Ecological Risk Evaluation and Source Identification of Heavy Metal Pollution in Urban Village Soil Based on XRF Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
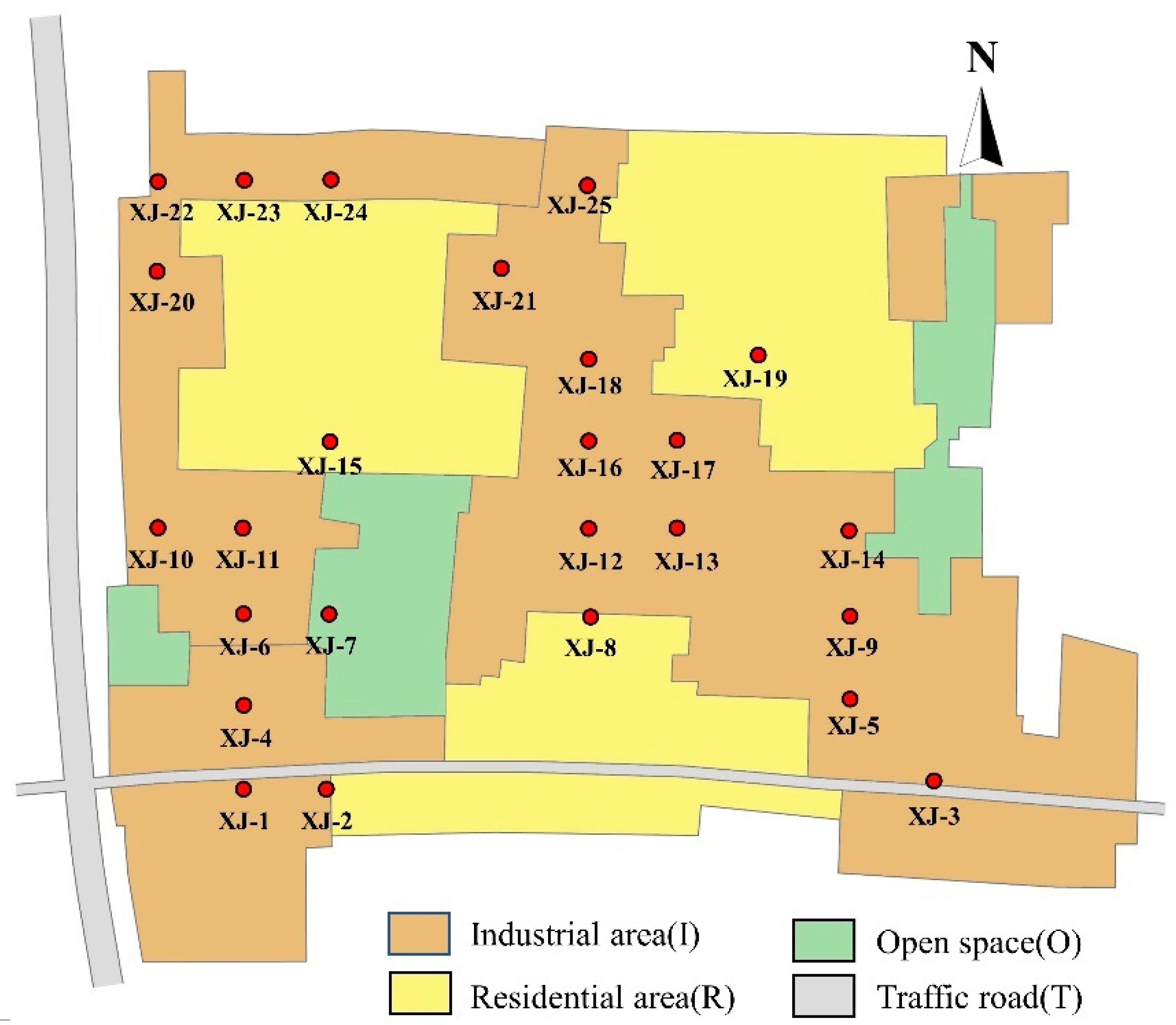
2.1. Research Area and Detection Points
2.2. Analytic Methods
2.3. Comprehensive Pollution Index (CPI) Method
2.4. Geo-Accumulation Index (Igeo) Method
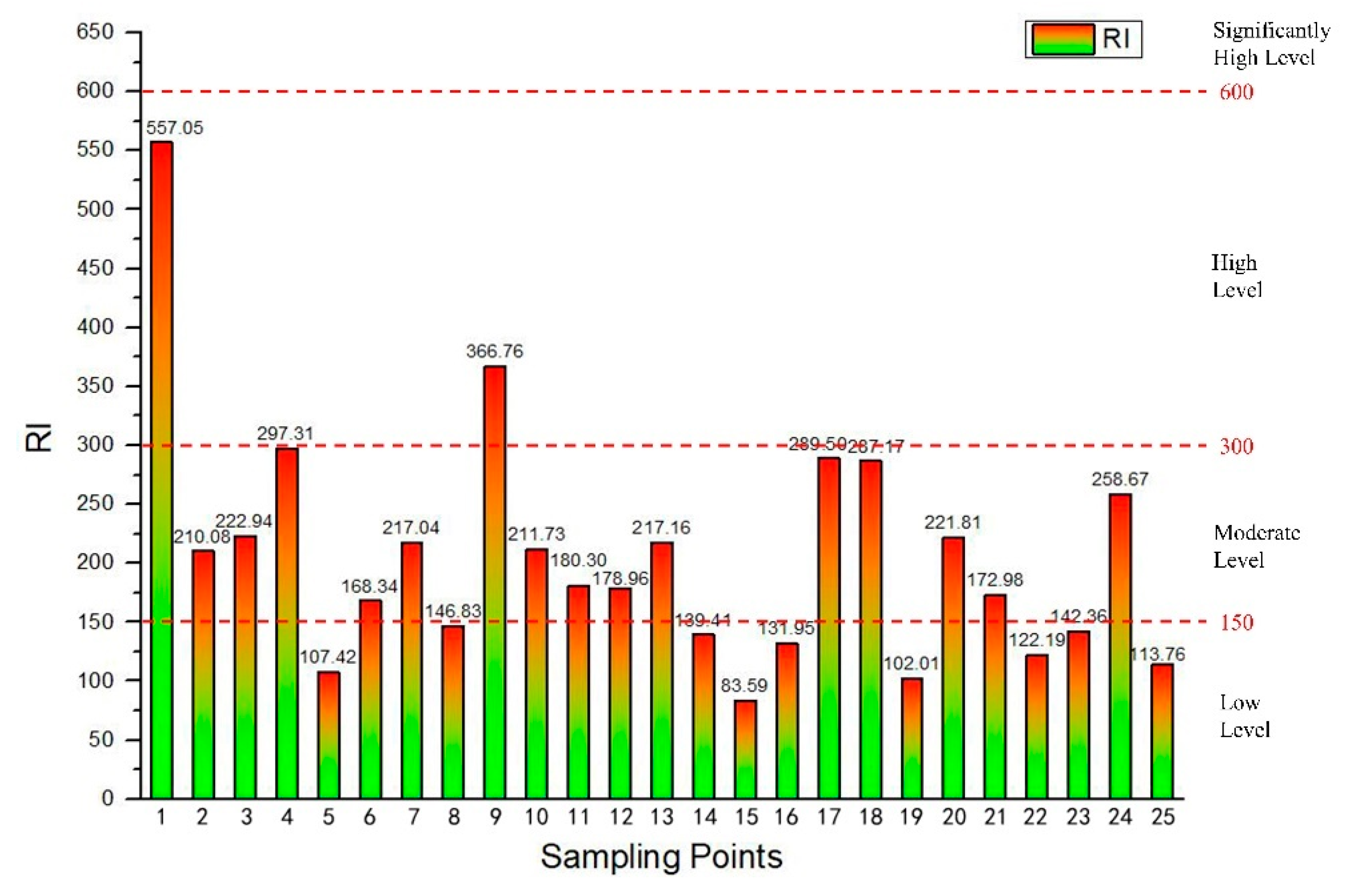
2.5. Potential Ecological Risk Index (RI) Method
