Analysis of the Effectiveness of Green Waste Composting under Hyperbaric Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Properties of Substrates
- mowed grass from the green areas of the city of Wrocław, 50 mm long,
- mowed grass from the green areas of the city of Wrocław, 150 mm long.
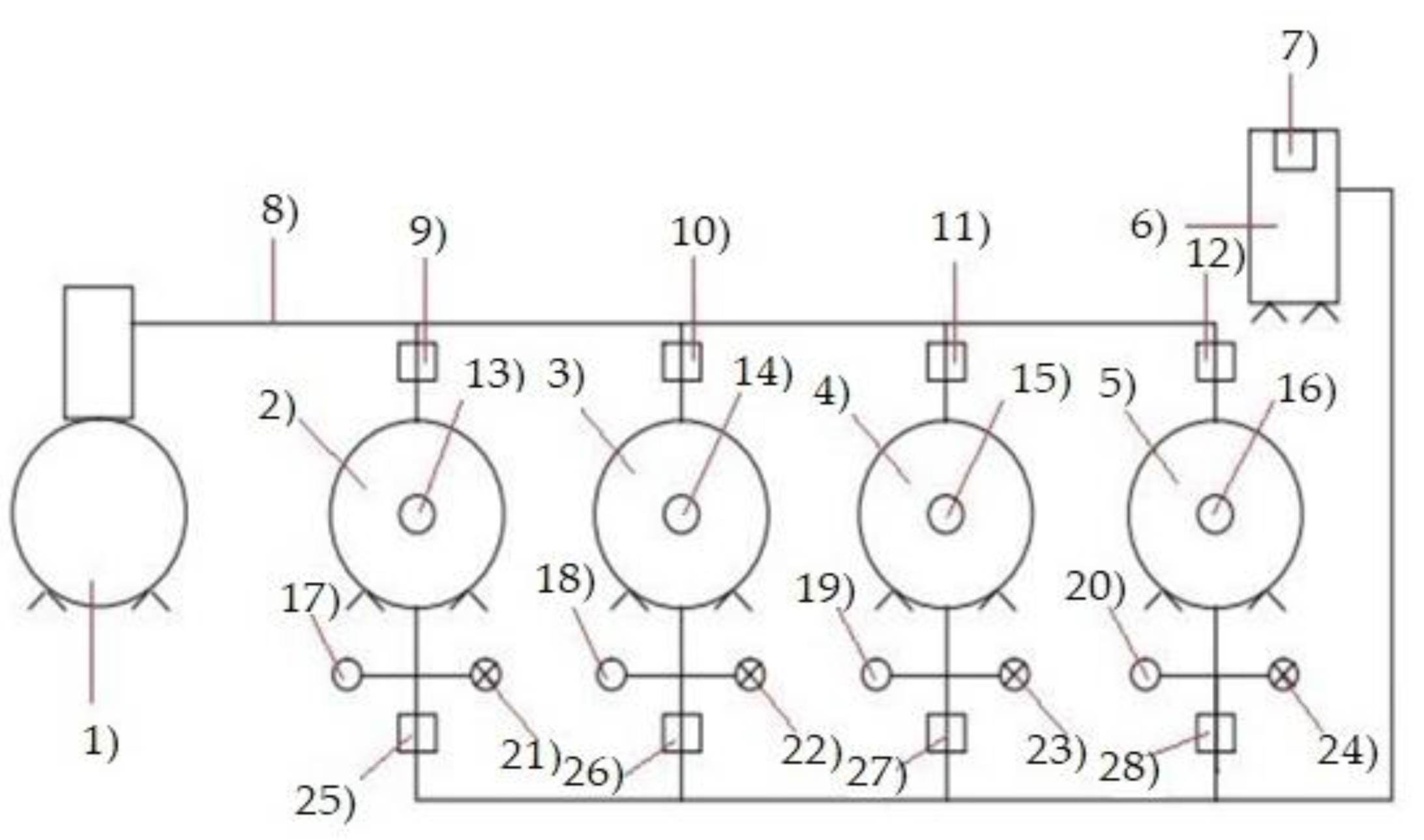
2.2. Description of the Test Stand
2.3. Plan of the Experiment
- (a)
- air exchange frequencies: 4 and 8 h;
- (b)
- preset overpressures: 0, 50, 100, and 200 kPa;
- (c)
- the number of repetitions for each set overpressure and the air exchange frequency: 5.
2.4. Waste Research Methods
2.5. Statistical Data Analysis
- for all measured quantitative variables, basic descriptive statistics were calculated, i.e., mean values (M), standard deviations (SD), medians (Me), lower (Q1) and upper (Q3) quartiles, as well as extreme values Min and Max;
- for all quantitative variables, the compliance of their distribution with the normal distribution was checked using the Shapiro–Wilk test, the homogeneity of variance was checked with the Bartlett and Levene test;
- the analysis of variance for the two-factor classification was used to assess the impact of the independent variables (p and tAE) on the dependent variables;
- for all the statistical tests used, the significance level α = 0.05 was adopted.
