern and a ground for continued aid at higher levels of development. At the same time, the absence of a disability and development gap found for other indicators, such as adequate housing and assets, suggests that disability inequalities may be similarly pertinent across all levels of development and, thus, should be a concern of all countries, regardless of development levels.
Our results raise some opportunities for further research, both in terms of exploring further evidence of the disability and development gap and refining our understanding of the mechanisms behind it. Specifically, future attention might be more closely dedicated to the differences in the evidence of the gap between various subgroups of the population. More broadly, the precise factors and processes driving the growth of the gap in countries at higher levels of development must also be studied further to improve our understanding of the strategies that might then be pursued to reduce them. Finally, while development may affect gaps in wellbeing between persons with and without disabilities, it could also be that development affects the onset of disabilities among persons with different levels of education [28] and employment statuses, including specific occupations [29]. More research is needed to consider the relationship between development and the onset, duration, and types of functional difficulties.
To conclude, development may be associated with growing within-country inequalities. For the first time, this study considers inequalities associated with disability across countries and how they vary by development levels. While larger such inequalities are found for education and employment outcomes in countries with higher HDI, more research is needed to investigate what might drive such an association.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.L., S.M. and J.Y.; methodology, E.L., S.M. and J.Y.; software, E.L.; validation, E.L., S.M. and J.Y.; formal analysis, E.L.; investigation, E.L. and S.M.; resources, E.L.; data curation, E.L.; writing—original draft preparation, E.L.; writing—review and editing, E.L., S.M. and J.Y.; visualization, E.L.; supervision, S.M.; project administration, S.M.; funding acquisition, S.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Wellspring Philanthropic Fund and Fordham College at Rose Hill.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this paper can be found at: https://disabilitydata.ace.fordham.edu/result-tables/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for valuable comments by participants of the 2022 Sustainable Development conference.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Regression of disability gaps on HDI (with controls).
Table A1.
Regression of disability gaps on HDI (with controls).
| Dependent Variable | Subgroup Analysis | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1) All Adults | (2) Females | (3) Males | (4) Rural Areas | (5) Urban Areas | (6) Ages 15 to 29 | (7) Ages 30 to 44 | (8) Ages 45 to 64 | (9) Ages 65+ | |
| Multidimensional poverty headcount | 55.864 *** (14.305) | 60.037 *** (15.793) | 51.280 *** (14.559) | 69.118 *** (16.142) | 47.769 ** (22.744) | 50.400 *** (12.821) | 45.458 *** (10.947) | 39.531 *** (7.617) | 37.159 *** (8.063) |
| Less than primary | 38.656 *** (13.261) | 45.181 *** (14.344) | 35.029 ** (13.018) | 61.227 *** (18.187) | 42.780 ** (19.279) | 65.298 *** (12.039) | 44.366 *** (9.476) | 31.271 *** (7.372) | 31.669 *** (4.916) |
| Employment population ratio | 72.742 *** (12.225) | 57.484 *** (12.316) | 86.425 *** (13.739) | 54.570 *** (14.505) | 66.319 *** (17.049) | 39.141 *** (10.109) | 56.440 *** (10.818) | 39.735 *** (7.452) | −7.666 (16.428) |
| Safely managed water | −0.545 (5.372) | 2.297 (4.865) | −1.377 (6.137) | −0.782 (6.651) | −3.491 (5.740) | −2.312 (5.900) | 6.876 (6.482) | 11.919 * (6.015) | 3.010 (6.556) |
| Safely managed sanitation | −6.885 (7.020) | −9.533 (7.895) | −2.836 (6.780) | −13.318 * (7.779) | −9.195 (9.756) | −10.144 (8.465) | −0.239 (8.508) | 4.804 (8.430) | −5.911 (11.958) |
| Clean fuel | 13.628 ** (6.117) | 12.871 ** (6.246) | 15.159 ** (6.454) | 13.849 *** (3.592) | −6.332 (11.553) | 9.519 (6.551) | 22.103 ** (8.472) | 12.206 ** (5.436) | 8.021 (5.124) |
| Electricity | −7.221 (4.817) | −3.879 (5.120) | −9.216 * (5.411) | −0.462 (4.521) | −18.099 * (9.888) | −2.743 (6.158) | 9.059 (6.646) | 6.516 (5.305) | 1.071 (5.963) |
| Adequate housing | 0.533 (6.128) | 4.876 (6.523) | −4.072 (6.588) | 2.210 (4.959) | −12.833 (11.551) | −0.146 (6.368) | 8.074 (8.091) | 16.086 *** (5.676) | 6.962 (8.138) |
| Owns assets | 3.714 (4.513) | 4.357 (4.804) | 3.766 (4.535) | −0.720 (2.877) | −4.137 (7.757) | 0.047 (4.870) | 11.464 ** (5.113) | 15.638 *** (5.056) | 11.555 * (5.673) |
Source: Authors’ calculations based on data from Mitra and Yap [18], UNDP [21], UN High Commissioner for Human Rights [23], World Policy Analysis Center [24]. Notes: Each cell gives the results of a separate regression of the disability gap in one indicator (e.g., for the multidimensional poverty headcount) on a development measure (HDI) without any control variables for a given sample (e.g., all adults, females). *, **, and *** for 10%, 5%, and 1% significance, respectively. Numbers in parentheses are standard errors.

