Calcium-Rich Pigeonpea Seed Coat: A Potential Byproduct for Food and Pharmaceutical Industries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Layout and Soil Properties
2.2. Agronomic Practices
2.3. Whole Grain Nutrient Analysis of the Entire Set
2.4. Selection Criteria for the Formation of Subset
2.5. Cotyledon and Seed Coat Nutrient Analysis in the Subset
2.6. Calculation of Whole Grain Nutrient Content and Percentage of Seed Fractions Nutrients in Whole Grain
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
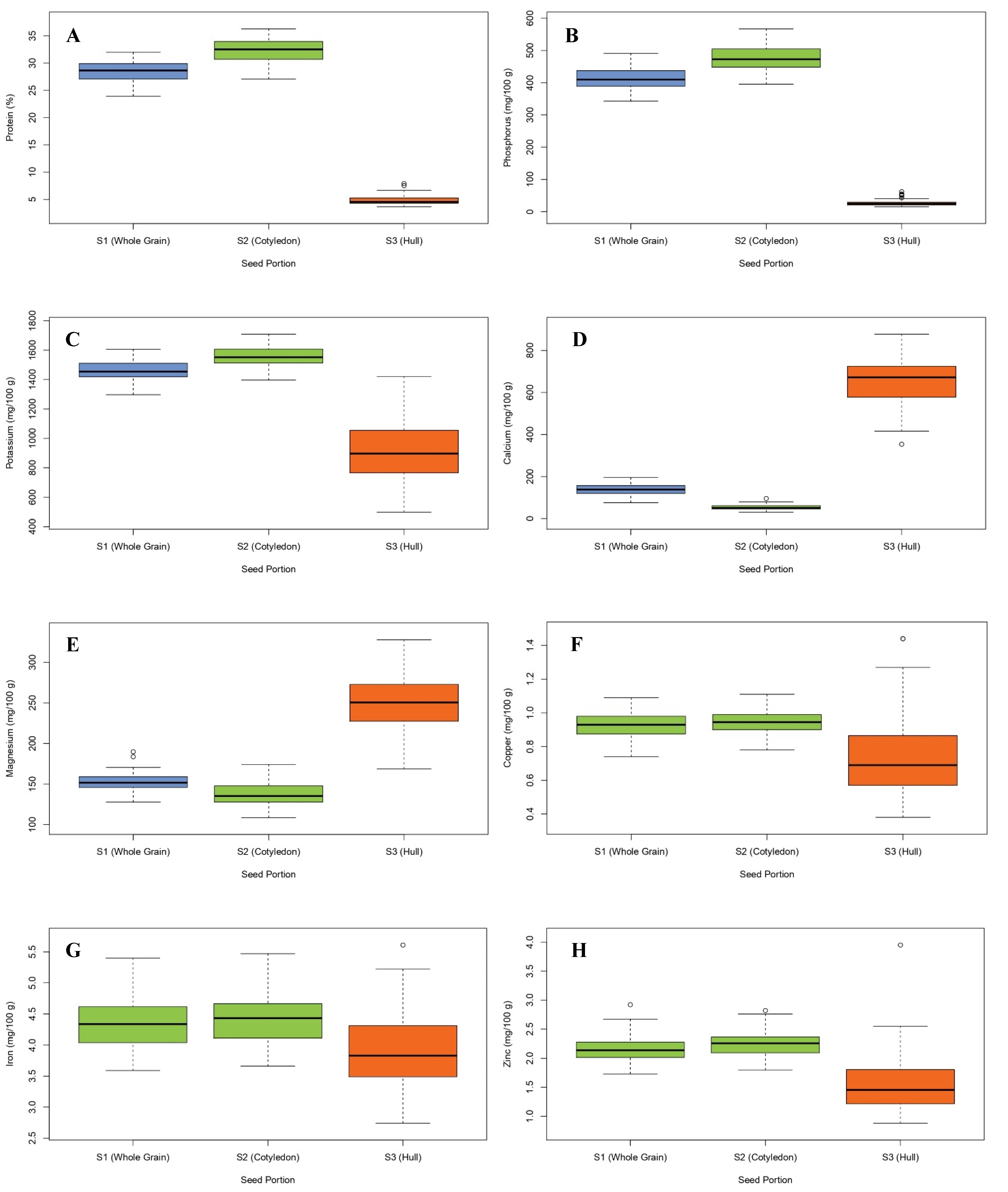
3.1. Distribution of Nutrients in Cotyledon and Seed Coat
3.2. Correlations between Nutrient Content Per 100 g in Cotyledon and Seed Coat with 100-Seed Weight
3.3. Nutrient Contribution by Cotyledon and Seed Coat to Whole Grain
3.4. Nutrient Loss due to Dehulling
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutrient Contents in Major Seed Fractions
4.2. Nutrient Contribution by Cotyledon and Seed Coat to Whole Grain
4.3. Nutrient Loss due to Dehulling
4.4. Scope of Seed Coat in Value Addition
5. Future Prospects and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Saxena, K.B.; Kumar, R.V.; Sultana, R. Quality Nutrition through Pigeonpea—A Review. Health 2010, 2, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salunkhe, D.K.; Chavan, J.K.; Kadam, S.S. Pigeonpea as an Important Food Source. CRC Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1986, 23, 103–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangari, C.; Mwema, C.; Siambi, M.; Silim, S.; Ubwe, R.; Malesi, K.; Anitha, S.; Kane-Potaka, J. Changing Perception through a Participatory Approach by Involving Adolescent School Children in Evaluating Smart Food Dishes in School Feeding Programs–Real-Time Experience from Central and Northern Tanzania. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2020, 59, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Singh, H.D.; Sikka, K.C. Distribution of Nutrients in the Anatomical Parts of Common Indian Pulses. Cereal Chem. 1968, 45, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Moraghan, J.T.; Etchevers, J.D.; Padilla, J. Contrasting Accumulations of Calcium and Magnesium in Seed Coats and Embryos of Common Bean and Soybean. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, N.D.; Maziero, S.M.; Prigol, M.; Nogueira, C.W.; Rosa, D.P.; Possobom, M.T.D.F. Mineral Concentrations in the Embryo and Seed Coat of Common Bean Cultivars. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 26, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blair, M.W.; Izquierdo, P.; Astudillo, C.; Grusak, M.A. A Legume Biofortification Quandary: Variability and Genetic Control of Seed Coat Micronutrient Accumulation in Common Beans. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, L.; Fang, Z.