Environmental Competencies for Sustainability: A Training Experience with High School Teachers in a Rural Community
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Environmental Education for Sustainable Development
1.2. The Teacher as an Agent of Change
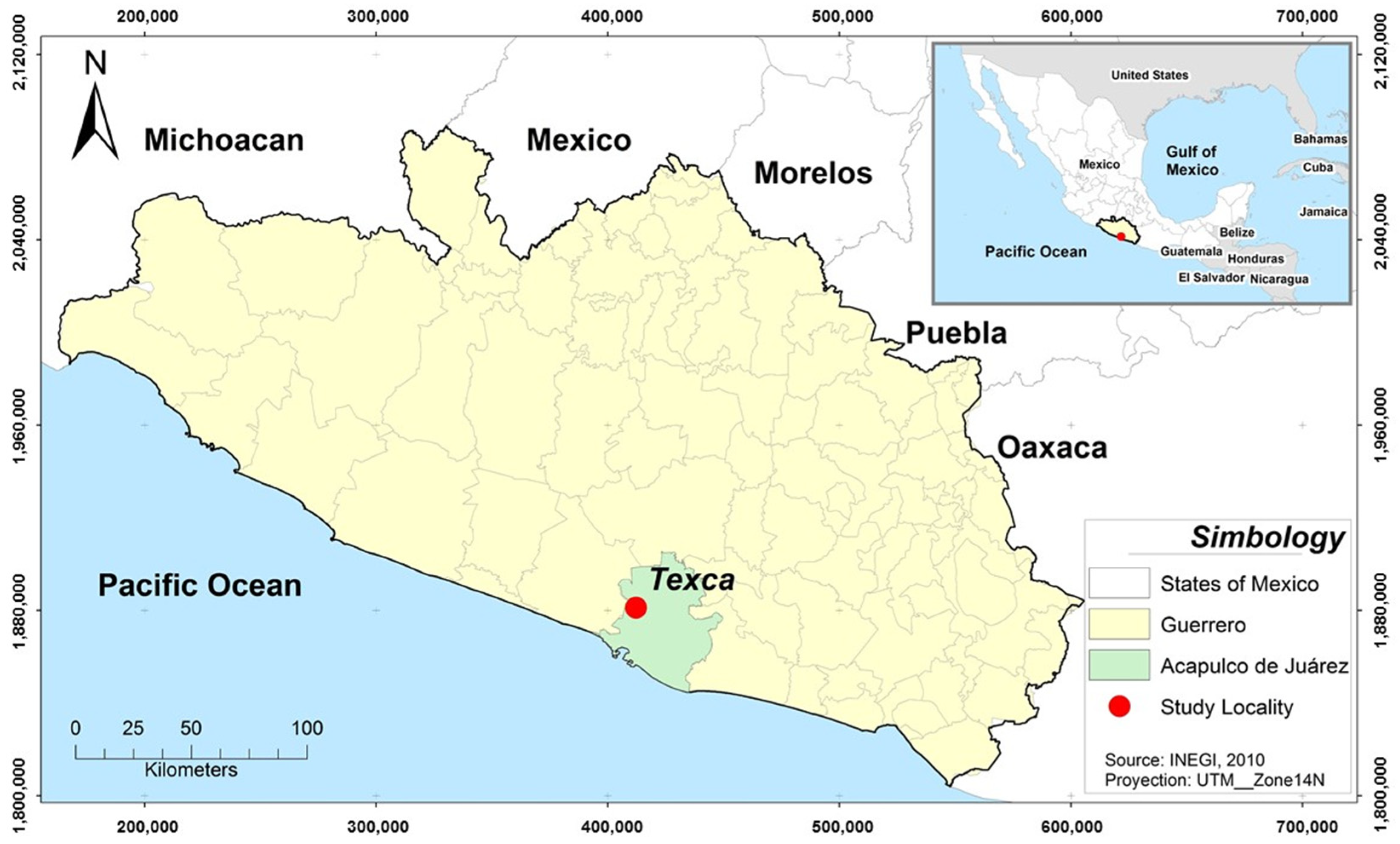
2. Materials and Methods
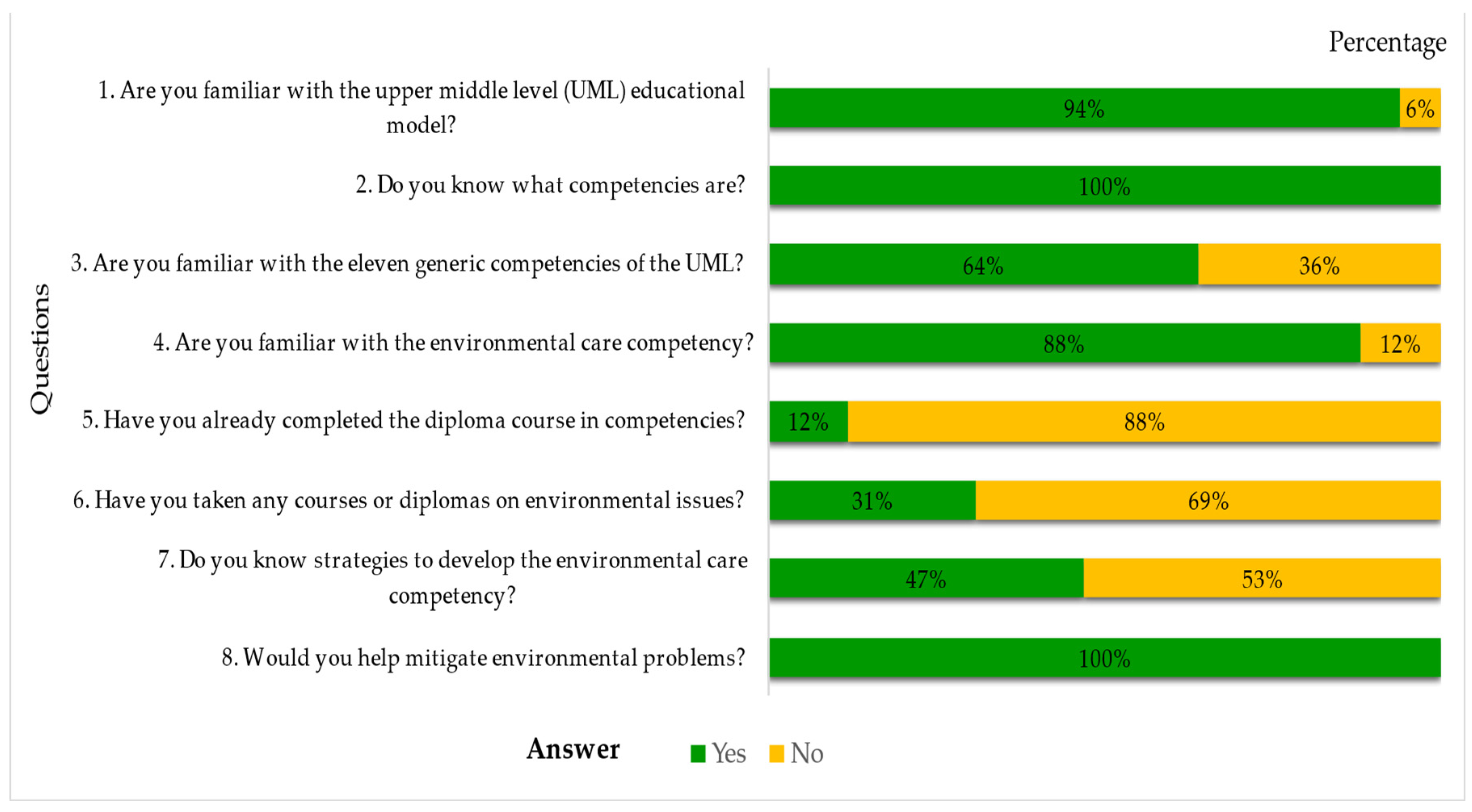
2.1. Phase I. Diagnosis
2.2. Phase II. Design and Implementation of a Course-Workshop
3. Results
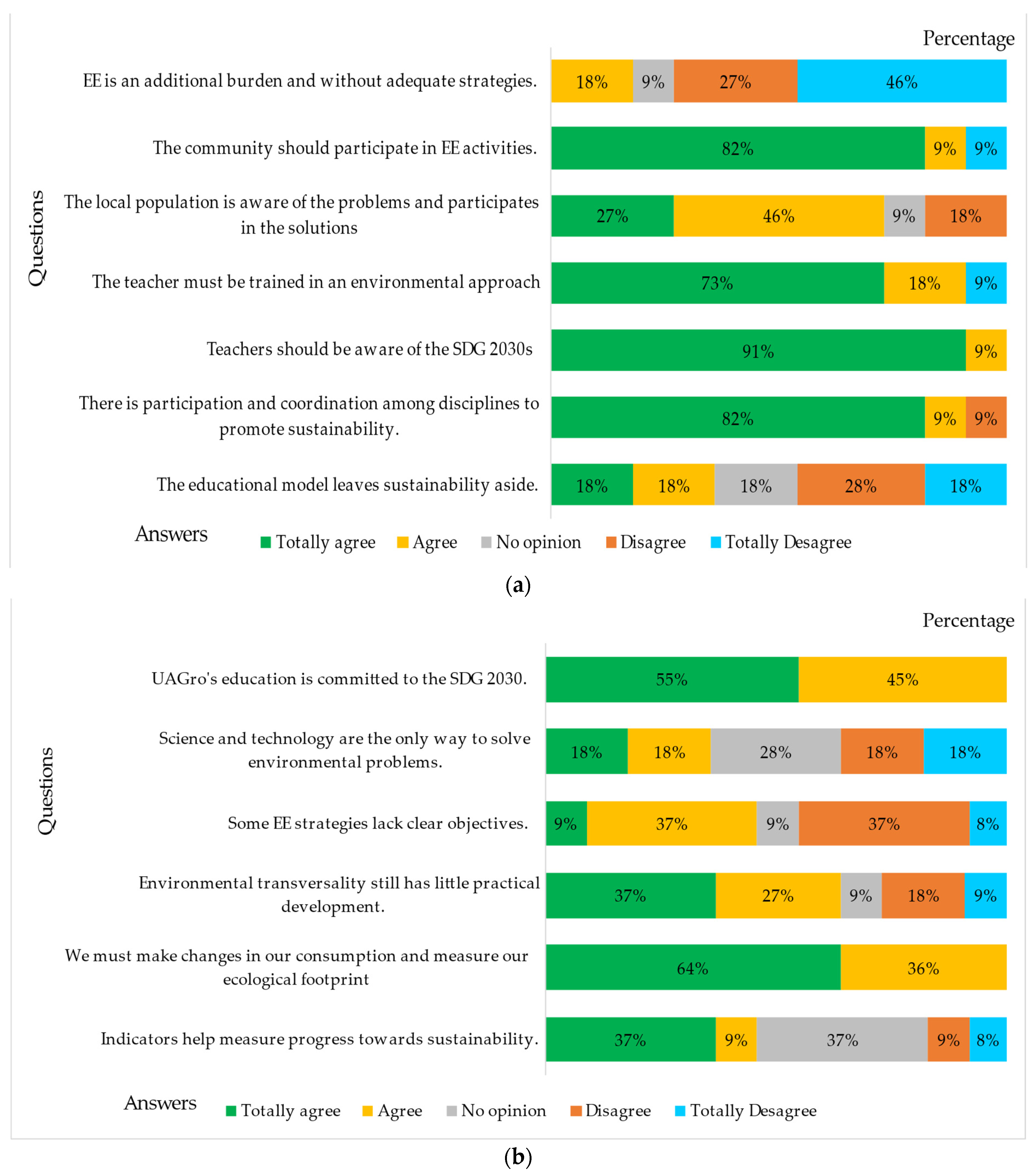
3.1. Results of the Course-Workshop
3.1.1. First Session: Environmental Problems
3.1.2. Second Session: Environmental Education, Education for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals 2030
3.1.3. Third Session: Transversality
3.1.4. Fourth Session: EE Educational Strategies to Develop with Students
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. ANNEX Section
| Session Working Hours | Topics | Facilitator | |||
| 1–4 | Session 1: The socio-natural relationship and the socio-environmental problems of the context. | PhD. Erick A. Galán Castro. MSc. Luis Miguel Moctezuma | |||
| 2–4 | Session 2: The evolution of EE, the emergence of education for sustainable development, and the Sustainable Development Goals SDG 2030. | MSc. Esmeralda Vilchis P. MSc. Luis Miguel Moctezuma | |||
| 3–4 | Session 3: The cross curricular transversality of the environmental axis. | PhD. Columba Rodríguez A. PhD. José Luis Aparicio L. | |||
| 4–4 | Session 4: Didactic strategies to address environmental issues in the classroom. | PhD. Héctor P. Tapia, Dr. José Luis Aparicio. MSEt. (Master in English teaching) Concepción Rojas Casarrubias. | |||
| Opening | Presentation of the course objectives and work dynamics. Comments by the teachers on the expectations of the course. | ||||
| Session 1 Environmental problems and the socio-natural relationship. | Test of previous knowledge on environmental issues. | ||||
| Subtopic 1 The multicausality of environmental problems and their different consequences. | Didactic strategy Conference | Resources Power Point Presentation | Supporting Material Suggested References: [5,11,38,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83] | Objective Teachers understand the complexity of environmental problems. | |
| Problematization of the topics presented: What is a socio-environmental problem? How to strengthen teacher performance? and What role do young people have in addressing environmental problems in their community? | Brainstorming | Raising doubts and reflective comments on the presentation | Logbook | Teachers recognize global and local issues | |