2.6. Methods of Sources Identification
3. Results
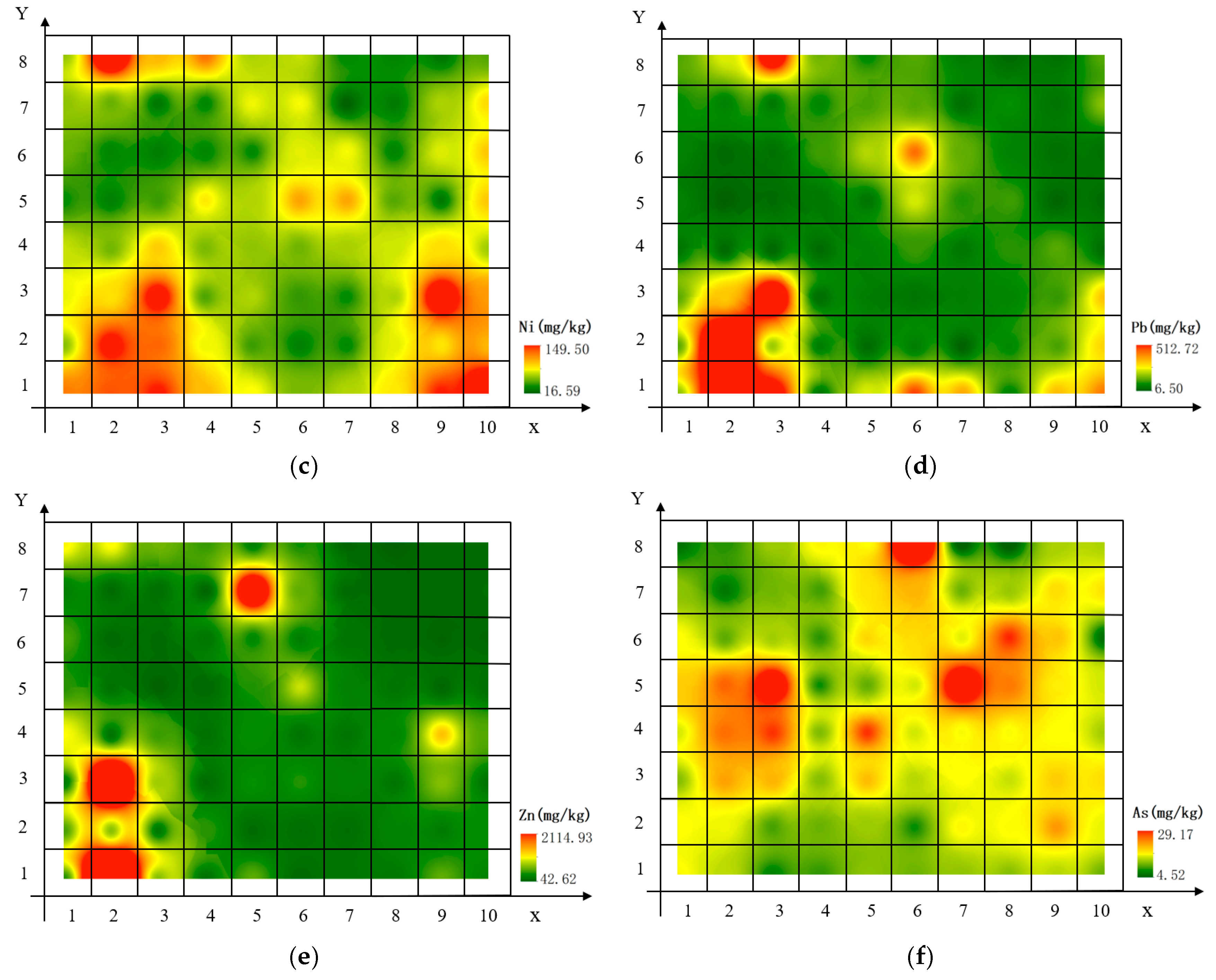
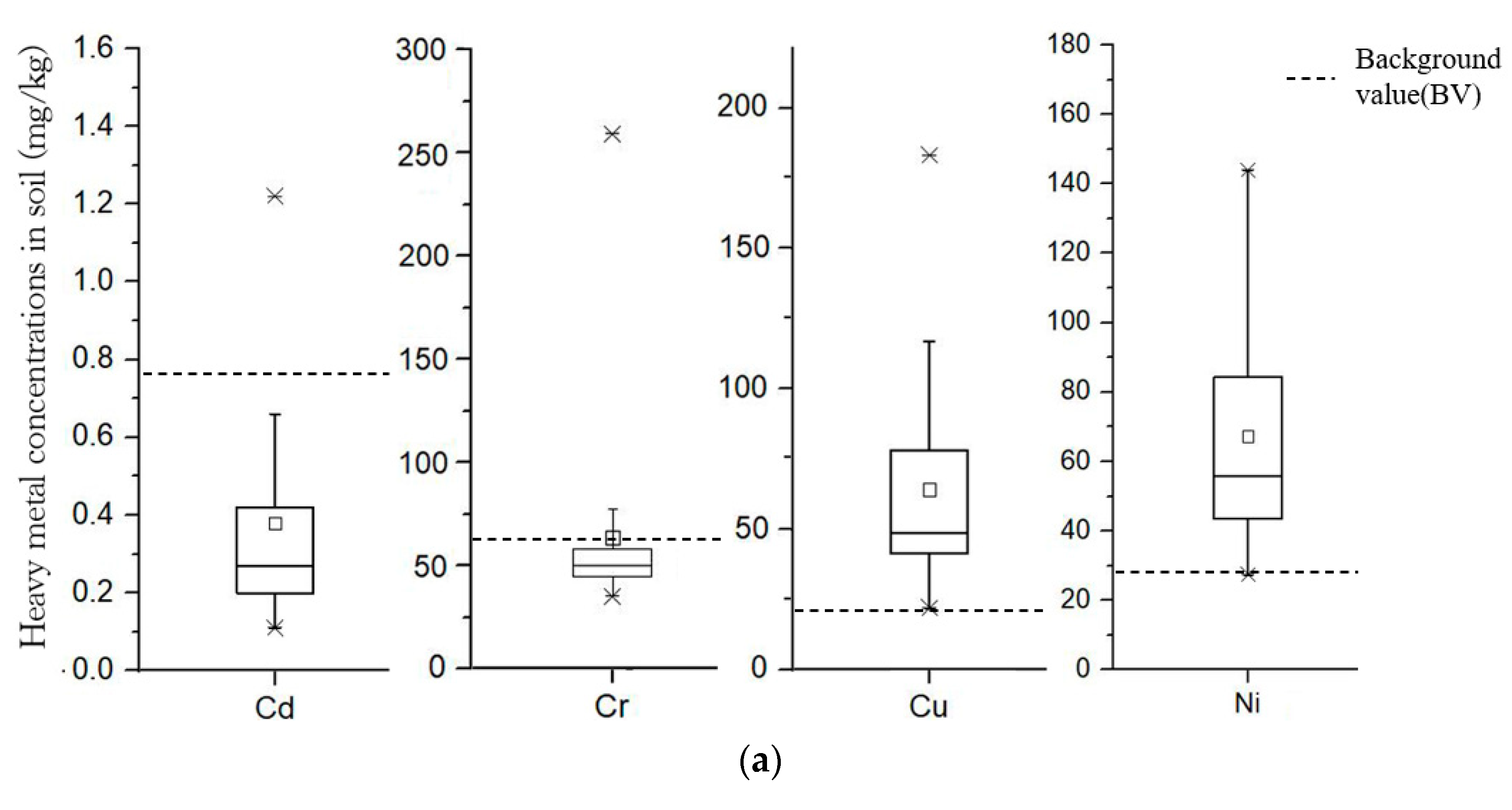
3.1. Soil Analyses with XRF
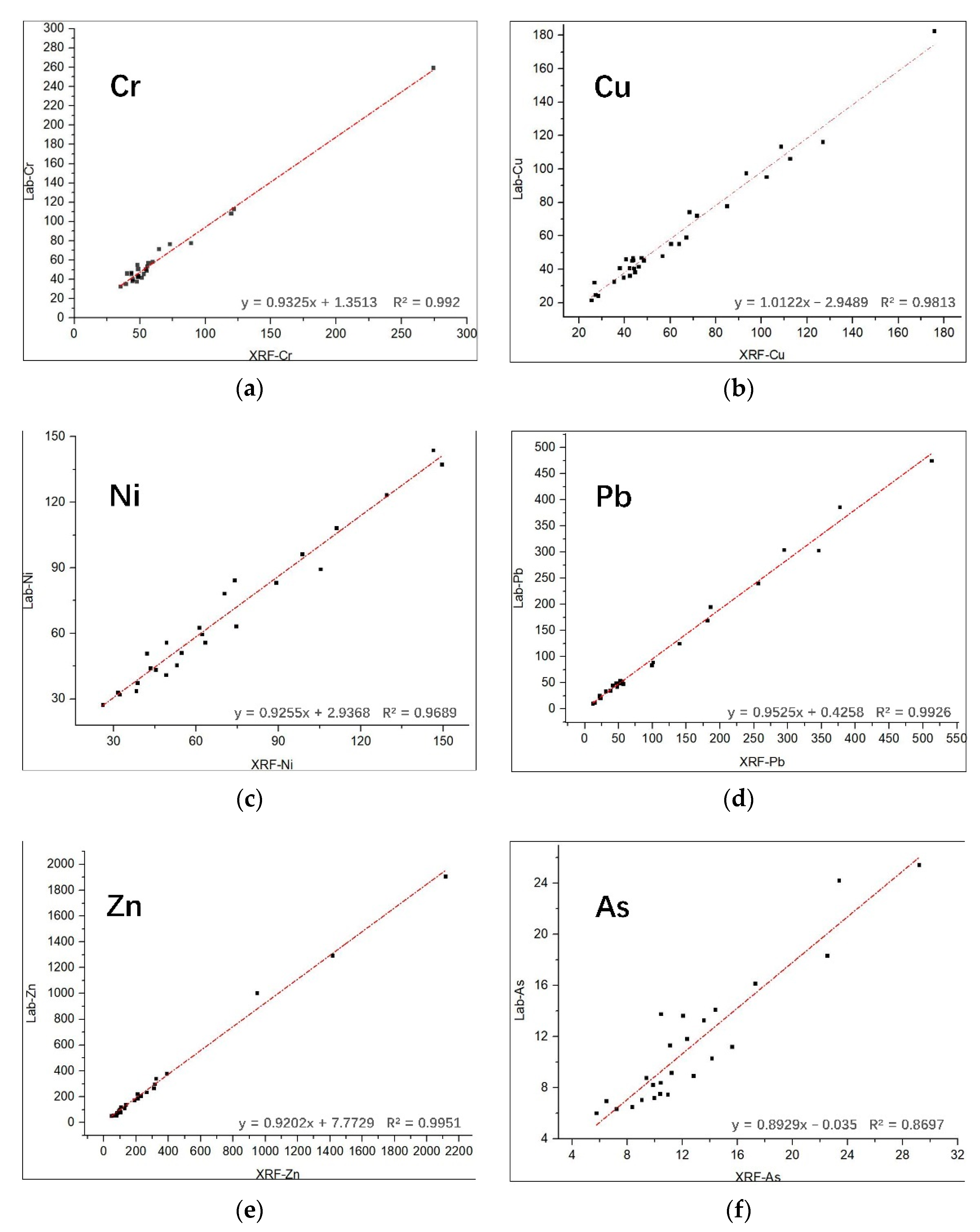
3.2. Confirmation Laboratory Analyses
3.3. Source Identification
4. Discussion
4.1. Method of Investigation
4.2. Multi-Sources of Pollution
4.3. Sustainability of Urban Village
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawler, J.J.; Lewis, D.J.; Nelson, E.; Plantinga, A.J.; Polasky, S.; Withey, J.C.; Helmers, D.P.; Martinuzzi, S.; Pennington, D.; Radeloff, V.C. Projected land-use change impacts on ecosystem services in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7492–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; He, Y.F.; Choi, Y.; Chen, Q.R.; Cheng, H. Warning of negative effects of land-use changes on ecological security based on GIS. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 32–49.