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; Wu, G.; Hodgson, J.M.; Johnson, S.K. Seed Coats of Pulses as a Food Ingredient: Characterization, Processing, and Applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, F.; Diwakar, B. Nutritive Value and Uses of Pigeonpea and Groundnut; ICRISAT Human Resource Development Program: Hyderabad, India, 1993; pp. 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kurien, P.P.; Parpia, H.A.B. Pulse Milling in India—I—Processing and Milling of Tur, Arhar (Cajanus cajan Linn.). J. Food Sci. Technol. 1968, 5, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Silky; Gupta, M.P.; Tiwari, A. Development of High Protein Biscuits Using Pigeon Pea Brokens Flour. Int. J. Eng. Innov. Technol. 2014, 4, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Tapal, A.; Vegarud, G.E.; Sreedhara, A.; Kaul Tiku, P. Nutraceutical Protein Isolate from Pigeon Pea (Cajanus cajan) Milling Waste by-Product: Functional Aspects and Digestibility. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2710–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgetty, D.D.; Baik, B.K. Fortification of Bread with Hulls and Cotyledon Fibers Isolated from Peas, Lentils, and Chickpeas. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Banerjee, R.; Sharma, B.D. Quality of Low Fat Chicken Nuggets: Effect of Sodium Chloride Replacement and Added Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Hull Flour. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 25, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, Q.; Ranawana, V.; Hayes, H.E.; Hayward, N.J.; Stead, D.; Raikos, V. Addition of Broad Bean Hull to Wheat Flour for the Development of High-Fiber Bread: Effects on Physical and Nutritional Properties. Foods 2020, 9, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; Yılmaz Tuncel, N.; Tuncel, N.B. Utilization of Lentil, Pea, and Faba Bean Hulls in Turkish Noodle Production. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1734–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-León, C.; Ramírez-Guzman, N.; Londoño-Hernandez, L.; Martinez-Medina, G.A.; Díaz-Herrera, R.; Navarro-Macias, V.; Alvarez-Pérez, O.B.; Picazo, B.; Villarreal-Vázquez, M.; Ascacio-Valdes, J.; et al. Food Waste and Byproducts: An Opportunity to Minimize Malnutrition and Hunger in Developing Countries. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Vega-Vega, V.; Rosas-Domínguez, C.; Palafox-Carlos, H.; Villa-Rodriguez, J.A.; Siddiqui, M.W.; Dávila-Aviña, J.E.; González-Aguilar, G.A. Agro-Industrial Potential of Exotic Fruit Byproducts as a Source of Food Additives. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1866–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicka, B.H.; Ziarati, P.; Krochmal-Marczak, B.; Skiba, D. Nutraceuticals in Food and Pharmacy. A Review. Agron. Sci. 2020, 74, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susmitha, D.; Kalaimagal, T.; Senthil, R.; Vetriventhan, M.; Reddymalla, S.; Ovais, P.; Kuldeep, S. Genetic Variability Assessment in Pigeonpea Landraces for Grain Nutrients Improvement, Patancheru, India, 2022; Manuscript in preparation.