| Subtopic 2 Socio-environmental problems of the context | Conference | Power Point Presentation | Diagnosis of the community [11] | Teachers recognize the elements that participate in the generation of socio-environmental problems in the community. | |
| Closing: Summary of the teachers’ doubts and comments on the importance of knowing the socio-environmental problems in order to contribute to their mitigation. It is suggested that participants take a tour of the community to identify and learn about local environmental problems. | |||||
| Session 2 Environmental Education, Education for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals 2030 | Opening: Introduction of the speakers. The module begins with the following question: What are the SDGs 2030 and what is their function? Teachers’ comments and contributions are noted. | ||||
| Subtopic 1 The SDG-2030 The importance and purpose of the SDG-2030 is described. | Didactic strategy Educational video Conference | Digital Resources Power Point presentation | Supporting Material The SDGs—what they are and how to achieve them. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MCKH5xk8X-g (accessed on 20 April 2021). Suggested references: [25,26,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83] | Goal Teachers recognize the importance of the SDG-2030 and the need to contribute to their development. | |
| Subtopic 2 Environmental education (EE) and environmental education for sustainable development (ESD) (its evolution, concepts and objectives). Sustainability indicators. (examples). | Conference Videos | Power Point presentation | Suggested references: [11,15,40,41] “La historia de las cosas” (The history of things). Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i3mnDp1B9_Y (accessed on 20 April 2021). “La historia de las soluciones” (The history of solutions).Available online: www.youtube.com/watch?v=YORUqmHpUlk (accessed on 20 April 2021). | Teachers understand the importance of sustainable development as a way of life and the need to generate strategies for its development. | |
| Closing: Based on the videos, generate a debate on the need to contribute to sustainable development and the SDGs. | |||||
| Session 3 Transversality. | Opening: Presentation of the facilitators. The starting point is to know the meaning that teachers give to transversality and competencies. | ||||
| Subtopic 1 Competencies: (Concepts and their attributes) The integration of the environmental care competency in the high school level at UAGro. | Didactic strategy Conference | Digital Resources Power Point presentation | Supporting Material Suggested references: [23,32,53,56,57,65,84,85,86,87] | Objective Teachers understand the concept of competencies and their objectives. | |