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China (MOHURD). China Construction Statistical Yearbook. Beijing. 2020. Available online: http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/xytj/tjzljsxytjgb/jstjnj/index.html (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Ning, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Kuang, W.H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yan, C. Spatial-temporal patterns and characteristics of land-use change in China during 2010-2015. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Tian, C.H. Construction land quotas as a tool for managing urban expansion. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 195, 103727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zeng, F.; Liu, S.; Yang, M.; Xu, F. The effects of China’s sustainable development policy for resource-based cities on local industrial transformation. Resour. Policy 2021, 71, 101940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Huang, H.P.; Kung, C.C. Ecological impact assessment of land use in eco-industrial park based on life cycle assessment: A case study of Nanchang High-tech development zone in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 300, 126816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, D.X.; Huang, L.Y.; Wen, H.Z.; Zhao, G.C.; Zhan, D.S. Spatial distribution and influential factors of industrial land productivity in China’s rapid urbanization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Liu, J.; Gu, X.K. Reduction of industrial land beyond Urban Development Boundary in Shanghai: Differences in policy responses and impact on towns and villages. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertaud, A.; Renaud, B. Socialist Cities without Land Markets. J. Urban Econ. 1997, 41, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Ma, K.X.; Liu, H.M. Policy evolution of the economical and intensive utilization of industrial land in China since 1978. China Land Sci. 2013, 27, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Shang, Y.P.; Song, M.L. Industrial structure distortion and urban ecological efficiency from the perspective of green entrepreneurial ecosystems. Soc.-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2020, 72, 100757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.Y.; Lin, Z.L.; Jiang, X.L.; Qiu, M.L.; Sun, J. How do the industrial land use intensity and dominant industries guide the urban land use? Evidences from 19 industrial land categories in ten cities of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 53, 101978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; He, Y.L.; Guo, C.H.; Xiao, X.Y.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soils of major cities in China. Environ. Sci. 2021, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.H.; Xue, N.D.; Han, Z.G. A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Guo, D.K.; Liu, K.; Meng, H.; Zheng, Y.J.; Yuan, F.Q.; Zhu, G.H. Levels, sources, and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils from a typical coal industrial city of Tangshan, China. CATENA 2019, 175, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environmental of P. R. China (MEE); Ministry of Natural Resources of P. R. China (MNR). The Communique for Soil Contamination Status Survey in China. Beijing. 2014. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/sthjbgw/qt/201404/t20140417_270670.htm (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Chen, T.B.; Zheng, Y.M.; Lei, M.; Huang, Z.C.; Wu, H.T.; Chen, H.; Fan, K.K.; Yu, K.; Wu, X.; Tian, Q.Z. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.H.; Wu, F.C.; Xie, F.Z.; Zhang, R.Q. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in urban soils from southwest China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taati, A.; Salehi, M.H.; Mohammadi, J.; Mohajer, R.; Díezc, S. Pollution assessment and spatial distribution of trace elements in soils of Arak industrial area, Iran: Implications for human health. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaeva, O.; Tikhonov, V.; Vecherskii, M.; Kostina, N.; Fedoseeva, E.; Astaikina, A. Ecotoxicological effects of traffic-related pollutants in roadside soils of Moscow. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 172, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Sodhi, K.K.; Kumar, M.; Singh, D.K. Heavy metal pollution: Insights into chromium eco-toxicity and recent advancement in its remediation. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.J.; Wang, D.J.; Li, T.L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.Q. Accumulation and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediments, and aquatic organisms in rural rivers in the Taihu Lake region, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 6721–6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepanosyan, G.; Maghakyan, N.; Sahakyan, L.; Saghatelyan, A. Heavy metals pollution levels and children health risk assessment of Yerevan kindergartens soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Che, L.; Sun, D.Q. The coupling coordination development between urbanization and economic growth and its influencing factors in China. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, W.; Du, J. Towards sustainable urban transition: A critical review of strategies and policies of urban village renewal in Shenzhen, China. Land Use Policy 2021, 111, 105744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Z.; Yu, J.H.; Zhang, D.S.; Ma, R.F. A Study of Livable Cities in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.L.; Walker, T.R.; Davis, E.; Ma, G.F. Ecological risk assessment of metals in small craft harbour sediments in Nova Scotia, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.S. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in Haikou urban soils. Chin. J. Ecol. 2014, 33, 421–428. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, M.; Sünbül, M.R.; Aytop, H.; Yılmaz, C.H. Environmental, ecological and health risks of trace elements, and their sources in soils of Harran Plain, Turkey. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Sun, X.F.; Sun, L.H.; Choguill, C.L. Optimizing the governance model of urban villages based on integration of inclusiveness and urban service boundary (USB): A Chinese case study. Cities 2020, 96, 102427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Z.; He, J.; Han, H.Y.; Zhang, W.W. Evaluating residents’ satisfaction with market-oriented urban village transformation: A case study of Yangji Village in Guangzhou, China. Cities 2019, 95, 102394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, S.; Li, J. The dawn of vulnerable groups: The inclusive reconstruction mode and strategies for urban villages in China. Habitat Int. 2021, 110, 102347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zhang, X. Framing social sustainability and justice claims in urban regeneration: A comparative analysis of two cases in Guangzhou. Land Use Policy 2021, 102, 105224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, M.Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, X.; Lu, J.X. A study on migration tendency of floating population in urban villages: Taking the city of Xi’an as an example. Mod. Urban Res. 2021, 8, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environmental of P. R. China (MEE). Technical Guidelines for Investigation on Soil Contamination of Land for Construction. 2019. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk01/201912/t20191209_748070.html (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environmental of P. R. China (MEE). The Technical Specification for Soil Environmental Monitoring. 2004. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/200412/t20041209_63367.shtml (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Brent, R.N.; Wines, H.; Luther, J.; Irving, N.; Collins, J.; Drake, B.L. Validation of handheld X-ray fluorescence for in situ measurement of mercury in soils. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). SW-846 Test Method 6200: Field Portable X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry for the Determination of Elemental Concentrations in Soil and Sediment. 2007. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-test-method-6200-field-portable-x-ray-fluorescence-spectrometry-determination (accessed on 26 March 2022).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA). SW-846 Test Method 3050B: Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, and Soils. 1996. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-test-method-3050b-acid-digestion-sediments-sludges-and-soils (accessed on 26 March 2022).