- Longvah, T.; Ananthan, R.; Bhaskarachary, K.; Venkaiah, K. Indian Food Composition Tables; National Institute of Nutrition: Hyderabad, India, 2017; pp. 1–505. [Google Scholar]
- Aivaz, M.; Mosharraf, L. Influence of Different Treatments and Particle Size of Wheat Bran on Its Mineral and Physicochemical Characteristics. Int. Acad. J. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 3, 608–619. [Google Scholar]
- Bhosale, S.; Vijayalakshmi, D. Processing and Nutritional Composition of Rice Bran. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, 3, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrawat, K.L.; Kumar, G.R.; Murthy, K.V.S. Sulfuric Acid-Selenium Digestion for Multi-Element Analysis in a Single Plant Digest. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2002, 33, 3757–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheal, M.S.; Fowles, T.O.; Palmer, L.T. A Cost-Effective Acid Digestion Method Using Closed Polypropylene Tubes for Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) Analysis of Plant Essential Elements. Anal. Meth. 2011, 3, 2854–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi, H.B.; Hingane, A.J.; Sekhar, M.R.; Kumar, C.V.S.; Srivarsha, J. Genetic Variability for Yield, Physiological and Quality Traits in Novel Super-Early Pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.). India J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2019, 7, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.T.; Rao, P.J.M. Studies on Genetic Variability and Character Association in Pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Mill Sp.). Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2020, 8, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, A.; Tabil, L.; Sundaram, J.; Crerar, W.J.; Park, S.J. Conditioning and Dehulling of Pigeon Peas and Mung Beans. Can. Soc. Eng. Agric. Food Biol. Syst. 2003, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, K.B.; Kumar, R.V.; Rao, P.V. Pigeonpea Nutrition and Its Improvement. J. Crop Prod. 2002, 5, 227–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- Tukey, J.W. Exploratory Data Analysis; Mosteller, F., Ed.; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1977; pp. 1–677. [Google Scholar]
- de Mendiburu, F. Agricolae: Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research. R Package Version 1.3–5. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=agricolae (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. Simultaneous Inference in General Parametric Models. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 346–363. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=multcompView (accessed on 18 March 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makowski, D.; Ben-Shachar, M.; Patil, I.; Lüdecke, D. Methods and Algorithms for Correlation Analysis in R. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JME. The UNICEF/WHO/WB Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates (JME) Group Released New Data for 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malnutrition (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- BMZ. Supplementation, Food Fortification and Dietary Diversification a Three-Pronged Approach to Reducing Hidden Hunger; Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ), Division for Public Relations, Information and Education BMZ, Directorate for Rural Development and Global Food Security: Bonn, Germany, 2012; Available online: https://www.bmz.be (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Meenakshi, J.V.; Johnson, N.L.; Manyong, V.M.; De Groote, H.; Javelosa, J.; Yanggen, D.R.; Naher, F.; Gonzalez, C.; García, J.; Meng, E. How Cost-Effective Is Biofortification in Combating Micronutrient Malnutrition? An Ex Ante Assessment. World Dev. 2010, 38, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanumanthappa, D.; Maruthi, S.N.; Shakuntala, J.B. Enrichment of Iron and Zinc Content in Pigeonpea Genotypes through Agronomic Biofortification to Mitigate Malnutrition. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 4334–4342. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, S.K.; Shukla, A.K.; Tiwari, P.K.; Tripathi, A.; Singh, P.; Trivedi, V.; Patra, A.K.; Das, S. Classification of Pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (l.) Millsp.) Genotypes for Zinc Efficiency. Plants 2020, 9, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreerama, Y.N.; Neelam, D.A.; Sashikala, V.B.; Pratape, V.M. Distribution of Nutrients and Antinutrients in Milled Fractions of Chickpea and Horse Gram: Seed Coat Phenolics and Their Distinct Modes of Enzyme Inhibition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4322–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.A.; Knights, E.J.; Campbell, G.M.; Choct, M. Differences between Easy- and Difficult-to-Mill Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Genotypes. Part I: Broad Chemical Composition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Mathpal, P.; Malik, S.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, S.; Chugh, V.; Sheikh, I.; Sharma, P.; Singh, T.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; et al. Evaluation of Iron and Zinc in Grain and Grain Fractions of Hexaploid Wheat and Its Related Species for Possible Utilization in Wheat Biofortification. Plant Genet. Resour. Charact. Util. 2016, 14, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziarati, P.; Azizi, N. Chemical Characteristics and Mineral Contents in Whole Rice Grains, Hulls, Brown Rice, Bran, and Polished Ali Kazemi Rice in Gilan Province—North of Iran. Int. J. Farming Allied Sci. 2013, 2, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Cvitanich, C.; Przybyłowicz, W.J.; Urbanski, D.F.; Jurkiewicz, A.M.; Mesjasz-Przybyłowicz, J.; Blair, M.W.; Astudillo, C.; Jensen, E.T.; Stougaard, J. Iron and Ferritin Accumulate in Separate Cellular Locations in Phaseolus Seeds. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reichert, A.O.F.; Ehiwe, R.D. Variability in Dehulling Quality of Cowpea, Pigeonpea, Mung Bean Cultivars Determined with the Tangential Abrasive Dehulling Device. Cereal Chem. 1987, 2, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, K.B.; Faris, D.G.; Singh, U.; Kumar, R.V. Relationship between Seed Size and Protein Content in Newly Developed High Protein Lines of Pigeonpea. Qual. Plant. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1987, 36, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obala, J.; Saxena, R.K.; Singh, V.K.; Vechalapu, S.; Das, R.; Sameer-Kumar, C.V.; Saxena, K.; Tongoona, P.; Sibiya, J.; Rajeev, K. Genetic Variation and Relationships of Total Seed Protein Content with Some Agronomic Traits in Pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.). Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2018, 12, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOM (Institute of Medicine). Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D; The National Academic Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Harinarayan, C.V.; Akhila, H.; Shanthisree, E. Modern India and Dietary Calcium Deficiency—Half a Century Nutrition Data—Retrospect–Introspect and the Road Ahead. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 583654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Food Data Central. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168872/nutrients (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- ICMR-NIN. Nutrient Requirements for Indians—ICMR-NIN. 2020. Available online: https://www.metabolichealthdigest.com/nutrient-requirements-for-indians-icmr-nin-2020/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Yan, N.; Chen, X. Sustainability: Don’t Waste Seafood Waste. Nature 2015, 524, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kelkar, N.; Natarajan, K.; Selvaraj, S. Review on the Extraction of Calcium Supplements from Eggshells to Combat Waste Generation and Chronic Calcium Deficiency. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46985–46998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, R.; Chaudhary, C.; Jain, V.; Chawla, S.; Saxena, A.K. Effect of Soaking on Anti-Nutritional Factors in the Sun-Dried Seeds of Hybrid Pigeon Pea to Enhance Their Nutrients Bioavailability. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 675–680. [Google Scholar]
- Onwuka, G.I. Soaking, Boiling and Antinutritional Factors in Pigeon Peas (Cajanus cajan) and Cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata). J. Food Process. Preserv. 2006, 30, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| S. No. | 100-Seed Weight (g) | Number of Accessions | Range of Calcium (mg/kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Set | Subset | Original Set | Subset | ||
| 1 | ≤5.00 | 2 | - | 1968.03–2045.30 | - |
| 2 | 5.01–10.00 | 349 | 31 | 1020.04–2304.69 | 1023.26–2304.69 |
| 3 | 10.01–15.00 | 204 | 18 | 913.53–2043.89 | 963.33–2043.89 |
| 4 | 15.01–20.00 | 41 | 9 | 840.16–2304.05 | 840.16–1848.74 |
| 5 | ≥20.01 | 4 | 2 | 1171.77–1714.11 | 1303.55–1714.11 |
| Total | 600 | 60 | 840.16–2304.05 | 840.16–2304.70 | |
| Trait | Original Set (600 Accessions) | Subset (60 Accessions) |
|---|---|---|
| Protein (%) | 19.24–32.43 | 22.69–30.63 |
| P (mg/100 g) | 268.10–637.64 | 319.20–577.91 |
| K (mg/100 g) | 1237.62–1911.44 | 1309.46–1691.09 |
| Ca (mg/100 g) | 84.02–230.47 | 84.02–230.47 |
| Mg (mg/100 g) | 120.42–200.06 | 131.05–200.06 |
| Fe (mg/100 g) | 2.46–4.83 | 2.93–4.23 |
| Zn (mg/100 g) | 2.18–3.80 | 2.46–3.74 |
| Cu (mg/100 g) | 0.70–1.52 | 0.95–1.44 |
| Mn (mg/100 g) | 0.78–1.60 | 0.78–1.33 |
| 100-seed weight (g) | 1.59–22.58 | 6.35–20.74 |