- X1—p, overpressure in the bioreactor chamber (0, 50, 100, and 200 kPa);
- X2—tAE, frequency of air exchange in the bioreactor (4 and 8 h).
- Y1—AT4, respiratory activity of microorganisms within 4 days, mg O2·g DM−1,
- Y2—MC, moisture content of the material, %,
- Y3—LOI, loss on dry matter ignition, %,
- Y4—Δm, loss of dry matter, %,
- Y5—pH value,
- Y6—N, average share of nitrogen, %,
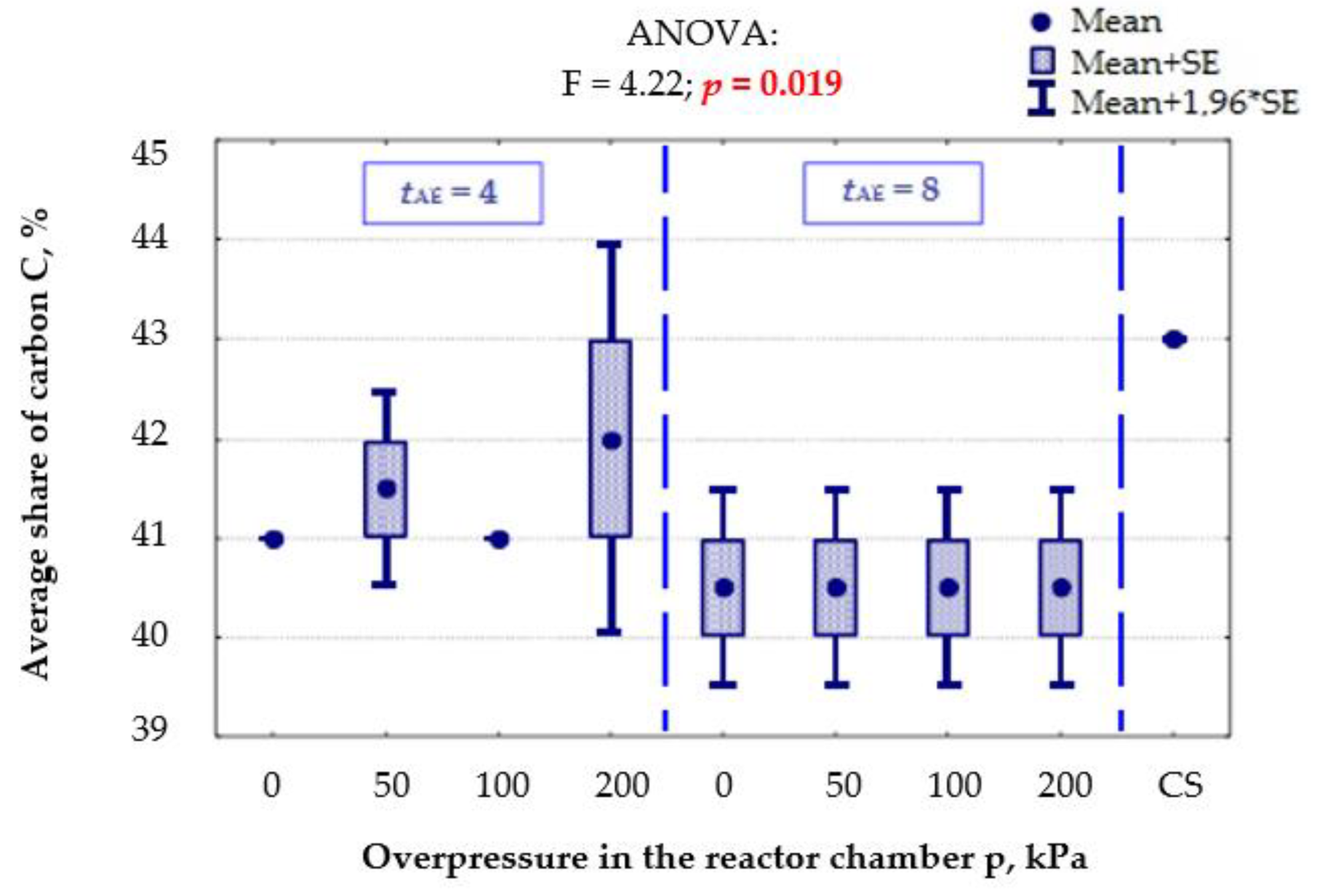
- Y7—C, average share of carbon, %,
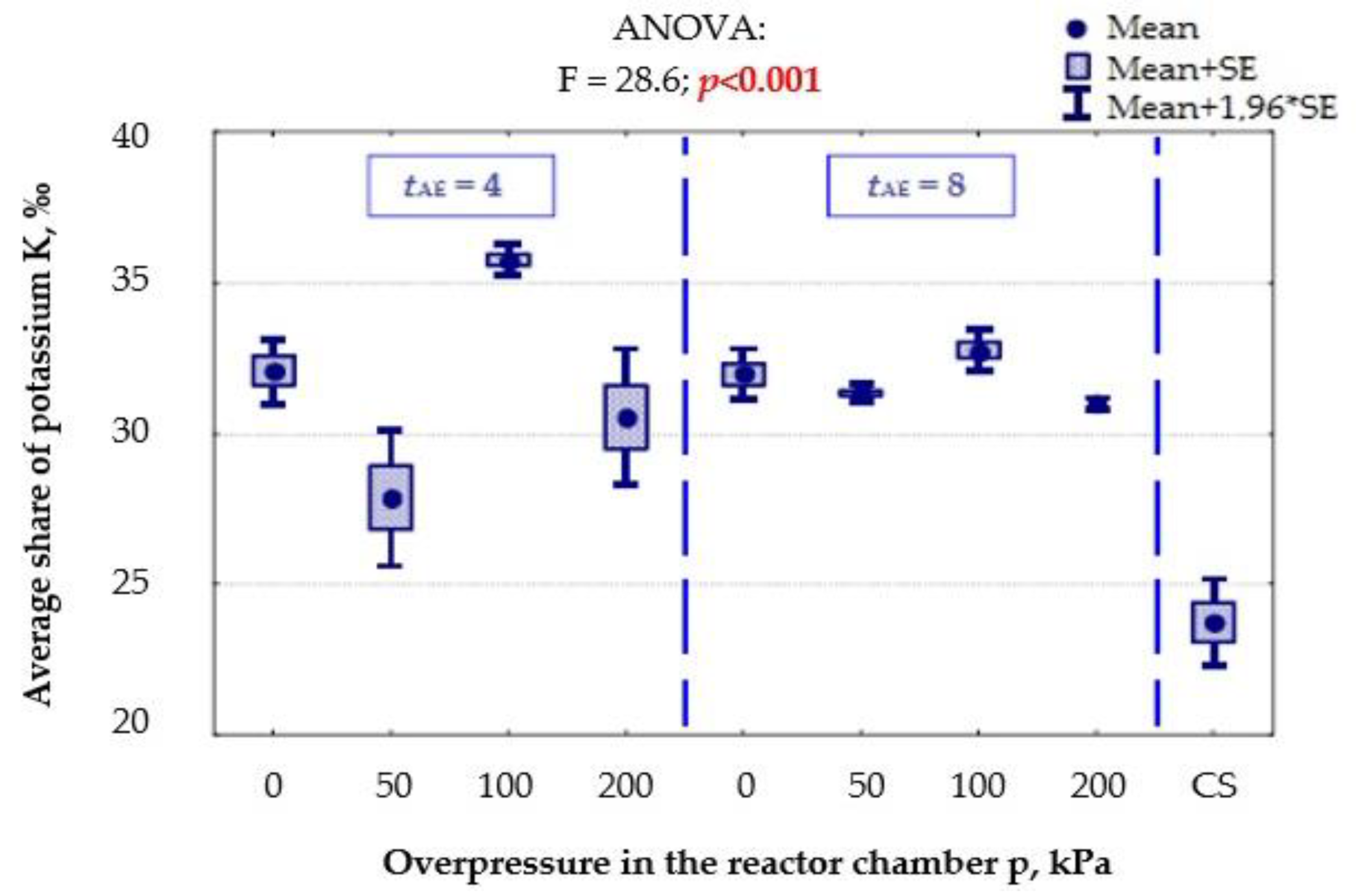
- Y8—K, average share of potassium, ‰,
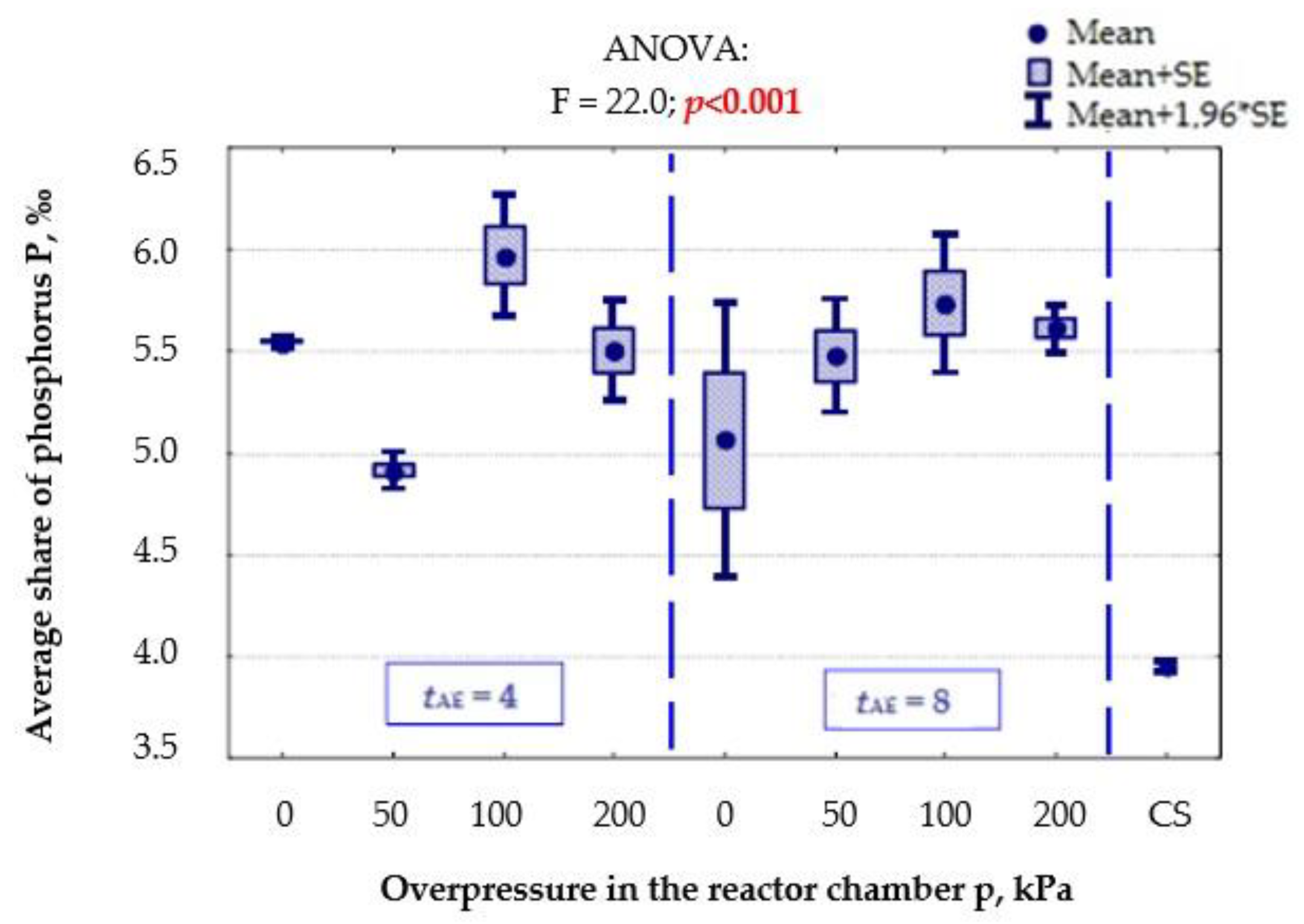
- Y9—P, average share of phosphorus, ‰.