- Xu, G.L.; Wen, Y.; Cai, S.Y.; Luo, X.F. Review for the effects of urban topsoil on the ecological health. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 2941–2956. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.B.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.K.; Dong, J. Comparative study between Nemerow Index method and Compound Index method for the risk assessment of soil heavy metal pollution. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 16, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environmental of P. R. China (MEE). Soil Environment Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Development Land. 2018. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/trhj/201807/t20180703_446027.shtml (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environmental of P. R. China (MEE). Soil Environment Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. 2018. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/trhj/201807/t20180703_446029.shtml (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China; China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Background Values of Soil Elements in China; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 87–90.
- Feng, Q.W.; Wang, B.; Ma, X.J.; Jiang, Z.H.; Chen, M. Pollution Characteristics and Source Analysis of Heavy Metal in Soils of Typical Lead-Zinc Mining Areas in Northwest Guizhou, China. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2020, 39, 863–870. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.H.; Zhu, Y.W.; Shao, K.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, G.H.; Shen, J. Metals source apportionment in farmland soil and the prediction of metal transfer in the soil-rice-human chain. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, E.; Pérez, G.; Ojeda, G.; Alcañiz, J.M.; Valiente, M.; López-Mesas, M.; Sánchez-Martín, M.-J. Heavy metal availability assessment using portable X-ray fluorescence and single extraction procedures on former vineyard polluted soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, C.; Margui Grabulosa, E.; Pili, E.; Floor, G.H.; Roman-Ross, G.; Charlet, L. Quantification of trace arsenic in soils by field-portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry: Considerations for sample preparation and