| Subtopic 2 Environmental Education as a transversal theme. | Conference. | Power Point presentation | Suggested references: [19,23,32,53,61,65] | Teachers reflect on the importance of addressing EE. | |
| Subtopic 3 Methodology for the transversality of the environmental axis. | Conference Diagnosis | Power Point presentation Instrument: Diagnosis on the linkage of the transversal axis “Environment” in the graduate profile. | Methodology proposed by Aparicio, et al., (2014) [61,64,84,85,86,87] Suggested. | Teachers reflec on the need for collaborative work to address socio-environmental problems. | |
| Closing: Final reflections on the importance of developing environmental content in its sequence following three steps: (1) the design of strategies, (2) implementation with students and (3) evaluation of the results obtained, to assess progress and make adjustments. | |||||
| Session 4 EE educational strategies to develop with students. | Opening: Participants express their opinion regarding the advantages and disadvantages of being able to address EA in their learning units. | ||||
| Subtopic 1 Strategies to address EE in the classroom (definition, type and purpose). Reflection: What is a pedagogical strategy? SEP (School Environmental Projects). | Didactic strategy Conference Discussion Educational Video | Digital resources Power Point presentation PRAE. (SEP) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qvU0kV-JLRE (accessed on 20 April 2021). PRAES (SEP) in Bogotá D.C. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e3UT0wV9u3c (accessed on 20 April 2021). | Supporting material Suggested references: [22,33,34,58,68,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92] Comments sheet | Goal Teachers recognize the advantages and disadvantages of addressing the strategies in their learning units. | |
| Subtopic 2 Pedagogical proposals to transversalize the Sustainable Development competence in the HSL of the UAGro. | Conference Presentation | Power Point presentation Teachers narrate their experiences with their students. | Didactic Strategies developed by Tapia et al. (2018) [30,58,85,86,87,88,89,90] | Teachers recognize the importance of incorporating strategies into their sequence to promote EE. | |
| Closing: Final reflections on the purpose and achievement of the course and how it will help them to generate changes in their activity. Audio recording of the contributions that the course generated for each teacher. | |||||
References