Table A2.
Descriptive statistics for indicators when using alternative calculation of disability gap.
Table A2.
Descriptive statistics for indicators when using alternative calculation of disability gap.
| Indicator | Mean | Median | Std. Dev. | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disability gaps: | |||||
| Multidimensional poverty headcount (✗) | 21.14 | 21 | 12.51 | 3 | 54 |
| Less than primary (✗) | 29.50 | 28 | 11.30 | 11 | 53 |
| Employment population ratio | 21.70 | 24 | 15.26 | −7 | 59 |
| Safely managed water | 3.53 | 4 | 3.74 | −4 | 12 |
| Safely managed sanitation | 2.20 | 2 | 4.35 | −8 | 10 |
| Clean fuel | 3.90 | 3 | 5.06 | −7 | 15 |
| Electricity | 4.16 | 2 | 4.62 | −1 | 14 |
| Adequate housing | 3.86 | 3 | 4.85 | −5 | 14 |
| Owns assets | 5.39 | 5 | 2.97 | −1 | 14 |
| At least secondary | 15.01 | 14 | 10.29 | 1 | 45 |
| Youth idle rate (✗) | 18.78 | 13 | 20.88 | −6 | 63 |
| Informal work (✗) | 6.20 | 6 | 9.00 | −14 | 28 |
| Cell phone | 11.63 | 12 | 6.69 | 2 | 24 |
| Control variables: | |||||
| CRPD ratification | 0.74 | 1 | 0.44 | 0 | 1 |
| Constitutional provision | 0.29 | 0 | 0.46 | 0 | 1 |
| Anti-discrimination legislation | 0.65 | 1 | 0.49 | 0 | 1 |
| Prevalence of at least a lot of functional difficulties (%) | 3.83 | 3.00 | 2.66 | 0.82 | 12.17 |
Source: Authors’ calculations based on data from Mitra and Yap [18], UN High Commissioner for Human Rights [23], World Policy Analysis Center [24]. Notes: The table includes disability gaps in percentage points for various indicators (e.g., safely managed water). For positive indicators reflecting an achievement in wellbeing (e.g., access to safely managed water), the disability gap is the difference between the indicator for persons without functional difficulties and the indicator for persons with at least a lot of functional difficulties. For negative indicators reflecting a deprivation in wellbeing (multidimensional poverty headcount), the disability gap is the difference between the indicator for persons with at least a lot of functional difficulties and the indicator for persons without functional difficulties. Indicators with ✗ are measures of deprivation. The table includes statistics for 35 countries, reduced from the 40 countries included in the main analysis.

Table A3.
Regression of disability gaps (using alternate calculation) on various development indicators with controls for all adults.
Table A3.
Regression of disability gaps (using alternate calculation) on various development indicators with controls for all adults.
| Dependent Variable | Independent Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDI Value | Share of Employment in Agriculture | Share of Population in Rural Areas | Natural Log of GDP per Capita | |
| Multidimensional poverty headcount | 72.421 *** (21.437) | −0.177 (0.118) | −0.141 (0.108) | 5.616 ** (2.658) |
| Less than primary | 36.615 * (18.359) | −0.108 (0.093) | −0.057 (0.092) | 4.706 ** (2.080) |
| Employment population ratio | 85.678 *** (21.995) | −0.119 (0.130) | −0.095 (0.128) | 7.612 ** (2.801) |
| Safely managed water | −8.140 (8.082) | 0.042 (0.038) | −0.006 (0.036) | −0.304 (0.920) |
| Safely managed sanitation | −6.451 (9.928) | −0.004 (0.047) | −0.036 (0.043) | 0.398 (1.117) |
| Clean fuel | 14.788 (9.453) | −0.030 (0.048) | −0.021 (0.043) | 1.590 (1.130) |
| Electricity | −15.483 (9.564) | 0.076 (0.045) | 0.021 (0.043) | −0.205 (1.122) |
| Adequate housing | −0.381 (10.433) | −0.037 (0.048) | −0.073 * (0.042) | 0.364 (1.145) |
| Owns assets | 6.075 (6.075) | −0.023 (0.029) | −0.067 ** (0.024) | 1.294 * (0.645) |
| Other indicators: | ||||
| At least secondary | 61.962 *** (17.788) | −0.130 (0.101) | −0.096 (0.099) | 4.210 * (2.323) |
| Youth idle rate | 101.981 ** (46.926) | 0.034 (0.366) | −0.296 (0.234) | 9.630 * (5.166) |
| Informal work | 24.817 (18.883) | −0.107 (0.087) | −0.095 (0.091) | 2.502 (2.334) |
| Cell phone | 2.599 (14.586) | 0.019 (0.066) | −0.045 (0.061) | 1.729 (1.615) |
Source: Authors’ calculations based on data from Mitra and Yap [18], UNDP [21], World Bank [25], UN High Commissioner for Human Rights [23], World Policy Analysis Center [24]. Notes: Each cell gives the results of a separate regression of the disability gap in one indicator (e.g., for the multidimensional poverty headcount) on a development measure (e.g., HDI) and four control variables. *, **, and *** for 10%, 5%, and 1% significance, respectively. Numbers in parentheses are standard errors.