3. Results
3.1. Effectiveness of the Composting Process in Hyperbaric Conditions
- change in the respiratory activity of microorganisms within 4 days,
- change in material moisture,
- change in organic matter content,
- weight loss of the material subjected to the experiment,
- change in the pH of the composted material,
- change in the macronutrient content of the material.
3.1.1. Degree of Respiratory Stabilization of the Product AT4
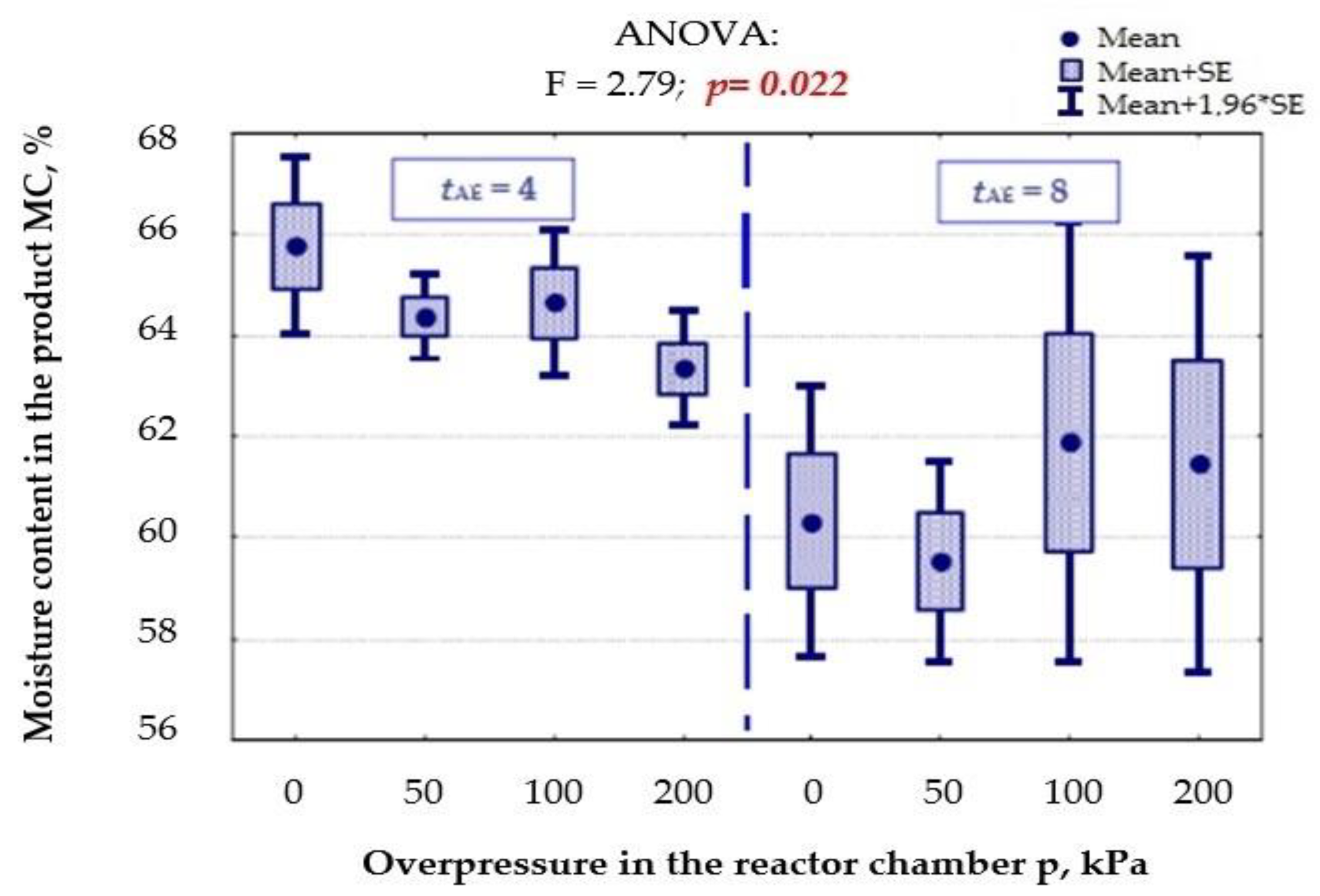
3.1.2. Moisture Content in the Material
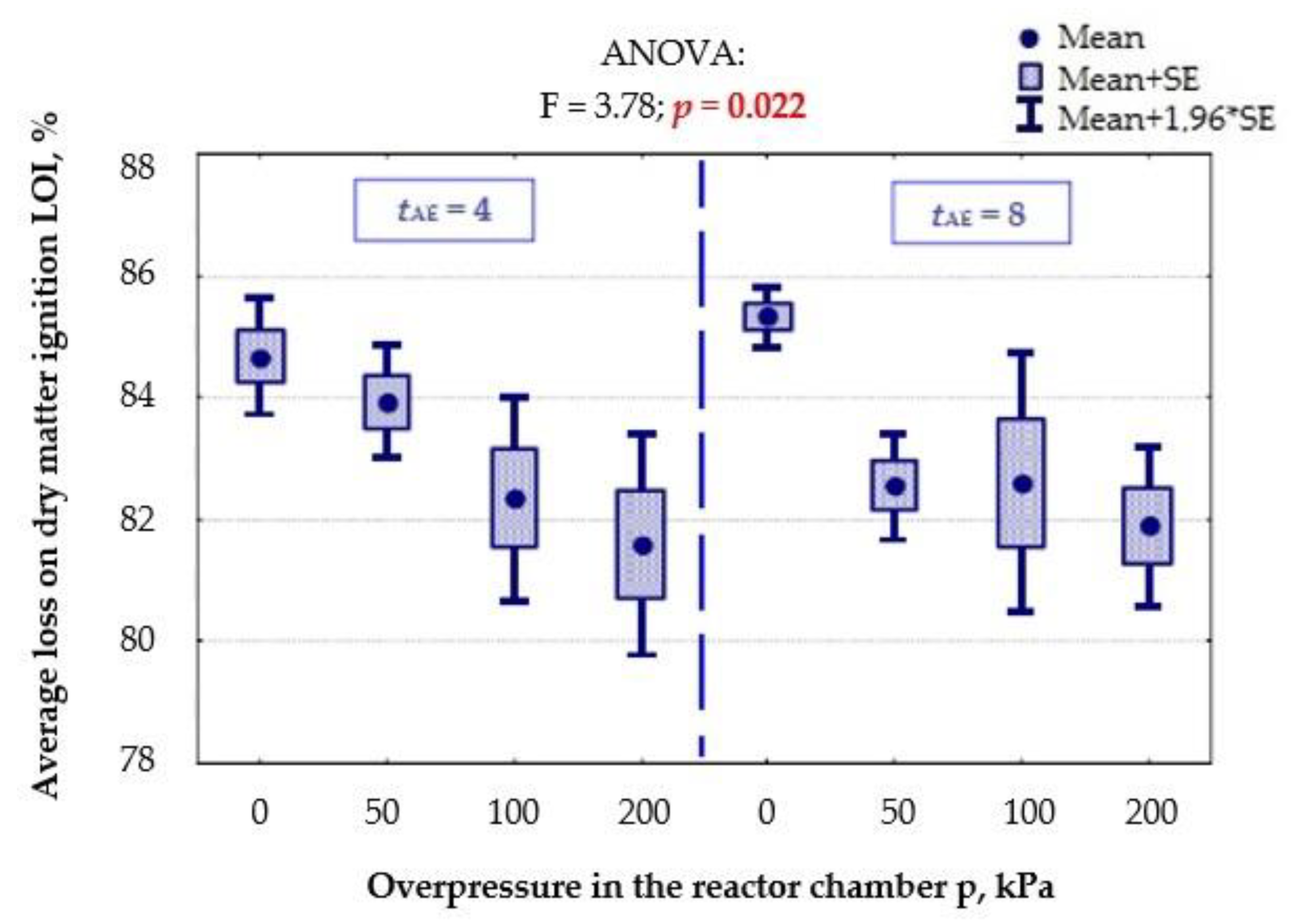
3.1.3. Loss on Dry Matter Ignition