- Miñano, R.; Uribe, D.; Moreno, A.; Yáñez, S. Embedding Sustainability Competences into Engineering Education. The Case of Informatics Engineering and Industrial Engineering Degree Programs at Spanish Universities. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.; Regina, C. The Challenges and Difficulties of Teachers in the Insertion and Practice of Environmental Education in the School Curriculum. Int. J. Soc. Educ. Sci. 2020, 2, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, M.; Musitu, D.; Amador, L.V.; Claros, F.M.; Olmedo, F.J. University as Change Manager of Attitudes towards Environment (The Importance of Environmental Education). Sustainability 2020, 12, 4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumwood, V. A Review of Deborah Bird Rose’s Reports from a Wild Country: Ethics of Decolonisation; Rooney, M., Ed.; Australian Humanities Review Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2007; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Medio Ambiente. Perspectivas del Medio Ambiente Mundial, GEO 6: Planeta Sano, Personas Sanas; PNUMA: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Medio Ambiente. Hacer las Paces con la Naturaleza: Plan Científico Para Hacer Frente a las Emergencias del Clima, la Biodiversidad y la Contaminación; PNUMA: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Moctezuma, L.M.; Aparicio, J.L.; Rodríguez, C.; Gervacio, H.; Galán, E.A.; Sánchez, M.L. Diagnóstico socioambiental participativo en una comunidad rural: El caso de Texca, Guerrero. In Procesos Territoriales: Un Enfoque Multidisciplinario; Ciccolella, J.C., Ed.; Lugar Editorial: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2021; p. 295. [Google Scholar]
- Kopnina, H. Education for sustainable development (ESD): The turn away from ‘environment’ in environmental education? Environ. Educ. Res. 2012, 18, 699–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vare, P.; Arro, G.; de Hamer, A.; Del Gobbo, G.; de Vries, G.; Farioli, F.; Kadji-Beltran, C.; Kangur, M.; Mayer, M.; Millican, R.; et al. Devising a Competence-Based Training Program for Educators of Sustainable Development: Lessons Learned. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D.; Ríos, D. Educación ambiental y cultura evaluativa. Algunas reflexiones para la construcción de eco-consciencias. Estud. Pedagógicos XLIII 2017, 43, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.J.; Meira-Cartea, P.Á.; Martínez-Fernández, C.N. Sustentabilidad y Universidad: Retos, ritos y posibles rutas. Rev. Educ. Super. 2015, xliv, 69–93. [Google Scholar]
- Espejel, A.; Castillo, M.I. Educación Ambiental para el nivel medio superior: Propuesta y evaluación. Rev. Iberoam. Educ. 2008, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Espejel, A.; Flores, A. Educación ambiental escolar y comunitaria en el nivel medio superior, Puebla-Tlaxcala, México. Rev. Mex. Investig. Educ. 2012, 17, 1173–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, G.; España, J.N.; Villanueva, D.J. La educación ambiental y la cultura de sustentabilidad de dos escuelas preparatorias. Educ. Cienci. 