References
- Sen, A.K. Development as Freedom; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Deaton, A. The Great Escape; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- United Nations. Disability and Development Report: Realizing the Sustainable Development Goals by, for and with Persons with Disabilities; United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Available online: https://social.un.org/publications/UN-Flagship-Report-Disability-Final.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Yeo, R.; Moore, K. Including disabled people in poverty reduction work: Nothing about us, without us. World Dev. 2003, 31, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M. Disability and poverty: A conceptual review. J. Disabil. Policy Stud. 2011, 21, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, J.; Mont, D. Disability and poverty: A survey of world bank poverty assessments and implications. ALTER Eur. J. Disabil. Res. 2009, 3, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitra, S.; Posarac, A.; Vick, B. Disability and poverty in developing countries: A multidimensional study. World Dev. 2013, 41, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizunoya, S.; Mitra, S. Is There a disability gap in employment rates in developing countries? World Dev. 2013, 42, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banks, L.M.; Kuper, H.; Polack, S. Poverty and disability in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinilla-Roncancio, M.; Mactaggart, I.; Kuper, H.; Dionicio, C.; Naber, J.; Murthy, G.V.S.; Polack, S. Multidimensional poverty and disability: A case control study in India, Cameroon, and Guatemala. SSM–Popul. Health 2020, 11, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinilla-Roncancio, M.; Alkire, S. How poor are people with disabilities? Evidence based on the global multidimensional poverty index. J. Disabil. Policy Stud. 2020, 31, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groce, N.; Kett, M. The Disability and Development Gap; Leonard Cheshire Disability and Inclusive Development Center Working Paper Series: No. 21; Leonard Cheshire Disability and Inclusive Development Center, University College London: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Principles and Recommendations for Population and Housing Censuses; United Nations Department of Social and Economic Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Available online: https://unstats.un.org/unsd/demographic-social/Standards-and-Methods/files/Principles_and_Recommendations/Population-and-Housing-Censuses/Series_M67rev3-E.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- World Health Organization. The International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S. Disability, Health and Human Development; Palgrave: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Goodley, D. Disability Studies: An Interdisciplinary Introduction; Sage: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S.; Yap, J. The Disability Data Report; Fordham Research Consortium on Disability, Fordham University: Bronx, NY, USA, 2021; Available online: https://disabilitydata.ace.fordham.edu/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- The World Bank Group. World Bank Country and Lending Groups. Available online: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Alkire, S.; Foster, J. Counting and multidimensional poverty measurement. J. Public Econ. 2011, 95, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). Human Development Report 2020. The Next Frontier: Human Development and the Anthropocene; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: http://hdr.undp.org/en/content/human-development-report-2020 (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). Technical Notes: Calculating the Human Development Indices—Graphical Presentation; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/hdr2020_technical_notes.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights. Status of Ratification Interactive Dashboard. Available online: https://indicators.ohchr.org/ (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- World Policy Analysis Center. Disability. Available online: https://worldpolicycenter.org/topics/disability/policies (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- The World Bank Group. World Development Indicators. Available online: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/world-development-indicators/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Lang, R.; Schneider, M.; Kett, M.; Cole, E.; Groce, N. Policy development: An analysis of disability inclusion in a selection of African Union policies. Dev. Policy Rev. 2017, 37, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bump, J. Global health aid allocation in the 21st century. Health Policy Plan. 2013, 33, i1–i3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cutler, D.M.; Lleras-Muney, A. The education gradient in old age disability. In Research Findings in the Economics of Aging; Wise, D.A., Ed.; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2010; pp. 101–120. Available online: https://www.nber.org/books-and-chapters/research-findings-economics-aging/education-gradient-old-age-disability (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Andrasfay, T.; Raymo, N.; Goldman, N.; Pebley, A.R. Physical work conditions and disparities in later life functioning: Potential pathways. SSM–Popul. Health 2021, 16, 100990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).