| Source of Variation | df | Mean Sum of Squares (MSS) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | P | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | Zn | Cu | Mn | ||
| A | 1 | 78 ** | 6304 ** | 2,529,448 ** | 2261 | 9877 ** | 35.7 ** | 0.933 ** | 0.941 ** | 0.6448 ** |
| B | 1 | 45,205 ** | 12,112,858 ** | 26,695,154 ** | 21,511,986 ** | 747,261 ** | 15.37 ** | 30.062 ** | 0.134 ** | 2.3721 ** |
| C | 59 | 6 ** | 1678 ** | 44,947 ** | 15,535 ** | 994 ** | 0.76 ** | 0.373 ** | 0.121 ** | 0.0677 ** |
| A × B | 1 | 48 ** | 14,565 ** | 1,172,575 ** | 5783 * | 8180 ** | 5.29 ** | 0.081 * | 0.252 ** | 0.0889 ** |
| A × C | 59 | 2 | 435 | 9598 | 1510 | 225 | 0.28 | 0.106 ** | 0.021 * | 0.0245 ** |
| B × C | 59 | 6 ** | 1572 ** | 35,407 ** | 11,173 ** | 1741 ** | 0.33 * | 0.219 ** | 0.133 ** | 0.0569 ** |
| Within | 59 | 2 | 413 | 8565 | 1193 | 193 | 0.2 | 0.049 | 0.0124 | 0.0109 |
| Nutrients | Whole Grain (Calculated) | Cotyledon | Seed Coat | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD | Range | |||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| Protein (%) | 29.41 ± 2.45 a | 27.62 ± 2.25 b | 24.49– 36.44 | 21.55– 32.65 | 33.38 ± 2.87 a | 31.33 ± 2.58 b | 27.47– 41.52 | 24.40– 37.03 | 5.03 ± 0.87 a | 4.78 ± 1.14 a | 3.58– 8.01 | 3.48– 8.41 |
| P (mg/100 g) | 402.87 ± 40.01 b | 424.34 ± 35.30 a | 325.08– 496.55 | 343.46– 502.3 | 463.59 ± 46.71 b | 489.42 ± 40.49 a | 374.29– 574.13 | 397.37– 571.45 | 29.86 ± 9.66 a | 24.53 ± 13.55 b | 17.66– 66.85 | 7.34– 77.50 |
| K (mg/100 g) | 1621.36 ± 103.78 a | 1315.39 ± 81.40 b | 1428.46– 1849.82 | 1083.78– 1530.17 | 1734.32 ± 109.85 a | 1389.20 ± 87.43 b | 1532.87– 1977.21 | 1172.90– 1686.13 | 927.50 ± 197.61 a | 861.97 ± 199.39 a | 563.81– 1412.91 | 430.66– 1430.59 |
| Ca (mg/100 g) | 137.54 ± 28.39 a | 136.61 ± 24.58 a | 69.57– 208.43 | 81.66– 181.98 | 55.08 ± 14.28 a | 51.41 ± 13.10 a | 29.34– 105.25 | 30.64– 85.74 | 644.04 ± 127.40 a | 660.00 ± 113.15 a | 316.68– 900.43 | 390.74– 893.38 |
| Mg (mg/100 g) | 155.43 ± 11.05 a | 151.01 ± 14.00 a | 133.29– 192.97 | 122.21– 186.49 | 138.17 ± 13.66 a | 137.02 ± 17.00 a | 110.58– 169.92 | 102.18– 182.32 | 261.45 ± 38.46 a | 236.94 ± 34.62 b | 156.02– 349.93 | 169.73– 307.2 |
| Fe (mg/100 g) | 4.63 ± 0.47 a | 4.07 ± 0.43 b | 3.75– 5.76 | 3.12– 5.14 | 4.66 ± 0.50 a | 4.18 ± 0.44 b | 3.69– 5.86 | 3.23– 5.25 | 4.45 ± 0.80 a | 3.38 ± 0.70 b | 2.69– 6.31 | 2.28– 5.04 |
| Zn (mg/100 g) | 2.20 ± 0.29 a | 2.10 ± 0.21 b | 1.55– 3.27 | 1.58– 2.57 | 2.29 ± 0.28 a | 2.20 ± 0.21 a | 1.64– 3.17 | 1.65– 2.61 | 1.62 ± 0.61 a | 1.46 ± 0.50 a | 0.83– 4.53 | 0.59– 3.36 |
| Cu (mg/100 g) | 1.05 ± 0.14 a | 0.97 ± 0.11 b | 0.78– 1.35 | 0.77– 1.34 | 0.92 ± 0.15 b | 0.98 ± 0.12 a | 0.66– 1.14 | 0.82– 1.23 | 0.68 ± 0.24 b | 0.82 ± 0.29 a | 0.34– 1.42 | 0.41– 1.7 |
| Mn (mg/100 g) | 0.88 ± 0.10 b | 0.96 ± 0.09 a | 0.62– 1.11 | 0.78– 1.21 | 1.05 ± 0.10 a | 0.99 ± 0.08 b | 0.74– 1.38 | 0.81– 1.4 | 1.07 ± 0.35 a | 0.88 ± 0.36 b | 0.57– 2.23 | 0.49– 2.14 |
| Nutrient | Mean ± SD | Range | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Grain (Calculated) | Cotyledon | Seed Coat | Whole Grain (Calculated) | Cotyledon | Seed Coat | |
| Protein (%) | 28.45 ± 1.97 b | 32.28 ± 2.29 a | 4.91 ± 0.88 c | 23.94–31.99 | 27.09–36.30 | 3.67–7.93 |