3.1.4. Product Weight Loss
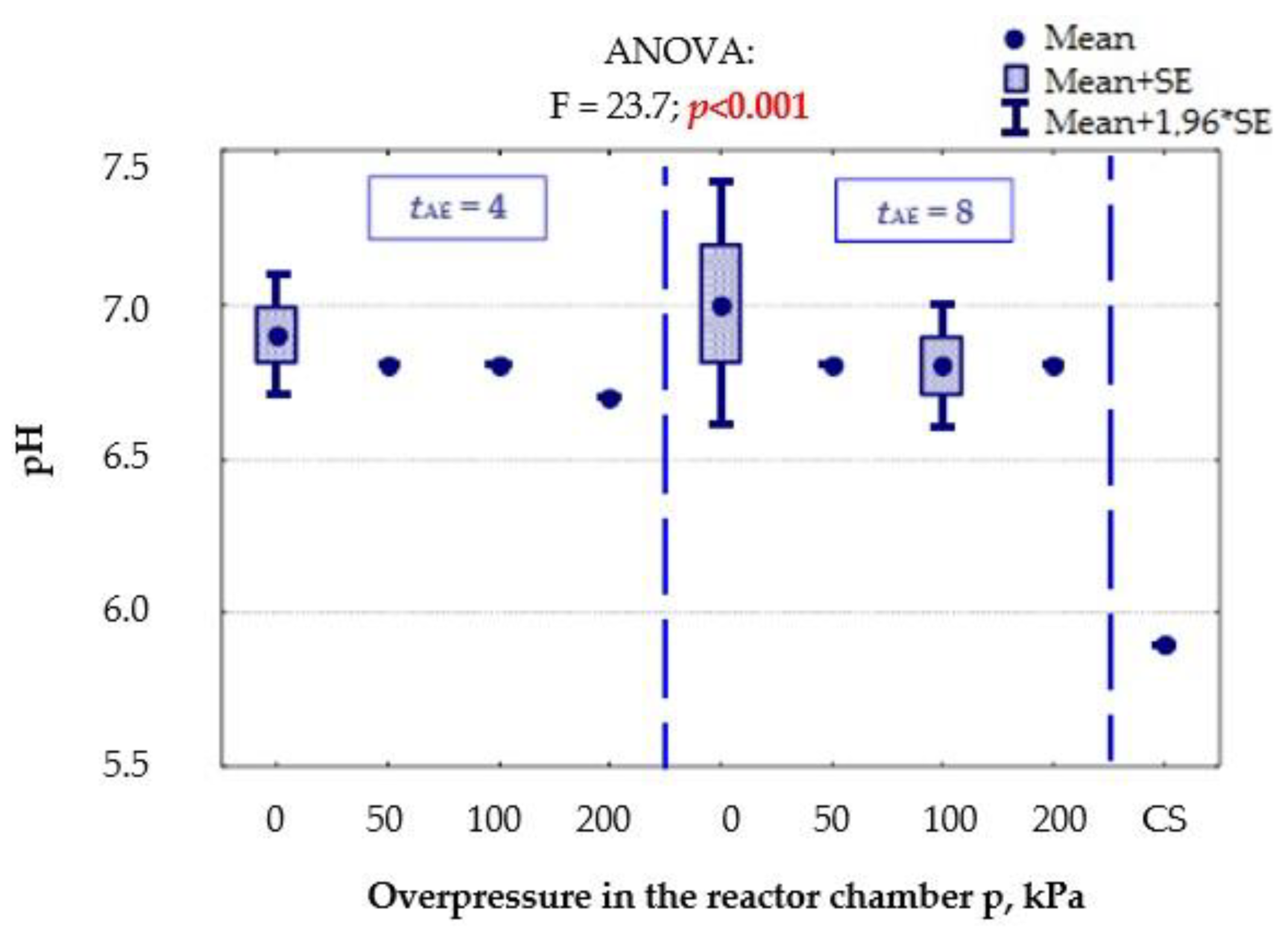
3.1.5. pH Value
3.1.6. Elemental Composition Content in the Product
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (a)
- the highest weight losses of the product at the overpressure variant of 200 kPa (tAE = 4 h—23.7% and tAE = 8 h—25.5%).