measurement conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, T.; Diamond, D. Comparison of soil pollution concentrations determined using AAS and portable XRF techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporale, A.G.; Adamo, P.; Capozzi, F.; Langella, G.; Terribile, F.; Vingiani, S. Monitoring metal pollution in soils using portable-XRF and conventional laboratory-based techniques: Evaluation of the performance and limitations according to metal properties and sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messager, M.L.; Davies, I.P.; Levin, P.S. Development and validation of in-situ and laboratory X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy methods for moss biomonitoring of metal pollution. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Darijani, T.; Alipour, V. Heavy metal pollution of road dust in a city and its highly polluted suburb; quantitative source apportionment and source-specific ecological and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 129656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walraven, N.; van Os, B.J.H.; Klaver, G.T.; Middelburg, J.J.; Davies, G.R. The lead (Pb) isotope signature, behaviour and fate of traffic-related lead pollution in roadside soils in The Netherlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Ryu, J.S.; Ra, k. Characteristics of potentially toxic elements and multi-isotope signatures (Cu, Zn, Pb) in non-exhaust traffic emission sources. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.J.; Kwon, Y.K.; Yu, S.Y.; Lee, P.K.; Park, H.S.; Song, N. Assessment of Zn pollution sources and apportionment in agricultural soils impacted by a Zn smelter in South Korea. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.Y.; Yan, T.; Wang, K.; Huang, S.M.; Yuan, W.Z.; Qin, F.G.F. Soil heavy metal lead pollution and its stabilization remediation technology. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hao, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Li, F.; Li, C.; Yu, H. Development of a new framework to estimate the environmental risk of heavy metal(loid)s focusing on the spatial heterogeneity of the industrial layout. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 106315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, T.