2016, 5, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Espejel, A.; Flores, A. Experiencias Exitosas De Educación Ambiental En Los Jóvenes Del Bachillerato De Tlaxcala, México. Luna Azul. 2017, 294–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Li, H. Environmental Education, Knowledge, and High School Students’ Intention toward Separation of Solid Waste on Campus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espejel, A.; Castillo, I. Educación ambiental en el bachillerato: De la escuela a la familia. Alteridad 2019, 14, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, L.O. Educación ambiental y cambio climático en el bachillerato tecnológico de México. Educ. Química 2019, 30, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rodríguez, U.; Varela-Losada, M.; Lorenzo-Rial, M.-A.; Vega-Marcote, P. Tendencias actitudinales del profesorado en formación hacia una educación ambiental transformadora. Rev. Psicodidáctica 2017, 22, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama-Hernández, R.; Alcántara, L.; Limón, D. The Complexity of Environmental Education: Teaching Ideas and Strategies from Teachers. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2017, 237, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnio-Linnanvuori, E. How do teachers perceive environmental responsibility? Environ. Educ. Res. 2019, 25, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, N.; Stevenson, R.B.; Lasen, M.; Ferreira, J.-A.; Davis, J. Approaches to embedding sustainability in teacher education: A synthesis of the literature. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2017, 63, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albareda-Tiana, S.; Vidal-Raméntol, S.; Pujol-Valls, M.; Fernández-Morilla, M. Holistic Approaches to Develop Sustainability and Research Competencies in Pre-Service Teacher Training. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanchana, Y.; Inprom, P.; Rawang, W.; Na Ayudhya, A.-O.J. A Model of Environmental Education Competency Development for Teachers in Secondary Schools. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2019, 14, 511–520. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Educación para los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible Objetivos de Aprendizaje; UNESCO: París, Francia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Declaración de INCHEON y ODS 4—Educación 2030 Marco de Acción; UNESCO: París, Francia, 2015; pp. 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- CEPAL. Acuerdo Regional Sobre el Acceso a la Información, la Participación Pública y el Acceso a la Justicia en Asuntos Ambientales en América Latina y el Caribe; Naciones Unidas: Escazú, Costa Rica, 2018.