| P (mg/100 g) | 413.60 ± 33.70 b | 476.51 ± 39.05 a | 27.20 ± 10.03 c | 343.28–491.28 | 395.29–567.19 | 15.12–61.89 |
| K (mg/100 g) | 1464.91 ± 68.14 b | 1557.73 ± 66.82 a | 894.73 ± 18.80 c | 1296.95–1606.25 | 1396.86–1709.04 | 497.23–1421.75 |
| Ca (mg/100 g) | 137.07 ± 25.42 b | 53.25 ± 13.02 c | 652.02 ± 114.82 a | 75.62–195.21 | 30.34–95.50 | 353.71–877.66 |
| Mg (mg/100 g) | 153.22 ± 11.33 b | 137.60 ± 14.26 c | 249.19 ± 34.12 a | 127.75–189.73 | 108.48–174.21 | 168.63–327.95 |
| Fe (mg/100 g) | 4.35 ± 0.39 a | 4.42 ± 0.41 a | 3.91 ± 0.62 b | 3.59–5.40 | 3.66–5.47 | 2.74–5.61 |
| Zn (mg/100 g) | 2.15 ± 0.22 a | 2.25 ± 0.21 a | 1.54 ± 0.50 b | 1.73–2.92 | 1.80–2.82 | 0.88–3.95 |
| Cu (mg/100 g) | 0.92 ± 0.08 a | 0.95 ± 0.07 a | 0.75 ± 0.24 b | 0.74–1.09 | 0.78–1.11 | 0.38–1.44 |
| Mn (mg/100 g) | 1.01 ± 0.11 a | 1.02 ± 0.12 a | 0.97 ± 0.34 a | 0.79–1.26 | 0.78–1.32 | 0.58–2.18 |
| Nutrient | No. of Accessions | Accessions | Whole Grain (Calculated) | Cotyledon | Seed Coat |
| Protein (%) | 13 | ICP# 4370, 4729, 5925, 7903, 8194, 8392, 10876, 11465, 11487, 12043, 15245, 16844, 11850 | 28.88– 31.99 | 32.72– 36.30 | 4.94– 6.70 |
| P (mg/100 g) | 10 | ICP# 9137, 9146, 11487, 7903, 11465, 11472, 10876, 15099, 8392, 8354 | 416.62– 480.98 | 479.47– 549.20 | 27.65– 61.89 |
| K (mg/100 g) | 14 | ICP# 4370, 4729, 5925, 7903, 9132, 9139, 9146, 10176, 11350, 11465, 11487, 13828, 13857, 14167 | 1511.10– 1606.25 | 1581.53– 1709.04 | 925.32– 1421.75 |
| Ca (mg/100 g) | 25 | ICP# 844, 1514, 3451, 6834, 7869, 7870, 7982, 8178, 8354, 8392, 8407, 9137, 9146, 9152, 9317, 10876, 11472, 11850, 12023, 12043, 14598, 14866, 15242, 15597, 7221 | 139.22– 195.21 | 54.00– 95.50 | 654.36– 877.66 |
| Mg (mg/100 g) | 9 | ICP# 7869, 11348, 12043, 12048, 15242, 4400, 15597, 7870, 8863 | 156.54– 189.73 | 140.20– 170.39 | 254.01– 308.57 |
| Fe (mg/100 g) | 18 | ICP# 844, 3451, 4729, 6834, 7870, 8194, 8392, 8407, 10176, 10876, 11487, 12041, 13828, 15242, 15245, 16844, 4400, 8863 | 4.41– 5.40 | 4.43– 5.47 | 3.94– 5.61 |
| Zn (mg/100 g) | 13 | ICP# 4729, 5925, 11350, 11485, 11487, 12041, 13828,13857, 14598, 15245, 15489, 16844, 8863 | 2.21– 2.92 | 2.27– 2.82 | 1.68– 3.95 |
| Cu (mg/100 g) | 15 | ICP# 7407, 9146, 10876, 11350, 11485, 11487, 12041,13542, 13828, 13857, 14378, 14598, 9152, 16844, 15597 | 0.95– 1.09 | 0.95– 1.11 | 0.78– 1.44 |
| Mn (mg/100 g) | 9 | ICP# 7870, 7982, 8178, 8392, 10876, 11472, 12023, 12043, 13828 | 1.04– 1.26 | 1.03– 1.24 | 0.98– 1.43 |
| P | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | Zn | Cu | Mn | SW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | 0.448 *** | 0.400 ** | 0.123 | 0.381 ** | 0.573 *** | 0.709 *** | 0.083 | 0.374 ** | −0.680 *** |
| P | 0.374 ** | −0.168 | 0.067 | 0.230 | 0.607 *** | 0.415 *** | −0.075 | −0.161 | |
| K | −0.026 | 0.111 | 0.103 | 0.368 ** | 0.181 | 0.061 | −0.122 | ||
| Ca | 0.742 *** | 0.052 | 0.073 | −0.089 | 0.821 *** | −0.166 | |||
| Mg | 0.233 | 0.223 | −0.058 | 0.782 *** | −0.394 ** | ||||
| Fe | 0.630 *** | 0.315 * | 0.227 | −0.547 *** | |||||
| Zn | 0.463 *** | 0.183 | −0.453 *** | ||||||
| Cu | −0.102 | 0.073 | |||||||
| Mn | −0.386 *** |