- (b)
- the highest efficiency of organic matter removal for overpressure variants 100 and 200 kPa (tAE = 4 h), and for overpressure variants 50, 100, and 200 kPa (tAE = 8 h).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heimowska, A. Hazards Drifting Polymeric Materials to the Marine Environment. Zesz. Nauk. Akad. Mor. W Gdyni 2016, 93, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Rosik-Dulewska, C. Podstawy Gospodarki Odpadami; Wyd. Nauk. PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 2021; ISBN 9788301180744. [Google Scholar]
- Klatka, J.; Kuźniak, M. Gospodarowanie Odpadami Komunalnymi; Poradnik dla Gmin. Wolters Kluwer SA.: Warsaw, Poland, 2012; ISBN 978-83-264-3880-6. [Google Scholar]
- Jędrczak, A. Biologiczne Przetwarzanie Odpadów; Wyd. Nauk. PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 2008; ISBN 978-83-01-15166-9. [Google Scholar]
- Czekal, W.; Witaszek, K.; Rodriguez Carmona, P.C.; Grzelak, M. Composting Systems for Industrial Biowastes: Advantages and Disadvantages. Tech. Rol. Ogrod. Leśna 2013, 2, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kostecka, J.; Koc-Jurczyk, J.; Brudzisz, K. Waste Management in Poland and European Union. Waste Manag. 2014, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Majoch, A.; Jabłońska, M.M. Bio-waste as a New Source of Renewable Energy. Nafta-Gaz 2013, 69, 673–682. [Google Scholar]
- Central Statistical Office. Environmental Protection 2018; Central Statistical Office: Warsaw, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Krzysztof Rać’s Doctoral Dissertation; Wroclaw, Poland. 2020. Available online: https://bip.upwr.edu.pl/uniwersytet/doktoraty-habilitacje/przewody-doktorskie/krzysztof-rac-10.html (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Polish Parliament. Act of 19 July 2019 Amending the Act on Maintaining Cleanliness and Order in Municipalities and Certain other Acts; Monitor of Poland of 2019; Polish Parliament: Warsaw, Poland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Public Information Bulletin of the Jelcz-Laskowice Commune. Available online: https://www.um.jelcz-laskowice.finn.pl/ (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Szewczyk, P. Kompostowanie/Stabilizacja Tlenowa. Przegląd Komunal. 2016, 4, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Glanz, R. Teoretyczne Podstawy Kompostowania. Pract. Inst. Ceram. I Mater. Bud. 2012, 5, 80–97. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Inbar, Y.; Chefetz, B.; Hadar, Y. Composting and Recycling of Organic Wastes, Modern Agriculture and the Environment. Mod. Agric. Environ. 1997, 71, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrczak, A. Technologie Przetwarzania Odpadów Biodegradowalnych. Inżynieria Ekol. 2005, 10, 78–90. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, L.F.; Savage, G.M.; Eggerth, L.L.; Chiumenti, A. Systems Used in Composting. Waste Manag. Ser. 2007, 8, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekała, J.; Dach, J.; Wolna-Maruwka, A. Wykorzystanie Bioreaktora do Badań Modelowych Kompostowania Osadu Ściekowego. Woda-Sr. -Obsz. Wiej. 2006, 6, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ciesielczuk, T.; Karwaczyńska, U.; Rosik-Dulewska, C. Possibilities of Application of Compost from Waste for Remove C6-C9 Aliphatic Hydrocarbons from Solution. Rocz. Ochr. Sr. 2011, 13, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Dach, J.; Wolna- Maruwka, A.; Zbytek, Z. Wpływ Dodatku Efektywnych Mikroorganizmów (EM) na Przebieg Kompostowania i Wielkość Emisji Gazowych. J. Res. Appl. Agric. Eng. 2009, 54, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sołowiej, P.; Neugebauer, M.; Piechocki, J. Wpływ Napowietrzania Złoża na Przebieg Pierwszej Fazy Procesu Kompostowania. Inżynieria Rol. 2010, 14, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Bilitewski, B.; Hardtle, G.; Marek, K. Podręcznik Gospodarki Odpadami; Teoria i praktyka; Seidel-Przywecki: Warsaw, Poland, 2006; ISBN 83-919449-8-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lasaridi, K.E.; Manios, T.; Stamatiadis, S.; Chroni, C.; Kyriacou, A. The Evaluation of Hazards to Man and the Environment during the Composting of Sewage Sludge. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lasaridi, K.E.; Stentiford, E.I.; Evans, T. Windrow Composting of Wastewater Biosolids: Process Performance and Product Stability Assessment. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 42, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidełko, R.; Siebielska, I.; Szymański, K.; Skubała, A.; Kołacz, N. Ocena Stabiloności Kompostu w Czasie Rzeczywistym. Inżynieria I Ochr. Sr. 2014, 2, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Lornage, R.; Redon, E.; Lagier, T.; Hebe, I.; Carre, J. Performance of a Low Cost MBT Prior to Landfilling: Study of the Biological Treatment of Size Reduced MSW without Mechanical Sorting. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, R.; Coromina, N.; Malińska, K.; Marfà, O. Evolution of Process Control Parameters During Extended Co-composting of Green Waste and Solid Fraction of Cattle Slurry to Obtain Growing Media. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, L.; Gea, T.; Mompeó, M.; Sayara, T.; Sánchez, A. Performance of Different Systems for the Composting of the Source-selected Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste. Biosyst. Eng. 2008, 101, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ball, A.S.; Esmaeil, S.; Aburto-Medina, A.; Kadali Krishna, K.; Shaiban Amer, A.J.; Stewart, R.J. Biostabilization of Municipal Solid Waste Fractions from an Advanced Waste Treatment Plant. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2017, 29, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrena, R.; Font, X.; Gabarrell, X.; Sánchez, A. Home Composting Versus Industrial Composting: Influence of Composting System on Compost Quality with Focus on Compost Stability. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, R.; Li, G.; Jiang, T.; Schuchardt, F.; Chen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y. Effect of Aeration Rate, C/N Ratio and Moisture Content on the Stability and Maturity of Compost. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.A.; Singh, J.; Pal Vig, A. Instrumental Characterization of Organic Wastes for Evaluation of Vermicompost Maturity. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hogg, D.; Eaviono, E.; Caimi, V.; Amlinger, F.; Devliegher, W.; Brinton, W.; Antler, S. Comparison of Composts Standards within the EU, North America, and Australasia. Oxon 2002, 10, 1–98. Available online: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5d333ff40424070001b85a08/t/5d41c996c557b50001ce0ab6/1564592545133/WRAP_Comparison_of_Compost_Standards_2002.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Cáceres, R.; Flotats, X.; Marfà, O. Changes in the Chemical and Physicochemical Properties of the Solid Fraction of Cattle Slurry during Composting Using Different Aeration Strategies. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, T.; Troy, S.N.; Healy, M.G.; Kwapinski, W.; Leahy, J.J.; Lawlor, P.G. Characterization of Compost Produced from Separated Pig Manure and Variety of Bulking Agents at Low initial C/N Ratios. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7131–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaseñor, J.; Rodríguez, L.; Fernández, F.J. Composting Domestic Sewage Sludge with Natural Zeolites in a Rotary Drum Reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, P.; Ghosh, G.K.; Ghosal, P.K.; Banik, P. Changes in Organic –C, N, P and K and Enzyme Activities in Vermicompost of Biodegradable Organic Wastes Under Limiting and Microbial Inoculants. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaosol, T.; Kiepukdee, S.; Towatana, P. Influence of Nitrogen Containing Wastes Addition on Natural Aerobic Composting of Rice Straw. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2012, 7, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Unit | Mean Value and Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk density | kg·m−3 | 280 |
| Moisture content | % | 60 |
| pH | - | 5.90 |
| Total nitrogen | % | 2.33 (0.21) |
| Total carbon | % | 43 |
| Potassium content | g·kg DM−1 | 23.73 (1.26) |
| Phosphorus content | g·kg DM−1 | 3.95 (0.02) |
| Loss on ignition | % | 88.97 (0.16) |
| Respiratory activity of microorganisms | mg O2·g DM−1 | 109.73 (2.48) |
| Parameter | Determination Method | Device |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture content | PN-EN 14346: 2011 | PS 3500 R2 laboratory scale, KbC-65W laboratory dryer |
| pH | PN-EN 15011-3:2001 | VOLTCRAFT PHT-200 pH meter |
| Elemental composition | Gas chromatography | CE Instruments CHNS elemental composition analyzer |
| Macronutrients | PN-EN ISO 11885:2009 | ICP-AES iCAP 7400 atomic emission spectrometers |
| Respiratory activity AT4 | OxiTop® Control | OxiTop®-C 110 set, Q-Cell 140/40 laboratory incubator |
| Loss of ignition | PN-EN 15169:2011 | AS 220.R2 laboratory scale, SNOL 8.2/1100 muffle furnace |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bieniek, J.; Gaze, B.; Knutel, B.; Rać, K.; Góraj, S. Analysis of the Effectiveness of Green Waste Composting under Hyperbaric Conditions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095108
Bieniek J, Gaze B, Knutel B, Rać K, Góraj S. Analysis of the Effectiveness of Green Waste Composting under Hyperbaric Conditions. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095108
Chicago/Turabian StyleBieniek, Jerzy, Błażej Gaze, Bernard Knutel, Krzysztof Rać, and Sara Góraj. 2022. "Analysis of the Effectiveness of Green Waste Composting under Hyperbaric Conditions" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095108
APA StyleBieniek, J., Gaze, B., Knutel, B., Rać, K., & Góraj, S. (2022). Analysis of the Effectiveness of Green Waste Composting under Hyperbaric Conditions. Sustainability, 14(9), 5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095108