- Mogensen, F.; Schnack, K. The action competence approach and the ‘new’ discourses of education for sustainable development, competence and quality criteria. Environ. Educ. Res. 2010, 16, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, R.; Bhargava, A.; Bothner, C.; Browne, K.; Kusano, S.; Golrokhian, A.; Wright, M.; Zeng, P.Z.; Agrawal, A. Towards a revolution in sustainability education: Vision, architecture, and assessment in a case-based approach. World Dev. Perspect. 2016, 1, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Secretaría de Educación Pública. Planes de Estudio de Referencia del Componente Básico del Marco Curricular Común de la Educación Media Superior, Primera ed.; SEP: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, H.; Cardona, L.C. La educación ambiental como estrategia necesaria para la planificación de nuevos enfoques regionales en el departamento del Meta. Sophia 2015, 11, 169–184. [Google Scholar]
- Aznar, P.; Ull, M.Á. La formación de competencias básicas para el desarrollo sostenible: El papel de la Universidad. Rev. Educ. 2009, 210–237. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, M.; Lucena, I.V.; Amador, L.V.; Mateos, F. Environmental Education, an Essential Instrument to Implement the Sustainable Development Goals in the University Context. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laso, S.; Ruiz, M.; Marbán, J.M. Impacto de un programa de intervención metacognitivo sobre la Conciencia Ambiental de docentes de Primaria en formación inicial. Rev. Eureka Sobre Enseñ. Divulg. Cienc. 2019, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Education for Sustainable Development: A Roadmap; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen, R.G. Interdisciplinary education: A case study. Eur. J. Eng. Educ. 2018, 43, 842–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos, E. Planeación de la Educación Ambiental en el Ámbito Universitario: Una Mirada Transdisciplinaria. Rev. Sci. 2017, 2, 92–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Novo-Corti, I.; García-Álvarez, M.T.; Varela-Candamio, L. The importance of environmental education in the determinants of green behavior: A meta-analysis approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1565–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, J.P.; Cruz, B.; Maldonado, M.Á. Proposal of Training in Topics for the Curriculum Sustainability of the Program of Engineering in Systems of the Escuela Superior de Cómputo of the Instituto Politécnico Nacional, México. In Strategic Innovative Marketing and Tourism; Kavoura, A., Kefallonitis, E., Theodoridis, P., Eds.; Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caride, J.A. Educación Ambiental y Desarrollo Humano: Nuevas perspectivas conceptuales y estratégicas. In Proceedings of the III Congreso lberoamericano de Educación Ambiental, Caracas, Venezuela, 21–26 October 2000; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Caride, J.A. Educación ambiental, crisis ecológica y desarrollo sustentable. Rev. Investig. En Educ. 2002, 2, 11–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, G.K.; Morales, J.A. Diagnóstico ambiental comunitario como una estrategia de educación ambiental desde la universidad. In Educación, Tecnología e Innovación, 1st ed.; Armenta, J.A., Valdés, A.A., Mortis, S.V.J., Ramona, I., Eds.; Instituto Tecnologico de Sonora: Sonora, México, 2010; pp. 820–827. [Google Scholar]
- Calixto, R. Investigación en educación ambiental. Rev. Mex. Investig. Educ. 2012, 17, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Prada, E.A. Conciencia, concientizacion y educacion ambiental: Conceptos y relaciones. Rev. Temas 2013, 7, 231–244. [Google Scholar]
- Hubers, M.D. In pursuit of sustainable educational change-Introduction to the special section. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2020, 93, 103084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibay, V.V.; Gutiérrez, J.J.; Martínez, M. Importance of Teacher Training Incorporating Sustainability in their Subjects from the Life Cycle Approach in Higher School of Computation (ESCOM-IPN). In Strategic Innovative Marketing and Tourism, 8th ed.; Kavoura, A., Kefallonitis, E., Theodoridis, P., Eds.; Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R. Envisioning sustainability three-dimensionally. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.; Figueroa, L. Los Valores Ambientales en los Procesos Educativos: Realidades y Desafíos. Red Iberoam. Investig. Sobre Cambio Efic. Esc. 2009, 7, 95–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, W.M. Ambientalización curricular en la educación superior: Un estudio cualitativo de las ideas del profesorado. Rev. Currículum Form. Profr. 2012, 16, 77–103. [Google Scholar]
- Arias, G. La ambientalización curricular en las humanidades. In El Caso de la Universidad Madrileña; Universidad Carlos III de Madrid: Getafe, España, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa, H.A.; Orozco, A.E.; Bonifaz, L.A.F. La educación ambiental en proyectos de intervención universitaria. La experiencia del Parque Ecológico de Tepic, Nayarit. RAITES 2017, 3, 12–30. [Google Scholar]