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Non-inverted U-shaped challenges to regional sustainability: The health risk of soil heavy metals in coastal China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Yang, T.; Ma, S.; Ni, W. Heavy Metal Pollution of Soils in the Site of a Retired Paint and Ink Factory. Energy Procedia 2012, 16, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Deng, M.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Xu, X.D. Research hotspots and trend of city village renovation. Urban Probl. 2018, 8, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.B.; Ma, X.G.; Li, G.C. Formation and governance of informality in urban village under the rapid urbanization process. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 34, 162–168. [Google Scholar]


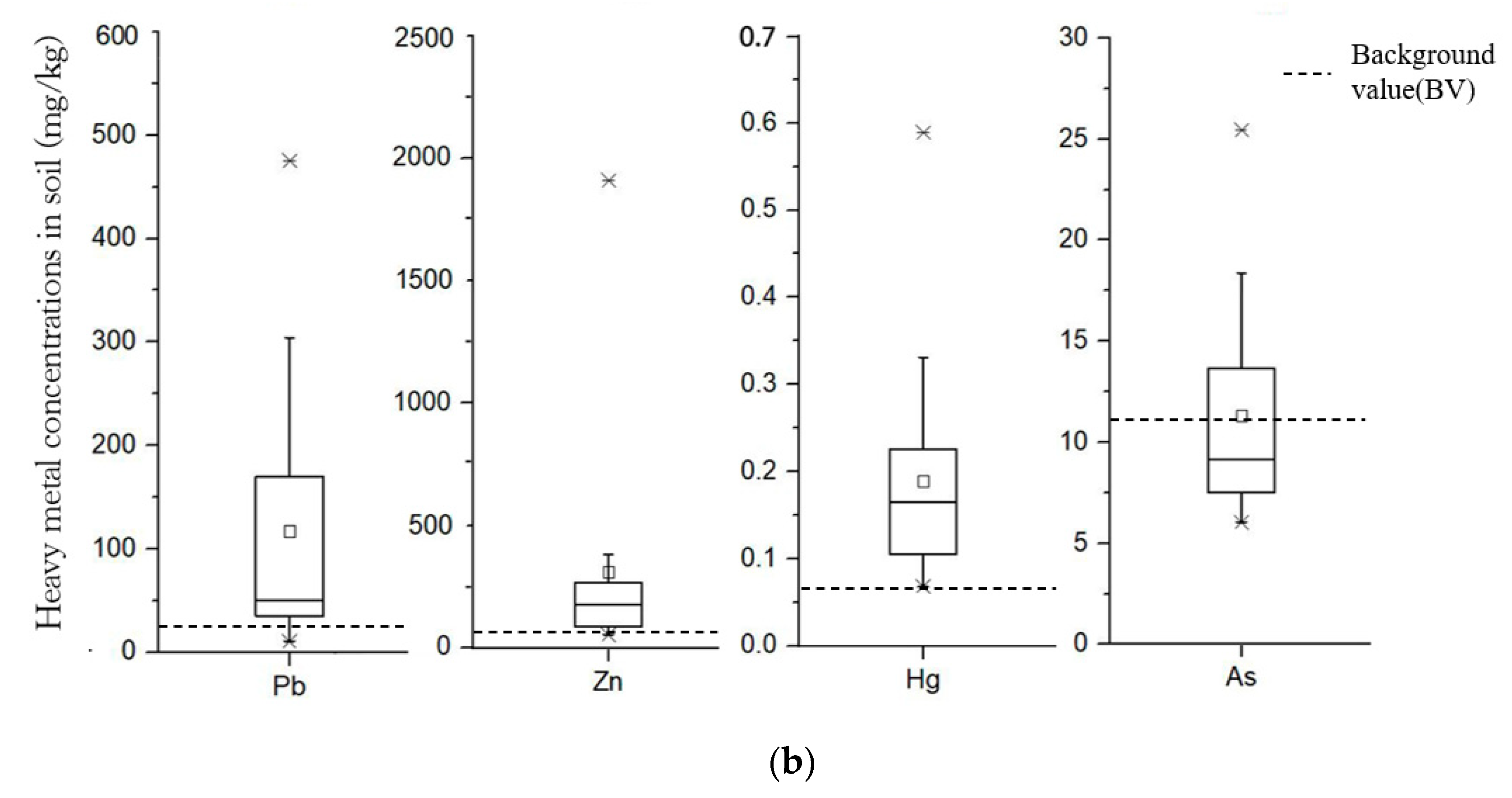
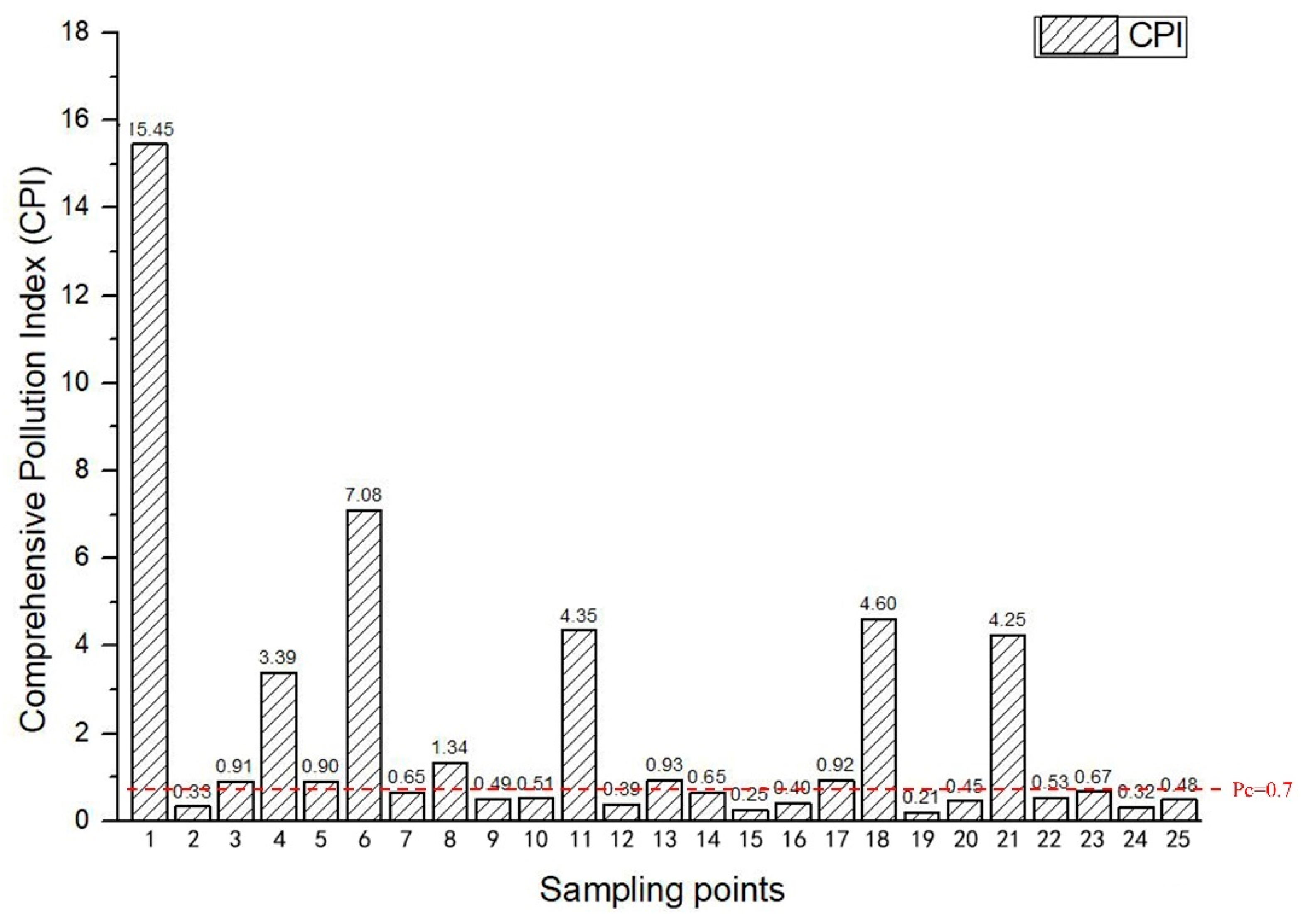
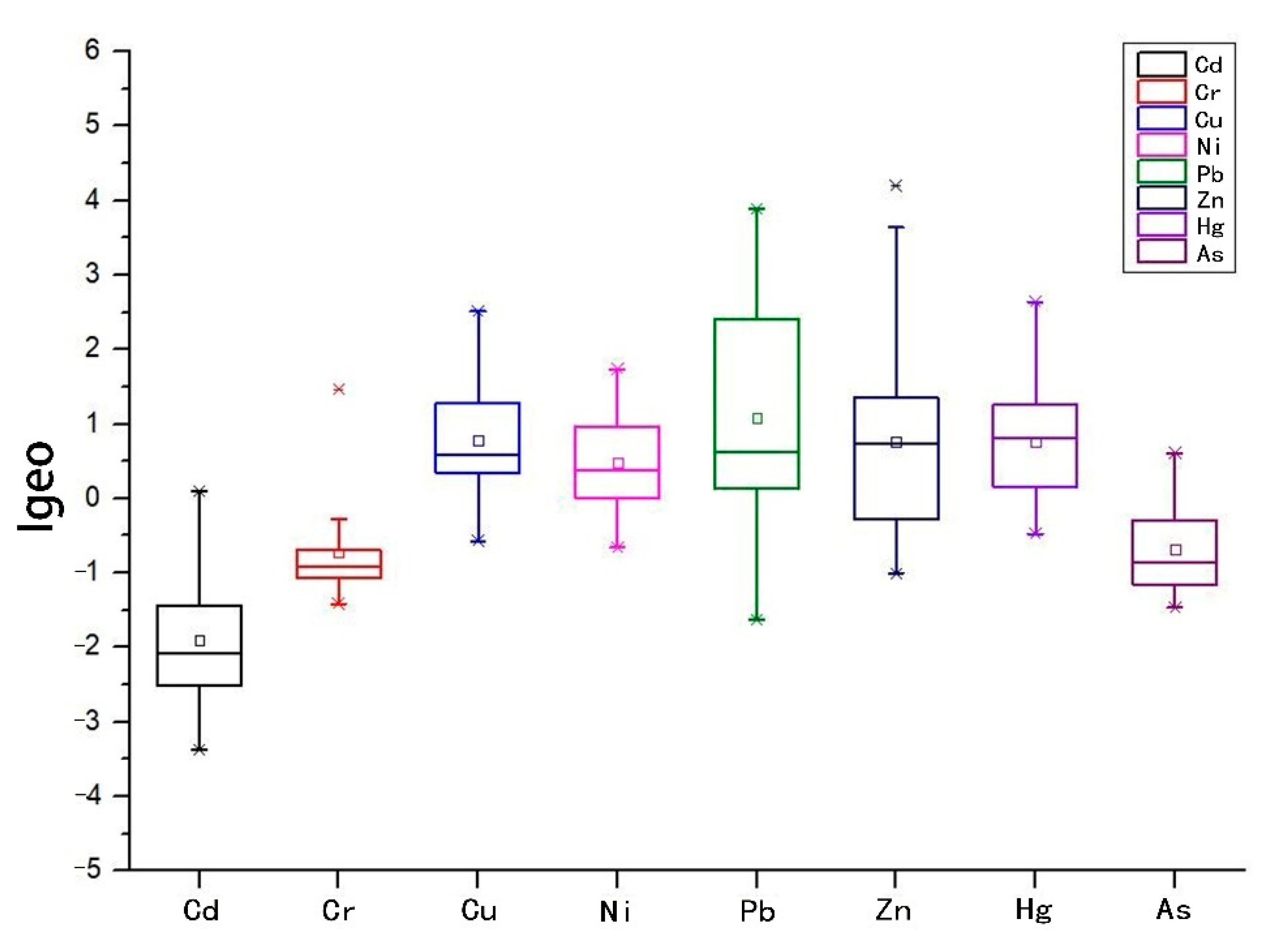
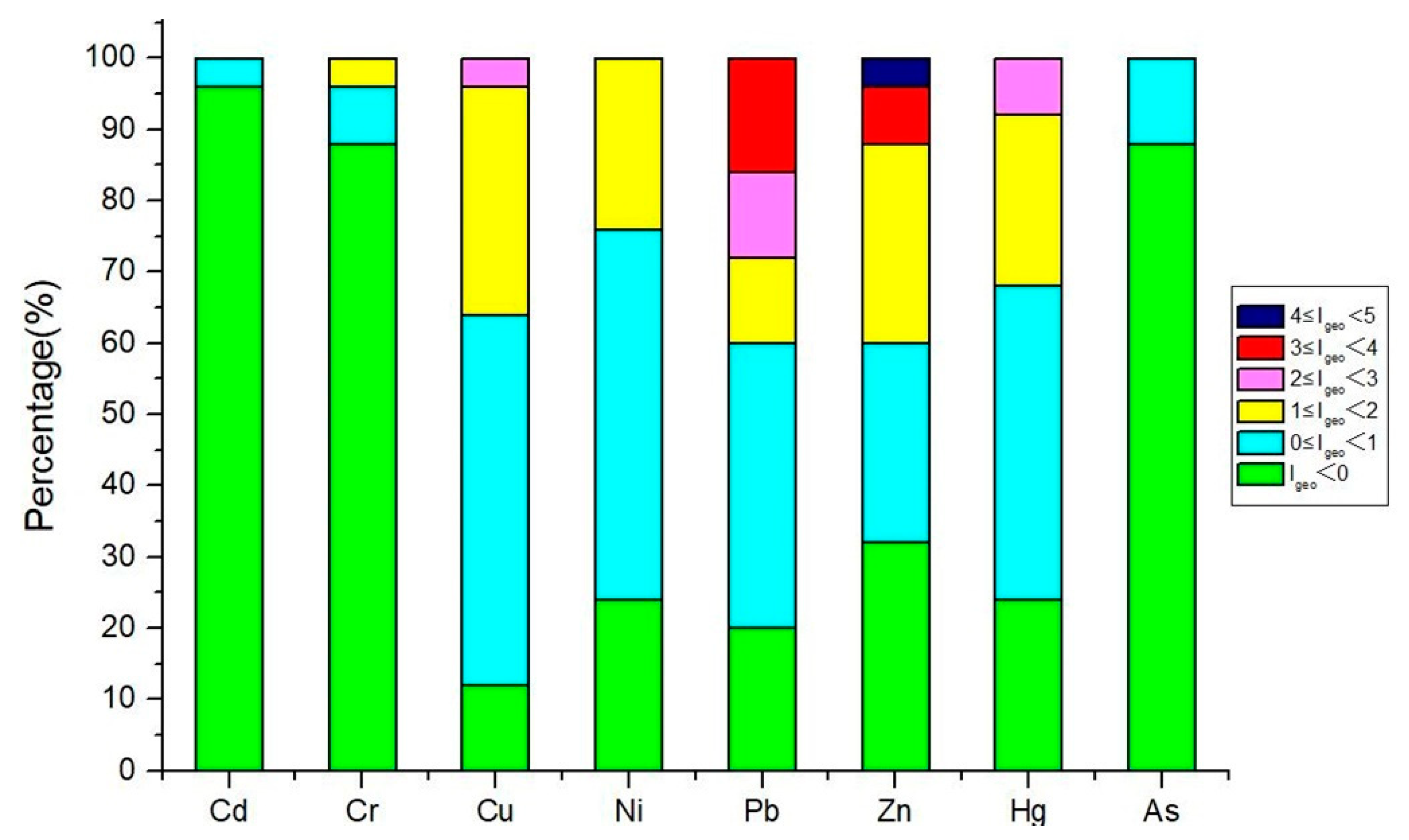


| Mode | Detectable Elements (Beam 1) | Detectable Elements (Beam 2) | Detectable Elements (Beam 3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Sr, Rb, Zr, Mo, W, Tl, Hg, Pb, Bi | Mg, Al, Si, P, S | Ag, Cd, Sn, Sb, Ba |
| Heavy Metals | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | Hg | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cni (mg·kg−1) | 0.76 | 62.5 | 21.4 | 28.8 | 21.4 | 69.4 | 0.063 | 11.1 |
| Tri | 30 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 40 | 10 |
| Heavy Metals | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | Hg | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 0.38 | 63.90 | 63.81 | 67.25 | 116.95 | 309.98 | 0.19 | 11.30 |
| (mg·kg−1) | ||||||||
| Median | 0.27 | 49.89 | 48.07 | 55.93 | 49.72 | 173.84 | 0.17 | 9.17 |
| (mg·kg−1) | ||||||||
| SD | 0.29 | 45.20 | 37.53 | 33.43 | 128.54 | 442.37 | 0.13 | 5.23 |
| Min | 0.11 | 35.26 | 21.64 | 27.38 | 10.37 | 51.89 | 0.07 | 6.03 |
| (mg·kg−1) | ||||||||
| Max | 1.22 | 259.32 | 182.81 | 143.90 | 475.15 | 1908.13 | 0.59 | 25.44 |
| (mg·kg−1) | ||||||||
| CV | 75.45 | 70.74 | 58.82 | 49.71 | 109.91 | 142.71 | 67.01 | 46.30 |
| (%) |
| Heavy Metals | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 1 | |||||
| Cu | 0.097 | 1 | ||||
| Ni | 0.102 | 0.148 | 1 | |||
| Pb | 0.160 | 0.132 | 0.557 ** | 1 | ||
| Zn | 0.047 | 0.104 | 0.254 * | 0.417 ** | 1 | |