| P | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | Zn | Cu | Mn | SW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | 0.816 *** | 0.534 *** | 0.192 | −0.065 | 0.400 | −0.038 | 0.339 ** | 0.661 *** | 0.273 * |
| P | 0.341 ** | 0.179 | −0.234 | 0.319 * | −0.046 | 0.226 | 0.404 ** | −0.013 | |
| K | 0.000 | 0.273 * | 0.273 * | 0.159 | 0.357 ** | 0.609 *** | 0.470 ** | ||
| Ca | −0.382 ** | 0.025 | −0.402 ** | 0.342 ** | 0.404 ** | 0.143 | |||
| Mg | 0.154 | 0.386 ** | 0.038 | 0.033 | 0.242 | ||||
| Fe | 0.254 * | 0.212 | 0.183 | 0.065 | |||||
| Zn | 0.285 * | −0.187 | −0.079 | ||||||
| Cu | 0.544 *** | 0.441 *** | |||||||
| Mn | 0.653** |
| Nutrient | Cotyledon (%) | Seed Coat (%) or Dehulling Nutrient Loss (%) | Range of Nutrient Loss and/or Contribution (%) * | No. of Accessions with Dehulling Nutrient Loss Lesser than the Trial Mean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Min | Max | Mean ± SD | Min | Max | |||
| Protein | 97.58 ± 0.45 | 95.90 | 98.30 | 2.42 ± 0.45 | 1.70 | 4.10 | 2.40 | 40 |
| P | 99.08 ± 0.33 | 98.20 | 99.55 | 0.92 ± 0.33 | 0.45 | 1.80 | 1.35 | 35 |
| K | 91.48 ± 1.61 | 87.61 | 94.66 | 8.52 ± 1.61 | 5.34 | 12.39 | 7.05 | 30 |
| Ca | 33.22 ± 3.33 | 27.79 | 42.07 | 66.78 ± 3.33 | 57.93 | 72.21 | 14.28 | 33 |
| Mg | 77.11 ± 3.50 | 69.46 | 85.74 | 22.89 ± 3.50 | 14.26 | 30.54 | 16.28 | 29 |
| Fe | 87.40 ± 1.61 | 83.55 | 90.47 | 12.60 ± 1.61 | 9.53 | 16.45 | 6.92 | 34 |
| Zn | 90.05 ± 2.49 | 81.09 | 94.05 | 9.95 ± 2.49 | 5.95 | 18.91 | 12.96 | 36 |
| Cu | 88.68 ± 3.09 | 79.85 | 93.57 | 11.32 ± 3.09 | 6.43 | 20.15 | 13.72 | 36 |
| Mn | 86.59 ± 4.17 | 72.45 | 92.88 | 13.41 ± 4.17 | 7.12 | 27.55 | 20.43 | 37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Susmitha, D.; Kalaimagal, T.; Senthil, R.; Vetriventhan, M.; Anitha, S.; Manonmani, S.; Jeyakumar, P.; Reddymalla, S.; Peerzada, O.; Arveti, V.N.; et al. Calcium-Rich Pigeonpea Seed Coat: A Potential Byproduct for Food and Pharmaceutical Industries. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4918. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094918
Susmitha D, Kalaimagal T, Senthil R, Vetriventhan M, Anitha S, Manonmani S, Jeyakumar P, Reddymalla S, Peerzada O, Arveti VN, et al. Calcium-Rich Pigeonpea Seed Coat: A Potential Byproduct for Food and Pharmaceutical Industries. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):4918. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094918
Chicago/Turabian StyleSusmitha, Dhanapal, Thiyagarajan Kalaimagal, Ramachandran Senthil, Mani Vetriventhan, Seetha Anitha, Swaminathan Manonmani, Prabhakaran Jeyakumar, Surender Reddymalla, Ovais Peerzada, Venkata Narayana Arveti, and et al. 2022. "Calcium-Rich Pigeonpea Seed Coat: A Potential Byproduct for Food and Pharmaceutical Industries" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 4918. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094918
APA StyleSusmitha, D., Kalaimagal, T., Senthil, R., Vetriventhan, M., Anitha, S., Manonmani, S., Jeyakumar, P., Reddymalla, S., Peerzada, O., Arveti, V. N., Azevedo, V. C. R., & Singh, K. (2022). Calcium-Rich Pigeonpea Seed Coat: A Potential Byproduct for Food and Pharmaceutical Industries. Sustainability, 14(9), 4918. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094918