- Del Carmen Bustamante Gazabón, N.; Cruz, M.I.; Vergara, C. Proyectos ambientales escolares y la cultura ambiental en la comunidad estudiantil de las instituciones educativas de Sincelejo, Colombia. Rev. Logos Cienc. Tecnol. 2017, 9, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piza-Flores, V.; Aparicio, J.L.; Rodríguez, C.; Beltrán, J. Transversalidad del eje “Medio ambiente” en educación superior: Un diagnóstico de la Licenciatura en Contaduría de la UAGro/Transversality of the environment axis in higher education: A diagnosis of the bachelor’s degree in Accounting from UAGro. RIDE Rev. Iberoam. Investig. Desarro. Educ. 2018, 8, 598–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez-Espinosa, G.-M.; Velásquez-Sarria, J.-A.; Arroyave-Escobar, M.-C. Formación ambiental y reconocimiento de la realidad: Dos aspectos esenciales para la inclusión de la educación ambiental en la escuela. Luna Azul. 2017, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Sampieri, R.; Fernández, C.; Baptista, M.d.P. Metodología de la Investigación, 6th ed.; Rocha Martínez, M.I., Ed.; McGraw-Hill/Interamericana Editores, S.A. de C.V.: Mexico City, México, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Universidad Autónoma de Guerrero. Modelo Educativo de la UAGro 2013; UAGro: Chilpancingo, Mexico, 2013; pp. 1–92. [Google Scholar]
- Universidad Autónoma de Guerrero. Plan de Desarrollo Institucional 2017–2021; UAGro: Guerrero, Mexico, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tapia, H.P.; Rodríguez, C.; Aparicio, J.L.; Castro, M. Transversalización de la competencia desarrollo sustentable en el nivel medio superior de la Universidad Autónoma de Guerrero. Rev. Dilemas Contemp. Educ. Política Valores 2019, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Isaac-Márquez, R.; Salavarría, O.O.; Eastmond, A.; Ayala, M.E.; Arteaga, M.A.; Isaac-Márquez, A.P.; Sandoval, J.L.; Manzanero, L.A. Cultura ambiental en estudiantes de bachillerato. Estudio de caso de la educación ambiental en el nivel medio superior de Campeche. REDIE. Rev. Electrón. Investig. Educ. 2011, 13, 83–99. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, M.I.; Carballo, L. La educación ambiental rural desde las escuelas básicas y por estas. Rev. Electrón. Educ. 2013, 17, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Pedretti, E. Negotiating the Complexities of Environmental Education: A Study of Ontario Teachers. Can. J. Sci. Math. Technol. Educ. 2010, 10, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yus, R. Síntesis un modelo didáctico para la transversalidad. In Temas Transversales, Hacia una Nueva Escuela; Graó: Barcelona, Spain, 1998; pp. 200–213. [Google Scholar]
- Sá, M.; Serpa, S. Transversal Competences: Their Importance and Learning Processes by Higher Education Students. Educ. Sci. 2018, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.M. La importancia de la educación ambiental ante la problemática actual. Revista Electrónica Educare 2010, 14, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasek de Pinto, E. El docente y su nivel de conciencia ambiental. Rev. Artes Humanid. UNICA 2006, 7, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, S.; Patrick, P.G.; Moseley, C. Experiential learning theory: The importance of outdoor classrooms in environmental education. Int. J. Sci. Educ. Part B 2017, 7, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W. Online and Remote Learning in Higher Education Institutes: A Necessity in light of COVID-19 Pandemic. High. Educ. Stud. 2020, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrián, G.; Palau, R.; Mogas, J. The Smart Classroom as a Means to the Development of ESD Methodologies. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacheron, F. Head in Charge of UNESCO Office in Mexico|International Day of Education, 8th ed.; Youtube: San Bruno, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Arias, F.A. Economía política del ambiente: Voz y eco en el análisis social de los problemas ambientales. Hallazgos 2019, 16, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, M.; Del, P. Por qué hacer educación ambiental: La necesidad de una toma de conciencia. Rev. Virtual Edipe 2017, 6, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Eschenhagen, M.L. Las cumbres ambientales internacionales y la educación ambiental. OASIS 2007, 12, 39–76. [Google Scholar]
- Foladori, G. Una tipología del Pensamiento Ambientalista. En: Pierri y Foladori, Guillermo. ¿Sustentabilidad? Desacuerdos Sobre el Desarrollo Sustentable. Uruguay: Trabajo y Capital. 2001, pp. 83–136. Available online: http://www.ecominga.uqam.ca/PDF/BIBLIOGRAPHIE/GUIDE_LECTURE_1/Foladori-Tipolog%C3%ADa-pensamiento-ambientalista.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Gil, D.; Vilches, A.; Toscano, J.; y Macías, O. Década para la Educación para un Futuro Sostenible (2005–2014): Un punto de inflexión necesario en la atención a la situación del planeta. Rev. Iberoam. Educ. 2006, 40, 125–178. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, T. Marx: La naturaleza y la mercancía. Nómadas 2018, 48, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.J. Otra lectura a la historia de la educación ambiental en América Latina y el Caribe. Tópicos Educ. Ambient. 1999, 1, 9–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo, G.A.; Martínez, T.C.; Romero, S.P. Transformación conductual promovida por la Gestión Ambiental Comunitaria desde una percepción rural. Noved. Poblac. 2017, 26, 244–254. [Google Scholar]