| As | 0.196 | 0.171 | −0.008 | −0.047 | 0.033 | 1 |
| Heavy Metal | Cluster | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Cr | 51.19 | 57.18 | 45.23 | 57.43 |
| Cu | 47.49 | 43.67 | 67.00 | 68.68 |
| Ni | 49.25 | 85.45 | 92.04 | 56.97 |
| Pb | 47.10 | 359.23 | 335.82 | 91.79 |
| Zn | 108.09 | 1953.93 | 200.18 | 1095.01 |
| As | 9.73 | 8.85 | 8.96 | 11.65 |
| Cluster Quantity | 73 | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extracted Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 1.938 | 32.293 | 32.293 | 1.938 | 32.293 | 32.293 |
| 2 | 1.248 | 20.801 | 53.094 | 1.248 | 20.801 | 53.094 |
| 3 | 0.908 | 15.129 | 68.223 | 0.908 | 15.129 | 68.223 |
| 4 | 0.807 | 13.443 | 81.667 | 0.807 | 13.443 | 81.667 |
| 5 | 0.701 | 11.688 | 93.355 | |||
| 6 | 0.399 | 6.645 | 100.000 | |||
| Heavy Metals | Component | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Cr | 0.318 | 0.554 | −0.655 | −0.224 |
| Cu | 0.362 | 0.464 | 0.673 | −0.368 |
| Ni | 0.763 | −0.184 | −0.032 | −0.253 |
| Pb | 0.838 | −0.223 | −0.103 | −0.046 |
| Zn | 0.640 | −0.159 | 0.110 | 0.611 |
| As | 0.107 | 0.786 | 0.050 | 0.426 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Peng, B.; Li, J. Ecological Risk Evaluation and Source Identification of Heavy Metal Pollution in Urban Village Soil Based on XRF Technique. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5030. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095030
Liu S, Peng B, Li J. Ecological Risk Evaluation and Source Identification of Heavy Metal Pollution in Urban Village Soil Based on XRF Technique. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5030. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095030
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Siqi, Biao Peng, and Jianfeng Li. 2022. "Ecological Risk Evaluation and Source Identification of Heavy Metal Pollution in Urban Village Soil Based on XRF Technique" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5030. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095030
APA StyleLiu, S., Peng, B., & Li, J. (2022). Ecological Risk Evaluation and Source Identification of Heavy Metal Pollution in Urban Village Soil Based on XRF Technique. Sustainability, 14(9), 5030. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095030