- Left, E. Pensamiento Ambiental Latinoamericano: Patrimonio de un Saber para la Sustentabilidad; ISEE Publicación: México, Mexico, 2009; Available online: wordpress.com (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Leff, E. Sustentabilidad y racionalidad ambiental: Hacia ‘otro’ programa de sociología ambiental. Rev. Mex. Sociol. 2013, 73, 5–46. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, B.; Aliste, A.; Neira, I.; y Urquiza, A. La compleja definición del problema socioambiental: Racionalidades y controversias. Rev. Magíster Anál. Sist. Apl. Soc. 2019, 40, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Caraveo, L.M. Sabemos Pero no Actuamos ¿Cuál es el Papel de la Educación Ambiental? Rev. Univ. 2004, XII, 56–61. Available online: nanopdf.com (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Selman, P. Community participation in the planning and management of cultural landscapes. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2004, 47, 365–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, H.R.; y Solís, E.C. Investigación Acción Participativa Como Estrategia de Transformación Social y Ambiental. Investig. Esc. 2015, 86, 49–59. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303719108_Investigacion_accion_participativa_como_estrategia_de_transformacion_social (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Aparicio, J.L.; Rodríguez, C.; Beltrán, J.y.; Sampedro, L. Metodología para la transversalidad del eje medio ambiente. Rev. Iberoam. Cienc. Soc. Hum. 2014, 3, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, B.A. Construcción de programas de estudio en la perspectiva del enfoque de desarrollo de competencias. Perf. Educ. 2014, XXXVI, 142–162. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, J.G. Competencias para la Sustentabilidad en el Currículo de Bachillerato en México, Congreso Nacional de Investigación Educativa. San Luis Potosí. 2017. Available online: https://www.comie.org.mx/congreso/memoriaelectronica/v14/doc/1424.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Tobón, S.; Pimienta, J.y.; García, J. Secuencias Didácticas: Aprendizaje y Evaluación de Competencias; Capítulo 1, el modelo de competencias; Pearson Education: Naucalpan Edo, Mexico, 2010; pp. 1–23, Cap. III; Available online: https://ctezona141.webnode.mx/_files/200000004-8ed038fca3/secuencias-didacticastobon-120521222400-phpapp02.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- CONAM. Educación Ambiental como Tema Transversal; Solano, D., Vera, C., Eds.; Didi de Arteta S. A.: Lima, Perú, 2007; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337846255_Educacion_Ambiental_como_Tema_Transversal_Manual_para_Trabajar_en_la_Programacion_de_Aula (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Luna, G.; Luna, L. Manual de Educación Ambiental para Comunidades de la RAAS; Proyecto para el Desarrollo Integral de la Pesca Artesanal en la Región Autónoma Atlántico sur: Bluefields, Nicaragua, 2001; Available online: http://www.bio-nica.info/biblioteca/luna&luna2001.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Rodríguez, M.; Córdova, A. Manual de Compostaje Municipal. SEMARNAT-INE-GTZ, Primera ed.; SEMARNAT: Ciudad de México City, Mexico, 2006. Available online: https://biblioteca.semarnat.gob.mx/janium/Documentos/Ciga/libros2009/200277.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Röben, E. Manual de Compostaje para Municipios. Loja, Ecuador. 2002. Available online: http://www.resol.com.br/Cartilha7/ManualCompostajeparaMunicipios.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Muñoz, J.M. La Educación Ambiental Como Tema Transversal en el Currículo. Innovación y Experiencias Educativas. 2010. Available online: https://archivos.csif.es/archivos/andalucia/ensenanza/revistas/csicsif/revista/pdf/Numero_29/JOSE_MARIA_MUNOZ_VIDAL_02.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2021).

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moctezuma Teresa, L.M.; Aparicio López, J.L.; Rodríguez Alviso, C.; Gervacio Jiménez, H.; Brito Carmona, R.M. Environmental Competencies for Sustainability: A Training Experience with High School Teachers in a Rural Community. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4946. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094946
Moctezuma Teresa LM, Aparicio López JL, Rodríguez Alviso C, Gervacio Jiménez H, Brito Carmona RM. Environmental Competencies for Sustainability: A Training Experience with High School Teachers in a Rural Community. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):4946. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094946
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoctezuma Teresa, Luis Miguel, José Luis Aparicio López, Columba Rodríguez Alviso, Herlinda Gervacio Jiménez, and Rosa María Brito Carmona. 2022. "Environmental Competencies for Sustainability: A Training Experience with High School Teachers in a Rural Community" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 4946. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094946
APA StyleMoctezuma Teresa, L. M., Aparicio López, J. L., Rodríguez Alviso, C., Gervacio Jiménez, H., & Brito Carmona, R. M. (2022). Environmental Competencies for Sustainability: A Training Experience with High School Teachers in a Rural Community. Sustainability, 14(9), 4946. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094946







